Influence of Scleral Contact Lenses on Optical Coherence Tomography Parameters in Keratoconus Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Ethics
2.2. Patients
2.3. Scleral Contact Lens Details and Fitting Process
2.4. Optical Coherence Tomography Assessments
2.5. Examination Protocol
2.6. Parameters
2.7. Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Corneal Topographic Values
3.2. Changes in OCT Measurements With and Without Scleral Contact Lenses
3.3. Correlation Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, N.J.; Raiskup, F.; Pillunat, L.E.; Wang, Q.M.; Cui, L.L.; Herber, R. New keratoconus grading system based on OCT: Threshold adjustment for SS-OCT. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2025, 51, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourgues, E.; Saunier, V.; Smadja, D.; Touboul, D.; Saunier, V. Forme fruste keratoconus detection with OCT corneal topography using artificial intelligence algorithms. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2024, 50, 1247–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Maeno, S.; Wang, Y.; Koh, S.; Chen, S.; Quantock, A.J.; Morgan, S.R.; Hayes, S.; McAlinden, C. Early diagnosis of keratoconus using corneal biomechanics and OCT derived technologies. Eye Vis. 2025, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeno, S.; Koh, S.; Inoue, R.; Oie, Y.; Maeda, N.; Jhanji, V.; Nishida, K. Fourier Analysis on Irregular Corneal Astigmatism Using Optical Coherence Tomography in Various Severity Stages of Keratoconus. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 243, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulpus, A.; Henry, R.; White, L.; Lopes, B.T.; Romano, V.; Abass, A. Non-orthogonal spectacle correction for irregular astigmatism. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2025, 45, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toprak, İ.; Martin, Ç.; Güneş, C.E.; Alio, J. Revisiting Pentacam Parameters in the Diagnosis of Subclinical and Mild Keratoconus Based on Different Grading System Definitions. Turk. J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 53, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povedano-Montero, F.J.; Álvarez-Peregrina, C.; Hidalgo Santa Cruz, F.; Villa-Collar, C.; Sánchez Valverde, J. Bibliometric Study of Scientific Research on Scleral Lenses. Eye Contact Lens. 2018, 44 (Suppl. 2), S285–S291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, M.; Zhao, C.; You, J.; Ding, W.; Jiang, D.; Tian, Y.; Shi, L.; Leng, L. Bibliometric and Visual Analysis of the Status of Scleral Lens Research Based on the Web of Science Database and Scopus Database (2014–2024). Clin. Optom. 