Advances in Endo-Hepatology: The Role of Endoscopic Ultrasound in the Management of Portal Hypertension
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Endoscopic Ultrasound Guided Elastography
3.1. Strain Elastography
3.2. Shear Wave Elastography
4. Liver Biopsy
5. Portal Pressure Gradient Measurement
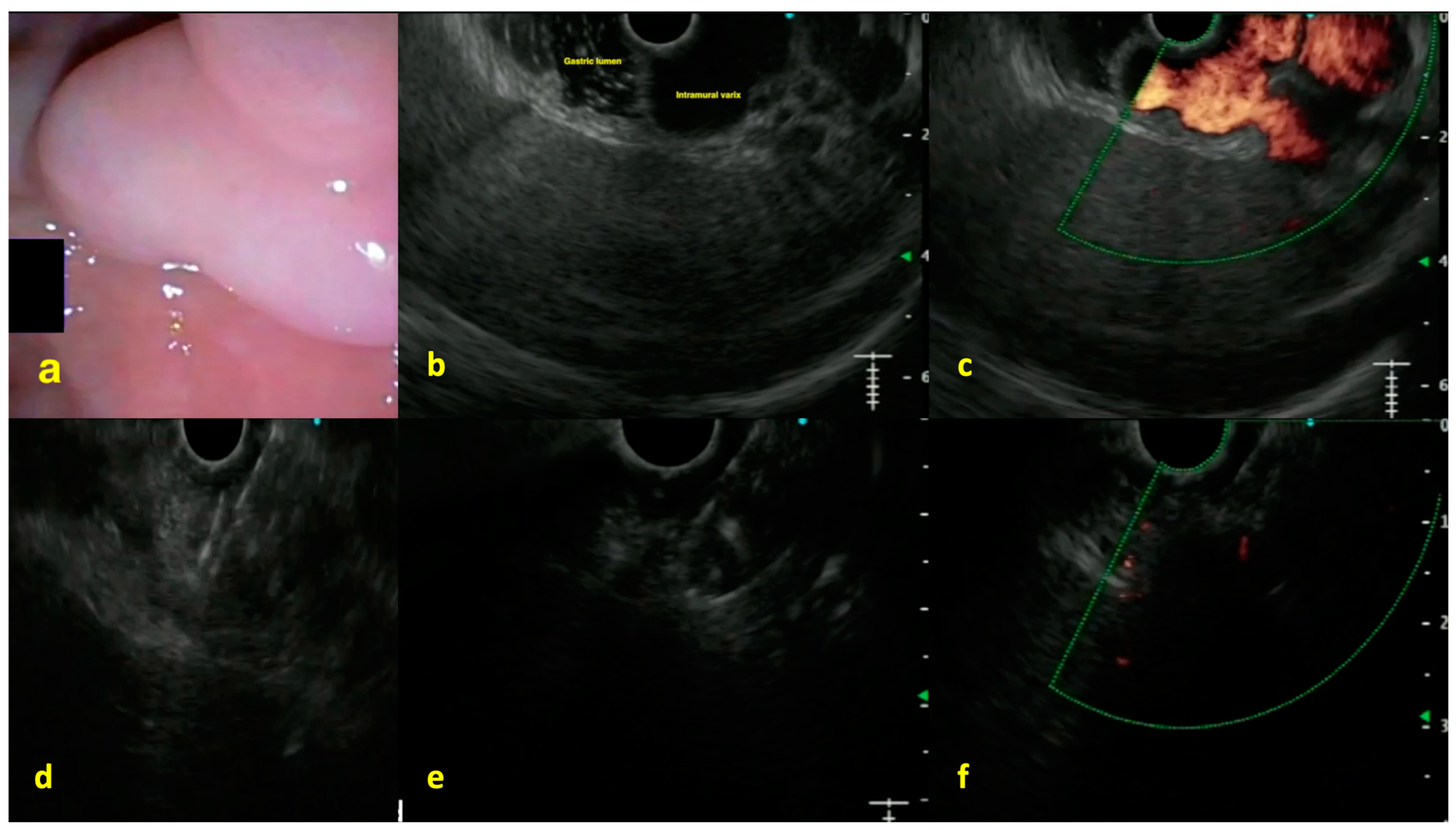
6. EUS-Guided IPSS and Portal Blood Sampling
7. Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Vascular Interventions
8. Additional Role of EUS-Guided Ablation in Liver Tumors
9. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CE-EUS | Contrast-enhanced EUS |
| EUS | Endoscopic Ultrasound |
| EUS-PPG | Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Portal Pressure Gradient |
| EUS-LB | Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Liver Biopsy |
| EUS-SWE | Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Shear Wave Elastography |
| HVAT | Hepatic Vein Arrival Time |
| IPSS | Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt |
| PH | Portal Hypertension |
| PSVD | Porto-Sinusoidal Vascular Disorder |
| HVPG | Hepatic Venous Pressure Gradient |
| TE | Transient Elastography |
| MRE | Magnetic Resonance Elastography |
| NASH | Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis |
| TIPS | Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt |
| LAMS | Lumen-Apposing Metal Stent |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| AUROC | Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve |
References
- Chang, K.J.; Samarasena, J.B.; Iwashita, T.; Nakai, Y.; Lee, J.G. Endo-hepatology: A new paradigm. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 22, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell’Anna, G.; Ogura, T.; Vanella, G.; Nishikawa, H.; Lakhtakia, S.; Arcidiacono, P.G. Endoscopic ultrasound guided biliary interventions. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2022, 60–61, 101810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, A.Y.; Kolb, J.; Shah, S.; Chahine, A.; Hashimoto, R.; Patel, A.; Tsujino, T.; Huang, J.; Hu, K.Q.; Chang, K.; et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided portal pressure gradient with liver biopsy: 6 years of endo-hepatology in practice. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 37, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilen, J.; McGrath, K. EUS-guided liver biopsy: The optimal technique? Endosc. Int. Open 2023, 11, E169–E171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbiMansour, J.; Chin, J.Y.; Kaur, J.; Vargas, E.J.; Abu Dayyeh, B.K.; Law, R.; Garimella, V.; Levy, M.J.; Storm, A.C.; Dierkhising, R.; et al. Endoscopic Ultrasound-based Shear Wave Elastography for Detection of Advanced Liver Disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2024, 59, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, F.; Rustagi, T.; Frederick, R.T. Endo-hepatology: Updates for the clinical hepatologist. Clin. Liver. Dis. 2023, 22, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvanderan, S.P.; Lam, E.; Shahidi, N. Endohepatology: Arrival at the frontier of interventional endosonography. World J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 30, 2397–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo-Hepatology: Updates for the Clinical Hepatologist—PMC. Available online: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10473324/ (accessed on 18 January 2025).
