Detectability of Iodine in Mediastinal Lesions on Photon Counting CT: A Phantom Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
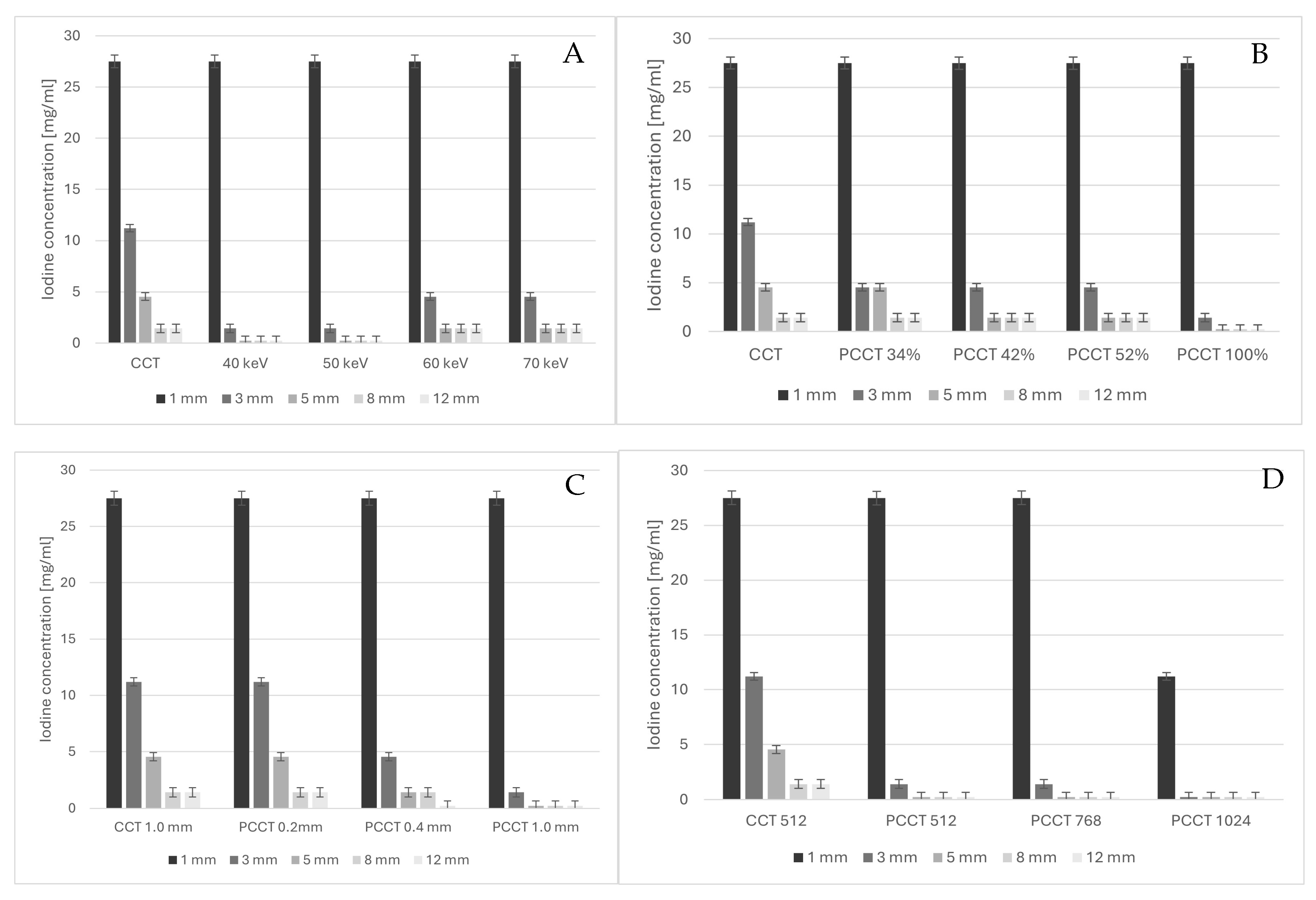
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, H.; Fan, F.; Gong, Y.; Jing, X.; Lin, X.; Wang, H.; Lin, F.; Li, Z. Diagnostic Challenges in Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology of Mediastinal Tumors and Lesions. In Archives of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine; College of American Pathologists: Northfield, MN, USA, 2022; pp. 960–974. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, S.H.; Choi, S.H.; Kang, C.H.; Goo, J.M. Incidental Anterior Mediastinal Nodular Lesions on Chest CT in Asymptomatic Subjects. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si-Mohamed, S.A.; Boccalini, S.; Lacombe, H.; Diaw, A.; Varasteh, M.; Rodesch, P.A.; Dessouky, R.; Villien, M.; Tatard-Leitman, V.; Bochaton, T.; et al. Coronary CT Angiography with Photon-counting CT: First-In-Human Results. Radiology 2022, 303, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrolinska, M.M.; van der Werf, N.R.; van der Bie, J.; de Groen, J.; Dijkshoorn, M.; Booij, R.; Budde, R.P.J.; Greuter, M.J.W.; van Straten, M. Radiation dose optimization for photon-counting CT coronary artery calcium scoring for different patient sizes: A dynamic phantom study. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 4668–4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flohr, T.; Schmidt, B.; Ulzheimer, S.; Alkadhi, H. Cardiac imaging with photon counting CT. Br. J. Radiol. 2023, 96, 20230407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greffier, J.; Villani, N.; Defez, D.; Dabli, D.; Si-Mohamed, S. Spectral CT imaging: Technical principles of dual-energy CT and multi-energy photon-counting CT. Diagn. Interv. Imaging. 2023, 104, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartoretti, T.; Wildberger, J.E.; Flohr, T.; Alkadhi, H. Photon-counting detector CT: Early clinical experience review. Br. J. Radiol. 2023, 96, 20220544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flohr, T.; Petersilka, M.; Henning, A.; Ulzheimer, S.; Ferda, J.; Schmidt, B. Photon-counting CT review. Phys. Med. 2020, 79, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCollough, C.H.; Rajendran, K.; Baffour, F.I.; Diehn, F.E.; Ferrero, A.; Glazebrook, K.N.; Horst, K.K.; Johnson, T.F.; Leng, S.; Mileto, A.; et al. Clinical applications of photon counting detector CT. Eur Radiol. 