Role of Toll-like Receptors Nine and Ten Polymorphisms in Childhood Bronchial Asthma Control and Their Relation to Cardiac Function
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Method
2.1. Sample Size
2.2. Participant Groups Involved in the Study
- The asthma group:
- Well-controlled group, including 20 children
- Partially controlled group, including 20 children
- Uncontrolled group, including 20 children
2.3. Inclusion Criteria
2.4. Exclusion Criteria
- The control group:
2.5. Operational Design
2.6. Pulmonary Function Testing
2.7. Conventional Echocardiography and Two-Dimensional Speckle Tracking Analysis (Transthoracic)
2.8. Study Outcome
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
- Primary outcome
- Secondary outcome
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Gewely, M.S.; El-Hosseiny, M.; Abou Elezz, N.F.; El-Ghoneimy, D.H.; Hassan, A.M. Health-related quality of life in childhood bronchial asthma. Egypt. J. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 11, 83–93. [Google Scholar]
- Global Asthma Network Study Group. The Global Asthma Report 2014; Global Asthma Network Study Group: Auckland, New Zealand, 2014; Available online: http://www.globalasthmanetwork.org/publications/Global_Asthma_Report_2014.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Rahimian, N.; Aghajanpour, M.; Jouybari, L.; Ataee, P.; Fathollahpour, A.; LamuchDeli, N.; Kalmarzi, R.N. The Prevalence of Asthma among Iranian Children and Adolescent: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 6671870. [Google Scholar]
- Masoli, M.; Fabian, D.; Holt, S.; Beasley, R. Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) Program. The global burden of asthma: Executive summary of the GINA Dissemination Committee report. Allergy 2004, 59, 469–478. [Google Scholar]
- Nakayasu, H.; Araga, S.; Takahashi, K.; Otsuki, K.; Murata, M. Two cases of adult Down’s syndrome presenting parietal low uptake in 123I-IMP-SPECT. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 1991, 31, 557–560. [Google Scholar]
- Asher, I.; Pearce, N. Global burden of asthma among children. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2014, 18, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar]
- Vos, T.; Flaxman, A.D.; Naghavi, M.; Lozano, R.; Michaud, C.; Ezzati, M.; Shibuya, K.; Salomon, J.A.; Abdalla, S.; Aboyans, V.; et al. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990-2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2163–2196. [Google Scholar]
- Dharmage, S.C.; Perret, J.L.; Custovic, A. Epidemiology of asthma in children and adults. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 246. [Google Scholar]
- Gans, M.D.; Gavrilova, T. Understanding the immunology of asthma: Pathophysiology, biomarkers, and treatments for asthma endotypes. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2020, 36, 118–127. [Google Scholar]
- Behzadi, P.; García-Perdomo, H.A.; Karpiński, T.M. Toll-like receptors: General molecular and structural biology. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 9914854. [Google Scholar]
- Bezemer, G.F.; Sagar, S.; Van Bergenhenegouwen, J.; Georgiou, N.A.; Garssen, J.; Kraneveld, A.D.; Folkerts, G. Dual role of Toll-like receptors in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 337–358. [Google Scholar]
- Forfia, P.R.; Vaidya, A.; Wiegers, S.E. Pulmonary heart disease: The heart lung interaction and its impact on patient phenotypes. Pulm. Circ. 2013, 3, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Initiative for Asthma. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. 2019. Available online: https://ginasthma.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/GINA-2019-main-report-June-2019-wms.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Sharifi, A.; Ghadiri, A.; Salimi, A.; Ghandil, P.; Esmaeili, S.A. Evaluating the distribution of (+2044G/A, R130Q) rs20541 and (−1112 C/T) rs1800925 polymorphism in IL-13 gene: An association-based study with asthma in Ahvaz, Iran. Int. J. Med. Lab. 2021, 8, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacon-Cortes, D.; Griffiths, L. Methods for extracting genomic DNA from whole blood samples: Current perspectives. J. Biorepos. Sci. Appl. Med. 2014, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, M.; Hankinson, J.; Brusasco, V.; Burgos, F.; Casaburi, R.; Coates, A.; Crapo, R.; Enright, P.; van der Grinten, C.P.; Gustafsson, P.; et al. Standardization of Spirometry. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ober, C.; Yao, T.C. The genetics of asthma and allergic disease: A 21st century perspective. Immunol. Rev. 2011, 242, 10–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Lucas, R.M.; Liu, L.; Stow, J.L. SCIMP is a universal Toll-like receptor adaptor in macrophages. J. Cell Sci. 2020, 133, jcs239194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, C.D.; Casanello, P.; Harris, P.R.; Castro-Rodríguez, J.A.; Iturriaga, C.; Perez-Mateluna, G.; Farías, M.; Urzúa, M.; Hernandez, C.; Serrano, C.; et al. Early origins of allergy and asthma (ARIES): Study protocol for a prospective prenatal birth cohort in Chile. BMC Pediatr. 2020, 20, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Su, F.; Wang, L.B.; Hemminki, K.; Dharmage, S.C.; Bowatte, G.; Bui, D.; Qian, Z.; Vaughn, M.G.; Aaron, H.E.; et al. The Asthma Family Tree: Evaluating Associations between Childhood, Parental, and Grandparental Asthma in Seven Chinese Cities. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 720273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.L.; Liu, F.; Ren, C.J.; Xing, C.H.; Wang, Y.J. Correlations of LTα and NQO1 gene polymorphisms with childhood asthma. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 7557–7562. [Google Scholar]
