Mortality Prediction from Patient’s First Day PAAC Radiograph in Internal Medicine Intensive Care Unit Using Artificial Intelligence Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Preprocessing
2.2. Ethics Committee Approval
2.3. Feature Extraction
Radiologic Feature Extraction
2.4. Software and Statistical Analysis
2.5. Classification and Model Training
3. Results
3.1. Analyses
3.1.1. Performance with 74 Features
3.1.2. Feature Selection and Performance with 15 Selected Features
3.1.3. Performance with 10 Optimal Features
3.1.4. Performance with 4 Core Features
3.1.5. Overall Performance Summary
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Genc, A.C.; Özmen, E.; Cekic, D.; Issever, K.; Türkoğlu Genc, F.; Genc, A.B.; Toçoğlu, A.; Durmaz, Y.; Özkök, H.; Yaylacı, S.; et al. Comprehensive Analyses Using Machine Learning Models for Mortality Prediction in the Intensive Care Unit of Internal Medicine. J. Investig. Med. 2025, 73, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulur, O.; Kaplan Efe, F.; Ispir Iynem, H.K.; Koc, S.; Beyan, E. Comparison of APACHE II and Modified Charlson Index in Mortality Prediction in Patients at Medical Intensive Care Unit. Osman. J. Med. 2022, 44, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, R.-E.; Cho, J.; Shin, M.-K.; Oh, S.W.; Seong, Y.; Jeon, J.; Jeon, K.; Paik, S.; Lim, J.S.; Shin, S.J.; et al. Machine Learning-Based Mortality Prediction Model for Critically Ill Cancer Patients Admitted to the Intensive Care Unit (CanICU). Cancers 2023, 15, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kwon, Y.S.; Baek, M.S. Machine Learning Models to Predict 30-Day Mortality in Mechanically Ventilated Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.; Oh, A.R.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, D.Y.; Lee, J.