- Jearth, V.; Sundaram, S.; Rana, S.S. Diagnostic and interventional EUS in hepatology: An updated review. Endosc. Ultrasound 2022, 11, 355–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Anna, G.; Nunziata, R.; Delogu, C.; Porta, P.; Grassini, M.V.; Dhar, J.; Barà, R.; Bencardino, S.; Fanizza, J.; Mandarino, F.V.; et al. The Role of Therapeutic Endoscopic Ultrasound in Management of Malignant Double Obstruction (Biliary and Gastric Outlet): A Comprehensive Review with Clinical Scenarios. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 7731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, C.F.; Bibby, E.; Jenssen, C.; Saftoiu, A.; Iglesias-Garcia, J.; Havre, R.F. EUS elastography: How to do it? Endosc. Ultrasound 2018, 7, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, C.F.; Burmeister, S.; Hollerbach, S.; Arcidiacono, P.G.; Braden, B.; Fusaroli, P.; Hocke, M.; Iglesias-Garcia, J.; Kitano, M.; Larghi, A.; et al. Do we need elastography for EUS? Endosc. Ultrasound 2020, 9, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, S.; Wallace, M.B.; Cohen, J.; Pike, I.M.; Adler, D.G.; Kochman, M.L.; Lieb, J.G., 2nd; Park, W.G.; Rizk, M.K.; Sawhney, M.S.; et al. Quality indicators for EUS. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 81, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iglesias-Garcia, J.; de la Iglesia-Garcia, D.; Lariño-Noia, J.; Dominguez-Muñoz, J.E. Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS) Guided Elastography. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias-García, J.; Lariño-Noia, J.; Domínguez-Muñoz, J.E. New Imaging Techniques: Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Elastography. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 27, 551–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.; Samanta, J.; Muktesh, G.; Dhar, J.; Kumar, A.; Shah, J.; Spadaccini, M.; Gupta, P.; Fugazza, A.; Gupta, V.; et al. Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Rendezvous Technique Versus Precut Sphincterotomy as Salvage Technique in Patients With Benign Biliary Disease and Difficult Biliary Cannulation: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2024, 177, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons-Linares, C.R.; Wander, P.; Vargo, J.; Chahal, P. Endoscopic ultrasonography: An inside view. Cleve Clin. J. Med. 2020, 87, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisotti, A.; Serrani, M.; Caletti, G.; Fusaroli, P. EUS liver assessment using contrast agents and elastography. Endosc. Ultrasound 2018, 7, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, Y.; Yamazaki, H.; Shimokawa, T.; Kawaji, Y.; Tamumra, T.; Hatamaru, K.; Itonaga, M.; Ashida, R.; Kitano, M. Shear-wave versus strain elastography in endoscopic ultrasound for the diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2023, 23, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, D.R.; Mettman, D.; Andraws, N.; Haer, E.; Porter, J.; Ulusurac, O.; Ullery, S.; Desai, M.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Sharma, P. Comparative accuracy of endosonographic shear wave elastography and transcutaneous liver stiffness measurement: A pilot study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2023, 97, 35–41.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.J.; Jirapinyo, P.; Shah, R.; Schuster, K.; Papke, D.J.; Thompson, C.C.; Doyon, L.; Lautz, D.B.; Ryou, M. EUS-guided shear wave elastography for fibrosis screening in patients with obesity and metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease: A pilot study (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2024, 101, 456–462.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albayrak, F. Endoscopic Ultrasonography In Diagnostic Endohepatology: The Hepatologist’s Swiss Army Knife. Eurasian J. Med. 2023, 55, S131–S137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laleman, W.; Peiffer, K.H.; Tischendorf, M.; Ullerich, H.J.; Praktiknjo, M.; Trebicka, J. Role of endoscopy in hepatology. Dig. Liver Dis. 2024, 56, 1185–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, D.L.; Sangwan, V.; Khurana, S.; Khara, H.S.; Zhang, J.; Confer, B.D. Reproducibility of EUS-guided shear wave elastography for assessment of hepatic fibrosis: A prospective pilot cohort study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2024, 101, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, A.; Cain, O.; Chauhan, A.; Webb, G.J. Medical liver biopsy: Background, indications, procedure and histopathology. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2020, 11, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facciorusso, A.; Ramai, D.; Conti Bellocchi, M.C.; Bernardoni, L.; Manfrin, E.; Muscatiello, N.; Crinò, S.F. Diagnostic Yield of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Liver Biopsy in Comparison to Percutaneous Liver Biopsy: A Two-Center Experience. Cancers 2021, 13, 3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, M.; Samanta, J.; Spadaccini, M.; Fugazza, A.; Crinò, S.F.; Gkolfakis, P.; Triantafyllou, K.; Dhar, J.; Maida, M.; Pugliese, N.; et al. Diagnostic Yield of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Liver Biopsy in Comparison to Percutaneous Liver Biopsy: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials and Trial Sequential Analysis. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuja, A.; Alkhasawneh, A.; Fialho, A.; Fialho, A.; Shukri, A.; Harris, C.; Smotherman, C.; Malespin, M.; de Melo, S.W., Jr. Comparison of EUS-guided versus percutaneous and transjugular approaches for the performance of liver biopsies. Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 826–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhok, I.K.; Parsa, N.; Nieto, J.M. Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Liver Biopsy. Clin. Liver Dis. 2022, 26, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching-Companioni, R.A.; Diehl, D.L.; Johal, A.S.; Confer, B.D.; Khara, H.S. 19G aspiration needle versus 19G core biopsy needle for endoscopic ultrasound-guided liver biopsy: A prospective randomized trial. Endoscopy 2019, 51, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasugai, H.; Yamamoto, R.; Tatsuta, M.; Okano, Y.; Okuda, S.; Kishigami, Y.; Kitamura, T.; Wada, A.; Tamura, H. Value of heparinized fine-needle aspiration biopsy in liver malignancy. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1985, 144, 243–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewitt, J.; McGreevy, K.; Cummings, O.; Sherman, S.; Leblanc, J.K.; McHenry, L.; Al-Haddad, M.; Chalasani, N. Initial experience with EUS-guided Tru-cut biopsy of benign liver disease. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2009, 69, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diehl, D.; Mok, S.; Khara, H.; Johal, A.; Kirchner, H.; Lin, F. Heparin priming of EUS-FNA needles does not adversely affect tissue cytology or immunohistochemical staining. Endosc. Int. Open 2018, 6, E356–E362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akay, E.; Atasoy, D.; Altınkaya, E.; Koç, A.; Ertan, T.; Karaman, H.; Caglar, E. Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Using a 22-G Needle for Hepatic Lesions: Single-Center Experience. Clin. Endosc. 2021, 54, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, D.; Lin, A.; Khirfan, K.; Rahim, U.; Tavangar, A.; Dang, F.; Chang, K.; Samarasena, J. Dynamic suction: A novel technique to optimize EUS-guided liver biopsy. VideoGIE 2024, 9, 326–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajifathalian, K.; Chang, K.J.; Sharaiha, R.Z. Radiology-guided percutaneous approach is superior to EUS for performing liver biopsies. Gut 2022, 71, 845–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandan, S.; Deliwala, S.; Khan, S.R.; Mohan, B.P.; Dhindsa, B.S.; Bapaye, J.; Goyal, H.; Kassab, L.L.; Kamal, F.; Sayles, H.R.; et al. EUS-guided versus percutaneous liver biopsy: A comprehensive review and meta-analysis of outcomes. Endosc. Ultrasound 2023, 12, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, D.L.; Confer, B.; Adler, D.G.; Khara, H.S.; Johal, A.S. EUS-guided versus percutaneous liver biopsy: Do we have a winner? Endosc. Ultrasound 2022, 11, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Lakhtakia, S.; Jagtap, N.; Sekaran, A.; Kalapala, R.; Jahangeer, B.; Kulkarni, A.; Ramchandani, M.; Gupta, R.; Samudraala, S.; et al. EUS-guided left lobe liver biopsy: Safer modality with similar diagnostic yield as right lobe: A pilot study. Endosc. Int. Open 2023, 11, E172–E178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.; Majeed, A.; Kumar, P.; Rajput, M.; Goel, A.; Rao, R.N. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided liver biopsy using a single-pass, slow-pull technique with a 19-G Franseen tip fine-needle biopsy needle: A prospective study. Indian. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 42, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, S.; Arora, A.; Varghese, J.; Kumar, A.; Jain, S.; Khandelwal, A.; Mittal, A.; Misra, S.; Anikhindi, S.; Kumar, M.; et al. Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Liver Biopsy (EUS-LB): An Endoscopic Solution to the Unmet Needs of Liver Tissue Acquisition and Beyond. J. Dig. Endosc. 2024, 15, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelfattah, T.S.; Hassouneh, R.; Sarairah, H.; Puri, P.; Mutha, P.R.; Singh, S.J.; Fuchs, M.; Shah, T. S0974 Post-Procedure Pain and Complications From Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Liver Biopsy Compared to Percutaneous Liver Biopsy for Benign Parenchymal Liver Disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, S496–S497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajifathalian, K.; Chang, K.J.; Sharaiha, R.Z. Radiology-guided percutaneous approach is superior to EUS for performing liver biopsies. Gut 2021, 70, 2224–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuberger, J.; Patel, J.; Caldwell, H.; Davies, S.; Hebditch, V.; Hollywood, C.; Hubscher, S.; Karkhanis, S.; Lester, W.; Roslund, N.; et al. Guidelines on the use of liver biopsy in clinical practice from the British Society of Gastroenterology, the Royal College of Radiologists and the Royal College of Pathology. Gut 2020, 69, 1382–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarty, T.R.; Bazarbashi, A.N.; Njei, B.; Ryou, M.; Aslanian, H.R.; Muniraj, T. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided, percutaneous, and transjugular liver biopsy: A comparative systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Endosc. 2020, 53, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Franchis, R.; Bosch, J.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Reiberger, T.; Ripoll, C.; Baveno VII Faculty. Baveno VII—Renewing consensus in portal hypertension. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 959–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerome, C.E.; Scott, F.D.E.; John, G.Q.; Cyrus, V.E.; Eric, M.M.; Christian, L.H.; John, P.M.; Don, C.R. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided portal pressure gradient identifies patients with previously undiagnosed clinically significant portal hypertension. Portal Hypertens. Cirrhosis 2024, 3, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassegoda, O.; Olivas, P.; Turco, L.; Mandorfer, M.; Serra-Burriel, M.; Tellez, L.; Kwanten, W.; Laroyenne, A.; Farcau, O.; Alvarado, E.; et al. Decompensation in Advanced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease May Occur at Lower Hepatic Venous Pressure Gradient Levels Than in Patients With Viral Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 2276–2286.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baffy, G. Origins of Portal Hypertension in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2018, 63, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.Y.; Samarasena, J.B.; Tsujino, T.; Chang, K.J. EUS-guided portal pressure gradient measurement with a novel 25-gauge needle device versus standard transjugular approach: A comparison animal study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2016, 84, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Peng, C.; Zhang, S.; Huang, S.; Shen, S.; Xu, G.; Zhang, F.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhuge, Y.; et al. EUS-guided portal pressure gradient measurement in patients with acute or subacute portal hypertension. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 93, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii-Lau, L.L.; Leise, M.D.; Kamath, P.S.; Gleeson, F.C.; Levy, M.J. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided portal-systemic pressure gradient measurement. Endoscopy 2014, 46, E654–E656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samarasena, J.B.; Chang, K.J. Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Interventions for the Measurement and Treatment of Portal Hypertension. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 29, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, D.G. Top Tips: EUS-Guided Portal Pressure Gradient Measurement. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2024, 101, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryou, M.; DeWitt, J.M.; Das, K.K.; Shami, V.M. AGA Clinical Practice Update on Interventional EUS for Vascular Investigation and Therapy: Commentary. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 21, 1699–1705.