- Yalçın, S.S.; Emiralioğlu, N.; Yalçın, S. Evaluation of blood and tooth element status in asthma cases: A preliminary case–control study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2021, 21, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardura-Garcia, C.; Vaca, M.; Oviedo, G.; Sandoval, C.; Workman, L.; Schuyler, A.J.; Perzanowski, M.S.; Platts-Mills, T.A.; Cooper, P.J. Risk factors for acute asthma in tropical America: A case–control study in the City of Esmeraldas, Ecuador. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2015, 26, 423–430. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Qerem, W.; Ling, J. Pulmonary function tests in Egyptian schoolchildren in rural and urban areas. East. Mediterr. Health J. 2018, 24, 325–332. [Google Scholar]
- Nahhas, M.; Bhopal, R.; Anandan, C.; Elton, R.; Sheikh, A. Investigating the association between obesity and asthma in 6-to 8-year-old Saudi children: A matched case–control study. npj Prim. Care Respir. Med. 2014, 24, 14004. [Google Scholar]
- Hassane, F.M.; Khatab, A.A.; Saliem, S.S.; Fahmy, M.S. Low magnesium concentration in erythrocytes of children with acute asthma. Menoufia Med. J. 2015, 28, 477. [Google Scholar]
- Betül, B.K.; Ayhan, H. Early Impairment of Right Ventricular Functions in Patients with Moderate Asthma and the Role of Isovolumic Acceleration. Koşuyolu Heart 2022, 25, 157–164. [Google Scholar]
- Özkan, E.; Khosroshahi, H. Evaluation of the Left and Right Ventricular Systolic and Diastolic Function in Asthmatic Children. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2016, 16, 145. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelmohsen, G.; Mohamed, H.; Mohsen, M.; Abdelaziz, O.; Ahmed, D.; Abdelsalam, M.; Dohain, A. Evaluation of cardiac function in pediatric patients with mild to moderate bronchial asthma in the era of cardiac strain imaging. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2019, 54, 1905–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozde, C.; Dogru, M.; Ozde, Ş.; Kayapinar, O.; Kaya, A.; Korkmaz, A. Subclinical right ventricular dysfunction in intermittent and persistent mildly asthmatic children on tissue Doppler echocardiography and serum NT-pro BNP: Observational study. Pediatr. Int. 2018, 60, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasu, B.B.; Aydıncak, H.T. Right ventricular-pulmonary arterial uncoupling in mild-to-moderate asthma. J. Asthma 2023, 60, 543–552. [Google Scholar]
- Manti, S.; Parisi, G.F.; Giacchi, V.; Sciacca, P.; Tardino, L.; Cuppari, C.; Salpietro, C.; Chikermane, A.; Leonardi, S. Pilot study shows right ventricular diastolic function impairment in young children with obstructive respiratory disease. Acta Paediatr. 2019, 108, 740–744. [Google Scholar]
