Potential for Misinterpretation in the Laboratory Diagnosis of Clostridioides difficile Infections
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Samples
2.3. DNA-Extraction
2.4. Molecular Methods
2.5. CLIA
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, S.; Lavergne, V.; Skinner, A.M.; Gonzales-Luna, A.J.; Garey, K.W.; Kelly, C.P.; Wilcox, M.H. Clinical Practice Guideline by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA): 2021 Focused Update Guidelines on Management of Clostridioides difficile Infection in Adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 5, e1029–e1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivian, G.L.; Bourgault, A.; Poirier, L.; Lamothe, F.; Michaud, S.; Turgeon, N.; Toye, B.; Beaudoin, A.; Frost, E.H.; Gilca, R.; et al. Host and Pathogen Factors for Clostridium difficile Infection and Colonization. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 18, 1693–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareja-Sierra, T. Diarrea asociada a Clostridium difficile en el anciano: Nuevas perspectivas. Rev. Española Geriatría Gerontol. 2015, 4, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letourneur, O.; Ottone, S.; Delauzun, V.; Bastide, M.-C.; Foussadier, A. Molecular cloning, overexpression in Escherichia coli, and purification of 6x his-tagged C-terminal domain of Clostridium difficile toxins A and B. Protein Expr. Purif. 2003, 31, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, E.J.; Tiruvoipati, R. Management of Clostridioides difficile infection in adults and challenges in clinical practice: Review and comparison of current IDSA/SHEA, ESCMID and ASID guidelines. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2022, 78, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Carey-Ann, B.D.; Carroll, K.C. Diagnosis of Clostridium difficile Infection: An Ongoing Conundrum for Clinicians and for Clinical Laboratories. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 604–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poutanen, S.M.; Simor, A.E. Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea in adults. CMAJ 2004, 171, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Crobach, M.T.; Vernon, J.J.; Loo, V.G.; Kong, L.Y.; Péchiné, S.; Wilcox, M.H.; Kuijper, E.J. Understanding Clostridium difficile Colonization. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00021-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cymbal, M.; Chatterjee, A.; Baggott, B.; Auron, M. Management of Clostridioides difficile Infection: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Future Perspectives. Am. J. Med. 2024, 137, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, L.C.; Gerding, D.N.; Johnson, S.; Bakken, J.S.; Carroll, K.C.; Coffin, S.E.; Dubberke, E.R.; Garey, K.W.; Gould, C.V.; Kelly, C.; et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines for Clostridium difficile Infection in Adults and Children: 2017 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 7, e1–e48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyanova, L.; Markovska, R.; Hadzhiyski, P.; Yordanov, D.; Yaneva, P.; Mitov, I. Recurrent Clostridioides (Clostridium) difficile infection in a patient suffering from inflammatory bowel disease and benefits of resistotyping. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 94, 334–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simor, A.E. Diagnosis, management, and prevention of Clostridium difficile infection in long-term care facilities: A review. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2010, 58, 1556–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chilton, C.H.; Pickering, D.S.; Freeman, J. Microbiologic factors affecting Clostridium difficile recurrence. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, A.E.; Theriot, C.M.; Bergin, I.L.; Huffnagle, G.B.; Schloss, P.D.; Young, V.B. The interplay between microbiome dynamics and pathogen dynamics in a murine model of Clostridium difficile Infection. Gut Microbes 2011, 2, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chumpitazi, B.P.; Self, M.M.; Czyzewski, D.I.; Cejka, S.; Swank, P.R.; Shulman, R.J. Bristol Stool Form Scale reliability and agreement decreases when determining Rome III stool form designations. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 3, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Janczura, A.; Smutnicka, D.; Junka, A.; Gościniak, G. The detection and expression of enterotoxinencoding lth gene among Klebsiella spp. isolated from diarrhea. Cent. Eur. J. Biol. 2013, 8, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Prehn, J.; Reigadas, E.; Vogelzang, E.; Bouza, E.; Hristea, A.; Guery, B.; Krutova, M.; Norén, T.; Allerberger, F.; Coia, J.; et al. European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases: 2021 update on the treatment guidance document for Clostridioides difficile infection in adults. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 2, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bella, S.; Ascenzi, P.; Siarakas, S.; Petrosillo, N.; Di Masi, A. Clostridium difficile Toxins A and B: Insights into Pathogenic Properties and Extraintestinal Effects. Toxins 2016, 8, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobreva, E.G.; Ivanov, I.N.; Vathcheva-Dobrevska, R.S.; Ivanova, K.I.; Asseva, K.; Petrov, P.K.; Kantardjiev, T.V. Advances in molecular surveillance of Clostridium difficile in Bulgaria. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 62, 1428–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobreva, E.; Ivanov, I.N.; Vatcheva-Dobrevska, R.; Ivanova, K.; Marina, M.; Petrov, P.; Kantardjiev, T.; Kuijper, E. Toxin encoding genes characterization of Bulgarian Clostridium difficile clinical strains. C. R. Acad. Bulg. Sci. 2012, 65, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar]
- Forward, L.J.; Tompkins, D.S.; Brett, M.M. Detection of Clostridium difficile cytotoxin and Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin in cases of diarrhoea in the community. J. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 52, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youn, Y.; Lee, S.W.; Cho, H.H.; Park, S.; Chung, H.S.; Seo, J.W. Antibiotics-Associated Hemorrhagic Colitis Caused by Klebsiella oxytoca: Two Case Reports. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2018, 2, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Selvaraj, V.; Alsamman, M.A. Antibiotic-Associated Diarrhea Beyond C. difficile: A Scoping Review. J. Brown Hosp. Med. 2022, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanafer, N.; Vanhems, P.; Bennia, S.; Martin-Gaujard, G.; Juillard, L.; Rimmelé, T.; Argaud, L.; Martin, O.; Huriaux, L.; Marcotte, G.; et al. Factors Associated with Clostridioides (Clostridium) difficile Infection and Colonization: Ongoing Prospective Cohort Study in a French University Hospital. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gateau, C.; Couturier, J.; Coia, J.; Barbut, F. How to: Diagnose infection caused by Clostridium difficile. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaei Chamgordani, S.; Yadegar, A.; Ghourchian, H. C. difficile biomarkers, pathogenicity and detection. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2024, 558, 119674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
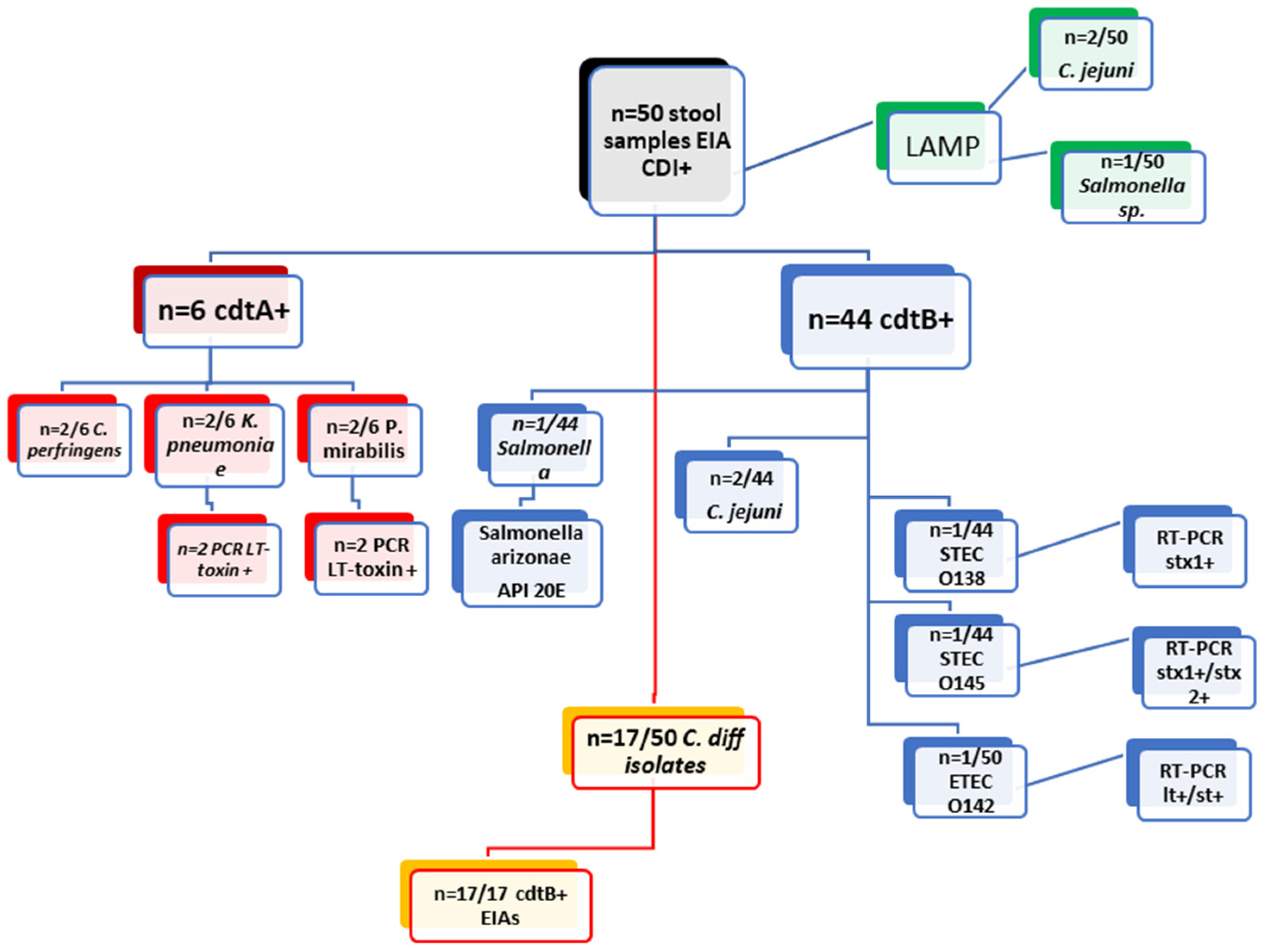
| Examination of 50 Clinical Stool Samples cdtA+/cdtB+ by EIAs from DT-Hospital | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methods | EIA cdtA+ (n = 6/50) | EIA cdtB+ (n = 44/50) | |||||||
| culture | C. perfringens (2/6) | K. pneumoniae (2/6) | P. Mirabilis (2/6) | Salmonella | C. difficile (17/44) | C. jejuni (2/44) | STEC O138 (1/44) | STEC O145 (n = 1) | ETEC 142 (1/44) |
