Development of Rapid Extraction Method of Mycobacterium avium Subspecies paratuberculosis DNA from Bovine Stool Samples
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Origin
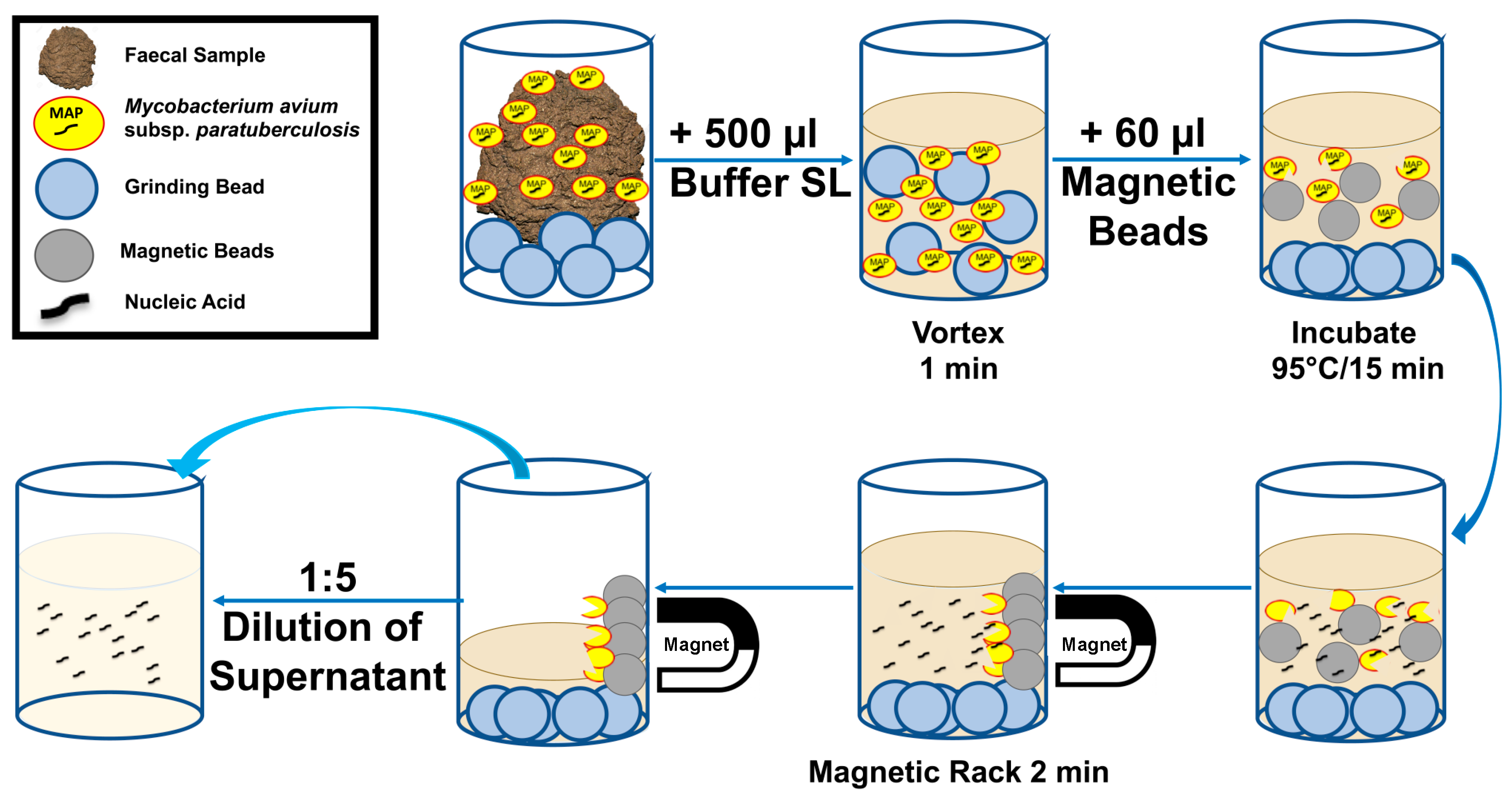
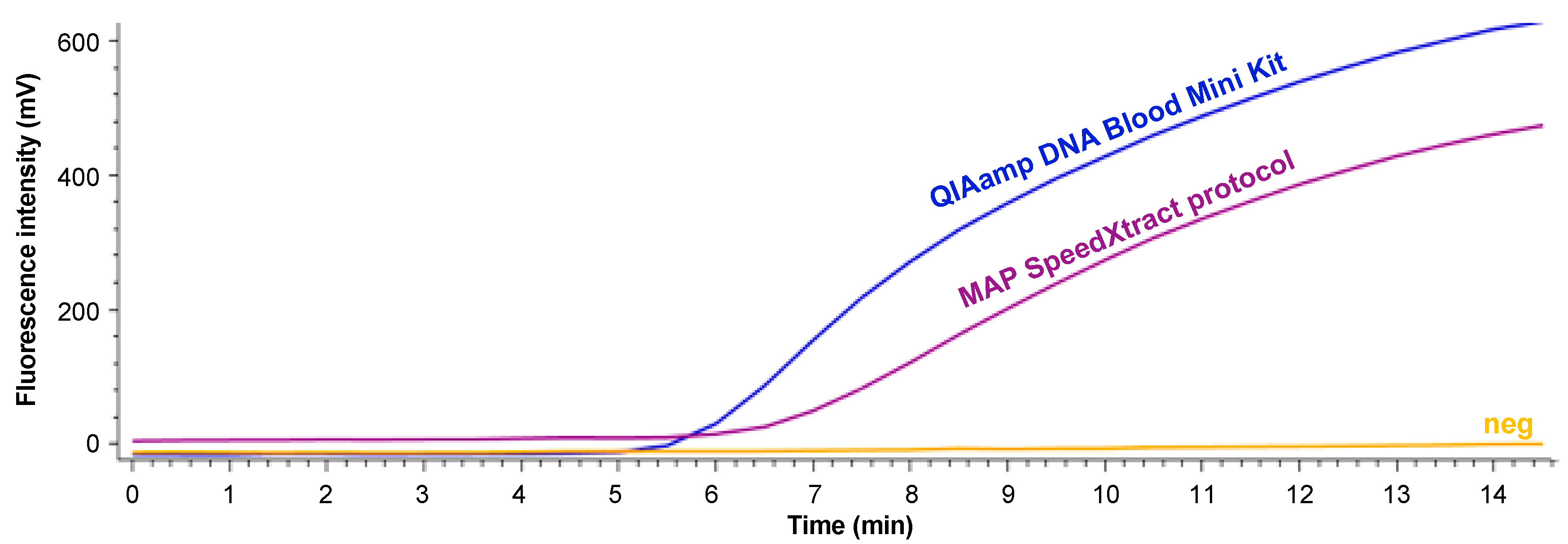
2.2. Development of MAP SpeedXtract Protocol
2.3. RPA Assay
2.4. Clinical Sensitivity and Specificity
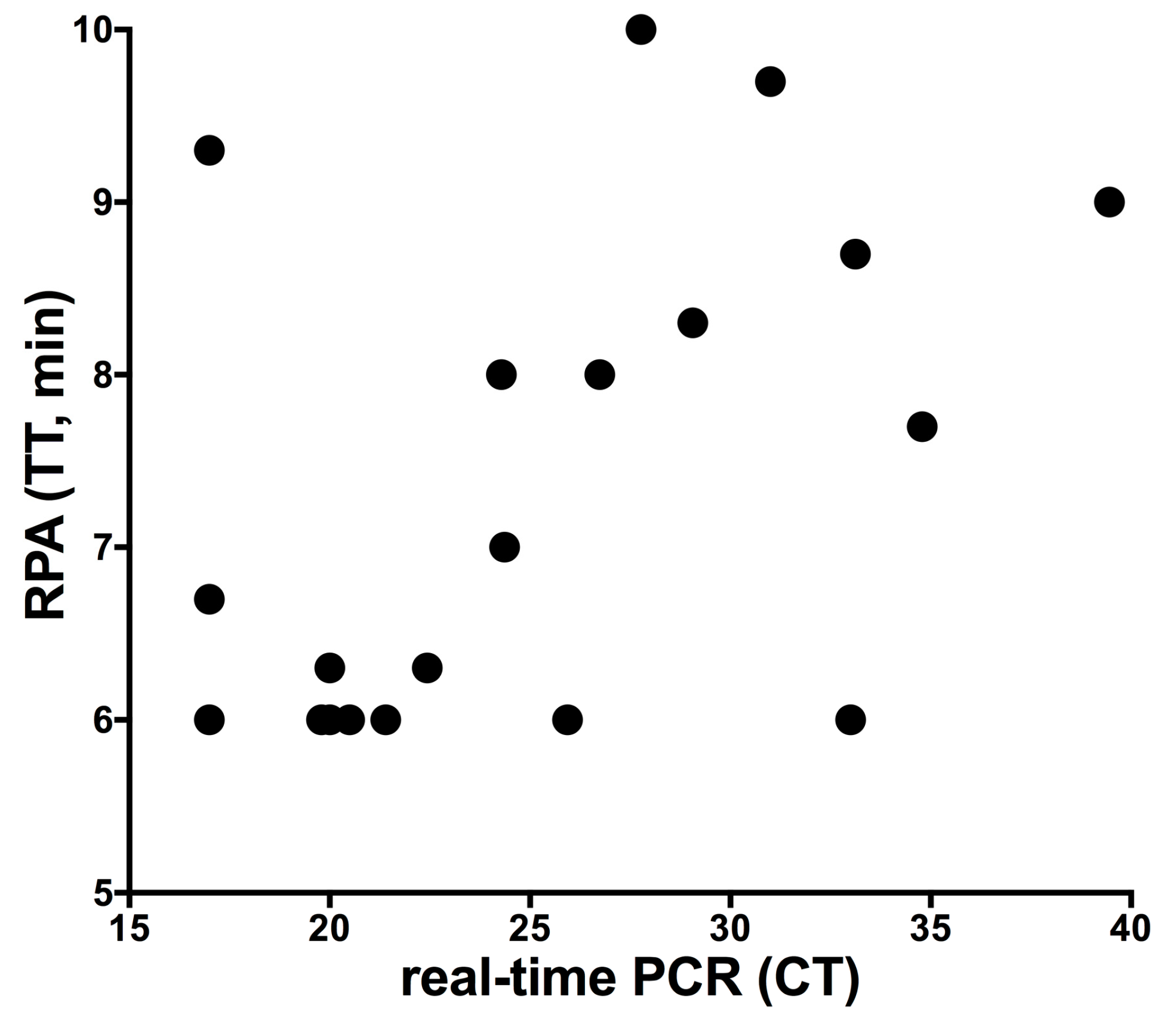
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manning, E.J.; Collins, M.T. Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis: Pathogen, pathogenesis and diagnosis. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2001, 20, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, A.; VanLeeuwen, J.A.; Dohoo, I.R.; Keefe, G.P.; Weersink, A. Estimate of the direct production losses in Canadian dairy herds with subclinical Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis infection. Can. Vet. J. 2008, 49, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Corbett, C.S.; De Buck, J.; Orsel, K.; Barkema, H.W. Fecal shedding and tissue infections demonstrate transmission of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in group-housed dairy calves. Vet. Res. 2017, 48, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albuquerque, P.P.; Santos, A.S.; Souza Neto, O.L.; Kim, P.C.; Cavalcanti, E.F.; Oliveira, J.M.; Mota, R.A.; Junior, J.W. Detection of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in bovine milk from the state of Pernambuco, Brazil. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2017, 48, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobius, P.; Hotzel, H.; Rassbach, A.; Kohler, H. Comparison of 13 single-round and nested PCR assays targeting IS900, ISMav2, f57 and locus 255 for detection of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 126, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, S.; Schafer, J.; Fechner, K.; Czerny, C.P.; Abd El Wahed, A. Development of a Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay for Rapid Detection of the Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, N.; Carletti, S.; Ghidoli, N.; Cichero, P.; Burioni, R.; Clementi, M. The era of molecular and other non-culture-based methods in diagnosis of sepsis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.Z.; Zhang, S. An efficient DNA extraction method for polymerase chain reaction-based detection of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis in bovine fecal samples. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 2011, 23, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeil, M.R.; Brennan, P.J. Structure, function and biogenesis of the cell envelope of mycobacteria in relation to bacterial physiology, pathogenesis and drug resistance; some thoughts and possibilities arising from recent structural information. Res. Microbiol. 1991, 142, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaro, A.; Duarte, E.; Amado, A.; Ferronha, H.; Botelho, A. Comparison of three DNA extraction methods for Mycobacterium bovis, Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium subsp. avium. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 47, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munster, P.; Volkel, I.; Wemheuer, W.; Schwarz, D.; Doring, S.; Czerny, C.P. A longitudinal study to characterize the distribution patterns of Mycobacterium avium ssp. paratuberculosis in semen, blood and faeces of a naturally infected bull by IS 900 semi-nested and quantitative real-time PCR. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2013, 60, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fechner, K.; Schafer, J.; Wiegel, C.; Ludwig, J.; Munster, P.; Sharifi, A.R.; Wemheuer, W.; Czerny, C.P. Distribution of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis in a Subclinical Naturally Infected German Fleckvieh Bull. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2015, 64, 916–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunaratna, G.; Manamperi, A.; Bohlken-Fascher, S.; Wickremasinge, R.; Gunawardena, K.; Yapa, B.; Pathirana, N.; Pathirana, H.; de Silva, N.; Sooriyaarachchi, M.; et al. Evaluation of rapid extraction and isothermal amplification techniques for the detection of Leishmania donovani DNA from skin lesions of suspected cases at the point of need in Sri Lanka. Parasit Vectors 2018, 11, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faye, O.; Faye, O.; Soropogui, B.; Patel, P.; El Wahed, A.A.; Loucoubar, C.; Fall, G.; Kiory, D.; Magassouba, N.; Keita, S.; et al. Development and deployment of a rapid recombinase polymerase amplification Ebola virus detection assay in Guinea in 2015. Euro. Surveill 2015, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, D.; Ghosh, P.; Khan, M.A.; Hossain, F.; Bohlken-Fascher, S.; Matlashewski, G.; Kroeger, A.; Olliaro, P.; Abd El Wahed, A. Mobile suitcase laboratory for rapid detection of Leishmania donovani using recombinase polymerase amplification assay. Parasit Vectors 2016, 9, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite, F.L.; Stokes, K.D.; Robbe-Austerman, S.; Stabel, J.R. Comparison of fecal DNA extraction kits for the detection of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis by polymerase chain reaction. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 2013, 25, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El Wahed, A.; Patel, P.; Faye, O.; Thaloengsok, S.; Heidenreich, D.; Matangkasombut, P.; Manopwisedjaroen, K.; Sakuntabhai, A.; Sall, A.A.; Hufert, F.T.; et al. Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Assay for Rapid Diagnostics of Dengue Infection. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidmann, M.; Faye, O.; Faye, O.; Abd El Wahed, A.; Patel, P.; Batejat, C.; Manugerra, J.C.; Adjami, A.; Niedrig, M.; Hufert, F.T.; et al. Development of Mobile Laboratory for Viral Hemorrhagic Fever Detection in Africa. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 1622–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlottau, K.; Freuling, C.M.; Muller, T.; Beer, M.; Hoffmann, B. Development of molecular confirmation tools for swift and easy rabies diagnostics. Virol. J. 2017, 14, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, M.; Verdugo, C.; Heuer, C.; Castillo, P.; Zamorano, P. A novel low-cost method for Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis DNA extraction from an automated broth culture system for real-time PCR analysis. J. Vet. Sci. 2014, 15, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, V.; Guzman, A.; Mejia, G.; Caceres, D.; Robledo, J.; Rouzaud, F. Evaluation of Simple and Cost-Effective DNA Preparation and Subsequent PCR Amplification for Clinically Relevant Mycobacteria. Br. J. Med. Med. Res. 2015, 8, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tell, L.A.; Foley, J.; Needham, M.L.; Walker, R.L. Comparison of four rapid DNA extraction techniques for conventional polymerase chain reaction testing of three Mycobacterium spp. that affect birds. Avian. Dis. 2003, 47, 1486–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- QIAgen; (Hilden; Germany). RNeasy® Mini Handbook. Available online: https://www.arabidopsis.org/download_files/Protocols/RNeasy.pdf (accessed on 29 March 2019).