- De-Paula, C.R.; Magalhães, G.S.; Jentzsch, N.S.; Botelho, C.F.; Mota, C.D.C.C.; Murça, T.M.; Ramalho, L.F.C.; Tan, T.C.; Capuruço, C.A.B.; Rodrigues-Machado, M.D.G. Echocardiographic assessment of ventricular function in young patients with asthma. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2018, 110, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuleta, I.; Eckstein, N.; Aurich, F.; Nickenig, G.; Schaefer, C.; Skowasch, D.; Schueler, R. Reduced longitudinal cardiac strain in asthma patients. J. Asthma 2019, 56, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baysal, S.S.; Has, M. Assessment of biventricular function with speckle tracking echocardiography in newly-diagnosed adult-onset asthma. J. Asthma 2022, 59, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özdemir, R.; Karadeniz, C.; Döğer, F.K.; Poyrazoglu, H.G. Right ventricular function in children with asthma: Evaluation using two-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiograph. J. Pediatr. 2021, 230, 166–172. [Google Scholar]
- Ozdemir, O.; Ceylan, Y.; Razi, C.H.; Ceylan, O.; Andiran, N. Assessment of ventricular functions by tissue Doppler echocardiography in children with asthma. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2013, 34, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesse, R.; Pandey, R.C.; Kabesch, M. Genetic variations in toll-like receptor pathway genes influence asthma and atopy. Allergy 2011, 66, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kormann, M.S.; Depner, M.; Hartl, D.; Klopp, N.; Illig, T.; Adamski, J.; Vogelberg, C.; Weiland, S.K.; von Mutius, E.; Kabesch, M. Toll-like receptor heterodimer variants protect from childhood asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 122, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaassen, E.M.; Thönissen, B.E.; van Eys, G.; Dompeling, E.; Jöbsis, Q. A systematic review of CD14 and toll-like receptors in relation to asthma in Caucasian children. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2013, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puthothu, B.; Heinzmann, A. Is toll-like receptor 6 or toll-like receptor 10 involved in asthma genetics--or both? Allergy 2006, 61, 649–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

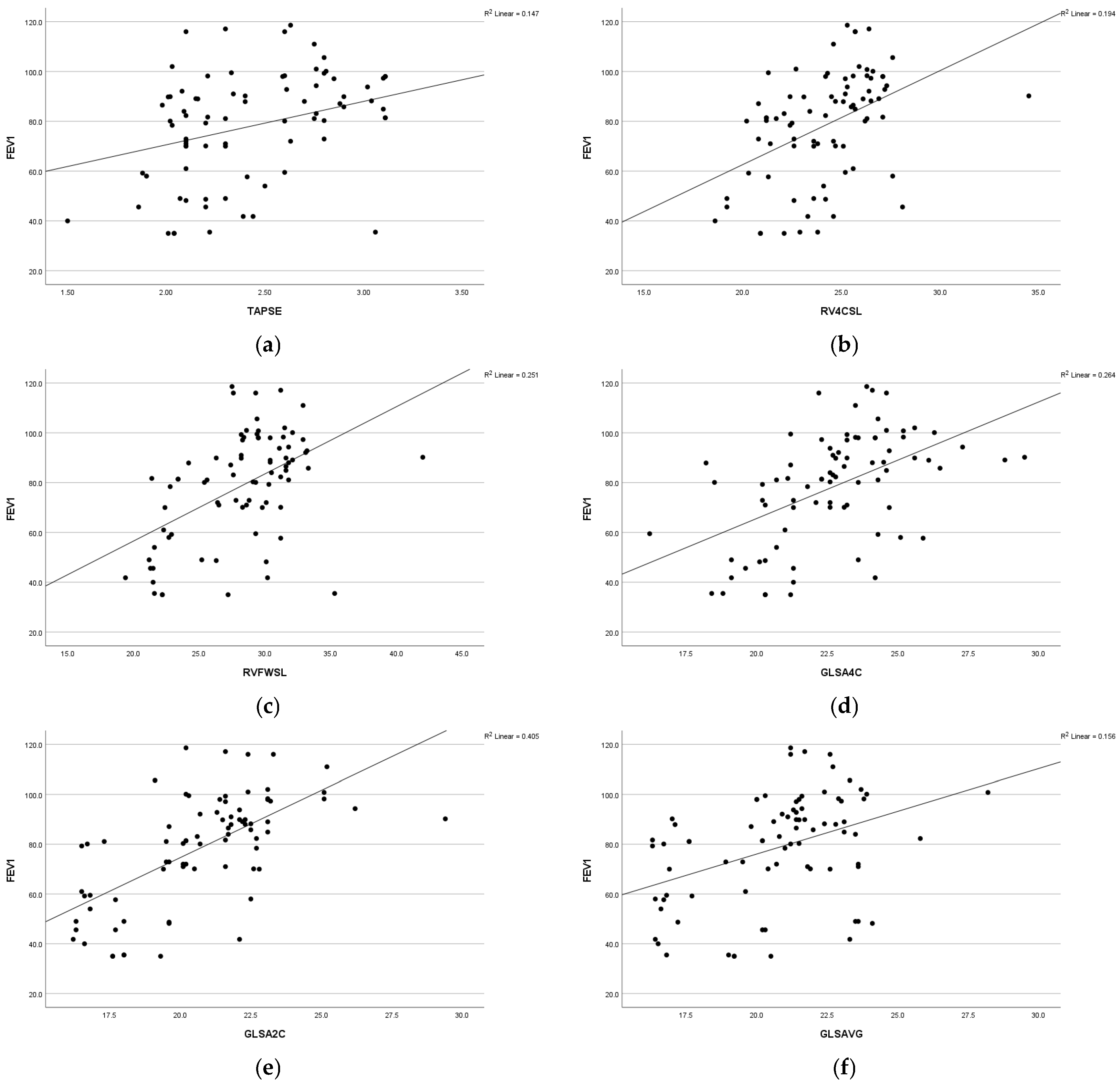
| Variable | Uncontrolled | Partially Controlled | Well-Controlled | Control | Tests | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | Group | Group | Group | F | p-Value | |
| (n = 20) | (n = 20) | (n = 20) | (n = 20) | |||
| Age (years) | ||||||
| Mean ± SD | 8.15 ± 2.78 | 9.40 ± 4.08 | 7.75 ± 2.73 | 9.05 ± 2.82 | 1.184 | 0.321 |
| Range | (5–13) | (5–15) | (5–14) | (5–14) | ||
| Height (cm) | ||||||
| Mean ± SD | 133.55 ± 20.27 | 132.05 ± 18.96 | 126.25 ± 14.74 | 134.7 ± 17.67 | 0.867 | 0.462 |
| Range | (106–168) | (105–165) | (106–155) | (106–165) | ||
| Weight (kg) | ||||||
| Mean ± SD | 35.65 ± 14.12 | 34.30 ± 13.76 | 28.75 ± 10.43 | 32.50 ± 12.55 | 1.094 | 0.357 |
| Range | (21–63) | (18–66) | (17–50) | (19–66) | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | ||||||
| Mean ± SD | 19.41 ± 4.27 | 19.12 ± 4.43 | 17.53 ± 3.19 | 17.34 ± 2.92 | 1.59 | 1.79 |
| Range | (14.8–24) | (11.03–29.33) | (13.43–24.45) | (12.77 ± 24.4) | ||