2025, 17, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Xu, Y. Bibliometric and visual analysis of scleral contact lenses: Global characteristics and research trends from 1976 to 2023. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2025, 18, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izatt, J.A.; Hee, M.R.; Swanson, E.A.; Lin, C.P.; Huang, D.; Schuman, J.S.; Puliafito, C.A.; Fujimoto, J.G. Micrometer-scale resolution imaging of the anterior eye in vivo with optical coherence tomography. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1994, 112, 1584–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, S.H.; Sharma, T. Optical Coherence Tomography. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2025, 1467, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, H.; Chan, E. Optical coherence tomography imaging in keratoconus. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2019, 102, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, S.J.; Alonso-Caneiro, D.; Collins, M.J. Optical coherence tomography and scleral contact lenses: Clinical and research applications. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2019, 102, 224–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahedi, H.; Abdollahi, M.; Moshfeghinia, R.; Emami, S.; Sobhi, N.; Sorkhabi, R.; Jafarizadeh, A. Retinal thickness and vascular density changes in Keratoconus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Heliyon 2025, 11, e42099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, Y.; Nomura, R.; Hiraoka, T.; Kinoshita, K.; Ohara, M.; Oshika, T. Comparison of corneal irregular astigmatism by the type of corneal regular astigmatism. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Y.J.; Azzopardi, M.; Hussain, G.; Recchioni, A.; Gandhewar, J.; Loizou, C.; Giachos, I.; Barua, A.; Ting, D.S.J. Clinical Applications of Anterior Segment Optical Coherence Tomography: An Updated Review. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Pavlatos, E.; Chamberlain, W.; Huang, D.; Li, Y. Keratoconus detection using OCT corneal and epithelial thickness map parameters and patterns. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2021, 47, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naujokaitis, T.; Khoramnia, R.; Friedrich, M.; Son, H.S.; Auffarth, G.U.; Augustin, V.A. Inter-zonal epithelial thickness differences for early keratoconus detection using optical coherence tomography. Eye 2024, 38, 2968–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abtahi, M.A.; Beheshtnejad, A.H.; Latifi, G.; Akbari-Kamrani, M.; Ghafarian, S.; Masoomi, A.; Sonbolastan, S.A.; Jahanbani-Ardakani, H.; Atighechian, M.; Banan, L.; et al. Corneal Epithelial Thickness Mapping: A Major Review. J. Ophthalmol. 