Long-Term (>10 Years) Effects of Medical and Surgical Airway Obstruction Treatment on Dentofacial Morphology
Abstract
1. Introduction
- evaluate, at more than 10 years follow-up, the craniofacial changes in a unique population of children treated for airway obstruction, and
- compare long-term orofacial changes in children who had adenoidectomy versus children who were treated medically.
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
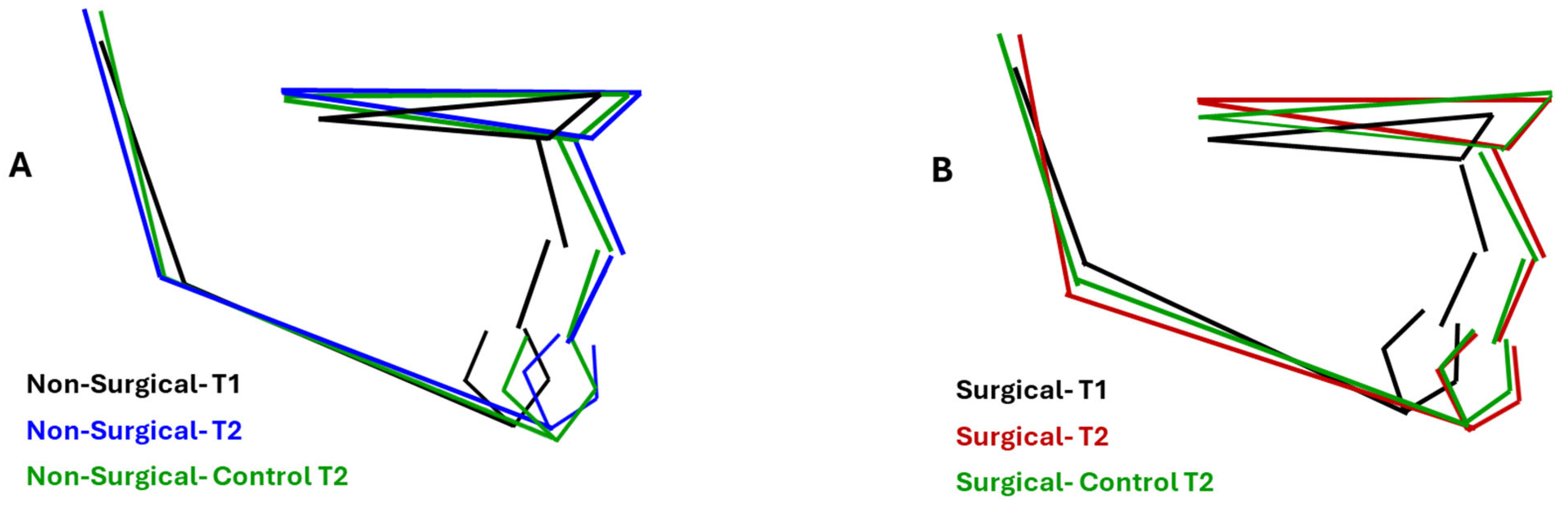
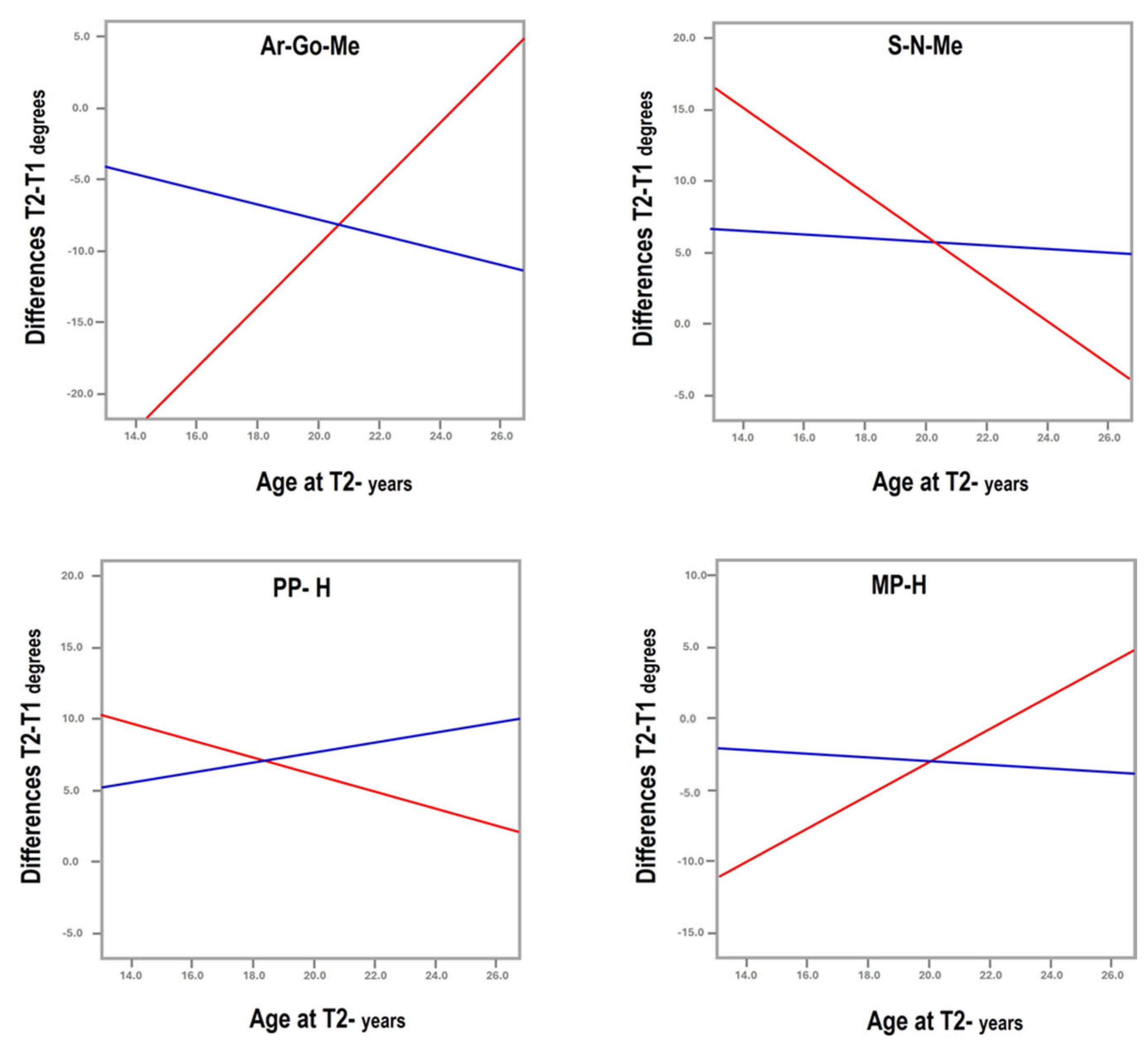
- Medical and surgical treatment can be beneficial, as both showed improvement in facial cephalometric features; however, surgery resulted in more improvement in mandibular shape and position. While the mandibular angle (Ar-Go-Me) closed in both treatment groups, the T2-T1 difference was statistically significantly greater in the surgical group (nearly 5°, Table 1). The closure indicates anterior rotation of the mandible and decrease in mandibular plane divergence. The consequent flattening of facial convexity (S-N-Me) was significantly greater in the surgical than the non-surgical group (T2-T1 difference = 4.4°, Table 1), further accentuating the efficacy of surgery (Figure 3).
