Apparent Diffusion Coefficient as a Predictor of Microwave Ablation Response in Thyroid Nodules: A Prospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection and Study Design
2.2. Diffusion-Weighted MRI Protocol and Analysis
2.3. Microwave Ablation Procedure
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
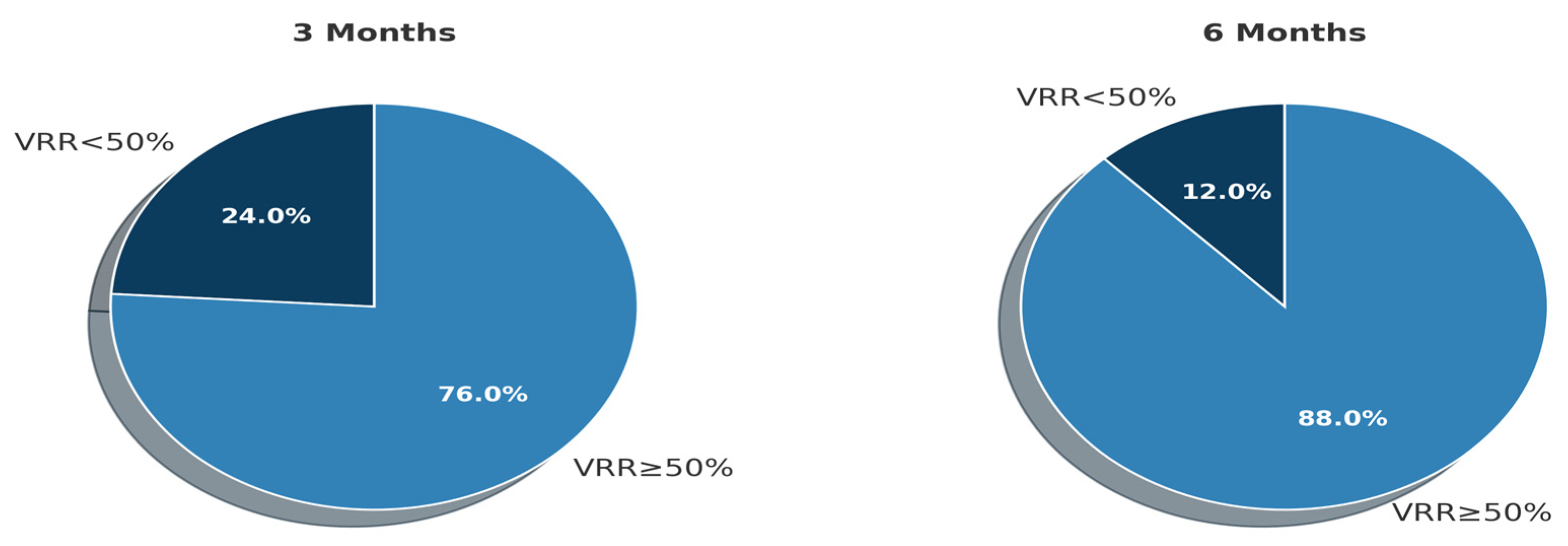
3.2. Volume Reduction at 1, 3, and 6 Months Follow-Up
3.3. Predictors of Nodule Volume Reduction After Ablation
3.4. Multivariable Linear Regression Analysis
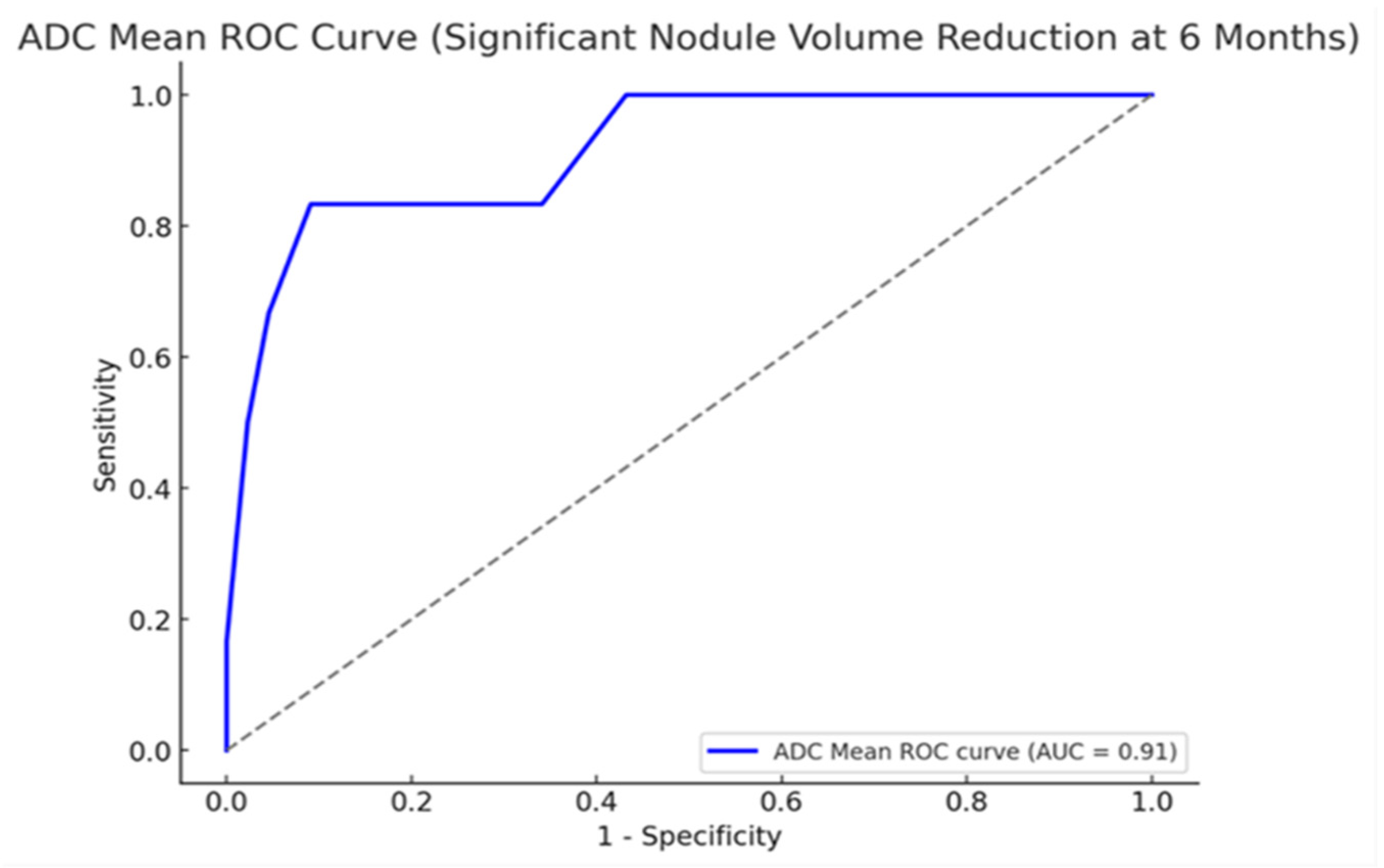
3.5. Diagnostic Performance of ADC in Predicting the 6-Month Response
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Durante, C.; Costante, G.; Lucisano, G.; Bruno, R.; Meringolo, D.; Paciaroni, A.; Puxeddu, E.; Torlontano, M.; Tumino, S.; Attard, M.; et al. The Natural History of Benign Thyroid Nodules. JAMA 2015, 313, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharib, H.; Papini, E.; Garber, J.R.; Duick, D.S.; Harrell, R.M.; Hegedüs, L.; Paschke, R.; Valcavi, R.; Vitti, P. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, American College of Endocrinology, and Associazione Medici Endocrinologi Medical Guidelines for Clinical Practice for the Diagnosis and Management of Thyroid Nodules—2016 Update Appendix. Endocr. Pract. 2016, 22, 1–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grani, G.; Sponziello, M.; Pecce, V.; Ramundo, V.; Durante, C. Contemporary Thyroid Nodule Evaluation and Management. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, 2869–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesareo, R.; Palermo, A.; Pasqualini, V.; Manfrini, S.; Trimboli, P.; Stacul, F.; Fabris, B.; Bernardi, S. Radiofrequency Ablation on Autonomously Functioning Thyroid Nodules: A Critical Appraisal and Review of the Literature. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papini, E.; Monpeyssen, H.; Frasoldati, A.; Hegedüs, L. 2020 European Thyroid Association Clinical Practice Guideline for the Use of Image-Guided Ablation in Benign Thyroid Nodules. Eur. Thyroid. J. 2020, 9, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papini, E.; Pacella, C.M.; Hegedus, L. Diagnosis of endocrine disease: Thyroid ultrasound (US) and US-assisted procedures: From the shadows into an array of applications. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 170, R133–R146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, E.J.; Baek, J.H.; Kim, K.W.; Pyo, J.; Lee, J.H.; Baek, S.H.; Døssing, H.; Hegedüs, L. Comparative Efficacy of Radiofrequency and Laser Ablation for the Treatment of Benign Thyroid Nodules: Systematic Review Including Traditional Pooling and Bayesian Network Meta-analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 1903–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, R.; Zhong, J.; Chen, W.; Shuai, J.; Chen, M.; Deng, F.; Wei, T.; Tang, H.; Li, Z.; et al. A multicenter cohort study of thyroidectomy-related decision regret in patients with low-risk papillary thyroid microcarcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, K.; Happel, C.; Grünwald, F.; Korkusuz, H. Percutaneous microwave ablation of thyroid nodules: Effects on thyroid function and antibodies. Int. J. Hyperth. 2015, 31, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, W.-W.; Qi, L.; Wang, D.-D.; Yu, S.-J.; Wang, X.-J.; Xu, H.-X.; Wang, S.-R. US-guided Microwave Ablation of Low-Risk Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: Longer-Term Results of a Prospective Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, 1791–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayganfar, A.; Azin, N.; Hashemi, P.; Ghanei, A.M.; Hajiahmadi, S. Diagnostic Accuracy of Multiple MRI Parameters in Dealing with Incidental Thyroid Nodules. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 2022, 4, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobnig, H.; Amrein, K. Value of monopolar and bipolar radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of benign thyroid nodules. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 33, 101283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linh, L.T.; Cuong, N.N.; Hung, T.V.; Van Hieu, N.; Van Lenh, B.; Hue, N.D.; Pham, V.H.; Nga, V.T.; Chu, D.-T. Value of Diffusion Weighted MRI with Quantitative ADC Map in Diagnosis of Malignant Thyroid Disease. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razek, A.A.; Sadek, A.; Kombar, O.; Elmahdy, T.; Nada, N. Role of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Values in Differentiation Between Malignant and Benign Solitary Thyroid Nodules. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2008, 29, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surov, A.; Meyer, H.J.; Wienke, A. Correlation between apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and cellularity is different in several tumors: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 59492–59499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, W.; Wang, S.; Wang, B.; Xu, Q.; Yu, S.; Yonglin, Z.; Wang, X. Ultrasound guided percutaneous microwave ablation of benign thyroid nodules: Safety and imaging follow-up in 222 patients. Eur. J. Radiol. 2013, 82, e11–e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.-F.; Zhou, P.; Zhao, Y.-F.; Liu, W.-G.; Tian, S.-M.; Liang, Y.-P. Microwave Ablation Compared with Laser Ablation for Treating Benign Thyroid Nodules in a Propensity-Score Matching Study. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Huang, L.; Gong, X.; Han, Z.; Liu, F.; Cheng, Z.; Dou, J.; Yu, X.; Liang, P.; Yu, J. Microwave ablation of benign thyroid nodules: 3-year follow-up outcomes. Head Neck 2021, 43, 3437–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.F.; Feng, Q.; Qiang, J.W.; Li, R.K.; Wang, L.; Yu, J.P. Utility of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in Differentiating Malignant from Benign Thyroid Nodules with Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Pathologic Correlation. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2013, 37, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutlu, H.; Sivrioglu, A.K.; Sonmez, G.; Velioglu, M.; Sildiroglu, H.O.; Basekim, C.C.; Kizilkaya, E. Role of apparent diffusion coefficient values and diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in differentiation between benign and malignant thyroid nodules. Clin. Imaging 2012, 36, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özer, B.M.; Pabuşçu, Y.; Tarhan, S.; Ovalı, G.Y.; Aydede, H.; Demireli, P.; Karadeniz, T. Effectiveness of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DW-MRI) in the differentiation of thyroid nodules. Thyroid Res. 2024, 17, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, W.B.; Sung, T.Y.; Baek, J.H. Complications encountered in ultrasonography-guided radiofrequency ablation of benign thyroid nodules and recurrent thyroid cancers. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 3128–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, X.; Zhao, N.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.-B.; Teng, C.; Qian, L. Microwave ablation compared to thyroidectomy to treat benign thyroid nodules. Int. J. Hyperth. 2018, 34, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Gao, Y.; Xue, Q.; Niu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Zhao, C. Ultrasound-based radiomics to predict the volume reduction rate of benign thyroid nodules after microwave ablation. Endocrine 2024, 88, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motaghed, Z.; Chegeni, H.; Mosadeghkhah, A.; Aval, M.A.; Gerami, R.; Ebrahiminik, H. Effect of ultrasound parameters of benign thyroid nodules on radiofrequency ablation efficacy. BMC Med. Imaging 2023, 23, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.-Y.; Zhou, Y.; Bo, X.-W.; Li, X.-L.; Luo, J.; Li, C.-N.; Peng, C.-Z.; Chai, H.-H.; Yue, W.-W.; Sun, L.-P. A Prediction Model for Assessing the Efficacy of Thermal Ablation in Treating Benign Thyroid Nodules ≥ 2 cm: A Multi-Center Retrospective Study. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2024, 50, 1515–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, H.S.; Na, D.G.; Baek, J.H.; Sung, J.Y.; Kim, J. False negative rate of fine-needle aspiration in thyroid nodules: Impact of nodule size and ultrasound pattern. Head Neck 2019, 41, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giles, W.H.; Maclellan, R.A.; Gawande, A.A.; Ruan, D.T.; Alexander, E.K.; Moore, F.D.; Cho, N.L. False Negative Cytology in Large Thyroid Nodules. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 22, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
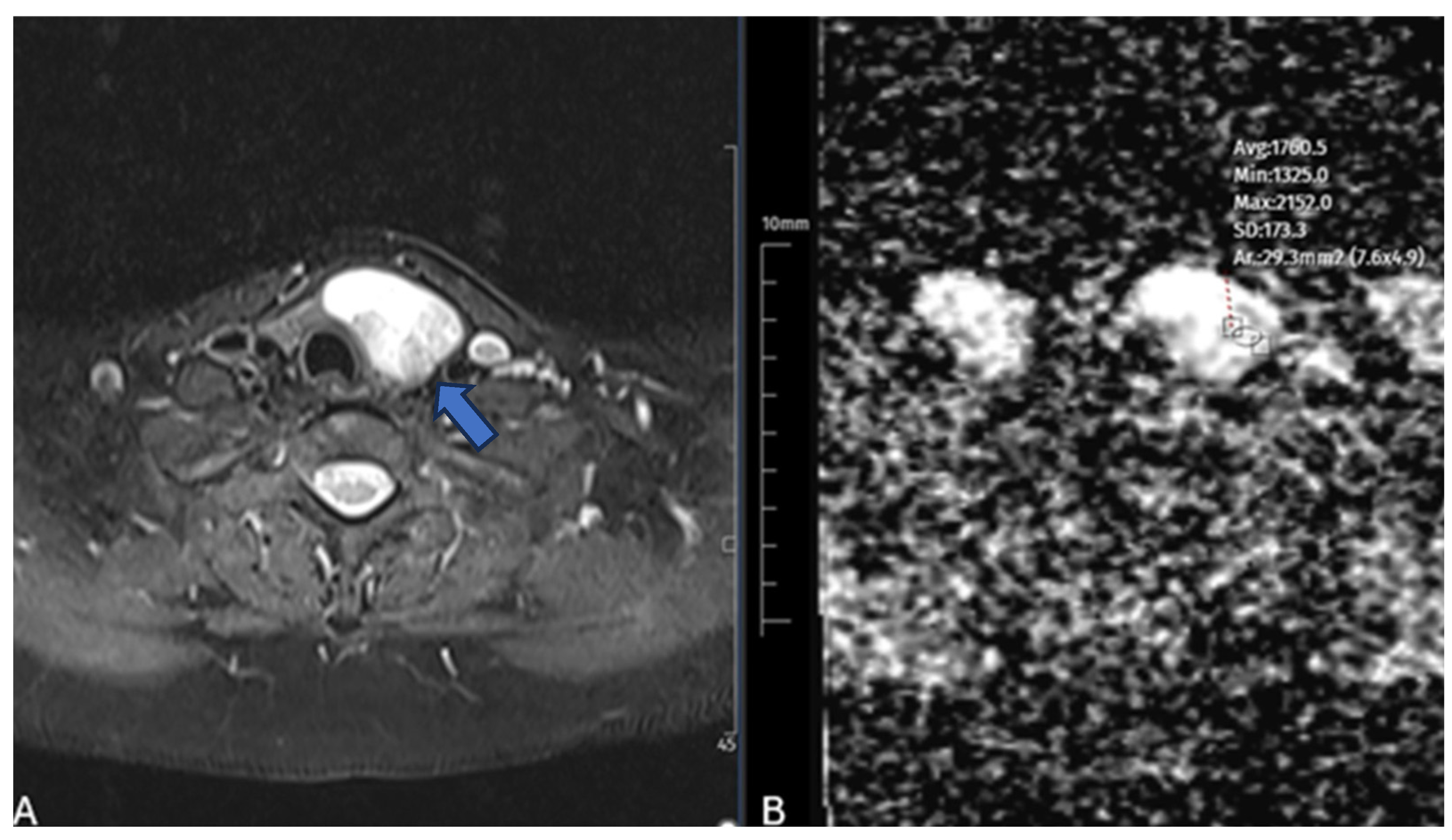

| Variable | Value |
|---|---|
| No. of patients | 48 |
| Mean age (years) | 45.6 ± 8.3 |
| Sex (F/M) | 28/20 (58.0%/42.0%) |
| No. of nodules | 50 |
| Mean nodule volume (mL) | 19.2 ± 15.7 |
| Ablation duration (minutes) | 12.2 ± 5.1 |
| ADC mean ± SD (×10−3 mm2/s) | 1.58 ± 0.46 |
| Growth location | |
| Left lobe | 18 (36.0%) |
| