Abstract
Background: Asthma is designated as the most widely spread chronic disease in children. Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are linked to several human diseases, including allergic diseases. We aimed to assess the link between TLR9 (rs187084) and TLR10 (rs11096956) gene polymorphisms and bronchial asthma and its control and their relation to respiratory and cardiac functions. Methods: This is a case-control study comprising 80 participants aged between 5 and 12 years old, divided into 20 healthy non-asthmatic participants and 60 asthmatic ones. The asthmatic group members were diagnosed clinically according to the diagnosis guidelines of The Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) 2019 and subdivided according to GINA 2019 guidelines for asthma control into three subgroups (well-controlled, partially controlled, and uncontrolled). Genetic polymorphisms in TLR9 (rs187084) and TLR10 (rs11096956) were detected using real-time PCR. Results: We found a significant increase in TLR9 polymorphisms among asthmatic cases compared to the control (OR = 9.09 for the CT genotype and 5.24 for the TT genotype) and a similar increase in TLR10 polymorphisms (OR = 4.29 for the GT genotype and 10.71 for the TT genotype). Also, there was a significant increase in TLR9 and TLR10 polymorphisms among uncontrolled cases compared to both well-controlled cases and the control group. We discovered a significant association between TLR9 (rs187084) gene polymorphisms and pulmonary function tests (PFTs), with better results in the CC genotype. Additionally, a significant association with both RVFWSL (right ventricle free-wall longitudinal strain) and GLS (left ventricle global longitudinal strain apical 2-chamber view) with better values was linked to the CC genotype. Regarding TLR10 (rs11096956), there was a significant association between gene polymorphisms and PFTs, with better function in the GG genotype. Additionally, there was a significant association between TLR10 (rs11096956) gene polymorphisms and GLS AVG (left ventricle global longitudinal strain average), with the GG type having significantly better cardiac function. Conclusion: Subclinical cardiac dysfunction of the left and right ventricles was detected in asthmatic children. The CC genotype of TLR9 and the GG genotype of TLR10 are associated with better asthma control and better cardiac function. Therefore, TLR9 and TLR10 have a role in asthma control and cardiac dysfunction.
1. Introduction
The most common chronic illness affecting children is asthma, which puts persistent stress on the healthcare system. Recently, the occurrence of asthma symptoms in children and adolescents has increased worldwide, especially in low-middle income countries (LMICs). It places a heavy load on people and the community over the course of their lives [1]. It is a serious public health problem worldwide, which can influence the quality of life. Globally, asthma ranks 16th among the leading causes of years lived with disabilities and 28th among the primary causes of burden of disease, as assessed by disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) [2]. The global prevalence of BA in children ranges from 9.1% to 9.5%, rising to 10.4% in adolescents [3]; the prevalence of asthma and its rate of mortality in children have increased significantly over the past 40 years. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that approximately 300 million people worldwide suffer from asthma, and this figure is expected to reach 400 million by 2025 [4]. Globally, the mortality rate of pediatric asthma ranges from 0 to 0.7 per 100,000 people [5,6]. Among children, asthma is the most common chronic disease, ranking among the top 20 causes of DALYs worldwide in children of all ages [7].
The available information indicates that asthma is a multifaceted illness, and its development is becoming progressively more linked to an interplay of genetic susceptibility, environmental factors, and host factors [8]. Furthermore, a thorough understanding of the immunology of this condition can substantially help all asthmatics receive personalized, targeted treatment [9].
The initial line of defense against germs is made up of a family of receptors called toll-like receptors (TLRs). They are essential in bridging innate and adaptive immunity because they can detect both external pathogens and dangerous internal chemicals generated by injured or dying cells [10]. TLRs are widely distributed in the respiratory tract epithelium, where they help to activate immunological responses. Principally, the function of some TLRs during inflammation has raised the possibility that they have a role in the pathophysiology of asthma [11].
Several mechanisms can explain the impact of chronic lung diseases on the heart, including recurrent hypoxemia, the release of inflammatory mediators, changes in the pulmonary vasculature, and increased intra-thoracic pressure. These mechanisms directly affect the right ventricle by increasing the pulmonary artery pressure. Left ventricular dysfunction was also reported with chronic lung diseases, secondary to changes in the interaction between the right and left ventricles and changes in the ventricular preload and afterload [12].
Therefore, we intended to assess the relation between TLR9 and TLR10 gene polymorphisms and asthma and its control and the effect of asthma and gene polymorphisms on the respiratory and cardiac functions of the left and right ventricles using a new model of echocardiography (speckle tracking method) to detect subclinical cardiac dysfunction, if present.
2. Patients and Method
This case-control study was conducted at the Pulmonology Unit, Pediatric Department, Zagazig University Children’s Hospital in cooperation with the Echocardiography Unit, Pediatric Department, Zagazig University Children’s Hospital, and the Scientific and Medical Research Center of the Faculty of Medicine, Zagazig University, over a period of 35 months between December 2019 and October 2022.
2.1. Sample Size
The sample size was calculated using G power 3.1.9.7 based on the large expected effect size between the asthmatic group and control group for the frequency of TLR10 polymorphisms (d = 0.5), with CI 95%, power 80%, and an allocation ratio of 3:1. Therefore, the sample size was calculated to be at least 56 cases, with 14 in each group.
2.2. Participant Groups Involved in the Study
- The asthma group:
This study encompassed 60 asthmatic children. This group was divided into the following 3 subgroups according to the GINA 2019 guidelines [13] for asthma control:
- Well-controlled group, including 20 children
- Partially controlled group, including 20 children
- Uncontrolled group, including 20 children
2.3. Inclusion Criteria
Aged between 5 and 12 years and diagnosed with bronchial asthma based on The Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) diagnosis guidelines for 2019 [13].
