Updates on the Prevalence, Quality of Life, and Management of Chronic Cough in Interstitial Lung Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Disease | Prevalence | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| IPF | 83.3% reported CC | Öz et al., ILD patients (total n = 69), 24 patients with IPF, 2022 [2] |
| 79.1% reported CC | Chikina et al., IPF patients (n = 1353), 2023 [5] | |
| 87% reported CC | Cheng et al., total n = 176, 77 patients with IPF, 2017 [9] | |
| HP | 92.1% reported CC | Wang et al., HP patients (n = 101), 2019 [4] |
| 83% reported CC | Cheng et al., total n = 176, 32 with chronic HP, 2017 [9] | |
| 3.7-fold more frequent in patients with IIPs compared to patients with CTD-ILDs or HP (95% CI 1.7–8.2; p = 0.001) | Sato et al., ILD patients (total n = 129), 10 patients with chronic HP, 70 patients with IIPs, 49 with CTD-ILDs, 2019 [8] | |
| CTD-ILDs | 56.2% reported CC | Öz et al., ILD patients (total n = 69), 32 patients with CTD-ILDs, 2022 [2] |
| 68% reported CC | Cheng et al., total n = 176, 67 patients with CTD-ILDs, 2017 [9] | |
| 44.72% reported CC, ranging from 32.9% to 75% depending on the different CTD-ILDs | Lu et al., CTD-ILD patients (n = 161), 2022 [7] | |
| IPAF | 76.9% reported CC | Öz et al., ILD patients (total n = 69), 13 patients with IPAF, 2022 [2] |
| 41.67% reported CC | Lu et al., CTD-ILD patients (n = 161), 2022 [7] | |
| Sarcoidosis | 54.8% reported CC | Sinha et al., patients with sarcoidosis (n = 32), 2016 [6] |
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection
3. Results
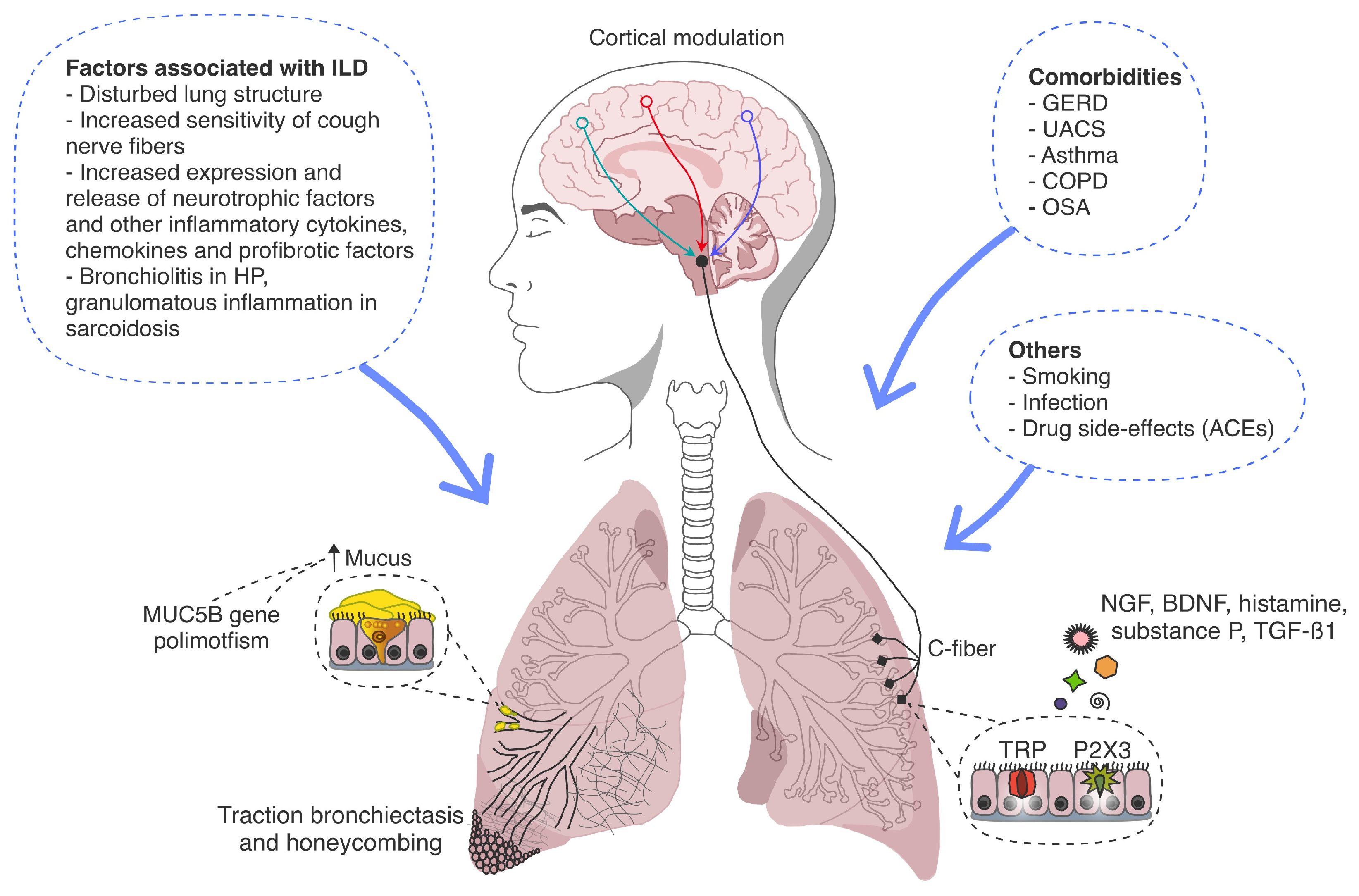
3.1. Pathogenesis of Cough in ILDs
3.1.1. Cough Hypersensitivity Syndrome
3.1.2. MUC5B Gene Polymorphism
3.1.3. Gastroesophageal Reflux
3.1.4. Disease-Specific Mechanisms
3.2. Clinical Importance of Cough in ILDs
3.2.1. Health-Related Quality of Life
3.2.2. Progression of ILDs
3.3. Treatment of Cough in ILDs
3.3.1. Antifibrotic Therapy
3.3.2. Inhaled Therapy
3.3.3. Immunomodulating Therapy
3.3.4. Anti-Reflux Therapy
3.3.5. Neuromodulating Therapy
3.3.6. Novel Antitussive Agents
3.3.7. Opiates
3.3.8. Non-Pharmacological Therapy
4. Discussion
5. Future Studies
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guler, S.A.; Corte, T.J. Interstitial Lung Disease in 2020: A History of Progress. Clin. Chest Med. 2021, 42, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öz, M.; Erol, S.; Küçükşahin, O.; Kar, İ.; Atasoy, K.Ç.; Özdemir Kumbasar, Ö. Clinical, Functional, and Prognostic Evaluation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis, Connective Tissue Disease-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease, Interstitial Pneumonia with Autoimmune Features: A Single-Center Prospective Study. Turk. Thorac. J. 2022, 23, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Møller, J.; Altraja, A.; Sjåheim, T.; Rasmussen, F.; Madsen, L.B.; Bendstrup, E. International multidisciplinary team discussions on the diagnosis of idiopathic non-specific interstitial pneumonia and the development of connective tissue disease. Eur. Clin. Respir. J. 2021, 8, 1933878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.J.; Cai, H.R.; Xiao, Y.L.; Wang, Y.; Cao, M.S. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of hypersensitivity pneumonitis: A population-based study in China. Chin. Med. J. 2019, 132, 1283–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikina, S.; Cherniak, A.; Merzhoeva, Z.; Tyurin, I.; Trushenko, N.; Proshkina, A.; Ataman, K.; Avdeev, S. Russian Registry of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Clinical Features, Treatment, Management and Outcomes. Life 2023, 13, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.; Lee, K.K.; Rafferty, G.F.; Yousaf, N.; Pavord, I.D.; Galloway, J.; Birring, S.S. Predictors of objective cough frequency in pulmonary sarcoidosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 47, 1461–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Gong, L.; Huang, C.; Ye, M.