Rapid and Efficient Screening of Helicobacter pylori in Gastric Samples Stained with Warthin–Starry Using Deep Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
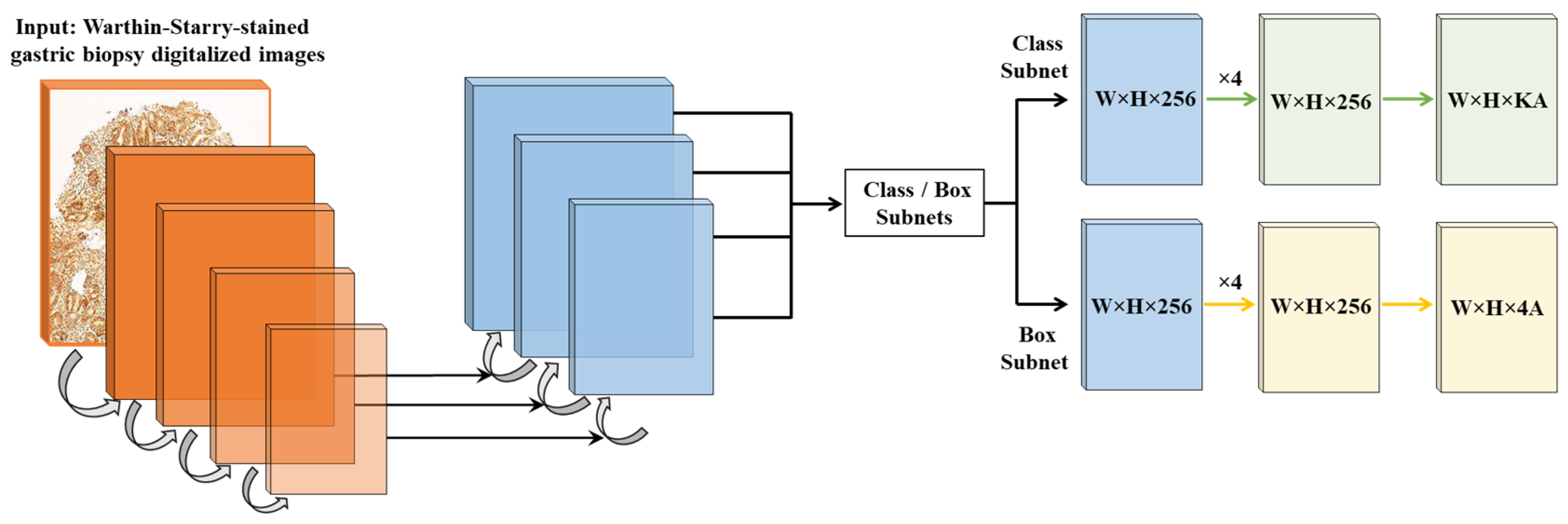
2.1. Algorithm Design and Development
2.2. Efficiency of AI-Assisted vs. Traditional Digital Pathology Diagnosis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
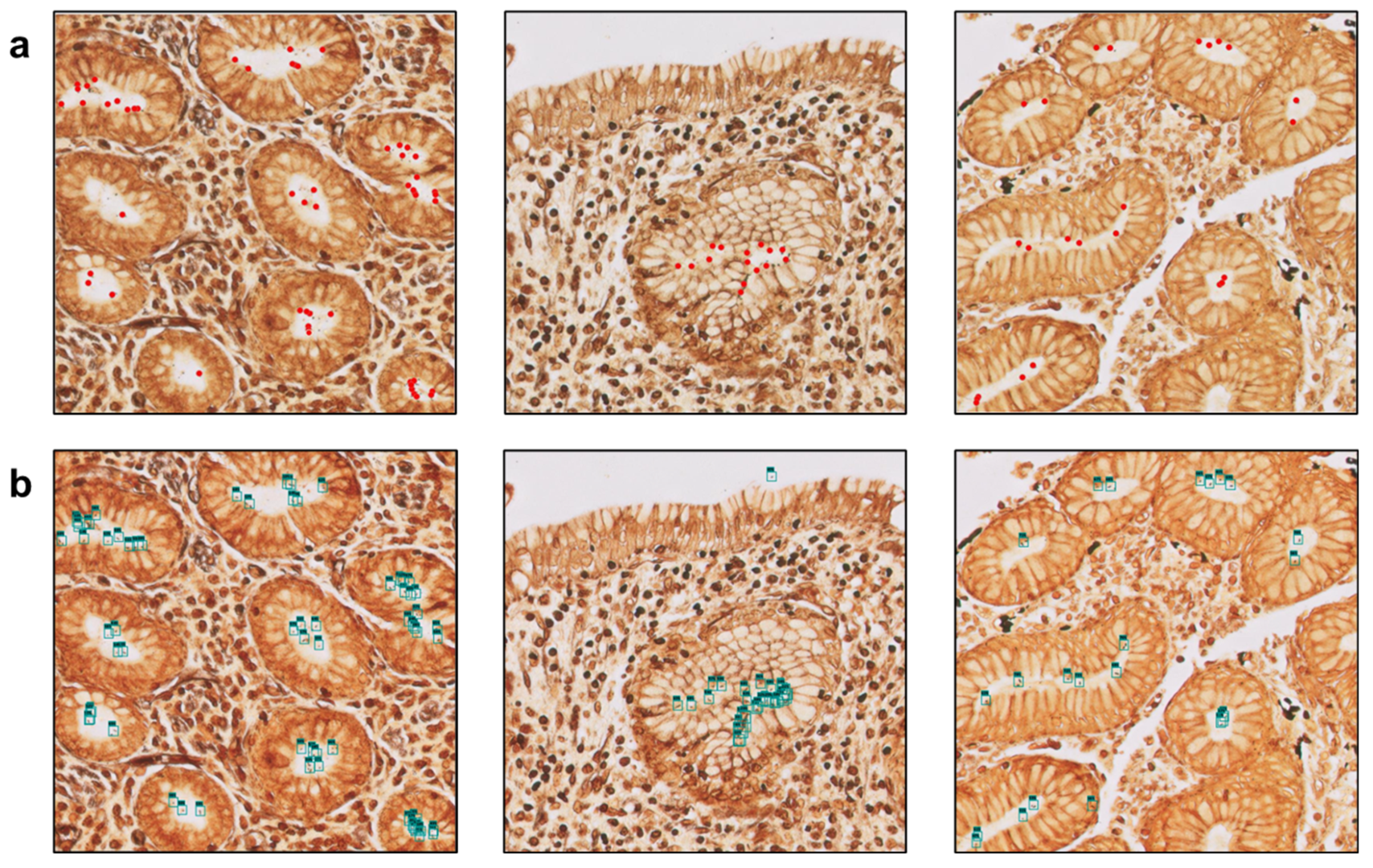
3.1. The Algorithm Can Automatically Detect H. Pylori on Gastric Samples
3.2. Utilization of the Algorithm Drastically Reduces Diagnostic Turnaround Time
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robin Warren, J.; Marshall, B. Unidentified Curved Bacilli on Gastric Epithelium in Active Chronic Gastritis. Lancet 1983, 321, 1273–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignon, M. The Nobel Prize in Medicine, 2005. Barry J. Marshall and J. Robin Warren. Helicobacter pylori Honored. Med. Sci. 2005, 21, 993–994. [Google Scholar]
- López-Brea, M. La Infección Por Helicobacter pylori: Premio Nobel de Medicina. Rev. Esp. Quimioterapia 2005, 18, 271–272. [Google Scholar]
- Reshetnyak, V.I.; Burmistrov, A.I.; Maev, I.V. Helicobacter pylori: Commensal, Symbiont or Pathogen? World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 545–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisbert, J.P. A Critical Review of the Diagnostic Methods for Helicobacter pylori Infection. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2000, 23, 135–143. [Google Scholar]
- Gravina, A.G.; Zagari, R.M.; De Musis, C.; Romano, L.; Loguercio, C.; Romano, M. Helicobacter pylori and Extragastric Diseases: A Review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 3204–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowe, S.E. Helicobacter pylori Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1158–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, N.R.; Hartung, M.L.; Müller, A. Life in the Stomach: Persistence Strategies Helicobacter pylori. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Brito, B.B.; da Silva, F.A.F.; Soares, A.S.; Pereira, V.A.; Santos, M.L.C.; Sampaio, M.M.; Neves, P.H.M.; de Melo, F.F. Pathogenesis and Clinical Management of Helicobacter pylori Gastric Infection. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 5578–5589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayali, S.; Manfredi, M.; Gaiani, F.; Bianchi, L.; Bizzarri, B.; Leandro, G.; Di Mario, F.; De’angelis, G.L. Helicobacter pylori, Transmission Routes and Recurrence of Infection: State of the Art. Acta Biomed. 2018, 89, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.K.; Kuo, F.C.; Liu, C.J.