2.4. Exclusion Criteria
Patients outside the age group, asthmatic patients with clinical impairment other than asthma (e.g., congenital heart diseases, congenital pulmonary diseases, chronic lung, heart, or kidney diseases, endocrinal or congenital or acquired immune deficiency diseases).
- The control group:
It involved twenty healthy children matched in age, sex, and BMI with the asthmatic case group to overcome any confounding factors; these participants were specifically chosen based on the absence of any indications of bronchial asthma, other pulmonary diseases, allergy, or atopy by clinical assessment and careful history taking. They were selected randomly from children coming to the pediatric outpatient clinic for other causes besides respiratory or cardiac symptoms (e.g., error of refraction, audiometric assessment).
2.5. Operational Design
All patients involved in the study underwent the following: 1—Demographic data, such as socio-economic status, age, and sex. 2—Full medical history focusing on the family history of asthma and other atopic diseases, when symptoms first appeared, the frequency of daytime symptoms, the frequency of awakening at night from exacerbations, the effect on normal activities, including school attendance, the types and route of drugs used, and previous hospital admissions. 3—Careful clinical examination, including general examination, anthropometric measurements, local pulmonary examination, and other system examinations to rule out other chronic diseases. 4—Laboratory investigations, including complete blood counting, liver function testing, kidney function testing, and C-reactive protein measuring. 5—Identification of exposure to TLR9 and TLR10 gene polymorphisms [14] via real-time PCR. Each participant had two ml of venous blood drawn into sterile EDTA-containing tubes under strict aseptic conditions. To extract DNA, samples were kept at −20 °C or below. Following the manufacturer’s guidelines, the Gene JETTM whole blood genomic DNA purification mini kit (Thermo Scientific, Waltham MA, USA) was employed to extract DNA from the entire blood. The extracted DNA was then kept at −20 °C for a genotyping test [15]. The DNA concentration in each sample was assessed using a Nanodrop spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, USA). The real-time PCR thermal cycler (Applied Biosystems, Brooklyn, NY, USA) was used to identify the TLR9 (rs 187084 T/C) and TLR10 (rs11096956 T/G) SNPs. Using the TaqManTM genotyping master mix (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and TaqMan Genotyping assays for TLR9 (rs 187084) and TLR10 (rs 11096956) (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), a total reaction volume of 20 μL was procured, encompassing 10 μL TaqManTM genotyping master mix, 1 μL SNP genotyping assay, and 20 ng genomic DNA diluted with DNA/RNA-free water to 9 μL. The following cycling conditions were used: 10 min polymerase activation at 95 °C, followed by 40 cycles that include a 15 s denaturation step at 95 °C and annealing/extension at 60 °C for 1 min.
2.6. Pulmonary Function Testing
Using the Jaeger Master Screen TM IOS, version 5.2, produced by VIASYS Healthcare GmbH, Hoechberg, Germany, under standard conditions and in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions, pulmonary function testing was carried out at our pulmonology unit. Forced vital capacity (FVC) and forced expiratory volume in the first second (FEV1) were all tested using the standardized criteria [16].
2.7. Conventional Echocardiography and Two-Dimensional Speckle Tracking Analysis (Transthoracic)
To perform echocardiography, a 35-MHz phased array transducer (Philips EPIQ CVx, Amsterdam, The Netherlands) was utilized following the guidelines of the American Society of Echocardiography. Apical, subcostal, and parasternal views were obtained.
2.8. Study Outcome
Primary outcome: The role of toll-like receptors nine and ten polymorphisms in the occurrence of childhood bronchial asthma.
Secondary outcome: The role of toll-like receptors nine and ten polymorphisms in bronchial asthma control and their relation to respiratory and cardiac functions in bronchial asthma cases.
2.9. Statistical Analysis
The data were analyzed using Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS), version 26, where qualitative data were presented as frequencies and percentages. For quantitative variables (e.g., mean, standard deviation (SD), and minimum–maximum), Chi square (χ2) with Yate’s correction and one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey test were employed. Also, Pearson’s correlation coefficient was determined to evaluate the relationship between various study variables. The results were considered statistically significant and highly statistically significant when the significant probability (p-value) was <0.05 and <0.001, respectively.
