Congenital Myasthenic Syndrome-4C in a Consanguineous Romani Family: Genetic Insights and Clinical Implications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
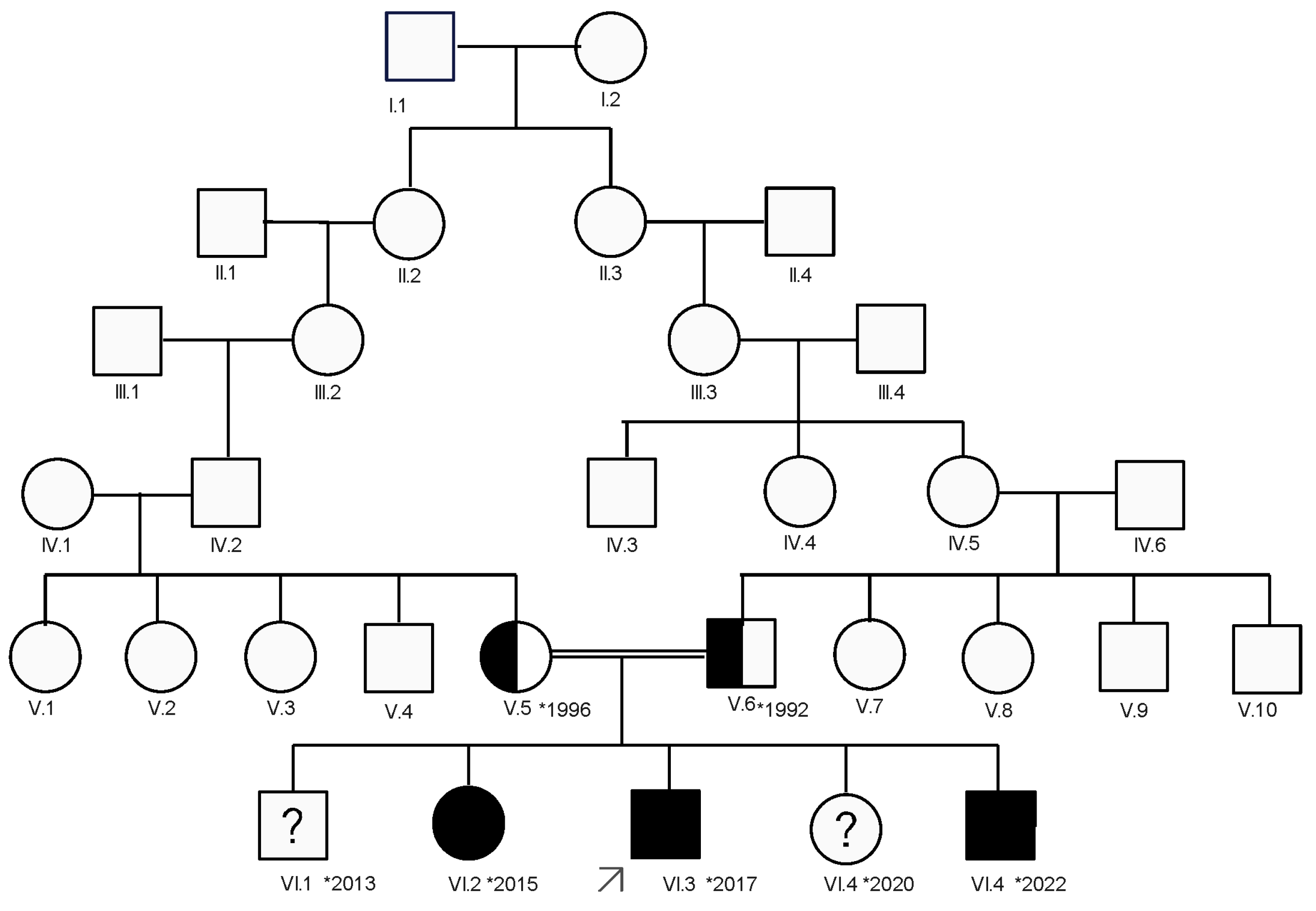
2. Case Presentation
2.1. Methods
2.2. Clinical Evaluation of the Patient
