Strain Elastography Ultrasound: An Overview with Emphasis on Breast Cancer Diagnosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Elastographic Technique
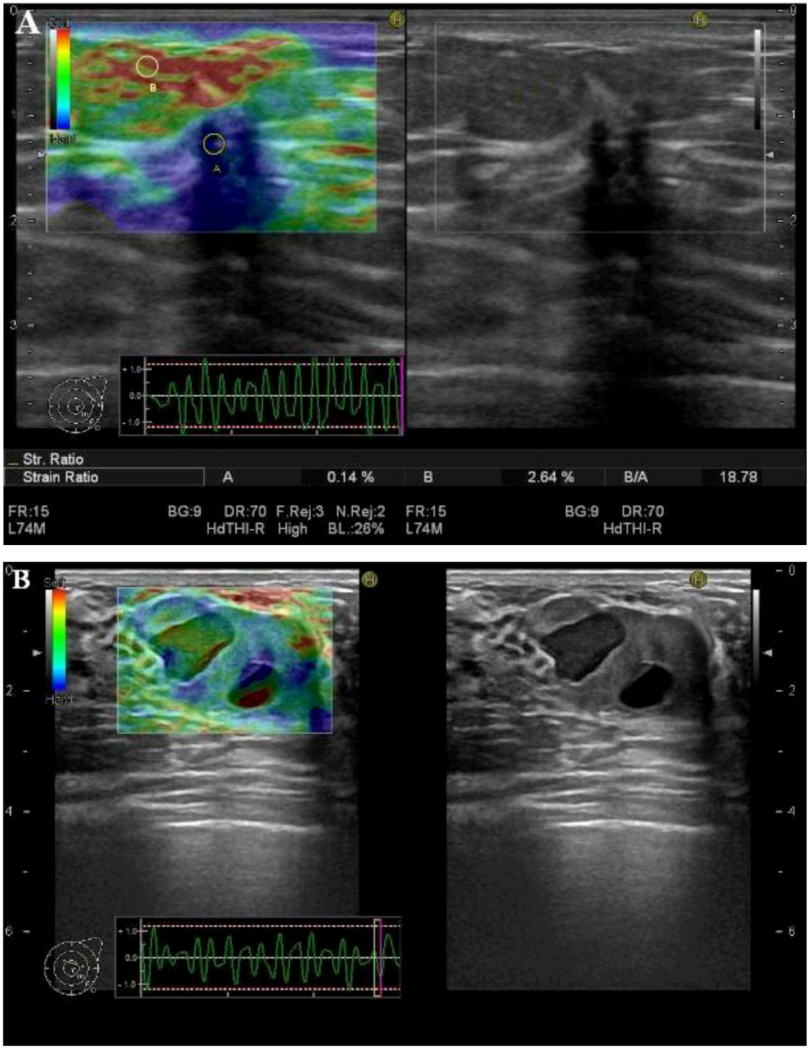
3. Clinical Applications
| Study | Lesions biopsied (No. of patients) | Malignant/benign lesions (ratio) | Sensitivity | Specificity | Accuracy | Included lesions | ||||||
| B-mode | SE | Combined | B-mode | SE | Combined | B-mode | SE | Combined | ||||
| Zhi et al. [15] | 401(370) | 155/246 (0.63) | 90.3 | 72.3 | 83.9 | 68.3 | 91.9 | 87.8 | 76.8 | 84.4 | 86.3 | Lesions <2 cm |
| Lee et al. [16] | 315(278) | 48/267 (0.18) | 95.8 | 35.4 (68.8)# | 93.8 | 27.3 | 98.9¤ (64.8)# | 51.7 | 37.3* | 89*¤ (65.4)# | 58.6* | Lesions <1 cm SFB |
| Fu et al. [17] | 308(283) | 104/204 (0.51) | 82.7 | 66 | 97.1 | 87.7 | 88 | 71.9 | 86.0 | 81 | 80.5 | All lesions <2 cm |
| Wojcinski et al. [18] | 779(779) | 360/419 (0.86) | 95.0 | 81.2 | na | 76.1 | 89.0 | na | 84.9* | 85.4* | na | Visible on B-mode, SFB |
| Zhi et al. [19] | 559(437) | 144/415 (0.35) | na | 70.1 (92.4)# | na | na | 93.0 (91.1)# | na | na | 87.2 (91.4)# | na | BI-RADS 2-5 |
| Kumm et al. [20] | 310(288) | 87/223 (0.39) | na | 76 (79)# | na | na | 81 (76)# | na | na | 79 (77)# | na | Visible on B-mode, SFB |
| Sohn et al. [21] | 281(267) | 59/222 (0.27) | 98.2 | 65.5 | 89.1 | 44.1 | 79 | 50.5 | 55.5* | 76.2* | 58.6* | Visible on B-mode, SFB |
| Tan et al. [22] | 415(550) | 119/431 (0.28) | 86.6 | 78.0 | Na | 98.8 | 98.5 | na | 86.2 | 96.2 | na | Visible on B-mode |
| Zhi et al. [23] | 296(232) | 87/209 (0.42) | 71.2 | 70.1 | 89.7 | 73.2 | 95.7 | 85.7 | 72.6 | 95.0 | 93.9 | Solid breast lesions |
| Yi et al. [24] | 1,786(1,538) | 263/1,523 (0.17) | 98.5 | 34.2 | Na | 16.3 | 97.2 | na | 28.4* | 87.9* | na | Non-palpable lesions |
3.1. Diagnostic Performance of SE
3.2. Combination of B-Mode and SE
| Elasticity-Score | |||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Downgrade BI-RADS 4–5 by one | Unchanged | Upgrade BI-RADS 1–3 by one | |||
| Lee et al. [16] | Downgrade all | Unchanged BI-RADS score | Upgrade all BI-RADS by one | ||
| Fu et al. [17] | Unchanged BI-RADS score | Upgrade BI-RADS 1–3 to malignant (≥4) | |||
| Sohn. et al. [21] | Upgrade or downgrade of BI-RADS done unformalized by the evaluator | ||||
| Zhi et al. [23] | Method of combination of SE and B-mode US not described | ||||
3.3. SR-Measurements
4. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
References
- Ophir, J.; Céspedes, I.; Ponnekanti, H.; Yazdi, Y.; Li, X. Elastography: A quantitative method for imaging the elasticity of biological tissues. Ultrason. Imag. 1991, 13, 111–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garra, B.S.; Cespedes, E.I.; Ophir, J.; Spratt, S.R.; Zuurbier, R.A.; Magnant, C.M.; Pennanen, M.F. Elastography of breast lesions: initial clinical results. Radiology 1997, 202, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garra, B.S. Elastography. Ultrasound Q 2011, 27, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoskins, P.R. Principles of ultrasound elastography. Ultrasound 2012, 20, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, H. Realtime-elastographie. Der Radiologe 2003, 43, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, A.; Ueno, E.; Tohno, E.; Kamma, H.; Takahashi, H.; Shiina, T.; Yamakawa, M.; Matsumura, T. Breast disease: Clinical application of US elastography for diagnosis. Radiology 2006, 239, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, E.