Microvascular Imaging of Hepatic Hemangiomas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Ethics
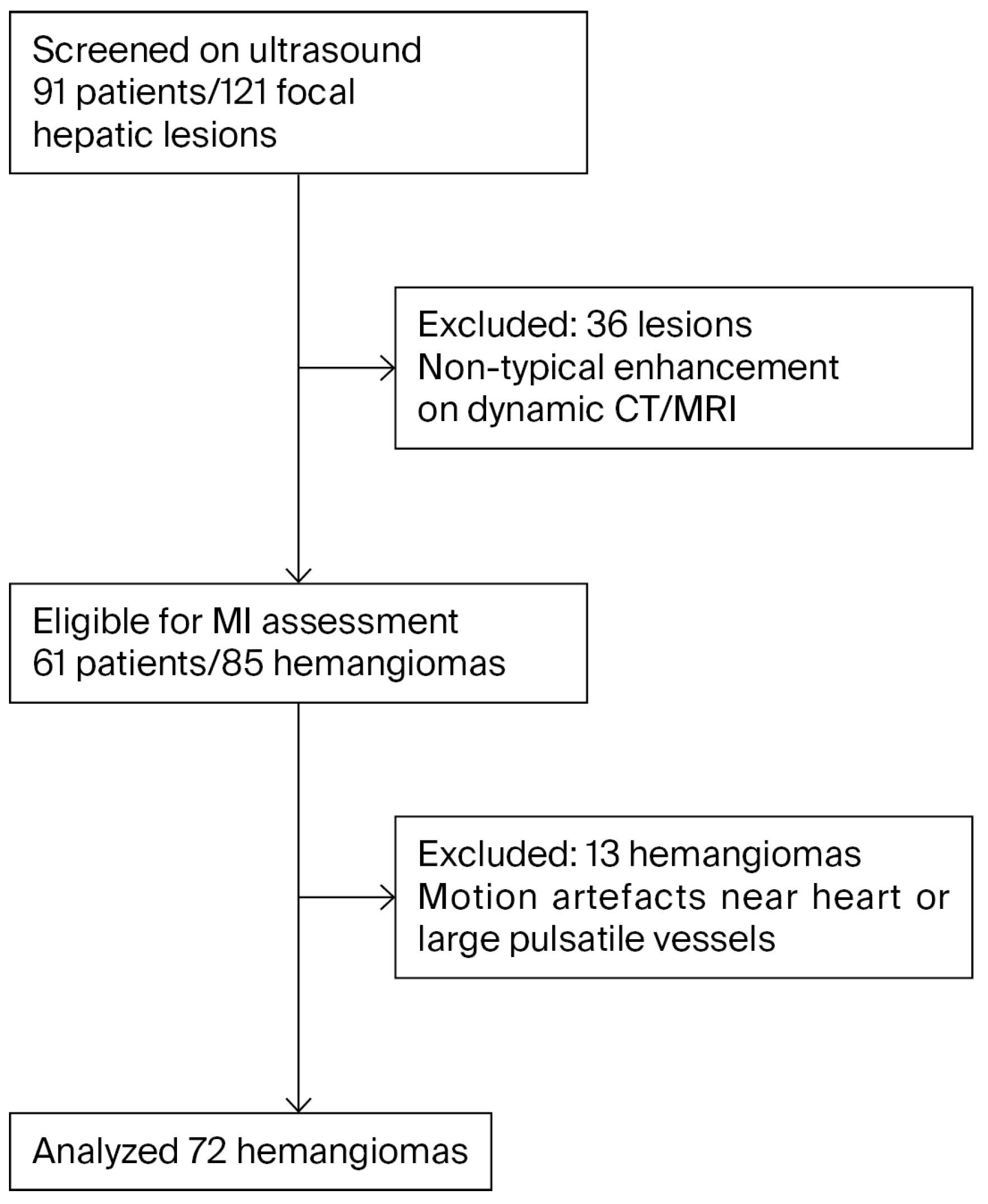
2.2. Patient Selection
2.3. Image Acquisition
2.4. Image Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| US | Ultrasound |
| B-mode | Brightness-mode ultrasonography |
| HH | Hepatic Hemangioma |
| MI | Microvascular Imaging |
| MFlow | Vendor-specific MI implementation (Samsung Medison) |
| CEUS | Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| FHL | Focal Hepatic Lesion |
| CECT | Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography |
| MFlow | Microvascular Flow (brand-specific MI modality) |
| DICOM | Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine |
| CDI | Color Doppler Imaging |
| PDI | Power Doppler Imaging |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| κ (kappa) | Cohen’s Kappa Statistic |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
References
- Collin, P.; Rinta-Kiikka, I.; Raty, S.; Laukkarinen, J.; Sand, J. Diagnostic workup of liver lesions: Too long time with too many examinations. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 50, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Onofrio, M.; Crosara, S.; De Robertis, R.; Canestrini, S.; Mucelli, R.P. Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound of Focal Liver Lesions. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 205, W56–W66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, C.F.; Sharma, M.; Gibson, R.N.; Schreiber-Dietrich, D.; Jenssen, C. Fortuitously discovered liver lesions. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 3173–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.K.; Lee, J.Y.; Han, J.K. Superb microvascular imaging technology of ultrasound examinations for the evaluation of tumor vascularity in hepatic hemangiomas. Ultrasonography 2021, 40, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhao, J.; Liu, C.; Mao, Y.; Mu, J.; Wei, X.; Jia, J.; Zhang, S.; Xin, X.; Tan, J. Superb microvascular imaging technique in depicting vascularity in focal liver lesions: More hypervascular supply patterns were depicted in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Imaging 2019, 19, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klotz, T.; Montoriol, P.F.; Da Ines, D.; Petitcolin, V.; Joubert-Zakeyh, J.; Garcier, J.M. Hepatic haemangioma: Common and uncommon imaging features. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2013, 94, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, R.P.; Sam, M.; Raubenheimer, M.; Patel, V.; Low, G. Hepatic hemangiomas: The various imaging avatars and its mimickers. Radiol. Med. 2020, 125, 801–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moga, T.V.; Lupusoru, R.; Danila, M.; Ghiuchici, A.M.; Popescu, A.; Miutescu, B.; Ratiu, I.; Burciu, C.; Bizerea-Moga, T.; Voron, A.; et al. Challenges in Diagnosing Focal Liver Lesions Using Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound. Diagnostics 2024, 15, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, Y.R.; Youn, S.Y.; Kim, H.; Chun, H.J.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Oh, S.N. Comparative Safety Profiles and Usage Patterns of Iodinated Contrast Media in Medical Imaging. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.; Heo, S.; McDonald, J.S.; Choi, S.H.; Choi, W.-M.; Lee, J.B.; Lee, E.A.; Park, S.H.; Seol, S.; Gan, S.; et al. Risk of Contrast-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Computed Tomography. Investig. Radiol. 