Metabolic Syndrome and Hemorrhagic Stroke in Hispanic Elderly Patients with Cerebral Cavernous Malformations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
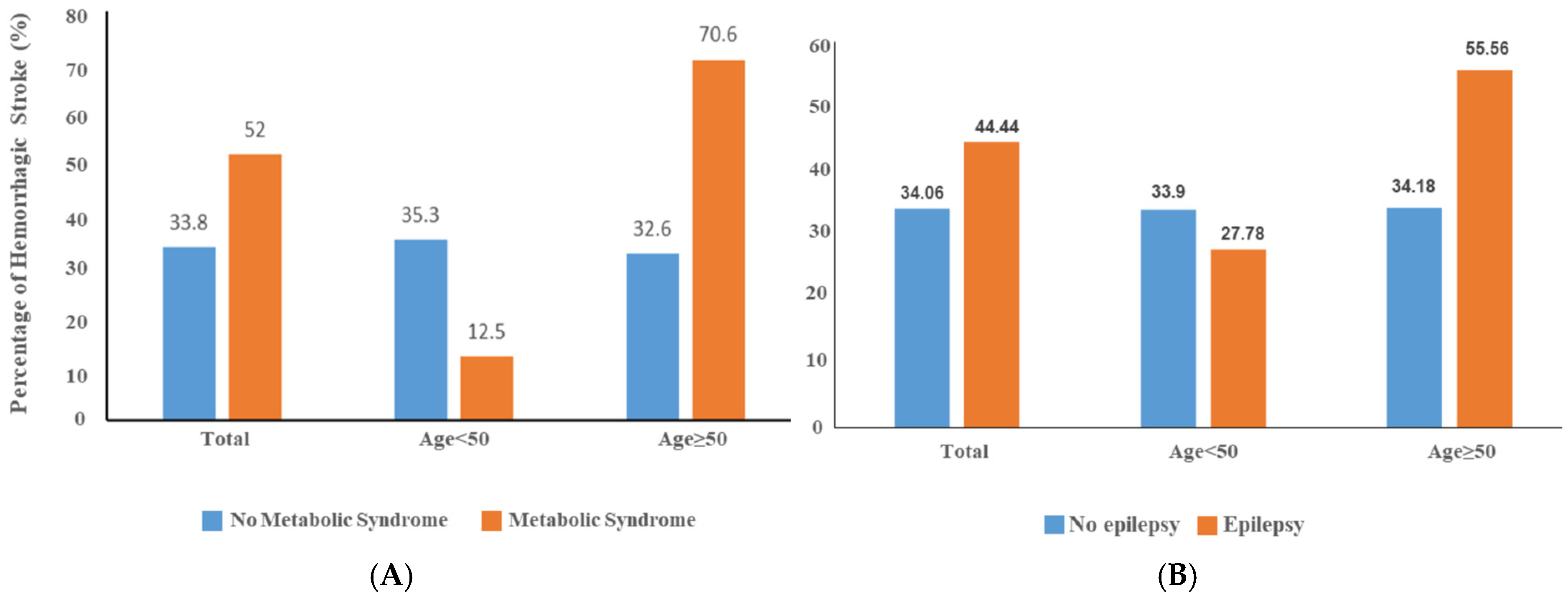
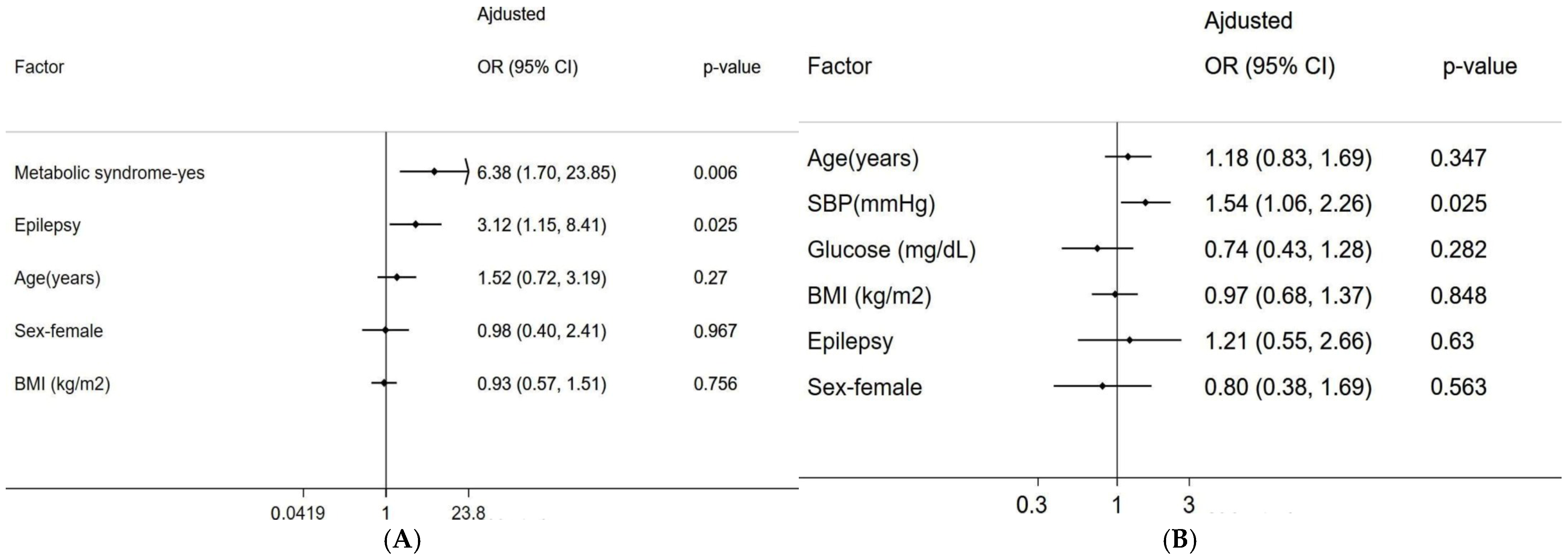
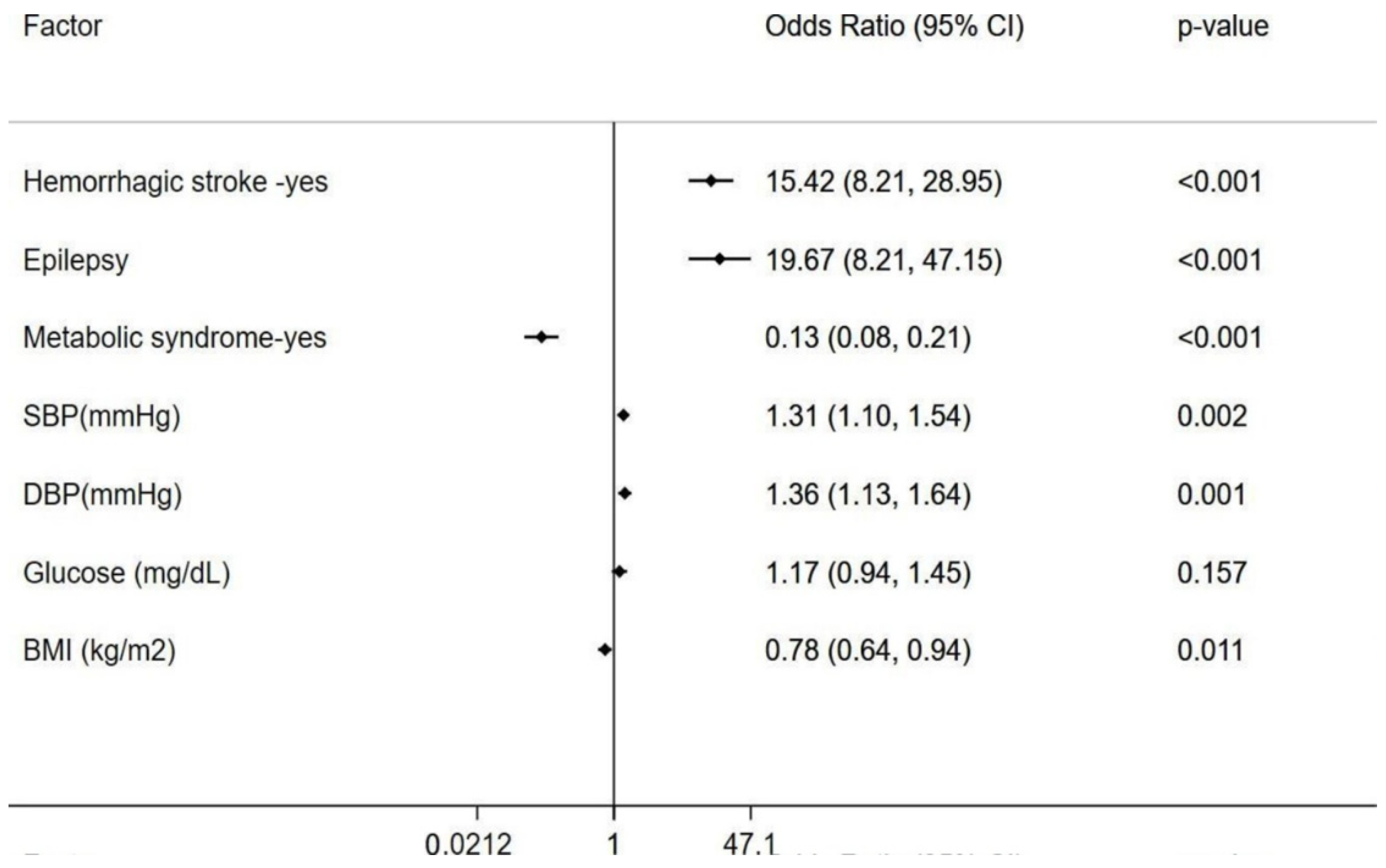
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Batra, S.; Lin, D.; Recinos, P.F.; Zhang, J.; Rigamonti, D. Cavernous malformations: Natural history, diagnosis and treatment. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2009, 5, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigamonti, D.; Spetzler, R.F. The association of venous and cavernous malformations. Report of four cases and discussion of the pathophysiological, diagnostic, and therapeutic implications. Acta Neurochir. 1988, 92, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Clatterbuck, R.E.; Rigamonti, D.; Dietz, H.C. Cloning of the murine Krit1 Cdna reveals novel mammalian 5′ coding exons. Genomics 2000, 70, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Abou-Fadel, J.; Renteria, M.; Belkin, O.; Chen, B.; Zhu, Y.; Dammann, P.; Rigamonti, D. Cerebral cavernous malformations do not fall in the spectrum of PIK3CA-related overgrowth. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2022, 93, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyre, M.; Miyagishima, D.; Bielle, F.; Chapon, F.; Sierant, M.; Venot, Q.; Lerond, J.; Marijon, P.; Abi-Jaoude, S.; Le Van, T.; et al. Somatic PIK3CA Mutations in Sporadic Cerebral Cavernous Malformations. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Clatterbuck, R.E.; Rigamonti, D.; Chang, D.D.; Dietz, H.C. Novel insights regarding the pathogenesis of cerebral cavernous malformation (CCM). Am. J. Human. Genet. 2001, 69, 178. [Google Scholar]
- Padarti, A.; Zhang, J. Recent advances in cerebral cavernous malformation research. Vessel Plus 2018, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimble, B.; Morgenstern, L.B. Stroke in minorities. Neurol. Clin. 2008, 26, 1177–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertz, R.P.; Unger, A.N.; Ferrario, C.M. Diabetes, hypertension, and dyslipidemia in Mexican Americans and non-Hispanic whites. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2006, 30, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrocola, R.; Aimaretti, E.; Ferreira Alves, G.; Cento, A.S.; Fornelli, C.; Dal Bello, F.; Ferraris, C.; Goitre, L.; Perrelli, A.; Retta, S.F. Heterozygous Loss of KRIT1 in Mice Affects Metabolic Functions of the Liver, Promoting Hepatic Oxidative and Glycative Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retta, S.F.; Glading, A.J. Oxidative stress and inflammation in cerebral cavernous malformation disease pathogenesis: Two sides of the same coin. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 81, 254–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antognelli, C.; Perrelli, A.; Armeni, T.; Nicola Talesa, V.; Retta, S.F. Dicarbonyl Stress and S Glutathionylation in Cerebrovascular Diseases: A Focus on Cerebral Cavernous Malformations. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choquet, H.; Trapani, E.; Goitre, L.; Trabalzini, L.; Akers, A.; Fontanella, M.; Hart, B.L.; Morrison, L.A.; Pawlikowska, L.; Kim, H.; et al. Cytochrome P450 and matrix metalloproteinase genetic modifiers of disease severity in Cerebral Cavernous Malformation type 1. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 92, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, M.A.; Zabramski, J.M. Developmental venous anomalies. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2017, 143, 279–282. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, T.A.; Morrison, L.A.; Schrader, R.M.; Hart, B.L. Familial versus sporadic cavernous malformations: Differences in developmental venous anomaly association and lesion phenotype. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2010, 31, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idiculla, P.S.; Gurala, D.; Philipose, J.; Rajdev, K.; Patibandla, P. Cerebral Cavernous Malformations, Developmental Venous Anomaly, and Its Coexistence: A Review. Eur. Neurol. 2020, 83, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinjikji, W.; El-Masri, A.E.; Wald, J.T.; Flemming, K.D.; Lanzino, G. Prevalence of cerebral cavernous malformations associated with developmental venous anomalies increases with age. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2017, 33, 1539–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timerman, D.; Thum, J.A.; Larvie, M. Quantitative Analysis of Metabolic Abnormality Associated with Brain Developmental Venous Anomalies. Cureus 2016, 8, e799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larvie, M.; Timerman, D.; Thum, J.A. Brain metabolic abnormalities associated with developmental venous anomalies. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2015, 36, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazor, J.W.; Schmitt, J.E.; Loevner, L.A.; Nabavizadeh, S.A. Metabolic Changes of Brain Developmental Venous Anomalies on (18)F-FDG-PET. Acad. Radiol. 2019, 26, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Saban, D.; Rauscher, S.; Herten, A.; Rauschenbach, L.; Santos, A.; Li, Y.; Schmidt, B.; Zhu, Y.; Jabbarli, R.; et al. Modifiable Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Patients With Sporadic Cerebral Cavernous Malformations: Obesity Matters. Stroke 2021, 52, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choquet, H.; Nelson, J.; Pawlikowska, L.; McCulloch, C.E.; Akers, A.; Baca, B.; Khan, Y.; Hart, B.; Morrison, L.; Kim, H. Association of cardiovascular risk factors with disease severity in cerebral cavernous malformation type 1 subjects with the common Hispanic mutation. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2014, 37, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mottillo, S.; Filion, K.B.; Genest, J.; Joseph, L.; Pilote, L.; Poirier, P.; Rinfret, S.; Schiffrin, E.L.; Eisenberg, M.J. The metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular risk a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 56, 1113–1132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alberti, K.G.; Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Cleeman, J.I.; Donato, K.A.; Fruchart, J.C.; James, W.P.; Loria, C.M.; Smith, S.C., Jr. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: A joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation 2009, 120, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, P.; Reddy, S.Y.; Singh, V.; Shi, T.; Coltharp, M.; Clegg, D.; Dwivedi, A.K. Association of Exposure to Phthalate Metabolites With Sex Hormones, Obesity, and Metabolic Syndrome in US Women. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2233088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, A.K.; Mallawaarachchi, I.; Lee, S.; Tarwater, P. Methods for estimating relative risk in studies of common binary outcomes. J. Appl. Stat. 2014, 41, 484–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, A.K.; Shukla, R. Evidence-based statistical analysis and methods in biomedical research (SAMBR) checklists according to design features. Cancer Rep. 2020, 3, e1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, A.K. How to write statistical analysis section in medical research. J. Investig. Med. 2022, 70, 1759–1770. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, A.T.; Choi, J.P.; Kotzin, J.J.; Yang, Y.; Hong, C.C.; Hobson, N.; Girard, R.; Zeineddine, H.A.; Lightle, R.; Moore, T.; et al. Endothelial TLR4 and the microbiome drive cerebral cavernous malformations. Nature 2017, 545, 305–310. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.C.; Sun, C.A.; Yang, T.; Chu, C.H.; Bai, C.H.; You, S.L.; Hwang, L.C.; Chen, C.H.; Wei, C.Y.; Chou, Y.C. Impact of metabolic syndrome components on incident stroke subtypes: A Chinese cohort study. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2014, 28, 689–693. [Google Scholar]
- Chei, C.L.; Yamagishi, K.; Tanigawa, T.; Kitamura, A.; Imano, H.; Kiyama, M.; Sato, S.; Iso, H. Metabolic Syndrome and the Risk of Ischemic Heart Disease and Stroke among Middle-Aged Japanese. Hypertens. Res. 2008, 31, 1887–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborn, M.F.; Miller, C.C.; Badr, A.; Zhang, J. Metabolic syndrome associated with ischemic stroke among the Mexican Hispanic population in the El Paso/US-Mexico border region. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2014, 23, 1477–1484. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, T.; Harada, M.; Kikuno, T.; Ujihara, M.; Sadamitsu, D.; Manabe, Y.; Yasaka, M.; Takayama, H.; Kobori, S.; Araki, E. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in stroke patients: A prospective multicenter study in Japan. Acute Med. Surg. 2014, 1, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perrelli, A.; Retta, S.F. Polymorphisms in genes related to oxidative stress and inflammation: Emerging links with the pathogenesis and severity of Cerebral Cavernous Malformation disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 172, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Ma, X.J.; Xu, X.Y.; Liu, P.P.; Wu, Z.Y.; Zhang, L.W.; Zhang, J.T.; Wu, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, D. Five-year symptomatic hemorrhage risk of untreated brainstem cavernous malformations in a prospective cohort. Neurosurg. Rev. 2022, 45, 2961–2973. [Google Scholar]
