Soluble Immune Checkpoints, Gut Metabolites and Performance Status as Parameters of Response to Nivolumab Treatment in NSCLC Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patient Characteristics
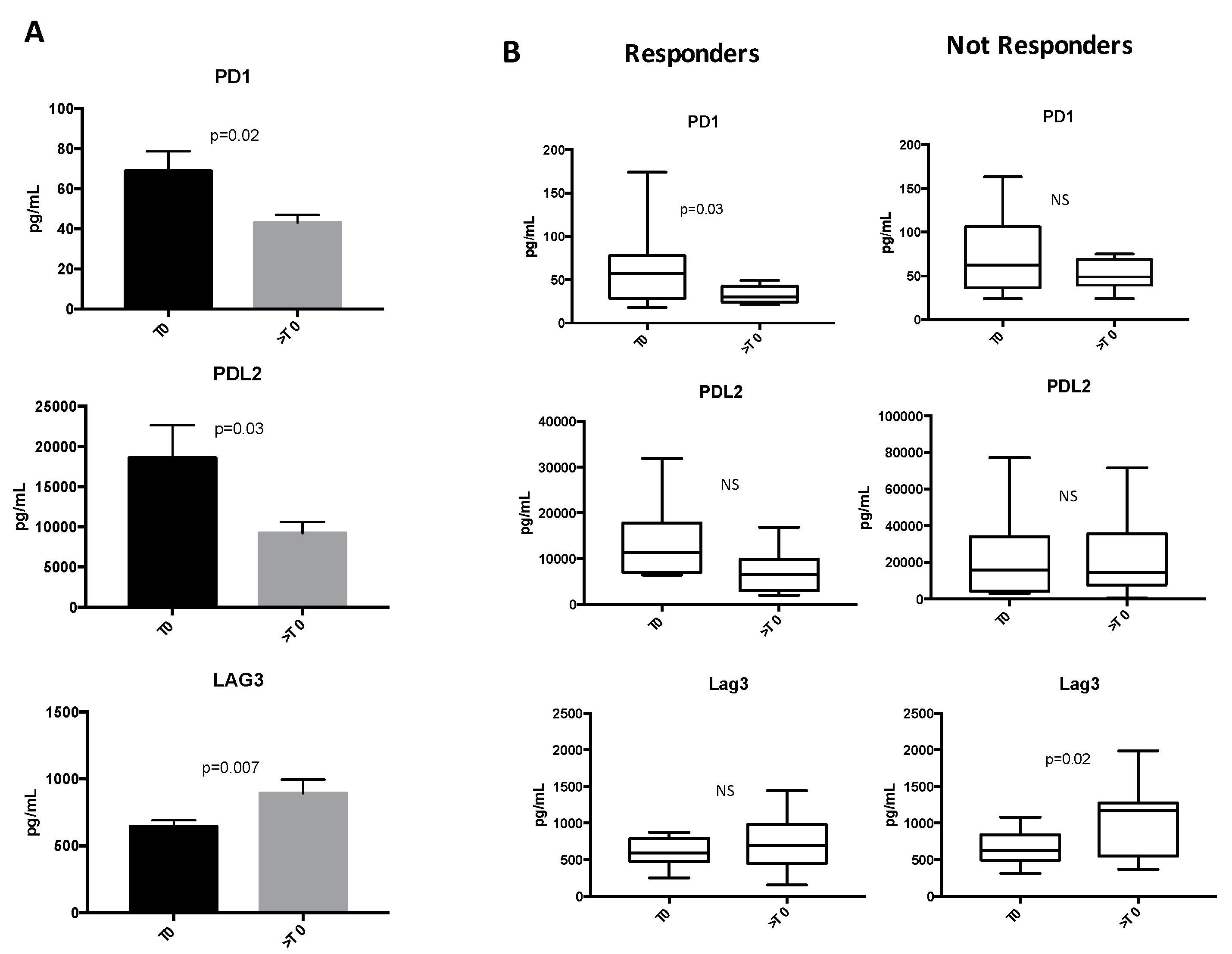
2.2. Soluble ICs Are Modulated during ICI Treatments
2.3. Low Levels of sICs Are Associated with Clinical Response in NSCLC Patients
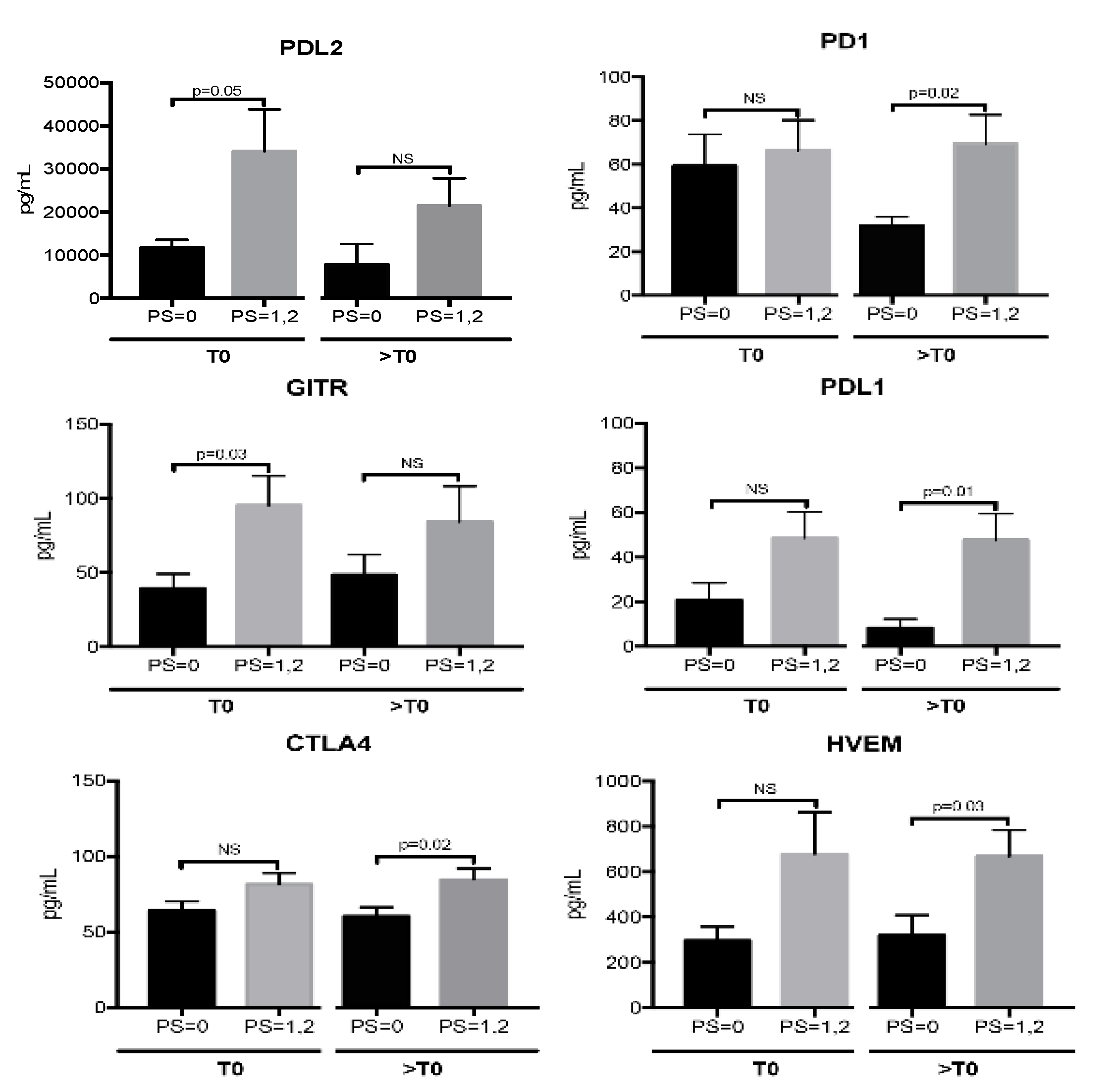
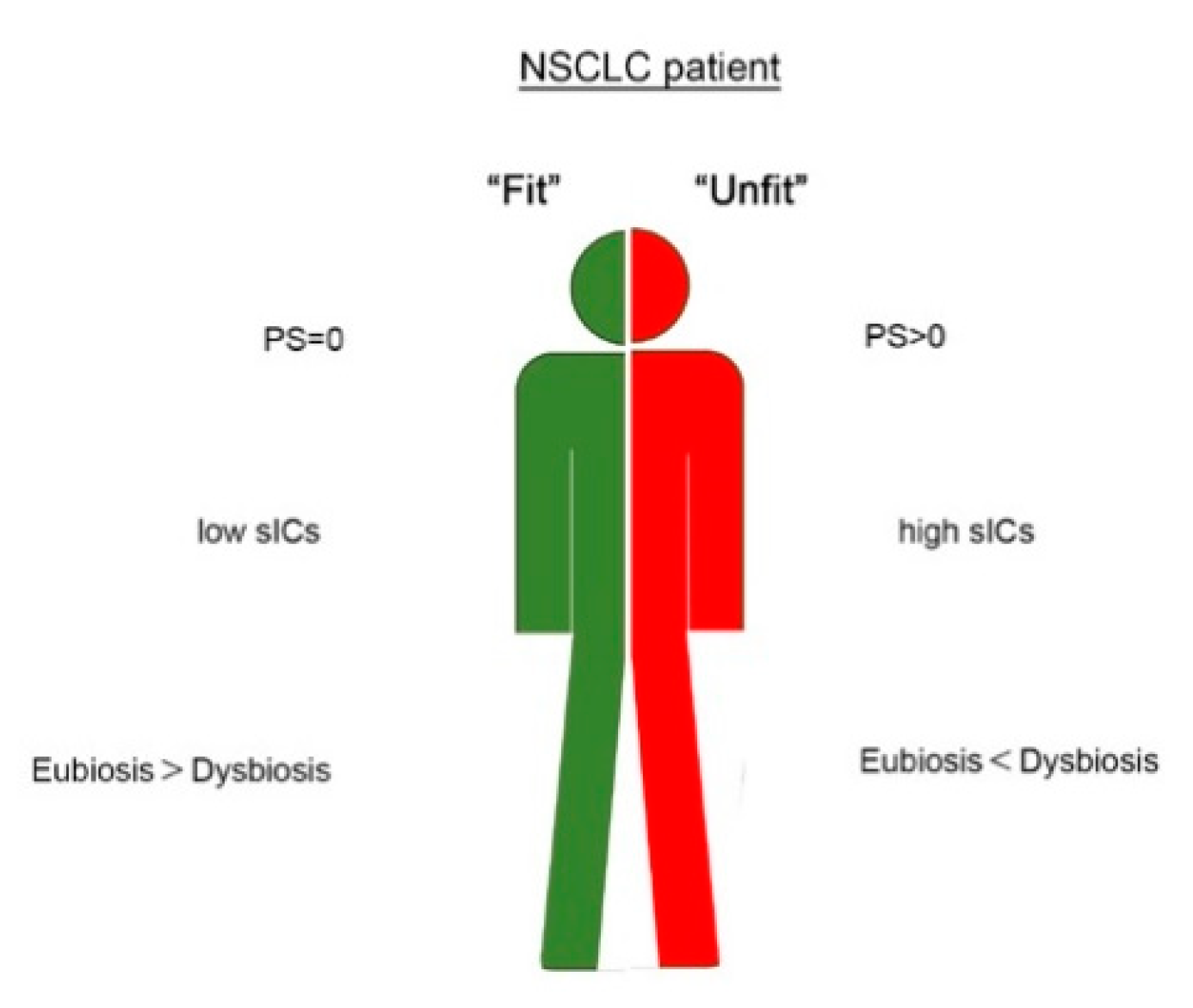
2.4. sICs Are Differently Modulated According to ECOG PS Scale
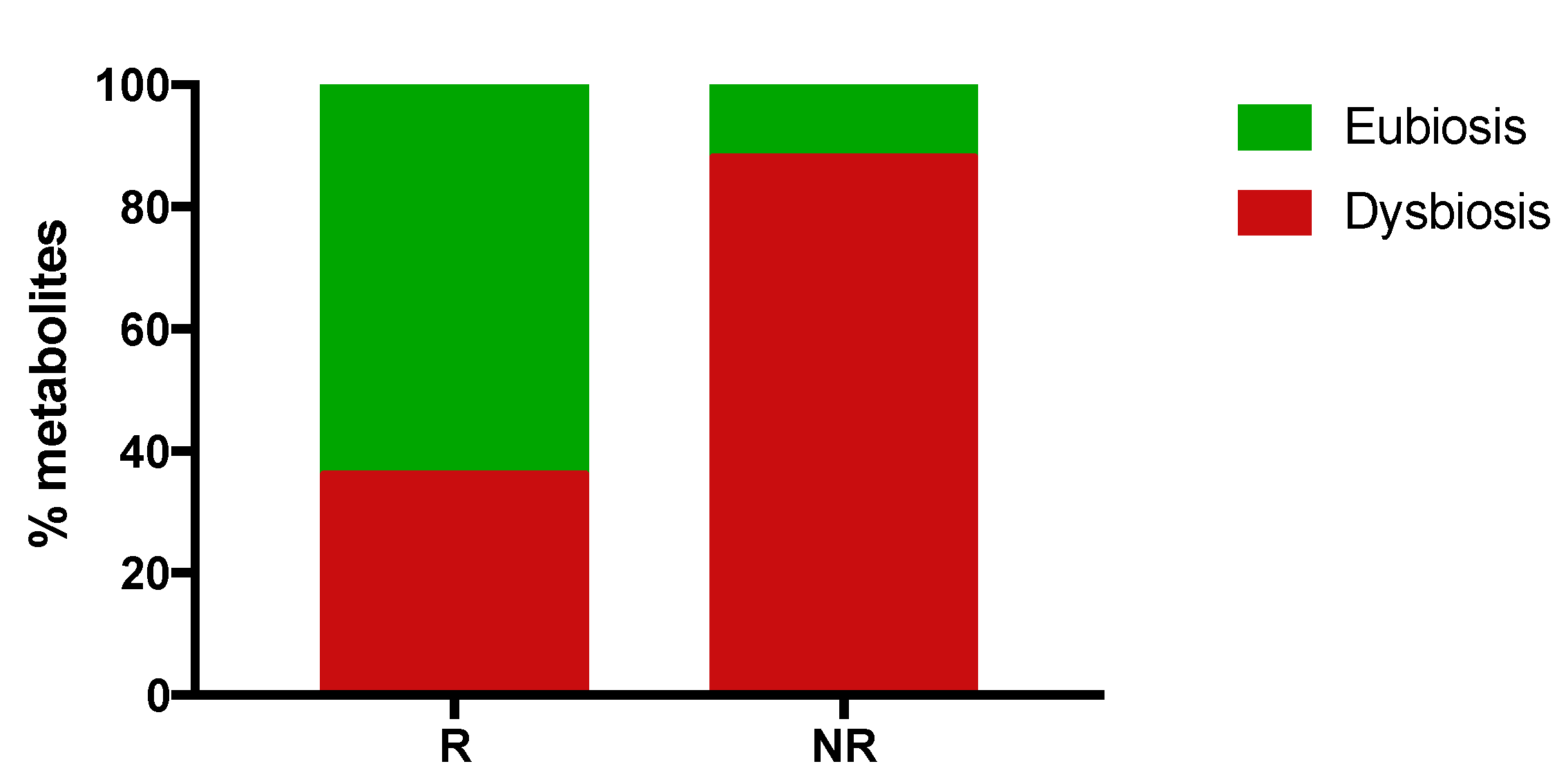
2.5. Responding Patients Have a High Proportion of Eubiosis-Associated Gut Metabolites
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. Treatment, Efficacy and Safety Assessments
4.3. Serum and Fecal Collection
4.4. Measurement of Soluble Immune Mediators in the Serum
4.5. Targeted Metagenomic on Fecal Microbiota
4.6. Gut Microbiome Metabolomics Profiling
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gomes, F.; Serra-Bellver, P.; Lorigan, P. The role of nivolumab in melanoma. Future Oncol. 2018, 14, 1241–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmer, J.R.; Reckamp, K.L.; Baas, P.; Crinò, L.; Eberhardt, W.E.; Poddubskaya, E.; Antonia, S.; Pluzanski, A.; Vokes, E.E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Squamous-Cell Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stühler, V.; Maas, J.M.; Rausch, S.; Stenzl, A.; Bedke, J. Immune checkpoint inhibition for the treatment of renal cell carcinoma. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2020, 20, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimi Koshkaki, H.; Minasi, S.; Ugolini, A.; Trevisi, G.; Napoletano, C.; Zizzari, I.G.; Gessi, M.; Giangaspero, F.; Mangiola, A.; Nuti, M.; et al. Immunohistochemical Characterization of Immune Infiltrate in Tumor Microenvironment of Glioblastoma. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litak, J.; Mazurek, M.; Grochowski, C.; Kamieniak, P.; Roliński, J. PD-L1/PD-1 Axis in Glioblastoma Multiforme. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camidge, D.R.; Doebele, R.C.; Kerr, K.M. Comparing and contrasting predictive biomarkers for immunotherapy and targeted therapy of NSCLC. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, J.; Fang, W.; Yu, J.; Chen, N.; Zhan, J.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, L. Expression of programmed death ligand-1 on tumor cells varies pre and post chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvin, P.; Toor, S.M.; Nair, V.S.; Elkord, E. Immune checkpoint inhibitors: Recent progress and potential biomarkers. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmann, M.D.; Ciuleanu, T.-E.; Pluzanski, A.; Lee, J.S.; Otterson, G.A.; Audigier-Valette, C.; Minenza, E.; Linardou, H.; Burgers, S.; Salman, P.; et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab in Lung Cancer with a High Tumor Mutational Burden. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 2093–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, D.P.; Reck, M.; Paz-Ares, L.; Creelan, B.; Horn, L.; Steins, M.; Felip, E.; van den Heuvel, M.M.; Ciuleanu, T.E.; Badin, F.; et al. First-Line Nivolumab in Stage IV or Recurrent Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2415–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marabelle, A.; Le, D.T.; Ascierto, P.A.; Di Giacomo, A.M.; De Jesus-Acosta, A.; Delord, J.-P.; Geva, R.; Gottfried, M.; Penel, N.; Hansen, A.R.; et al. Efficacy of Pembrolizumab in Patients with Noncolorectal High Microsatellite Instability/Mismatch Repair–Deficient Cancer: Results From the Phase II KEYNOTE-158 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routy, B.; Le Chatelier, E.; DeRosa, L.; Duong, C.P.M.; Alou, M.T.; Daillère, R.; Fluckiger, A.; Messaoudene, M.; Rauber, C.; Roberti, M.P.; et al. Gut microbiome influences efficacy of PD-1–based immunotherapy against epithelial tumors. Science 2018, 359, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botticelli, A.; Vernocchi, P.; Marini, F.; Quagliariello, A.; Cerbelli, B.; Reddel, S.; Del Chierico, F.; Di Pietro, F.; Giusti, R.; Tomassini, A.; et al. Gut metabolomics profiling of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients under immunotherapy treatment. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daassi, D.; Mahoney, K.M.; Freeman, G.J. The importance of exosomal PDL1 in tumour immune evasion. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Ao, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xu, X. Soluble immune checkpoints in cancer: Production, function and biological significance. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuma, Y.; Hosomi, Y.; Nakahara, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Sagawa, Y.; Homma, S. High plasma levels of soluble programmed cell death ligand 1 are prognostic for reduced survival in advanced lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2017, 104, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, A.; Takam Kamga, P.; Dumenil, C.; Chinet, T.; Emile, J.F.; Giroux Leprieur, E. Plasma Biomarkers and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: New Tools for Better Patient Selection? Cancers 2019, 11, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, A.; Julie, C.; Dumenil, C.; Hélias-Rodzewicz, Z.; Tisserand, J.; Dumoulin, J.; Giraud, V.; Labrune, S.; Chinet, T.; Emile, J.-F.; et al. Predictive role of plasmatic biomarkers in advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated by nivolumab. OncoImmunology 2018, 7, e1452581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyo, M.T.; Jouinot, A.; Giroux-Leprieur, E.; Fabre, E.; Wislez, M.; Alifano, M.; Leroy, K.; Boudou-Rouquette, P.; Tlemsani, C.; Khoudour, N.; et al. Predictive Value of Soluble PD-1, PD-L1, VEGFA, CD40 Ligand and CD44 for Nivolumab Therapy in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Case-Control Study. Cancers 2020, 12, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedlaender, A.; Banna, G.L.; Buffoni, L.; Addeo, A. Poor-Performance Status Assessment of Patients with Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Remains Vague and Blurred in the Immunotherapy Era. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 21, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, T.; Takada, M.; Kubo, A.; Matsumura, A.; Fukai, S.; Tamura, A.; Saito, R.; Maruyama, Y.; Kawahara, M.; Ou, S.