2.3. Laboratory Investigations
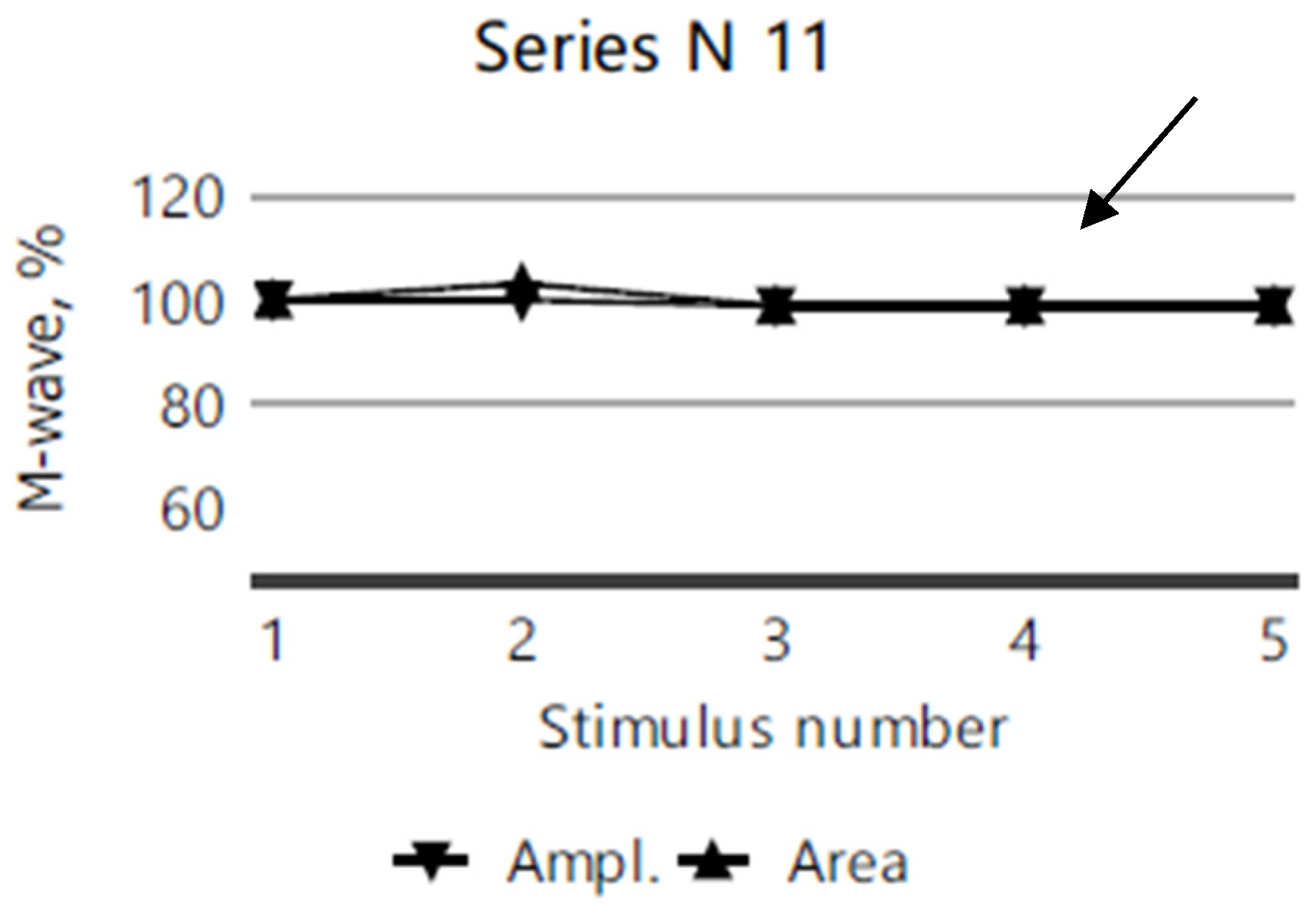
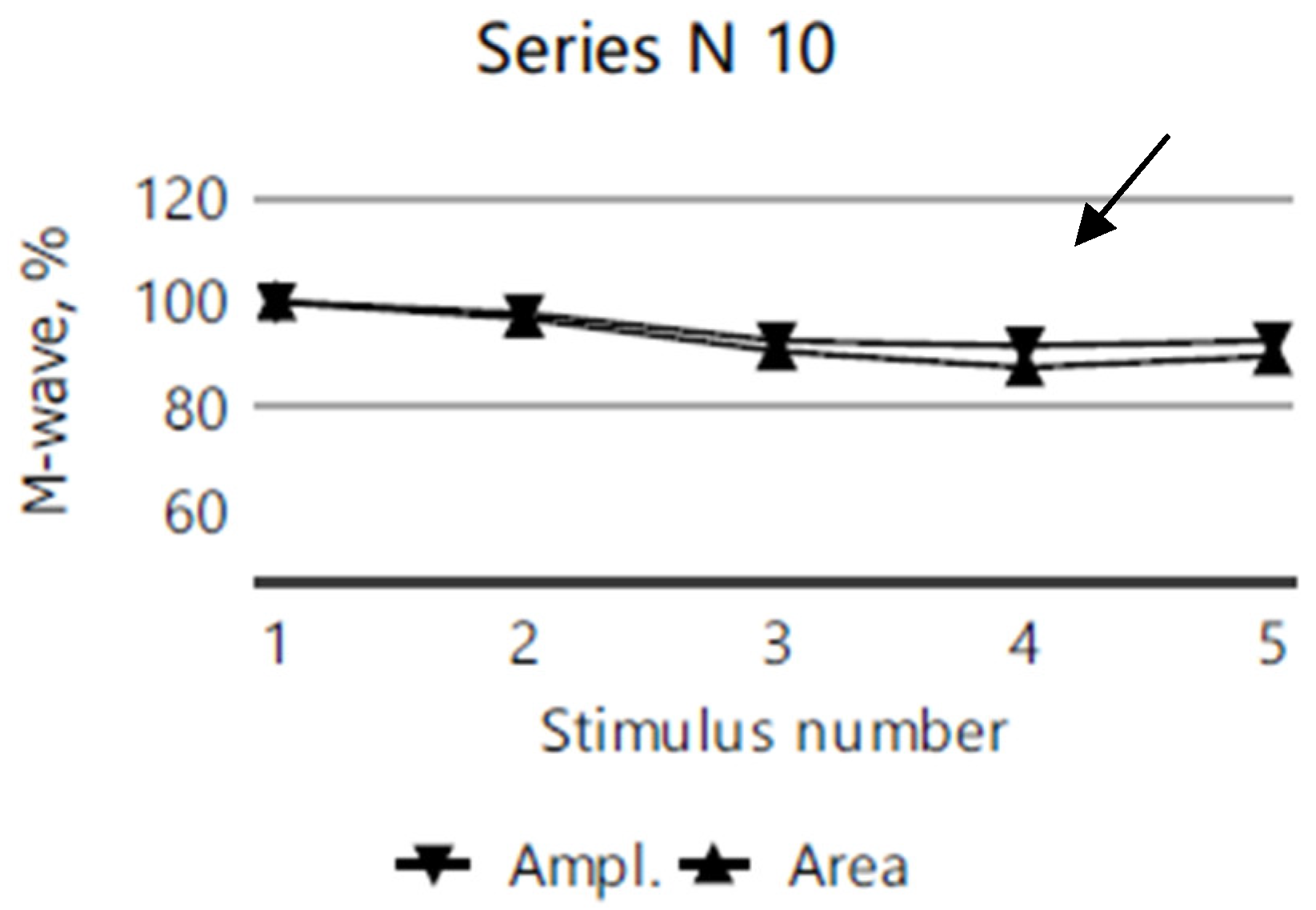
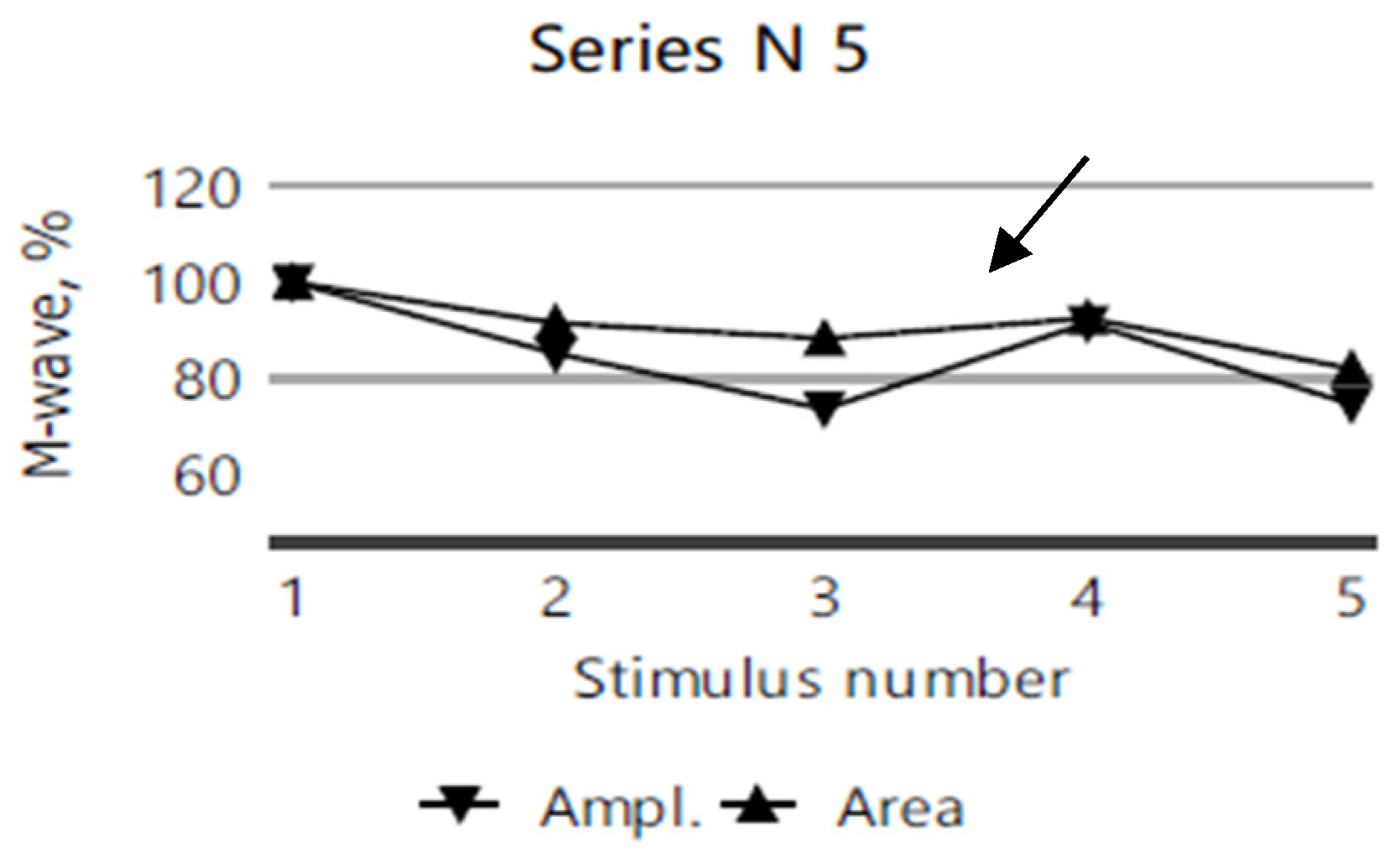
2.4. Electromyography
2.5. Molecular Investigations
3. Discussion
3.1. Gene and Genetics
3.2. Clinical and Paraclinical Aspects
3.3. Treatment
3.4. Evolution and Monitoring
3.5. Genetic Counseling
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, K.; Cheng, H.; Yuan, F.; Meng, L.; Yin, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Lu, Y.; Xi, J.; et al. CHRNE compound heterozygous mutations in congenital myasthenic syndrome: A case report. Medicine 2018, 97, e0347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Medline. Available online: https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/congenital-myasthenic-syndrome/#frequency. (accessed on 21 November 2024).