- Galovic, M.; Ferreira-Atuesta, C.; Abraira, L.; Dohler, N.; Sinka, L.; Brigo, F.; Bentes, C.; Zelano, J.; Koepp, M.J. Seizures and Epilepsy After Stroke: Epidemiology, Biomarkers and Management. Drugs Aging 2021, 38, 285–299. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, A.T.; El Rakawy, M.H.; Abdelhamid, Y.A.E.; Hazzou, A.M.; Wahid el din, M.M. Stroke-related early seizures: Clinical and neurophysiological study in a sample of Egyptian population. Egypt. J. Neurol. Psychiatry Neurosurg. 2023, 59, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, G.; Sarti, C.; Jousilahti, P.; Peltonen, M.; Qiao, Q.; Antikainen, R.; Tuomilehto, J. The impact of history of hypertension and type 2 diabetes at baseline on the incidence of stroke and stroke mortality. Stroke 2005, 36, 2538–2543. [Google Scholar]
| Parameter | Total Cohort | MetS-0 (No) | MetS-1 (Yes) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample size (N) | 184 | 154 | 25 | |
| Age (years), mean (SD) | 52.8 (17.2) (n = 184) | 51.9 (17.4) | 56.2 (14.9) | 0.24 |
| Sex | 0.67 | |||
| Male | 86 (46.7%) | 71 (46.1%) | 13 (52.0%) | |
| Female | 98 (53.3%) | 83 (53.9%) | 12 (48.0%) | |
| Systolic blood pressure (SBP), mean (SD) | 134.3 (23.0) (n = 175) | 132.4 (21.6) | 139.6 (26.9) | 0.14 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (DBP), mean (SD) | 76.0 (13.2) (n = 175) | 75.7 (13.7) | 76.2 (10.0) | 0.85 |
| Blood glucose levels, mean (SD) | 135.3 (85.4) (n = 145) | 126.2 (55.1) | 178.7 (170.3) | 0.007 |
| BMI, mean (SD) | 29.1 (6.2) (n = 169) | 28.1 (5.2) | 35.0 (8.2) | <0.001 |
| Metabolic syndrome | ||||
| 0 (No) | 154 (83.7%) | |||
| 1 (Yes) | 25 (13.6%) | |||
| Missing | 5 (2.7%) | |||
| Epilepsy | 0.63 | |||
| 0 (No) | 138 (75.0%) | 114 (74.0%) | 20 (80.0%) | |
| 1 (Yes) | 45 (24.5%) | 40 (26.0%) | 5 (20.0%) | |
| Missing | 1 (0.5%) | |||
| Stroke | 0.11 | |||
| 0 (No) | 116 (63.0%) | 102 (66.2%) | 12 (48.0%) | |
| 1 (Yes) | 67 (36.4%) | 52 (33.8%) | 13 (52.0%) | |
| 1 (0.5%) |
| Factor | No Stroke | Stroke | OR | 95%CI | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample size (N) | 116 | 67 | ||||
| Age (years), mean (SD) | 51.6 (16.3) | 54.8 (18.8) | 1.01 | 0.99 | 1.03 | 0.226 |
| Gender | ||||||
| Male | 53 (45.7%) | 33 (49.3%) | 0.87 | 0.47 | 1.58 | 0.642 |
| Female | 63 (54.3%) | 34 (50.7%) | ||||
| SBP, mean (SD) | 129.9 (20.2) | 140.8 (25.4) | 1.02 | 1.01 | 1.04 | 0.003 |
| DBP, mean (SD) | 74.7 (11.3) | 78.0 (15.7) | 1.02 | 1.00 | 1.04 | 0.117 |