-H.I. Performance Status and Smoking Status Are Independent Favorable Prognostic Factors for Survival in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: A Comprehensive Analysis of 26,957 Patients with NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shen, Y. Imbalance of circulating T-lymphocyte subpopulation in gastric cancer patients correlated with performance status. Clin. Lab. 2013, 59, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahal, L.N.; Schwarz, H.; Ward, F.J. Hiding in Plain Sight: Soluble Immunomodulatory Receptors. Trends Immunol. 2018, 39, 771–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Tu, H.; Liang, D.; Chang, D.W.; Ye, Y.; Wu, X. Soluble immune checkpoint-related proteins as predictors of tumor recurrence, survival, and T cell phenotypes in clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, K.; Shao, Z.; Schwarz, H. The relevance of soluble CD137 in the regulation of immune responses and for immunotherapeutic intervention. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 107, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernocchi, P.; Del Chierico, F.; Putignani, L. Gut Microbiota Profiling: Metabolomics Based Approach to Unravel Compounds Affecting Human Health. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gettinger, S.; Horn, L.; Jackman, D.; Spigel, D.; Antonia, S.; Hellmann, M.; Powderly, J.; Heist, R.; Sequist, L.V.; Smith, D.C.; et al. Five-Year Follow-Up of Nivolumab in Previously Treated Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Results From the CA209-003 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1675–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, J.S.; Teng, M.W.L.; Smyth, M.J. Cancer immunoediting and resistance to T cell-based immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 1511–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catakovic, K.; Klieser, E.; Neureiter, D.; Geisberger, R. T cell exhaustion: From pathophysiological basics to tumor immunotherapy. Cell Commun. Signal. 