2023, 33, 5309–5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, S.; Bruesewitz, M.; Tao, S.; Rajendran, K.; Halaweish, A.F.; Campeau, N.G.; Fletcher, J.G.; McCollough, C.H. Photon-counting detector CT: System design and clinical applications of an emerging technology. Radiographics 2019, 39, 729–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandfort, V.; Persson, M.; Pourmorteza, A.; Noël, P.B.; Fleischmann, D.; Willemink, M.J. Spectral photon-counting CT in cardiovascular imaging. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2021, 15, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielsson, M.; Persson, M.; Sjölin, M. Photon-counting x-ray detectors for CT. Phys. Med. Biol. 2021, 66, 03TR01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozguner, O.; Dhanantwari, A.; Halliburton, S.; Wen, G.; Utrup, S.; Jordan, D. Objective image characterization of a spectral CT scanner with dual-layer detector. Phys. Med. Biol. 2018, 63, 025027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greffier, J.; Faby, S.; Pastor, M.; Frandon, J.; Erath, J.; Beregi, J.P.; Dabli, D. Comparison of low-energy virtual monoenergetic images between photon-counting CT and energy-integrating detectors CT: A phantom study. Diagn. Interv. Imaging. 2024, 105, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bette, S.; Decker, J.A.; Braun, F.M.; Becker, J.; Haerting, M.; Haeckel, T.; Gebhard, M.; Risch, F.; Woźnicki, P.; Scheurig-Muenkler, C.; et al. Optimal Conspicuity of Liver Metastases in Virtual Monochromatic Imaging Reconstructions on a Novel Photon-Counting Detector CT—Effect of keV Settings and BMI. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pannenbecker, P.; Huflage, H.; Grunz, J.P.; Gruschwitz, P.; Patzer, T.S.; Weng, A.M.; Heidenreich, J.F.; Bley, T.A.; Petritsch, B. Photon-counting CT for diagnosis of acute pulmonary embolism: Potential for contrast medium and radiation dose reduction. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 7830–7839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racine, D.; Mergen, V.; Viry, A.; Eberhard, M.; Becce, F.; Rotzinger, D.C.; Alkadhi, H.; Euler, A. Photon-Counting Detector CT with Quantum Iterative Reconstruction: Impact on Liver Lesion Detection and Radiation Dose Reduction. Investig. Radiol. 