From Prompts to Practice: Evaluating ChatGPT, Gemini, and Grok Against Plastic Surgeons in Local Flap Decision-Making
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| LLM | Large Language Model |
| TLA | Three-letter acronym |
References
- Thamm, O.C.; Eschborn, J.; Schäfer, R.C.; Schmidt, J. Advances in Modern Microsurgery. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Hoz, E.C.; Verstockt, J.; Verspeek, S.; Clarys, W.; Thiessen, F.E.F.; Tondu, T.; Tjalma, W.A.A.; Steenackers, G.; Vanlanduit, S. Automated thermographic detection of blood vessels for DIEP flap reconstructive surgery. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2024, 19, 1733–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, K.; Kurz, A.; Haggenmüller, S.; Maron, R.C.; von Kalle, C.; Utikal, J.S.; Meier, F.; Hobelsberger, S.; Gellrich, F.F.; Sergon, M.; et al. Explainable artificial intelligence in skin cancer recognition: A systematic review. Eur. J. Cancer 2022, 167, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Hou, S.; Wang, X.; Li, D.; Lu, L. A Medical Image Segmentation Method Based on Improved UNet 3+ Network. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcaccini, G.; Seth, I.; Novo, J.; McClure, V.; Sacks, B.; Lim, K.; Ng, S.K.-H.; Cuomo, R.; Rozen, W.M. Leveraging Artificial Intelligence for Personalized Rehabilitation Programs for Head and Neck Surgery Patients. Technologies 2025, 13, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, T.; Nibali, A.; He, Z. Semi-supervised learning for medical image classification using imbalanced training data. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2022, 216, 106628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdar, M.; Samami, M.; Mahmoodabad, S.D.; Doan, T.; Mazoure, B.; Hashemifesharaki, R.; Liu, L.; Khosravi, A.; Acharya, U.R.; Makarenkov, V.; et al. Uncertainty quantification in skin cancer classification using three-way decision-based Bayesian deep learning. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 135, 104418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirikharaji, Z.; Abhishek, K.; Bissoto, A.; Barata, C.; Avila, S.; Valle, E.; Celebi, M.E.; Hamarneh, G. A survey on deep learning for skin lesion segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 2023, 88, 102863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, K.; Zanib, A.; Shabir, I.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Mahmood, T.; Rehman, A. Skin cancer detection using dermoscopic images with convolutional neural network. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlà, M.M.; Gambini, G.; Baldascino, A.; Giannuzzi, F.; Boselli, F.; Crincoli, E.; D’oNofrio, N.C.; Rizzo, S. Exploring AI-chatbots’ capability to suggest surgical planning in ophthalmology: ChatGPT versus Google Gemini analysis of retinal detachment cases. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2024, 108, 1457–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Kim, B.C. Diagnostic Performance of Large Language Models in Multimodal Analysis of Radiolucent Jaw Lesions. Int. Dent. J. 2025, 75, 103910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, W.; Du, Z.; Han, S. Semi-supervised skin cancer diagnosis based on self-feedback threshold focal learning. Discov. Oncol. 2024, 15, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Flores, L.A.; López-Martínez, J.B.; Rosales-De-La-Rosa, J.J.; Aillaud-De-Uriarte, D.; Contreras-Garduño, S.; Cortés-González, R. Assessment of Challenging Oncologic Cases: A Comparative Analysis Between ChatGPT, Gemini, and a Multidisciplinary Tumor Board. J. Surg. Oncol. 2025, 131, 1562–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzi, A.; Pugliese, G.; Maniaci, A.; Lechien, J.R.; Allevi, F.; Boscolo-Rizzo, P.; Vaira, L.A.; Saibene, A.M. Reliability of large language models for advanced head and neck malignancies management: A comparison between ChatGPT 4 and Gemini Advanced. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngology 2024, 281, 5001–5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efimenko, M.; Ignatev, A.; Koshechkin, K. Review of medical image recognition technologies to detect melanomas using neural networks. BMC Bioinform. 2020, 21, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, A.; Sarkar, S.; Schwenker, F.; Sarkar, R. Decoding skin cancer classification: Perspectives, insights, and advances through researchers’ lens. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 30542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elaziz, M.A.; Dahou, A.; Mabrouk, A.; El-Sappagh, S.; Aseeri, A.O. An Efficient Artificial Rabbits Optimization Based on Mutation Strategy For Skin Cancer Prediction. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 163, 107154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Huang, J.; Liu, K.; Liu, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Zong, Z.; Mao, S. ChatGPT-4o outperforms gemini advanced in assisting multidisciplinary decision-making for advanced gastric cancer. