Genomic Characterization of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: Age Differences in Tumor Aggressiveness and Immune Infiltration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection and Clinical Data
2.1.1. TCGA Cohort
2.1.2. Institutional Cohort
2.2. Transcriptome Analysis
2.2.1. RNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.2.2. Differential Gene Expression Analysis
2.2.3. Functional Enrichment Analysis
2.2.4. Correlation and Core Gene Analysis
2.3. Immune-Cell Infiltration Analysis
2.4. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Immunohistochemical Score (H-Score)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics
3.1.1. TCGA Cohort
3.1.2. Institutional Cohort
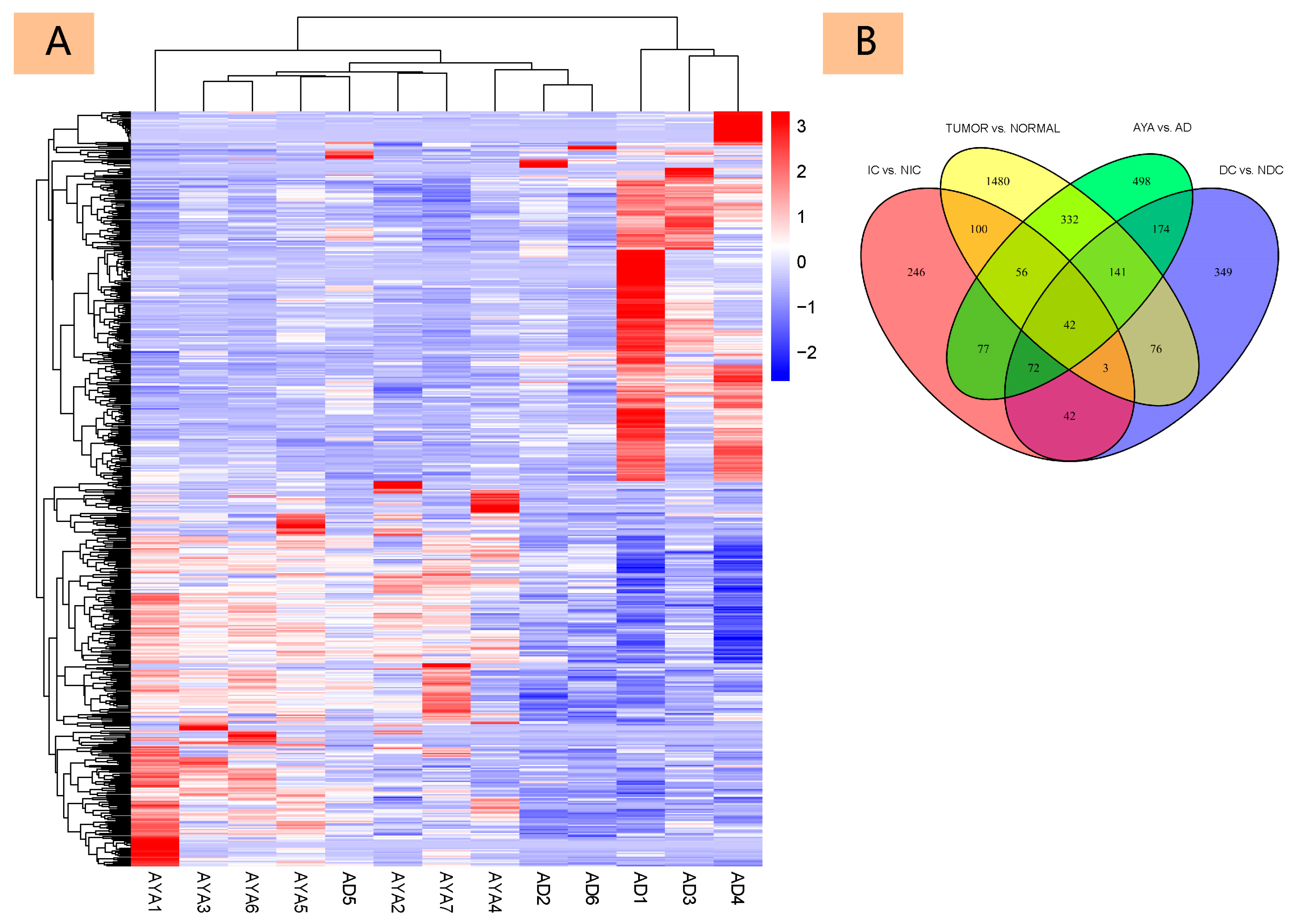
3.2. Differential Gene Expression
3.2.1. Differential Gene Expression Analysis
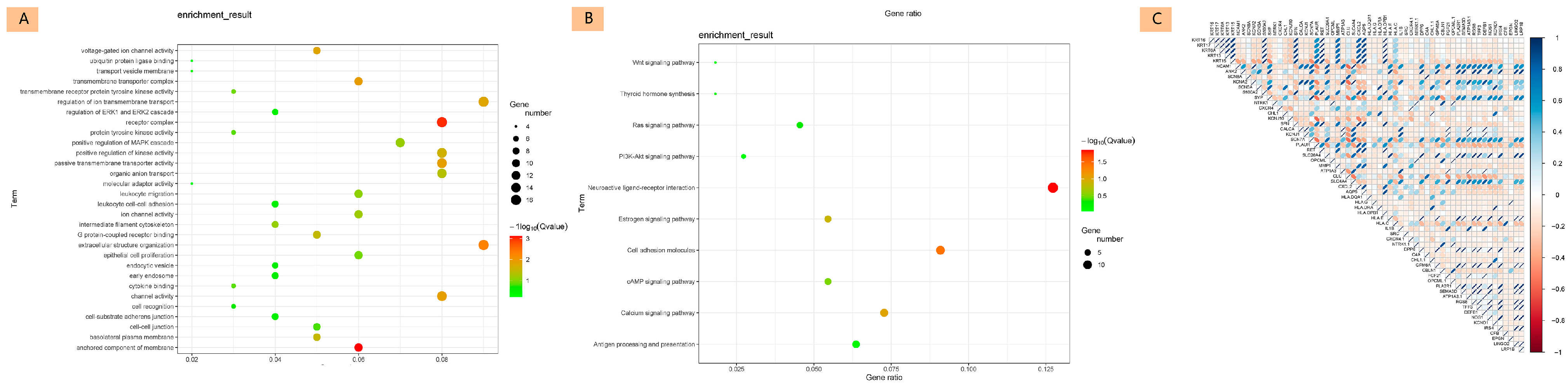
3.2.2. Functional Enrichment Analysis
3.2.3. Correlation and Core Gene Analysis
3.2.4. Differential Expression of Core Genes
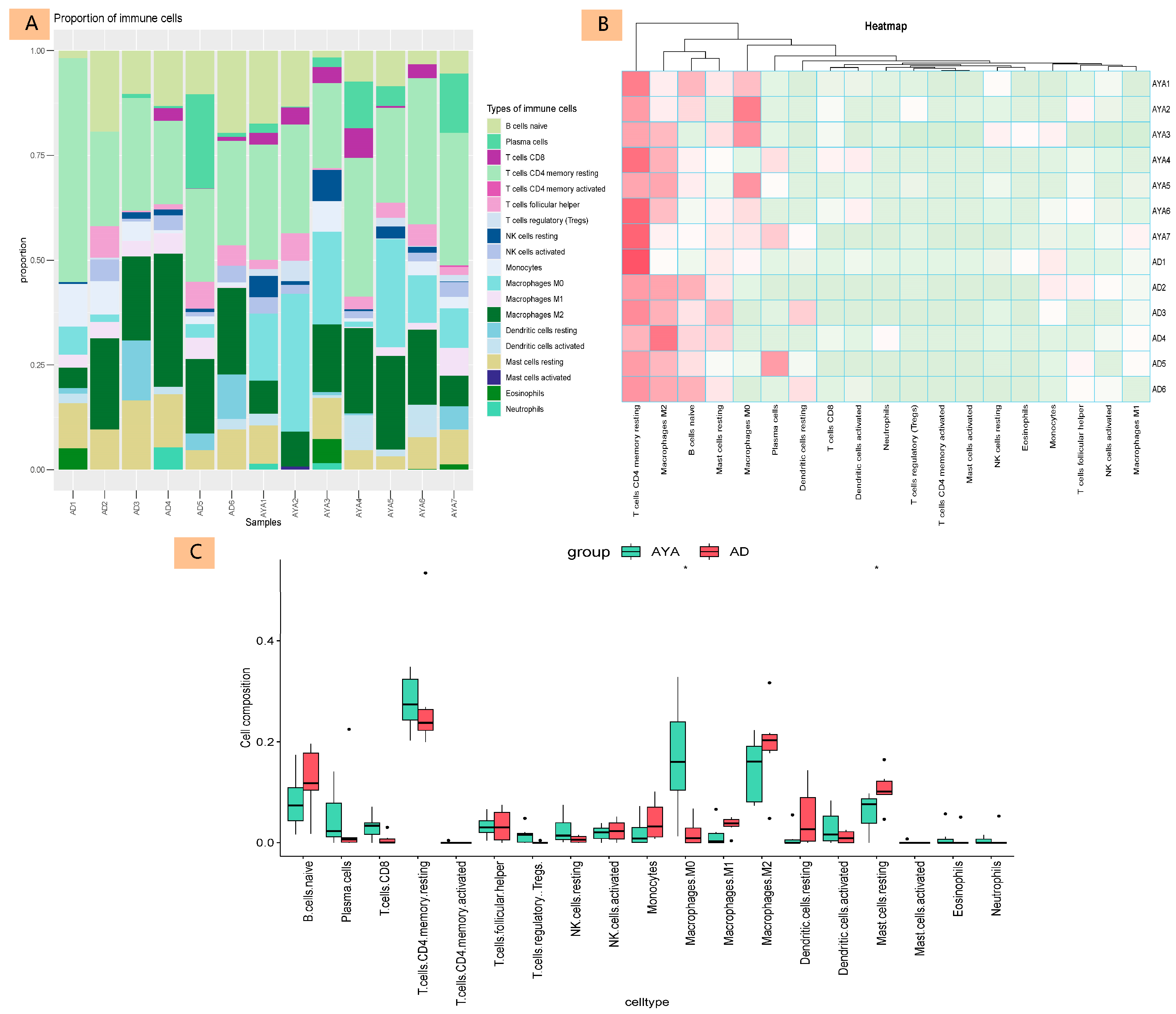
3.3. Immune-Cell Infiltration Analysis
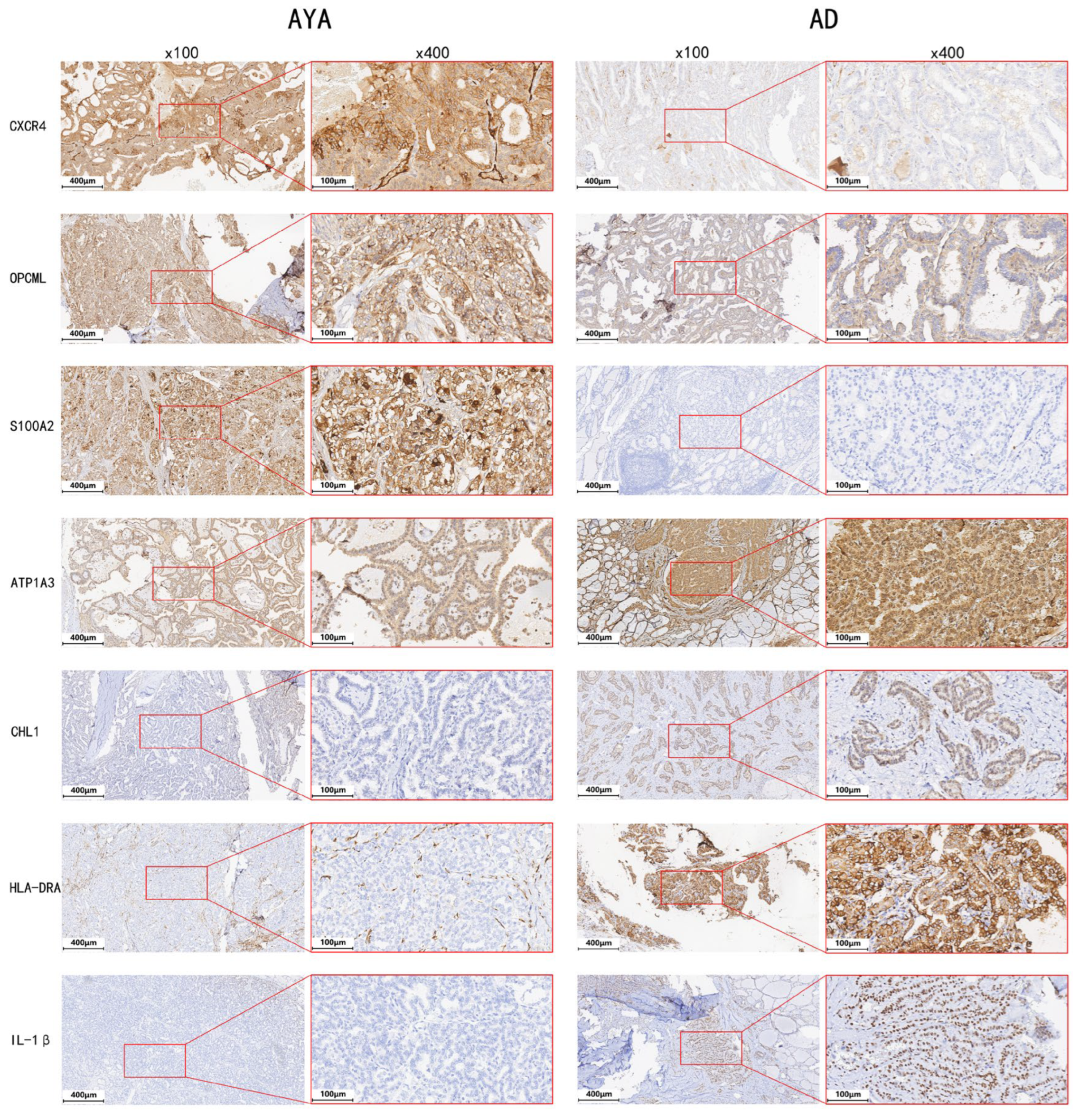
3.4. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AYA | adolescents and young adults |
| PTC | papillary thyroid carcinoma |
| AD | adults |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas |
| DEGs | differentially expressed genes |
| IHC | immunohistochemistry |
| NCI | National Cancer Institute |
| TSH | thyroid-stimulating hormone |
| TERT | telomerase reverse transcriptase |
| TP53 | tumor protein p53 |
| ADCs | antibody drug conjugates |
| LNM | lymph node metastasis |
| ETE | extrathyroidal extension |
| FFPE | formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded |
| RIN | RNA Integrity Number |
| IC | Invasion-related Cancer |
| NIC | Non-Invasion-related Cancer |
| DC | Dissemination-related Cancer |
| NDC | Non-Dissemination-related Cancer |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| BP | Biological Processes |
| MF | Molecular Functions |
| CC | Cellular Components |
| PPI | protein–protein interaction |