- Ohno, K.; Ohkawara, B.; Shen, X.-M.; Selcen, D.; Engel, A.G. Clinical and Pathologic Features of Congenital Myasthenic Syndromes Caused by 35 Genes—A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abicht, A.; Dusl, M.; Gallenmüller, C.; Guergueltcheva, V.; Schara, U.; Della Marina, A.; Wibbeler, E.; Almaras, S.; Mihaylova, V.; von der Hagen, M.; et al. Congenital myasthenic syndromes: Achievements and limitations of phenotype-guided gene-after-gene sequencing in diagnostic practice: A study of 680 patients. Hum. Mutat. 2012, 33, 1474–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, P.; Gaudon, K.; Fournier, E.; Jackson, C.; Bauché, S.; Haddad, H.; Koenig, J.; Echenne, B.; Hantaï, D.; Eymard, B. A synonymous CHRNE mutation responsible for an aberrant splicing leading to congenital myasthenic syndrome. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2007, 17, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenen, M.; Peter, C.; Villarroel, A.; Witzemann, V.; Sakmann, B. Acetylcholine receptor channel subtype directs the innervation pattern of skeletal muscle. EMBO Rep. 2005, 6, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sanes, J.R.; Lichtman, J.W. Induction, assembly, maturation and maintenance of postsynaptic apparatus. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 2, 791–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuetze, S.M.; Role, L.W. Developmental regulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1987, 10, 403–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, H.; Beeson, D.; Vincent, A.; Webster, R. The Structure, Function, and Physiology of the Fetal and Adult Acetylcholine Receptor in Muscle. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 581097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeson, D.; Brydson, M.; Betty, M.; Jeremiah, S.; Povey, S.; Vincent, A.; Newsom-Davis, J. Primary structure of the human muscle acetylcholine receptor cDNA cloning of the gamma and epsilon subunits. Europ. J. Biochem. 1993, 215, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CHRNE. Hugo Gene Nomenclature Committee. Available online: https://www.genenames.org/data/gene-symbol-report/#!/hgnc_id/HGNC:1966 (accessed on 1 November 2024).
- Ealing, J.; Webster, R.; Brownlow, S.; Abdelgany, A.; Oosterhuis, H.; Muntoni, F.; Vaux, D.J.; Vincent, A.; Beeson, D. Mutations in congenital myasthenic syndromes reveal an epsilon subunit C-terminal cysteine, C470, crucial for maturation and surface expression of adult AChR. Hum. Molec. Genet. 2002, 11, 3087–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, A.G.; Ohno, K.; Bouzat, C.; Sine, S.M.; Griggs, R.C. End-plate acetylcholine receptor deficiency due to nonsense mutations in the epsilon subunit. Ann. Neurol. 1996, 40, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, A.G.; Ohno, K.; Milone, M.; Wang, H.-L.; Nakano, S.; Bouzat, C.; Pruitt, J.N., II; Hutchinson, D.O.; Brengman, J.M.; Bren, N.; et al. New mutations in acetylcholine receptor subunit genes reveal heterogeneity in the slow-channel congenital myasthenic syndrome. Hum. Molec. Genet. 1996, 5, 1217–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMacken, G.; Abicht, A.; Evangelista, T.; Spendiff, S.; Lochmüller, H. The Increasing Genetic and Phenotypical Diversity of Congenital Myasthenic Syndromes. Neuropediatrics 2017, 48, 294–308. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Engel, A.G.; Shen, X.M.; Selcen, D.; Sine, S.M. Congenital myasthenic syndromes: Pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 420–434, Erratum in Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finsterer, J. Congenital myasthenic syndromes. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2019, 14, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardissone, A.; Moroni, I.; Bernasconi, P.; Brugnoni, R. Congenital myasthenic syndrome: Phenotypic variability in patients harbouring p.T159P mutation in CHRNE gene. Acta Myol. 2017, 36, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Almatrafi, A.M.; Alluqmani, M.M.; Basit, S. Homozygous Duplication in the CHRNE in a Family with Congenital Myasthenic Syndrome 4C: 18-Year Follow Up. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abicht, A.; Müller, J.S.; Lochmüller, H. Congenital Myasthenic Syndromes Overview. In GeneReviews® [Internet]; Adam, M.P., Feldman, J., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J.H., Gripp, K.W., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20301347/ (accessed on 19 December 2024).
