Intratumoral SPP1+BCL2A1+ Tumor-Associated Macrophages Predict Poor Response to PD1 Blockade
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Dataset Analysis
2.2. Association with ICB Therapy Response
2.3. Post-Treatment Immune Transcriptomic Profiling
2.4. KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analysis for Longevity Signatures
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
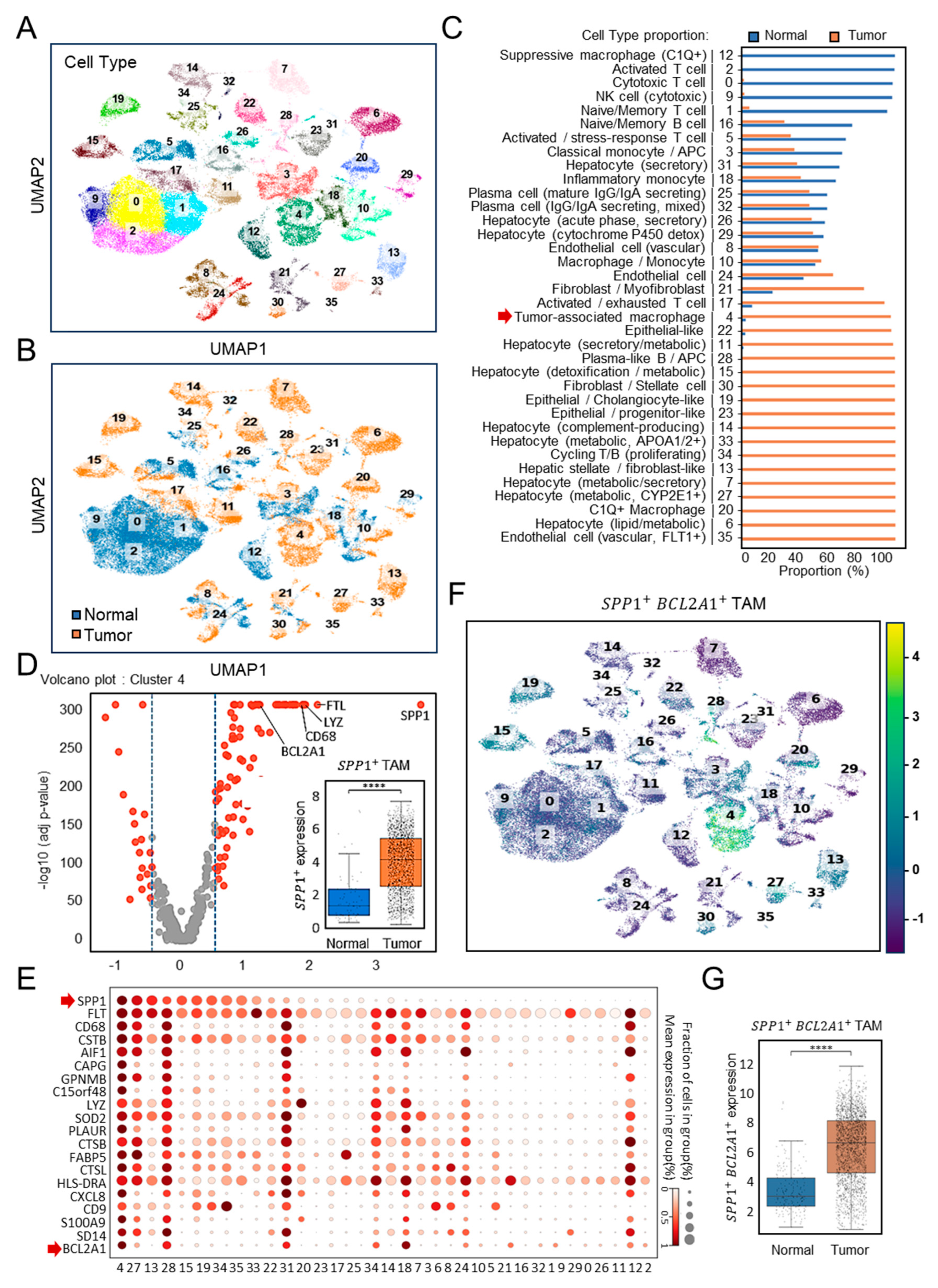
3.1. Single-Cell Identification of a New Subtype of SPP1+BCL2A1+ Tumor-Associated Macrophages (TAMs) in HCC (GSE149614)
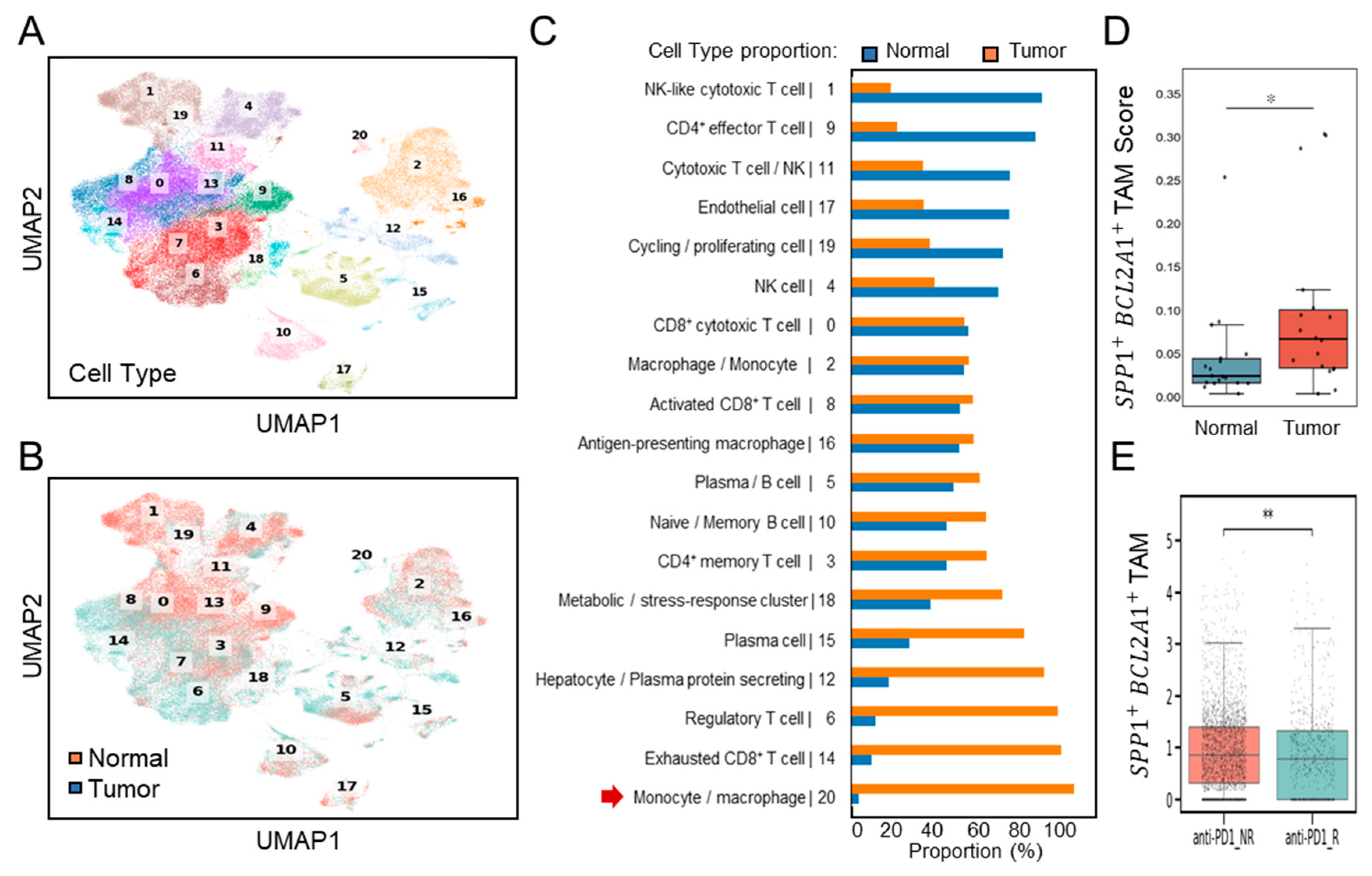
3.2. Association of SPP1+BCL2A1+ TAMs Enrichment with Response to PD-1 Blockade (GSE151530)
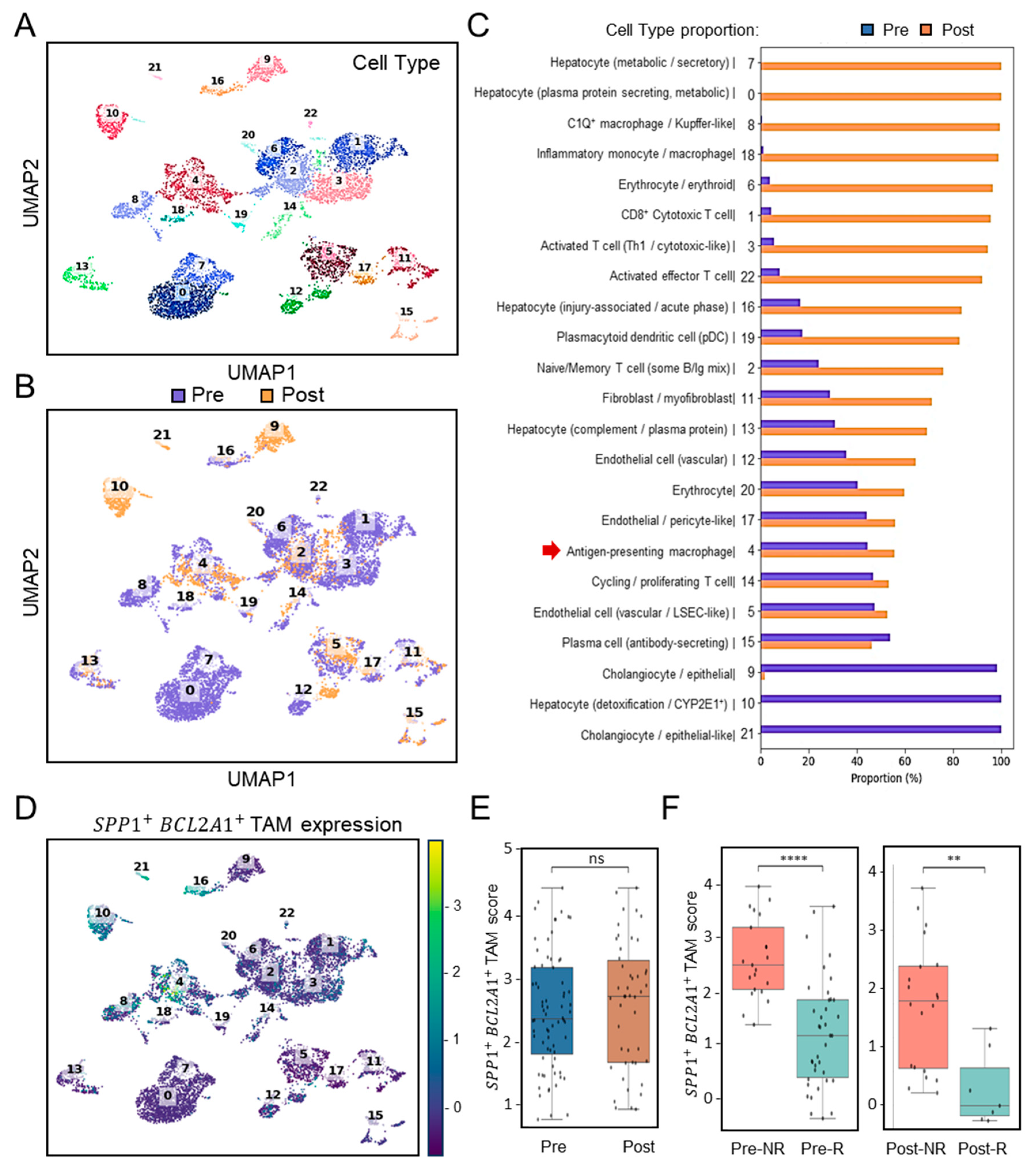
3.3. Validation of SPP1+BCL2A1+ TAMs Enrichment and Its Significance Across Independent HCC Cohort in the ICB Setting (GSE206325)
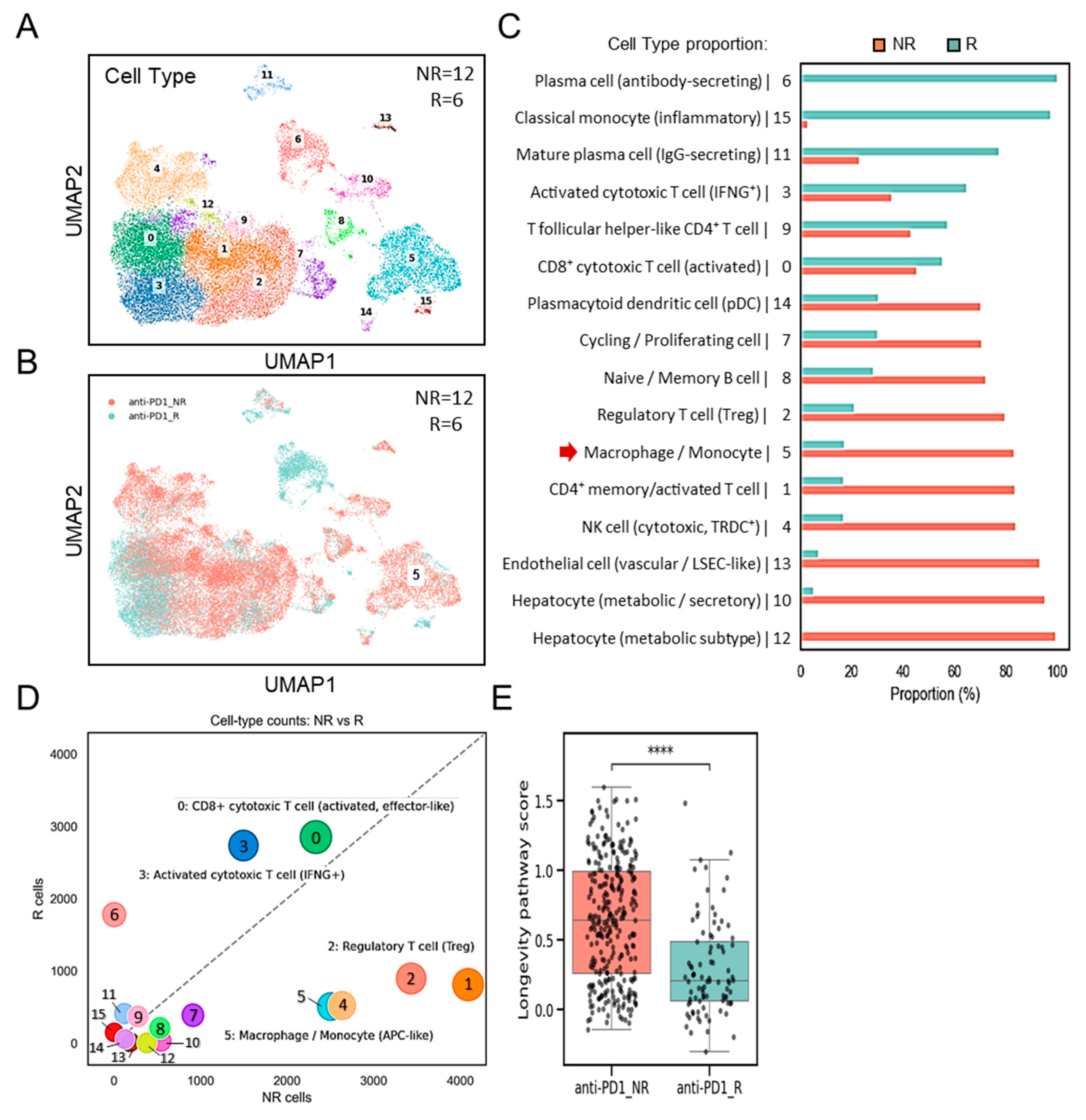
3.4. Distinct Enrichment of SPP1+BCL2A1+ TAMs Versus Cytotoxic T-Cell Responses in Non-Responders and Responders
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Llovet, J.M.; Kelley, R.K.; Villanueva, A.; Singal, A.G.; Pikarsky, E.; Roayaie, S.; Lencioni, R.; Koike, K.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Finn, R.S. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singal, A.G.; Salem, R.; Pinato, D.J.; Pillai, A. Advances in Locoregional and Systemic Treatments for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2025, 169, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, B.M.; Lim, H.J.; Brahmania, M.; Liu, D.M.; Tam, V.C.; McLeod, D.; Ramjeesingh, R.; Knox, J.J.; Vogel, A. Role of immune checkpoint inhibitor combinations in resectable and unresectable, embolization-eligible hepatocellular carcinoma. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2025, 17, 17588359251357719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Han, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y. PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint inhibitors in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1070961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Lu, M.; Che, J.; Chu, Q.; Zhang, P.; Chen, Y. Biomarkers and Future Perspectives for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Immunotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 716844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, G.; Gu, J.; Chen, Z.; Wu, J. Role of tumor-associated macrophages in hepatocellular carcinoma: Impact, mechanism, and therapy. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1429812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, N.; Su, X.; Gao, Y.; Yang, R. Novel tumor-associated macrophage populations and subpopulations by single cell RNA sequencing. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1264774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Kang, T.; Chen, S. The role of tumor-associated macrophages in tumor immune evasion. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 150, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, H.H.M.; Lee, R.Y.; Goh, S.; Tay, I.S.Y.; Lim, X.; Lee, B.; Chew, V.; Li, H.; Tan, B.; Lim, S.; et al. Immunohistochemical scoring of CD38 in the tumor microenvironment predicts responsiveness to anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sia, D.; Jiao, Y.; Martinez-Quetglas, I.; Kuchuk, O.; Villacorta-Martin, C.; de Moura, M.C.; Putra, J.; Camprecios, G.; Bassaganyas, L.; Akers, N.; et al. Identification of an Immune-specific Class of Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Based on Molecular Features. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 812–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Muller, W.J. The Multifaceted Role of Osteopontin in Modulating the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2025. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Zou, F.; He, S.; Pi, Y.; Song, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, L. Serum Osteopontin Enhances Hepatocellular Carcinoma Diagnosis and Predicts Anti-PD-L1 Immunotherapy Benefit. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2025, 12, 729–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lian, J.; Lu, H. The role of SPP1(+)TAMs in cancer: Impact on patient prognosis and future therapeutic targets. Int. J. Cancer 2025, 157, 1763–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Zhao, L.; Yang, Y.G.; Liu, W. The Role of Osteopontin in Tumor Progression Through Tumor-Associated Macrophages. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 953283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trehan, R.; Huang, P.; Zhu, X.B.; Wang, X.; Soliman, M.; Strepay, D.; Nur, A.; Kedei, N.; Arhin, M.; Ghabra, S.; et al. SPP1+ macrophages cause exhaustion of tumor-specific T cells in liver metastases. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xun, Z.; Ma, K.; Liang, S.; Li, X.; Zhou, S.; Sun, L.; Liu, Y.; Du, Y.; Guo, X.; et al. Identification of a tumour immune barrier in the HCC microenvironment that determines the efficacy of immunotherapy. J. Hepatol. 