| EMT | epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
| TSG | tumor suppressor gene |
| AITD | autoimmune thyroid diseases |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keegan, T.H.; Abrahão, R.; Alvarez, E.M. Survival Trends Among Adolescents and Young Adults Diagnosed With Cancer in the United States: Comparisons With Children and Older Adults. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucai, L.; Zafereo, M.; Cabanillas, M.E. Thyroid Cancer: A Review. JAMA 2024, 331, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saab, R. Burden of cancer in adolescents and young adults. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vriens, M.R.; Moses, W.; Weng, J.; Peng, M.; Griffin, A.; Bleyer, A.; Pollock, B.H.; Indelicato, D.J.; Hwang, J.; Kebebew, E. Clinical and molecular features of papillary thyroid cancer in adolescents and young adults. Cancer 2011, 117, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherella, C.E.; Wassner, A.J. Pediatric thyroid cancer: Recent developments. Best practice & research. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 37, 101715. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, M.; Cao, H.; Baranova, A.; Kural, K.C.; Hou, L.; He, S.; Shao, Q.; Fang, J. Aging-associated genes TNFRSF12A and CHI3L1 contribute to thyroid cancer: An evidence for the involvement of hypoxia as a driver. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 3634–3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, T.; Zeng, Y.; Xu, W.; Shi, X.; Shen, C.; Du, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Ding, P.; et al. A spatially resolved transcriptome landscape during thyroid cancer progression. Cell Rep. Med. 2025, 6, 102043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonkin, D.; Thomas, A.; Teicher, B.A. Cancer treatments: Past, present, and future. Cancer Genet. 2024, 286–287, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Han, R.; Zhou, L.; Luo, M.; Zeng, L.; Zhao, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, L. Comparative performance of the GenoLab M and NovaSeq 6000 sequencing platforms for transcriptome and LncRNA analysis. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.M.; Liu, C.L.; Green, M.R.; Gentles, A.J.; Feng, W.; Xu, Y.; Hoang, C.D.; Diehn, M.; Alizadeh, A.A. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Specht, E.; Kaemmerer, D.; Sänger, J.; Wirtz, R.M.; Schulz, S.; Lupp, A. Comparison of immunoreactive score, HER2/neu score and H score for the immunohistochemical evaluation of somatostatin receptors in bronchopulmonary neuroendocrine neoplasms. Histopathology 2015, 67, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, H.; Zhong, N.; Luo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tu, F.; Zhong, J.; Wang, X.; He, J.; et al. TELO2 induced progression of colorectal cancer by binding with RICTOR through mTORC2. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 45, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Ye, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Lu, J.; Chen, G. Association between different regional lymph node metastases of papillary thyroid carcinoma in adolescents and young adults. Oncol. Lett. 2024, 27, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.A.; Lim, J.; Jin, H.Y.; Park, M.; Park, H.J.; Park, J.W.; Kim, J.H.; Kang, H.G.; Won, Y.J. Osteosarcoma in Adolescents and Young Adults. Cells 2021, 10, 2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrello, M.G.; Alberti, L.; Fischer, A.; Degl’INnocenti, D.; Ferrario, C.; Gariboldi, M.; Marchesi, F.; Allavena, P.; Greco, A.; Collini, P.; et al. Induction of a proinflammatory program in normal human thyrocytes by the RET/PTC1 oncogene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14825–14830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Kong, Y.; Wei, G.; Sun, K.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, C.; et al. CCDC6-RET fusion protein regulates Ras/MAPK signaling through the fusion-GRB2-SHC1 signal niche. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2322359121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Zhang, J.; Qing, G.; Liu, D.