2024, 60, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampofo, R.Y.; Kyei, K.A.; Daniels, J.; Nyantakyi, A.Y. Determination of redundant scan coverages along the Z-axis and dose implications for common paediatric computed tomography imaging examinations in a limited resource setting. BMC Med. Imaging 2025, 25, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swensson, J.; McCrate, M.; Halappa, V.G.; Stethen, T.; Akisik, F. Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Compared with Hepatobiliary Agent MRI for Differentiation of Focal Nodular Hyperplasia and Hepatic Adenoma: A Prospective Trial. Ultrasound Q. 2024, 40, e00696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oybek, D.; Annaev, M.; Erkinovich, U.I.; Ahn, B.; Lee, H. Diagnosis of Hepatic Hemangioma in a 35-Year-Old Female with an Incidental Liver Lesion Detected on Ultrasound Examination. J. Med. Imaging 2024, 7, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaia, E.; Bertolotto, M.; Dalla Palma, L. Characterization of liver hemangiomas with pulse inversion harmonic imaging. Eur. Radiol. 2002, 12, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaiani, S.; Volpe, L.; Piscaglia, F.; Bolondi, L. Vascularity of liver tumours and recent advances in doppler ultrasound. J. Hepatol. 2001, 34, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, A.Y.; Seo, B.K. Up-to-date Doppler techniques for breast tumor vascularity: Superb microvascular imaging and contrast-enhanced ultrasound. Ultrasonography 2018, 37, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolotta, T.V.; Taibbi, A.; Midiri, M.; Lagalla, R. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound of hepatocellular carcinoma: Where do we stand? Ultrasonography 2019, 38, 200–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Cao, J.-Y.; Jin, Z.; Yu, T.-Q.; Chen, S.-T.; Zhang, Y. Enhanced Diagnostic Imaging: Arrival-Time Parametric Imaging in Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound for Multi-Organ Assessment. Med. Sci. Monit. 2024, 30, e945281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caserta, M.P.; Fetzer, D.T.; Swensson, J.K.; Rodgers, S.K.; Boyum, J.H. When Benign Behaves Badly. Ultrasound Q. 2021, 38, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannella, R.; Pilato, G.; Mazzola, M.; Bartolotta, T.V. New microvascular ultrasound techniques: Abdominal applications. La. Radiol. Medica 2023, 128, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabeti, S.; Ternifi, R.; Larson, N.B.; Olson, M.C.; Atwell, T.D.; Fatemi, M.; Alizad, A. Morphometric analysis of tumor microvessels for detection of hepatocellular carcinoma using contrast-free ultrasound imaging: A feasibility study. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1121664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirli, R.; Sporea, I.; Săndulescu, D.L.; Popescu, A.; Dănilă, M.; Săftoiu, A.; Spârchez, Z.; Badea, R. Contrast enhanced ultrasound for the diagnosis of liver hemangiomas—Results of a Romanian multicentre study. Med. Ultrason. 2015, 17, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Liu, M.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Niu, C. The clinical application of ultrasonography with superb microvascular imaging-a review. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2022, 50, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL). EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of benign liver tumours. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Han, J.K. Superb microvascular imaging technology for ultrasound examinations: Initial experiences for hepatic tumors. Eur. J. Radiol. 