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. (EJSO) 2025, 51, 110096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcaccini, G.; Seth, I.; Shadid, O.; Cuomo, R.; Rozen, W.M. Drawing the Surgical Blueprint: Evaluating ChatGPT Versus Gemini Across Diverse Plastic Aesthetic Procedures. Surgeries 2025, 6, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, J.M.; Ryu, H.S.; Kim, J.S.; Cheong, J.Y.; Baek, S.; Kwak, J.M. Conversational artificial intelligence (chatGPT™) in the management of complex colorectal cancer patients: Early experience. ANZ J. Surg. 2023, 94, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karampinis, E.; Tzetzi, D.A.B.; Pappa, G.; Koumaki, D.; Sgouros, D.; Vakirlis, E.; Liakou, A.; Papakonstantis, M.; Papadakis, M.; Mantzaris, D.; et al. Use of a Large Language Model as a Dermatology Case Narrator: Exploring the Dynamics of a Chatbot as an Educational Tool in Dermatology. JMIR Dermatol. 2025, 8, e72058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Clinical Case | ChatGPT Response | Gemini Response | Grok Response | Surgeons’ Consensus Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
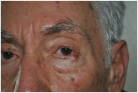 | Small post-surgical skin defect of approximately 0.5–0.7 cm at the medial third of the right lower eyelid margin, involving epidermis and dermis with partial eyelid contour irregularity. | A 0.5 cm ulcerated lesion with rolled borders and surrounding erythema and telangiectasias located on the lateral aspect of the left lower eyelid margin, involving the skin and underlying tarsal plate. | The ulcerated skin lesion is located on the right upper eyelid, measuring approximately 0.5 cm in greatest dimension, and involves partial-thickness skin with surrounding erythema. | Nodular lesion measuring approximately 0.5 cm in diameter, showing superficial ulceration and telangiectasias, with poorly defined margins in the upper portion and pearly, elevated borders in the lower portion; located at the lateral canthus of the left lower eyelid; with involvement of the conjunctiva and probable extension to the dermis. |
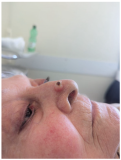 | Solitary, exophytic, pigmented nodular lesion measuring approximately 6–7 mm in diameter located on the nasal tip, limited to the cutaneous and subcutaneous tissue without deeper structural involvement. | A single, dome-shaped, and hyperpigmented nodule is located on the tip of the nose, measuring approximately 0.8 cm in diameter, with full-thickness involvement of the skin. | The skin lesion is a small, dark, crusted nodule approximately 0.5 cm in diameter located on the side of the nose, involving the epidermis and possibly the upper dermis. | Exophytic nodular cutaneous lesion, measuring approximately 0.5 cm in diameter, with a crusted apical surface and well-defined, erythematous margins; located just superior to the right nasal ala; with probable invasion of the superficial dermis only. |
 | Ulcerated, exophytic, pigmented-crusted lesion measuring approximately 15–18 mm in diameter located on the midline of the lower lip, involving the vermilion border and adjacent cutaneous tissue. | A solitary, exophytic, ulcerated, and crusted lesion is present on the central lower lip, measuring approximately 1.5 cm in diameter, with full-thickness involvement of the lip vermilion and extending to the surrounding skin. | The skin lesion is a dark, crusted, ulcerative mass approximately 1 cm in diameter located on the upper lip, involving the epidermis and possibly the dermis. | Exophytic and ulcerated cutaneous lesion of oval shape, with central crust and a maximum diameter of approximately 2 cm, exhibiting ill-defined erythematous margins; located at the mid-portion of the lower lip, involving the vermilion with probable extension to subcutaneous and submucosal tissues and adjacent perilesional skin. |
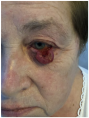 | Ulcerated nodular lesion of approximately 2.5–3 cm located at the left infraorbital region, involving the lower eyelid margin and extending to the medial canthus with partial distortion of the eyelid contour. | A well-defined, multi-lobulated, flesh-colored, friable mass of approximately 2 cm in diameter, with central ulceration and surrounding telangiectasias, located on the medial aspect of the left lower eyelid, involving the eyelid margin and extending into the conjunctival tissue. | The ulcerated skin lesion is located on the left lower eyelid, measuring approximately 1 cm in greatest dimension, and involves full-thickness skin with exposed subcutaneous tissue and surrounding erythema. | Elevated nodular lesion, reddish-violaceous in color, measuring approximately 3 cm in diameter, with a crusted area and central ulceration showing a necrotic and exudative base; located in the mid-portion of the left lower eyelid, with involvement of the eyelid margin and conjunctiva. |