-H.; Yang, K.; Kim, H.Y.; Park, R.W.; Park, J. Prediction Model for 30-Day Mortality after Non-Cardiac Surgery Using Machine-Learning Techniques Based on Preoperative Evaluation of Electronic Medical Records. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, K.-C.; Tau, E.; Chen, N.-C.; Chang, M.-C.; Yu, T.-C.; Wang, C.-C.; Liu, C.-F.; Kuo, C.-L. Machine Learning Algorithm Predicts Mortality Risk in Intensive Care Unit for Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammos, A.; Bechlioulis, A.; Chatzipanteliadou, S.; Sioros, S.A.; Floros, C.D.; Stamou, I.; Lakkas, L.; Kalogeras, P.; Bouratzis, V.; Katsouras, C.S.; et al. The Role of Prognostic Scores in Assessing the Prognosis of Patients Admitted in the Cardiac Intensive Care Unit: Emphasis on Heart Failure Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, I.U.; Aslam, N.; Aljabri, M.; Aljameel, S.S.; Kamaleldin, M.M.A.; Alshamrani, F.M.; Chrouf, S.M.B. Computational Intelligence-Based Model for Mortality Rate Prediction in COVID-19 Patients. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estiri, H.; Strasser, Z.H.; Klann, J.G.; Naseri, P.; Wagholikar, K.B.; Murphy, S.N. Predicting COVID-19 Mortality with Electronic Medical Records. NPJ Digit. Med. 2021, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olowolayemo, A.; Shams, W.K.; Omer, A.Y.I.; Mohammed, Y.; Batha, R.S. COVID-19 Mortality Risk Prediction Using Small Dataset of Chest X-ray Images. Artif. Intell. Appl. 2023, 3, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iori, M.; Di Castelnuovo, C.; Verzellesi, L.; Meglioli, G.; Lippolis, D.G.; Nitrosi, A.; Monelli, F.; Besutti, G.; Trojani, V.; Bertolini, M.; et al. Mortality Prediction of COVID-19 Patients Using Radiomic and Neural Network Features Extracted from a Wide Chest X-ray Sample Size. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, J.; Raghu, V.K.; Bontempi, D.; Christiani, D.C.; Mak, R.H.; Lu, M.T.; Aerts, H.J. Deep Learning to Estimate Lung Disease Mortality from Chest Radiographs. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Hwang, E.J.; Choi, Y.R.; Choi, H.; Goo, J.M.; Kim, Y.; Choi, J.; Park, C.M. A Deep Learning Model Using Chest Radiographs for Prediction of 30-Day Mortality in Patients with Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2023, 221, 586–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, S.M.; Hong, K.S.; Park, D.J. Deep Learning Approach for Early Prediction of COVID-19 Mortality Using Chest X-ray and Electronic Health Records. BMC Bioinform. 2023, 24, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Yang, J.; Yin, M.; Tang, Y.; Chen, L.; Xu, C.; Zhu, S.; Gao, J.; Liu, L.; Liu, X.; et al. Development and Validation of Multimodal Models to Predict the 30-Day Mortality of ICU Patients Based on Clinical Parameters and Chest X-rays. J. Digit. Imaging 2024, 37, 1312–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravi, V.; Narasimhan, H.; Pham, T.D. A Cost-Sensitive Deep Learning-Based Meta-Classifier for Pediatric Pneumonia Classification Using Chest X-Rays. Expert Syst. 2022, 39, e12966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Lv, W. Identification of Pneumonia in Chest X-Ray Image Based on Transformer. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2022, 2022, 5072666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Eom, S.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, C.O.; Rhee, Y.; You, S.C.; Hong, N. Chest X-ray-based opportunistic screening of sarcopenia using deep learning. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2023, 14, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitaula, C.; Shahi, T.B.; Marzbanrad, F.; Aryal, S. Automated Deep Learning Framework for COVID-19 Detection Using Chest X-Ray Images: A Novel Approach. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, D.M.; Elshennawy, N.M.; Sarhan, A.M. Deep-chest: Multi-classification deep learning model for diagnosing COVID-19, pneumonia, and lung cancer chest diseases. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 132, 104348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazi, F.; Benkuider, A.; Zraidi, M.; Ayoub, F.; Ibrahimi, K. Neighborhood Feature Extraction and Haralick Attributes for Medical Image Analysis: Application to Breast Cancer Mammography Image. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Wireless Networks and Mobile Communications (WINCOM), Istanbul, Turkiye, 26-28 October 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genc, A.C.; Arıcan, E. Obesity Classification: A Comparative Study of Machine Learning Models Excluding Weight and Height Data. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2025, 71, e20241282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verzellesi, L.; Botti, A.; Bertolini, M.; Trojani, V.; Carlini, G.; Nitrosi, A.; Monelli, F.; Besutti, G.; Castellani, G.; Remondini, D.; et al. Machine and Deep Learning Algorithms for COVID-19 Mortality Prediction Using Clinical and Radiomic Features. Electronics 2023, 12, 3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qin, D.; Qi, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X. Development and Validation of a Multimodal Feature Fusion Prognostic Model for Lumbar Degenerative Disease Based on Machine Learning: A Study Protocol. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e072139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardak, B.; Tan, M. Prediction of Mortality and Length of Stay with Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 29th Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU), Istanbul, Turkey, 9–11 June 2021; IEEE: Istanbul, Türkiye, 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ince, F.M.; Alkan Bilik, O.; Ince, H. Evaluating Mortality Predictors in COVID-19 Intensive Care Unit Patients: Insights into Age, Procalcitonin, Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, and Ferritin Lactate Index. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elghalid, R.A.M.; Aldeeb, F.H.A.; Alwirshiffani, A.; Andiasha, A.; Mohamed, A.A.I. Comparison of Some Machine Learning Algorithms for Predicting Heart Failure. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Engineering & MIS (ICEMIS), Benghazi, Libya, 4–6 July 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Dou, J.; Wang, H.; Lv, J. Comparison of Three Machine Learning Algorithms for Cardiovascular Disease Prediction. In Proceedings of the 7th IEEE Information Technology and Mechatronics Engineering Conference (ITOEC), Tianjin, China, 15–17 September 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 1513–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołodziejczak, M.M.; Sierakowska, K.; Tkachenko, Y.; Kowalski, P. Artificial Intelligence in the Intensive Care Unit: Present and Future in the COVID-19 Era. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, P.; Aggarwal, S.; Adam, S.; Imam, M. Parametric Optimization and Comparative Study of Machine Learning and Deep Learning Algorithms for Breast Cancer Diagnosis. Breast Dis. 2024, 43, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Hu, C.; Wei, S.; Yan, X. Breast Cancer Prediction Based on Multiple Machine Learning Algorithms. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2024, 25, 15330338241234791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, W.Y.; Thomson, R.M. Haralick Texture Feature Analysis for Characterization of Specific Energy and Absorbed Dose Distributions across Cellular to Patient Length Scales. Phys. Med. Biol. 2023, 68, 075006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeevitha, V.; Aroquiaraj, I.L. Haralick