2024, 2024, 6674747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toprak, I.; Gunes, C.E.; Martin-Seker, C.; Parca, O. A novel metric to monitor early progression in keratoconus: Epithelial backscatter. Int. Ophthalmol. 2025, 45, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toprak, I.; Gunes, C.E. Increased epithelial backscatter: A novel finding in subclinical and clinical keratoconus. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2021, 49, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.Y.; Lee, S.; Jeon, Y.J.; Min, J.S. Anterior segment characteristics in normal and keratoconus eyes evaluated with a new type of swept-source optical coherence tomography. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0274071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzunel, U.D.; Küsbeci, T.; Yüksel, B. Does the Stage of Keratoconus Affect Optical Coherence Tomography Measurements? Semin. Ophthalmol. 2017, 32, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özsaygılı, C.; Yıldırım, Y. The Relationship Between Keratoconus Stage and the Thickness of the Retinal Layers. Turk. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 51, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orman, G.; Fırat, P.G.; Doganay, S.; Doganay, D. Assessment of ganglion cell complex, macular thickness, and optic disc parameters in keratoconus patients. Saudi J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 34, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youm, D.J.; Kim, J.M.; Park, K.H.; Choi, C.Y. The effect of soft contact lenses during the measurement of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness using optical coherence tomography. Curr. Eye Res. 2009, 34, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aviram, T.; Beeri, I.; Berkow, D.; Zayit-Soudry, S.; Blumenthal, E.Z.; Shapira, Y. The effect of contact lens wear on retinal spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2020, 103, 792–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrid-Costa, D.; Isla-Paradelo, L.; García-Lázaro, S.; Albarrán-Diego, C.; Ruiz-Alcocer, J. Effect of multizone refractive multifocal contact lenses on the Cirrus HD OCT retinal measurements. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2013, 96, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkenstock, M.K.; Parikh, R.A.; Collins, M.D.; Ricard, D.A.; Rozar, S.R.; Castoro, C.J.; Scott, A.W. Use of Contact Lenses to Optimize OCT Scans of the Optic Nerve in Glaucoma Suspects or Patients with Glaucoma with High Myopia. Ophthalmol. Glaucoma 2020, 3, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, A.K.; Lau, K.K.; Wong, H.Y.; Lam, J.P.; Yeung, M.F. Fixation stability and deviation in optical coherence tomography angiography using soft contact lens correction in myopes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzunel, U.D.; Kusbeci, T.; Yuce, B.; Yüksel, B. Effects of rigid contact lenses on optical coherence tomographic parameters in eyes with keratoconus. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2015, 98, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro-Costa, J.; Ribeiro, M.; Moura, R.; Madeira, D.; Falcão-Reis, F.; Carneiro, Â. Macular parameters with and without scleral contact lens in keratoconus using Spectralis optical coherence tomography. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2023, 106, 930–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, H.; Heirani, M.; Ambrósio RJr Hafezi, F.; Naroo, S.A.; Khorrami-Nejad, M. The link between Keratoconus and posterior segment parameters: An updated, comprehensive review. Ocul. Surf. 2022, 23, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.H.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, Y.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Yoo, C. Astigmatism and optical coherence tomography measurements. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2012, 250, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo-de-Araújo, R.J.; Amorim-de-Sousa, A.; González-Méijome, J.M. Influence of midday removal and re-application of a scleral lens on fluid reservoir thickness, pre-lens tear film quality and visual acuity. Cont. Lens Anterior Eye 2025, 48, 102250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogt, J.S. Midday Fogging of Scleral Contact Lenses: Current Perspectives. Clin. Optom. 2021, 13, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schornack, M.M.; Fogt, J.; Harthan, J.; Nau, C.B.; Nau, A.; Cao, D.; Shorter, E. Factors associated with patient-reported midday fogging in established scleral lens wearers. Cont. Lens Anterior Eye 2020, 43, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, A.; Khan, M.S.; Dakhil, T.A. Understanding Corneal Epithelial Thickness Mapping. Middle East Afr. J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 29, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinstein, D.Z.; Archer, T.J.; Vida, R.S. Applications of epithelial thickness mapping in corneal refractive surgery. Saudi J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 36, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; Xu, Y.; Luo, B.; Qian, Y. Effects of long-term soft contact lens wear on corneal epithelial thickness after small incision lenticule extraction. Exp. Ther. Med. 2022, 23, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardin, J.S.; Taibbi, G.; Nelson, S.C.; Chao, D.; Vizzeri, G. Factors Affecting Cirrus-HD OCT Optic Disc Scan Quality: A Review with Case Examples. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 2015, 746150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, A.; Akman, A. Artifacts and Anatomic Variations in Optical Coherence Tomography. Turk. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 50, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Ma, L.; Lv, A.; Liu, H.; Pan, Q.; Cao, K.; Jia, X.; Fan, S.; Wu, J.; Wang, N. Macular ganglion cell complex layer thickness measured with spectral-domain OCT in a large population-based cohort study. BMC Ophthalmol. 2025, 25, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikorski, B.L. Ultra-Widefield Retinal Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) and Angio-OCT Using an Add-On Lens. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidi Mohamed Hamida, A.; Marta, G.B.; Pedro, R.F.; Piñero, D.P. Characterization and prediction of the clinical result with a specific model of mini-scleral contact lens in corneas with keratoconus. Eye Vis. 2022, 9, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathi, V.M.; Mandathara, P.S.; Dumpati, S.; Sangwan, V.S. Change in vault during scleral lens trials assessed with anterior segment optical coherence tomography. Cont. Lens Anterior Eye 2017, 40, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkaya Turhan, S.; Özarslan Özcan, D.; Toker, E. Use of a Mini-Scleral Lens in Patients with Keratoconus. Turk. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 50, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
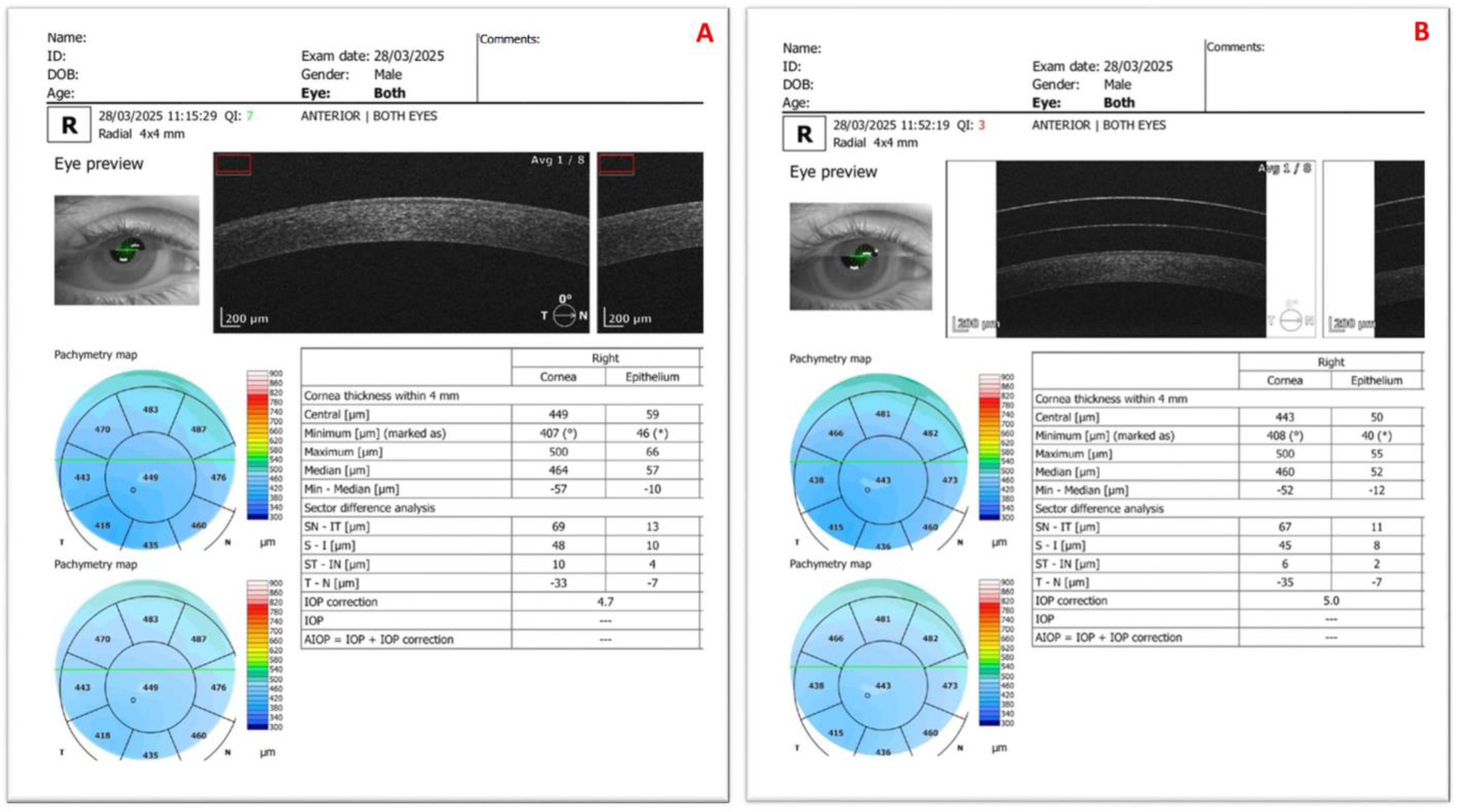

| Mean ± SD | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without Lenses (n = 28) | With Lenses (n = 28) | Difference (n = 28) | ||
| Anterior segment analysis | ||||
| QI | 6.76 ± 1.73 | 5.57 ± 2.34 | −1.19 ± 2.14 | 0.019 1 |
| Corneal thickness (µm) | ||||
| Central | 431.05 ± 50.73 | 431.05 ± 55.28 | 0.0 ± 9.52 | 0.794 2 |
| Maximum | 512.29 ± 41.08 | 510.35 ± 41.14 | −1.94 ± 20.01 | 0.694 1 |
| Minimum | 392.81 ± 56.34 | 382.95 ± 73.49 | −9.86 ± 30.76 | 0.643 2 |
| Epithelial thickness (µm) | ||||
| Central | 50.53 ± 6.66 | 47.59 ± 7.2 | −2.94 ± 3.65 | 0.007 2 |
| Maximum | 63.24 ± 10.87 | 62.24 ± 18.18 | −1.0 ± 10.71 | 0.093 2 |