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.Y.; Wang, S.S.W.; Wu, J.Y.; Kuo, C.H.; Huang, Y.K.; Wu, D.C. Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori Infection: Current Options and Developments. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 11221–11235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallone, C.A.; Chiba, N.; van Zanten, S.V.; Fischbach, L.; Gisbert, J.P.; Hunt, R.H.; Jones, N.L.; Render, C.; Leontiadis, G.I.; Moayyedi, P.; et al. The Toronto Consensus for the Treatment of Helicobacter pylori Infection in Adults. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 51–69.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.M.; O’Morain, C.; McNamara, D. Helicobacter pylori Resistance to Current Therapies. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2019, 35, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardos, A.I.; Maghiar, A.; Zaha, D.C.; Pop, O.; Fritea, L.; Miere, F.; Cavalu, S. Evolution of Diagnostic Methods for Helicobacter pylori Infections: From Traditional Tests to High Technology, Advanced Sensitivity and Discrimination Tools. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kim, N. Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori by Invasive Test: Histology. Ann. Transl. Med. 2015, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía-Parra, J.L.J.; Guerrero-Espinoza, A.E.; Flores-Arrascue, C.P.; Chiclayo-Padilla, A.S. Estandarización de Nuevo Protocolo Inmunohistoquímico Para Identificar Helicobacter pylori de Biopsias Gástricas y Valoración Frente a La Tinción Hematoxilina-Eosina. Rev. Cuerpo Médico Hosp. Nac. Almanzor Aguinaga Asenjo 2020, 13, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton-Key, M.; Diss, T.C.; Isaacson, P.G. Detection of Helicobacter pylori in Gastric Biopsy and Resection Specimens. J. Clin. Pathol. 1996, 49, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akeel, M.; Elhafey, A.; Shehata, A.; Elmakki, E.; Aboshouk, T.; Ageely, H.; Mahfouz, M.S. Efficacy of Immunohistochemical Staining in Detecting Helicobacter pylori in Saudi Patients with Minimal and Atypical Infection. Eur. J. Histochem. 2021, 65, 3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginestet, F.; Guibourg, B.; Doucet, L.; Théreaux, J.; Robaszkiewicz, M.; Marcorelles, P.; Uguen, A. Upfront Immunohistochemistry Improves Specificity of Helicobacter pylori Diagnosis. A French Pathology Laboratory Point of View. Helicobacter 2017, 22, e12424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, A.; Hoyeau, N.; Fléjou, J.F. Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori Infection on Gastric Biopsies: Standard Stain, Special Stain or Immunohistochemistry? Ann. Pathol. 