Molecular Genetic Architecture of Monogenic Pediatric IBD Differs from Complex Pediatric and Adult IBD
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Evidence selected: All_Experimental;
- Network specificity: medium (default);
- Use GO term fusion: not selected;
- Show only pathways with pV < 0.05 (default);
- Advanced term/pathway selection options: none selected;
- Statistical options: none selected;
- Grouping options: none selected.
3. Results
3.1. Literature Search
3.2. Gene Subgroup Definition
3.3. Gene Ontology Analysis Results
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adamiak, T.; Walkiewicz-Jedrzejczak, D.; Fish, D.; Brown, C.; Tung, J.; Khan, K.; Faubion, W.; Park, R.; Heikenen, J.; Yaffee, M.; et al. Incidence, clinical characteristics, and natural history of pediatric IBD in Wisconsin: A population-based epidemiological study. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2013, 19, 1218–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, S.B.; Monteiro, I.M. Diagnosis and management of inflammatory bowel disease in children. BMJ 2017, 357, j2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urlep, D.; Blagus, R.; Orel, R. Incidence Trends and Geographical Variability of Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Slovenia: A Nationwide Study. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 921730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Limbergen, J.; Russell, R.K.; Drummond, H.E.; Aldhous, M.C.; Round, N.K.; Nimmo, E.R.; Smith, L.; Gillett, P.M.; McGrogan, P.; Weaver, L.T.; et al. Definition of phenotypic characteristics of childhood-onset inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 1114–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prenzel, F.; Uhlig, H.H. Frequency of indeterminate colitis in children and adults with IBD—A metaanalysis. J. Crohns Colitis 2009, 3, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socha, P.; Ryzko, J.; Koletzko, B.; Celinska-Cedro, D.; Woynarowski, M.; Czubkowski, P.; Socha, J. Essential fatty acid depletion in children with inflammatory bowel disease. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 40, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlig, H.H.; Schwerd, T.; Koletzko, S.; Shah, N.; Kammermeier, J.; Elkadri, A.; Ouahed, J.; Wilson, D.C.; Travis, S.P.; Turner, D.; et al. The diagnostic approach to monogenic very early onset inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 990–1007.e1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovics, Z.H.; Michail, S.; Nicholson, M.R.; Kociolek, L.K.; Pai, N.; Hansen, R.; Schwerd, T.; Maspons, A.; Shamir, R.; Szajewska, H.; et al. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation for Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection and Other Conditions in Children: A Joint Position Paper from the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition and the European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2019, 68, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ridder, L.; Assa, A.; Bronsky, J.; Romano, C.; Russell, R.K.; Afzal, N.A.; Hauer, A.C.; Knafelz, D.; Lionetti, P.; Strisciuglio, C.; et al. Use of Biosimilars in Paediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease: An Updated Position Statement of the Paediatric IBD Porto Group of ESPGHAN. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2019, 68, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, S.; Thomson, M.; de Ridder, L.; Martín-de-Carpi, J.; Van Biervliet, S.; Braegger, C.; Dias, J.A.; Kolacek, S.; Miele, E.; Buderus, S.; et al. Endoscopy in Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Position Paper on Behalf of the Porto IBD Group of the Espghan. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 67, 414–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapar, N.; Saliakellis, E.; Benninga, M.A.; Borrelli, O.; Curry, J.; Faure, C.; De Giorgio, R.; Gupte, G.; Knowles, C.H.; Staiano, A.; et al. Paediatric Intestinal Pseudo-Obstruction: Evidence and Consensus-Based Recommendations from an ESPGHAN-Led Expert Group. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 66, 991–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, D.; Ruemmele, F.M.; Orlanski-Meyer, E.; Griffiths, A.M.; Carpi, J.M.; Bronsky, J.; Veres, G.; Aloi, M.; Strisciuglio, C.; Braegger, C.P.; et al. Management of Paediatric Ulcerative Colitis, Part 1: Ambulatory Care—An Evidence-Based Guideline from ECCO and ESPGHAN. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 67, 257–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, D.; Ruemmele, F.M.; Orlanski-Meyer, E.; Griffiths, A.M.; Carpi, J.M.; Bronsky, J.; Veres, G.; Aloi, M.; Strisciuglio, C.; Braegger, C.P.; et al. Management of Paediatric Ulcerative Colitis, Part 2: Acute Severe Colitis; An Evidence-based Consensus Guideline from ECCO and ESPGHAN. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 67, 292–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovasz, B.D.; Lakatos, L.; Horvath, A.; Szita, I.; Pandur, T.; Mandel, M.; Vegh, Z.; Golovics, P.A.; Mester, G.; Balogh, M.; et al. Evolution of disease phenotype in adult and pediatric onset Crohn’s disease in a population-based cohort. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 2217–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartono, S.; Ippoliti, M.R.; Mastroianni, M.; Torres, R.; Rider, N.L. Gastrointestinal Disorders Associated with Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 57, 145–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lega, S.; Pin, A.; Arrigo, S.; Cifaldi, C.; Girardelli, M.; Bianco, A.M.; Malamisura, M.; Angelino, G.; Faraci, S.; Rea, F.; et al. Diagnostic Approach to Monogenic Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Clinical Practice: A Ten-Year Multicentric Experience. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2020, 26, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, E.; Warner, N.; Pan, J.; Khalouei, S.; Elkadri, A.; Fiedler, K.; Foong, J.; Turinsky, A.L.; Bronte-Tinkew, D.; Zhang, S.; et al. Prevalence and Clinical Features of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Associated with Monogenic Variants, Identified by Whole-Exome Sequencing in 1000 Children at a Single Center. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 2208–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, J.J.; Mossotto, E.; Stafford, I.S.; Haggarty, R.; Coelho, T.A.F.; Batra, A.; Afzal, N.A.; Mort, M.; Bunyan, D.; Beattie, R.M.; et al. Genetic Sequencing of Pediatric Patients Identifies Mutations in Monogenic Inflammatory Bowel Disease Genes that Translate to Distinct Clinical Phenotypes. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2020, 11, e00129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jostins, L.; Ripke, S.; Weersma, R.K.; Duerr, R.H.; McGovern, D.P.; Hui, K.Y.; Lee, J.C.; Schumm, L.P.; Sharma, Y.; Anderson, C.A.; et al. Host-microbe interactions have shaped the genetic architecture of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 2012, 491, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, E.E.; Pe’er, I.; Karban, A.; Ozelius, L.; Mitchell, A.A.; Ng, S.M.; Erazo, M.; Ostrer, H.; Abraham, C.; Abreu, M.T.; et al. A genome-wide scan of Ashkenazi Jewish Crohn’s disease suggests novel susceptibility loci. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, K.; Umeno, J.; Takahashi, A.; Hirano, A.; Johnson, T.A.; Kumasaka, N.; Morizono, T.; Hosono, N.; Kawaguchi, T.; Takazoe, M.; et al. A genome-wide association study identifies 2 susceptibility Loci for Crohn’s disease in a Japanese population. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.K.; Hong, M.; Zhao, W.; Jung, Y.; Baek, J.; Tayebi, N.; Kim, K.M.; Ye, B.D.; Kim, K.J.; Park, S.H.; et al. Genome-wide association study of Crohn’s disease in Koreans revealed three new susceptibility loci and common attributes of genetic susceptibility across ethnic populations. Gut 2014, 63, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.Z.; van Sommeren, S.; Huang, H.; Ng, S.C.; Alberts, R.; Takahashi, A.; Ripke, S.; Lee, J.C.; Jostins, L.; Shah, T.; et al. Association analyses identify 38 susceptibility loci for inflammatory bowel disease and highlight shared genetic risk across populations. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellinghaus, D.; Jostins, L.; Spain, S.L.; Cortes, A.; Bethune, J.; Han, B.; Park, Y.R.; Raychaudhuri, S.; Pouget, J.G.; Hübenthal, M.; et al. Analysis of five chronic inflammatory diseases identifies 27 new associations and highlights disease-specific patterns at shared loci. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lange, K.M.; Moutsianas, L.; Lee, J.C.; Lamb, C.A.; Luo, Y.; Kennedy, N.A.; Jostins, L.; Rice, D.L.; Gutierrez-Achury, J.; Ji, S.G.; et al. Genome-wide association study implicates immune activation of multiple integrin genes in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherr, R.; Essers, J.; Hakonarson, H.; Kugathasan, S. Genetic determinants of pediatric inflammatory bowel disease: Is age of onset genetically determined? Dig. Dis. 2009, 27, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrowski, J.; Paziewska, A.; Lazowska, I.; Ambrozkiewicz, F.; Goryca, K.; Kulecka, M.; Rawa, T.; Karczmarski, J.; Dabrowska, M.; Zeber-Lubecka, N.; et al. Genetic architecture differences between pediatric and adult-onset inflammatory bowel diseases in the Polish population. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleynen, I.; Boucher, G.; Jostins, L.; Schumm, L.P.; Zeissig, S.; Ahmad, T.; Andersen, V.; Andrews, J.M.; Annese, V.; Brand, S.; et al. Inherited determinants of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis phenotypes: A genetic association study. Lancet 2016, 387, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswaran, S.; Prince, J.; Cutler, D.J.; Marigorta, U.M.; Okou, D.T.; Prahalad, S.; Mack, D.; Boyle, B.; Walters, T.; Griffiths, A.; et al. Enhanced Contribution of HLA in Pediatric Onset Ulcerative Colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2018, 24, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolio, T.A.; Collins, F.S.; Cox, N.J.; Goldstein, D.B.; Hindorff, L.A.; Hunter, D.J.; McCarthy, M.I.; Ramos, E.M.; Cardon, L.R.; Chakravarti, A.; et al. Finding the missing heritability of complex diseases. Nature 2009, 461, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, H.J.; Hansen, L.; Narimatsu, Y.; Freeze, H.H.; Henrissat, B.; Bennett, E.; Wandall, H.H.; Clausen, H.; Schjoldager, K.T. Glycosyltransferase genes that cause monogenic congenital disorders of glycosylation are distinct from glycosyltransferase genes associated with complex diseases. Glycobiology 2018, 28, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batura, V.; Muise, A.M. Very early onset IBD: Novel genetic aetiologies. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 18, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivas, M.A.; Beaudoin, M.; Gardet, A.; Stevens, C.; Sharma, Y.; Zhang, C.K.; Boucher, G.; Ripke, S.; Ellinghaus, D.; Burtt, N.; et al. Deep resequencing of GWAS loci identifies independent rare variants associated with inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Fang, M.; Jostins, L.; UmićevićMirkov, M.; Boucher, G.; Anderson, C.A.; Andersen, V.; Cleynen, I.; Cortes, A.; Crins, F.; et al. Fine-mapping inflammatory bowel disease loci to single-variant resolution. Nature 2017, 547, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerbino, D.R.; Achuthan, P.; Akanni, W.; Amode, M.R.; Barrell, D.; Bhai, J.; Billis, K.; Cummins, C.; Gall, A.; Girón, C.G.; et al. Ensembl 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D754–D761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonsdale, J.; Thomas, J.; Salvatore, M.; Phillips, R.; Lo, E.; Shad, S.; Hasz, R.; Walters, G.; Garcia, F.; Young, N.; et al. The Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M. KEGG as a reference resource for gene and protein annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D457–D462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindea, G.; Mlecnik, B.; Hackl, H.; Charoentong, P.; Tosolini, M.; Kirilovsky, A.; Fridman, W.H.; Pagès, F.; Trajanoski, Z.; Galon, J. ClueGO: A Cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1091–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Sasahara, Y.; Kikuchi, A.; Kakuta, H.; Kashiwabara, T.; Ishige, T.; Nakayama, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Hoshino, A.; Kanegane, H.; et al. Targeted Sequencing and Immunological Analysis Reveal the Involvement of Primary Immunodeficiency Genes in Pediatric IBD: A Japanese Multicenter Study. J. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 37, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charbit-Henrion, F.; Parlato, M.; Hanein, S.; Duclaux-Loras, R.; Nowak, J.; Begue, B.; Rakotobe, S.; Bruneau, J.; Fourrage, C.; Alibeu, O.; et al. Diagnostic Yield of Next-Generation Sequencing in Very Early-Onset Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Multicenter Study. J. Crohns Colitis 2018, 12, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, K.A.; Cutler, D.J.; Okou, D.; Dodd, A.; Aronow, B.J.; Haberman, Y.; Stevens, C.; Walters, T.D.; Griffiths, A.; Baldassano, R.N.; et al. Genetic variants and pathways implicated in a pediatric inflammatory bowel disease cohort. Genes Immun. 2019, 20, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Chen, F.; Liu, Z.; Cong, Y. Microbiota-specific Th17 Cells: Yin and Yang in Regulation of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, A.; Rudra, D.; Treuting, P.; Samstein, R.M.; Liang, Y.; Kas, A.; Rudensky, A.Y. CD4+ regulatory T cells control TH17 responses in a Stat3-dependent manner. Science 2009, 326, 986–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Lierop, P.P.; Swagemakers, S.M.; de Bie, C.I.; Middendorp, S.; van Baarlen, P.; Samsom, J.N.; van Ijcken, W.F.; Escher, J.C.; van der Spek, P.J.; Nieuwenhuis, E.E. Gene expression analysis of peripheral cells for subclassification of pediatric inflammatory bowel disease in remission. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hueber, W.; Sands, B.E.; Lewitzky, S.; Vandemeulebroecke, M.; Reinisch, W.; Higgins, P.D.; Wehkamp, J.; Feagan, B.G.; Yao, M.D.; Karczewski, M.; et al. Secukinumab, a human anti-IL-17A monoclonal antibody, for moderate to severe Crohn’s disease: Unexpected results of a randomised, double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Gut 2012, 61, 1693–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuss, I. IL-17: Intestinal effector or protector? Mucosal Immunol. 2011, 4, 366–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Tato, C.M.; Joyce-Shaikh, B.; Gulen, M.F.; Gulan, F.; Cayatte, C.; Chen, Y.; Blumenschein, W.M.; Judo, M.; Ayanoglu, G.; et al. Interleukin-23-Independent IL-17 Production Regulates Intestinal Epithelial Permeability. Immunity 2015, 43, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockmann, L.; Giannou, A.D.; Gagliani, N.; Huber, S. Regulation of TH17 Cells and Associated Cytokines in Wound Healing, Tissue Regeneration, and Carcinogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walrath, T.; Malizia, R.A.; Zhu, X.; Sharp, S.P.; D’Souza, S.S.; Lopez-Soler, R.; Parr, B.; Kartchner, B.; Lee, E.C.; Stain, S.C.; et al. IFN-γ and IL-17A regulate intestinal crypt production of CXCL10 in the healthy and inflamed colon. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2020, 318, G479–G489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.K.; Pai, J.; Panaccione, R.; Beck, P.; Ferraz, J.G.; Jijon, H. Crohn’s-like disease in a patient exposed to anti-Interleukin-17 blockade (Ixekizumab) for the treatment of chronic plaque psoriasis: A case report. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019, 19, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivera, P.A.; Lasa, J.S.; Bonovas, S.; Danese, S.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Safety of Janus Kinase Inhibitors in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases or Other Immune-mediated Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1554–1573.e1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salas, A.; Hernandez-Rocha, C.; Duijvestein, M.; Faubion, W.; McGovern, D.; Vermeire, S.; Vetrano, S.; Vande Casteele, N. JAK-STAT pathway targeting for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 323–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
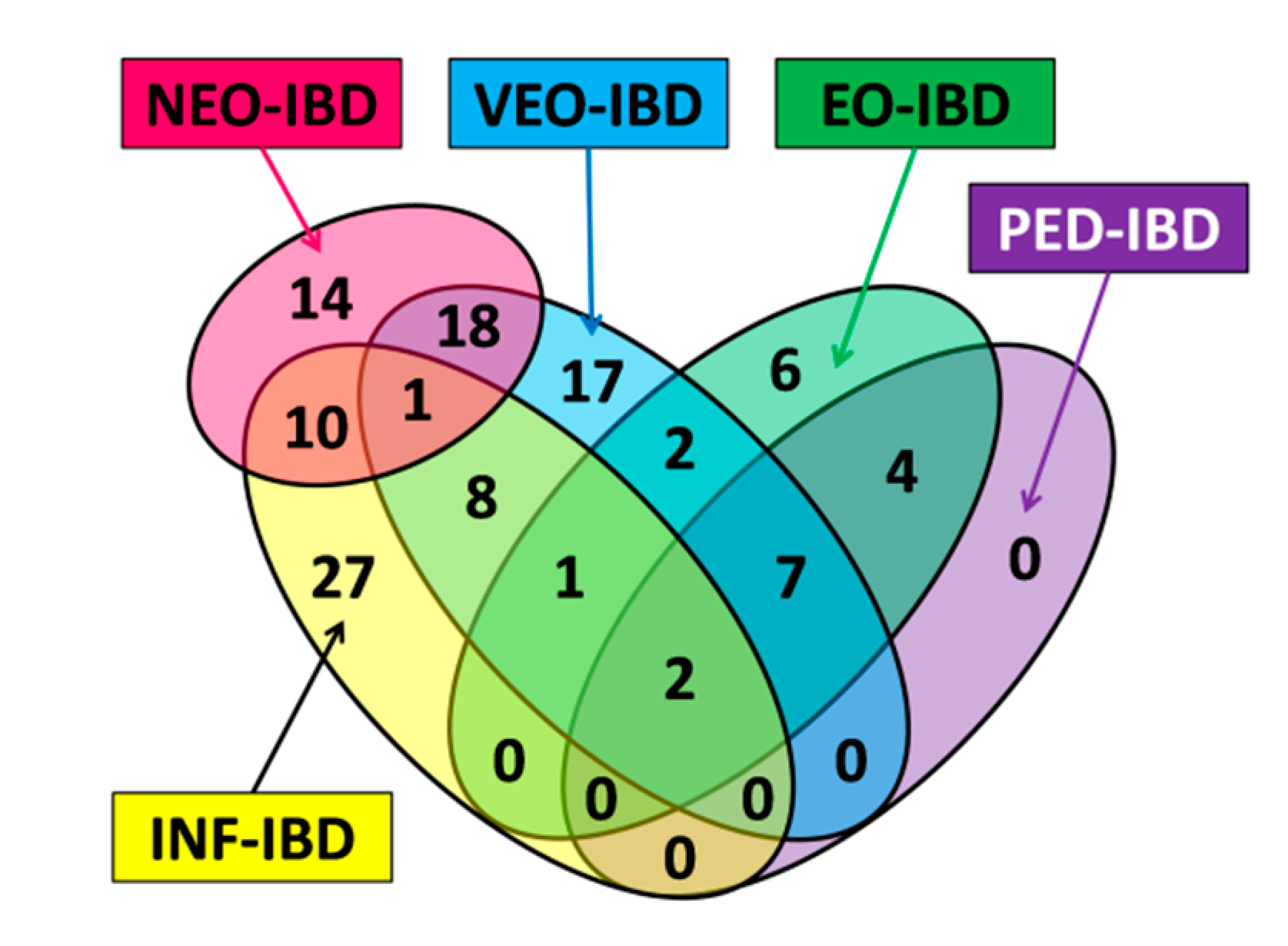
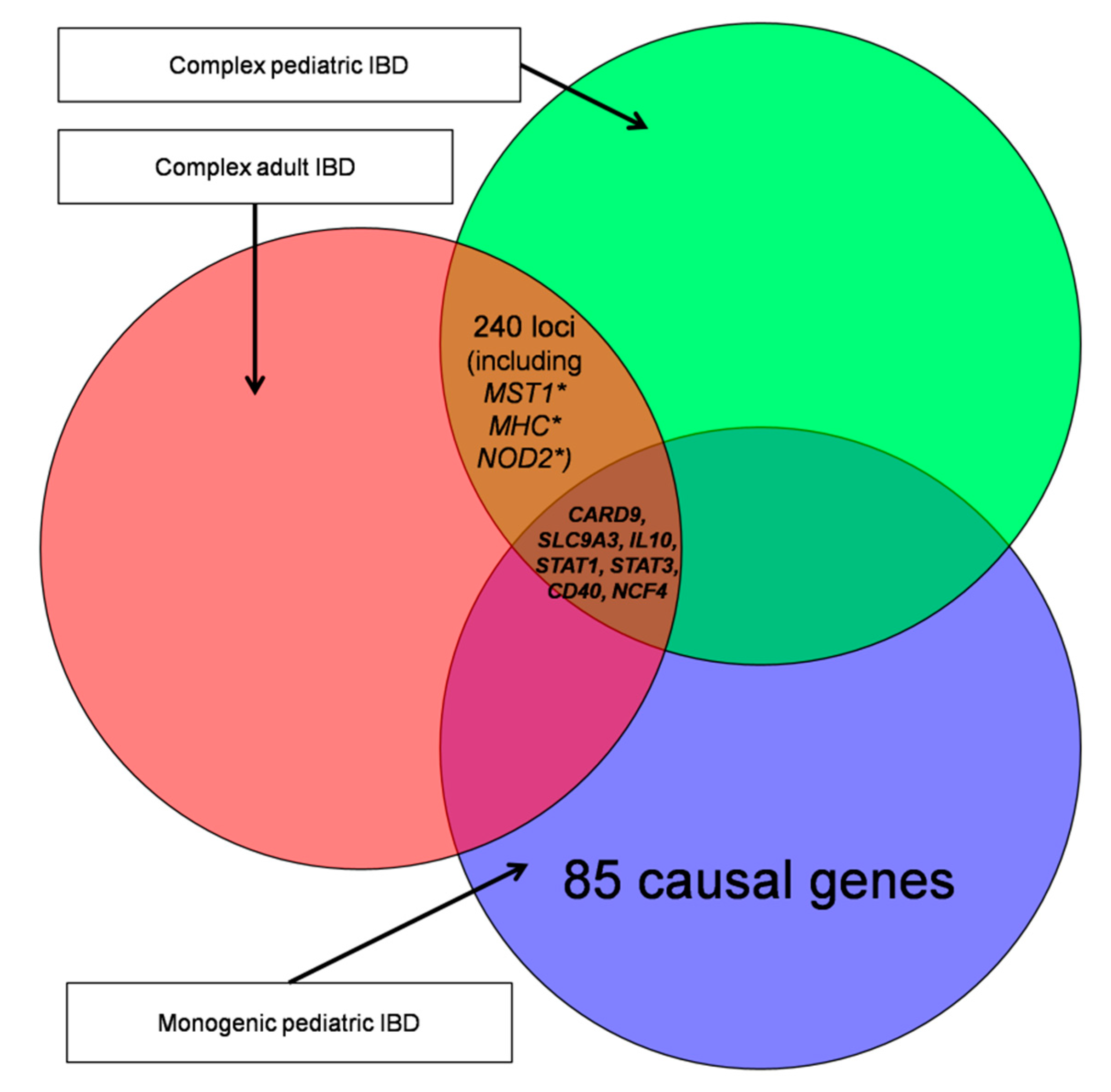



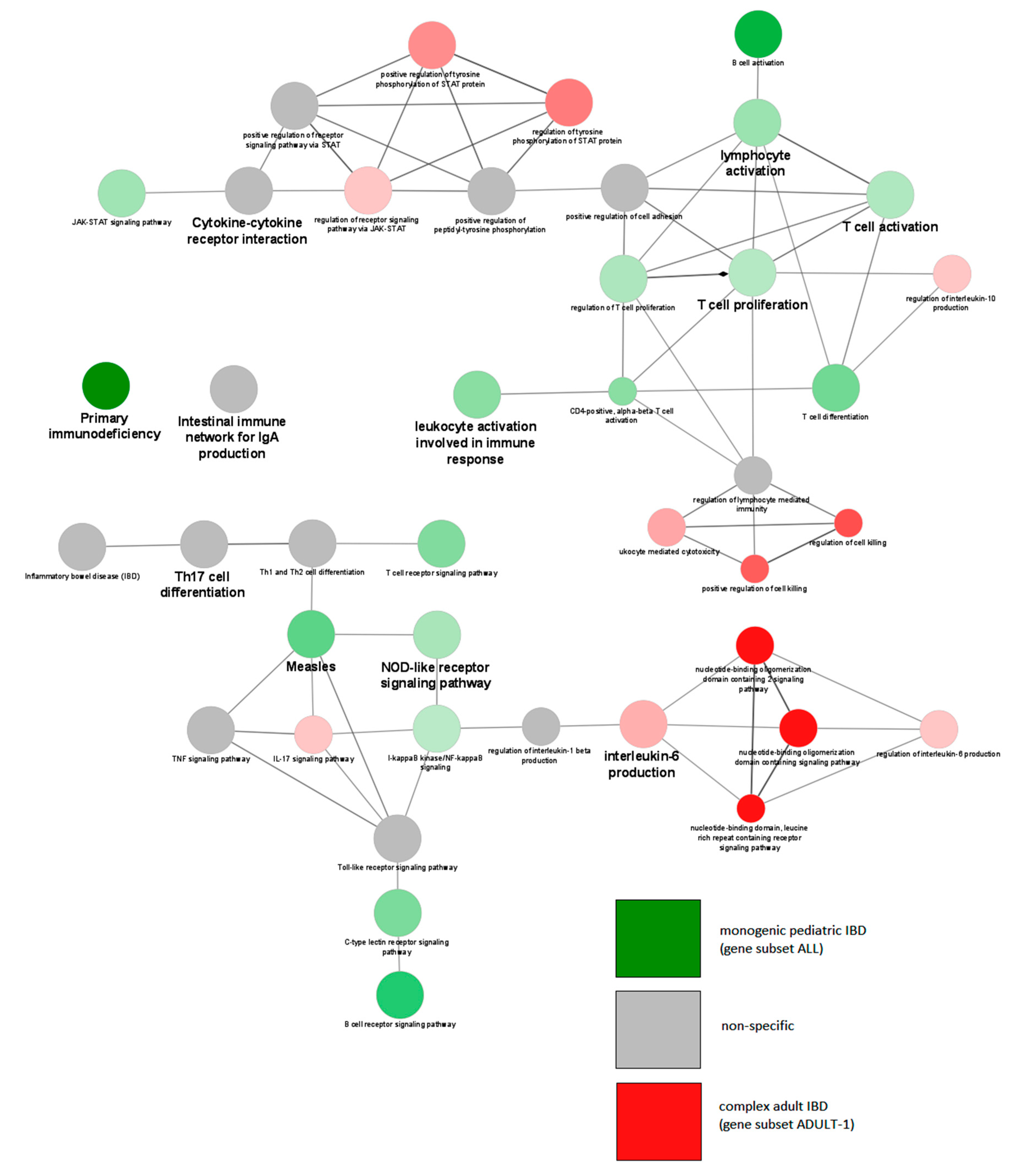