- The patients who underwent surgery had more severe facial characteristics and were younger at pre-treatment (5.31 ± 1.99 years vs. 6.77 ± 2.84 years in surgical and non-surgical groups, Table 1). This initial condition may have been the reason for the otolaryngologist to perform and the parents to accept surgery. Treatment selection reflects the protocol followed by the treating otolaryngologist, technically indicating a selection bias, even if unavoidable in reference to the pertinent protocol. Consequently, the differences observed between groups may be attributed not only to the treatment modality but also to the initial severity of the condition, suggesting that severe obstructions are diagnosed early and are eligible for surgical treatment to reach the improvements observed in this study.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mattar, S.E.; Anselmo-Lima Val era, F.C.; Matsumoto, M.A. Skeletal and occlusal characteristics in mouth-breathing pre-school children. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 2004, 28, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proffit, W.R. The etiology of orthodontic problems-Respiratory pattern. In Contemporary Orthodontics, 4th ed.; Proffit, W.R., Fields, H.W., Jr., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 154–158. [Google Scholar]
- Trotman, C.A.; McNamara, J.A., Jr.; Dibbets, J.M.; van der Weele, L.T. Association of lip posture and the dimensions of the tonsils and sagittal airway with facial morphology. Angle Orthod. 1997, 67, 425–432. [Google Scholar]
- Macari, A.T.; Ghafari, J.G. Secondary analysis of airway obstruction in children with adenoid hypertrophy: Association with jaw size and position. Semin. Orthod. 2024, 29, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Yang, Z.; Ngan, P.; Luo, P.; Zhang, J.; Hua, F.; He, H. Association between adenotonsillar hypertrophy and dentofacial characteristics of children seeking for orthodontic treatment: A cross-sectional study. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 125, 101751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Wang, M.; Ngan, P.; Tao, Z.; Yu, X.; Hua, F.; He, H. Is adenotonsillar hypertrophy associated with dentofacial morphology? A systematic review and meta-analyses. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2025, 168, 524–541.e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angle, E.H. Treatment of Malocclusion of the Teeth, 7th ed.; SS White: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1907. [Google Scholar]