2016, 85, 2090–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.S.; Lee, J.M.; Jeon, S.K.; Jang, S. Comparison of MicroFlow Imaging with color and power Doppler imaging for detecting and characterizing blood flow signals in hepatocellular carcinoma. Ultrasonography 2020, 39, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.-J.; Lee, J.M.; Jeon, S.K.; Ryu, H.; Yoo, J.; Lee, J.K.; Han, J.K. Microvascular Flow Imaging of Residual or Recurrent Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Transarterial Chemoembolization: Comparison with Color/Power Doppler Imaging. Korean J. Radiol. 2019, 20, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Járay, Á.; Farkas, P.I.; Semjén, D.; Battyáni, I.; Botz, B. Additional value of microvascular flow imaging in the assessment of cystic and solid renal lesions. Physiol. Int. 2023, 110, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rónaszéki, A.; Budai, B.K.; Stollmayer, R.; Győri, G.; Maurovich-Horvat, P.; Kaposi, P.N. Detection of a Spoke-Wheel Pattern Of Focal Nodular Hyperplasia with Novel Microvascular Flow Imaging. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2022, 48, S14–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rónaszéki, A.D.; Dudás, I.; Zsély, B.; Budai, B.K.; Stollmayer, R.; Hahn, O.; Csongrády, B.; Park, B.-s.; Maurovich-Horvat, P.; Győri, G.; et al. Microvascular flow imaging to differentiate focal hepatic lesions: The spoke-wheel pattern as a specific sign of focal nodular hyperplasia. Ultrasonography 2023, 42, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, E.M.; Moran, V.O.; Engel, M.; Krüger-Genge, A.; Stroszczynski, C.; Jung, F. Modified contrast-enhanced ultrasonography with the new high-resolution examination technique of high frame rate contrast-enhanced ultrasound (HiFR-CEUS) for characterization of liver lesions: First results. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2023, 83, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Xie, X.; Chen, H.; Zhong, Z.; Zhou, W.; Jiang, H.; Xie, X.; Zhou, L. Development of a pediatric liver CEUS criterion to classify benign and malignant liver lesions in pediatric patients: A pilot study. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 6747–6757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Numata, K.; Nihonmatsu, H.; Chuma, M.; Ideno, N.; Nozaki, A.; Ogushi, K.; Tanab, M.; Okada, M.; Luo, W.; et al. Added Value of Ultrasound-Based Multimodal Imaging to Diagnose Hepatic Sclerosed Hemangioma before Biopsy and Resection. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möller, K.; Safai Zadeh, E.; Görg, C.; Dong, Y.; Cui, X.; Lim, A.; Molo, C.d.; Serra, C.; Martín Algíbez, A.; Berzigotti, A.; et al. Focal liver lesions other than hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: Diagnostic challenges. J. Transl. Intern. Med. 2022, 10, 308–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschner, C.A.; Rübenthaler, J.; Froelich, M.F.; Schwarze, V.; Clevert, D.-A. Benefits of contrast-enhanced ultrasonography for interventional procedures. Ultrasonography 2021, 40, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, K.; Zhai, H.; Jiang, Y.; Liang, P.; Xu, H.-X.; Du, L.; Chou, Y.-H.; Xie, X.; Luo, Y.; Lee, Y.J.; et al. Prospective assessment of diagnostic efficacy and safety of SonazoidTM and SonoVue® ultrasound contrast agents in patients with focal liver lesions. Abdom. Radiol. 