| PCR | x | LT toxin (n = 2) | LT toxin (n = 2) | x | x | x | stx1+ (n = 1) | stx1+/stx2+ (n = 1) | lt+/st+ (n = 1) |
| API20E | x | x | x | Salmonella arizonae | x | x | x | x | x |
| LAMP (Salmonella/Campylobacter) | negative | negative | negative | Salmonella | negative | C. jejuni (2/44) | negative | negative | negative |
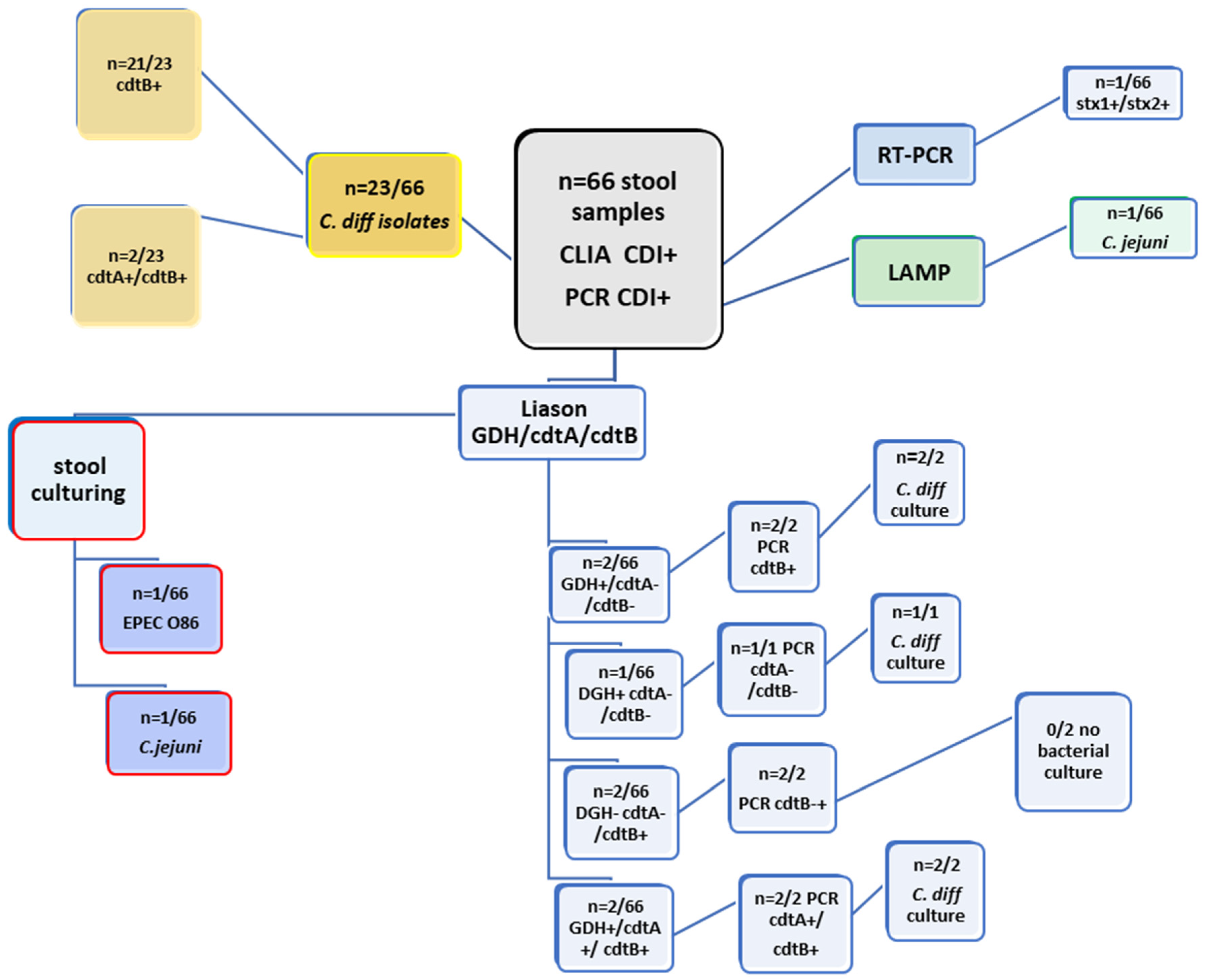
| Examination of 66 Clinical Stool Samples by CLIA (GDH; cdtA/B) and PCR (cdtA; cdtB) from SF Hospital | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methods | Liaison GDH | Liaison cdtA | Liaison cdtB | PCR cdtA | PCR cdtB | Culture | LAMP | RT-PCR (STEC) |
| 2/66 | negative | negative | negative | 2/66 | C. difficile (n = 2/66) | negative | x | |
| 1/66 | negative | negative | negative | negative | C. difficile (n = 1/66) | negative | x | |
| negative | negative | 2/66 | negative | 2/66 | negative | negative | x | |
| negative | negative | 1/66 | negative | 1/66 | C. jejuni (n = 1/66) | C. jejuni | x | |
| negative | negative | 1/66 | negative | 1/66 | EPEC O86 | negative | stx1+/stx2+ | |
| 2/66 | 2/66 | 2/66 | 2/66 | 2/66 | 2/66 | negative | x | |
| negative | negative | 21/23 | negative | 21/23 | C. difficile (n = 23/66) | negative | x | |
| negative | 2/23 | 2/23 | negative | 2/23 | C. difficile (n = 23/66) | negative | x | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalacheva, A.; Popov, M.; Velev, V.; Stoyanova, R.; Mitova-Mineva, Y.; Velikova, T.; Pavlova, M. Potential for Misinterpretation in the Laboratory Diagnosis of Clostridioides difficile Infections. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091166
Kalacheva A, Popov M, Velev V, Stoyanova R, Mitova-Mineva Y, Velikova T, Pavlova M. Potential for Misinterpretation in the Laboratory Diagnosis of Clostridioides difficile Infections. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(9):1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091166
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalacheva, Alexandra, Metodi Popov, Valeri Velev, Rositsa Stoyanova, Yordanka Mitova-Mineva, Tsvetelina Velikova, and Maria Pavlova. 2025. "Potential for Misinterpretation in the Laboratory Diagnosis of Clostridioides difficile Infections" Diagnostics 15, no. 9: 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091166
APA StyleKalacheva, A., Popov, M., Velev, V., Stoyanova, R., Mitova-Mineva, Y., Velikova, T., & Pavlova, M. (2025). Potential for Misinterpretation in the Laboratory Diagnosis of Clostridioides difficile Infections. Diagnostics, 15(9), 1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091166