| Minimum | 41.65 ± 4.82 | 38.29 ± 4.67 | −3.35 ± 3.69 | 0.002 1 |
| Ganglion analysis | ||||
| QI | 2.52 ± 1.03 | 5.76 ± 2.17 | 3.24 ± 2.05 | <0.001 1 |
| GCIPL thickness (µm) | ||||
| Average | 86.59 ± 5.55 | 86.09 ± 4.7 | −0.5 ± 1.87 | 0.153 2 |
| Minimum | 42.55 ± 8.86 | 44.64 ± 8.0 | 2.09 ± 8.02 | 0.235 1 |
| Superior | 86.77 ± 4.88 | 86.5 ± 4.02 | −0.27 ± 2.57 | 0.623 1 |
| Superior nasal | 88.64 ± 6.0 | 88.77 ± 4.58 | 0.14 ± 2.55 | 0.884 2 |
| Superior temporal | 83.64 ± 5.62 | 83.59 ± 4.4 | −0.05 ± 2.84 | 0.751 2 |
| Inferior | 87.32 ± 5.78 | 86.05 ± 5.72 | −1.27 ± 1.45 | 0.001 1 |
| Inferior nasal | 88.5 ± 6.84 | 88.05 ± 6.28 | −0.45 ± 2.3 | 0.14 2 |
| Inferior temporal | 85.0 ± 6.59 | 84.36 ± 5.6 | −0.64 ± 2.04 | 0.158 1 |
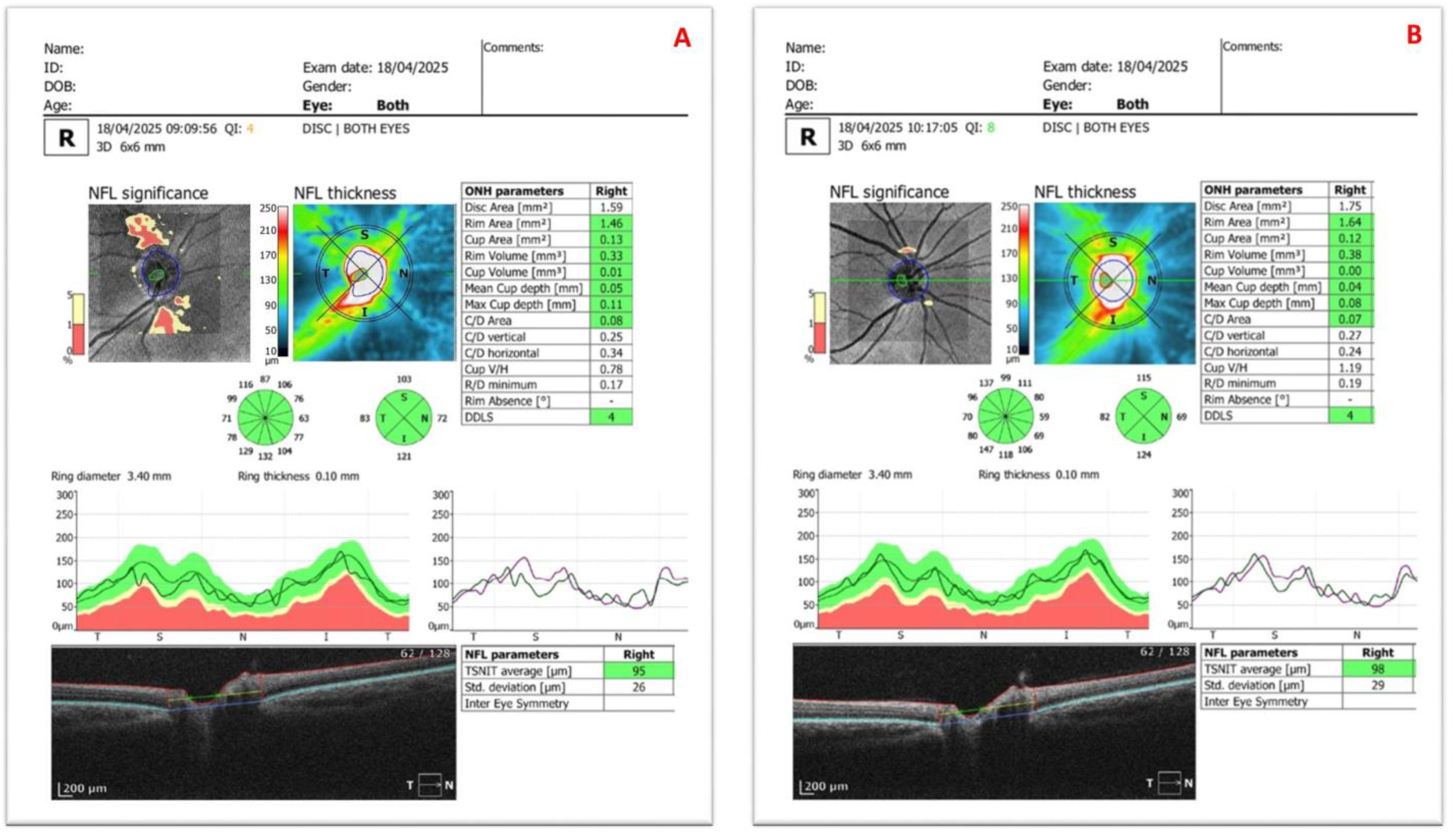
| Disc analysis | ||||
| QI | 2.82 ± 0.94 | 4.39 ± 1.87 | 1.57 ± 1.85 | <0.001 2 |
| Disc area (mm2) | 2.36 ± 0.76 | 2.18 ± 0.55 | −0.18 ± 0.64 | 0.25 2 |
| Vertical C/D | 0.55 ± 0.24 | 0.49 ± 0.23 | −0.06 ± 0.21 | 0.167 2 |
| RNFL thickness (µm) | ||||
| Average | 93.15 ± 12.66 | 93.74 ± 9.51 | 0.59 ± 6.98 | 0.07 2 |
| Superior | 106.5 ± 18.33 | 112.71 ± 16.07 | 6.21 ± 10.72 | 0.005 1 |
| Nasal | 76.64 ± 14.6 | 74.5 ± 11.5 | −2.14 ± 8.57 | 0.164 2 |
| Inferior | 118.89 ± 21.87 | 120.82 ± 16.47 | 1.93 ± 14.62 | 0.085 2 |
| Temporal | 68.75 ± 11.08 | 66.64 ± 9.95 | −2.11 ± 6.31 | 0.024 2 |
| Age (Years) | K1 (D) | K2 (D) | Kmax (D) | Astigmatism (D) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | |
| Anterior segment analysis | ||||||||||
| QI | 0.301 | 0.152 | −0.393 | 0.039 | −0.332 | 0.084 | −0.471 | 0.011 | −0.12 | 0.544 |
| Corneal thickness (µm) | ||||||||||
| Central | 0.072 | 0.738 | −0.09 | 0.648 | −0.024 | 0.905 | 0.177 | 0.367 | 0.394 | 0.038 |
| Maximum | 0.387 | 0.062 | 0.179 | 0.361 | 0.189 | 0.336 | 0.395 | 0.038 | 0.068 | 0.73 |
| Minimum | −0.189 | 0.375 | 0.028 | 0.887 | 0.102 | 0.606 | 0.288 | 0.137 | 0.393 | 0.038 |
| Epithelial thickness (µm) | ||||||||||
| Central | 0.096 | 0.655 | −0.501 | 0.007 | −0.483 | 0.009 | −0.42 | 0.026 | 0.043 | 0.828 |
| Maximum | 0.246 | 0.246 | −0.318 | 0.099 | −0.388 | 0.041 | −0.268 | 0.168 | −0.227 | 0.246 |
| Minimum | −0.1 | 0.641 | −0.273 | 0.159 | −0.252 | 0.196 | −0.198 | 0.311 | 0.152 | 0.44 |
| Ganglion analysis | ||||||||||
| QI | −0.39 | 0.08 | −0.328 | 0.109 | −0.46 | 0.021 | −0.454 | 0.023 | 0.103 | 0.626 |
| GCIPL thickness (µm) | ||||||||||
| Average | −0.41 | 0.052 | 0.078 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.62 | 0.159 | 0.427 | 0.278 | 0.161 |
| Minimum | −0.425 | 0.043 | −0.323 | 0.101 | −0.271 | 0.172 | −0.253 | 0.203 | 0.179 | 0.371 |