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, D. Analysis of Clinical Characteristics of Connective Tissue Disease-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease in 161 Patients: A Retrospective Study. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2022, 15, 8617–8625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, R.; Handa, T.; Matsumoto, H.; Kubo, T.; Hirai, T. Clinical significance of self-reported cough intensity and frequency in patients with interstitial lung disease: A cross-sectional study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2019, 19, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.Z.; Wilcox, P.G.; Glaspole, I.; Corte, T.J.; Murphy, D.; Hague, C.J.; Ryerson, C.J. Cough is less common and less severe in systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease compared to other fibrotic interstitial lung diseases. Respirology 2017, 22, 1592–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garner, J.; George, P.M.; Renzoni, E. Cough in interstitial lung disease. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 35, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaudet, C.; Malaty, J. Chronic Cough: Evaluation and Management. Am. Fam. Physician 2017, 96, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; White, E.; Freiheit, E.; Scholand, M.B.; Strek, M.E.; Podolanczuk, A.J.; Patel, N.M.; Pulmonary Fibrosis Foundation. Pulmonary Fibrosis Foundation. Cough-specific quality of life predicts disease progression among patients with interstitial lung disease: Data from the Pulmonary Fibrosis Foundation patient registry. Chest 2022, 162, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khor, Y.H.; Johannson, K.A.; Marcoux, V.; Fisher, J.H.; Assayag, D.; Manganas, H.; Khalil, N.; Kolb, M.; Ryerson, C.J. Epidemiology and Prognostic Significance of Cough in Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 210, 1035–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaman, T.; Moua, T.; Vittinghoff, E.; Ryu, J.H.; Collard, H.R.; Lee, J.S. Differences in clinical characteristics and outcomes between men and women with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A multicenter retrospective cohort study. Chest 2020, 158, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryerson, C.J.; Abbritti, M.; Ley, B.; Elicker, B.M.; Jones, K.D.; Collard, H.R. Cough predicts prognosis in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respirology 2011, 16, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, J.M.V.; Holland, A.E.; Goh, N.S.L.; Khor, Y.H. Understanding patient experience of chronic cough in interstitial lung disease. ERJ Open Res. 2023, 9, 00039–02023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirons, B.; Rhatigan, K.; Wright, L.; Kesavan, H.; Mackay, E.; Cho, P.S.P.; Birring, S.S.; Myall, K.J. Patient Perception of Cough in Interstitial Lung Disease; Impact of Cough Hypersensitivity. Lung 2024, 202, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.M.; Hilldrup, S.; Hope-Gill, B.D.; Eccles, R.; Harrison, N.K. Mechanical induction of cough in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Cough 2011, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myall, K.J.; Kavanagh, J.E.; Birring, S.S. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis-associated cough: Mechanisms and management. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 56, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froese, A.R.; Shimbori, C.; Bellaye, P.S.; Inman, M.; Obex, S.; Fatima, S.; Jenkins, G.; Gauldie, J.; Ask, K.; Kolb, M. Stretch-induced Activation of Transforming Growth Factor-β1 in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 194, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargagli, E.; Di Masi, M.; Perruzza, M.; Vietri, L.; Bergantini, L.; Torricelli, E.; Biadene, G.; Fontana, G.; Lavorini, F. The pathogenetic mechanisms of cough in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2019, 14, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, N.K. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A nervous cough? Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 17, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schertel, A.; Funke-Chambour, M.; Geiser, T.; Brill, A.K. Novel insights in cough and breathing patterns of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis performing repeated 24-hour-respiratory polygraphies. Respir. Res. 2017, 18, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholand, M.B.; Wolff, R.; Crossno, P.F.; Sundar, K.; Winegar, M.; Whipple, S.; Carey, P.; Sunchild, N.; Coon, H. Severity of cough in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is associated with MUC5B genotype. Cough 2014, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, C.; Montero-Fernandez, A.; Borg, E.; Osadolor, T.; Viola, P.; De Lauretis, A.; Stock, C.J.; Bonifazi, M.; Bonini, M.; Caramori, G.; et al. Mucins MUC5B and MUC5AC in distal airways and honeycomb spaces: Comparison among idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis/usual interstitial pneumonia, fibrotic nonspecific interstitial pneumonitis, and control lungs. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 462–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, P.; Wu, Z.; Fahy, W.A.; Stewart, I.D.; Saini, G.; Smith, D.J.F.; Braybrooke, R.; Stock, C.; Renzoni, E.A.; Johnson, S.R.; et al. The burden and impact of cough in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: An analysis of the prospective observational PROFILE study. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2023, 20, 1267–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madison, J.M.; Irwin, R.S. Chronic cough in adults with interstitial lung disease. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2005, 11, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baqir, M.; Vasirreddy, A.; Vu, A.N.; Moua, T.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Frank, R.D.; Frank, R.D.; Ryu, J.H. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and gastroesophageal reflux disease: A population-based, case-control study. Respir. Med. 2021, 178, 106309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avdeev, S.N.; Aisanov, Z.R.; Belevskiy, A.S.; Ilkovich, M.M.; Kogan, E.A.; Merzhoeva, Z.M.; Petrov, D.V.; Samsonova, M.V.; Terpigorev, S.A.; Trushenko, N.V.; et al. Federal clinical guidelines on diagnosis and treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Pulmonologiya 2022, 32, 473–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.; Krishnan, A.; Zeybel, G.L.; Dookun, E.; Pearson, J.P.; Simpson, A.J.; Griffin, S.M.; Ward, C.; Forrest, I.A. Reflux in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Treatment informed by an integrated approach. ERJ Open Res. 2018, 4, 00051–02018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polychronopoulos, V.S.; Prakash, U.B.S. Airway involvement in sarcoidosis. Chest 