- Macari, A.T.; Bitar, M.A.; Ghafari, J.G. New insights on age-related association between nasopharyngeal airway clearance and facial morphology. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2012, 15, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linder-Aronson, S.; Woodside, D.G.; Lundstrom, A. Mandibular growth direction following adenoidectomy. Am. J. Orthod. 1986, 89, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, W.J.; McWilliam, J.S.; Linder-Aronson, S. Mandibular form and position related to changed mode of breathing—A 5-year longitudinal study. Angle Orthod. 1989, 59, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Woodside, D.G.; Linder-Aronson, S.; Lundstrom, A.; McWilliam, J. Mandibular and maxillary growth after changed mode of breathing. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1991, 100, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder-Aronson, S.; Woodside, D.G.; Hellsing, E.; Emerson, W. Normalization of incisor position after adenoidectomy. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1993, 103, 412–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattar, S.E.; Valera, F.C.; Faria, G.; Matsumoto, M.A.; Anselmo-Lima, W.T. Changes in facial morphology after adenotonsillectomy in mouth-breathing children. Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2011, 21, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahadir, O.; Caylan, R.; Bektas, D.; Bahadir, A. Effects of adenoidectomy in children with symptoms of adenoidal hypertrophy. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2006, 263, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arun, T.; Isik, F.; Sayinsu, K. Vertical growth changes after adenoidectomy. Angle Orthod. 2003, 73, 146–150. [Google Scholar]
- Mahony, D.; Karsten, A.; Linder-Aronson, S. Effects of adenoidectomy and changed mode of breathing on incisor and molar dentoalveolar heights and anterior face heights. Aust. Orthod. J. 2004, 20, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becking, B.E.; Verweij, J.P.; Kalf-Scholte, S.M.; Valkenburg, C.; Bakker, E.W.P.; van Merkesteyn, J.P.R. Impact of adenotonsillectomy on the dentofacial development of obstructed children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Orthod. 2017, 39, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorrees, C.F.A. Natural head position: The key to cephalometry. In Radiographic Cephalometry—From Basics to 3-D Imaging, 2nd ed.; Jacobson, A., Jacobson, R.L., Eds.; Quintessence Publishing Co.: Chicago, IL, USA, 2006; pp. 153–160. [Google Scholar]
- Macari, A.T.; Haddad, R.V. The Case for Environmental Etiology of Malocclusion in Modern Civilizations: Airway Morphology and Facial Growth. Semin. Orthod. 2016, 22, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, G.F.; Green, L.J.; Cunat, J.J. Relationships between variation of mandibular morphology and variation of nasopharyngeal airway size in monozygotic twins. Angle Orthod. 1973, 43, 129–135. [Google Scholar]