Feature-Based Texture Analysis from GLCM and SRDM for Breast Cancer Detection in Mammogram Images. In Proceedings of the 2025 4th International Conference on Sensors and Related Networks (SENNET)—Special Focus on Digital Healthcare, Vellore, India, 24–27 July 2025; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokhande, N.L.; Jaware, T.H. Innovative Approach to Lung Nodule Detection Using Random Walker Segmentation and Texture Analysis on CT Images. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Advancement in Electronics & Communication Engineering (AECE), GHAZIABAD, India, 23–24 November 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundra, S.; Vijay, S.; Mundra, A.; Gupta, P.; Goyal, M.K.; Kaur, M.; Khaitan, S.; Rajpoot, A.K. Classification of Imbalanced Medical Data: An Empirical Study of Machine Learning Approaches. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 43, 1933–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, T.; Yuan, Z.; He, Y.; Xu, H.; Guo, X.; Liu, Y. Prediction of T Stage of Rectal Cancer After Neoadjuvant Therapy by Multi-Parameter Magnetic Resonance Radiomics Based on Machine Learning Algorithms. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2024, 23, 15330338241305463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, T.; Panda, S.P. A Comparison of Machine Learning Algorithms in Predicting Pulmonary Diseases. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Machine Learning, Big Data, Cloud and Parallel Computing (COM-IT-CON), Faridabad, India, 26–27 May 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, I.; Bajaj, A.; Sharma, V. Comparative Analysis of Machine Learning Algorithms for Heart Disease Prediction. Int. J. Hybrid Intell. Syst. 2025, 21, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahyuni, W.; Kusrini, K.; Setyanto, A.; Utami, E. Feature Extraction Techniques for Patterned Images: A Systematic Literature Review. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Technology Innovation and Its Applications (ICTIIA), Medan, Indonesia, 12–13 September 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