| Variable | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | N (%) | χ2 | p-value |
| Sex | ||||||
| 11 (55) | 9 (45) | 7 (35) | 9 (45) | 1.616 | 0.656 (ns) |
| 9 (45) | 11 (55) | 13 (65) | 11 (55) | ||
| Family history | ||||||
| Negative | 5 (25) | 1 (5) | 3 (15) | 20 (100) | 48.627 | <0.001 ** |
| Positive | 15 (75) | 19 (95) | 17 (85) | 0 | ||
| Variable | Uncontrolled Group (n = 20) | Partially Controlled (n = 20) | Well-Controlled (n = 20) | Control Group (n = 20) | Tests | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | p-Value | Post Hoc | |||||
| Ejection Fraction EF% Mean ± SD Range | 70.43 ± 3.95 (62–75.1) | 70.08 ± 2.74 (64.3–74.3) | 71.40 ± 3.67 (63–78.1) | 71.54 ± 2.51 (66.6–77) | 0.961 | 0.416 | P1 = 0.740 P2 = 0.349 P3 = 0.287 P4 = 0.206 P5 = 0.164 P6 = 0.897 |
| Fractional Shortening FS% Mean ± SD Range | 36.3 ± 8.84 (2–44.1) | 37.71 ± 2.93 (32.3–44.3) | 39.06 ± 2.67 (32.6–43.2) | 39.36 ± 2.58 (34.1–43.5) | 1.570 | 0.204 | P1 = 0.375 P2 = 0.085 P3 = 0.057 P4 = 0.397 P5 = 0.301 P6 = 0.850 |
| Pulmonary Artery Systolic Pressure PASP (mm Hg) Mean ± SD Range | 28.8 ± 7.35 (2–35) | 27.5 ± 2.84 (24–33) | 26 ± 3.76 (20–33) | 25 ± 2.25 (22–29) | 2.745 | 0.049 * | P1 = 0.365 P2 = 0.053 P3 = 0.009 * P4 = 0.296 P5 = 0.083 P6 = 0.485 |
| TAPSE (cm) Mean ± SD Range | 2.18 ± 0.34 (1.5–3.06) | 2.39 ± 0.36 (2.02–3.11) | 2.49 ± 0.38 (1.98–3.1) | 2.74 ± 0.64 (2.02–3.07) | 5.480 | 0.002 * | P1 = 0.133 P2 = 0.031 * P3 < 0.001 ** P4 = 0.449 P5 = 0.016 * P6 = 0.077 |
| RV4CSL Mean ± SD Range | −22.94 ± 2.62 (−28.1)–(−18.6) | −23.26 ± 1.95 (−27.1)–(−20.2) | −25.33 ± 2.86 (−34.5)–(−20.8) | −25.49 ± 1.36 (−27.6)–(−2.4) | 6.95 | <0.001 * | P1 = 0.658 P2 = 0.001 * P3 = 0.001 * P4 = 0.005 * P5 = 0.003 * P6 = 0.825 |
| RVFWSL Mean ± SD Range | −24.89 ± 4.32 (−35.3)–(−19.4) | −27.28 ± 3.02 (−31.8)–(−21.4) | −30.71 ± 3.47 (−42)–(−24.2) | −30.2 ± 2.05 (−33.3)–(−26.3) | 13.36 | <0.001 * | P1 = 0.025 * P2 < 0.001 ** P3 < 0.001 ** P4 = 0.002 * P5 = 0.007 * P6 = 0.628 |
| GLS A4C Mean ± SD Range | −18.95 ± 9.79 (−25.9)–(−21.3) | −22.08 ± 1.68 (−25.1)–(−18.5) | −23.78 ± 2.62 (−29.5)–(−26.5) | −24.31 ± 1.19 (−26.5)–(−22.2) | 4.360 | 0.007 * | P1 = 0.059 P2 = 0.0048 * P3 = 0.002 * P4 = 0.302 P5 = 0.178 P6 = 0.749 |
| GLS A2C Mean ± SD Range | −18.12 ± 1.88 (−22.5)–(−16.2) | −20.29 ± 1.98 (−24.1)–(−16.5) | −22.31 ± 2.14 (−29.4)–(−19.6) | −22.69 ± 1.85 (−26.7)–(−19.1) | 22.8 | <0.001 * | P1 = 0.001 * P2 < 0.001 * P3 < 0.001 * P4 = 0.002 * P5 < 0.001 * P6 = 0.548 |
| GLS A3C Mean ± SD Range | −18.37 ± 1.42 (−21.3)–(-16.2) | −19.5 ± 1.91 (−22.8)–(-16.1) | −19.83 ± 1.6 (−24.1)–(−16.9) | −20.83 ± 1.35 (−22.9)–(−18.6) | 8.14 | <0.001 * | P1 = 0.027 * P2 = 0.005 * P3 < 0.001 ** P4 = 0.519 P5 = 0.010 * P6 = 0.050 |
| GLS AVG Mean ± SD Range | −16.98 ± 9.24 (−24.1)–20 | 20.12 ± 2.53 (−24)–(−16.3) | 21.35 ± 1.99 (−25.8)–(−17) | 22.61 ± 1.67 (−28.2)–(−20) | 4.72 | <0.001 * | P1 = 0.049 * P2 = 0.007 * P3 = 0.001 * P4 = 0.436 P5 = 0.117 P6 = 0.425 |