- Do Nascimento, R.R.; Masterson, D.; Trindade Mattos, C.; de Vasconcellos Vilella, O. Facial growth direction after surgical intervention to relieve mouth breathing: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Orofac. Orthop. 2018, 79, 412–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markkanen, S.; Rautiainen, M.; Niemi, P.; Helminen, M.; Peltomäki, T. Is securing normal dentofacial development an indication for tonsil surgery in children? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 133, 110006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghafari, J.G.; Macari, A.T. Interaction between the orthodontist and medical airway specialists on respiratory and nonrespiratory disturbances. In Integrated Clinical Orthodontics, 2nd ed.; Krishnan, V., Kuijpers-Jagtman, A.M., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 248–271. [Google Scholar]
- Redline, S.; Cook, K.; Chervin, R.D.; Ishman, S.; Baldassari, C.M.; Mitchell, R.B.; Tapia, I.E.; Amin, R.; Hassan, F.; Ibrahim, S.; et al. Pediatric Adenotonsillectomy Trial for Snoring (PATS) Study Team. Adenotonsillectomy for Snoring and Mild Sleep Apnea in Children: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2023, 330, 2084–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habumugisha, J. Contemporary Approaches to Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Review of Orthodontic and Non-Orthodontic Interventions in Children and Adults. Oral 2025, 5, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habumugisha, J.; Cheng, B.; Ma, S.Y.; Zhao, M.Y.; Bu, W.Q.; Wang, G.L.; Liu, Q.; Zou, R.; Wang, F. A non-randomized concurrent controlled trial of myofunctional treatment in the mixed dentition children with functional mouth breathing assessed by cephalometric radiographs and study models. BMC Pediatr. 2022, 22, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
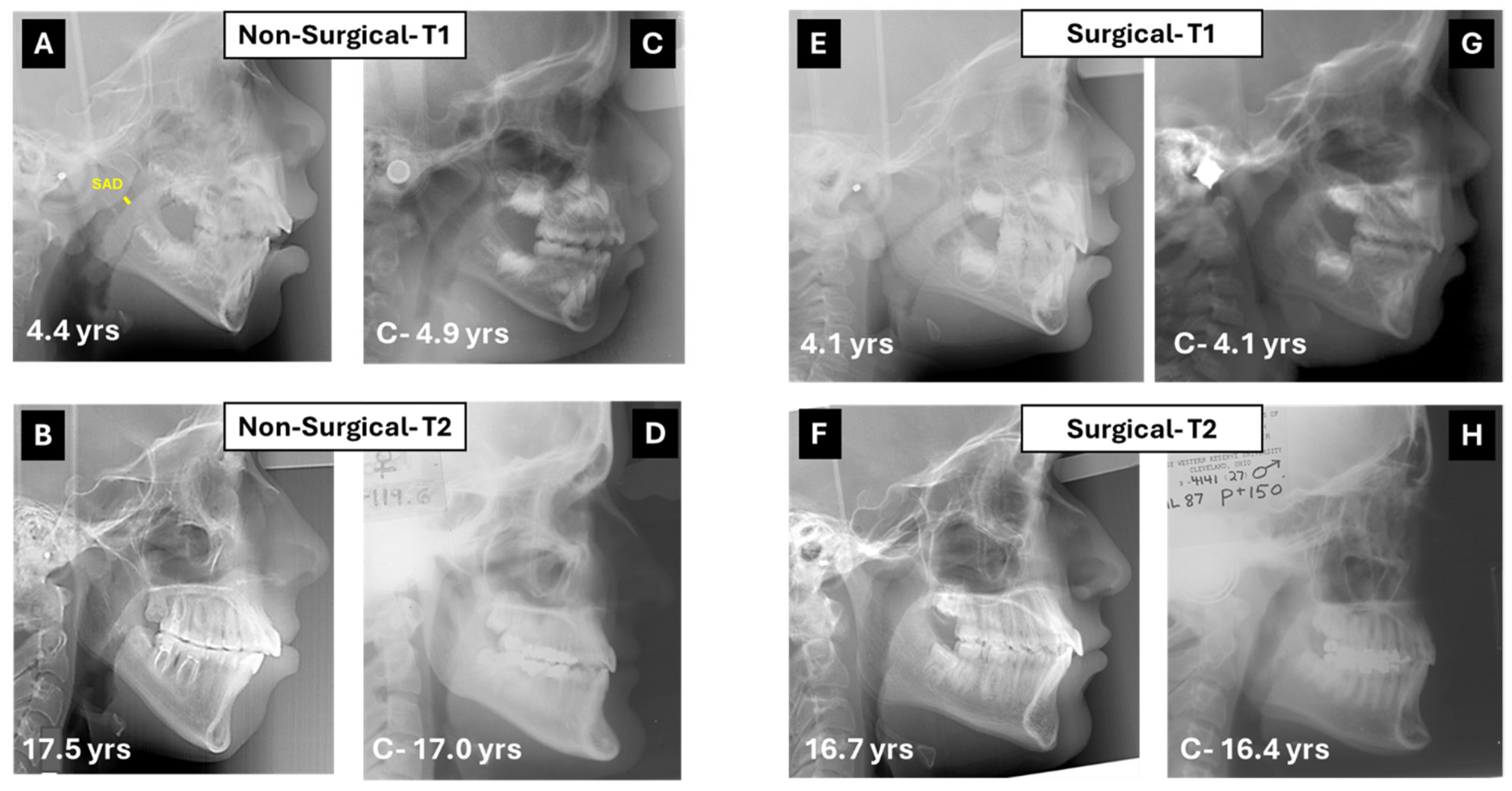
| Non-Surgical Group N = 23 | Surgical Group N = 34 | Non-Surgical | Surgical | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | Sig. | T1 | T2 | Sig. | T2-T1 Diff. | T2-T1 Diff. | Sig. | |||||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||||
| Age (years) | 6.77 | 2.84 | 19.4 | 3.07 | 5.31 | 1.99 | 18.4 | 2.03 | 12.63 | 2.86 | 13.09 | 2.11 | |||
| Skeletal Measurements | |||||||||||||||
| ANB° | 4.40 | 2.88 | 3.61 | 3.54 | 0.20 | 4.47 | 2.39 | 2.61 | 1.82 | 0.00 | −0.79 | 2.84 | −1.86 | 2.00 | 0.10 |
| PP-MP° | 30.00 | 4.81 | 25.66 | 7.18 | 0.00 | 29.37 | 4.39 | 23.80 | 5.72 | 0.00 | −4.34 | 5.39 | −5.57 | 5.48 | 0.41 |
| LFH/TFH | 56.84 | 2.27 | 55.52 | 2.08 | 0.05 | 57.43 | 2.05 | 55.96 | 2.66 | 0.00 | −1.32 | 3.06 | −1.47 | 2.51 | 0.97 |
| SNA° | 84.67 | 3.45 | 84.57 | 3.73 | 0.92 | 86.06 | 2.94 | 83.43 | 3.43 | 0.00 | −0.10 | 4.81 | −2.63 | 3.31 | 0.02 |
| ANS-PNS mm | 43.41 | 3.52 | 52.83 | 3.93 | 0.00 | 42.01 | 3.04 | 52.07 | 3.84 | 0.00 | 9.42 | 4.95 | 10.06 | 4.08 | 0.59 |
| PP-H° | −5.20 | 4.40 | 2.47 | 2.60 | 0.00 | −5.23 | 5.76 | 2.23 | 2.53 | 0.00 | 7.67 | 4.75 | 7.46 | 5.40 | 0.89 |