2009, 136, 1371–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin-Min, D.; Qin-Zhi, X.; Yun-You, D.; Chun-Yan, Z.; Chao-Sheng, P.; Hao-Yong, N.; Yong-Qun, L.; Ji-Guang, M.; Zhou-Shan, N.; Hua-Song, F. Impact of tracheal mucosa involvement on clinical characteristics of sarcoidosis. South. Med. J. 2011, 104, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagnell, C.; Grunewald, J.; Kramar, M.; Haugom-Olsen, H.; Elmberger, G.P.; Eklund, A.; Olgart Höglund, C. Neurotrophins and neurotrophin receptors in pulmonary sarcoidosis—Granulomas as a source of expression. Respir. Res. 2010, 11, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Key, A.L.; Holt, K.; Hamilton, A.; Smith, J.A.; Earis, J.E. Objective cough frequency in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Cough 2010, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamura, K.; Hara, J.; Watanabe, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Kase, K.; Takeda, Y.; Terada, N.; Koba, H.; Tambo, Y.; Ohkura, N.; et al. Patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and refractory cough have traction bronchiectasis and distorted airway architecture: A retrospective case review study. J. Thorac. Dis. 2024, 16, 2159–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.F.; McGarvey, L.; Song, W.J.; Chang, A.B.; Lai, K.; Canning, B.J.; Birring, S.S.; Smith, J.A.; Mazzone, S.B. Cough hypersensitivity and chronic cough. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2022, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brignall, K.; Jayaraman, B.; Birring, S.S. Quality of life and psychosocial aspects of cough. Lung 2008, 186, S55–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, R.; Baldwin, M.; Pooley, N.; Misso, K.; Mölken, M.P.R.; Patel, N.; Wijsenbeek, M.S. The burden of cough in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and other interstitial lung diseases: A systematic evidence synthesis. Respir. Res. 2024, 25, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morice, A.H.; Millqvist, E.; Bieksiene, K.; Birring, S.S.; Dicpinigaitis, P.; Domingo Ribas, C.; Hilton Boon, M.; Kantar, A.; Lai, K.; McGarvey, L.; et al. ERS guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of chronic cough in adults and children. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1901136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veit, T.; Barnikel, M.; Kneidinger, N.; Munker, D.; Arnold, P.; Barton, J.; Crispin, A.; Milger, K.; Behr, J.; Neurohr, C.; et al. Clinical impact of physical activity and cough on disease progression in fibrotic interstitial lung disease. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodore, A.C.; Tseng, C.H.; Li, N.; Elashoff, R.M.; Tashkin, D.P. Correlation of cough with disease activity and treatment with cyclophosphamide in scleroderma interstitial lung disease: Findings from the Scleroderma Lung Study. Chest 2012, 142, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tashkin, D.P.; Volkmann, E.R.; Tseng, C.H.; Roth, M.D.; Khanna, D.; Furst, D.E.; Clements, P.J.; Theodore, A.; Kafaja, S.; Kim, G.H.; et al. Improved cough and cough-specific quality of life in patients treated for scleroderma-related interstitial lung disease: Results of Scleroderma Lung Study II. Chest 2017, 151, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, T.; Toth, N.M.; Palmer, E.; Polivka, L.; Csoma, B.; Nagy, A.; Eszes, N.; Vincze, K.; Bárczi, E.; Bohács, A.; et al. Clinical predictors of lung-function decline in systemic-sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease patients with normal spirometry. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Ramirez, D.C.; Kosowan, L.; Singer, A. Management of cough in patients with idiopathic interstitial lung diseases in primary care. Chron. Respir. Dis. 2022, 19, 14799731221089319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, N.S.H.; Moore, I.; Lake, F. Understanding cough in interstitial lung disease: A cross-sectional study on the adequacy of treatment. Intern. Med. J. 2021, 51, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Manen, M.J.G.; Birring, S.S.; Vancheri, C.; Vindigni, V.; Renzoni, E.; Russel, A.M.; Wapenaar, M.; Cottin, V.; Wijsenbeek, M.S. Effect of pirfenidone on cough in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1701157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, A.; Taguchi, Y.; Ogura, T.; Ebina, M.; Taniguchi, H.; Kondoh, Y.; Suga, M.; Takahashi, H.; Nakata, K.; Sato, A.; et al. Pirfenidone Clinical Study Group in Japan. Exploratory analysis of a phase III trial of pirfenidone identifies a subpopulation of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis as benefiting from treatment. Respir. Res. 2011, 12, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Lin, H.C.; Wang, Y.H.; Wang, C.Y.; Lin, Y.S.; Lai, C.C. The safety of nintedanib for the treatment of interstitial lung disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijsenbeek, M.; Swigris, J.J.; Inoue, Y.; Kreuter, M.; Maher, T.M.; Suda, T.; Baldwin, M.; Mueller, H.; Rohr, K.B.; Flaherty, K.R.; et al. INBUILD Trial Investigators. Effects of nintedanib on symptoms in patients with progressive pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2024, 63, 2300752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birring, S.S.; Wijsenbeek, M.S.; Agrawal, S.; van den Berg, J.W.K.; Stone, H.; Maher, T.M.; Tutuncu, A.; Morice, A.H. A novel formulation of inhaled sodium cromoglicate (PA101) in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and chronic cough: A randomised, double-blind, proof-of-concept, phase 2 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, F.J.; Wijsenbeek, M.S.; Raghu, G.; Flaherty, K.R.; Maher, T.M.; Wuyts, W.A.; Kreuter, M.; Kolb, M.; Chambers, D.C.; Fogarty, C.; et al. Phase 2B study of inhaled RVT-1601 for chronic cough in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled study (SCENIC Trial). Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 205, 1084–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milman, N.; Graudal, N.; Grode, G.; Munch, E. No effect of high-dose inhaled steroids in pulmonary sarcoidosis: A double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J. Intern. Med. 1994, 236, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- du Bois, R.M.; Greenhalgh, P.M.; Southcott, A.M.; Johnson, N.M.; Harris, T.A. Randomized trial of inhaled fluticasone propionate in chronic stable pulmonary sarcoidosis: A pilot study. Eur. Respir. J. 1999, 13, 1345–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baughman, R.P.; Iannuzzi, M.C.; Lower, E.E.; Moller, D.R.; Balkissoon, R.C.; Winget, D.B.; Judson, M.A. Use of fluticasone in acute symptomatic pulmonary sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2002, 19, 198–204. [Google Scholar]