 | Erythematous nodular lesion with central ulceration and crusting, approximately 10–12 mm in diameter, located on the vertex scalp, involving skin and superficial subcutaneous tissue. | A nodular and ulcerated lesion is present on the scalp, measuring approximately 1.5 cm in diameter, with full-thickness skin involvement. | The skin lesion is a small, dark, crusted ulcer approximately 0.5 cm in diameter located on the top of the scalp, involving the epidermis and possibly the upper dermis. | Nodular cutaneous lesion with central ulceration, measuring approximately 1.5 cm, with irregular yet well-defined margins; located at the vertex of the scalp, with probable invasion of the upper dermis but without apparent involvement of the surrounding skin. |
 | Ulcerated, exophytic, necrotic-crusted lesion measuring approximately 20–25 mm in diameter located on the nasal tip and columella, involving cutaneous and subcutaneous tissues with partial obstruction of the nostrils. | A necrotic lesion is present on the nasal dorsum and tip, measuring approximately 2.0 × 2.5 cm, with full-thickness involvement of the skin, including cartilage. | The skin lesion is a dark, crusted, ulcerative mass approximately 1.5 cm in diameter located on the tip of the nose, involving the epidermis, dermis, and possibly underlying cartilage. | Exophytic crusted cutaneous lesion with hyperkeratotic and necrotic features, rhomboid in shape, measuring approximately 2 × 2 cm, with well-defined margins and no apparent involvement of the surrounding skin; located at the tip of the nose; involvement probably limited to subcutaneous tissue. |
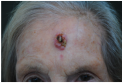 | Ulcerated nodular lesion with central necrosis and peripheral induration, approximately 15–18 mm in diameter, located on the central forehead, involving cutaneous and superficial subcutaneous tissue. | A centrally ulcerated and crusted lesion with a raised erythematous border is located on the central forehead, measuring approximately 2.0 cm in diameter, with full-thickness involvement of the skin. | The skin lesion is a dark, crusted, ulcerative mass approximately 1.5 cm in diameter located on the center of the forehead, involving the epidermis and possibly the dermis. | Multinodular cutaneous lesion measuring approximately 2 cm in maximum diameter, characterized by a necrotic-crusted area on the superior portion and a hyperkeratotic component on the left side, with indistinct erythematous margins and a peripheral pearly rim; located on the central forehead; with probable full-thickness skin involvement. |
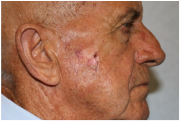 | Atrophic, erythematous lesion with central ulceration and crusting, approximately 10–12 mm in diameter, located on the left malar region, involving cutaneous and superficial subcutaneous tissue. | A pinkish, irregular, and centrally ulcerated skin defect is located on the right cheek, measuring approximately 1.5 × 1.0 cm, with full-thickness involvement of the skin. | The skin lesion is a pinkish, ulcerated defect with central crust and exudate approximately 2 cm in diameter located on the cheek, involving the epidermis and dermis. | Flat cutaneous lesion measuring approximately 1 cm, with ulceration in the superior portion, a centrally atrophic and depressed area, and inferior hyperkeratosis; margins are slightly elevated, irregular, and ill-defined. Located over the right zygomatic region, with probable involvement of the deep dermis. Superoposteriorly, a smaller lesion with similar characteristics is also visible. |
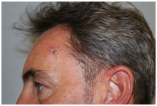 | Crusted ulcerated lesion measuring approximately 8–10 mm in diameter located on the left temporal region, involving cutaneous and superficial subcutaneous tissue. | A nodular, centrally ulcerated lesion is located on the right frontal scalp, measuring approximately 1.5 cm in diameter, with full-thickness involvement of the skin. | The skin lesion is a small, crusted, erythematous ulcer approximately 1 cm in diameter located on the forehead near the hairline, involving the epidermis and possibly the upper dermis. | Flat, hyperkeratotic skin lesion measuring approximately 1.5 cm in its largest diameter, with irregular and ill-defined margins. Located on the left temporal region; with probable involvement of the dermis. Perilesional skin demonstrates the presence of telangiectasias. |
 | Ulcerated lesion with granulation tissue and peripheral induration, approximately 25–30 mm in diameter, located on the anterior aspect of the lower leg, involving skin and subcutaneous tissue. | A solitary, exophytic, ulcerated, and friable lesion is located on the anterior aspect of the lower leg, measuring approximately 2.0 × 2.5 cm, with full-thickness involvement of the skin. | The image shows a skin lesion on the lower leg, approximately 2 cm in diameter, appearing as a reddish, ulcerated, and crusted area, possibly involving the epidermis and dermis, with a bandage nearby. | Exophytic, ulcerated cutaneous lesion of rounded shape, measuring approximately 3 cm in diameter, with peripheral fibrinous areas and raised, irregular margins. Located on the antero-medial aspect of the left leg; with probable full-thickness skin involvement. Surrounding skin is mildly erythematous. |