| SNB° | 80.26 | 3.13 | 80.97 | 3.49 | 0.46 | 81.71 | 3.66 | 80.85 | 3.57 | 0.17 | 0.71 | 4.48 | −0.86 | 3.56 | 0.15 |
| MP-SN° | 34.16 | 5.38 | 31.14 | 5.07 | 0.01 | 34.29 | 2.59 | 31.75 | 5.21 | 0.00 | −3.02 | 4.70 | −2.54 | 4.64 | 0.70 |
| S-N-Me° | 57.37 | 4.84 | 63.80 | 4.12 | 0.00 | 55.02 | 5.15 | 64.85 | 3.48 | 0.00 | 6.43 | 4.73 | 9.83 | 6.32 | 0.03 |
| Co-Gn mm | 91.46 | 7.48 | 115.58 | 10.63 | 0.00 | 87.12 | 8.01 | 115.16 | 8.36 | 0.00 | 24.12 | 10.15 | 28.04 | 9.55 | 0.14 |
| Ar-Go-Me° | 133.90 | 7.83 | 126.66 | 6.42 | 0.00 | 137.69 | 8.66 | 125.31 | 6.43 | 0.00 | −7.24 | 4.97 | −12.38 | 8.25 | 0.01 |
| N-Gn mm | 98.82 | 8.55 | 119.49 | 8.76 | 0.00 | 93.30 | 8.96 | 120.06 | 7.29 | 0.00 | 20.67 | 8.21 | 26.76 | 10.07 | 0.02 |
| Dentoalveolar Measurements | |||||||||||||||
| U1/NA° | 15.06 | 7.58 | 22.37 | 8.77 | 0.01 | 13.90 | 7.52 | 25.52 | 5.56 | 0.00 | 7.31 | 12.09 | 11.62 | 9.61 | 0.14 |
| U1/PP° | 102.87 | 7.54 | 111.98 | 6.82 | 0.00 | 102.78 | 7.45 | 115.59 | 5.64 | 0.00 | 9.11 | 11.48 | 12.80 | 9.50 | 0.19 |
| L1/NB° | 23.86 | 6.20 | 26.44 | 7.15 | 0.03 | 23.39 | 3.18 | 27.09 | 5.83 | 0.00 | 2.58 | 0.95 | 3.7 | 2.65 | 0.17 |
| L1/MP° | 89.90 | 6.73 | 93.63 | 8.81 | 0.02 | 89.01 | 4.52 | 94.92 | 7.62 | 0.00 | 3.73 | 6.79 | 5.91 | 7.57 | 0.27 |
| OB mm | 0.49 | 2.45 | 0.97 | 1.79 | 0.26 | 0.39 | 1.77 | 1.24 | 1.61 | 0.03 | 0.48 | 2.00 | 0.85 | 2.18 | 0.52 |
| OJ mm | 2.93 | 2.26 | 3.33 | 1.64 | 0.37 | 2.88 | 2.18 | 3.34 | 1.74 | 0.34 | 0.40 | 2.12 | 0.46 | 2.73 | 0.94 |
| Airway | |||||||||||||||
| SAD mm | 4.39 | 2.95 | 11.84 | 2.81 | 0.00 | 2.96 | 2.49 | 16.25 | 2.94 | 0.00 | 7.45 | 3.31 | 13.29 | 3.22 | 0.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Macari, A.T.; Babakhanian, A.; Karam, I.; Ghafari, J.G. Long-Term (>10 Years) Effects of Medical and Surgical Airway Obstruction Treatment on Dentofacial Morphology. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 3079. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15233079
Macari AT, Babakhanian A, Karam I, Ghafari JG. Long-Term (>10 Years) Effects of Medical and Surgical Airway Obstruction Treatment on Dentofacial Morphology. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(23):3079. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15233079
Chicago/Turabian StyleMacari, Anthony T., Annie Babakhanian, Ingrid Karam, and Joseph G. Ghafari. 2025. "Long-Term (>10 Years) Effects of Medical and Surgical Airway Obstruction Treatment on Dentofacial Morphology" Diagnostics 15, no. 23: 3079. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15233079
APA StyleMacari, A. T., Babakhanian, A., Karam, I., & Ghafari, J. G. (2025). Long-Term (>10 Years) Effects of Medical and Surgical Airway Obstruction Treatment on Dentofacial Morphology. Diagnostics, 15(23), 3079. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15233079