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, S. S100A2 silencing relieves epithelial–mesenchymal transition in pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. DNA Cell Biol. 2021, 40, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, Y.; Yoshida, H.; Tomoda, C.; Uruno, T.; Miya, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Matsuzuka, F.; Kakudo, K.; Kuma, K.; Miyauchi, A. Expression of S100A2 and S100A6 in thyroid carcinomas. Histopathology 2005, 46, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.-N.; Zhang, W.-C.; Lin, Y.-Z.; Jiang, H.-Y.; He, R.; Li, S.-L.; Zhang, Y.-N.; Shao, C.-Y.; Zheng, C.-M.; Xu, J.-J.; et al. Single-cell and bulk RNA sequencing reveal heterogeneity and diagnostic markers in papillary thyroid carcinoma lymph-node metastasis. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2023, 47, 1513–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.M.; Whelan, J.S.; Barber, J.A.; Alvarez-Galvez, J.; Feltbower, R.G.; Gibson, F.; Stark, D.P.; Fern, L.A. The Impact of Specialist Care on Teenage and Young Adult Patient-Reported Outcomes in England: A BRIGHTLIGHT Study. J. Adolesc. Young Adult Oncol. 2024, 13, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiadou, D.P.; Quesnel, A.; Duran, C.L.; Filippou, P.S.; Karagiannis, G.S. An emerging paradigm of CXCL12 involvement in the metastatic cascade. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2024, 75, 12–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coperchini, F.; Croce, L.; Marinò, M.; Chiovato, L.; Rotondi, M. Role of chemokine receptors in thyroid cancer and immunotherapy. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2019, 26, R465–R478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Lei, W.; Wang, H.; Ni, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yan, H.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Z.; et al. CXCL12-CXCR4/CXCR7 Axis in Cancer: From Mechanisms to Clinical Applications. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 19, 3341–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antony, J.; Zanini, E.; Birtley, J.R.; Gabra, H.; Recchi, C. Emerging roles for the GPI-anchored tumor suppressor OPCML in cancers. Cancer Gene Ther. 2021, 28, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Chen, Y.; Lin, W.; Zheng, J.; Liu, Y.; Zou, J.; Cai, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y. Prognostic and Immune-Infiltrate Significance of miR-222-3p and Its Target Genes in Thyroid Cancer. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 710412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senchenko, V.N.; Krasnov, G.S.; Dmitriev, A.A.; Kudryavtseva, A.V.; Anedchenko, E.A.; Braga, E.A.; Pronina, I.V.; Kondratieva, T.T.; Ivanov, S.V.; Zabarovsky, E.R.; et al. Differential expression of CHL1 gene during development of major human cancers. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e15612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Q.; Tu, Z.; Liu, J.; Huang, K.; Zhu, X.; Li, J. Identification of a robust scoring system based on metabolic genes followed by in-depth validation of ATP1A3 in glioma. Life Sci. 2023, 315, 121377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Com, E.; Clavreul, A.; Lagarrigue, M.; Michalak, S.; Menei, P.; Pineau, C. Quantitative proteomic Isotope-Coded Protein Label (ICPL) analysis reveals alteration of several functional processes in the glioblastoma. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 3898–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yang, S.; Li, B.; Huang, L.; Lou, G. Comprehensive analysis of the expression of sodium/potassium-ATPase α subunits and prognosis of ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Qian, K.; Shi, Y.; Sun, T.; Chen, L.; Mei, D.; Dong, K.; Gu, S.; Liu, J.; Lv, Z.; et al. Clinical and Molecular Characterizations of Papillary Thyroid Cancer in Children and Young Adults: A Multicenter Retrospective Study. Thyroid 2021, 31, 1693–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Sun, W.; Zhang, H. Roles and new insights of macrophages in the tumor microenvironment of thyroid cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 875384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elia, G.; Ferrari, S.M.; Ragusa, F.; Paparo, S.R.; Mazzi, V.; Ulisse, S.; Benvenga, S.; Antonelli, A.; Fallahi, P. Advances in pharmacotherapy for advanced thyroid cancer of follicular origin (PTC, FTC). New approved drugs and future therapies. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2022, 23, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Shi, R.; Zhang, X.; Fang, D.; Rauch, J.; Lu, S.; Wang, X.; Käsmann, L.; Ma, J.; Belka, C.; et al. Characterization of immune landscape in papillary thyroid cancer reveals distinct tumor immunogenicity and implications for immunotherapy. Oncoimmunology 2021, 10, e1964189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Langevin, A.M.; Houghton, P.J.; Zheng, S. Genomic disparities between cancers in adolescent and young adults and in older adults. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristic | Number of Cases (%) |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | |
| <30 years | 64 (12.8%) |
| ≥30 years | 437 (87.2%) |
| Gender | |
| Male | 134 (26.7%) |
| Female | 367 (73.3%) |
| Number of Foci | |
| Unifocal | 264 (53.8%) |
| Multifocal | 227 (46.2%) |
| Extra-thyroidal Extension (ETE) | |
| None | 333 (68.9%) |
| Minimal (T3) | 131 (27.1%) |
| Moderate/Advanced (T4a) | 18 (3.7%) |
| Very Advanced (T4b) | 1 (0.2%) |
| Lymph Node Metastasis | |
| None | 168 (43.5%) |
| Present | 218 (56.5%) |
| T Stage | |
| T1/2 | 308 (61.7%) |
| T3/4 | 191 (38.3%) |
| N Stage | |
| N0 | 226 (50.1%) |
| N1 | 225 (49.9%) |
| M Stage | |
| M0 | 281 (96.9%) |
| M1 | 9 (3.1%) |
| Cancer Stage | |
| Stage I/II | 331 (66.3%) |
| Stage III/IV | 168 (33.7%) |
| Characteristic | Adolescents and Young Adults (Age < 30 years) | Adults (Age ≥ 30 years) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 0.522 | ||
| Male | 15 (23.4%) | 119 (27.2%) | |
| Female | 49 (76.6%) | 318 (72.8%) | |
| Extra-thyroidal Extension (ETE) | 0.049 | ||
| None | 50 (79.4%) | 283 (67.4%) | |
| Minimal (T3) | 12 (19.0%) | 119 (28.3%) | |
| Moderate/Advanced (T4a) | 1 (1.6%) | 17 (4.0%) | |