2021, 46, 4647–4659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huf, S.; Platz Batista da Silva, N.; Wiesinger, I.; Hornung, M.; Scherer, M.; Lang, S.; Stroszczynski, C.; Fischer, T.; Jung, E. Analysis of Liver Tumors Using Preoperative and Intraoperative Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS/IOCEUS) by Radiologists in Comparison to Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Histopathology. RöFo—Fortschritte Auf Dem Geb. der Röntgenstrahlen und der Bildgeb. Verfahr. 2017, 189, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; King, J.; Chatterji, M.; Miller, B.R.; Siddoway, R.L. Superb Microvascular Imaging-Based Vascular Index to Assess Adult Hepatic Steatosis: A Feasibility Study. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2022, 48, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, A.Y.; Seo, B.K.; Cha, S.H.; Yeom, S.K.; Lee, S.W.; Chung, H.H. An Innovative Ultrasound Technique for Evaluation of Tumor Vascularity in Breast Cancers: Superb Micro-Vascular Imaging. J. Breast Cancer 2016, 19, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.U.; Eisenbrey, J.R.; Deganello, A.; Zahid, M.; Sharbidre, K.; Sidhu, P.; Robbin, M.L. Microvascular Flow Imaging: A State-of-the-Art Review of Clinical Use and Promise. Radiology 2022, 305, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, C.F.; Mertens, J.C.; Braden, B.; Schuessler, G.; Ott, M.; Ignee, A. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound of histologically proven liver hemangiomas†. Hepatology 2007, 45, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, B.; Ding, H.; Mao, F.; Li, C.; Zeng, M.; Zhou, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.; et al. A comparative study of contrast enhanced ultrasound and contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for the detection and characterization of hepatic hemangiomas. Biosci. Trends 2015, 9, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, C. Comments and Illustrations Regarding the Guidelines and Good Clinical Practice Recommendations for Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS)—Update 2008. Ultraschall Der Med. Eur. J. Ultrasound 2008, 29, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denis de Senneville, B.; Frulio, N.; Laumonier, H.; Salut, C.; Lafitte, L.; Trillaud, H. Liver contrast-enhanced sonography: Computer-assisted differentiation between focal nodular hyperplasia and inflammatory hepatocellular adenoma by reference to microbubble transport patterns. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 2995–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.Y. Contrast Enhanced Ultrasound for the Differentiation of Hepatic Mass. Clin. Ultrasound 2016, 1, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloth, C.; Kratzer, W.; Schmidberger, J.; Beer, M.; Clevert, D.A.; Graeter, T. Ultrasound 2020—Diagnostics & Therapy: On the Way to Multimodal Ultrasound: Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS), Microvascular Doppler Techniques, Fusion Imaging, Sonoelastography, Interventional Sonography. RöFo—Fortschritte Auf Dem Geb. der Röntgenstrahlen und der Bildgeb. Verfahr. 2020, 193, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.W. Clinical Application of a New Ultrasound Technique: Microvascular Imaging of the Liver. Clin. Ultrasound 2023, 8, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.-N.; Lv, K.; Jiang, Y.-X.; Jiang, T.-A. Application of superb microvascular imaging in focal liver lesions. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 7765–7775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, T.; Clevert, D.