| Variable | Cases | Control | p | χ2 | OR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 60) | (n = 20) | ||||||
| N | % | N | % | ||||
| TLR9: | |||||||
| CC | 11 | 18.3 | 12 | 60 | -- | -- | Reference |
| CT | 25 | 41.7 | 3 | 15 | 10.45 | 0.001 * | 9.09 (2.13–38.77) |
| TT | 24 | 40 | 5 | 25 | 7.11 | 0.008 * | 5.24 (1.48–18.53) |
| Allele: | |||||||
| C | 47 | 39.2 | 27 | 67.5 | 9.69 | 0.002 * | 3.23 (1.51–6.87) |
| T | 73 | 60.8 | 13 | 32.5 | |||
| TLR10: | |||||||
| GG | 21 | 35 | 15 | 75 | -- | --- | Reference |
| GT | 24 | 40 | 4 | 20 | 5.66 | 0.02 * | 4.29 (1.23–14.94) |
| TT | 15 | 25 | 1 | 5 | 6.52 | 0.01 * | 10.71 (1.27–90.14) |
| Allele: | |||||||
| G | 66 | 55 | 34 | 85 | 11.52 | <0.001 | 4.64 (1.81–11.86) |
| T | 54 | 45 | 6 | 15 | ** | ||
| Variable | Uncontrolled Group (n = 20) | Partially Controlled Group (n = 20) | Well-Controlled Group (n = 20) | Control Group (n = 20) | Tests | Multi Comparison Analysis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| χ2 | p-Value | ||||||||||
| N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | ||||
| TLR9 polymorphism | |||||||||||
| CC (n = 23) | 0 | 0 | 3 | 15 | 8 | 40 | 12 | 60 | 21.887 | 0.001 * | P1 = 0.139 P2 = 0.007 * P3 < 0.001 ** P4 = 0.187 P5 = 0.009 * P6 = 0.389 |
| TC (n = 28) | 9 | 45 | 10 | 50 | 6 | 30 | 3 | 15 | |||
| TT (n = 29) | 11 | 55 | 7 | 35 | 6 | 30 | 5 | 25 | |||
| TLR9 Allele | |||||||||||
| C (n = 74) | 9 | 22.5 | 16 | 40.0 | 22 | 55.0 | 27 | 67.5 | 18.2 | 0.001 * | P1 = 0.09 P2 = 0.002 * P3 < 0.001 ** P4 = 0.178 P5 = 0.013 * P6 = 0.251 |
| T (n = 86) | 31 | 77.5 | 24 | 60.0 | 18 | 45.0 | 13 | 32.5 | |||
| TLR10 polymorphism | |||||||||||
| GG (n = 36) | 4 | 20 | 7 | 35 | 10 | 50 | 15 | 75 | 18.8 | 0.004 * | P1 = 0.557 P2 = 0.018 * P3 = 0.001 ** P4 = 0.114 P5 = 0.026 * P6 = 0.232 |
| GT (n = 28) | 8 | 40 | 7 | 35 | 9 | 45 | 4 | 20 | |||
| TT (n = 16) | 8 | 40 | 6 | 30 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 5 | |||
| TLR10 Allele | |||||||||||
| G (n = 100) | 16 | 40 | 21 | 52.5 | 29 | 72.5 | 34 | 85 | 20.6 | 0.001 ** | P1 = 0.262 P2 = 0.003 * P3 = 0.001 ** P4 = 0.06 P5 = 0.001 ** P6 = 0.171 |
| T (n = 60) | 24 | 60 | 19 | 47.5 | 11 | 27.5 | 6 | 15 | |||
| Variable | TLR9 | Tests | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC | CT | TT | F | p-Value | Post Hoc | |
| Respiratory function | ||||||
| FEV1% | P1 = 0.006 * | |||||
| Mean ± SD | 85.72 ± 6.42 | 67.32 ± 19.62 | 67.59 ± 19.29 | 4.694 | 0.013 * | P2 = 0.007 * |
| Range | (71–94.3) | (35–97.1) | (35–99.5) | P3 = 0.958 | ||
| FVC% | P1 = 0.244 | |||||
| Mean ± SD | 83.02 ± 11.99 | 76.5 ± 14.62 | 71.18 ± 17.19 | 2.337 | P2 = 0.038 * | |
| Range | (60.2–97.4) | (52–104) | (29.5–96) | 0.0.04 * | P3 = 0.229 | |
| Cardiac function | ||||||
| Ejection Fraction EF% | P1 = 0.083 | |||||
| Mean ± SD | 72.41 ± 2.87 | 70.22 ± 3 | 70.26 ± 4.03 | 1.801 | 0.174 | P2 = 0.091 |
| Range | (69.1–78.1) | (63–75.1) | (62–77.4) | P3 = 0.966 | ||
| Fractional Shortening FS% | P1 = 0.424 | |||||
