Evaluation of MRI-Based Measurements for Patellar Dislocation: Reliability and Reproducibility
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. MRI Scanning
- Trochlear dysplasia measurements
- Lateralization measurements
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balcarek, P.; Radebold, T.; Schulz, X.; Vogel, D. Geometry of Torsional Malalignment Syndrome: Trochlear Dysplasia but Not Torsion Predicts Lateral Patellar Instability. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2019, 7, 2325967119829790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, J.L.; Stewart, C. Patellar instability. Orthop. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 46, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistovich, R.J.; Urwin, J.W.; Fabricant, P.D.; Lawrence, J.T.R. Patellar tendon-lateral trochlear ridge distance: A novel measurement of patellofemoral instability. Am. J. Sports Med. 2018, 46, 3400–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillanpää, P.; Mattila, V.M.; Iivonen, T.; Visuri, T.; Pihlajamäki, H. Incidence and risk factors of acute traumatic primary patellar dislocation. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2008, 40, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, M.; Blønd, L.; Hölmich, P.; Steensen, R.N.; Diederichs, G.; Feller, J.A.; Barfod, K.W. Quality assessment of radiological measurements of trochlear dysplasia; a literature review. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2018, 26, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejour, H.; Walch, G.; Nove-Josserand, L.; Guier, C. Factors of patellar instability: An anatomic radiographic study. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 1994, 2, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitlinger, G.; Scheurecker, G.; Högler, R.; Labey, L.; Innocenti, B.; Hofmann, S. Tibial tubercle-posterior cruciate ligament distance: A new measurement to define the position of the tibial tubercle in patients with patellar dislocation. Am. J. Sports Med. 2012, 40, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dejour, D.; Le Coultre, B. Osteotomies in patello-femoral instabilities. Sports Med. Arthrosc. Rev. 2007, 15, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrillon, Y.; Abidi, H.; Dejour, D.; Fantino, O.; Moyen, B.; Tran-Minh, V.A. Patellar instability: Assessment on MR images by measuring the lateral trochlear inclination-initial experience. Radiology 2000, 216, 582–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berruto, M.; Ferrua, P.; Carimati, G.; Uboldi, F.; Gala, L. Patellofemoral instability: Classification and imaging. Joints 2013, 1, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Charles, M.D.; Haloman, S.; Chen, L.; Ward, S.R.; Fithian, D.; Afra, R. Magnetic