2017, 15, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gao, J.; Li, Y.; Nie, J.; Dai, L.; Hu, W.; Chen, X.; Han, J.; Ma, X.; Tian, G.; et al. Circulating PD-L1 in NSCLC patients and the correlation between the level of PD-L1 expression and the clinical characteristics. Thorac. Cancer 2015, 6, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castello, A.; Rossi, S.; Toschi, L.; Mansi, L.; Lopci, E. Soluble PD-L1 in NSCLC Patients Treated with Checkpoint Inhibitors and Its Correlation with Metabolic Parameters. Cancers 2020, 12, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Q.; Shi, B.; Xu, P.; Hu, Z.; Bai, L.; Zhang, X. Development of a sandwich ELISA for evaluating soluble PD-L1 (CD274) in human sera of different ages as well as supernatants of PD-L1+ cell lines. Cytokine 2011, 56, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuipers, H.; Muskens, F.; Willart, M.; Hijdra, D.; Van Assema, F.B.J.; Coyle, A.J.; Hoogsteden, H.C.; Lambrecht, B.N. Contribution of the PD-1 ligands/PD-1 signaling pathway to dendritic cell-mediated CD4+ T cell activation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2006, 36, 2472–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbour, K.C.; Mezquita, L.; Long, N.; Rizvi, H.; Auclin, E.; Ni, A.; Martínez-Bernal, G.; Ferrara, R.; Lai, W.V.; Hendriks, L.E.L.; et al. Impact of Baseline Steroids on Efficacy of Programmed Cell Death-1 and Programmed Death-Ligand 1 Blockade in Patients with Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2872–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matson, V.; Fessler, J.; Bao, R.; Chongsuwat, T.; Zha, Y.; Alegre, M.-L.; Luke, J.J.; Gajewski, T.F. The commensal microbiome is associated with anti–PD-1 efficacy in metastatic melanoma patients. Science 2018, 359, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bersanelli, M.; Brighenti, M.; Buti, S.; Barni, S.; Petrelli, F. Patient performance status and cancer immunotherapy efficacy: A meta-analysis. Med Oncol. 2018, 35, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butaney, M.; Satkunasivam, R.; Goldberg, H.; Freedland, S.J.; Patel, S.P.; Hamid, O.; Pal, S.K.; Klaassen, Z.; Wallis, C.J.D. Analysis of Heterogeneity in Survival Benefit of Immunotherapy in Oncology According to Patient Demographics and Performance Status: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Overall Survival Data. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 43, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, G.; Brock, K.; Savage, J.; Mant, R.; Summers, Y.; Connibear, J.; Shah, R.; Ottensmeier, C.; Shaw, P.; Lee, S.-M.; et al. Pembrolizumab in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer of performance status 2 (PePS2): A single arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaak, E.E.; Canfora, E.E.; Theis, S.; Frost, G.; Groen, A.K.; Mithieux, G.; Nauta, A.; Scott, K.; Stahl, B.; van Harsselaar, J.; et al. Short chain fatty acids in human gut and metabolic health. Benef. Microbes 2020, 11, 411–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingeo, G.; Brito, A.; Samouda, H.; Iddir, M.; La Frano, M.; Bohn, T. Phytochemicals as Modifiers of Gut Microbial Communities. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 8444–8471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Chierico, F.; Nobili, V.; Vernocchi, P.; Russo, A.; De Stefanis, C.; Gnani, D.; Furlanello, C.; Zandonà, A.; Paci, P.; Capuani, G.; et al. Gut microbiota profiling of pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and obese patients unveiled by an integrated meta-omics-based approach. Hepatology 2017, 65, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernocchi, P.; Del Chierico, F.; Russo, A.; Majo, F.; Rossitto, M.; Valerio, M.; Casadei, L.; La Storia, A.; De Filippis, F.; Rizzo, C.; et al. Gut microbiota signatures in cystic fibrosis: Loss of host CFTR function drives the microbiota enterophenotype. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cani, P.D.; Bibiloni, R.; Knauf, C.; Waget, A.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Delzenne, N.M.; Burcelin, R. Changes in Gut Microbiota Control Metabolic Endotoxemia-Induced Inflammation in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity and Diabetes in Mice. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1470–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garner, C.E.; Smith, S.; de Lacy Costello, B.; White, P.; Spencer, R.; Probert, C.S.J.; Ratcliffe, N.M. Volatile organic compounds from feces and their potential for diagnosis of gastrointestinal disease. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 1675–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keefe, S.J.D. Diet, microorganisms and their metabolites, and colon cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Andersen, G.L.; Knight, R. PyNAST: A fexible tool for aligning sequences to a template alignment. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 266–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSantis, T.Z.; Hugenholtz, P.; Larsen, N.; Rojas, M.; Brodie, E.L.; Keller, K.; Huber, T.; Dalevi, D.; Hu, P.; Andersen, G.L. Greengenes, a Chimera-Checked 16S rRNA Gene Database and Workbench Compatible with ARB. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5069–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasili, E.; Hassimotto, N.M.A.; Del Chierico, F.; Marini, F.; Quagliariello, A.; Sciubba, F.; Miccheli, A.; Putignani, L.; Lajolo, F. Daily Consumption of Orange Juice from Citrus sinensis L. Osbeck cv. Cara Cara and cv. Bahia Differently Affects Gut Microbiota Profiling as Unveiled by an Integrated Meta-Omics Approach. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 1381–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasili, E.; Mengheri, E.; Tomassini, A.; Capuani, G.; Roselli, M.; Finamore, A.; Sciubba, F.; Marini, F.; Miccheli, A. Lactobacillus acidophilus La5 and Bifidobacterium lactis Bb12 Induce Different Age-Related Metabolic Profiles Revealed by 1H-NMR Spectroscopy in Urine and Feces of Mice. J. Nutr. 2013, 143, 1549–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Jewison, T.; Guo, A.C.; Wilson, M.; Knox, C.; Liu, Y.; Djoumbou, Y.; Mandal, R.; Aziat, F.; Dong, E.; et al. HMDB 3.0—The Human Metabolome Database in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D801–D807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Patient Characteristics | N (%) |
|---|---|
| Age | |
| ≤65 | 12 (55) |
| >65 | 10 (45) |
| Gender | |
| Male | 16 (73) |
| Female | 6 (27) |
| Smoking | |
| Yes | 19 (86) |
| No | 3 (14) |
| Histology | |
| Adenocarcinoma | 4 (18) |
| Sq. Cell carcinoma | 18 (82) |
| Site of metastasis | |
| Lymph nodes | 15 (68) |
| Lung | 20 (91) |
| Liver | 3 (14) |
| Brain | 4 (18) |
| Bone | 4 (14) |
| Other | 5 (23) |