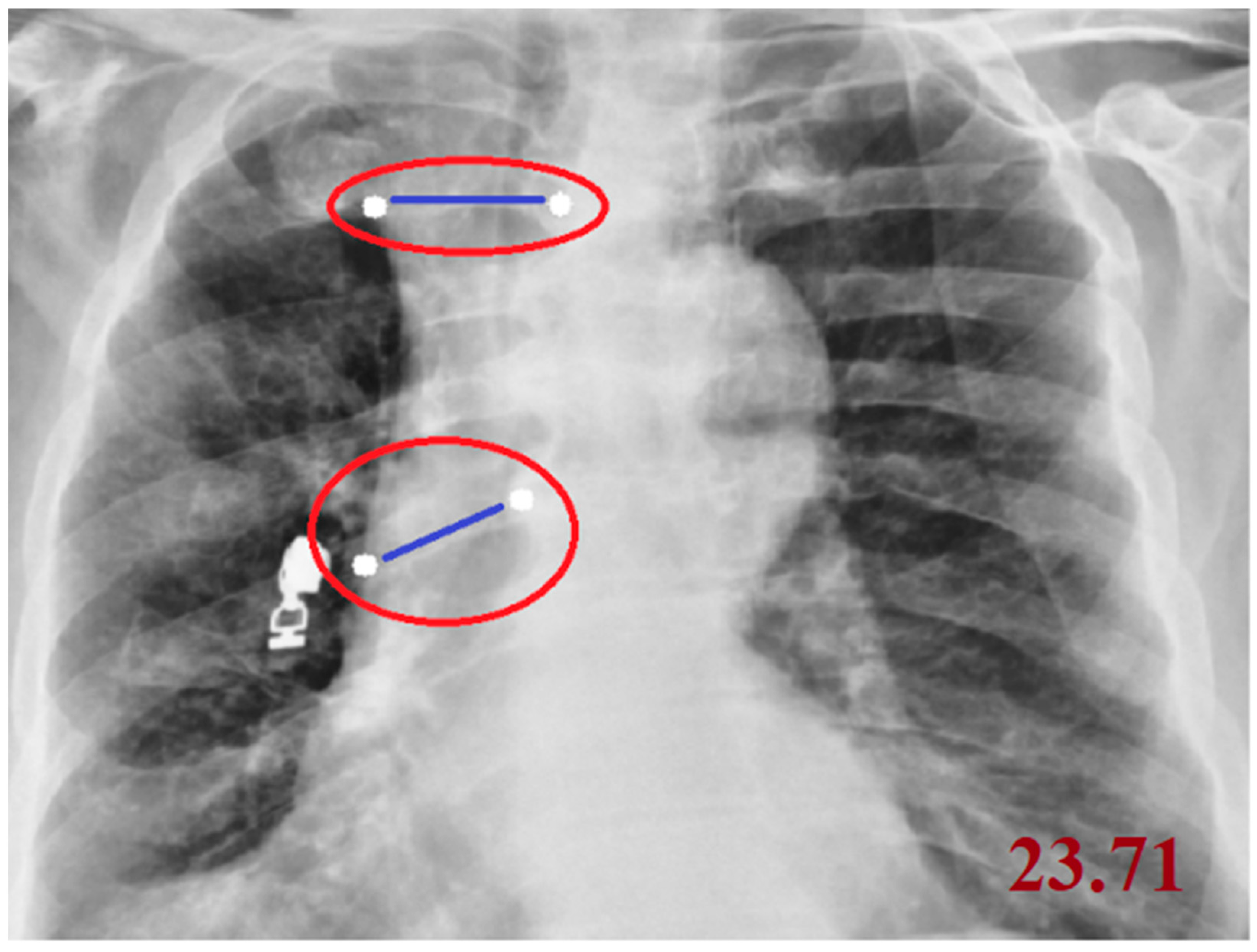
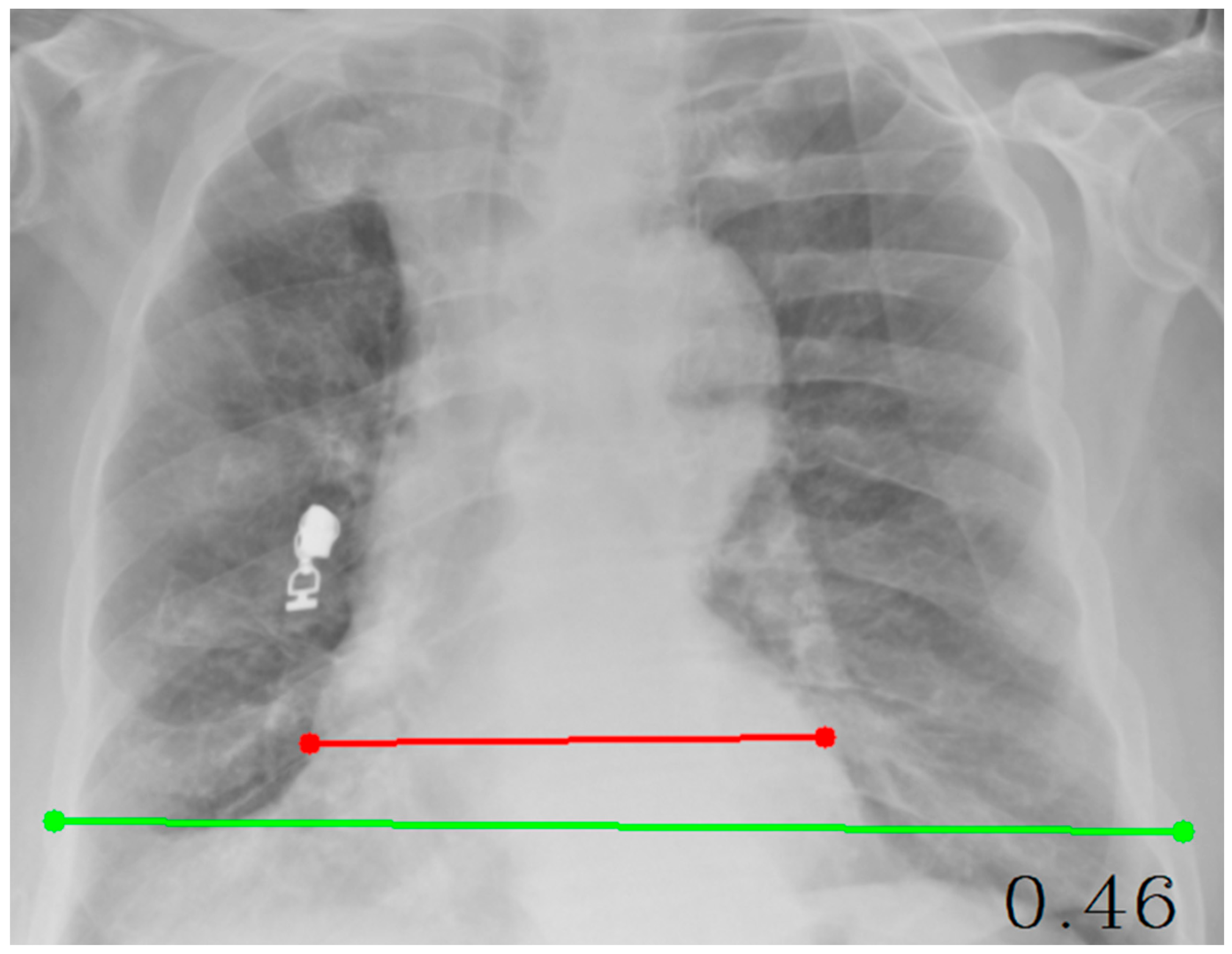
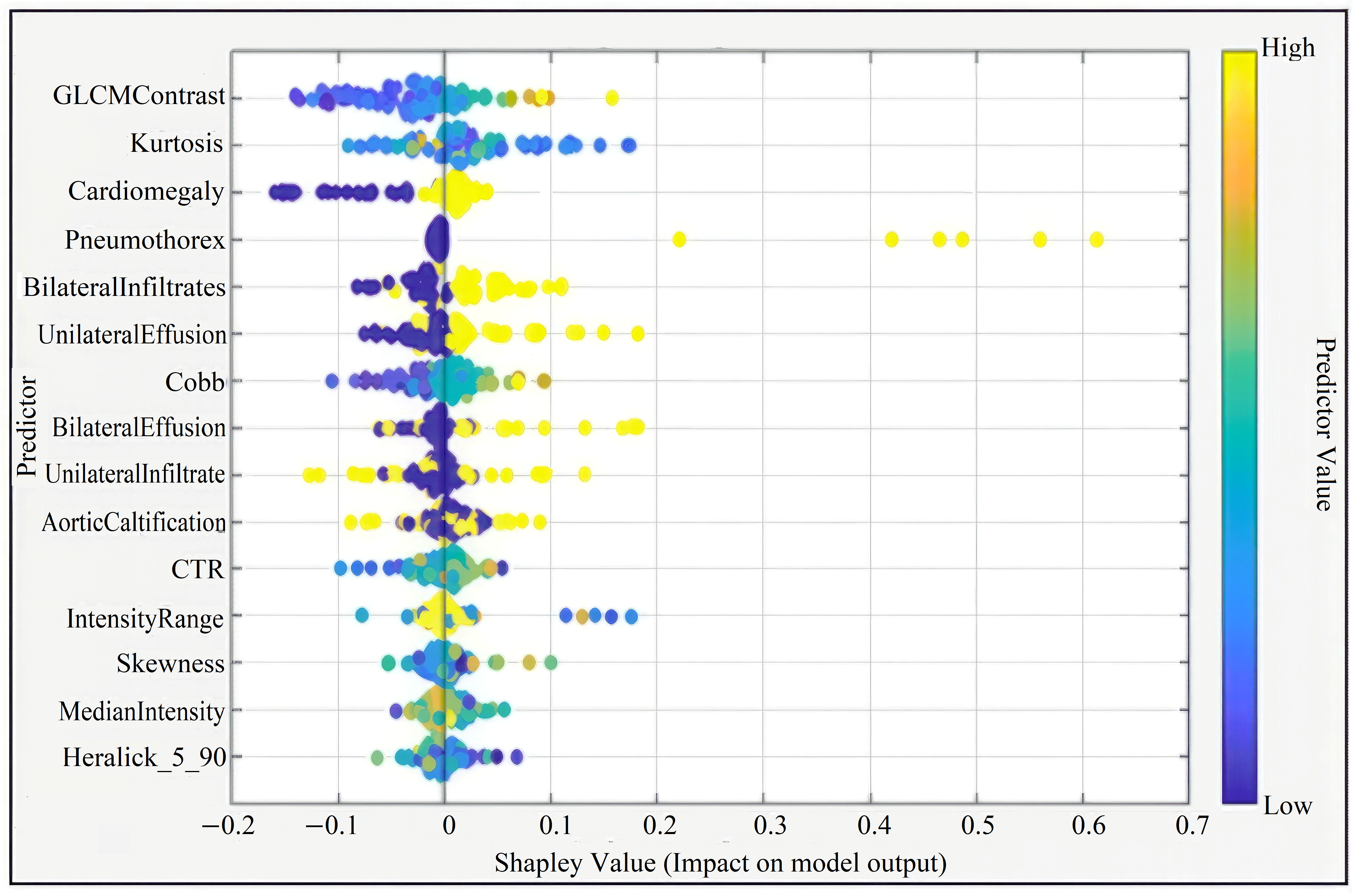
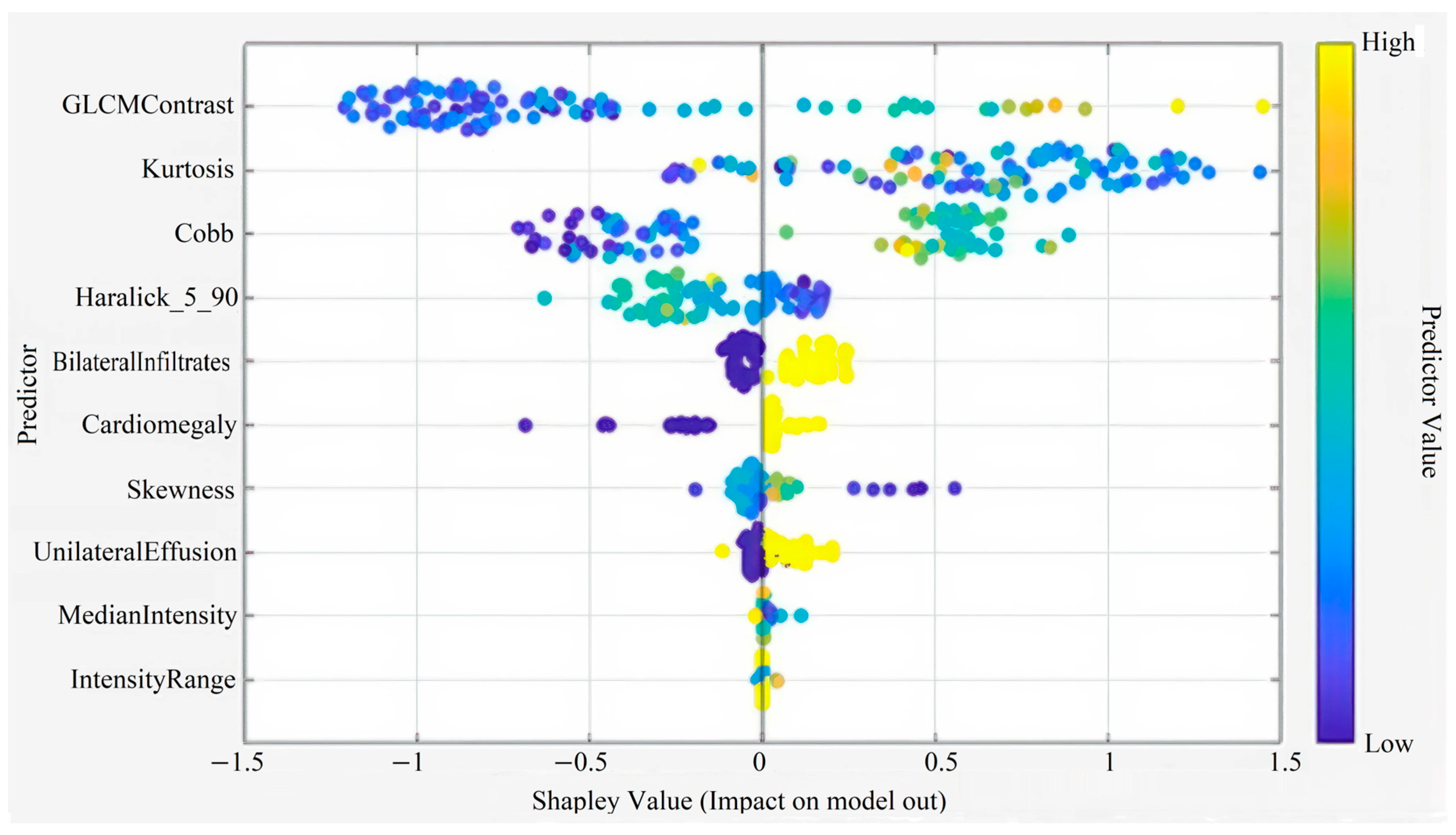
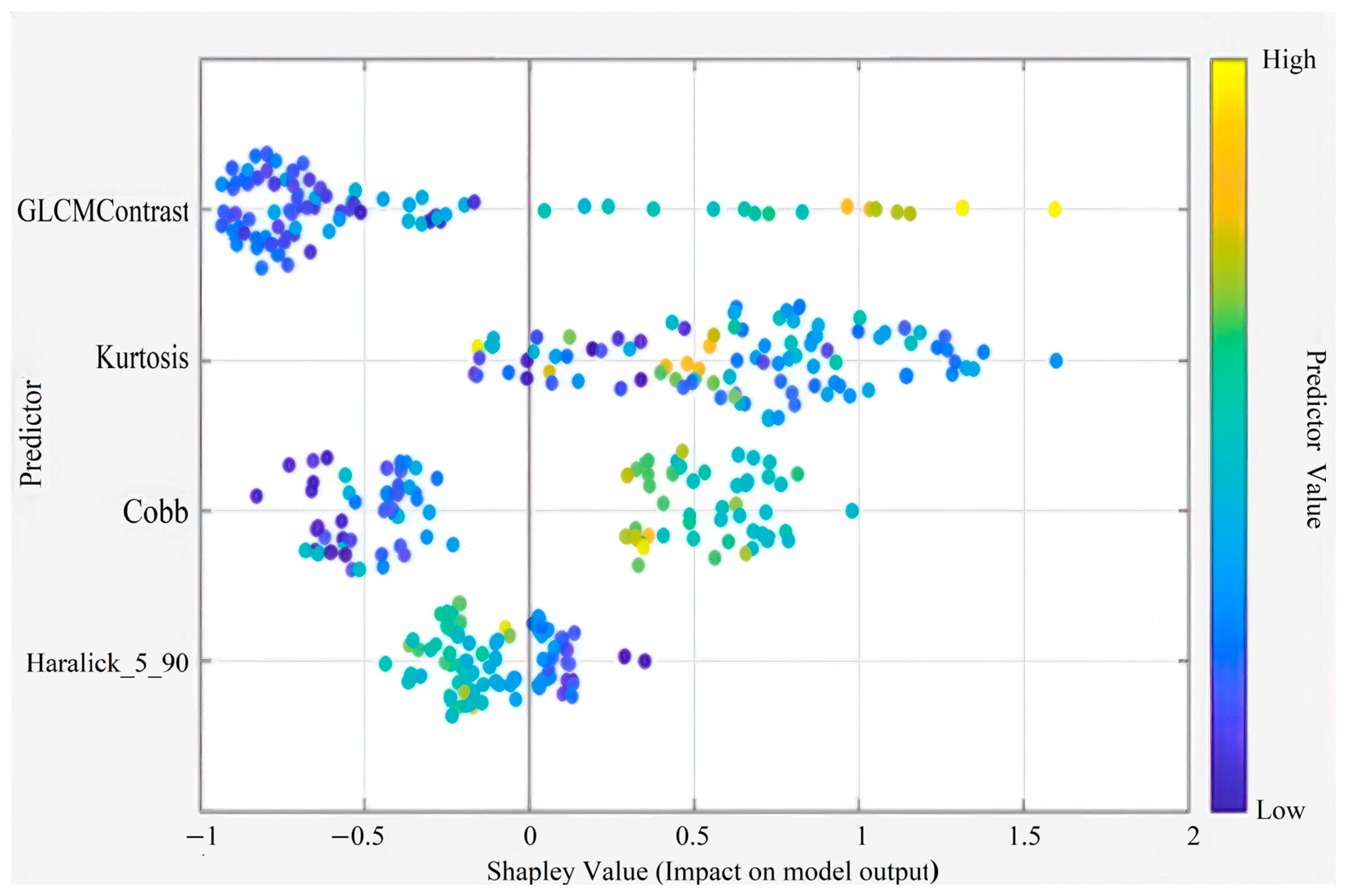
| Code Type | Libraries Used | Purpose/Task | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| CTR (Cardiothoracic Ratio) | cv2, numpy, tkinter | Calculates the ratio of cardiac width to thoracic width | Involves point selection and distance measurement |
| Cobb Angle | cv2, numpy, math, tkinter | Measures vertebral tilt and spinal curvature angle | Calculated using four manually selected points |
| Feature Extraction (GLCM/Haralick) | skimage, scipy, mahotas, numpy, cv2 | Extracts image texture and statistical features | Used for radiomic and texture-based analysis |
| Performance Metrics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Features | Best-Performing Algorithms | AUC | Sensitivity | Specificity | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
| 74 | WEİGHTED KNN | 0.91 | 0.79 | 0.90 | 0.92 | 0.79 | 0.85 |
| 74 | SVM KERNEL | 0.87 | 0.79 | 0.82 | 0.87 | 0.79 | 0.83 |
| 74 | MEDİUM KNN | 0.88 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.86 | 0.80 | 0.83 |
| 74 | QUADRATİC SVM | 0.87 | 0.71 | 0.90 | 0.92 | 0.71 | 0.80 |
| 74 | COSİNE KNN | 0.87 | 0.82 | 0.74 | 0.83 | 0.74 | 0.83 |
| 15 | M. GAUSSİAN SVM | 0.81 | 0.62 | 0.74 | 0.79 | 0.62 | 0.70 |
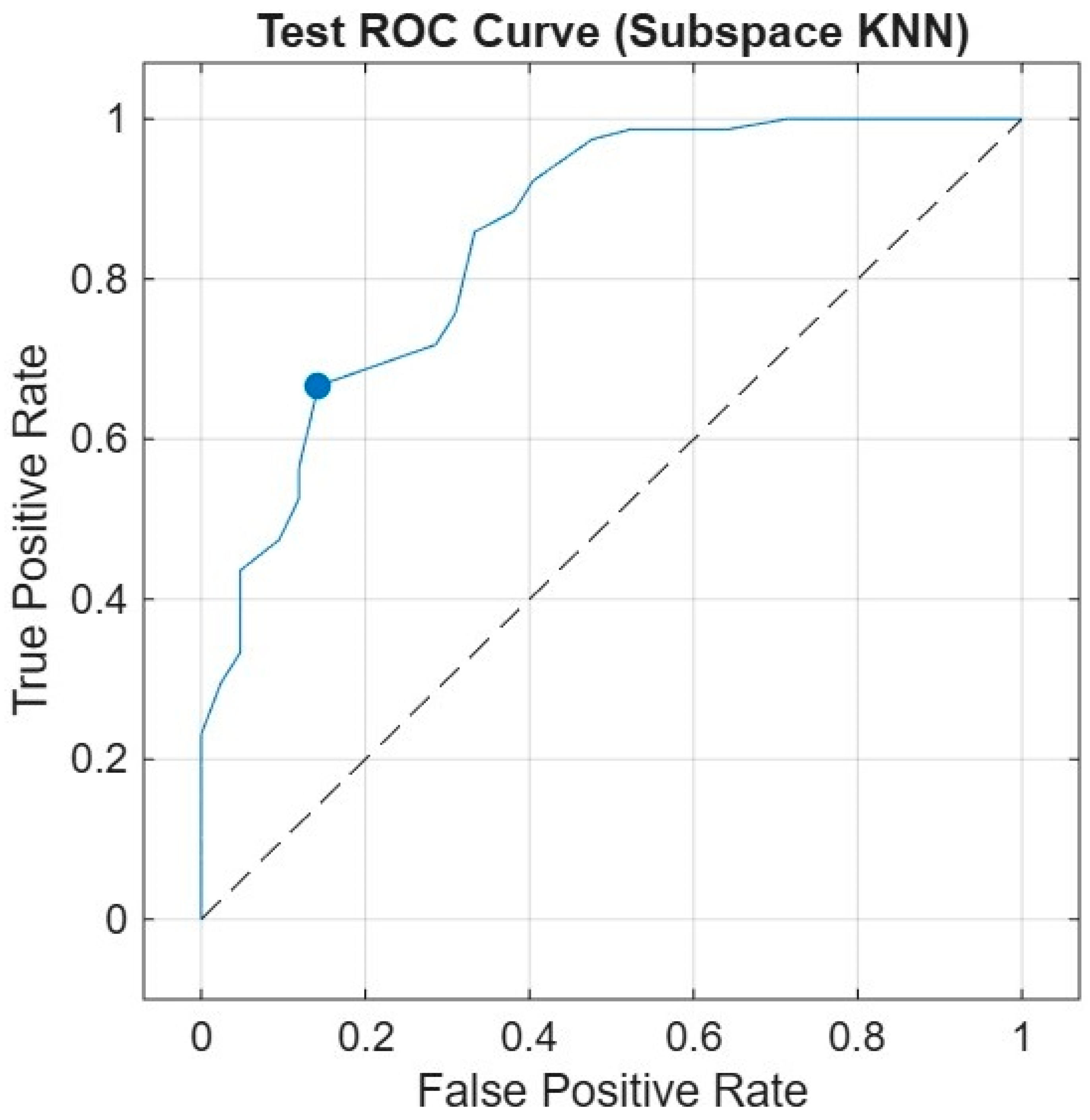
| 15 | SUBSPACE KNN | 0.79 | 0.62 | 0.77 | 0.81 | 0.62 | 0.70 |
| 15 | BOOSTED TREES | 0.79 | 0.75 | 0.74 | 0.82 | 0.75 | 0.74 |