| Very Advanced (T4b) | 0 (0%) | 1 (0.2%) | |
| Maximum Tumor Diameter (cm) | 2.75 ± 1.16 | 3.04 ± 1.69 | 0.222 |
| Number of Lymph Node Metastases | 5.00 ± 8.03 | 3.70 ± 6.36 | 0.246 |
| Lymph Node Metastasis | 0.132 | ||
| None | 20 (34.5%) | 148 (45.1%) | |
| Present | 38 (65.5%) | 180 (54.9%) | |
| Number of Foci | 0.134 | ||
| Unifocal | 44 (62.0%) | 220 (52.4%) | |
| Multifocal | 27 (38.0%) | 200 (47.6%) | |
| T Stage | <0.001 | ||
| T1/2 | 52 (72.2%) | 256 (60.0%) | |
| T3/4 | 20 (27.8%) | 171 (40.0%) | |
| N Stage | 0.031 | ||
| N0 | 25 (37.9%) | 201 (52.2%) | |
| N1 | 41 (62.1%) | 184 (47.8%) | |
| M Stage | 0.954 | ||
| M0 | 33 (97.1%) | 248 (96.9%) | |
| M1 | 1 (3.0%) | 8 (3.1%) | |
| Cancer Stage | <0.001 | ||
| Stage I/II | 73 (100%) | 258 (60.6%) | |
| Stage III/IV | 0 (0%) | 168 (39.4%) | |
| Clinical Outcomes | |||
| Follow-Up Time (months) | 44.43 ± 31.42 | 40.09 ± 32.84 | 0.326 |
| OS (Overall Survival) (months) | 42.82 ± 31.59 | 39.13 ± 32.60 | 0.389 |
| DFI (Disease-Free Interval) (months) | 40.58 ± 31.04 | 39.03 ± 33.03 | 0.745 |
| Characteristic | Adolescents and Young Adults (Age < 30 years) | Adults (Age ≥ 30 years) |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Patients | 7 | 6 |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 2 | 1 |
| Female | 5 | 5 |
| Age (years) | ||
| Mean Age | 23.6 | 52.8 |
| Age Range | 9–29 | 38–66 |
| Preoperative Blood Parameters | ||
| TSH (μIU/mL) | 1.99 ± 0.54 | 4.00 ± 2.83 |
| FT3 (pmol/L) | 5.51 ± 0.68 | 5.22 ± 0.68 |
| FT4 (pmol/L) | 11.15 ± 2.07 | 10.97 ± 1.47 |
| TG (ng/mL) | 89.2 ± 173.7 | 118.3 ± 180.4 |
| TGAb (IU/mL) | 0.6 ± 1.0 | 12.1 ± 29.5 |
| TPOAb (IU/mL) | 4.4 ± 9.4 | 1.0 ± 0.7 |
| Preoperative Ultrasound Evaluation | ||
| Tumor Size (cm) | 2.22 ± 0.58 | 1.68 ± 0.76 |
| Tumor Characteristics | ||
| Cystic/Solid | Solid: 5, Cystic: 2 | Solid: 5, Cystic: 1 |
| Invasion/Intrathyroidal Spread/Hashimoto’s | ||
| Invasion | 3/7 | 5/6 |
| Intrathyroidal Spread | 4/7 | 0/6 |
| Hashimoto’s | 3/7 | 1/6 |
| Lymph Node Metastasis | ||
| Central Compartment | 7/7 | 5/6 |
| Lateral Neck | 6/7 | 3/6 |