| Case | ChatGPT | Gemini | Grok | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site | Size | Tissue | Site | Size | Tissue | Site | Size | Tissue | |
| 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| 6 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| 7 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 8 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 9 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 10 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| AI | Parameter | Correct | % Correct | 95%CI Low | 95%CI High |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ChatGPT | Site | 4 | 40 | 16.8 | 68.7 |
| ChatGPT | Size | 9 | 90 | 59.6 | 98.2 |
| ChatGPT | Tissues | 1 | 10 | 1.8 | 40.4 |
| Gemini | Site | 3 | 30 | 10.8 | 60.3 |
| Gemini | Size | 9 | 90 | 59.6 | 98.2 |
| Gemini | Tissues | 2 | 20 | 5.7 | 51.0 |
| Grok | Site | 3 | 30 | 10.8 | 60.3 |
| Grok | Size | 5 | 50 | 23.7 | 76.3 |
| Grok | Tissues | 6 | 60 | 31.3 | 83.2 |
| AI | Parameter | Correct | % Correct | 95%CI Low | 95%CI High |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ChatGPT | Site | 8 | 80 | 49.0 | 94.3 |
| ChatGPT | Size | 10 | 100 | 72.2 | 100 |
| ChatGPT | Tissues | 9 | 90 | 59.6 | 98.2 |
| Gemini | Site | 9 | 90 | 59.6 | 98.2 |
| Gemini | Size | 9 | 90 | 59.6 | 98.2 |
| Gemini | Tissues | 8 | 80 | 49.0 | 94.3 |
| Grok | Site | 6 | 60 | 31.3 | 83.2 |
| Grok | Size | 5 | 50 | 23.7 | 76.3 |
| Grok | Tissues | 7 | 70 | 39.7 | 89.2 |
| Clinical Case | ChatGPT Response | Gemini Response | Grok Response | Surgeons’ Consensus Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tenzel flap | Tenzel semicircular flap | Tenzel flap | Tenzel flap |
| 2 | Bilobed flap | Dorsal nasal flap | Bilobed flap | Bilobed flap |
| 3 | Abbe flap | Abbe flap | Abbe flap | Abbe flap |
| 4 | Mustardé flap | Cutler–Beard bridge flap | Mustardé flap | Mustardé flap |
| 5 | Rotation flap | V-Y advancement flap | Rotation flap | Pinwheel rotation flap |
| 6 | Forehead flap | Medial cheek V-Y advancement flap | Bilobed flap | Forehead flap |
| 7 | A-to-T advancement flap | Glabellar flap | A-T flap | A-to-T flap |
| 8 | Limberg flap | Mustardé flap | Rhomboid flap | Limberg flap |
| 9 | O-to-H flap | Rhomboid flap | Note flap | O-to-H flap |
| 10 | Keystone flap | Fasciocutaneous propeller flap | Advancement flap | Keystone flap |
| Case | ChatGPT | Gemini | Grok |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 4 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| 5 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| 6 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 7 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| 8 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| 9 | 2 | 0 | 1 |
| 10 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Model | n Cases | n Correct (Score = 2) | % Correct (Score = 2) | 95% CI (Score = 2) Low | 95% CI (score = 2) High | n ≥ 1 | % ≥1 | 95% CI (≥1) Low | 95% CI (≥1) High | Mean Score (0–2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ChatGPT | 10 | 10 | 100 | 72.2 | 100 | 10 | 100 | 72.2 | 100 | 2.0 |
| Gemini | 10 | 2 | 20 | 5.7 | 51 | 4 | 40 | 16.8 | 68.7 | 0.6 |
| Grok | 10 | 7 | 70 | 39.7 | 89 | 9 | 90 | 59.6 | 98.2 | 1.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marcaccini, G.; Corradini, L.; Shadid, O.; Seth, I.; Rozen, W.M.; Grimaldi, L.; Cuomo, R. From Prompts to Practice: Evaluating ChatGPT, Gemini, and Grok Against Plastic Surgeons in Local Flap Decision-Making. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2646. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15202646
Marcaccini G, Corradini L, Shadid O, Seth I, Rozen WM, Grimaldi L, Cuomo R. From Prompts to Practice: Evaluating ChatGPT, Gemini, and Grok Against Plastic Surgeons in Local Flap Decision-Making. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(20):2646. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15202646
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarcaccini, Gianluca, Luca Corradini, Omar Shadid, Ishith Seth, Warren M. Rozen, Luca Grimaldi, and Roberto Cuomo. 2025. "From Prompts to Practice: Evaluating ChatGPT, Gemini, and Grok Against Plastic Surgeons in Local Flap Decision-Making" Diagnostics 15, no. 20: 2646. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15202646
APA StyleMarcaccini, G., Corradini, L., Shadid, O., Seth, I., Rozen, W. M., Grimaldi, L., & Cuomo, R. (2025). From Prompts to Practice: Evaluating ChatGPT, Gemini, and Grok Against Plastic Surgeons in Local Flap Decision-Making. Diagnostics, 15(20), 2646. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15202646