- Kastreva, K.; Chamova, T.; Blagoeva, S.; Bichev, S.; Mihaylova, V.; Meyer, S.; Thompson, R.; Cherninkova, S.; Guergueltcheva, V.; Lochmuller, H.; et al. Characterization of Clinical Phenotypes in Congenital Myasthenic Syndrome Associated with the c.1327delG Frameshift Mutation in CHRNE Encoding the Acetylcholine Receptor Epsilon Subunit. J. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2024, 11, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abicht, A.; Stucka, R.; Karcagi, V.; Herczegfalvi, A.; Horváth, R.; Mortier, W.; Schara, U.; Ramaekers, V.; Jost, W.; Brunner, J.; et al. A Common Mutation (Ε1267delG) in Congenital Myasthenic Patients of Gypsy Ethnic Origin. Neurology 1999, 53, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morar, B.; Gresham, D.; Angelicheva, D.; Tournev, I.; Gooding, R.; Guergueltcheva, V.; Schmidt, C.; Abicht, A.; Lochmüller, H.; Tordai, A.; et al. Mutation History of the Roma/Gypsies. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2004, 75, 596–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ena, G.F.; Aizpurua-Iraola, J.; Font-Porterias, N.; Calafell, F.; Comas, D. Population Genetics of the European Roma—A Review. Genes 2022, 13, 2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, P.; Gaudon, K.; Haddad, H.; Ben Ammar, A.; Genin, E.; Bauche, S.; Paturneau-Jouas, M.; Muller, J.S.; Lochmuller, H.; Grid, D.; et al. The CHRNE 1293insG founder mutation is a frequent cause of congenital myasthenia in North Africa. Neurology 2008, 71, 1967–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natera-de Benito, D.; Domínguez-Carral, J.; Muelas, N.; Nascimento, A.; Ortez, C.; Jaijo, T.; Arteaga, R.; Colomer, J.; Vilchez, J.J. Phenotypic heterogeneity in two large Roma families with a congenital myasthenic syndrome due to CHRNE 1267delG mutation. A long-term follow-up. Neuromuscul. Disord. NMD 2016, 26, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, P.V.; Batistella, G.N.; Lino, V.C.; Pinto, W.B.; Annes, M.; Oliveira, A.S. Clinical and genetic basis of congenital myasthenic syndromes. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2016, 74, 750–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogajski, J.H.; Kiernan, M.C.; Ouvrier, R.A.; Andrews, P.I. Congenital myasthenic syndromes. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2009, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaylova, V.; Muller, J.S.; Vilchez, J.J.; Salih, M.A.; Kabiraj, M.M.; D’Amico, A.; Bertini, E.; Wolfle, J.; Schreiner, F.; Kurlemann, G.; et al. Clinical and molecular genetic findings in COLQ-mutant congenital myasthenic syndromes. Brain 2008, 131, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzoni, P.J.; Dal-Pra Ducci, R.; Arndt, R.C.; Coblinski Hrysay, N.M.; Hernandez Fustes, O.J.; Töpf, A.; Lochmüller, H.; Werneck, L.C.; Kamoi Kay, C.S.; Scola, R.H. Congenital myasthenic syndrome in a cohort of patients with ‘double’ seronegative myasthenia gravis. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2021, 80, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, M.A.; Oystreck, D.T.; Al-Faky, Y.H.; Kabiraj, M.; Omer, M.I.; Subahi, E.M.; Beeson, D.; Abu-Amero, K.K.; Bosley, T.M. Congenital Myasthenic Syndrome Due to Homozygous CHRNE Mutations: Report of Patients in Arabia. J. Neuro-Ophthalmol. 2011, 31, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barisic, N.; Schmidt, C.; Sidorova, O.P.; Herczegfalvi, A.; Gekht, B.M.; Song, I.H.; Stucka, R.; Karcagi, V.; Abicht, A.; Lochmüller, H. Congenital myasthenic syndrome (CMS) in three European kinships due to a novel splice mutation (IVS7-2 A/G) in the epsilon acetylcholine receptor (AChR) subunit gene. Neuropediatrics 2002, 33, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Cruz, P.M.; Palace, J.; Beeson, D. The Neuromuscular Junction and Wide Heterogeneity of Congenital Myasthenic Syndromes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batheja, A.; Bayer-Vile, J.; Silverstein, E.; Couser, N. Congenital Myasthenic Syndrome associated with acetylcholine receptor deficiency: Case report and review of the literature. Ophthalmic Genet. 2024, 45, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spendiff, S.; Dong, Y.; Maggi, L.; Cruz, P.M.R.; Beeson, D.; Lochmüller, H.; ENMC 260th Workshop Study Group. 260th ENMC International Workshop: Congenital myasthenic syndromes 11–13 March 2022, Hoofddorp, The Netherlands. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2022, 33, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iuhas, A.; Jurca, C.; Kozma, K.; Riza, A.-L.; Streață, I.; Petcheși, C.; Dan, A.; Sava, C.; Balmoș, A.; Marinău, C.; et al. PAH Pathogenic Variants and Clinical Correlations in a Group of Hyperphenylalaninemia Patients from North-Western Romania. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaouch, A.; Beeson, D.; Hantaï, D.; Lochmüller, H. 186th ENMC international workshop: Congenital myasthenic syndromes 24–26 June 2011, Naarden, The Netherlands. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2012, 22, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servais, L.; Baudoin, H.; Zehrouni, K.; Richard, P.; Sternberg, D.; Fournier, E.; Eymard, B.; Stojkovic, T. Pregnancy in congenital myasthenic syndrome. J. Neurol. 2013, 260, 815–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
