3D Latent Diffusion Model for MR-Only Radiotherapy: Accurate and Consistent Synthetic CT Generation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Dataset and Preprocessing
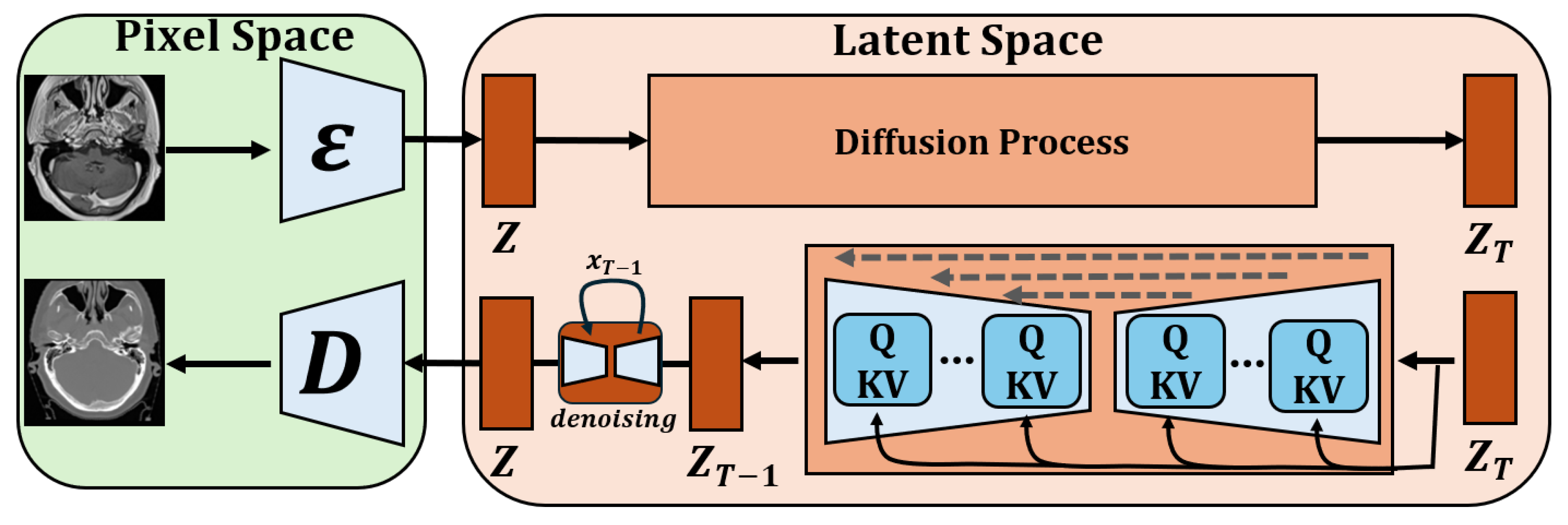
3.2. Model Architecture
3.3. Loss Functions and Optimization
3.4. Model Evaluation
3.5. Implementation Details
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Quantitative Analysis
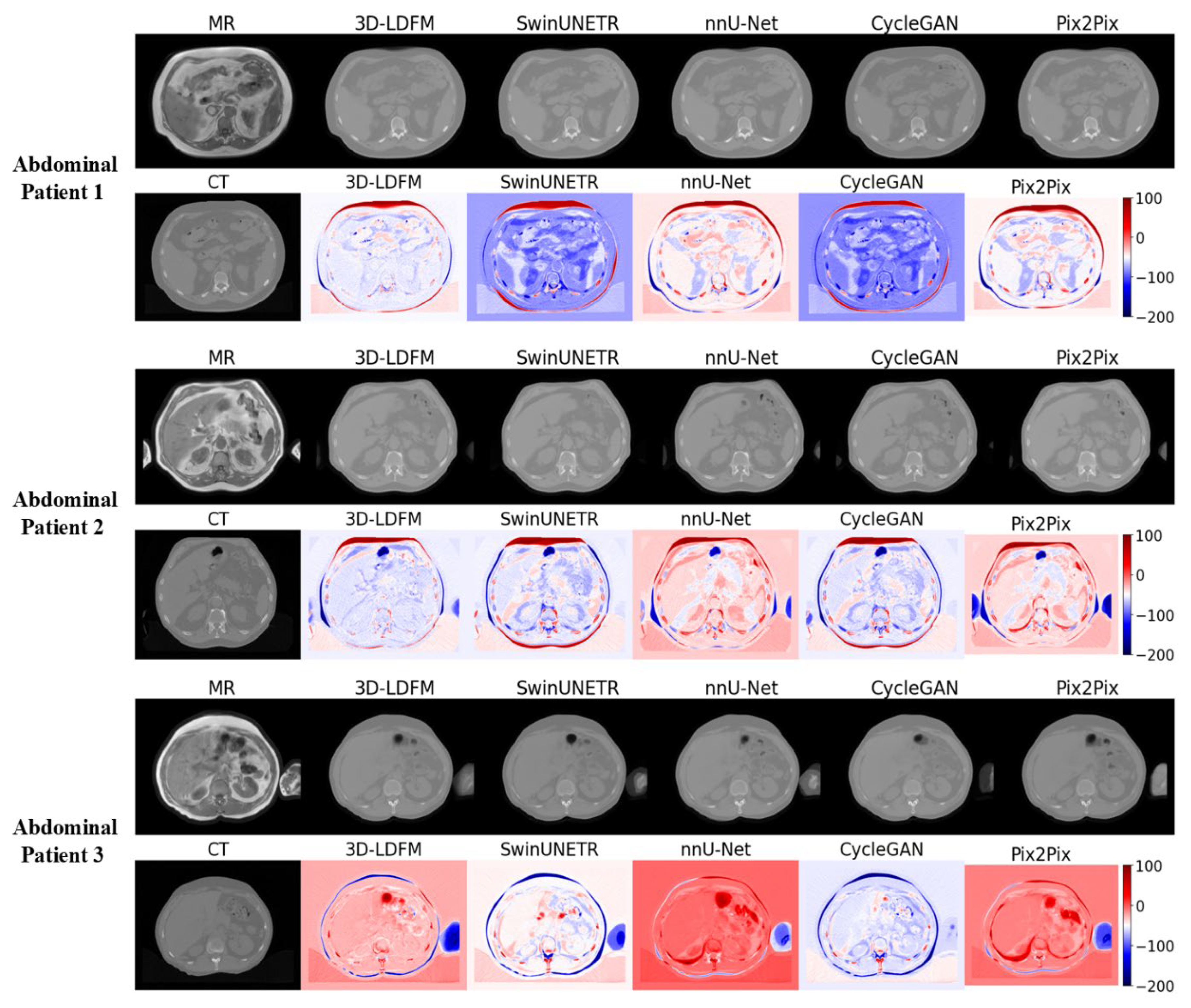
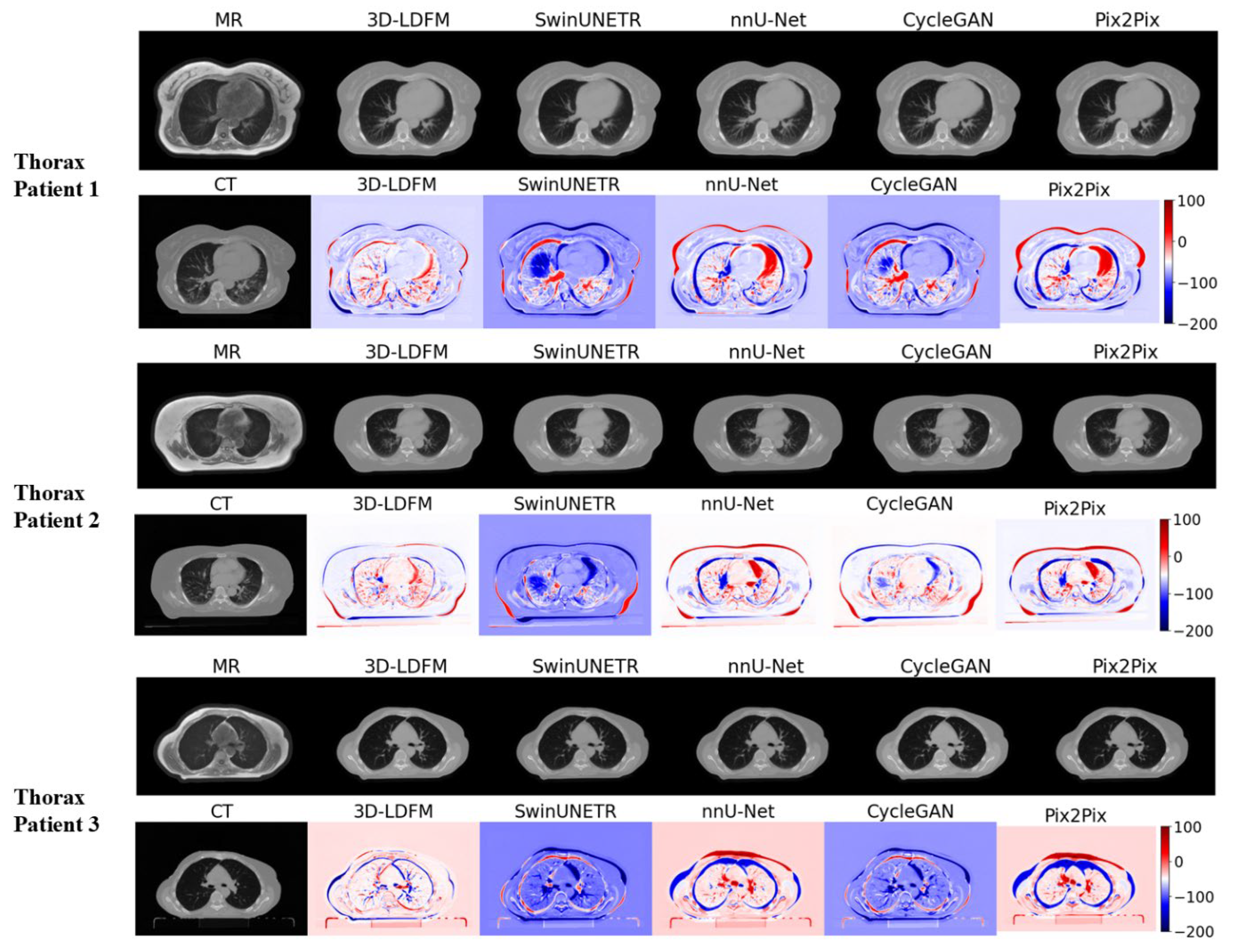
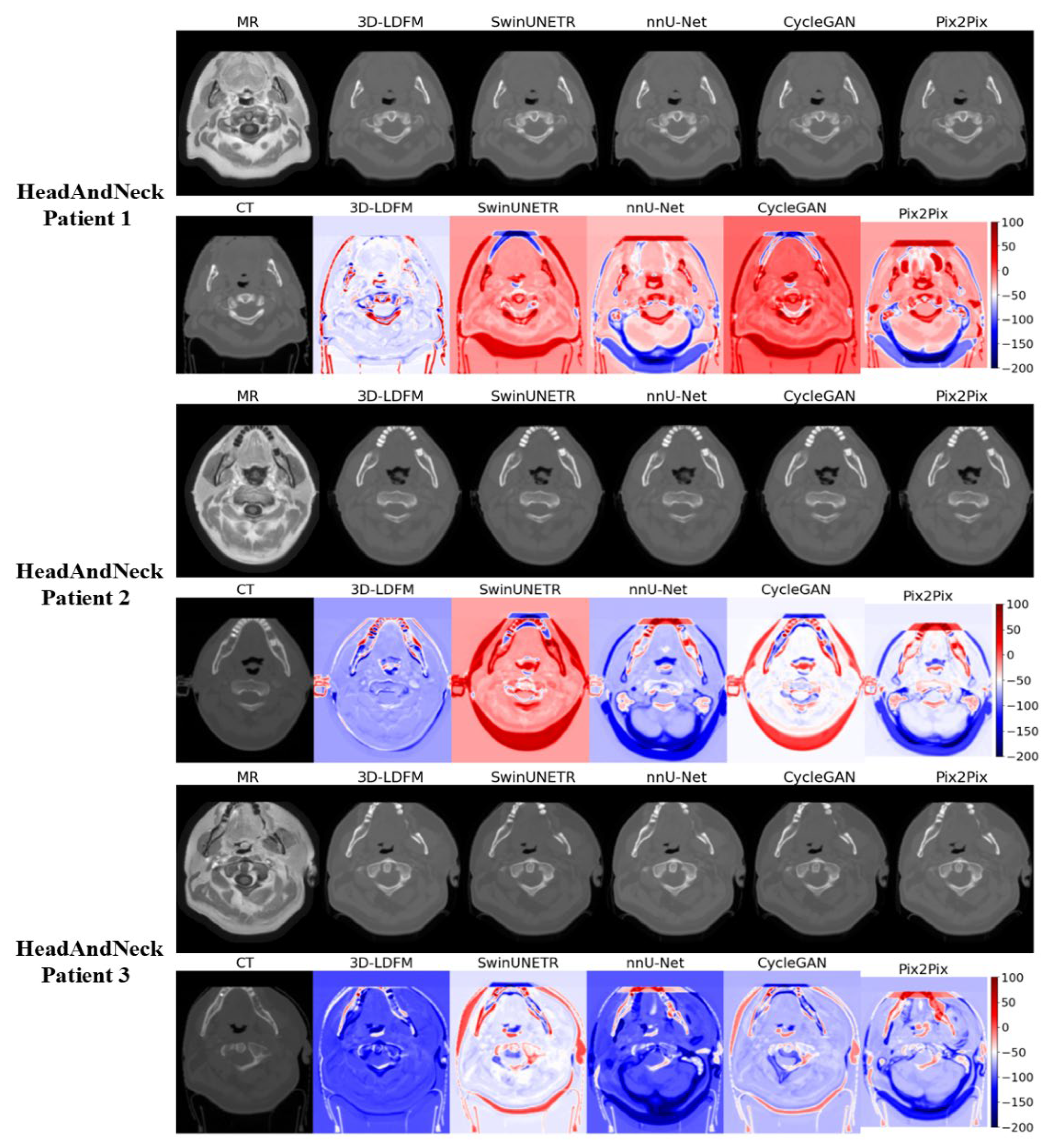
4.2. Assessment and Error Mapping
4.3. Proposed Model Benchmarking with State-of-the-Art Methods
4.4. Computational Efficiency
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3D | Three-Dimensional |
| AB | Abdomen (Anatomical Region) |
| AMP | Automatic Mixed Precision |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| DDPM | Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model |
| DSC | Dice Similarity Coefficient |
| GAN | Generative Adversarial Network |
| HN | Head and Neck (Anatomical Region) |
| HU | Hounsfield Unit |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| LDM | Latent Diffusion Model |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| MSE | Mean Squared Error |
| PSNR | Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio |
| sCT | Synthetic Computed Tomography |
| SSIM | Structural Similarity Index Measure |
| TH | Thorax (Anatomical Region) |
| VAE | Variational Autoencoder |
References
- Kitson, S.L. Modern Medical Imaging and Radiation Therapy; Open Med Science: Singapore, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Lazaros, K.; Adam, S.; Krokidis, M.G.; Exarchos, T.; Vlamos, P.; Vrahatis, A.G. Non-invasive biomarkers in the era of big data and machine learning. Sensors 2025, 25, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahloul, M.A.; Jabeen, S.; Benoumhani, S.; Alsaleh, H.A.; Belkhatir, Z.; Al-Wabil, A. Advancements in synthetic CT generation from MRI: A review of techniques, and trends in radiation therapy planning. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2024, 25, e14499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lother, D.; Robert, M.; Elwood, E.; Smith, S.; Tunariu, N.; Johnston, S.R.; Parton, M.; Bhaludin, B.; Millard, T.; Downey, K. Imaging in metastatic breast cancer, CT, PET/CT, MRI, WB-DWI, CCA: Review and new perspectives. Cancer Imaging 2023, 23, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, M.A.; Ahamad, S.; Saad, S.A.; Dafhalla, A.; Alqushaibi, A.; Qureshi, R. Enhancing Predictive Accuracy for Recurrence-Free Survival in Head and Neck Tumor: A Comparative Study of Weighted Fusion Radiomic Analysis. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, M.K.; Chaturvedi, R. Synthetic data revolutionizes rare disease research: How large language models and generative AI are overcoming data scarcity and privacy challenges. Int. J. Recent Innov. Trends Comput. Commun. 2023, 11, 1368–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, E.; Muneer, A.; Zhang, J.; Xia, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, C.; Heymach, J.V.; Wu, J.; Le, X. Progress and challenges of artificial intelligence in lung cancer clinical translation. npj Precis. Oncol. 2025, 9, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, J.; Taroni, J.N.; Allaway, R.J.; Prasad, D.V.; Guinney, J.; Greene, C. Machine learning in rare disease. Nat. Methods 2023, 20, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decherchi, S.; Pedrini, E.; Mordenti, M.; Cavalli, A.; Sangiorgi, L. Opportunities and challenges for machine learning in rare diseases. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 747612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.-C.; Tenenholtz, N.A.; Rogers, J.K.; Schwarz, C.G.; Senjem, M.L.; Gunter, J.L.; Andriole, K.P.; Michalski, M. Medical image synthesis for data augmentation and anonymization using generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Simulation and Synthesis in Medical Imaging, Granada, Spain, 16 September 2018; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Frid-Adar, M.; Diamant, I.; Klang, E.; Amitai, M.; Goldberger, J.; Greenspan, H. GAN-based synthetic medical image augmentation for increased CNN performance in liver lesion classification. Neurocomputing 2018, 321, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Al Khalil, Y.; Amirrajab, S.; Sun, C.; Breeuwer, M.; Pluim, J.; Elen, B.; Ertaylan, G.; Dumontier, M. Generative AI for synthetic data across multiple medical modalities: A systematic review of recent developments and challenges. Comput. Biol. Med. 2025, 189, 109834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Li, N.; Zhao, Z.; Fan, X.; Chang, E.I.-C.; Xu, Y. MRI cross-modality image-to-image translation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Harms, J.; Wang, T.; Liu, Y.; Shu, H.K.; Jani, A.B.; Curran, W.J.; Mao, H.; Liu, T.; Yang, X. MRI-only based synthetic CT generation using dense cycle consistent generative adversarial networks. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, 3565–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armanious, K.; Jiang, C.; Fischer, M.; Küstner, T.; Hepp, T.; Nikolaou, K.; Gatidis, S.; Yang, B. MedGAN: Medical image translation using GANs. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2020, 79, 101684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.; Hinton, G.; Wells, A.J.; Van Der Veken, J.; Bajger, M.; Lee, G.; Liu, Y.; Chong, C.; Poonnoose, S.; Agzarian, M. Imaging evaluation of a proposed 3D generative model for MRI to CT translation in the lumbar spine. Spine J. 2023, 23, 1602–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, A.; Karimian, A.; Fatemizadeh, E.; Arabi, H.; Zaidi, H. A new deep convolutional neural network design with efficient learning capability: Application to CT image synthesis from MRI. Med. Phys. 2020, 47, 5158–5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, B.; Albarqouni, S. MRI to CT translation with GANs. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.05259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, H.; Dong, M.; Nejad-Davarani, S.P.; Glide-Hurst, C.K. SA-GAN: Structure-aware GAN for organ-preserving synthetic CT generation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Strasbourg, France, 27 September–1 October 2021; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; pp. 471–481. [Google Scholar]
- van der Ouderaa, T.F.; Worrall, D.E.; van Ginneken, B. Chest CT super-resolution and domain-adaptation using memory-efficient 3D reversible GANs. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.00295. [Google Scholar]
- Chartsias, A.; Joyce, T.; Dharmakumar, R.; Tsaftaris, S.A. Adversarial image synthesis for unpaired multi-modal cardiac data. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Simulation and Synthesis in Medical Imaging, Québec City, QC, Canada, 10 September 2017; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; pp. 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Sherwani, M.K.; Gopalakrishnan, S. A systematic literature review: Deep learning techniques for synthetic medical image generation and their applications in radiotherapy. Front. Radiol. 