3. Results
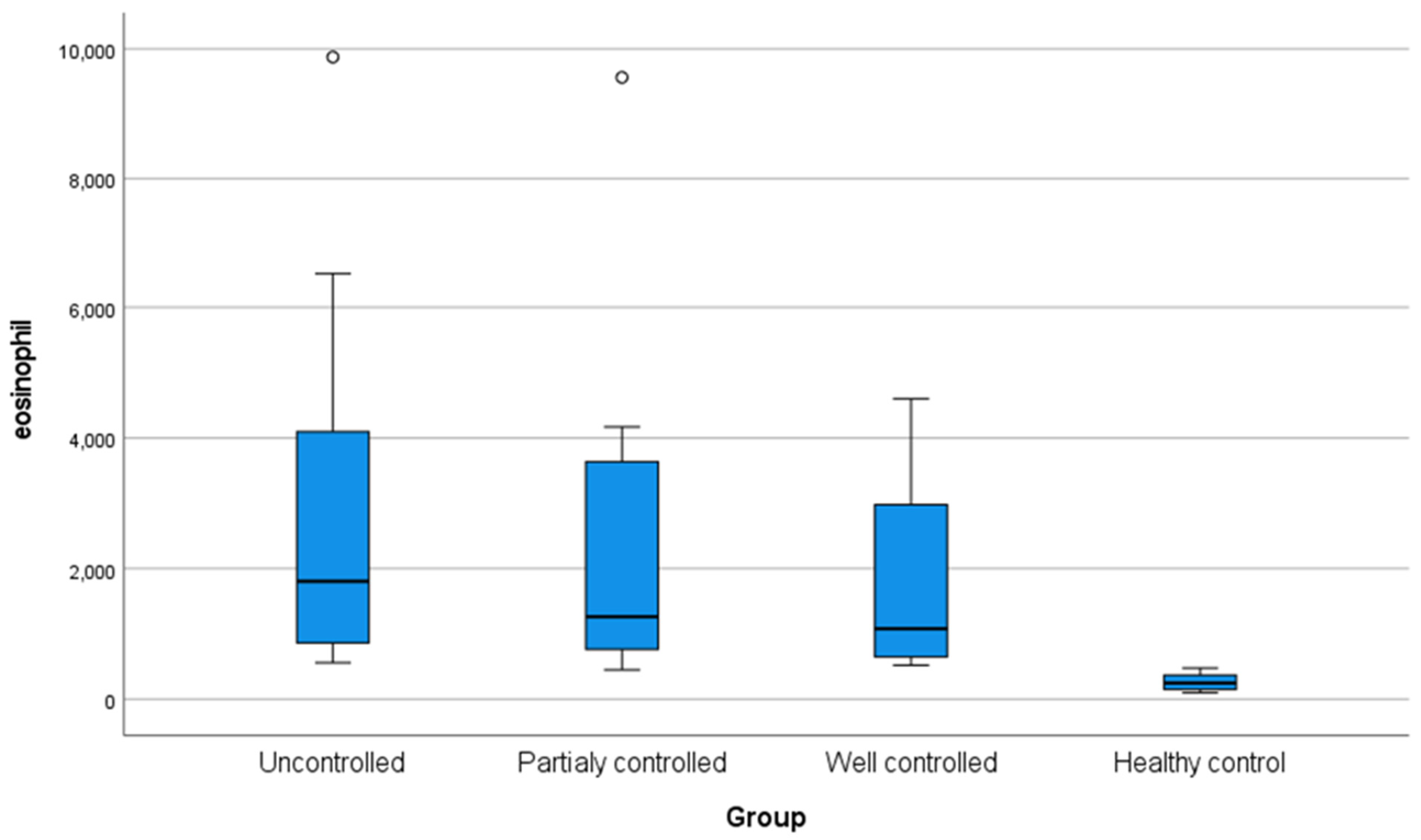
The current study showed no statistically significant differences in age, sex, weight, height, and body mass index among the four groups under investigation. However, the studied groups differed significantly in terms of family history, as 75% of the uncontrolled patients revealed a positive family history, whereas all control participants exhibited no positive family history (Table 1). The investigated groups revealed a significant statistical difference (p < 0.05) concerning eosinophilic count, with all asthmatic groups significantly elevated compared to the controls (Figure 1).

Table 1.
Demographic features of the four groups included in the study.
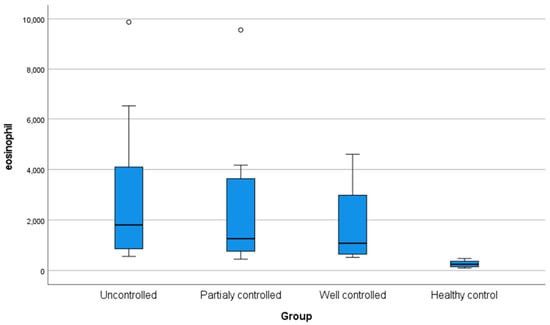
Figure 1.
Box plot demonstrating eosinophil level (cells/μL) in the studied groups.
Table 2 shows that there was no statistically significant difference between the four studied groups regarding the ejection fraction (EF) (p = 0.41) and fractional shortening (FS) (p = 0.20). Conversely, there was a statistically significant difference between the four studied groups regarding the pulmonary artery systolic pressure (PASP) (p = 0.049), with the highest mean value reported in the uncontrolled asthma group, and regarding the tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (TAPSE) (p = 0.002), with the highest mean values reported in the control group. In addition, there was a statistically significant difference between the four studied groups regarding the right ventricular echocardiographic measurements, such as right ventricle free-wall longitudinal strain (RVFWSL) (p < 0.001) and right ventricle global four-chamber longitudinal strain (RV4CSL) (p < 0.001), with the best measures reported in the control group and well-controlled asthmatic patients. There was a statistically significant difference between the studied groups regarding global longitudinal strain apical four-chamber (GLSA4C) (p = 0.007), global longitudinal strain apical two-chamber (GLSA2C) (p < 0.001), global longitudinal strain apical three-chamber (GLSA3C) (p < 0.001), and global longitudinal strain average (GLSAVG) (p < 0.001), with significantly better levels reported in the control group and well-controlled asthmatic patients.

Table 2.
Mean right ventricular echocardiographic measurements and longitudinal strain pattern in speckle tracking in the four studied groups.