2018, 38, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonkers, D.; Stobberingh, E.; De Bruine, A.; Arends, J.W.; Stockbrügger, R. Evaluation of Immunohistochemistry for the Detection of Helicobacter pylori in Gastric Mucosal Biopsies. J. Infect. 1997, 35, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrebinska, S.; Megraud, F.; Daugule, I.; Santare, D.; Isajevs, S.; Liepniece-Karele, I.; Bogdanova, I.; Rudzite, D.; Vangravs, R.; Kikuste, I.; et al. Who Could Be Blamed in the Case of Discrepant Histology and Serology Results for Helicobacter pylori Detection? Diagnostics 2022, 12, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berbís, M.A.; Aneiros-Fernández, J.; Olivares, F.J.M.; Nava, E.; Luna, A. Role of Artificial Intelligence in Multidisciplinary Imaging Diagnosis of Gastrointestinal Diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 4395–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteva, A.; Robicquet, A.; Ramsundar, B.; Kuleshov, V.; DePristo, M.; Chou, K.; Cui, C.; Corrado, G.; Thrun, S.; Dean, J. A Guide to Deep Learning in Healthcare. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topol, E.J. High-Performance Medicine: The Convergence of Human and Artificial Intelligence. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, R.Y.; Coyner, A.S.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Chiang, M.F.; Peter Campbell, J. Introduction to Machine Learning, Neural Networks, and Deep Learning. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Serajian, M.; Testagrose, C.; Prosperi, M.; Boucher, C. A Comparative Study of Antibiotic Resistance Patterns in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 5104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irani, H.; Metsis, V. Enhancing Time-Series Prediction with Temporal Context Modeling: A Bayesian and Deep Learning Synergy. Int. Flairs Conf. Proc. 2024, 37, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q.V. EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Lv, P.; Zhou, L.; Wang, H. EAR-U-Net: EfficientNet and Attention-Based Residual U-Net for Automatic Liver Segmentation in CT. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.01014. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature Pyramid Networks for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- McColl, K.E.L. Helicobacter pylori Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1597–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plummer, M.; Franceschi, S.; Vignat, J.; Forman, D.; De Martel, C. Global Burden of Gastric Cancer Attributable to Helicobacter pylori. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 487–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, A.C.; Yuan, Y.; Forman, D.; Hunt, R.; Moayyedi, P. Helicobacter pylori Eradication for the Prevention of Gastric Neoplasia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 11, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.; Gildenblat, J.; Ihle, M.A.; Merkelbach-Bruse, S.; Noh, K.W.; Peifer, M.; Quaas, A.; Büttner, R. Deep Learning for Sensitive Detection of Helicobacter pylori in Gastric Biopsies. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020, 20, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Marklund, H.; Blaha, O.; Desai, M.; Martin, B.; Bingham, D.; Berry, G.J.; Gomulia, E.; Ng, A.Y.; Shen, J. Deep Learning Assistance for the Histopathologic Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori. Intell. Based Med. 2020, 1–2, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Yan, L.; Xu, S.; Chen, G.; Gao, H. A Study on the Diagnosis of the Helicobacter pylori Coccoid Form with Artificial Intelligence Technology. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1008346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liscia, D.S.; D’Andrea, M.; Biletta, E.; Bellis, D.; Demo, K.; Ferrero, F.; Petti, A.; Butinar, R.; D’Andrea, E.; Davini, G. Use of Digital Pathology and Artificial Intelligence for the Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori in Gastric Biopsies. Pathologica 2022, 114, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berbís, M.A.; McClintock, D.S.; Bychkov, A.; Van der Laak, J.; Pantanowitz, L.; Lennerz, J.K.; Cheng, J.Y.; Delahunt, B.; Egevad, L.; Eloy, C.; et al. Computational Pathology in 2030: A Delphi Study Forecasting the Role of AI in Pathology Within the next Decade. eBioMedicine 2023, 88, 104427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Patch size | 1024 × 1024 px |
| Batch size | 32 |
| Optimizer | Adam |
| Learning rate | 0.0001 |
| Training epochs | 1500 |
| Loss function | Binary Cross-Entropy |
| Purpose | Samples | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Training | 2640 | Manually annotated by expert pathologists. Collected at the HT Medica AP centers. |
| Calibration (general) | 528 | To evaluate general performance of the algorithm. Collected at the HT Medica AP centers. |
| Validation | 132 | For model threshold adjustment. Collected at the HT Medica AP centers. |
| Calibration (efficiency study) | 100 | 20 images employed for iterative parameter adjustment and 80 images employed for testing. Collected at the UPIGAP. |
| Personnel training | 200 | Training of the pathology technician and the biotechnologist in the identification of H. pylori in gastric samples. Extracted from the algorithm training dataset.Collected at the HT Medica AP centers. |