| 15 | BAGGED TREES | 0.77 | 0.71 | 0.69 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.94 |
| 15 | QUADRATİC SVM | 0.79 | 0.62 | 0.82 | 0.84 | 0.62 | 0.72 |
| 10 | SUBSPACE KNN | 0.88 | 0.80 | 0.87 | 0.82 | 0.61 | 0.82 |
| 10 | BAGGED TREES | 0.75 | 0.69 | 0.69 | 0.80 | 0.71 | 0.75 |
| 10 | BOOSTED TREES | 0.76 | 0.67 | 0.80 | 0.81 | 0.79 | 0.80 |
| 4 | BAGGED TREES | 0.77 | 0.69 | 0.69 | 0.81 | 0.71 | 0.75 |
| 4 | RUSBoosted TREES | 0.76 | 0.66 | 0.85 | 0.87 | 0.66 | 0.75 |
| 4 | BOOSTED TREES | 0.80 | 0.67 | 0.80 | 0.84 | 0.67 | 0.75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gok, O.; Cavus, T.F.; Genc, A.C.; Yaylaci, S.; Ayhan, L.T. Mortality Prediction from Patient’s First Day PAAC Radiograph in Internal Medicine Intensive Care Unit Using Artificial Intelligence Methods. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 3138. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15243138
Gok O, Cavus TF, Genc AC, Yaylaci S, Ayhan LT. Mortality Prediction from Patient’s First Day PAAC Radiograph in Internal Medicine Intensive Care Unit Using Artificial Intelligence Methods. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(24):3138. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15243138
Chicago/Turabian StyleGok, Orhan, Türker Fedai Cavus, Ahmed Cihad Genc, Selcuk Yaylaci, and Lacin Tatli Ayhan. 2025. "Mortality Prediction from Patient’s First Day PAAC Radiograph in Internal Medicine Intensive Care Unit Using Artificial Intelligence Methods" Diagnostics 15, no. 24: 3138. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15243138
APA StyleGok, O., Cavus, T. F., Genc, A. C., Yaylaci, S., & Ayhan, L. T. (2025). Mortality Prediction from Patient’s First Day PAAC Radiograph in Internal Medicine Intensive Care Unit Using Artificial Intelligence Methods. Diagnostics, 15(24), 3138. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15243138