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Castro, R.; Carmona-Soria, I.; Jiménez-García, V.A.; Fernández-Álvarez, P.; Caunedo-Álvarez, Á.; Giovannini, M.; Irisawa, A. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided portal pressure gradient measurement: Improving safety and overcoming technical difficulties. Endoscopy 2023, 55 (Suppl. 1), E878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhindsa, B.S.; Tun, K.M.; Fiedler, A.; Deliwala, S.; Saghir, S.M.; Scholten, K.; Ramai, D.; Girotra, M.; Chandan, S.; Dhaliwal, A.; et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided portal pressure gradient measurement: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2024, 37, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajifathalian, K.; Westerveld, D.; Kaplan, A.; Dawod, E.; Herr, A.; Ianelli, M.; Saggese, A.; Kumar, S.; Fortune, B.E.; Sharaiha, R.Z. Simultaneous EUS-guided portosystemic pressure measurement and liver biopsy sampling correlate with clinically meaningful outcomes. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2022, 95, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscaglia, J.M.; Dray, X.; Shin, E.J.; Magno, P.; Chmura, K.M.; Surti, V.C.; Dillon, T.E.; Ducharme, R.W.; Donatelli, G.; Thuluvath, P.J.; et al. A new alternative for a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt: EUS-guided creation of an intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2009, 69, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulman, A.R.; Ryou, M.; Aihara, H.; Abidi, W.; Chiang, A.; Jirapinyo, P.; Sakr, A.; Ajeje, E.; Ryan, M.B.; Thompson, C.C. EUS-guided intrahepatic portosystemic shunt with direct portal pressure measurements: A novel alternative to transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunting. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2016, 85, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryou, M.; Stylopoulos, N. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided sampling and profiling of portal circulation in human patients for metabolic research studies and biomarker assessment. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2020, 319, G584–G588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trebicka, J.; Reiberger, T.; Laleman, W. Gut-Liver Axis Links Portal Hypertension to Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure. Visc. Med. 2018, 34, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.P.E.; Lim, J.K.; Francis, F.F.; Ahn, J. AGA Clinical Practice Update on Management of Portal Vein Thrombosis in Patients With Cirrhosis: Expert Review. Gastroenterology 2025, 168, 396–404.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florencio de Mesquita, C.; Antunes VL, J.; Milioli, N.J.; Fernandes, M.V.; Correa, T.L.; Martins, O.C.; Chavan, R.; Baraldo, S. EUS-guided coiling plus glue injection compared with endoscopic glue injection alone in endoscopic treatment for gastric varices: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2024, 101, 331–340.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolakis, A.; Tsagkidou, K.; Koumarelas, K.E. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided therapies in the treatment of gastric varices: An in-depth examination of associated adverse events. World J. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2024, 16, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binmoeller, K.F.; Weilert, F.; Shah, J.N.; Kim, J. EUS-guided transesophageal treatment of gastric fundal varices with combined coiling and cyanoacrylate glue injection (with videos). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2011, 74, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, B.P.; Chandan, S.; Khan, S.R.; Kassab, L.L.; Trakroo, S.; Ponnada, S.; Asokkumar, R.; Adler, D.G. Efficacy and safety of endoscopic ultrasound-guided therapy versus direct endoscopic glue injection therapy for gastric varices: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Endoscopy 2020, 52, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, J.; Nabi, Z.; Facciorusso, A.; Dhar, J.; Akbar, W.; Das, A.; Birda, C.L.; Mangiavillano, B.; Auriemma, F.; Crino, S.F.; et al. EUS-guided coil and glue injection versus endoscopic glue injection for gastric varices: International multicentre propensity-matched analysis. Liver Int. 2023, 43, 1783–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida Lôbo, M.R.; Chaves, D.M.; De Moura, D.T.H.; Ribeiro, I.B.; Ikari, E.; De Moura, E.G.H. Safety and Efficacy of Eus-Guided Coil plus Cyanoacrylate Versus Conventional Cyanoacrylate Technique in the Treatment of Gastric Varices: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arq. Gastroenterol. 