- Pietinalho, A.; Tukiainen, P.; Haahtela, T.; Persson, T.; Selroos, O. Oral prednisolone followed by inhaled budesonide in newly diagnosed pulmonary sarcoidosis: A double-blind, placebo-controlled multicenter study. Finnish Pulmonary Sarcoidosis Study Group. Chest 1999, 116, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hope-Gill, B.D.; Hilldrup, S.; Davies, C.; Newton, R.P.; Harrison, N.K. A study of the cough reflex in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 168, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guler, S.A.; Clarenbach, C.; Brutsche, M.; Hostettler, K.; Brill, A.K.; Schertel, A.; Geiser, T.K.; Funke-Chambour, M. Azithromycin for the treatment of chronic cough in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A randomized controlled crossover trial. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2021, 18, 2018–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, M.R.; Santopietro, V.; Mathew, L.; Horton, K.M.; Polito, A.J.; Liu, M.C.; Danoff, S.K.; Lechtzin, N. Thalidomide for the treatment of cough in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2012, 157, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, P.; Funston, W.; Mossop, H.; Ryan, V.; Jones, R.; Forbes, R.; Sen, S.; Pearson, J.; Griffin, S.M.; Smith, J.A.; et al. Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot trial of omeprazole in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Thorax 2019, 74, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilduff, C.E.; Counter, M.J.; Thomas, G.A.; Harrison, N.K.; Hope-Gill, B.D. Effect of acid suppression therapy on gastroesophageal reflux and cough in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: An intervention study. Cough 2014, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.M.; Misono, S. Use of specific neuromodulators in the treatment of chronic, idiopathic cough: A systematic review. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2013, 148, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, N.M.; Birring, S.S.; Gibson, P.G. Gabapentin for refractory chronic cough: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2012, 380, 1583–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGarvey, L.P.; Birring, S.S.; Morice, A.H.; Dicpinigaitis, P.V.; Pavord, I.D.; Schelfhout, J.; Nguyen, A.M.; Li, Q.; Tzontcheva, A.; Iskold, B.; et al. COUGH-1 and COUGH-2 Investigators. Efficacy and safety of gefapixant, a P2X3 receptor antagonist, in refractory chronic cough and unexplained chronic cough (COUGH-1 and COUGH-2): Results from two double-blind, randomised, parallel-group, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trials. Lancet 2022, 399, 909–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, F.J.; Afzal, A.S.; Smith, J.A.; Ford, A.P.; Li, J.J.; Li, Y.; Kitt, M.M. Chronic Cough in IPF Study Group. Treatment of persistent cough in subjects with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) with gefapixant, a P2X3 antagonist, in a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Pulm. Ther. 2021, 7, 471–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morice, A.H.; Menon, M.S.; Mulrennan, S.A.; Everett, C.F.; Wright, C.; Jackson, J.; Jackson, J.; Thompson, R. Opiate therapy in chronic cough. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 175, 312–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Spencer, L.G.; Banya, W.; Westoby, J.; Tudor, V.A.; Rivera-Ortega, P.; Chaudhuri, N.; Jakupovic, I.; Patel, B.; Thillai, M.; et al. Morphine for treatment of cough in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (PACIFY COUGH): A prospective, multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, two-way crossover trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2024, 12, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, T.M.; Avram, C.; Bortey, E.; Hart, S.P.; Hirani, N.; Molyneux, P.L.; Porter, J.C.; Smith, J.A.; Sciascia, T. Nalbuphine Tablets for Cough in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. NEJM Evid. 2023, 