2023, 78, 770–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.X.; Ye, Y.M.; Chen, J.L.; Guo, X.Y.; Li, C.; Luo, J.; Lu, L.B.; Chen, X. SPP1+ tumor-associated macrophages define a high-risk subgroup and inform personalized therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2025, 15, 1606195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.; Lei, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ye, Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, W.; Zhou, C.; Tan, J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Integrative multi-omics and Mendelian randomization analysis reveal SPP1(+) tumor-associated macrophage-driven prognostic signature for hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2025, 12, 1594610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Kim, W.; Yuan, M.; Li, X.; Yang, H.; Li, M.; Shi, M.; Turkez, H.; Uhlen, M.; Zhang, C.; et al. Identification of SPP1(+) macrophages as an immune suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma using single-cell and bulk transcriptomics. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1446453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Chen, S.; Fan, Z.; Dong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Sun, X.; Song, Y.; Yang, J.; Cao, Q.; et al. Multi-dimensional single-cell characterization revealed suppressive immune microenvironment in AFP-positive hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Discov. 2023, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wang, L.; Khatib, S.A.; Chang, C.W.; Heinrich, S.; Dominguez, D.A.; Forgues, M.; Candia, J.; Hernandez, M.O.; Kelly, M.; et al. Single-cell atlas of tumor cell evolution in response to therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 1397–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Yang, A.; Quan, C.