2024, 4, 1385742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muneer, A.; Waqas, M.; Saad, M.B.; Showkatian, E.; Bandyopadhyay, R.; Xu, H.; Li, W.; Chang, J.Y.; Liao, Z.; Haymaker, C. From Classical Machine Learning to Emerging Foundation Models: Review on Multimodal Data Integration for Cancer Research. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2507.09028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Jafarpour, F. Synthetic CT Generation from MR Images: A U-Net Deep Learning Approach. 2024. Available online: https://thesis.unipd.it/handle/20.500.12608/73701 (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- Liu, Y.; Chen, A.; Shi, H.; Huang, S.; Zheng, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, X. CT synthesis from MRI using multi-cycle GAN for head-and-neck radiation therapy. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2021, 91, 101953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.-Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2223–2232. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, S.; Aziz, M.T.; Nabil, H.R.; Jim, J.R.; Mridha, M.F.; Kabir, M.M.; Asai, N.; Shin, J. Generative adversarial networks (GANs) in medical imaging: Advancements, applications, and challenges. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 35728–35753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, M. Modeling Fine-grained Long-range Visual Dependency for Deep Learning-based Medical Image Analysis. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, S.; Abouei, E.; Wynne, J.; Chang, C.W.; Wang, T.; Qiu, R.L.; Li, Y.; Peng, J.; Roper, J.; Patel, P. Synthetic CT generation from MRI using 3D transformer-based denoising diffusion model. Med. Phys. 2024, 51, 2538–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinaya, W.H.; Tudosiu, P.