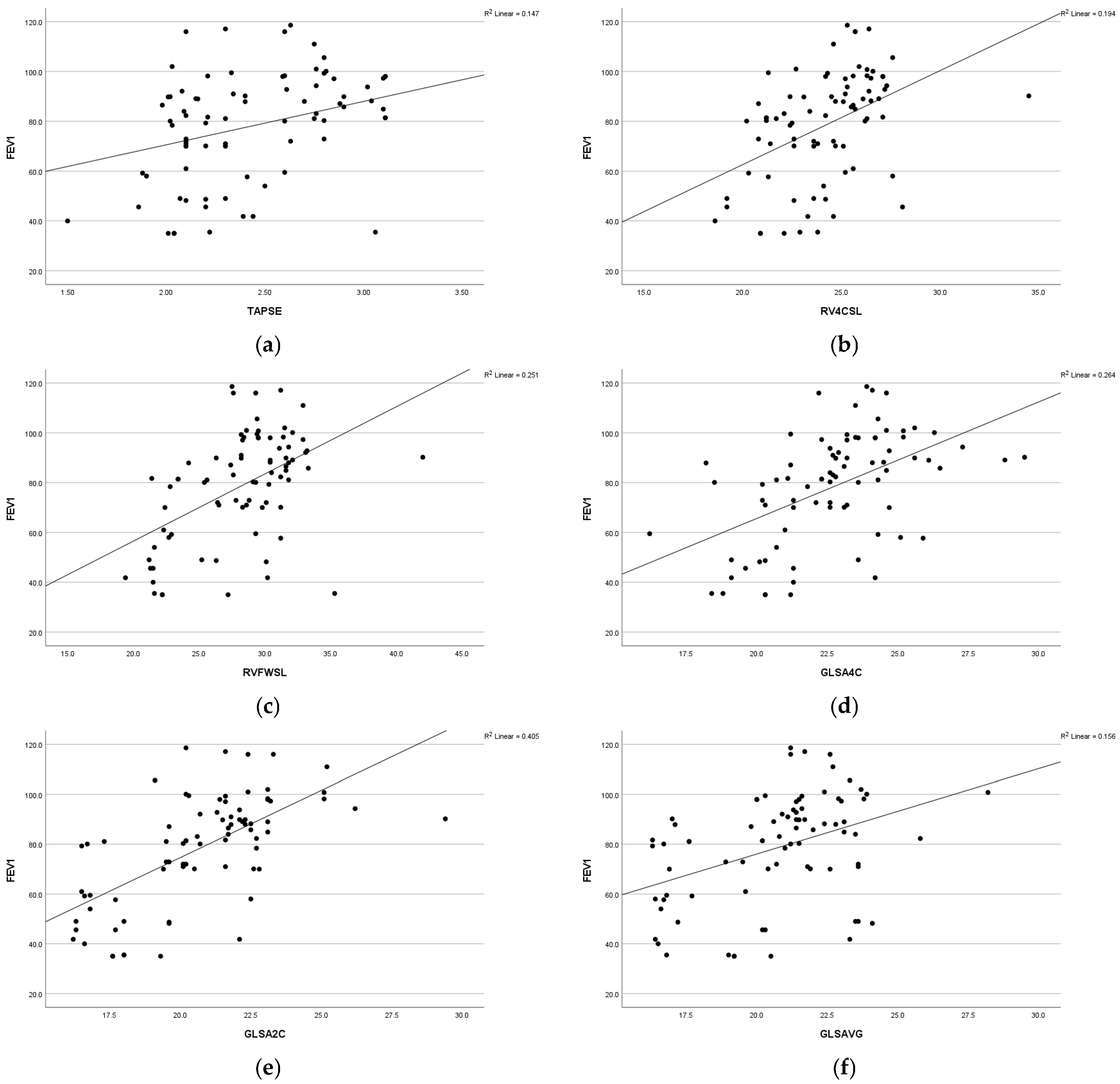
A statistically significant positive association was observed between respiratory function (FEV1) and various parameters, including global longitudinal strain apical four-chamber view (GLS A4C) (r = 0.44 and p = 0.009), left ventricular global longitudinal strain apical two-chamber view (GLS A2C) (r = 0.58 and p =<0.001), left ventricular global longitudinal strain apical three-chamber view (GLS A3C) (r = 0.40 and p = 0.001), left ventricular global longitudinal strain average (GLS AVG) (r = 0.35 and p = 0.007), right ventricle free-wall longitudinal strain (RVFWSL) (r = 0.48 and p =< 0.001), and right ventricle four-chamber strain (RV4CSL) (r = 0.36 and p = 0.005). Furthermore, a significant positive association was found between respiratory function, forced expiratory volume in the first second (FEV1), and tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (TAPSE) (r = 0.38 and p = 0.003). Statistically significant positive associations were observed among respiratory function, forced vital capacity (FVC), and the following parameters: GLSA2C (r = 0.43 and p =< 0.001), RV4CSL (r = 0.32 and p = 0.01), and RVFWSL (r = 0.39 and p = 0.002). Respiratory function (FVC) exhibited a positive correlation with fractional shortening (FS) (r = 0.34 and p = 0.008) (Figure 2).
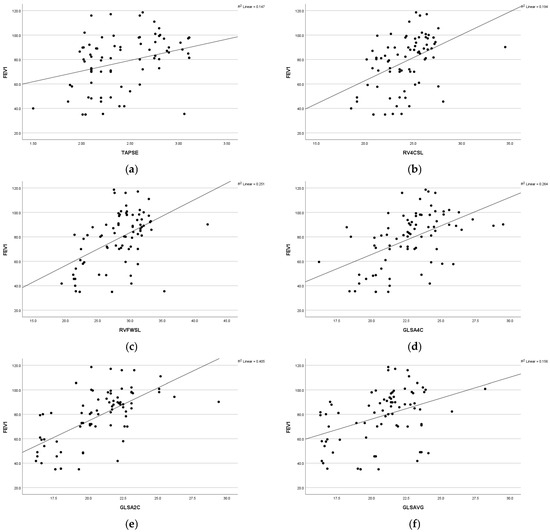
Figure 2.
Scatter diagram illustrating the positive correlation between FEV1 and the following parameters: (a) TAPSE, (b) RV4CSL, (c) RVFWSL, (d) GLSA4C, (e) GLSA2C, and (f) GLSAVG among the studied groups.
- Primary outcome
Table 3 shows that for TLR9 there was a statistically significant increase in the frequency of the CT and TT genotypes among asthmatic cases compared to the control group (OR = 9.09 and 5.24, respectively) and also in the T allele (OR = 3.23). TLR10 also showed a statistically significant increase in the frequency of the GT and TT genotypes among asthmatic cases compared to the control group (OR = 4.29 and 10.71, respectively) and also in the T allele (OR = 4.64).