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Gao, C.; Lu, H.; Wang, X.; Cao, P.; et al. A single-cell atlas of the multicellular ecosystem of primary and metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magen, A.; Hamon, P.; Fiaschi, N.; Soong, B.Y.; Park, M.D.; Mattiuz, R.; Humblin, E.; Troncoso, L.; D’Souza, D.; Dawson, T.; et al. Intratumoral dendritic cell-CD4(+) T helper cell niches enable CD8(+) T cell differentiation following PD-1 blockade in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 1389–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, W.; Ji, Z. Assessing GPT-4 for cell type annotation in single-cell RNA-seq analysis. Nat. Methods 2024, 21, 1462–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogler, M.; Braun, Y.; Smith, V.M.; Westhoff, M.A.; Pereira, R.S.; Pieper, N.M.; Anders, M.; Callens, M.; Vervliet, T.; Abbas, M.; et al. The BCL2 family: From apoptosis mechanisms to new advances in targeted therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogler, M. BCL2A1: The underdog in the BCL2 family. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 19, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafezi, S.; Rahmani, M. Targeting BCL-2 in Cancer: Advances, Challenges, and Perspectives. Cancers 2021, 13, 1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, J.; Yao, R.; Liu, J.; Su, L.; You, W. Focusing on the interplay between tumor-associated macrophages and tumor microenvironment: From mechanism to intervention. Theranostics 2025, 15, 7378–7408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reggio, A.; Fuoco, C.; Deodati, R.; Palma, A. SPP1 macrophages across diseases: A call for reclassification? FASEB J. 2025, 39, e70448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Li, H.; Ma, W.; Cao, J.; Chen, Q.; Lu, F.; Qiu, M.; Zhou, P.; Xia, Z.; Zeng, K.; et al. The BCL-2 inhibitor APG-2575 resets tumor-associated macrophages toward the M1 phenotype, promoting a favorable response to anti-PD-1 therapy via NLRP3 activation. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2024, 21, 60–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, T.; Zhu, G.; Tang, Z.; Qu, W.; Yang, R.; Pan, H.; Wang, Y.; Tian, R.; Chen, L.; Guan, Z.; et al. Metabolism archetype cancer cells induce protumor TREM2(+) macrophages via oxLDL-mediated metabolic interplay in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 6770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, C.-H.; Hung, Y.-P.; Tseng, P.-C.; Satria, R.D.; Lin, C.-F. Intratumoral SPP1+BCL2A1+ Tumor-Associated Macrophages Predict Poor Response to PD1 Blockade. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2680. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15212680
Lai C-H, Hung Y-P, Tseng P-C, Satria RD, Lin C-F. Intratumoral SPP1+BCL2A1+ Tumor-Associated Macrophages Predict Poor Response to PD1 Blockade. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(21):2680. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15212680
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Chun-Hao, Yu-Ping Hung, Po-Chun Tseng, Rahmat Dani Satria, and Chiou-Feng Lin. 2025. "Intratumoral SPP1+BCL2A1+ Tumor-Associated Macrophages Predict Poor Response to PD1 Blockade" Diagnostics 15, no. 21: 2680. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15212680
APA StyleLai, C.-H., Hung, Y.-P., Tseng, P.-C., Satria, R. D., & Lin, C.-F. (2025). Intratumoral SPP1+BCL2A1+ Tumor-Associated Macrophages Predict Poor Response to PD1 Blockade. Diagnostics, 15(21), 2680. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15212680