-D.; Dafflon, J.; Da Costa, P.F.; Fernandez, V.; Nachev, P.; Ourselin, S.; Cardoso, M.J. Brain imaging generation with latent diffusion models. In Proceedings of the MICCAI Workshop on Deep Generative Models, Singapore, 18–22 September 2022; pp. 117–126. [Google Scholar]
- Kui, X.; Liu, B.; Sun, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhang, M.; Liang, W.; Zou, B. Med-LVDM: Medical latent variational diffusion model for medical image translation. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2025, 106, 107735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rombach, R.; Blattmann, A.; Lorenz, D.; Esser, P.; Ommer, B. High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 10684–10695. [Google Scholar]
- Huijben, E.M.; Terpstra, M.L.; Pai, S.; Thummerer, A.; Koopmans, P.; Afonso, M.; Van Eijnatten, M.; Gurney-Champion, O.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y. Generating synthetic computed tomography for radiotherapy: SynthRAD2023 challenge report. Med. Image Anal. 2024, 97, 103276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Park, H. Adaptive latent diffusion model for 3d medical image to image translation: Multi-modal magnetic resonance imaging study. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2024; pp. 7604–7613. [Google Scholar]
- Parchur, A.; Paulson, E.; Ahunbay, E. End-to-End Clinical Evaluation Testing of Synthetic CT for MRI-Only Brain and Pelvis Radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2025, 123, e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusella, M.; Andres, E.A.; Villegas, F.; Milan, L.; Janssen, T.; Dal Bello, R.; Garibaldi, C.; Placidi, L.; Cusumano, D. Results of 2023 survey on the use of synthetic computed tomography for magnetic resonance Imaging-only radiotherapy: Current status and future steps. Phys. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 32, 100652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Task 1 | Head and Neck | Thorax | Abdominal | All |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Train | 177 | 146 | 140 | 463 |
| Test | 44 | 36 | 35 | 115 |
| All | 221 | 182 | 175 | 578 |
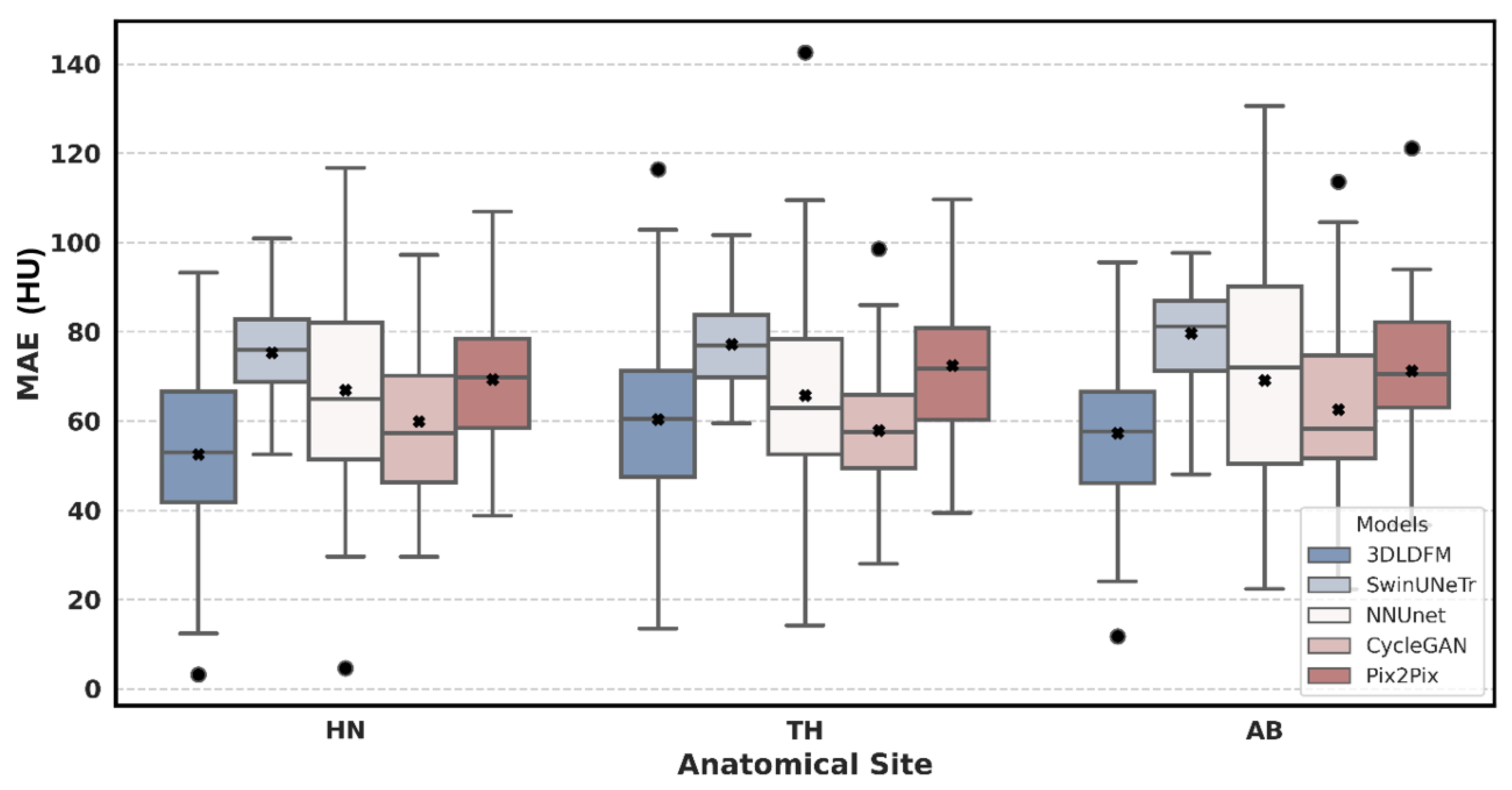
| Region | 3D-LDM (Ours) | SwinUNeTr | NNUNet | CycleGAN | Pix2Pix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abdomen (AB) | 57.24 (±18.48) | 79.70 (±12.07) *** | 69.13 (±28.87) | 62.54 (±20.19) | 71.24 (±16.44) ** |
| Head & Neck (HN) | 52.51 (±21.56) | 75.29 (±11.44) *** | 66.91 (±23.42) ** | 59.92 (±17.08) | 69.33 (±15.31) ** |
| Thorax (TH) | 60.34 (±24.11) | 77.19 (±11.34) *** | 65.71 (±25.49) | 57.91 (±15.18) | 72.39 (±15.98) ** |
| All | 56.44 (±21.63) | 77.23 (±11.65) *** | 67.20 (±25.63) ** | 60.07 (±17.47) | 70.89 (±15.78) *** |
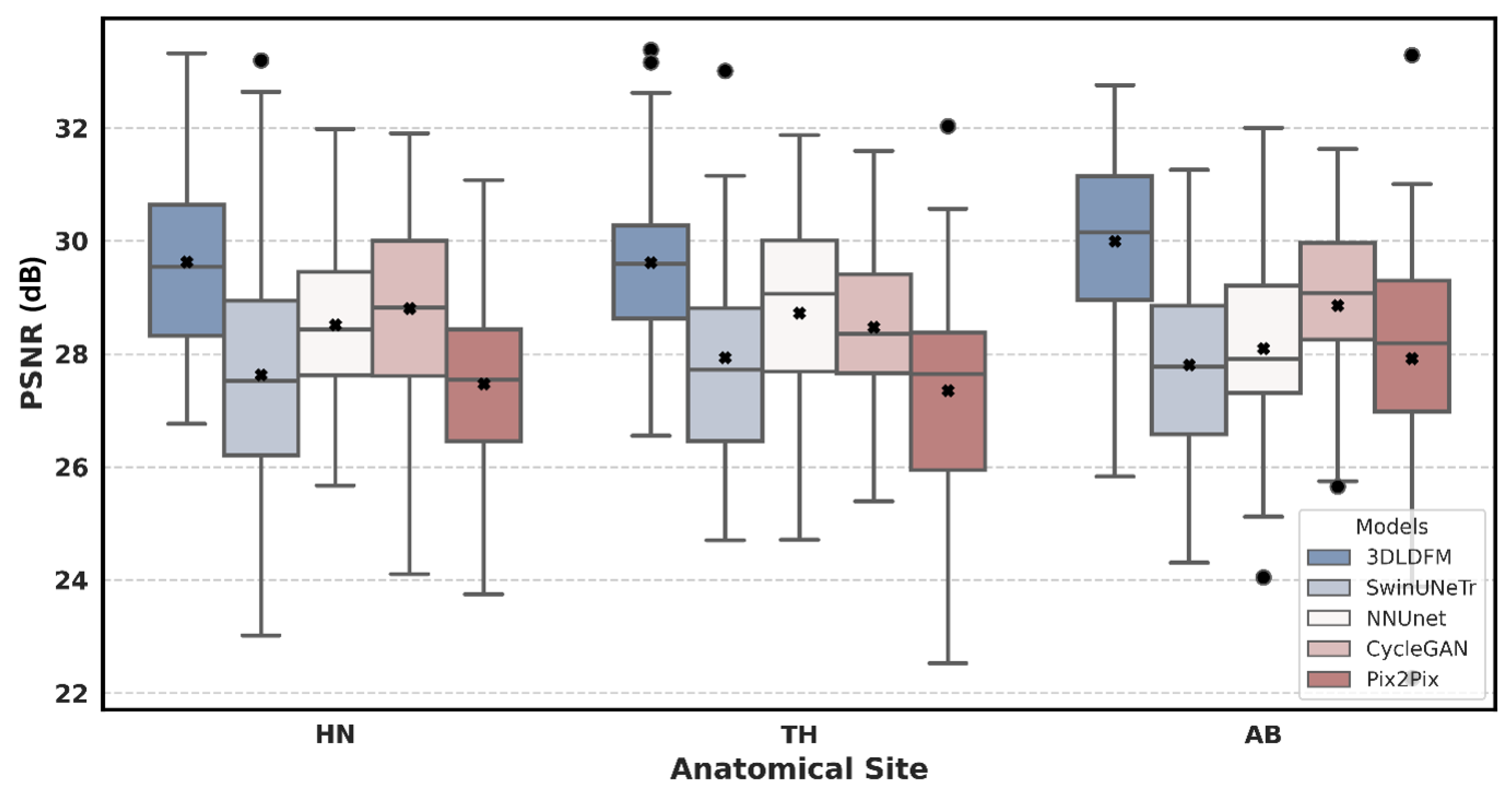
| Region | 3D-LDM (Ours) | SwinUNeTr | NNUNet | CycleGAN | Pix2Pix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AB | 29.99 (±1.58) | 27.80 (±1.77) *** | 28.10 (±1.70) *** | 28.86 (±1.55) ** | 27.92 (±2.22) *** |
| HN | 29.63 (±1.68) | 27.63 (±2.42) *** | 28.52 (±1.65) ** | 28.81 (±1.76) * | 27.46 (±1.72) *** |
| TH | 29.62 (±1.54) | 27.94 (±1.89) ** | 28.72 (±1.83) * | 28.47 (±1.47) ** | 27.35 (±1.94) *** |
| All | 29.73 (±1.60) | 27.78 (±2.06) *** | 28.46 (±1.73) *** | 28.72 (±1.61) *** | 27.56 (±1.95) *** |
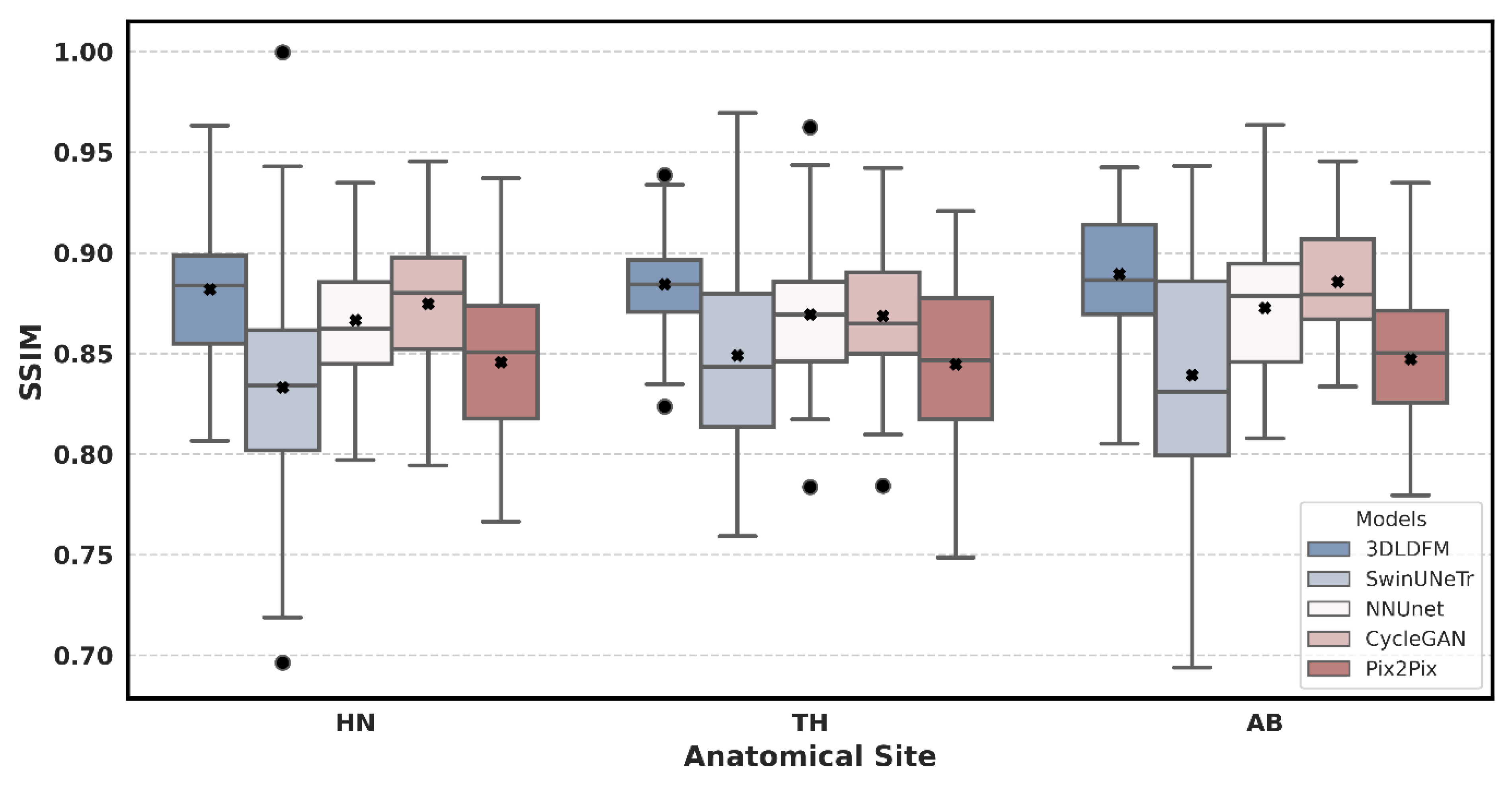
