Agreement Analysis Among Hip and Knee Periprosthetic Joint Infections Classifications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Laboratory Methods
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
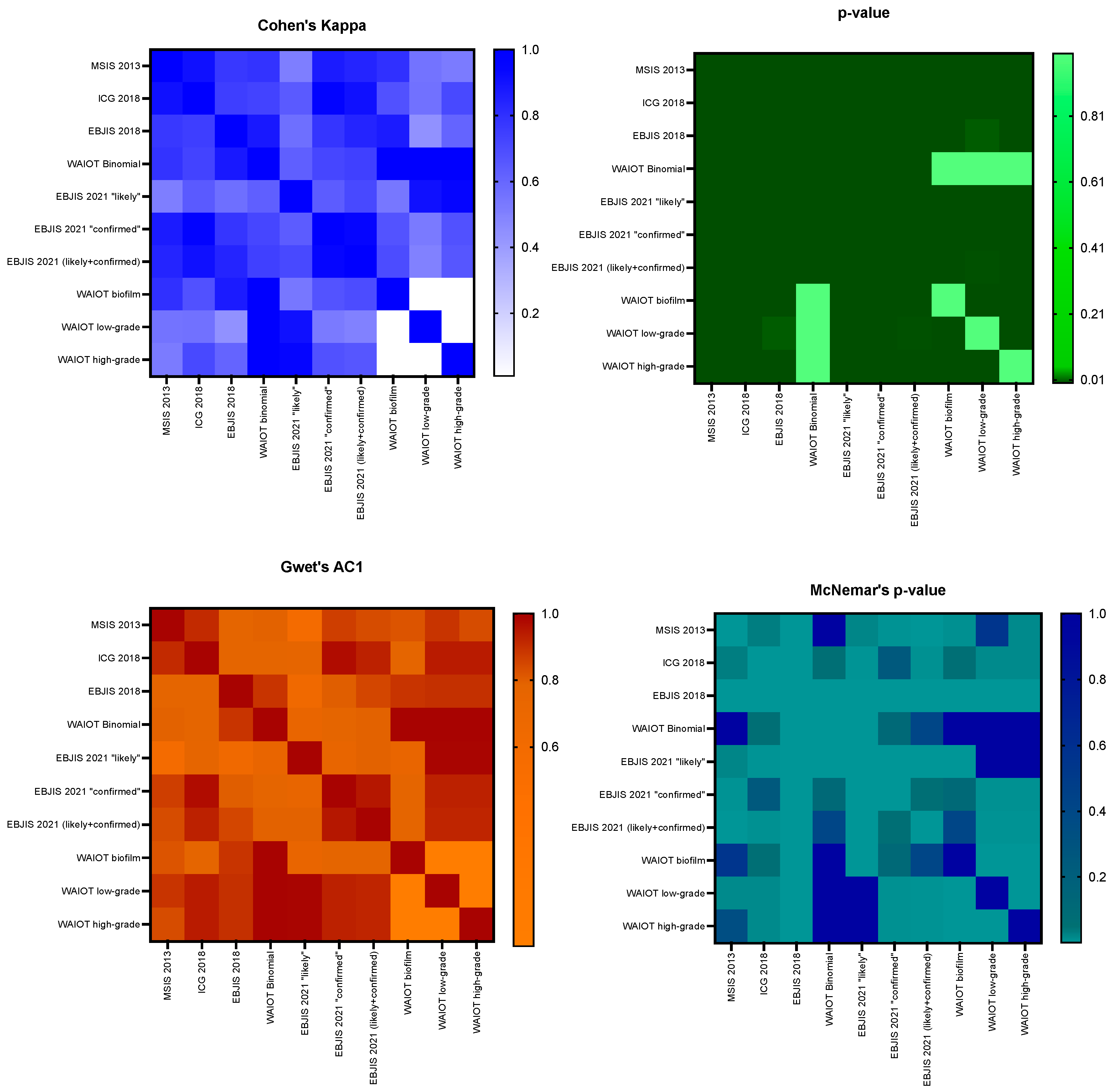
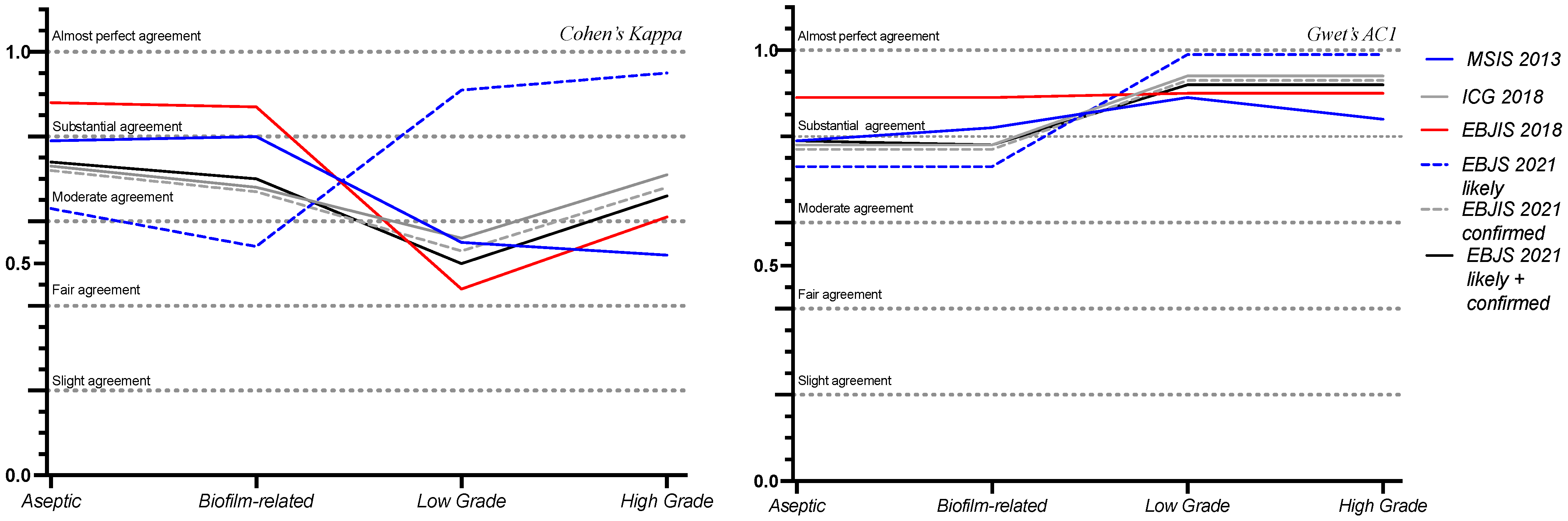
3.2. Agreement Among Classifications
3.3. Clinical Implications of Agreement Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zardi, E.M.; Franceschi, F. Prosthetic Joint Infection. A Relevant Public Health Issue. J. Infect. Public Health 2020, 13, 1888–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izakovicova, P.; Borens, O.; Trampuz, A. Periprosthetic Joint Infection: Current Concepts and Outlook. EFORT Open Rev. 2019, 4, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvizi, J.; Zmistowski, B.; Berbari, E.F.; Bauer, T.W.; Springer, B.D.; Della Valle, C.J.; Garvin, K.L.; Mont, M.A.; Wongworawat, M.D.; Zalavras, C.G. New Definition for Periprosthetic Joint Infection: From the Workgroup of the Musculoskeletal Infection Society. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2011, 469, 2992–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvizi, J.; Gehrke, T. International Consensus Group on Periprosthetic Joint Infection Definition of Periprosthetic Joint Infection. J. Arthroplast. 2014, 29, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvizi, J.; Tan, T.L.; Goswami, K.; Higuera, C.; Della Valle, C.; Chen, A.F.; Shohat, N. The 2018 Definition of Periprosthetic Hip and Knee Infection: An Evidence-Based and Validated Criteria. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 1309–1314.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanò, C.L.; Khawashki, H.A.; Benzakour, T.; Bozhkova, S.; Sel, H.; Hafez, M.; Johari, A.; Lob, G.; Sharma, H.K.; Tsuchiya, H.; et al. The W.A.I.O.T. Definition of High-Grade and Low-Grade Peri-Prosthetic Joint Infection. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renz, N.; Yermak, K.; Perka, C.; Trampuz, A. Alpha Defensin Lateral Flow Test for Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infection: Not a Screening but a Confirmatory Test. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2018, 100, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, M.; Sousa, R.; Wouthuyzen-Bakker, M.; Chen, A.F.; Soriano, A.; Vogely, H.C.; Clauss, M.; Higuera, C.A.; Trebše, R. The EBJIS Definition of Periprosthetic Joint Infection. Bone Jt. J. 2021, 103, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Kobayashi, N.; Tomoyama, A.; Choe, H.; Yamazaki, E.; Inaba, Y. Clinical Characteristics and Risk Factors for Culture-Negative Periprosthetic Joint Infections. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2021, 16, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palan, J.; Nolan, C.; Sarantos, K.; Westerman, R.; King, R.; Foguet, P. Culture-Negative Periprosthetic Joint Infections. EFORT Open Rev. 2019, 4, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersh, B.L.; Shah, N.B.; Rothenberger, S.D.; Zlotnicki, J.P.; Klatt, B.A.; Urish, K.L. Do Culture Negative Periprosthetic Joint Infections Remain Culture Negative? J. Arthroplast. 2019, 34, 2757–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Huang, Z.; Li, W.; Fang, X.; Zhang, W. Can Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing Identify the Pathogens Responsible for Culture-Negative Prosthetic Joint Infection? BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cretu, B.; Iordache, S.; Cursaru, A.; Serban, B.; Costache, M.; Cirstoiu, C.; Spiridonica, R. Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing for Periprosthetic Joint Infections. Cureus 2023, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan-Hughes, A.M.; Griffiths, A.; Evans, J.; Slater, D.; Eddowes, L.A. Investigating The Cost-Effectiveness Of Bacterial Whole-Genome Sequencing For Enabling Targeted Antibiotic Selection In Urinary Tract Infections. Value Health 2015, 18, A510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, D.; Kanitkar, T.; Narouz, M.; Azadian, B.S.; Moore, L.S.P.; Mughal, N. Clinical Utility and Cost-Effectiveness of Bacterial 16S rRNA and Targeted PCR Based Diagnostic Testing in a UK Microbiology Laboratory Network. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscato, F.; Corti, A.; Manlio Gambaro, F.; Chiappetta, K.; Loppini, M.; Corino, V.D.A. Combining Deep Learning and Machine Learning for the Automatic Identification of Hip Prosthesis Failure: Development, Validation and Explainability Analysis. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2023, 176, 105095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapf, A.; Castell, S.; Morawietz, L.; Karch, A. Measuring Inter-Rater Reliability for Nominal Data—Which Coefficients and Confidence Intervals Are Appropriate? BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2016, 16, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.F.; Krippendorff, K. Answering the Call for a Standard Reliability Measure for Coding Data. Commun. Methods Meas. 2007, 1, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwet, K.L. Handbook of Inter-Rater Reliability. In The Definitive Guide to Measuring The Extent of Agreement Among Raters, 4th ed.; Advanced Analytics, LLC.: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-0-9708062-8-4. [Google Scholar]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The Measurement of Observer Agreement for Categorical Data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Sloten, M.; Gómez-Junyent, J.; Ferry, T.; Rossi, N.; Petersdorf, S.; Lange, J.; Corona, P.; Abreu, M.A.; Borens, O.; Zlatian, O.; et al. Should All Patients with a Culture-Negative Periprosthetic Joint Infection Be Treated with Antibiotics?: A Multicentre Observational Study. Bone Jt. J. 2022, 104, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, K.; Clarkson, S.; Phillips, C.D.; Dennis, D.A.; Klatt, B.A.; O’Malley, M.J.; Smith, E.L.; Gililland, J.M.; Pelt, C.E.; Peters, C.L.; et al. An Enhanced Understanding of Culture-Negative Periprosthetic Joint Infection with Next-Generation Sequencing: A Multicenter Study. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2022, 104, 1523–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loppini, M.; Pisano, A.; Di Maio, M.; La Camera, F.; Casana, M.; Grappiolo, G. Outcomes of Patients with Unexpected Diagnosis of Infection at Total Hip or Total Knee Arthroplasty Revisions. Int. Orthop. 2021, 45, 2791–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Wang, S.; Yi, Q.; Xia, Y.; Geng, B. Diagnostic Value of Next-Generation Sequencing in Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Systematic Review. Orthop. Surg. 2022, 14, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moojen, D.J.F.; van Hellemondt, G.; Vogely, H.C.; Burger, B.J.; Walenkamp, G.H.I.M.; Tulp, N.J.A.; Schreurs, B.W.; de Meulemeester, F.R.A.J.; Schot, C.S.; van de Pol, I.; et al. Incidence of Low-Grade Infection in Aseptic Loosening of Total Hip Arthroplasty. Acta Orthop. 2010, 81, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, R.; Ribau, A.; Alfaro, P.; Burch, M.-A.; Ploegmakers, J.; McNally, M.; Clauss, M.; Wouthuyzen-Bakker, M.; Soriano, A. The European Bone and Joint Infection Society Definition of Periprosthetic Joint Infection Is Meaningful in Clinical Practice: A Multicentric Validation Study with Comparison with Previous Definitions. Acta Orthop. 2023, 94, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigmund, I.K.; Luger, M.; Windhager, R.; McNally, M.A. Diagnosing Periprosthetic Joint Infections: A Comparison of Infection Definitions: EBJIS 2021, ICM 2018, and IDSA 2013. Bone Jt. Res. 2022, 11, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josse, J.; Valour, F.; Maali, Y.; Diot, A.; Batailler, C.; Ferry, T.; Laurent, F. Interaction Between Staphylococcal Biofilm and Bone: How Does the Presence of Biofilm Promote Prosthesis Loosening? Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, M.M.; Chen, A.F. Biofilms in Periprosthetic Joint Infections: A Review of Diagnostic Modalities, Current Treatments, and Future Directions. J. Knee Surg. 2020, 33, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimy, M.S.; Buddhiraju, A.; Chen, T.L.-W.; Mittal, A.; Xiao, P.; Kwon, Y.-M. Machine Learning to Predict Periprosthetic Joint Infections Following Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty Using a National Database. Arch Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2025, 145, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Hu, X.; Gu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, L.; Pan, B.; Wu, X.; Sun, W.; Sheng, P. A Machine Learning-Based Model for “In-Time” Prediction of Periprosthetic Joint Infection. Digit. Health 2024, 10, 20552076241253531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Demographic Characteristics | Value (IQR) |