| Blood glucose levels, mean (SD) | 139.7 (106.1) | 128.8 (46.5) | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.463 |
| BMI, mean (SD) | 29.1 (6.4) | 29.1 (6.1) | 1.00 | 0.95 | 1.05 | 0.989 |
| Metabolic syndrome | ||||||
| 0 | 102 (89.5%) | 52 (80.0%) | ||||
| 1 | 12 (10.5%) | 13 (20.0%) | 2.13 | 0.91 | 4.99 | 0.083 |
| Epilepsy | ||||||
| 0 | 91 (78.4%) | 47 (70.1%) | ||||
| 1 | 25 (21.6%) | 20 (29.9%) | 1.55 | 0.78 | 3.07 | 0.211 |
| Age ≥ 50 | Age < 50 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95%CI | p-Value | OR | 95%CI | p-Value | |||
| MetS-1 (Yes) | 6.38 | 1.70 | 23.85 | 0.006 | 0.18 | 0.02 | 1.74 | 0.139 |
| Epilepsy-1 (Yes) | 3.12 | 1.15 | 8.41 | 0.025 | 0.40 | 0.11 | 1.46 | 0.166 |
| Age (years) | 1.02 | 0.98 | 1.07 | 0.27 | 1.00 | 0.95 | 1.06 | 0.923 |
| Sex—female | 0.98 | 0.40 | 2.41 | 0.967 | 0.38 | 0.12 | 1.19 | 0.098 |
| Standardized BMI | 0.93 | 0.57 | 1.51 | 0.756 | 0.99 | 0.53 | 1.85 | 0.981 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dwivedi, A.K.; Jang, D.; Belkin, O.; Aickareth, J.; Renteria, M.; Hawwar, M.; Croft, J.; Kalas, M.A.; Zuckerman, M.; Zhang, J. Metabolic Syndrome and Hemorrhagic Stroke in Hispanic Elderly Patients with Cerebral Cavernous Malformations. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091144
Dwivedi AK, Jang D, Belkin O, Aickareth J, Renteria M, Hawwar M, Croft J, Kalas MA, Zuckerman M, Zhang J. Metabolic Syndrome and Hemorrhagic Stroke in Hispanic Elderly Patients with Cerebral Cavernous Malformations. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(9):1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091144
Chicago/Turabian StyleDwivedi, Alok K., David Jang, Ofek Belkin, Justin Aickareth, Mellisa Renteria, Majd Hawwar, Jacob Croft, M Ammar Kalas, Marc Zuckerman, and Jun Zhang. 2025. "Metabolic Syndrome and Hemorrhagic Stroke in Hispanic Elderly Patients with Cerebral Cavernous Malformations" Diagnostics 15, no. 9: 1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091144
APA StyleDwivedi, A. K., Jang, D., Belkin, O., Aickareth, J., Renteria, M., Hawwar, M., Croft, J., Kalas, M. A., Zuckerman, M., & Zhang, J. (2025). Metabolic Syndrome and Hemorrhagic Stroke in Hispanic Elderly Patients with Cerebral Cavernous Malformations. Diagnostics, 15(9), 1144. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091144