resonance imaging-based topographical differences between control and recurrent patellofemoral instability patients. Am. J. Sports Med. 2013, 41, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, D.; Guermazi, A.; Kwoh, C.K. Clinical and translational potential of MRI evaluation in knee osteoarthritis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2014, 16, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mackenzie, R.; Dixon, A.K.; Keene, G.S.; Hollingworth, W.; Lomas, D.J.; Villar, R.N. Magnetic resonance imaging of the knee: Assessment of effectiveness. Clin. Radiol. 1996, 51, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandit, S.; Frampton, C.; Stoddart, J.; Lynskey, T. Magnetic resonance imaging assessment of tibial tuberosity-trochlear groove distance: Normal values for males and females. Int. Orthop. 2011, 35, 1799–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danieli, M.V.; Guerreiro, J.P.; Queiroz, A.; Pereira, H.; Tagima, S.; Marini, M.G.; Cataneo, D.C. Diagnosis and classification of chondral knee injuries: Comparison between magnetic resonance imaging and arthroscopy. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2016, 24, 1627–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, S.M.; Cheng, C.; Solomito, M.J.; Pace, J.L. Lateral trochlear inclination in children and adolescents: Modified measurement technique to characterize patellar instability. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2019, 7 (Suppl. S3), 2325967119S00146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, A.; Subhawong, T.K.; Carrino, J.A. A systematised MRI approach to evaluating the patellofemoral joint. Skelet. Radiol. 2011, 40, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfirrmann, C.W.; Zanetti, M.; Romero, J.; Hodler, J. Femoral trochlear dysplasia: MR findings. Radiology 2000, 216, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittstein, J.R.; O’Brien, S.D.; Vinson, E.N.; Garrett, W.E., Jr. MRI evaluation of anterior knee pain: Predicting response to nonoperative treatment. Skelet. Radiol. 2009, 38, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. Erratum to “A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research” [J Chiropr Med 2016;15(2):155-163]. J. Chiropr. Med. 2017, 16, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askenberger, M.; Ekström, W.; Finnbogason, T.; Janarv, P.M. Occult Intra-articular Knee Injuries in Children with Hemarthrosis. Am. J. Sports Med. 2014, 42, 1600–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkin, D.M.; Fithian, D.C.; Marangi, K.S.; Stone, M.L.; Dobson, B.E.; Mendelsohn, C. Characteristics of patients with primary acute lateral patellar dislocation and their recovery within the first 6 months of injury. Am. J. Sports Med. 2000, 8, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, C.A.; Pratte, E.L.; Sherman, S.L.; Arendt, E.A.; Hinckel, B.B. Reconstruction of the medial patellotibial ligament results in favorable clinical outcomes: A systematic review. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2018, 26, 2920–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steensen, R.N.; Bentley, J.C.; Trinh, T.Q.; Backes, J.R.; Wiltfong, R.E. The prevalence and combined prevalences of anatomic factors associated with recurrent patellar dislocation: A magnetic resonance imaging study. Am. J. Sports Med. 2015, 43, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arendt, E.A.; Askenberger, M.; Agel, J.; Tompkins, M.A. Risk of Redislocation After Primary Patellar Dislocation: A Clinical Prediction Model Based on Magnetic Resonance Imaging Variables. Am. J. Sports Med. 2018, 46, 3385–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelitz, M.; Lippacher, S.; Reichel, H.; Dornacher, D. Evaluation of trochlear dysplasia using MRI: Correlation between the classification system of Dejour and objective parameters of trochlear dysplasia. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2014, 22, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frings, J.; Dust, T.; Krause, M.; Ohlmeier, M.; Frosch, K.H.; Adam, G.; Warncke, M.; Maas, K.J.; Henes, F.O. Objective assessment of patellar maltracking with 3 T dynamic magnetic resonance imaging: Feasibility of a robust and reliable measuring technique. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvanifar, S.C.; Flesher, B.L.; Jones, K.C.; Elias, J.J. Lateral patellar maltracking due to trochlear dysplasia: A computational study. Knee 2019, 26, 1234–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, B.; Hess, S.; Moser, L.; Hirschmann, M.T.; Amsler, F.; Behrend, H. Correction to: Healthy knees have a highly variable patellofemoral alignment: A systematic review. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2020, 28, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Huyssteen, A.L.; Hendrix, M.R.; Barnett, A.J.; Wakeley, C.J.; Eldridge, J.D. Cartilage-bone mismatch in the dysplastic trochlea. An MRI study. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2006, 88, 688–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippacher, S.; Dejour, D.; Elsharkawi, M.; Dornacher, D.; Ring, C.; Dreyhaupt, J.; Reichel, H.; Nelitz, M. Observer agreement on the Dejour trochlear dysplasia classification: A comparison of true lateral radiographs and axial magnetic resonance images. Am. J. Sports Med. 2012, 40, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoettle, P.B.; Zanetti, M.; Seifert, B.; Pfirrmann, C.W.; Fucentese, S.F.; Romero, J. The tibial tuberosity-trochlear groove distance; a comparative study between CT and MRI scanning. Knee 2006, 13, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, M.V.; Hillen, T.J.; Misra, S.; Hildebolt, C.F.; Rubin, D.A. Quantitative variable assessment of patellar instability: An MRI-based Study. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 215, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace, J.L.; Cheng, C.; Joseph, S.M.; Solomito, M.J. Effect of trochlear dysplasia on commonly used radiographic parameters to assess patellar instability. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2020, 8, 2325967120938760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, V.R.; Sheehan, F.T.; Shen, A.; Yao, L.; Jackson, J.N.; Boden, B.P. The Relationship of static tibial tubercle-trochlear groove measurement and dynamic patellar tracking. Am. J. Sports Med. 2017, 45, 1856–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caplan, N.; Lees, D.; Newby, M.; Ewen, A.; Jackson, R.; St. Clair Gibson, A.; Kader, D. Is tibial tuberosity-trochlear groove distance an appropriate measure for the identification of knees with patellar instability? Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2014, 22, 2377–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Fu, B.; Mohamed, S.I.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, A. Tibial tubercle-Roman arch distance: A new measurement of patellar dislocation and indication of tibial tubercle osteotomy. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2020, 8, 2325967120914872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tensho, K.; Shimodaira, H.; Akaoka, Y.; Koyama, S.; Hatanaka, D.; Ikegami, S.; Kato, H.; Saito, N. Lateralization of the tibial tubercle in recurrent patellar dislocation: Verification using multiple methods to evaluate the tibial tubercle. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2018, 100, e58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camp, C.L.; Stuart, M.J.; Krych, A.J.; Levy, B.A.; Bond, J.R.; Collins, M.S.; Dahm, D.L. CT and MRI measurements of tibial tubercle-trochlear groove distances are not equivalent in patients with patellar instability. Am. J. Sports Med. 2013, 41, 1835–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennock, A.T.; Alam, M.; Bastrom, T. Variation in tibial tubercle-trochlear groove measurement as a function of age, sex, size, and patellar instability. Am. J. Sports Med. 2014, 42, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandmeier, R.H.; Burks, R.T.; Bachus, K.N.; Billings, A. The effect of reconstruction of the medial patellofemoral ligament on patellar tracking. Am. J. Sports Med. 2000, 28, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biyani, R.; Elias, J.J.; Saranathan, A.; Feng, H.; Guseila, L.M.; Morscher, M.A.; Jones, K.C. Anatomical factors influencing patellar tracking in the unstable patellofemoral joint. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2014, 22, 2334–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elias, J.J.; Smith, B.W.; Daney, B.T. Biomechanical analysis of tibial tuberosity medialization and medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction. Sports Med. Arthrosc. Rev. 2017, 25, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, J.M.; Rosencrans, A.S.; Shubin Stein, B.E. Use of TT-PCL versus TT-TG. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2018, 11, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, J.M.; Sullivan, J.P.; Nguyen, J.; Mintz, D.; Green, D.W.; Strickland, S.; Shubin Stein, B.E. The tibial tubercle-to-trochlear groove distance is reliable in the setting of trochlear dysplasia, and superior to the tibial tubercle-to-posterior cruciate ligament distance when evaluating coronal malalignment in patellofemoral instability. Arthroscopy 2017, 33, 2026–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anley, C.M.; Morris, G.V.; Saithna, A.; James, S.L.; Snow, M. Defining the role of the tibial tubercle-trochlear groove and tibial tubercle-posterior cruciate ligament distances in the work-up of patients with patellofemoral disorders. Am. J. Sports Med. 2015, 43, 1348–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gültekin, M.Z.; Keskin, Z.; Dinçel, Y.M.; Arslan, T. Effect of demographic features on morphometric variables of the knee joint: Sample of a 20 to 40-year-old Turkish population. Medicine 2023, 102, e33253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
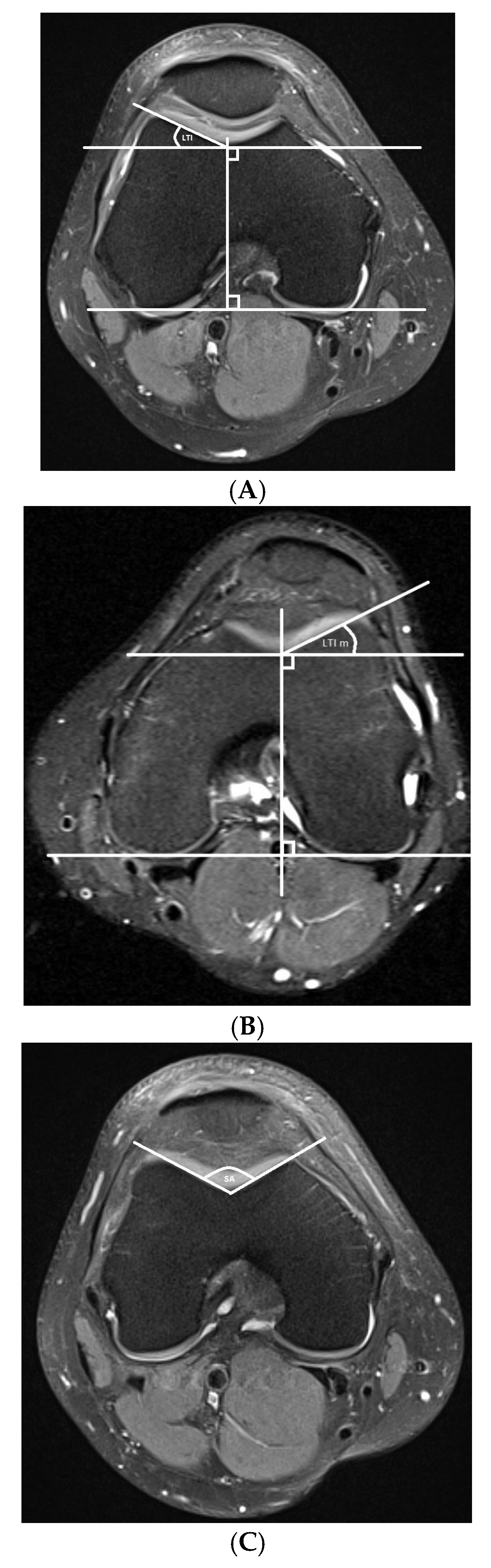
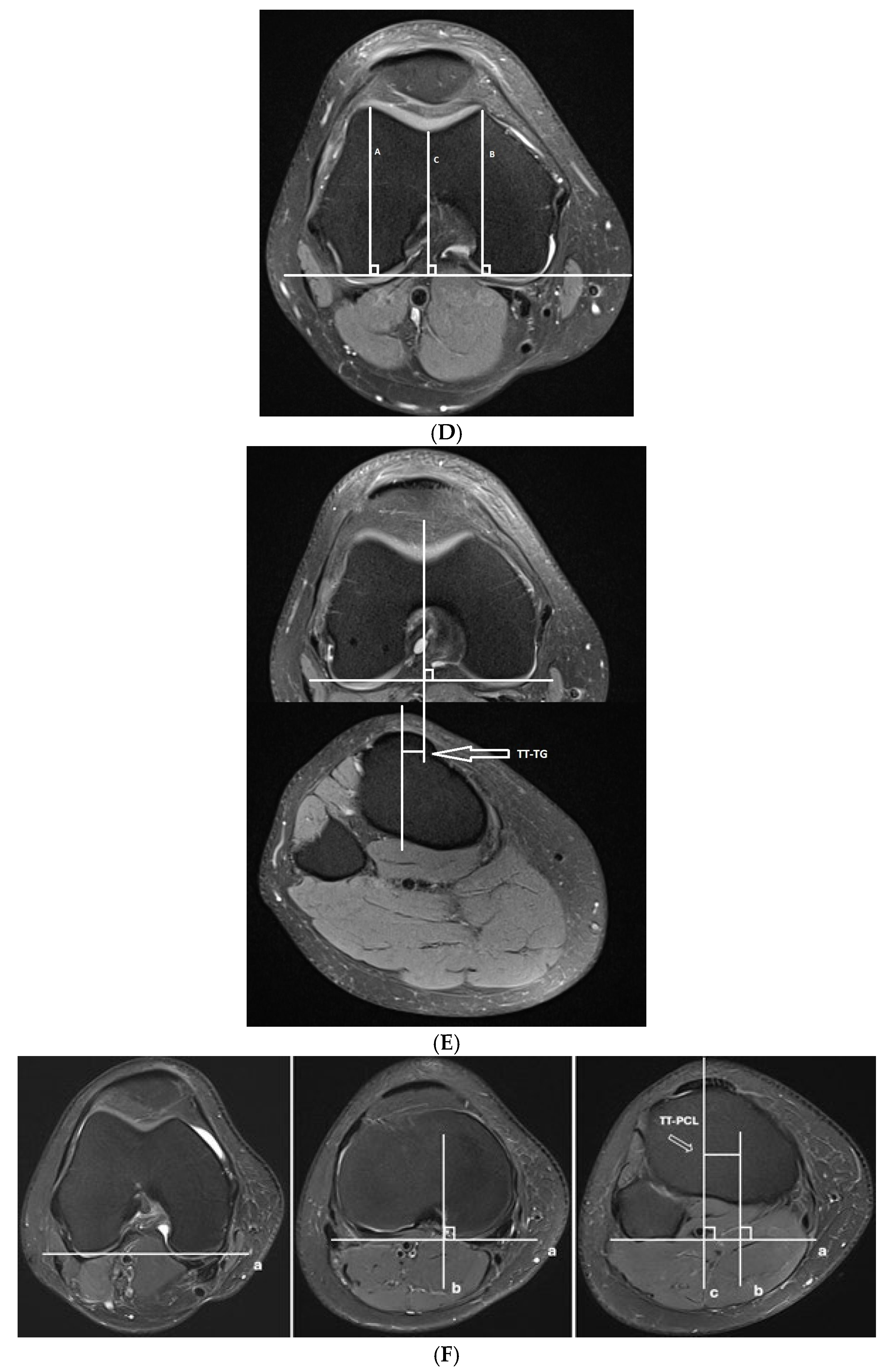
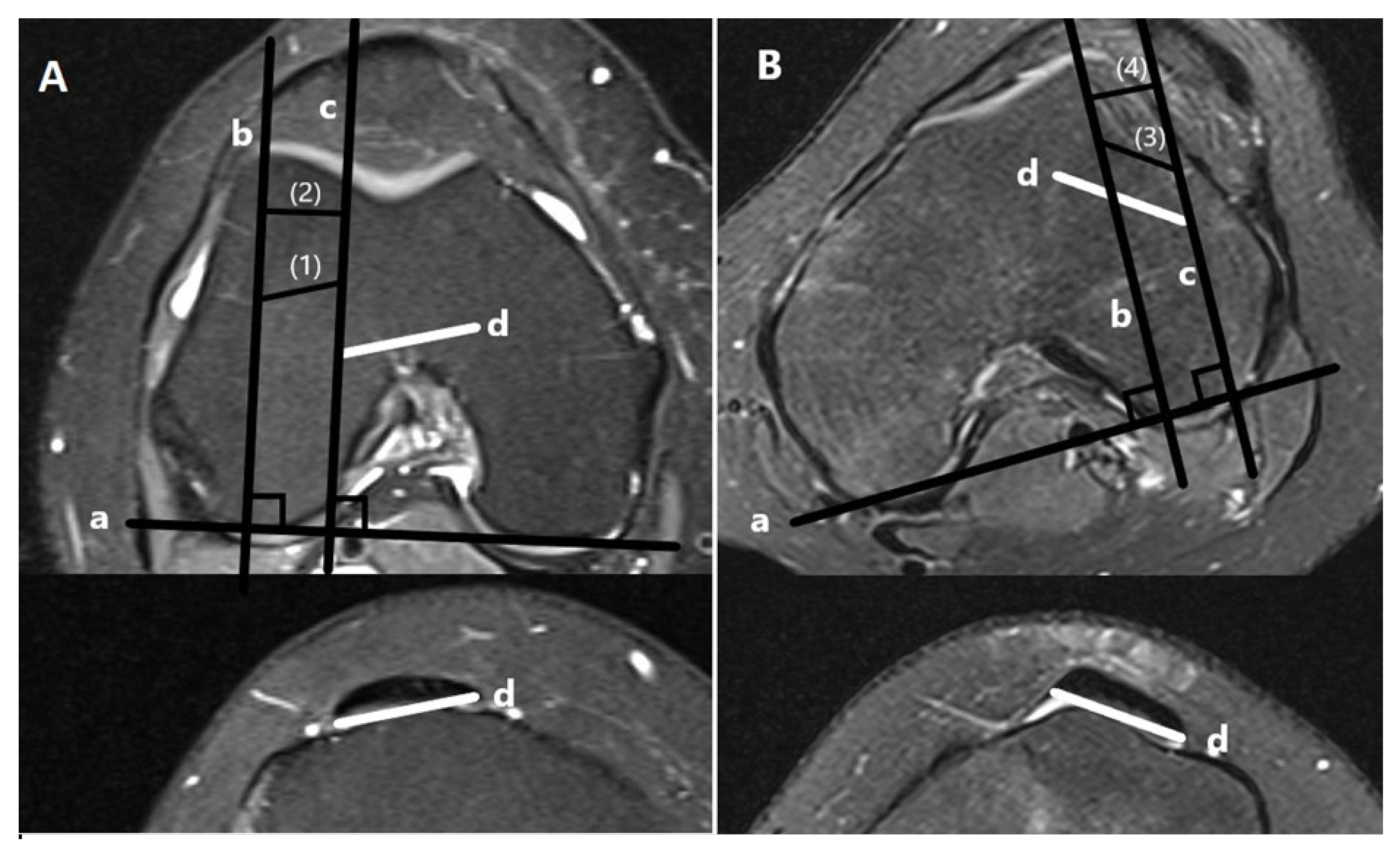

| FOV (cm) | Slice Thickness (mm) | TR | TE | Matrix (At Least) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coronal T1 SE | 32 | 3 | 500 | 15 | 288 × 288 |
| Coronal PD FS | 38 | 3 | >2500 | 20–30 | 288 × 288 |
| Sagittal PD FS | 38 | 3 | >2500 | 20–30 | 288 × 288 |
| Axial PD FS | 38 | 3 | >2500 | 20–30 | 256 × 256 |
| Sagittal PD | 32 | 0.6 | 1000 | 20–30 | 288 × 288 |
| Measurement | * ICC (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|
| Control Group | Dislocation Group | |
| PT-LTR | 0.708 (0.513–0.830) | 0.629 (0.221–0.821) |
| PT-LTR horizontal | 0.729 (0.550–0.841) | 0.613 (0.235–0.806) |
| SA | 0.432 (−0.033–0.707) | 0.453 (0.150–0.676) |
| TT-TG | 0.862 (0.593–0.941) | 0.788 (0.030–0.933) |