| Protocol | Pre-Treatment of the Sample | TT (min) | Exponential Curve | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 min; 40 °C | Ultrasonic (20 kHz, 4 min) (BANDELIN electronic, Berlin, Germany) | Bead Beating (1 min) using Soil Grinding SK38 Precellys Tube (Bertin Corp., Rockville, MD, USA) | SpeedXtract Kit (QIAgen Lake Constance, Stockach, Germany) | ||||||
| Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (20 %) 30 µL (Carl Roth, Karlsruhe, Germany) | Proteinase K 60 µL (Carl Roth, Karlsruhe, Germany) | Protease 5 µL (QIAgen, Hilden, Germany) | on Precellys 24 Tissue Homogenizer (6500 rpm) (Bertin Corp., Rockville, MD, USA) | on Vortex (Scientific Industries, Bohemia, NYC, USA) | |||||
| 1 | + | + | + | + | + | neg | |||
| 2 | + | + | + | + | 6.0 | + | |||
| 3 | + | + | + | + | 6.0 | + | |||
| 4 | + | + | + | neg | |||||
| 5 | + | + | neg | ||||||
| 6 | + | + | neg | ||||||
| 7 | + | + | + | 6.7 | + | ||||
| 8 | + | + | + | 6.7 | |||||
| 9 | + | + | 6.3 | + | |||||
| 10 | + | + | 6.7 | + | |||||
| 11 | + | neg | |||||||
| Reference | Kit Used | Kit Producing Company | Purification Method | Time Needed (min) | Sample Amount (mg) | Bead Beating | Heating Step (56 °C–70 °C) | Boiling Step | Proteinase K | Centrifugation | Costs Per reaction (€) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Münster et al., 2013 [11] | QIAmp DNA Blood Mini Kit | Qiagen Hilden, Hilden, Germany | silica gel membrane column | 150 | 100 | + | + | + | + | + | 5.90 |
| Zang and Zang, 2011 [8] | home-made recipe | silica gel membrane column | 160 | + | + | + | + | ||||
| Leite et al., 2013 [16] | MagMax Total Nucleic Acid Isolation Kit | Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA | magnetic nucleic acid binding beads | 40 | 300 | + | + | 5.52 | |||
| PowerSoil DNA Isolation Kit | MO BIO Laboratories Inc., Carlsbad, CA, USA | silica gel membrane column | 40 | 300 | + | + | + | + | 5.00 | ||
| QIAamp Stool DNA Mini Kit | Qiagen Hilden, Hilden, Germany | silica gel membrane column | 40 | 1000 | + | + | + | + | + | 5.78 | |
| ExtractMaster Fecal DNA Extraction Kit | Epicenter Biotechnologies, Madison, WI, USA | inhibitor removal spin column | 50 | 50 | + | + | + | unknown | |||
| ZR Fecal DNA MiniPrep | Zymo Research Corp., Irvine, CA, USA | Spin column | 20 | 150 | + | + | 2.65 | ||||
| MAP Extraction System | Tetracore Inc., Rockville, MD, USA | Spin column | 120 | 2000 | + | + | 4.85 | ||||
| Salgado et al., [20] | home-made recipe | centrifugation | 160 | 200 | + | + | + | + | + | ||
| MAP DNA SpeedXtract | SpeedXtract Nucleic Acid Kit | Qiagen Lake Constance, Stockach, Germany | inhibitor removal magnetic beads | 25 | 100 | + | + | 4.75 | |||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hansen, S.; Roller, M.; Alslim, L.M.A.; Böhlken-Fascher, S.; Fechner, K.; Czerny, C.-P.; Abd El Wahed, A. Development of Rapid Extraction Method of Mycobacterium avium Subspecies paratuberculosis DNA from Bovine Stool Samples. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics9020036
Hansen S, Roller M, Alslim LMA, Böhlken-Fascher S, Fechner K, Czerny C-P, Abd El Wahed A. Development of Rapid Extraction Method of Mycobacterium avium Subspecies paratuberculosis DNA from Bovine Stool Samples. Diagnostics. 2019; 9(2):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics9020036
Chicago/Turabian StyleHansen, Sören, Marco Roller, Lamia M. A. Alslim, Susanne Böhlken-Fascher, Kim Fechner, Claus-Peter Czerny, and Ahmed Abd El Wahed. 2019. "Development of Rapid Extraction Method of Mycobacterium avium Subspecies paratuberculosis DNA from Bovine Stool Samples" Diagnostics 9, no. 2: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics9020036
APA StyleHansen, S., Roller, M., Alslim, L. M. A., Böhlken-Fascher, S., Fechner, K., Czerny, C.-P., & Abd El Wahed, A. (2019). Development of Rapid Extraction Method of Mycobacterium avium Subspecies paratuberculosis DNA from Bovine Stool Samples. Diagnostics, 9(2), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics9020036