Table 3.
TLR9 and TLR10 gene polymorphisms among the studied groups.
- Secondary outcome
The studied groups revealed statistically significant differences concerning TLR9 polymorphism, as the T allele and TT genotype were significantly detected among uncontrolled and partially controlled cases, while the C allele and CC genotype were equally detected in the normal control and well-controlled groups (Table 4).

Table 4.
TLR9 and TLR10 gene polymorphism distribution in the studied groups.
Also, regarding TLR10 polymorphisms, the T allele and TT genotype were significantly detected among uncontrolled and partially controlled cases, while the G allele and GG genotype were significantly detected in the normal control and well-controlled groups, with no difference between the two groups (Table 4).
There was a statistically significant relation between the TLR9 gene polymorphisms and respiratory function FEV1% (p = 0.013) and FVC% (p = 0.004), as patients with the CC genotype had significantly better respiratory function (Table 5).

Table 5.
Comparison between TLR9 gene polymorphisms and respiratory and cardiac functions and ECHO findings within the studied groups.
No significant statistical association was found between the TLR9 gene polymorphism and conventional cardiac functions, but there was a statistically significant relationship between the TLR9 gene polymorphism and both RVFWSL (p = 0.02) and GLS A2C (p = 0.024), with better values associated with the CC genotype (Table 5).
There was also a statistically significant relationship between the TLR10 gene polymorphism and respiratory function FEV1% (p = 0.047) and FVC% (p = 0.04), with the GG genotype having significantly better respiratory function than the TT genotype (Table 6).

Table 6.
Comparison between the TLR10 gene polymorphisms and respiratory and cardiac functions and ECHO findings within the studied groups.
There was no statistically significant relationship between the TLR10 gene polymorphism and conventional cardiac functions, and there was no statistically significant relationship between the TLR10 gene polymorphism and cardiac functions except GLS AVG (p = 0.042), which had a statistically significant relationship with the GG genotype and had significantly better cardiac function (Table 6).
4. Discussion
Asthma is a disease with many factors. The lack of consistent replication of genetic connections across different studies highlights the intricate interplay between various environmental and genetic aspects that contribute to the development of this condition [17]. Currently, ten functioning human TLRs (TLRs 1–10) have been identified, and their canonical adaptors’ pathways in a variety of human disorders, such as allergy diseases, are linked to them [18]. The new points of our study that have not been discussed in any study before are the relationship between TLR9 and TLR10 polymorphisms and subclinical cardiac dysfunction in asthmatic patients.
Our study revealed that both groups (asthmatics and controls) are closely matched as regards their age and sex with no significant statistical differences among the investigated groups (p-values were 0.321 and 0.656, respectively). This can be explained by the fact that the asthmatic cases were recruited first, and then another non-asthmatic, unrelated, non-allergic age- and gender-matched control group with similar ethnicity was randomly chosen later on. In our study, we found a distinction among asthmatic children and children of the control group concerning family history. Most of the asthmatic patients confirmed a familial predisposition to asthma.
Our findings align with previous studies conducted by Hernandez et al. [19], Yu et al. [20], and Guo et al. [21]. These studies reported no significant statistical differences among the groups under study as regards age and gender. However, in these studies, significant differences were found among the investigated groups in terms of family history.
Regarding anthropometric measures, our results showed no significant difference between asthmatic children and control children concerning body mass index (BMI) due to matching between the two groups. In line with our findings, Yalçın et al. [22] and Ardura-Garcia et al. [23] indicated no significant differences in BMI among the examined groups.
On the other hand, several studies have found a significant association between BMI and asthma. An Egyptian study conducted by Al-Qerem and Ling [24] on children aged 7–12 years showed a positive association between asthma and increased BMI, and comparable findings were documented by Nahhas et al. [25] in Saudi children.
The current study found a highly statistically significant difference regarding eosinophilic count, with all asthmatic groups exhibiting considerably higher values compared to the controls. This finding agreed with those results obtained by Hassane et al. [26], who found a highly statistically significant high eosinophilic count in asthmatic children compared to the control group.
In our study, by using conventional echocardiography for the assessment of cardiac function in asthmatic patients and the control group, we found a significant difference between them regarding TAPSE. This result agreed with the results obtained by Betül et al. [27] and Özkan et al. [28], who found a significant difference between asthmatics and the control group regarding TAPSE, with the highest mean values reported in the control group. On the other hand, no significant difference in TAPSE between asthmatics and the control group was reported by other studies [29,30]. This difference in results may be related to the difference in the duration and severity of asthma among the studied populations.
Moreover, our study revealed that there was a statistically significant difference between asthmatics and the control group regarding pulmonary artery systolic pressure (PASP), with PASP being higher in asthmatics. Karasu et al. [31], Manti et al. [32], and De-Paula et al. [33] reported similar results to our study regarding PASP as they found PASP higher in asthmatics. This can be explained by recurrent hypoxemia and hypercapnia related to different cytokines and mediators associated with chronic inflammation of the airways in patients with asthma that lead to pulmonary vasoconstriction and pulmonary hypertension development [12].
On the other hand, by using the speckle tracking technique, our study revealed that there was a statistically significant difference between the asthmatic group and the control group regarding RV4CSL and RVFWSL, with the best measures reported in the control group.