| Superior | −0.449 | 0.031 | 0.036 | 0.858 | 0.081 | 0.688 | 0.158 | 0.432 | 0.22 | 0.271 |
| Superior nasal | −0.338 | 0.114 | −0.007 | 0.972 | −0.027 | 0.894 | 0.052 | 0.797 | 0.161 | 0.424 |
| Superior temporal | −0.432 | 0.039 | 0.121 | 0.548 | 0.141 | 0.484 | 0.182 | 0.364 | 0.302 | 0.125 |
| Inferior | −0.392 | 0.064 | 0.039 | 0.846 | 0.075 | 0.711 | 0.098 | 0.628 | 0.236 | 0.235 |
| Inferior nasal | −0.334 | 0.119 | −0.055 | 0.784 | −0.043 | 0.832 | 0.009 | 0.965 | 0.192 | 0.338 |
| Inferior temporal | −0.436 | 0.037 | 0.127 | 0.527 | 0.127 | 0.526 | 0.155 | 0.439 | 0.319 | 0.105 |
| Disc analysis | ||||||||||
| QI | −0.371 | 0.075 | −0.348 | 0.07 | −0.384 | 0.044 | −0.403 | 0.033 | 0.163 | 0.407 |
| Disc area (mm2) | 0.128 | 0.551 | −0.161 | 0.414 | 0.042 | 0.832 | −0.032 | 0.873 | 0.463 | 0.013 |
| Vertical C/D | 0.188 | 0.389 | 0.061 | 0.763 | 0.135 | 0.502 | 0.162 | 0.421 | 0.155 | 0.439 |
| RNFL thickness (µm) | ||||||||||
| Average | −0.277 | 0.2 | −0.552 | 0.003 | −0.437 | 0.023 | −0.498 | 0.008 | 0.173 | 0.388 |
| Superior | −0.142 | 0.508 | −0.213 | 0.276 | −0.199 | 0.309 | −0.266 | 0.172 | −0.131 | 0.507 |
| Nasal | −0.295 | 0.162 | −0.509 | 0.006 | −0.351 | 0.067 | −0.386 | 0.042 | 0.444 | 0.018 |
| Inferior | −0.039 | 0.855 | −0.449 | 0.017 | −0.429 | 0.023 | −0.476 | 0.01 | −0.162 | 0.411 |
| Temporal | −0.494 | 0.014 | 0.056 | 0.777 | 0.101 | 0.611 | 0.133 | 0.501 | 0.376 | 0.049 |
| Age (Years) | K1 (D) | K2 (D) | Kmax (D) | Astigmatism (D) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | |
| Anterior segment analysis | ||||||||||
| QI | 0.344 | 0.163 | −0.619 | 0.003 | −0.605 | 0.004 | −0.67 | 0.001 | −0.409 | 0.066 |
| Corneal thickness (µm) | ||||||||||
| Central | 0.359 | 0.143 | 0.055 | 0.814 | 0.154 | 0.505 | 0.276 | 0.227 | 0.343 | 0.129 |
| Maximum | 0.513 | 0.061 | −0.042 | 0.874 | 0.171 | 0.512 | 0.366 | 0.149 | 0.47 | 0.057 |
| Minimum | 0.038 | 0.88 | 0.247 | 0.281 | 0.379 | 0.09 | 0.496 | 0.022 | 0.444 | 0.044 |
| Epithelial thickness (µm) | ||||||||||
| Central | 0.741 | 0.002 | −0.605 | 0.01 | −0.616 | 0.009 | −0.483 | 0.05 | −0.177 | 0.496 |
| Maximum | 0.798 | 0.001 | −0.481 | 0.05 | −0.623 | 0.008 | −0.4 | 0.112 | −0.352 | 0.166 |
| Minimum | −0.162 | 0.58 | 0.007 | 0.978 | 0.165 | 0.528 | 0.287 | 0.264 | 0.196 | 0.451 |
| Ganglion analysis | ||||||||||
| QI | −0.308 | 0.214 | 0.397 | 0.068 | 0.352 | 0.108 | 0.327 | 0.137 | 0.238 | 0.286 |
| GCIPL thickness (µm) | ||||||||||
| Average | −0.366 | 0.135 | 0.254 | 0.253 | 0.205 | 0.361 | 0.348 | 0.113 | 0.195 | 0.385 |