| Name | Subgroup Contents | Age of Onset | Number of Genes | Number of Unique Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | Subset contains all genes with a pediatric onset tag (NEO-IBD, INF-IBD, VEO-IBD, EO-IBD and PED-IBD). | ≤18 years | 75 | N/A |
| NEO | Subset contains all genes with the NEO-IBD age of onset tag. | ≤28 days | 19 | 8 |
| INF | Subset contains all genes with the INF-IBD age of onset tag. | >28 days and ≤2 years | 36 | 18 |
| VEO | Subset contains all genes with the VEO-IBD age of onset tag. | >2 years and ≤6 years | 37 | 16 |
| EO | Subset contains all genes with the EO-IBD age of onset tag. | >6 years and ≤10 years | 19 | 4 |
| PED | Subset contains all genes with the PED-IBD age of onset tag. | >10 years And ≤18 years | 13 | 0 |
| ADULT-1 | Subset contains genes based on the review of 201 IBD-associated loci. | Adult | 148 | 145 |
| ADULT-2 | Subset contains all genes with the GO term ko05321. | Adult | 49 | 45 |
| UN6 | Subset contains only genes with the following tags or tag combinations: NEO-IBD, NEO-IBD and INF-IBD, INF-IBD, INF-IBD and VEO-IBD | <6 years | 67 | N/A |
| OV6 | Subset contains only genes with the following tags or tag combinations: VEO-IBD, VEO-IBD and EO-IBD, EO-IBD, EO-IBD and PED-IBD, PED-IBD | >6 years and ≤18 years | 19 | N/A |
| Subset | GOID a | GOTerm b | Term p-Value | Associated Gene Fraction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | KEGG:05340 | Primary immunodeficiency | 1.99 × 10−30 | 48.65 |
| ALL | KEGG:04659 | Th17 cell differentiation | 3.14 × 10−11 | 11.21 |
| ALL | KEGG:04068 | FoxO signaling pathway | 1.57 × 10−7 | 7.58 |
| ALL | KEGG:04630 | Jak/STAT signaling pathway | 1.07 × 10−6 | 6.17 |
| ALL | GO:0042100 | B-cell proliferation | 1.23 × 10−6 | 18.75 |
| ALL | KEGG:04064 | NF-kappa B signaling pathway | 2.89 × 10−6 | 8.42 |
| ALL | KEGG:04658 | Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation | 3.74 × 10−5 | 7.61 |
| INF | KEGG:05340 | Primary immunodeficiency | 1.22 × 10−22 | 32.43 |
| INF | KEGG:04659 | Th17 cell differentiation | 3.33 × 10−6 | 5.61 |
| INF | KEGG:04658 | Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation | 7.36 × 10−4 | 4.35 |
| INF | GO:0042100 | B-cell proliferation | 7.38 × 10−4 | 9.38 |
| VEO | KEGG:04659 | Th17 cell differentiation | 8.00 × 10−11 | 8.41 |
| VEO | KEGG:05340 | Primary immunodeficiency | 5.26 × 10−9 | 16.22 |
| VEO | KEGG:04658 | Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation | 1.32 × 10−6 | 6.52 |
| EO | KEGG:05340 | Primary immunodeficiency | 4.73 × 10−5 | 8.11 |
| EO | KEGG:04920 | Adipocytokine signaling pathway | 1.55 × 10−4 | 4.35 |
| Subgroups Compared | GOID a | GOTerm b | Term p-Value | Associated Gene Fraction (%) | Cluster Specific for Subset |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UN6 vs. OV6 | KEGG:05340 | Primary immunodeficiency- | 8.82 × 10−32 | 48.65 | UN6 |