Moreover, there was a statistically significant positive correlation between respiratory function (FEV1 and FVC) and RV4CSL and RVFWSL. It was noted that with decreased pulmonary function, there is a decrease in global longitudinal and free-wall strain of the RT ventricle. These results coincide with those found by Tuleta et al. [34], who reported reduced longitudinal strain values of the right ventricle in the asthmatic group in comparison to the non-asthmatic controls. The same results were obtained by Baystal and Has [35], who conducted a study on adult asthmatic patients in comparison to a control group. In addition, other study confirmed a significant correlation between pulmonary function tests (FEV1, FVC) and RV strain parameters, with lower pulmonary function associated with decreased RVGLS and RVFWS [36].
On the other hand, the study Abdelmohsen et al. [29] performed on 30 children with mild to moderate asthma found no significant difference between the asthmatic group and the control group regarding right ventricle strain patterns. These differences can be attributed to a small sample size and the focus of their study being on patients with mild to moderate asthma.
Regarding LV systolic functions detected by conventional echocardiography, our study revealed that ejection fraction (EF) and fractional shortening (FS) were preserved in the asthmatic group. This coincides with the results obtained by Abdelmohsen et al. [29] and Ozdemir et al. [37] regarding EF.
Using speckle tracking echocardiography, we detected statistically significant differences between the four studied groups regarding left ventricle longitudinal strain, with the best measures reported in the control group. Our results were similar to those of Tuleta et al. [34], who found reduced LV longitudinal strain in patients with severe and mild-to-moderate asthma.
On the other hand, Bystal and Has [35] and Abdelmohsen et al. [29] reported no left ventricular stain pattern in asthmatic patients. This could be due to the fact that their study focused on patients with mild asthma. Moreover, we investigated TLR9 (rs 187084) and TLR10 (rs 11096956) gene polymorphisms and their association with asthma.
In our study, we found a statistically significant difference between the studied groups regarding TLR9 polymorphisms with the TT genotype and T allele in the uncontrolled (55%) and partially controlled cases (35%). The CC genotype and C allele were significantly detected in the normal control (67.5%) and well-controlled groups (55%), with no difference between the two groups. Our data showed a statistically significant relation between TLR9 gene polymorphisms and respiratory function, with the CC genotype having significantly better respiratory function. This coincides with the results of Tesse et al. [38], who reported an association between TLR9 (rs 187084) and asthma. Also, Kormann et al. [39] evaluated assumed functional genetic variants in all 10 human TLR genes, including TLR9, for their relation to different asthma phenotypes in a case-control study, which revealed that TLR9 (rs 187084) was associated with asthma with a p-value of 0.03.
Moreover, our data revealed a statistically significant relationship between the TLR10 gene polymorphisms and respiratory function, with the GG genotype having significantly better respiratory function than the TT genotype. This agrees with the results obtained by Tesse et al. [38], who found a significant association between TLR10 gene polymorphisms and asthma. However, Klaassen et al. [40] carried out a systematic review of TLRs and CD14 in relation to asthma in Caucasian children and found no association with bronchial asthma. Puthothu and Heinzmann [41], who involved 322 asthmatic children and 270 randomly selected controls to assess whether TLR6, TLR10, or both were involved in asthma genetics, found no individual association between TLR10 (rs11096956) and bronchial asthma.
The degree of association between polymorphisms and asthma varies between different populations and sometimes in the same population depending on environmental factors, genetics, sex differences, age of the studied patients, study methodologies, and differences in the number of subjects [11]. Asthma is a complex disease influenced by both genetic and environmental factors. If a population was exposed to different environmental triggers (e.g., allergens, pollution, infections), TLR10 (rs11096956) might play a role in asthma susceptibility in the presence of specific environmental conditions. Additionally, interactions with other genetic variants (epistasis) might modulate the effect of TLR10 (rs11096956), making its association apparent in our study but not in other studies.
This study aimed to investigate the association between TLR9 and TLR10 gene polymorphisms and bronchial asthma susceptibility, disease control, and their impact on respiratory and cardiac functions. TLR9 and TLR10 were linked to better asthma control and improved cardiac function, while subclinical left and right ventricular dysfunction was observed in asthmatic children. These findings suggest that TLR9 and TLR10 polymorphisms may serve as potential biomarkers for predicting asthma control and assessing the risk of asthma-related cardiac dysfunction. Our findings open avenues for several future research directions, e.g., large-scale genetic association studies conducting multi-center genome-wide association studies (GWAS), longitudinal cohort studies following asthmatic patients over time to assess how TLR9 and TLR10 polymorphisms influence disease progression, exacerbations, and long-term cardiac and pulmonary outcomes, and therapeutic targeting of the TLR pathways could improve asthma control and reduce associated cardiac dysfunction.
Strengths and Limitations
This study represents the first attempt to examine the association between TLR gene polymorphisms, asthma control, and cardiac function in Egyptian children. It included several assessments (family history, clinical, laboratory, PFTs, and echo and gene polymorphism). The study results can be generalized due to the use of broad inclusion criteria that resulted in a study population that more closely resembles real-life patients, an adequate sample size, and an adjusted power and CI for the study.
It focused on TLR-9 and TLR-10 polymorphisms, prioritizing common variants due to resource limitations. Future research could expand to include rarer polymorphisms. Furthermore, although statistically adequate, the sample size could have been larger and had more depth for relationships within subgroups. Additionally, a more detailed evaluation of asthma treatments, patient history, and respiratory function is recommended (e.g., FEF 25%, FEF 50%, FEF 75%, FIF 50%, FEV/SVC, FEF 25–75%) as these factors were not comprehensively documented in the current study. In terms of cardiac parameters, future studies might benefit from employing more refined metrics (e.g., LVDs, LVDd, E velocity, A velocity, E/A).