| N° of affected organs | |
| 1 | 5 (23) |
| 2 | 10 (45) |
| 3 | 4 (18) |
| >3 | 2 (9) |
| cT before Nivolumab | |
| X | 1 (4) |
| 0 | 4 (18) |
| 1 | 2(9) |
| 2 | 0 |
| 3 | 6 (27) |
| 4 | 9 (41) |
| cN before Nivolumab | |
| 0 | 9 (41) |
| 1 | 11 (50) |
| 2 | 2 (9) |
| Treatment lines | |
| 2 | 20 (91) |
| >2 | 2 (9) |
| Response to Nivolumab | |
| Yes | 11 (50) |
| No | 11 (50) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zizzari, I.G.; Di Filippo, A.; Scirocchi, F.; Di Pietro, F.R.; Rahimi, H.; Ugolini, A.; Scagnoli, S.; Vernocchi, P.; Del Chierico, F.; Putignani, L.; et al. Soluble Immune Checkpoints, Gut Metabolites and Performance Status as Parameters of Response to Nivolumab Treatment in NSCLC Patients. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10040208
Zizzari IG, Di Filippo A, Scirocchi F, Di Pietro FR, Rahimi H, Ugolini A, Scagnoli S, Vernocchi P, Del Chierico F, Putignani L, et al. Soluble Immune Checkpoints, Gut Metabolites and Performance Status as Parameters of Response to Nivolumab Treatment in NSCLC Patients. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2020; 10(4):208. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10040208
Chicago/Turabian StyleZizzari, Ilaria Grazia, Alessandra Di Filippo, Fabio Scirocchi, Francesca Romana Di Pietro, Hassan Rahimi, Alessio Ugolini, Simone Scagnoli, Pamela Vernocchi, Federica Del Chierico, Lorenza Putignani, and et al. 2020. "Soluble Immune Checkpoints, Gut Metabolites and Performance Status as Parameters of Response to Nivolumab Treatment in NSCLC Patients" Journal of Personalized Medicine 10, no. 4: 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10040208
APA StyleZizzari, I. G., Di Filippo, A., Scirocchi, F., Di Pietro, F. R., Rahimi, H., Ugolini, A., Scagnoli, S., Vernocchi, P., Del Chierico, F., Putignani, L., Rughetti, A., Marchetti, P., Nuti, M., Botticelli, A., & Napoletano, C. (2020). Soluble Immune Checkpoints, Gut Metabolites and Performance Status as Parameters of Response to Nivolumab Treatment in NSCLC Patients. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 10(4), 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm10040208