2023, 58, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willemink, M.J.; Persson, M.; Pourmorteza, A.; Pelc, N.J.; Fleischmann, D. Photon-counting CT: Technical principles and clinical prospects. Radiology 2018, 289, 293–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawata, S.; Murakami, T.; Kim, T.; Hori, M.; Federle, M.P.; Kumano, S.; Sugihara, E.; Makino, S.; Nakamura, H.; Kudo, M. Multidetector CT: Diagnostic Impact of Slice Thickness on Detection of Hypervascular Hepatocellular Carcinoma H. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2002, 179, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalisz, K.; Buethe, J.; Saboo, S.S.; Abbara, S.; Halliburton, S.; Rajiah, P. Artifacts at cardiac CT: Physics and solutions. Radiographics 2016, 36, 2064–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, A.; Yanagawa, M.; Honda, O.; Kikuchi, N.; Miyata, T.; Tsukagoshi, S.; Uranishi, A.; Tomiyama, N. Effect of Matrix Size on the Image Quality of Ultra-high-resolution CT of the Lung: Comparison of 512 × 512, 1024 × 1024, and 2048 × 2048. Acad. Radiol. 2018, 25, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCollough, C.H.; Winfree, T.N.; Melka, E.F.; Rajendran, K.; Carter, R.E.; Leng, S. Photon-Counting Detector Computed Tomography Versus Energy-Integrating Detector Computed Tomography for Coronary Artery Calcium Quantitation. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2024, 48, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Gong, H.; Hsieh, S.S.; McCollough, C.H.; Yu, L. Contrast- and noise-dependent spatial resolution measurement for deep convolutional neural network-based noise reduction in CT using patient data. Proc. SPIE Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2023, 12463, 124631J. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Greffier, J.; Si-Mohamed, S.; Frandon, J.; Loisy, M.; de Oliveira, F.; Beregi, J.P.; Dabli, D. Impact of an artificial intelligence deep-learning reconstruction algorithm for CT on image quality and potential dose reduction: A phantom study. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 5052–5063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Gong, H.; Hsieh, S.; McCollough, C.H.; Yu, L. Image quality evaluation in deep-learning-based CT noise reduction using virtual imaging trial methods: Contrast-dependent spatial resolution. Med. Phys. 2024, 51, 5399–5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booij, R.; van der Werf, N.R.; Dijkshoorn, M.L.; van der Lugt, A.; van Straten, M. Assessment of Iodine Contrast-To-Noise Ratio in Virtual Monoenergetic Images Reconstructed from Dual-Source Energy-Integrating CT and Photon-Counting CT Data. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, M.J.; Bugenhagen, S.M.; Sanchez, A.; Kim, S.; Abadia, A.; Ramirez-Giraldo, J.C. Comparison of Radiation Dose and Image Quality of Pediatric High-Resolution Chest CT Between Photon-Counting Detector CT and Energy-Integrated Detector CT: A Matched Study. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2023, 221, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
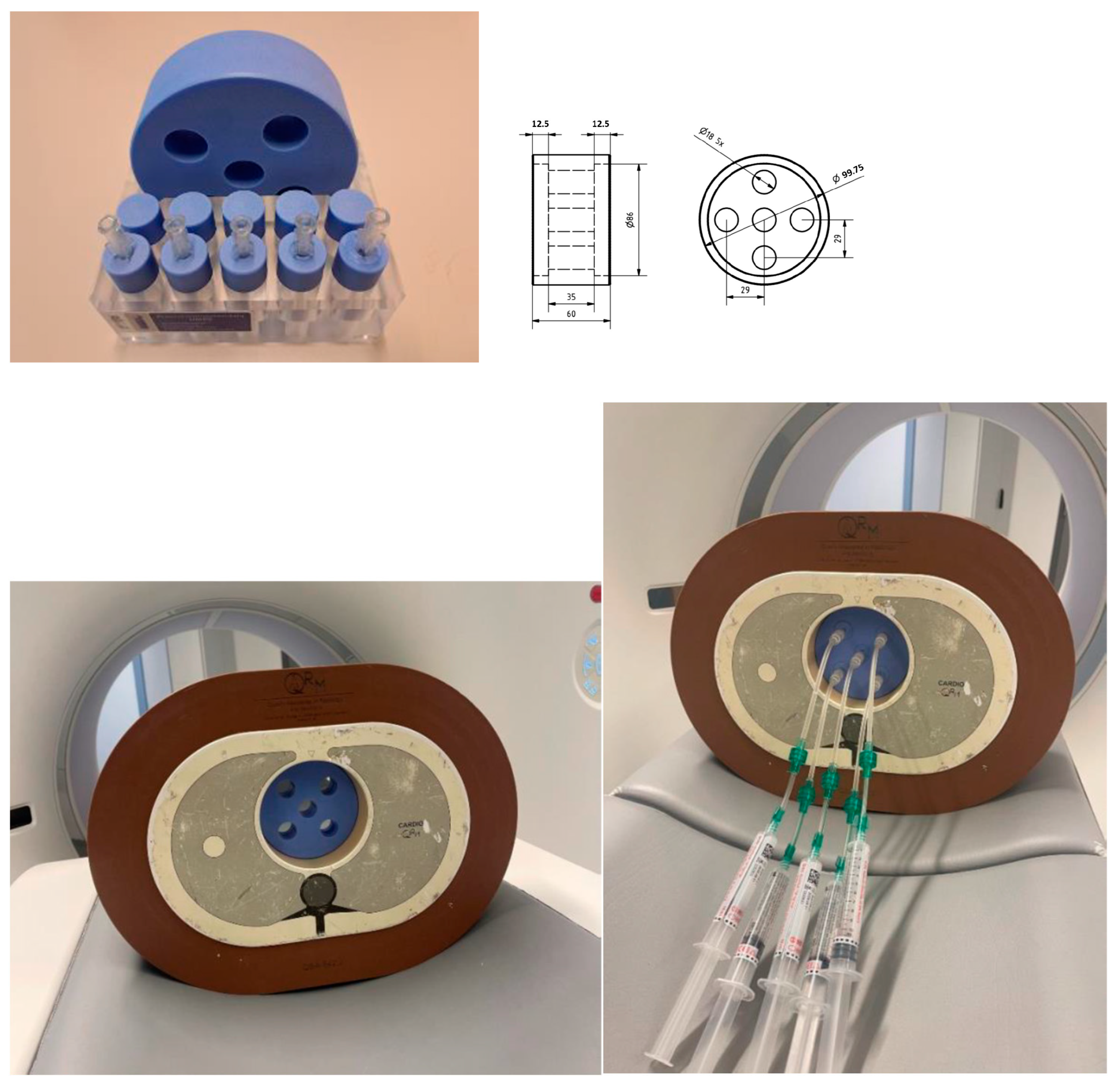

| Conventional CT | Photon-Counting CT | |
|---|---|---|
| Acquisition mode | Spiral | Spiral/quantum plus |
| Tube voltage [kV] | 120 | 120 |
| qref mAs/IQ level | 50 | 34/42/52/100% |
| Automatic Exposure Control | On | On |
| Collimation [mm] | 96 × 0.6 | 120 × 0.2 |
| Field of view [mm] | 250 | 250 |
| Rotation time [s] | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Pitch | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| Slice thickness [mm] | 1.0 | 1.0/0.4/0.2 |
| Increment [mm] | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Reconstruction kernel | Br40 | Br40 |
| Matrix size [pixels] | 512 | 512/768/1024 |
| Reconstruction method | ADMIRE 3 | QIR 2 |
| Virtual Monochromatic Image [keV] | n/a | 40/50/60/70 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Centen, J.R.; Greuter, M.J.W.; Prokop, M. Detectability of Iodine in Mediastinal Lesions on Photon Counting CT: A Phantom Study. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15060696
Centen JR, Greuter MJW, Prokop M. Detectability of Iodine in Mediastinal Lesions on Photon Counting CT: A Phantom Study. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(6):696. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15060696
Chicago/Turabian StyleCenten, Joric R., Marcel J. W. Greuter, and Mathias Prokop. 2025. "Detectability of Iodine in Mediastinal Lesions on Photon Counting CT: A Phantom Study" Diagnostics 15, no. 6: 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15060696
APA StyleCenten, J. R., Greuter, M. J. W., & Prokop, M. (2025). Detectability of Iodine in Mediastinal Lesions on Photon Counting CT: A Phantom Study. Diagnostics, 15(6), 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15060696