5. Conclusions
The study aimed to verify the link between TLR9 and TLR10 gene polymorphisms and bronchial asthma and its control. The CC genotype of TLR9 and the GG genotype of TLR10 are associated with better asthma control. Also, we aimed to find a relationship between TLR9 and TLR10 gene polymorphisms and respiratory and cardiac functions. Subclinical cardiac dysfunction of the left and right ventricles was detected in asthmatic children. The CC genotype of TLR9 and the GG genotype of TLR10 are associated with better cardiac function. So, we conclude that studying TLR9 and TLR10 polymorphisms can be of value in predicting bronchial asthma control in asthmatic patients and cardiac dysfunction.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.A.R., A.E.H., H.S.A. and M.S.N.; Data curation, A.E.H., H.A.N., D.S.E.-R., H.S.A. and H.T.A.; Formal analysis, N.A., H.A.N., D.S.E.-R., H.S.A. and H.T.A.; Investigation, H.S.A., S.A.S. and M.S.N.; Methodology, R.A.R., A.E.H., S.A.S., H.A.N., D.S.E.-R., H.S.A., N.A., H.T.A. and M.S.N.; Resources, A.E.H., H.S.A., M.S.N. and N.A.; Supervision, H.S.A. and S.A.S.; Validation, H.A.N., D.S.E.-R., H.S.A., H.T.A. and M.S.N.; Writing—original draft, R.A.R., A.E.H., H.S.A., S.A.S. and M.S.N.; Writing—review and editing, R.A.R., A.E.H., H.S.A., S.A.S., N.A., H.A.N., D.S.E.-R., H.T.A. and H.S.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors declare that financial support was sponsored by Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, researchers supporting project number (PNURSP2025R347), Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study approval was received from the Zagazig University Academic and Ethical Committee (IRB: 5758-11-12-2019). This study was conducted following The Code of Ethics of the World Medical Association (Declaration of Helsinki) for studies including humans.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent from a parent or legal guardian for study participation was acquired.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to all the participants for their cooperation and to Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, researchers supporting project number (PNURSP2025R347), Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Al-Gewely, M.S.; El-Hosseiny, M.; Abou Elezz, N.F.; El-Ghoneimy, D.H.; Hassan, A.M. Health-related quality of life in childhood bronchial asthma. Egypt. J. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 11, 83–93. [Google Scholar]
- Global Asthma Network Study Group. The Global Asthma Report 2014; Global Asthma Network Study Group: Auckland, New Zealand, 2014; Available online: http://www.globalasthmanetwork.org/publications/Global_Asthma_Report_2014.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Rahimian, N.; Aghajanpour, M.; Jouybari, L.; Ataee, P.; Fathollahpour, A.; LamuchDeli, N.; Kalmarzi, R.N. The Prevalence of Asthma among Iranian Children and Adolescent: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 6671870. [Google Scholar]
- Masoli, M.; Fabian, D.; Holt, S.; Beasley, R. Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) Program. The global burden of asthma: Executive summary of the GINA Dissemination Committee report. Allergy 2004, 59, 469–478. [Google Scholar]
- Nakayasu, H.; Araga, S.; Takahashi, K.; Otsuki, K.; Murata, M. Two cases of adult Down’s syndrome presenting parietal low uptake in 123I-IMP-SPECT. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 1991, 31, 557–560. [Google Scholar]
- Asher, I.; Pearce, N. Global burden of asthma among children. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2014, 18, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar]
- Vos, T.; Flaxman, A.D.; Naghavi, M.; Lozano, R.; Michaud, C.; Ezzati, M.; Shibuya, K.; Salomon, J.A.; Abdalla, S.; Aboyans, V.; et al. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990-2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2163–2196. [Google Scholar]
- Dharmage, S.C.; Perret, J.L.; Custovic, A. Epidemiology of asthma in children and adults. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 246. [Google Scholar]
- Gans, M.D.; Gavrilova, T. Understanding the immunology of asthma: Pathophysiology, biomarkers, and treatments for asthma endotypes. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2020, 36, 118–127. [Google Scholar]
- Behzadi, P.; García-Perdomo, H.A.; Karpiński, T.M. Toll-like receptors: General molecular and structural biology. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 9914854. [Google Scholar]
- Bezemer, G.F.; Sagar, S.; Van Bergenhenegouwen, J.; Georgiou, N.A.; Garssen, J.; Kraneveld, A.D.; Folkerts, G. Dual role of Toll-like receptors in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 337–358. [Google Scholar]
- Forfia, P.R.; Vaidya, A.; Wiegers, S.E. Pulmonary heart disease: The heart lung interaction and its impact on patient phenotypes. Pulm. Circ. 2013, 3, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Initiative for Asthma. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. 2019. Available online: https://ginasthma.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/GINA-2019-main-report-June-2019-wms.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Sharifi, A.; Ghadiri, A.; Salimi, A.; Ghandil, P.; Esmaeili, S.A. Evaluating the distribution of (+2044G/A, R130Q) rs20541 and (−1112 C/T) rs1800925 polymorphism in IL-13 gene: An association-based study with asthma in Ahvaz, Iran. Int. J. Med. Lab. 2021, 8, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacon-Cortes, D.; Griffiths, L. Methods for extracting genomic DNA from whole blood samples: Current perspectives. J. Biorepos. Sci. Appl. Med. 2014, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, M.; Hankinson, J.; Brusasco, V.; Burgos, F.; Casaburi, R.; Coates, A.; Crapo, R.; Enright, P.; van der Grinten, C.P.; Gustafsson, P.; et al. Standardization of Spirometry. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ober, C.; Yao, T.C. The genetics of asthma and allergic disease: A 21st century perspective. Immunol. Rev. 2011, 242, 10–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Lucas, R.M.; Liu, L.; Stow, J.L. SCIMP is a universal Toll-like receptor adaptor in macrophages. J. Cell Sci. 2020, 133, jcs239194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, C.D.; Casanello, P.; Harris, P.R.; Castro-Rodríguez, J.A.; Iturriaga, C.; Perez-Mateluna, G.; Farías, M.; Urzúa, M.; Hernandez, C.; Serrano, C.; et al. Early origins of allergy and asthma (ARIES): Study protocol for a prospective prenatal birth cohort in Chile. BMC Pediatr. 2020, 20, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Su, F.; Wang, L.B.; Hemminki, K.; Dharmage, S.C.; Bowatte, G.; Bui, D.; Qian, Z.; Vaughn, M.G.; Aaron, H.E.; et al. The Asthma Family Tree: Evaluating Associations between Childhood, Parental, and Grandparental Asthma in Seven Chinese Cities. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 720273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.L.; Liu, F.; Ren, C.J.; Xing, C.H.; Wang, Y.J. Correlations of LTα and NQO1 gene polymorphisms with childhood asthma. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 7557–7562. [Google Scholar]
- Yalçın, S.S.; Emiralioğlu, N.; Yalçın, S. Evaluation of blood and tooth element status in asthma cases: A preliminary case–control study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2021, 21, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardura-Garcia, C.; Vaca, M.; Oviedo, G.; Sandoval, C.; Workman, L.; Schuyler, A.J.; Perzanowski, M.S.; Platts-Mills, T.A.; Cooper, P.J. Risk factors for acute asthma in tropical America: A case–control study in the City of Esmeraldas, Ecuador. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2015, 26, 423–430. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Qerem, W.; Ling, J. Pulmonary function tests in Egyptian schoolchildren in rural and urban areas. East. Mediterr. Health J. 2018, 24, 325–332. [Google Scholar]
- Nahhas, M.; Bhopal, R.; Anandan, C.; Elton, R.; Sheikh, A. Investigating the association between obesity and asthma in 6-to 8-year-old Saudi children: A matched case–control study. npj Prim. Care Respir. Med. 2014, 24, 14004. [Google Scholar]
- Hassane, F.M.; Khatab, A.A.; Saliem, S.S.; Fahmy, M.S. Low magnesium concentration in erythrocytes of children with acute asthma. Menoufia Med. J. 2015, 28, 477. [Google Scholar]
- Betül, B.K.; Ayhan, H. Early Impairment of Right Ventricular Functions in Patients with Moderate Asthma and the Role of Isovolumic Acceleration. Koşuyolu Heart 2022, 25, 157–164. [Google Scholar]
- Özkan, E.; Khosroshahi, H. Evaluation of the Left and Right Ventricular Systolic and Diastolic Function in Asthmatic Children. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2016, 16, 145. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelmohsen, G.; Mohamed, H.; Mohsen, M.; Abdelaziz, O.; Ahmed, D.; Abdelsalam, M.; Dohain, A. Evaluation of cardiac function in pediatric patients with mild to moderate bronchial asthma in the era of cardiac strain imaging. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2019, 54, 1905–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozde, C.; Dogru, M.; Ozde, Ş.; Kayapinar, O.; Kaya, A.; Korkmaz, A. Subclinical right ventricular dysfunction in intermittent and persistent mildly asthmatic children on tissue Doppler echocardiography and serum NT-pro BNP: Observational study. Pediatr. Int. 2018, 60, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasu, B.B.; Aydıncak, H.T. Right ventricular-pulmonary arterial uncoupling in mild-to-moderate asthma. J. Asthma 2023, 60, 543–552. [Google Scholar]
- Manti, S.; Parisi, G.F.; Giacchi, V.; Sciacca, P.; Tardino, L.; Cuppari, C.; Salpietro, C.; Chikermane, A.; Leonardi, S. Pilot study shows right ventricular diastolic function impairment in young children with obstructive respiratory disease. Acta Paediatr. 2019, 108, 740–744. [Google Scholar]
- De-Paula, C.R.; Magalhães, G.S.; Jentzsch, N.S.; Botelho, C.F.; Mota, C.D.C.C.; Murça, T.M.; Ramalho, L.F.C.; Tan, T.C.; Capuruço, C.A.B.; Rodrigues-Machado, M.D.G. Echocardiographic assessment of ventricular function in young patients with asthma. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2018, 110, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuleta, I.; Eckstein, N.; Aurich, F.; Nickenig, G.; Schaefer, C.; Skowasch, D.; Schueler, R. Reduced longitudinal cardiac strain in asthma patients. J. Asthma 2019, 56, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baysal, S.S.; Has, M. Assessment of biventricular function with speckle tracking echocardiography in newly-diagnosed adult-onset asthma. J. Asthma 2022, 59, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özdemir, R.; Karadeniz, C.; Döğer, F.K.; Poyrazoglu, H.G. Right ventricular function in children with asthma: Evaluation using two-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiograph. J. Pediatr. 2021, 230, 166–172. [Google Scholar]
- Ozdemir, O.; Ceylan, Y.; Razi, C.H.; Ceylan, O.; Andiran, N. Assessment of ventricular functions by tissue Doppler echocardiography in children with asthma. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2013, 34, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesse, R.; Pandey, R.C.; Kabesch, M. Genetic variations in toll-like receptor pathway genes influence asthma and atopy. Allergy 2011, 66, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kormann, M.S.; Depner, M.; Hartl, D.; Klopp, N.; Illig, T.; Adamski, J.; Vogelberg, C.; Weiland, S.K.; von Mutius, E.; Kabesch, M. Toll-like receptor heterodimer variants protect from childhood asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 122, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaassen, E.M.; Thönissen, B.E.; van Eys, G.; Dompeling, E.; Jöbsis, Q. A systematic review of CD14 and toll-like receptors in relation to asthma in Caucasian children. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2013, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puthothu, B.; Heinzmann, A. Is toll-like receptor 6 or toll-like receptor 10 involved in asthma genetics--or both? Allergy 2006, 61, 649–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).