| Efficiency study | 300 | 150 H. pylori-positive and 150 H. pylori-negative images to test the proficiency of the CS-Bacter algorithm. Collected at the UPIGAP. |
| Samples | Time | Diagnostic Discrepancy | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DP | AI-Assisted DP | |||
| Pathologist 1 | 60 | 4318 s (71.97 min) | 512 s (8.53 min) | 1 case |
| Pathologist 2 | 60 | 4077 s (67.95 min) | 484 s (8.07 min) | 1 case |
| Pathology Resident | 60 | 5891 s (98.18 min) | 590 s (9.83 min) | 3 cases |
| Pathology Technician | 60 | 7103 s (118.38 min) | 632 s (10.53 min) | 3 cases |
| Biotechnologist | 60 | 7437 s (123.95 min) | 613 s (10.22 min) | 2 cases |
| Diagnostic Accuracy | ||
|---|---|---|
| Without AI assistance | With AI assistance | |
| Pathologist 1 | 98.3% | 100% |
| Pathologist 2 | 98.3% | 100% |
| Pathology Resident | 95.0% | 98.3% |
| Pathology Technician | 93.3% | 98.3% |
| Biotechnologist | 94.2% | 98.3% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aneiros-Fernández, J.; Montero Pavón, P.; García Gómez, N.; Palo Prian, R.M.; Sánchez García, I.; Romero Ortiz, A.I.; López Castro, R.; Casado-Sánchez, C.; Sánchez Turrión, V.; Luna, A.; et al. Rapid and Efficient Screening of Helicobacter pylori in Gastric Samples Stained with Warthin–Starry Using Deep Learning. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091085
Aneiros-Fernández J, Montero Pavón P, García Gómez N, Palo Prian RM, Sánchez García I, Romero Ortiz AI, López Castro R, Casado-Sánchez C, Sánchez Turrión V, Luna A, et al. Rapid and Efficient Screening of Helicobacter pylori in Gastric Samples Stained with Warthin–Starry Using Deep Learning. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(9):1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091085
Chicago/Turabian StyleAneiros-Fernández, José, Pedro Montero Pavón, Natalia García Gómez, Rosa María Palo Prian, Ismael Sánchez García, Ana Isabel Romero Ortiz, Rodrigo López Castro, César Casado-Sánchez, Víctor Sánchez Turrión, Antonio Luna, and et al. 2025. "Rapid and Efficient Screening of Helicobacter pylori in Gastric Samples Stained with Warthin–Starry Using Deep Learning" Diagnostics 15, no. 9: 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091085
APA StyleAneiros-Fernández, J., Montero Pavón, P., García Gómez, N., Palo Prian, R. M., Sánchez García, I., Romero Ortiz, A. I., López Castro, R., Casado-Sánchez, C., Sánchez Turrión, V., Luna, A., & Berbís, M. Á. (2025). Rapid and Efficient Screening of Helicobacter pylori in Gastric Samples Stained with Warthin–Starry Using Deep Learning. Diagnostics, 15(9), 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15091085