| Mean ± SD | 37.59 ± 3.06 | 39.2 ± 2.73 | 36.15 ± 8 | 1.861 | 0.165 | P2 = 0.479 |
| Range | (32.6–42.7) | (32.3–44.3) | (2–44.1) | P3 = 0.059 | ||
| Pulmonary Artery Systolic Pressure PASP (mm Hg) | P1 = 0.496 | |||||
| Mean ± SD | 26.36 ± 3.8 | 27.64 ± 3.76 | 27.71 ± 2 | 0.292 | 0.748 | P2 = 0.476 |
| Range | (20–31) | (23–35) | (2–34) | P3 = 0.963 | ||
| TAPSE (cm) | P1 = 0.853 | |||||
| Mean ± SD | 2.39 ± 0.35 | 2.36 ± 0.4 | 2.33 ± 0.38 | 0.091 | 0.913 | P2 = 0.686 |
| Range | (1.98–2.88) | (1.8–3.11) | (1.5–3.1) | P3 = 0.778 | ||
| RV4CSL | P1 = 0.328 | |||||
| Mean ± SD | −24.59 ± 2.37 | −23.62 ± 1.92 | −23.73 ± 3.45 | 0.523 | 0.596 | P2 = 0.386 |
| Range | (−27.3)–(−20.8) | (−27.6)–(−20.8) | (−34.5)–(−18.6) | P3 = 0.892 | ||
| RVFWSL | P1 = 0.230 | |||||
| Mean ± SD | −30.01 ± 2.5 | −28.21 ± 3.25 | −25.92 ± 5.29 | 4.183 | 0.02 * | P2 = 0.008* |
| Range | (−33.1)–(−25.6) | (−35.3)–(−22.2) | (−42)–(−19.4) | P3 = 0.056 | ||
| GLS A4C | P1 = 0.456 | |||||
| Mean ± SD | −23.7 ± 2.72 | −22.04 ± 2.06 | −20.19 ± 9.25 | 1.341 | 0.270 | P2 = 0.122 |
| Range | (−28.8)–(−20.3) | (−25.1)–(−16.2) | (−29.5)–(−21.3) | P3 = 0.297 | ||
| GLS A2C | P1 = 0.271 | |||||
| Mean ± SD | −21.62 ± 1.91 | −20.62 ± 1.68 | −19.22 ± 3.3 | 3.983 | 0.024 * | P2 = 0.011 * |
| Range | (−26.2)–(-19.5) | (−22.8)–(−16.8) | (−29.4)–(−16.2) | P3 = 0.055 | ||
| GLS A3C | −19.15 ± 1.39 | P1 = 0.337 | ||||
| Mean ± SD | −19.76 ± 1.94 | (−22.5)–(-17.1) | −19.08 ± 2 | 0.629 | 0.537 | P2 = 0.286 |
| Range | (−24.1)–(−16.9) | (−22.8)–(−16.1) | P3 = 0.885 | |||
| GLS AVG | P1 = 0.256 | |||||
| Mean ± SD | −21.46 ± 1.79 | −19.02 ± 8.58 | −19.05 ± 2.71 | 0.768 | 0.469 | P2 = 0.263 |
| Range | (−23.6)–(−17.6) | (−25.8)–(−20.5) | (−24)–(−16.3) | P3 = 0.990 | ||
| Variable | TLR10 | Tests | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC | CT | TT | F | p-Value | Post Hoc | |
| Respiratory function | ||||||
| FEV1% | P1 = 0.220 | |||||
| Mean ± SD | 77.05 ± 16.57 | 70.2 ± 19.73 | 63.01 ± 18.94 | 2.544 | 0.047 * | P2 = 0.029 * |
| Range | (41.8–97.1) | (35–99.5) | (35–90.2) | P3 = 0.242 | ||
| FVC% | P1 = 0.361 | |||||
| Mean ± SD | 80.38 ± 15.14 | 76.22 ± 13.46 | 67.77 ± 17.52 | 3.076 | 0.04 * | P2 = 0.017 * |
| Range | (43–104) | (52–97.4) | (29.5–86.8) | P3 = 0.095 | ||
| Cardiac function | ||||||
| Ejection Fraction EF% | P1 = 0.368 | |||||
| Mean ± SD | 70.37 ± 3.34 | 71.31 ± 3.09 | 69.93 ± 4.23 | 0.824 | 0.444 | P2 = 0.710 |
| Range | (63–78.1) | (64.3–75.5) | (62–77.4) | P3 = 0.232 | ||
| Fractional Shortening FS% | P1 = 0.498 | |||||
| Mean ± SD | 37.98 ± 3.26 | 39.09 ± 2.6 | 35.04 ± 9.77 | 2.576 | 0.085 | P2 = 0.118 |
| Range | (32.3–43.2) | (34.9–44.3) | (2–42.1) | P3 = 0.498 | ||
| Pulmonary Artery Systolic Pressure PASP (mm Hg) | P1 = 0.982 | |||||
| Mean ± SD | 27.29 ± 3.74 | 27.25 ± 4.11 | 27.93 ± 7.81 | 0.094 | 0.911 | P2 = 0.712 |
| Range | (21–35) | (20–34) | (2–34) | P3 = 0.689 | ||
| TAPSE (cm) | P1 = 0.148 | |||||