-K.; Kim, M.J.; Son, E.J.; Kwak, J.Y. Interobserver Agreement in assessing the sonographic and elastographic features of malignant thyroid nodules. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2009, 193, W416–W423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragazzoni, F.; Deandrea, M.; Mormile, A.; Ramunni, M.J.; Garino, F.; Magliona, G.; Motta, M.; Torchio, B.; Garberoglio, R.; Limone, P. High diagnostic accuracy and interobserver reliability of real-time elastography in the evaluation of thyroid nodules. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2012, 38, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, K.S.S.; Cho, C.C.M.; Yuen, Y.-H.; Rasalkar, D.D.; King, A.D.; Ahuja, A.T. Real-time qualitative ultrasound elastography of cervical lymph nodes in routine clinical practice: Interobserver agreement and correlation with malignancy. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2010, 36, 1990–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, K.S.S.; Rasalkar, D.D.; Lee, Y.-P.; Wong, K.-T.; King, A.D.; Yuen, Y.-H.; Ahuja, A.T. Real-time qualitative ultrasound elastography of miscellaneous non-nodal neck masses: Applications and limitations. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2010, 36, 1644–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, L.; Hou, Y.; Zheng, H.-M.; Lin, X.; Xie, Z.-L.; Hu, Y.-P. Real-time elastography for the differentiation of benign and malignant superficial lymph nodes: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2011, 81, 2576–2584. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fischer, T.; Peisker, U.; Fiedor, S.; Slowinski, T.; Wedemeyer, P.; Diekmann, F.; Grigoryev, M.; Thomas, A. Significant differentiation of focal breast lesions: Raw data-based calculation of strain ratio. Eur. J. Radiol. 2011, 33, 372–379. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, A.; Degenhardt, F.; Farrokh, A.; Wojcinski, S.; Slowinski, T.; Fischer, T. Significant differentiation of focal breast lesions: Calculation of strain ratio in breast sonoelastography. Acad. Radiol. 2010, 17, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havre, R.F.; Elde, E.; Gilja, O.H.; Ödegaard, S.; Eide, G.E.; Matre, K.; Nesje, L.B. Freehand real-time elastography: Impact of scanning parameters on image quality and in vitro intra- and interobserver validations. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2008, 34, 1638–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, H.; Xiao, X.-Y.; Ou, B.; Zhong, W.-J.; Zhao, Z.-Z.; Zhao, X.-B.; Yang, H.-Y.; Luo, B.-M. Could ultrasonic elastography help the diagnosis of small (≤2 cm) breast cancer with the usage of sonographic BI-RADS classification? Eur. J. Radiol. 2012, 81, 3216–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, B.J.; Choi, J.J.; Jeong, S.H.; Yim, H.W.; Song, B.J. Role and clinical usefulness of elastography in small breast masses. Acad. Radiol. 2011, 18, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y. Value of ultrasound elastography in detecting small breast tumors. Chin. Med. J. 2011, 124, 2384–2386. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wojcinski, S.; Farrokh, A.; Weber, S.; Thomas, A.; Fischer, T.; Slowinski, T.; Schmidt, W.; Degenhardt, F. Multicenter study of ultrasound real-time tissue elastography in 779 cases for the assessment of breast lesions: Improved diagnostic performance by combining the BI-RADS®-US classification system with sonoelastography. Ultraschall Der Medizin 2010, 31, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, H.; Xiao, X.-Y.; Yang, H.-Y.; Ou, B.; Wen, Y.-L.; Luo, B.-M. Ultrasonic elastography in breast cancer diagnosis: Strain ratio vs. 5-point scale. Acad. Radiol. 2010, 17, 1227–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumm, T.R.; Szabunio, M.M. Elastography for the characterization of breast lesions: Initial clinical experience. Canc. Contr. J. Moffitt Canc. Center 2010, 17, 156–161. [Google Scholar]
- Sohn, Y.-M.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, E.-K.; Kwak, J.Y.; Moon, H.J.; Kim, S.J. Sonographic elastography combined with conventional sonography: How much is it helpful for diagnostic performance? J. Ultrasound Med. 2009, 28, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.M.; Teh, H.S.; Mancer, J.F.K.; Poh, W.T. Improving B mode ultrasound evaluation of breast lesions with real-time ultrasound elastography—A clinical approach. Breast 2008, 17, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, H.; Ou, B.; Luo, B.-M.; Feng, X.; Wen, Y.-L.; Yang, H.-Y. Comparison of ultrasound elastography, mammography, and sonography in the diagnosis of solid breast lesions. J. Ultrasound Med. 2007, 26, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yi, A.; Cho, N.; Chang, J.M.; Koo, H.R.; La Yun, B.; Moon, W.K. Sonoelastography for 1,786 non-palpable breast masses: Diagnostic value in the decision to biopsy. Eur. Radiol. 2012, 22, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American College of Radiology. Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System® (BI-RADS®). Available online: http://www.birads.at/info.html (accessed on 31 December 2012).
- Gong, X.; Xu, Q.; Xu, Z.; Xiong, P.; Yan, W.; Chen, Y. Real-time elastography for the differentiation of benign and malignant breast lesions: A meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 130, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadigh, G.; Carlos, R.; Neal, C.; Dwamena, B. Accuracy of quantitative ultrasound elastography for differentiation of malignant and benign breast abnormalities: A meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 134, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Carlsen, J.F.; Ewertsen, C.; Lönn, L.; Nielsen, M.B. Strain Elastography Ultrasound: An Overview with Emphasis on Breast Cancer Diagnosis. Diagnostics 2013, 3, 117-125. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics3010117
Carlsen JF, Ewertsen C, Lönn L, Nielsen MB. Strain Elastography Ultrasound: An Overview with Emphasis on Breast Cancer Diagnosis. Diagnostics. 2013; 3(1):117-125. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics3010117
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarlsen, Jonathan F., Caroline Ewertsen, Lars Lönn, and Michael B. Nielsen. 2013. "Strain Elastography Ultrasound: An Overview with Emphasis on Breast Cancer Diagnosis" Diagnostics 3, no. 1: 117-125. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics3010117
APA StyleCarlsen, J. F., Ewertsen, C., Lönn, L., & Nielsen, M. B. (2013). Strain Elastography Ultrasound: An Overview with Emphasis on Breast Cancer Diagnosis. Diagnostics, 3(1), 117-125. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics3010117