2019, 56, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamwal, K.D.; Padhan, R.K.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, M.K. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided coiling and glue is safe and superior to endoscopic glue injection in gastric varices with severe liver disease: A retrospective case control study. Clin. Endosc. 2023, 56, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, Y.M.; Weilert, F.; Fredrick, R.T.; Kane, S.D.; Shah, J.N.; Hamerski, C.M.; Binmoeller, K.F. EUS-guided treatment of gastric fundal varices with combined injection of coils and cyanoacrylate glue: A large U.S. experience over 6 years (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2016, 83, 1164–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazarbashi, A.N.; Wang, T.J.; Jirapinyo, P.; Thompson, C.C.; Ryou, M. Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Coil Embolization With Absorbable Gelatin Sponge Appears Superior to Traditional Cyanoacrylate Injection for the Treatment of Gastric Varices. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2020, 11, E00175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Fu, S.; Shen, R. Efficacy and safety of EUS-guided coil embolization in combination with cyanoacrylate injection versus conventional endoscopic cyanoacrylate injection in the treatment of gastric varices with spontaneous portosystemic shunts. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2024, 12, goae026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Medranda, C.; Nebel, J.A.; Puga-Tejada, M.; Oleas, R.; Baquerizo-Burgos, J.; Ospina-Arboleda, J.; Valero, M.; Pitanga-Lukashok, H. Cost-effectiveness of endoscopic ultrasound-guided coils plus cyanoacrylate injection compared to endoscopic cyanoacrylate injection in the management of gastric varices. World J. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 13, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvis-García, E.S.; Zárate-Guzmán, Á.M.; Reding-Bernal, A.; Sobrino-Cossío, S. Embolización guiada por ultrasonido endoscópico con cianoacrilato solo o combinado con endo-coil para las várices gástricas. Cir. Cir. 2022, 90 (Suppl. 1), 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attili, F.; Boškoski, I.; Bove, V.; Familiari, P.; Costamagna, G. EUS-guided radiofrequency ablation of a hepatocellular carcinoma of the liver. VideoGIE 2018, 3, 149–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Nucci, G.; Della Corte, C.; Reati, R.; Imperatore, N.; Arena, I.; Larghi, A.; Manes, G. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: A case report test for efficacy and future perspectives. Endosc. Int. Open 2020, 8, E1713–E1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katrevula, A.; Singh, A.P.; Giovannini, M.; Lakhtakia, S.; Duvvur, N.R. Contrast-enhanced harmonic EUS–guided radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: A new horizon in endohepatology. VideoGIE 2023, 8, 354–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, A.; Kumar, Y.; Shastri, A.; Ganesh, C.P.; Singh, A.; Rathi, S.; Chaluvashetty, S.B.; Duseja, A. Endoscopic Ultrasound Guided Radiofrequency Ablation for Caudate Lobe Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A New Paradigm in Endohepatology. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2024, 14, 101438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabacelia, D.; Stroescu, C.; Dumitru, R.; Grigorescu, R.R.; Martiniuc, A.; Husar-Sburlan, I.A.; Copca, N. New approach for hepatocellular carcinoma treatment. J. Med. Life 2022, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, K.; Terrin, M.; Jovani, M.; Rizkala, T.; Spadaccini, M.; Pawlak, K.M.; Colombo, M.; Andreozzi, M.; Fugazza, A.; Facciorusso, A.; et al. A Comprehensive Guide to Artificial Intelligence in Endoscopic Ultrasound. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wu, C.; Yang, Z.; Yin, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Huang, H.; Jin, Z. The application of artificial intelligence in EUS. Endosc Ultrasound. 2024, 13, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajabnia, M.; Hatami, B.; Ketabi Moghadam, P.; Mohammadi, M.; Rafizadeh, M.; Mangeli, F.; Fathi, M.; Jahanian, A. Comparison of portal hypertensive gastropathy and gastric antral vascular ectasia: An update. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench 2022, 15, 204–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Yamazaki, K.; Toyota, J.; Karino, Y.; Ohmura, T.; Akaike, J.; Kuwata, Y.; Suga, T. Perforating veins in recurrent esophageal varices evaluated by endoscopic color Doppler ultrasonography with a galactose-based contrast agent. J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 39, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Yamazaki, K.; Toyota, J.; Karino, Y.; Ohmura, T.; Suga, T. Evaluation of hemodynamics in esophageal varices value of endoscopic color Doppler ultrasonography with a galactose-based contrast agent. Hepatol. Res. 2003, 25, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Shim, K.Y.; Baik, S.K. Diagnostic Accuracy of Hepatic Vein Arrival Time Performed with Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasonography for Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gut Liver 2017, 11, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.Y.; Suk, K.T.; Baik, S.K.; Kim, H.A.; Kim, Y.J.; Cha, S.H.; Kwak, H.R.; Cho, M.Y.; Park, H.J.; Jeon, H.K.; et al. Hepatic vein arrival time as assessed by contrast-enhanced ultrasonography is useful for the assessment of portal hypertension in compensated cirrhosis. Hepatology 2012, 56, 1053–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
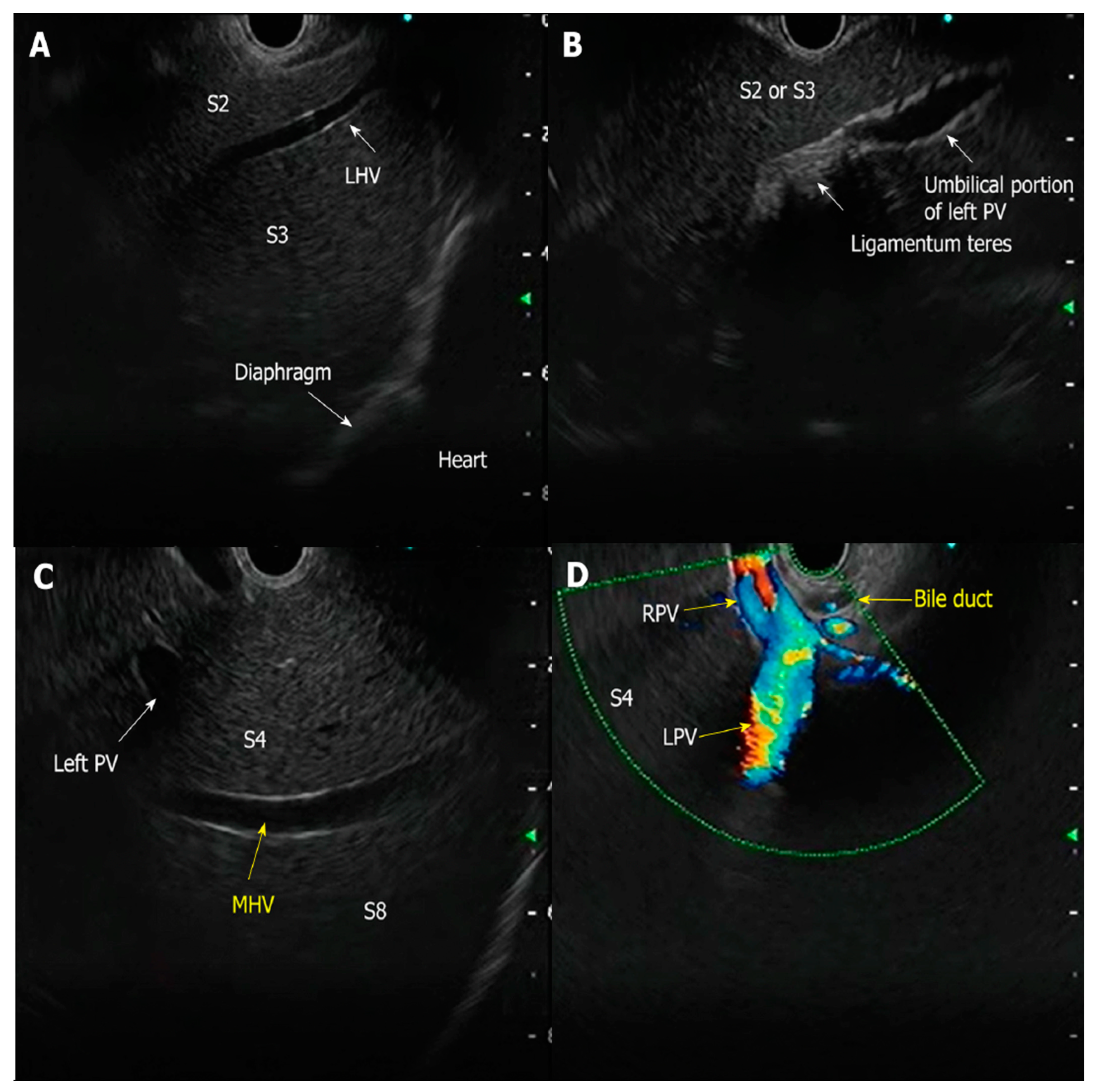
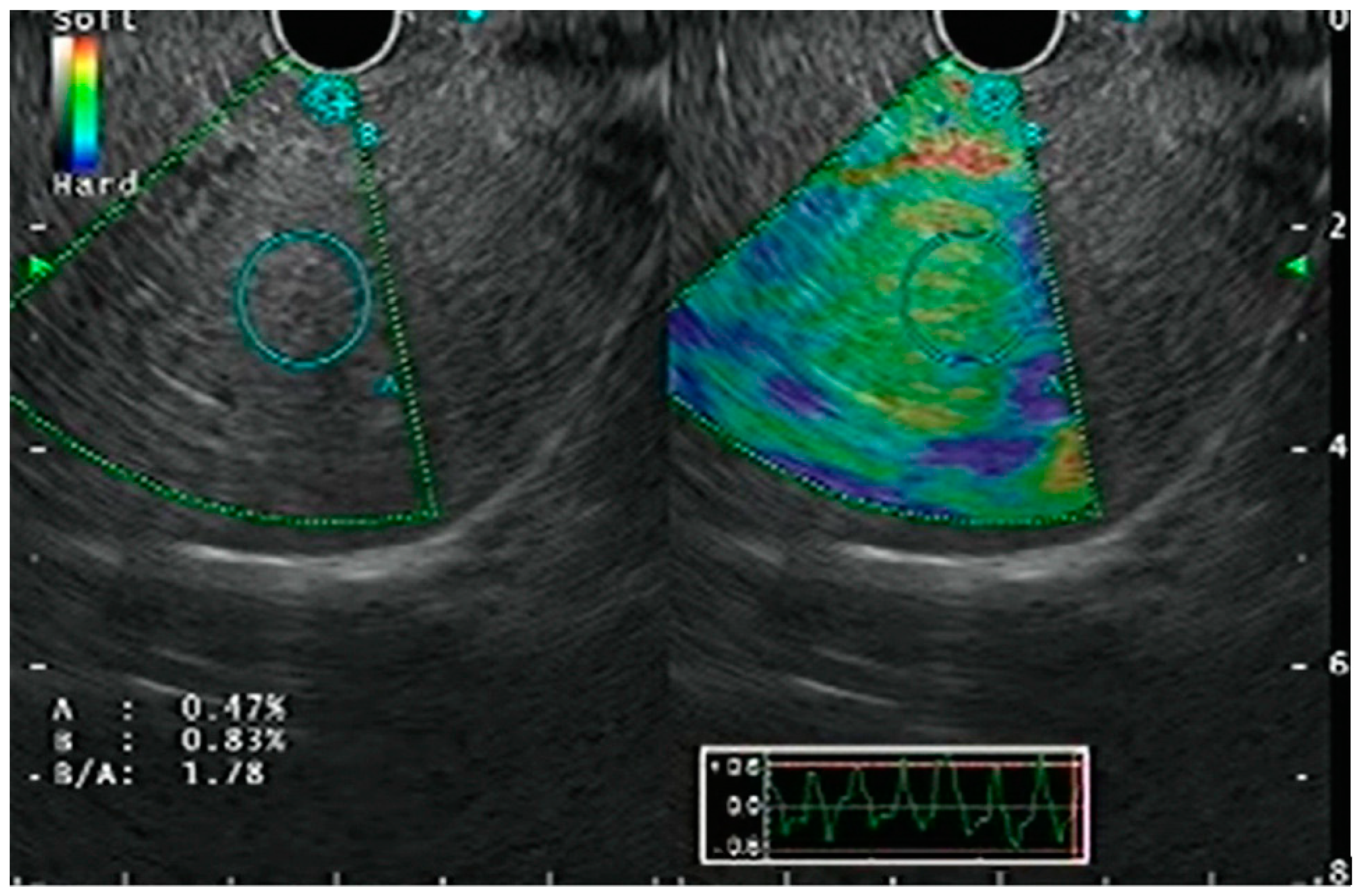
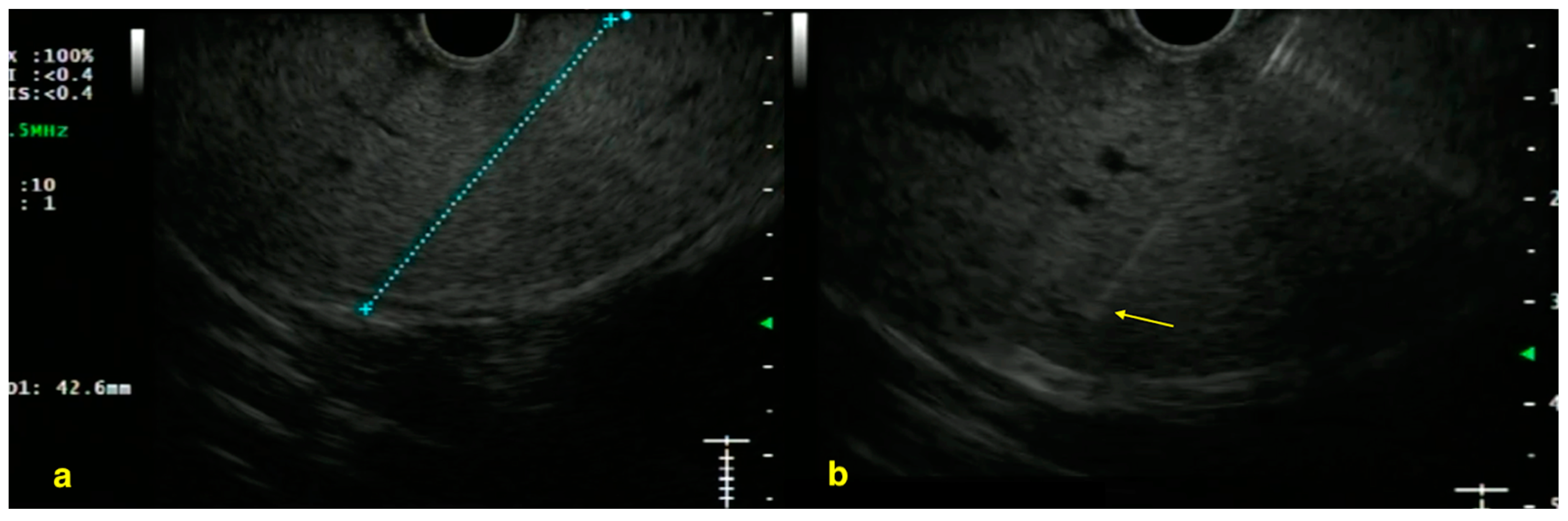
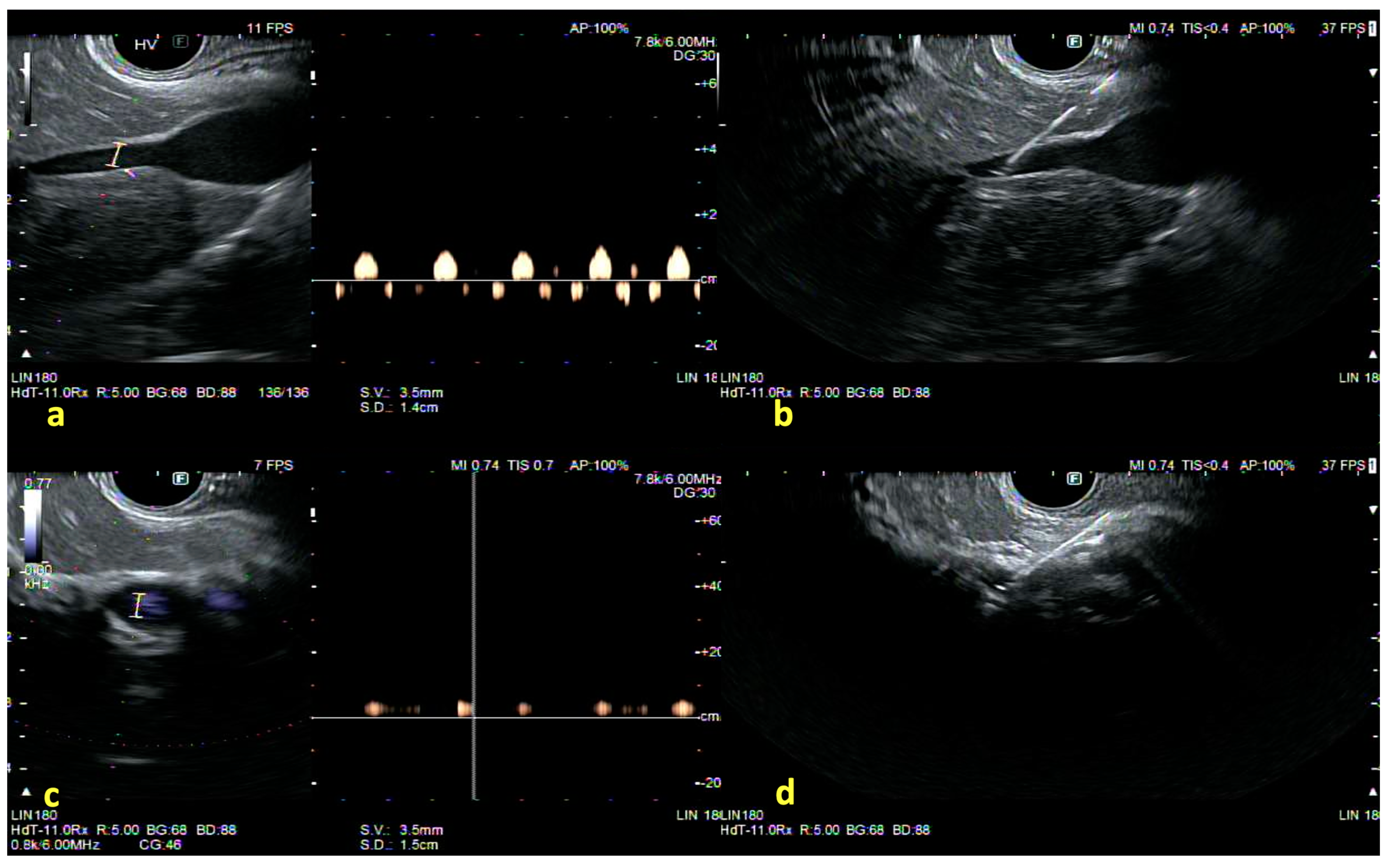
| Authors, Year | Study Design | Population | Methods | Key Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AbiMansour et al., 2025 [5] | Prospective cohort | A total of 199 patients, 25 with advanced liver disease (≥F3). | EUS-SWE on both lobes (10 readings each); correlated with ≥F3 or MRE. General anesthesia vs. sedation for reliability. | ALD patients had higher stiffness (p < 0.001). Right lobe AUROC = 0.80; left = 0.73. General anesthesia improved reliability. Left-lobe EUS-SWE correlated with MRE. |
| Kohli et al., 2023 [20] | Prospective cohort | A total of 42 suspected NAFLD patients. VCTE was unreliable in ~19%. | EUS-SWE on both lobes (10 readings each). Biopsy used as reference. Cutoffs (Youden’s index). | For ≥F3: VCTE AUROC = 0.87 vs. EUS-SWE 0.80 (left), 0.78 (right). EUS-SWE succeeded in VCTE-failed cases. |
| Wang et al., 2024 [21] | Prospective cohort | A total of 62 obese MASLD patients (BMI ≥ 30). | EUS-SWE (10 measurements); biopsies by EUS or surgery/IR. FIB-4, VCTE for comparison. | EUS-SWE outperformed FIB-4 for ≥F2 (AUROC = 0.87 vs. 0.61) and ≥F3 (0.93 vs. 0.63). Exceeded VCTE in advanced fibrosis. |
| Diehl et al., 2025 [24] | Prospective cohort | A total of 52 patients with abnormal LFTs were referred for EUS LB. Mean BMI was 35.1. | VCTE before EUS. EUS-SWE on both lobes (10 readings each). 19G Franseen LB. Compared the reproducibility of left vs. right lobe and correlation with biopsy staging. | Right-lobe EUS-SWE strongly correlated (r = 0.57) vs. left-lobe (0.37). EUS-SWE ~VCTE for advanced fibrosis accuracy; right side preferred for reproducibility. |
| Parameter | EUS-Guided Liver Biopsy | Percutaneous Liver Biopsy |
|---|---|---|
| Needle Gauge and Design | Commonly uses 19 G FNB (Franseen-tip, Fork-tip) or 19 G FNA needles Typically 1–2 passes per lobe, guided by macroscopic inspection | Generally, 16–18 G cutting needles (e.g., Menghini or Tru-Cut) Often one pass (two if needed for adequacy) |
| Specimen Length | Mean around 20–40 mm in most series Some randomized data report lengths up to ~30–40 mm with a 19 G FNB plus wet-suction approach | Typically ~25–30 mm (or more) with a 16 G needle |
| Number of Complete Portal Tracts | Typically 8–20 CPTs or more using a 19 G Franseen needle | Often 10–15 CPTs or more with a 16 G needle |
| Diagnostic Yield | A ~90–95% in prospective cohorts | A ~92–97% in most studies |
| Bilobar Sampling | Can biopsy both right and left lobes in one session Especially useful in conditions with heterogeneous involvement | Typically restricted to the right lobe unless extra passes |
| Adverse Event Rate | Overall complication rate ~2–10% Significant bleeding or hemoperitoneum ~1–2% Mortality is rare (case reports) | Complications ~2–5% Pain, subcapsular hematomas, occasional hemothorax, or bile leak Mortality ~0.01–0.1% in large series |
| Sedation and Procedure Time | Moderate-to-deep sedation or general anesthesia Typically >15 min | Local anesthesia ± mild sedation Usually 10–20 min |