| TNM Staging | ||
| T1/2 | 7 | 2 |
| T3/4 | 0 | 4 |
| N0 | 0 | 0 |
| N1a | 1 | 3 |
| N1b | 6 | 3 |
| M0 | 7 | 6 |
| M1 | 0 | 0 |
| Cancer Stage | ||
| Stage I/II | 7 | 3 |
| Stage III/IV | 0 | 3 |
| Gene | Description | log2 Fold Change (AYA vs. AD) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| CXCR4 | C-X-C Motif Chemokine Receptor 4 | 1.26 | 0.003 |
| S100A2 | S100 calcium binding protein A2 | 1.88 | 0.008 |
| OPCML | Opioid Binding Protein/Cell Adhesion Molecule-Like | 4.90 | <0.001 |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β | −1.82 | 0.021 |
| CHL1 | Cell adhesion molecule L1-like | −3.13 | <0.001 |
| ATP1A3 | ATPase Na+/K+ transporting subunit alpha 3 | −7.24 | <0.001 |
| HLA-DRA | Major Histocompatibility Complex, Class II, DR Alpha | −9.86 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ao, W.; Chen, S.; Liu, T.; Wang, B.; Zhao, W. Genomic Characterization of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: Age Differences in Tumor Aggressiveness and Immune Infiltration. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2937. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15232937
Ao W, Chen S, Liu T, Wang B, Zhao W. Genomic Characterization of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: Age Differences in Tumor Aggressiveness and Immune Infiltration. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(23):2937. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15232937
Chicago/Turabian StyleAo, Wei, Shuqian Chen, Tenghong Liu, Bo Wang, and Wenxin Zhao. 2025. "Genomic Characterization of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: Age Differences in Tumor Aggressiveness and Immune Infiltration" Diagnostics 15, no. 23: 2937. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15232937
APA StyleAo, W., Chen, S., Liu, T., Wang, B., & Zhao, W. (2025). Genomic Characterization of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: Age Differences in Tumor Aggressiveness and Immune Infiltration. Diagnostics, 15(23), 2937. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15232937