|---|---|
| Sex (M) | 93 (45.81%) |
| BMI | 27.11 (16.65–41.02) |
| Age at operation | 66.93 (18.32–90.31) |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index | |
| High Comorbidity Profile (CCI > 2) | 116 (57.14%) |
| Low Comorbidity Profile (CCI ≤ 2) | 87 (42.86%) |
| ASA score | |
| ASA score I | 30 (14.78%) |
| ASA score II | 121 (59.61%) |
| ASA score III | 52 (25.62%) |
| Compared Classifications | Cohen’s Kappa | p-Value | Gwet’s AC1 | McNemar’s p-Value | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSIS 2013—ICG 2018 | 0.91 | <0.001 | 0.91 | 0.031 | Almost perfect agreement |
| MSIS 2013—EBJIS 2018 | 0.77 | <0.001 | 0.77 | <0.001 | Substantial agreement |
| MSIS 2013—WAIOT | 0.79 | <0.001 | 0.79 | 1.000 | Substantial agreement |
| MSIS 2013—EBJIS 2021 | 0.84 | <0.001 | 0.84 | <0.001 | Almost perfect agreement |
| MSIS 2013—EBJIS 2021 likely | 0.51 | <0.001 | 0.57 | 0.022 | Moderate agreement |
| MSIS 2013—EBJIS 2021 confirmed | 0.87 | <0.001 | 0.87 | 0.004 | Almost perfect agreement |
| ICG 2018—EBJIS 2018 | 0.75 | <0.001 | 0.78 | <0.001 | Substantial agreement |
| ICG 2018—WAIOT | 0.73 | <0.001 | 0.78 | 0.064 | Substantial agreement |
| ICG 2018—EBJIS 2021 | 0.91 | <0.001 | 0.93 | 0.008 | Almost perfect agreement |
| ICG 2018—EBJIS 2021 likely | 0.65 | <0.001 | 0.76 | 0.003 | Substantial agreement |
| ICG 2018—EBJIS 2021 confirmed | 0.97 | <0.001 | 0.97 | 0.250 | Almost perfect agreement |
| EBJIS 2018—WAIOT | 0.88 | <0.001 | 0.89 | <0.001 | Almost perfect agreement |
| EBJIS 2018—EBJIS 2021 | 0.84 | <0.001 | 0.85 | <0.001 | Almost perfect agreement |
| EBJIS 2018—EBJIS 2021 likely | 0.57 | <0.001 | 0.63 | <0.001 | Moderate agreement |
| EBJIS 2018—EBJIS 2021 confirmed | 0.78 | <0.001 | 0.8 | <0.001 | Substantial agreement |
| WAIOT—EBJIS 2021 | 0.74 | <0.001 | 0.79 | 0.405 | Substantial agreement |
| WAIOT—EBJIS 2021 likely | 0.63 | <0.001 | 0.73 | <0.001 | Substantial agreement |
| WAIOT—EBJIS 2021 confirmed | 0.72 | <0.001 | 0.77 | 0.110 | Substantial agreement |
| Compared Classifications | Cohen’s Kappa | p-Value | Gwet’s AC1 | McNemar’s p-Value | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WAIOT BIOFILM—MSIS 2013 | 0.8 | <0.001 | 0.82 | 0.549 | Almost perfect agreement |
| WAIOT LOW GRADE—MSIS 2013 | 0.55 | <0.001 | 0.89 | 0.016 | Moderate agreement |
| WAIOT HIGH-GRADE—MSIS 2013 | 0.52 | 1.000 | 0.84 | 0.344 | Moderate agreement |
| WAIOT ASEPTIC—MSIS 2013 | 0.79 | <0.001 | 0.79 | 1.000 | Substantial agreement |
| WAIOT BIOFILM—ICG 2018 | 0.68 | <0.001 | 0.78 | 0.064 | Substantial agreement |