| Mean ± SD | 2.45 ± 0.38 | 2.29 ± 0.36 | 2.31 ± 0.39 | 1.198 | 0.309 | P2 = 0.265 |
| Range | (2.01–3.11) | (1.86–3.06) | (1.5–3.1) | P3 = 0.861 | ||
| RV4CSL | P1 = 0.726 | |||||
| Mean ± SD | −23.82 ± 2.24 | 23.53 ± 2.36 | −24.37 ± 3.69 | 0.444 | 0.643 | P2 = 0.548 |
| Range | (−27.2)–(−19.2) | (−28.1)–(−19.2) | (−34.5)–(−18.6) | P3 = 0.351 | ||
| RVFWSL | P1 = 0.775 | |||||
| Mean ± SD | −28.24 ± 3.33 | −27.87 ± 3.85 | −26.37 ± 6 | 0.876 | 0.422 | P2 = 0.207 |
| Range | (−33.2)–(−21.2) | (−35.3)–(−21.3) | (−42)–(−19.4) | P3 = 0.299 | ||
| GLS A4C | P1 = 0.159 | |||||
| Mean ± SD | −22.82 ± 2.06 | −20.2 ± 9.14 | −22.15 ± 3.34 | 1.096 | 0.341 | P2 = 0.750 |
| Range | (−28.8)–(−19.1) | (27.3-)–(−21.3) | (−29.5)–(−16.2) | P3 = 0.338 | ||
| GLS A2C | P1 = 0.358 | |||||
| Mean ± SD | −20.86 ± 1.67 | −20.13 ± 2.52 | −19.55 ± 3.65 | 1.135 | 0.328 | P2 = 0.143 |
| Range | (−23.1)–(−16.3) | (−26.2)–(−16.3) | (−29.4)–(−16.2) | P3 = 0.498 | ||
| GLS A3C | −19.21 ± 1.1 | −19.58 ± 1.9 | −18.71 ± 2.16 | P1 = 0.485 | ||
| Mean ± SD | (−21.6)–(−16.9) | (−24.1)–(−17.1) | (−22.8)–(−16.1) | 1.133 | 0.329 | P2 = 0.403 |
| Range | P3 = 0.138 | |||||
| GLS AVG | −21.98 ± 1.82 | −18.55 ± 8.53 | −17.47 ± 2.22 | P1 = 0.047 * | ||
| Mean ± SD | (−25.8)–(−17.6) | (−23.5)–(−20.5) | (−24)–(−16.2) | 3.344 | 0.042(S) | P2 = 0.021 * |
| Range | P3 = 0.560 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rabie, R.A.; Hussien, A.E.; Abdelhameed, H.S.; Shedeed, S.A.; Almadani, N.; Nofal, H.A.; El-Rafey, D.S.; Ali, H.T.; Naguib, M.S. Role of Toll-like Receptors Nine and Ten Polymorphisms in Childhood Bronchial Asthma Control and Their Relation to Cardiac Function. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 817. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070817
Rabie RA, Hussien AE, Abdelhameed HS, Shedeed SA, Almadani N, Nofal HA, El-Rafey DS, Ali HT, Naguib MS. Role of Toll-like Receptors Nine and Ten Polymorphisms in Childhood Bronchial Asthma Control and Their Relation to Cardiac Function. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(7):817. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070817
Chicago/Turabian StyleRabie, Rehab Ahmed, Asmaa Elsharkawy Hussien, Hesham Samy Abdelhameed, Soad Abdelsalam Shedeed, Noura Almadani, Hanaa A. Nofal, Dina S. El-Rafey, Hossam T. Ali, and Mohammed Sanad Naguib. 2025. "Role of Toll-like Receptors Nine and Ten Polymorphisms in Childhood Bronchial Asthma Control and Their Relation to Cardiac Function" Diagnostics 15, no. 7: 817. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070817
APA StyleRabie, R. A., Hussien, A. E., Abdelhameed, H. S., Shedeed, S. A., Almadani, N., Nofal, H. A., El-Rafey, D. S., Ali, H. T., & Naguib, M. S. (2025). Role of Toll-like Receptors Nine and Ten Polymorphisms in Childhood Bronchial Asthma Control and Their Relation to Cardiac Function. Diagnostics, 15(7), 817. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15070817