| Contraindications | Coagulopathy, inability to tolerate sedation, large gastric varices, and massive ascites Relative contraindications: certain post-surgical anatomies (e.g., Roux-en-Y) | Coagulopathy, difficult ascites, infection at the biopsy site Overlying bowel or lung may limit safe access |
| When to Prefer | If concurrent EUS-based interventions are indicated If percutaneous or transjugular access is contraindicated If bilobar sampling is needed | Standard approach when only liver tissue is required and the anatomy is favorable Ideal for easily accessible right-lobe lesions under normal coagulation |
| Aspect | HVPG | EUS-PPG |
|---|---|---|
| Portal pressure measurement | Indirect (via hepatic vein catheterization), measures hepatic venous pressure gradient (HVPG) | Direct (via endoscopic ultrasound-guided puncture) measures the portal pressure gradient (PPG) |
| Procedure type | Angiography | Endoscopy |
| Required equipment | Dedicated X-ray machine, contrast agents | Conventional EUS platform, fine needle for puncture |
| Types of portal hypertension assessed | Sinusoidal | Sinusoidal and presinusoidal |
| Accuracy and reproducibility | Highly validated, reproducible with inter-observer variability < 5% | Limited validation studies |
| Contraindications | Allergy to contrast, severe coagulopathy (platelets < 20 × 10⁹/L or PT < 30%) | Coagulopathy (platelets < 50 × 10⁹/L or PT < 50%), contraindications for upper GI endoscopy, altered anatomy |
| Additional procedures possible | Transjugular liver biopsy, cardiopulmonary pressure assessment | All types of additional endoscopic interventions (e.g., variceal assessment and treatment, mucosal biopsies, FNA/B of lesions, SWE measurement) |
| Patient sedation | Local anesthesia or mild sedation | Conscious sedation |
| Procedure time | 30–60 min | 30–60 min |
| Safety profile | Invasive, rare complications include bleeding, hematoma, or infection (<1% reported incidence) | Minimally invasive, rare complications include bleeding at the puncture site or transient bacteremia (<2%) |
| Grade of evidence | Validated in clinical practice | Preliminary data; requires validation against HVPG |
| Clinical utility | Established tool for diagnosing CSPH, assessing TIPS candidacy, and monitoring therapy efficacy | A promising alternative for CSPH diagnosis, with potential applicability in patients where HVPG is contraindicated or for the objective assessment of PSVD |
| Advantages | Gold reference with robust data | Combines diagnostic and therapeutic capabilities in one session, avoids radiation exposure, and provides direct measurement |
| Sensitivity and specificity | High sensitivity for sinusoidal portal hypertension; sensitivity > 90%, specificity > 95% for CSPH | Preliminary studies report sensitivity and specificity comparable to HVPG, but data are limited |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bruni, A.; Dell’Anna, G.; Samanta, J.; Fanizza, J.; Mandarino, F.V.; Dhar, J.; Facciorusso, A.; Annese, V.; Massironi, S.; Malesci, A.; et al. Advances in Endo-Hepatology: The Role of Endoscopic Ultrasound in the Management of Portal Hypertension. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15080967
Bruni A, Dell’Anna G, Samanta J, Fanizza J, Mandarino FV, Dhar J, Facciorusso A, Annese V, Massironi S, Malesci A, et al. Advances in Endo-Hepatology: The Role of Endoscopic Ultrasound in the Management of Portal Hypertension. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(8):967. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15080967
Chicago/Turabian StyleBruni, Angelo, Giuseppe Dell’Anna, Jayanta Samanta, Jacopo Fanizza, Francesco Vito Mandarino, Jahnvi Dhar, Antonio Facciorusso, Vito Annese, Sara Massironi, Alberto Malesci, and et al. 2025. "Advances in Endo-Hepatology: The Role of Endoscopic Ultrasound in the Management of Portal Hypertension" Diagnostics 15, no. 8: 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15080967
APA StyleBruni, A., Dell’Anna, G., Samanta, J., Fanizza, J., Mandarino, F. V., Dhar, J., Facciorusso, A., Annese, V., Massironi, S., Malesci, A., Marasco, G., Dajti, E., Eusebi, L. H., Barbara, G., Donatelli, G., Danese, S., & Fuccio, L. (2025). Advances in Endo-Hepatology: The Role of Endoscopic Ultrasound in the Management of Portal Hypertension. Diagnostics, 15(8), 967. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15080967