| WAIOT LOW-GRADE—ICG 2018 | 0.56 | <0.001 | 0.94 | 0.016 | Moderate agreement |
| WAIOT HIGH-GRADE—ICG 2018 | 0.71 | <0.001 | 0.94 | 0.016 | Substantial agreement |
| WAIOT ASEPTIC—ICG 2018 | 0.73 | <0.001 | 0.78 | <0.001 | Substantial agreement |
| WAIOT BIOFILM—EBJIS 2018 | 0.87 | <0.001 | 0.89 | <0.001 | Almost perfect agreement |
| WAIOT LOW-GRADE—EBJIS 2018 | 0.44 | 0.006 | 0.9 | <0.001 | Moderate agreement |
| WAIOT HIGH-GRADE—EBJIS 2018 | 0.61 | <0.001 | 0.9 | <0.001 | Substantial agreement |
| WAIOT ASEPTIC—EBJIS 2018 | 0.88 | <0.001 | 0.89 | <0.001 | Almost perfect agreement |
| WAIOT BIOFILM—EBJIS 2021 | 0.7 | <0.001 | 0.78 | <0.001 | Substantial agreement |
| WAIOT LOW-GRADE—EBJIS 2021 | 0.5 | 0.002 | 0.92 | <0.001 | Moderate agreement |
| WAIOT HIGH-GRADE—EBJIS 2021 | 0.66 | <0.001 | 0.92 | 1.000 | Substantial agreement |
| WAIOT ASEPTIC—EBJIS 2021 | 0.74 | <0.001 | 0.79 | <0.001 | Substantial agreement |
| WAIOT BIOFILM—EBJIS 2021 likely | 0.54 | <0.001 | 0.73 | 0.022 | Moderate agreement |
| WAIOT LOW-GRADE—EBJIS 2021 likely | 0.91 | <0.001 | 0.99 | 0.004 | Almost perfect agreement |
| WAIOT HIGH-GRADE—EBJIS 2021 likely | 0.95 | <0.001 | 0.99 | 0.405 | Almost perfect agreement |
| WAIOT ASEPTIC—EBJIS 2021 likely | 0.63 | <0.001 | 0.73 | <0.001 | Substantial agreement |
| WAIOT BIOFILM—EBJIS 2021 confirmed | 0.67 | <0.001 | 0.77 | 0.110 | Substantial agreement |
| WAIOT LOW-GRADE—EBJIS 2021 confirmed | 0.53 | 0.001 | 0.93 | 0.008 | Moderate agreement |
| WAIOT HIGH-GRADE—EBJIS 2021 confirmed | 0.68 | <0.001 | 0.93 | 0.008 | Substantial agreement |
| WAIOT ASEPTIC—EBJS 2021 confirmed | 0.72 | <0.001 | 0.77 | 0.110 | Substantial agreement |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rocchi, C.; Di Maio, M.; Bulgarelli, A.; Chiappetta, K.; La Camera, F.; Grappiolo, G.; Loppini, M. Agreement Analysis Among Hip and Knee Periprosthetic Joint Infections Classifications. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091172
Rocchi C, Di Maio M, Bulgarelli A, Chiappetta K, La Camera F, Grappiolo G, Loppini M. Agreement Analysis Among Hip and Knee Periprosthetic Joint Infections Classifications. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(9):1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091172
Chicago/Turabian StyleRocchi, Caterina, Marco Di Maio, Alberto Bulgarelli, Katia Chiappetta, Francesco La Camera, Guido Grappiolo, and Mattia Loppini. 2025. "Agreement Analysis Among Hip and Knee Periprosthetic Joint Infections Classifications" Diagnostics 15, no. 9: 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091172
APA StyleRocchi, C., Di Maio, M., Bulgarelli, A., Chiappetta, K., La Camera, F., Grappiolo, G., & Loppini, M. (2025). Agreement Analysis Among Hip and Knee Periprosthetic Joint Infections Classifications. Diagnostics, 15(9), 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091172