| KEGG:04659 | Th17 cell differentiation | 3.39 × 10−12 | 11.21 | None | |
| KEGG:04660 | T-cell receptor signaling pathway | 1.99 × 10−9 | 9.71 | OV6 | |
| KEGG:04662 | B-cell receptor signaling pathway | 5.64 × 10−8 | 11.27 | UN6 | |
| KEGG:04630 | Jak/STAT signaling pathway | 1.57 × 10−7 | 6.17 | UN6 | |
| KEGG:04658 | Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation | 7.91 × 10−6 | 7.61 | None | |
| KEGG:05321 | Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) | 1.76 × 10−5 | 9.23 | UN6 | |
| ALL vs. ADULT-1 | KEGG:05340 | Primary immunodeficiency | 8.12 × 10−22 | 48.65 | ALL |
| KEGG:04659 | Th17 cell differentiation | 9.52 × 10−19 | 21.50 | None | |
| KEGG:05321 | Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) | 1.62 × 10−16 | 27.69 | ADULT-1 | |
| KEGG:04658 | Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation | 6.67 × 10−10 | 16.30 | None | |
| KEGG:04630 | Jak/STAT signaling pathway | 3.27 × 10−9 | 11.11 | ADULT-1 | |
| KEGG:04068 | FoxO signaling pathway | 7.37 × 10−5 | 9.09 | ALL | |
| GO:0042100 | B cell proliferation | 9.82 × 10−4 | 18.75 | ALL | |
| ALL vs. ADULT-2 | KEGG:05321 | Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) | 2.33 × 10−90 | 73.85 | ADULT-2 |
| KEGG:04659 | Th17 cell differentiation | 3.17 × 10−49 | 33.64 | ADULT-2 | |
| KEGG:04658 | Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation | 2.17 × 10−32 | 28.26 | ADULT-2 | |
| KEGG:04630 | Jak/STAT signaling pathway | 1.72 × 10−28 | 17.28 | ADULT-2 | |
| KEGG:05340 | Primary immunodeficiency | 5.35 × 10−27 | 48.65 | ALL | |
| KEGG:04068 | FoxO signaling pathway | 1.24 × 10−11 | 11.36 | ALL | |
| GO:0042100 | B-cell proliferation | 6.79 × 10−7 | 21.88 | ALL |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jezernik, G.; Mičetić-Turk, D.; Potočnik, U. Molecular Genetic Architecture of Monogenic Pediatric IBD Differs from Complex Pediatric and Adult IBD. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10040243
Jezernik G, Mičetić-Turk D, Potočnik U. Molecular Genetic Architecture of Monogenic Pediatric IBD Differs from Complex Pediatric and Adult IBD. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2020; 10(4):243. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10040243
Chicago/Turabian StyleJezernik, Gregor, Dušanka Mičetić-Turk, and Uroš Potočnik. 2020. "Molecular Genetic Architecture of Monogenic Pediatric IBD Differs from Complex Pediatric and Adult IBD" Journal of Personalized Medicine 10, no. 4: 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10040243
APA StyleJezernik, G., Mičetić-Turk, D., & Potočnik, U. (2020). Molecular Genetic Architecture of Monogenic Pediatric IBD Differs from Complex Pediatric and Adult IBD. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 10(4), 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10040243