-A.; Schwarz, S.; Reidler, P.; Gassenmaier, S.; Knösel, T.; Rübenthaler, J.; Schwarze, V.; Armbruster, M. Diagnostic Value of CEUS Prompting Liver Biopsy: Histopathological Correlation of Hepatic Lesions with Ambiguous Imaging Characteristics. Diagnostics 2020, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chammas, M.C.; Bordini, A.L. Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography for the evaluation of malignant focal liver lesions. Ultrasonography 2022, 41, 4–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolotta, T.V.; Taibbi, A.; Randazzo, A.; Gagliardo, C. New frontiers in liver ultrasound: From mono to multi parametricity. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2021, 13, 1302–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alturkistany, S.; Jang, H.-J.; Yu, H.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, T.K. Fading hepatic hemangiomas on multiphasic CT. Abdom. Radiol. 2011, 37, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, J.; Lee, J.M.; Joo, I.; Yoon, J.H. Contrast vector imaging for differential diagnosis of focal liver lesions: Analysis of tumoral vascular structures and flow characteristics. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0314263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, W.; Liu, G.-J.; Chen, L.-D.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Liu, J.-Y.; Xie, X.-Y.; Lu, M.-D. Differentiation of Atypical Hepatocellular Carcinoma from Focal Nodular Hyperplasia: Diagnostic Performance of Contrast-enhanced US and Microflow Imaging. Radiology 2015, 275, 870–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Lv, X.-Z.; Zheng, X.; Ruan, S.-M.; Hu, H.-T.; Chen, L.-D.; Huang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.-Q.; Xie, X.-Y.; et al. Machine Learning-Based Ultrasomics Improves the Diagnostic Performance in Differentiating Focal Nodular Hyperplasia and Atypical Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 544979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Measure | Value |
|---|---|
| Panel A. Baseline lesion characteristics (overall, n = 72) | |
| Lesion size, mm—median (IQR) | 24.5 (16–37) |
| Skin-to-lesion length, mm—median (IQR) | 43 (28–62) |
| Hypoechoic—n (%) | 6 (8.3) |
| Hyperechoic—n (%) | 66 (91.7) |
| Panel B. Doppler/MI outcomes and MI signal distribution (appearance categories) | |
| CDI/PDI flow present—n (%) | 0 (0.0) |
| MI signal present—n (%) | 68 (94.4) |
| MI signal absent—n (%) | 4 (5.6) |
| Depth by MI signal (mm), median (IQR) | No MI signal: 85 (65.5–102) vs. MI-positive: 41.5 (27.5–59); p < 0.05 |
| MI patterns (calculated within MI-positive lesions, n = 68) | |
| Non-specific—n (%) | 17 (25.0) |
| Nodular-rim—n (%) | 15 (22.1) |
| Strip-rim—n (%) | 12 (17.6) |
| Central dot-like—n (%) | 11 (16.2) |
| Peripheral dot-like—n (%) | 7 (10.3) |
| Staining—n (%) | 6 (8.8) |
| Inter-observer agreement | κ = 0.821 (95% CI, 0.767–0.921) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baş, H.; Filiz, S. Microvascular Imaging of Hepatic Hemangiomas. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2917. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15222917
Baş H, Filiz S. Microvascular Imaging of Hepatic Hemangiomas. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(22):2917. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15222917
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaş, Hakan, and Süleyman Filiz. 2025. "Microvascular Imaging of Hepatic Hemangiomas" Diagnostics 15, no. 22: 2917. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15222917
APA StyleBaş, H., & Filiz, S. (2025). Microvascular Imaging of Hepatic Hemangiomas. Diagnostics, 15(22), 2917. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15222917