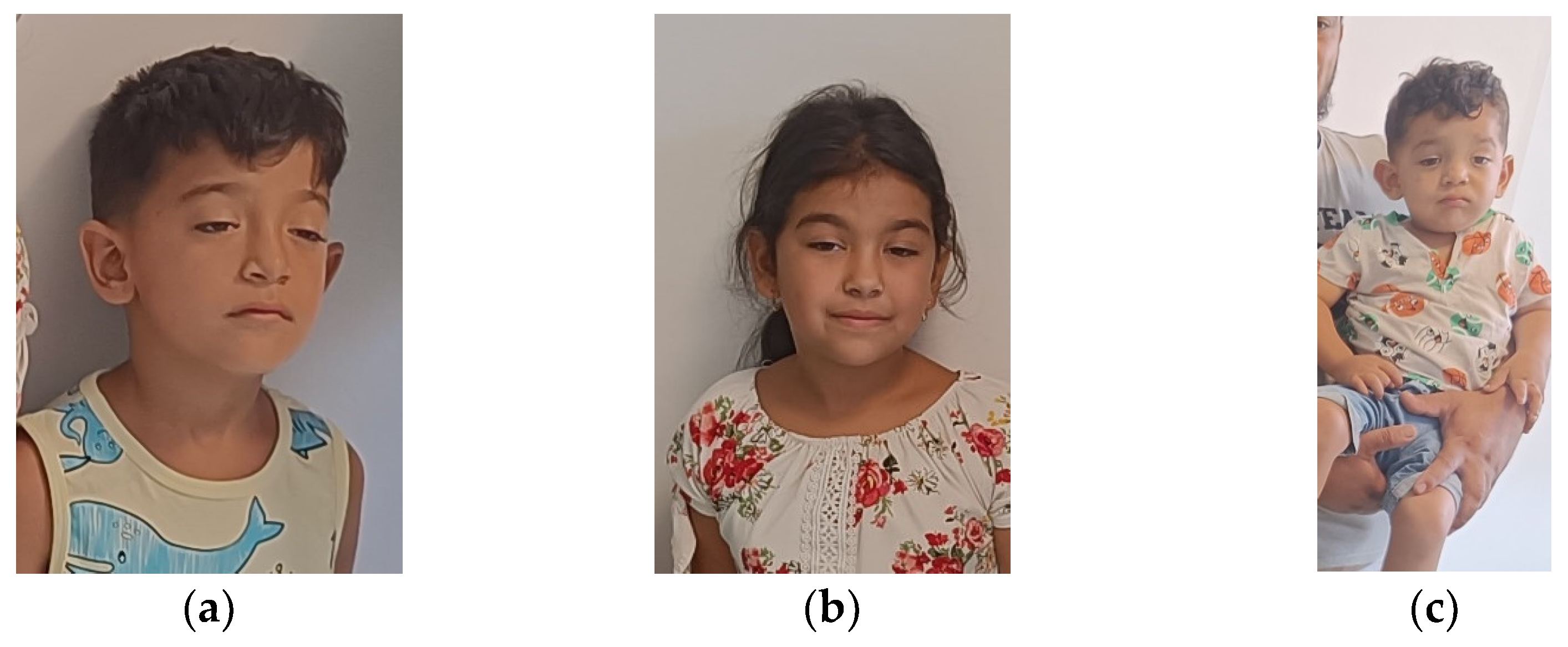



| Clinical Picture | Index Case (VI.3) | Older Sibling (VI.2) | Younger Sibling (VI.5). |
|---|---|---|---|
| Onset | At birth | Early age | Early age |
| Muscle fatigue | Present | Present | Present |
| Muscular weakness | Present | Present | Present |
| Bulbar symptoms | Not present | Not present | Not present |
| Ocular muscle impairment | Ptosis | Ptosis | Ptosis |
| Facial weakness | Present | Not present | Present |
| High-arched palate | Not present | Present | Present |
| Multiple dental anomalies | Present | Present | Present |
| Delayed motor milestones | Present | Not present | Present |
| Recurent respiratory infections: bronchitis and bronchopneumonias | Present | Not present | Not present |
| Pectus excavatum | Present | Present | Not present |
| Improvement with pyridostigmine | Present | Present | present |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petchesi, C.D.; Jurca, A.A.; Jurca, A.D.; Dorobantu, F.R.; Iuhas, A.R.; Severin, E.; Jurca, C.M. Congenital Myasthenic Syndrome-4C in a Consanguineous Romani Family: Genetic Insights and Clinical Implications. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15030235
Petchesi CD, Jurca AA, Jurca AD, Dorobantu FR, Iuhas AR, Severin E, Jurca CM. Congenital Myasthenic Syndrome-4C in a Consanguineous Romani Family: Genetic Insights and Clinical Implications. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(3):235. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15030235
Chicago/Turabian StylePetchesi, Codruta Diana, Aurora Alexandra Jurca, Alexandru Daniel Jurca, Florica Ramona Dorobantu, Alin Remus Iuhas, Emilia Severin, and Claudia Maria Jurca. 2025. "Congenital Myasthenic Syndrome-4C in a Consanguineous Romani Family: Genetic Insights and Clinical Implications" Diagnostics 15, no. 3: 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15030235
APA StylePetchesi, C. D., Jurca, A. A., Jurca, A. D., Dorobantu, F. R., Iuhas, A. R., Severin, E., & Jurca, C. M. (2025). Congenital Myasthenic Syndrome-4C in a Consanguineous Romani Family: Genetic Insights and Clinical Implications. Diagnostics, 15(3), 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15030235