| Minimum | −0.371 | 0.13 | 0.088 | 0.698 | 0.025 | 0.912 | 0.117 | 0.604 | 0.187 | 0.347 |
| Superior | −0.233 | 0.352 | 0.274 | 0.217 | 0.24 | 0.283 | 0.348 | 0.113 | 0.138 | 0.54 |
| Superior nasal | −0.289 | 0.246 | 0.216 | 0.334 | 0.146 | 0.516 | 0.255 | 0.252 | 0.049 | 0.827 |
| Superior temporal | −0.211 | 0.401 | 0.234 | 0.295 | 0.148 | 0.51 | 0.236 | 0.29 | 0.109 | 0.628 |
| Inferior | −0.359 | 0.143 | 0.19 | 0.396 | 0.203 | 0.364 | 0.33 | 0.134 | 0.267 | 0.23 |
| Inferior nasal | −0.382 | 0.118 | 0.06 | 0.792 | 0.039 | 0.864 | 0.216 | 0.335 | 0.163 | 0.469 |
| Inferior temporal | −0.348 | 0.157 | 0.291 | 0.189 | 0.171 | 0.447 | 0.329 | 0.135 | 0.151 | 0.502 |
| Disc analysis | ||||||||||
| QI | −0.513 | 0.01 | 0.013 | 0.946 | 0.058 | 0.769 | 0.05 | 0.8 | 0.414 | 0.028 |
| Disc area (mm2) | 0.047 | 0.829 | −0.444 | 0.018 | −0.298 | 0.124 | −0.257 | 0.187 | 0.35 | 0.068 |
| Vertical C/D | 0.343 | 0.109 | −0.095 | 0.638 | −0.062 | 0.757 | −0.053 | 0.794 | −0.043 | 0.831 |
| RNFL thickness (µm) | ||||||||||
| Average | −0.307 | 0.145 | −0.513 | 0.005 | −0.402 | 0.034 | −0.423 | 0.025 | 0.236 | 0.226 |
| Superior | −0.45 | 0.027 | −0.112 | 0.57 | −0.037 | 0.851 | −0.05 | 0.802 | 0.154 | 0.433 |
| Nasal | −0.133 | 0.535 | −0.578 | 0.001 | −0.371 | 0.052 | −0.425 | 0.024 | 0.504 | 0.006 |
| Inferior | −0.146 | 0.495 | −0.231 | 0.237 | −0.217 | 0.267 | −0.29 | 0.134 | −0.059 | 0.765 |
| Temporal | −0.263 | 0.214 | 0.13 | 0.51 | 0.111 | 0.574 | 0.166 | 0.397 | 0.221 | 0.259 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Demirtaş, A.A.; Arslan, A.; Yüce, B.; Küsbeci, T. Influence of Scleral Contact Lenses on Optical Coherence Tomography Parameters in Keratoconus Patients. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2541. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192541
Demirtaş AA, Arslan A, Yüce B, Küsbeci T. Influence of Scleral Contact Lenses on Optical Coherence Tomography Parameters in Keratoconus Patients. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(19):2541. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192541
Chicago/Turabian StyleDemirtaş, Atılım Armağan, Aytül Arslan, Berna Yüce, and Tuncay Küsbeci. 2025. "Influence of Scleral Contact Lenses on Optical Coherence Tomography Parameters in Keratoconus Patients" Diagnostics 15, no. 19: 2541. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192541
APA StyleDemirtaş, A. A., Arslan, A., Yüce, B., & Küsbeci, T. (2025). Influence of Scleral Contact Lenses on Optical Coherence Tomography Parameters in Keratoconus Patients. Diagnostics, 15(19), 2541. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192541