| LTR-TG | 0.638 (0.343–0.801) | 0.571 (0.121–0.793) |
| WPT | 0.949 (0.911–0.971) | 0.857 (0.735–0.924) |
| TT-PCL | 0.671 (0.482–0.800) | 0.530 (0.258–0.725) |
| LTI | 0.871 (0.726–0.934) | 0.916 (0.600–0.970) |
| LTI modified | 0.715 (0.543–0.829) | 0.542 (0.242–0.741) |
| TD | 0.471 (−0.061–0.753) | 0.378 (0.067–0.621) |
| Mean ± SD | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measurement | Control Group | Dislocation Group | p1 | c AUC | d 95% CI | p2 |
| PT-LTR/mm | −1.90 ± 2.95 | 4.88 ± 4.13 | <0.001 a | 0.898 | 0.814 to 0.953 | <0.001 |
| PT-LTR horizontal/mm | −1.79 ± 2.74 | 4.40 ± 3.79 | <0.001 a | 0.896 | 0.812 to 0.952 | <0.001 |
| SA/° | 130.89 ± 5.80 | 146.62 ± 7.79 | <0.001 b | 0.950 | 0.880 to 0.985 | <0.001 |
| TT-TG/mm | 9.14 ± 3.77 | 15.09 ± 4.07 | <0.001 b | 0.857 | 0.765 to 0.923 | <0.001 |
| LTR-TG/mm | 22.10 ± 3.45 | 22.99 ± 2.79 | 0.203 b | 0.590 | 0.479 to 0.695 | 0.146 |
| TT-PCL/mm | 19.49 ± 3.82 | 21.89 ± 4.97 | 0.013 b | 0.649 | 0.539 to 0.749 | 0.014 |
| LTI/° | 21.20 ± 3.93 | 8.33 ± 4.40 | <0.001 b | 0.981 | 0.957 to 1.00 | <0.001 |
| LTI modified/° | 24.58 ± 4.46 | 16.22 ± 3.78 | <0.001 b | 0.937 | 0.863 to 0.978 | <0.001 |
| TD/mm | 6.82 ± 1.34 | 3.57 ± 1.16 | <0.001 b | 0.972 | 0.912 to 0.996 | <0.001 |
| Measurement | Cut-Off | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PT-LTR horizontal/mm | >0 * | 81.6 | 87.5 |
| PT-LTR/mm | >0 * | 81.6 | 87.5 |
| SA/° | >137.82 | 89.5 | 93.7 |
| TT-TG/mm | >12.43 | 73.7 | 87.5 |
| LTI/° | ≤12.85 | 89.5 | 97.9 |
| LTI modified/° | ≤19.43 | 81.6 | 93.7 |
| TD/mm | ≤5.09 | 97.4 | 85.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brumini, I.; Pranjkovic, T.; Veljkovic Vujaklija, D. Evaluation of MRI-Based Measurements for Patellar Dislocation: Reliability and Reproducibility. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2647. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15202647
Brumini I, Pranjkovic T, Veljkovic Vujaklija D. Evaluation of MRI-Based Measurements for Patellar Dislocation: Reliability and Reproducibility. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(20):2647. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15202647
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrumini, Ivan, Tamara Pranjkovic, and Danijela Veljkovic Vujaklija. 2025. "Evaluation of MRI-Based Measurements for Patellar Dislocation: Reliability and Reproducibility" Diagnostics 15, no. 20: 2647. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15202647
APA StyleBrumini, I., Pranjkovic, T., & Veljkovic Vujaklija, D. (2025). Evaluation of MRI-Based Measurements for Patellar Dislocation: Reliability and Reproducibility. Diagnostics, 15(20), 2647. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15202647