2, EVIDoa2300083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khor, Y.H.; Holland, A.E.; Goh, N.S.L.; Miller, B.R.; Vlahos, R.; Bozinovski, S.; Lahham, A.; Glaspole, I.; McDonald, C.F. Ambulatory oxygen in fibrotic interstitial lung disease: A pilot, randomized, triple-blinded, sham-controlled trial. Chest 2020, 158, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamberlain Mitchell, S.A.; Garrod, R.; Clark, L.; Douiri, A.; Parker, S.M.; Ellis, J.; Fowler, S.J.; Ludlow, S.; Hull, J.H.; Chung, K.F.; et al. Physiotherapy, and speech and language therapy intervention for patients with refractory chronic cough: A multicentre randomised control trial. Thorax 2017, 72, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavorini, F.; Spina, D.; Walker, M.J.; Franciosi, L.; Page, C.P.; Fontana, G.A. Antitussive effect of carcainium chloride in patients with chronic cough and idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: A pilot study. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 40, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Manen, M.J.G.; Wijsenbeek, M.S. Cough, an unresolved problem in interstitial lung diseases. Curr. Opin. Support Palliat. Care 2019, 13, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birring, S.S.; Kavanagh, J.E.; Irwin, R.S.; Keogh, K.A.; Lim, K.G.; Ryu, J.H. Treatment of interstitial lung disease-associated cough: CHEST guideline and expert panel report. Chest 2018, 154, 904–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.J.; Lee, H.; Clayton, C.; Pointon, K.; Soomro, I.; Shaw, D.E.; Harrison, T.W. Idiopathic chronic productive cough and response to open-label macrolide therapy: An observational study. Respirology 2019, 24, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkhof, F.F.; Doornewaard-ten Hertog, N.E.; Uil, S.M.; Kerstjens, H.A.; van den Berg, J.W. Azithromycin and cough-specific health status in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and chronic cough: A randomised controlled trial. Respir. Res. 2013, 14, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, N.K.; Michael, C.P. Nerves, cough, and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. EMJ Respir. 2015, 3, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakwaya, Y.; Ramdurai, D.; Swigris, J.J. Managing cough in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 2021, 160, 1774–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niimi, A.; Sagara, H.; Kikuchi, M.; Arano, I.; Sato, A.; Shirakawa, M.; La Rosa, C.; Muccino, D. A phase 3, randomized, double-blind, clinical study to evaluate the long-term safety and efficacy of gefapixant in Japanese adult participants with refractory or unexplained chronic cough. Allergol. Int. 2022, 71, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulqawi, R.; Dockry, R.; Holt, K.; Layton, G.; McCarthy, B.G.; Ford, A.P.; Smith, J.A. P2X3 receptor antagonist (AF-219) in refractory chronic cough: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 study. Lancet 2015, 385, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slinger, C.; Mehdi, S.B.; Milan, S.J.; Dodd, S.; Matthews, J.; Vyas, A.; Marsden, P.A. Speech and language therapy for management of chronic cough. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 7, CD013067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vertigan, A.E.; Kapela, S.L.; Ryan, N.M.; Birring, S.S.; McElduff, P.; Gibson, P.G. Pregabalin and speech pathology combination therapy for refractory chronic cough: A randomized controlled trial. Chest 2016, 149, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasouki, S.; Quach, S.; Mancopes, R.; Mitchell, S.C.; Goldstein, R.; Brooks, D.; Oliveira, A. A non-pharmacological cough therapy for people with interstitial lung diseases: A case report. Physiother. Can. 2023, 75, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morice, A.H.; Millqvist, E.; Belvisi, M.G.; Bieksiene, K.; Birring, S.S.; Chung, K.F.; Dal Negro, R.W.; Dicpinigaitis, P.; Kantar, A.; McGarvey, L.P.; et al. Expert opinion on the cough hypersensitivity syndrome in respiratory medicine. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, 1132–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morice, A.; Dicpinigaitis, P.; McGarvey, L.; Birring, S.S. Chronic cough: New insights and future prospects. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2021, 30, 210127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, K.G.; Rank, M.A.; Hahn, P.Y.; Keogh, K.A.; Morgenthaler, T.I.; Olson, E.J. Long-term safety of nebulized lidocaine for adults with difficult-to-control chronic cough: A case series. Chest 2013, 143, 1060–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulqawi, R.; Satia, I.; Kanemitsu, Y.; Khalid, S.; Holt, K.; Dockry, R.; Woodcock, A.A.; Smith, J.A. A randomized controlled trial to assess the effect of lidocaine administered via throat spray and nebulization in patients with refractory chronic cough. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 1640–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, S.; Horita, N.; Hara, J.; Sasamoto, M.; Kanemitsu, Y.; Hara, Y.; Obase, Y.; Kaneko, T.; Niimi, A.; Mukae, H. Benefit-risk profile of P2X3 receptor antagonists for treatment of chronic cough: Dose-response model-based network meta-analysis. Chest 2024, 166, 1124–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Treatment | Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Pirfenidone/nintedanib |
|
|
| Inhaled cromolyn sodium |
| |
| Inhaled corticosteroids |
|
|
| Oral corticosteroids |
|
|
| Oral cyclophosphamide |
|
|
| Mycophenolate mofetil |
|
|
| Azithromycin |
|
|
| Thalidomide |
|
|
| Proton pump inhibitors |
| |
| Neuromodulators (gabapentin, pregabalin, amitriptyline, baclofen) |
| |
| P2X3 receptor antagonist (gefapixant) |
| |
| Opiates (morphine) and the opioid agonist-antagonist (nalbuphine) |
| |
| Supplemental oxygen |
|
|
| Speech therapy |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trushenko, N.V.; Suvorova, O.A.; Schmidt, A.E.; Chikina, S.Y.; Levina, I.A.; Lavginova, B.B.; Avdeev, S.N. Updates on the Prevalence, Quality of Life, and Management of Chronic Cough in Interstitial Lung Diseases. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1139. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091139
Trushenko NV, Suvorova OA, Schmidt AE, Chikina SY, Levina IA, Lavginova BB, Avdeev SN. Updates on the Prevalence, Quality of Life, and Management of Chronic Cough in Interstitial Lung Diseases. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(9):1139. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091139
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrushenko, Natalia V., Olga A. Suvorova, Anna E. Schmidt, Svetlana Y. Chikina, Iuliia A. Levina, Baina B. Lavginova, and Sergey N. Avdeev. 2025. "Updates on the Prevalence, Quality of Life, and Management of Chronic Cough in Interstitial Lung Diseases" Diagnostics 15, no. 9: 1139. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091139
APA StyleTrushenko, N. V., Suvorova, O. A., Schmidt, A. E., Chikina, S. Y., Levina, I. A., Lavginova, B. B., & Avdeev, S. N. (2025). Updates on the Prevalence, Quality of Life, and Management of Chronic Cough in Interstitial Lung Diseases. Diagnostics, 15(9), 1139. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091139