| Region | 3D-LDM (Ours) | SwinUNeTr | NNUNet | CycleGAN | Pix2Pix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AB | 0.890 (±0.0327) | 0.839 (±0.0587) ** | 0.873 (±0.0363) | 0.886 (±0.0280) | 0.847 (±0.037) *** |
| HN | 0.880 (±0.0333) | 0.833 (±0.0536) *** | 0.866 (±0.0317) * | 0.875 (±0.0336) | 0.845 (±0.038) *** |
| TH | 0.885 (±0.0264) | 0.849 (±0.047) ** | 0.869 (±0.0338) * | 0.869 (±0.0349) * | 0.844 (±0.040) *** |
| All | 0.885 (±0.0310) | 0.840 (±0.0532) *** | 0.869 (±0.0336) ** | 0.876 (±0.0328) * | 0.845 (±0.038) *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahdi, M.A.; Al-Shalabi, M.; Alnfrawy, E.T.; Elbarougy, R.; Hadi, M.U.; Ali, R.F. 3D Latent Diffusion Model for MR-Only Radiotherapy: Accurate and Consistent Synthetic CT Generation. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 3010. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15233010
Mahdi MA, Al-Shalabi M, Alnfrawy ET, Elbarougy R, Hadi MU, Ali RF. 3D Latent Diffusion Model for MR-Only Radiotherapy: Accurate and Consistent Synthetic CT Generation. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(23):3010. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15233010
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahdi, Mohammed A., Mohammed Al-Shalabi, Ehab T. Alnfrawy, Reda Elbarougy, Muhammad Usman Hadi, and Rao Faizan Ali. 2025. "3D Latent Diffusion Model for MR-Only Radiotherapy: Accurate and Consistent Synthetic CT Generation" Diagnostics 15, no. 23: 3010. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15233010
APA StyleMahdi, M. A., Al-Shalabi, M., Alnfrawy, E. T., Elbarougy, R., Hadi, M. U., & Ali, R. F. (2025). 3D Latent Diffusion Model for MR-Only Radiotherapy: Accurate and Consistent Synthetic CT Generation. Diagnostics, 15(23), 3010. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15233010









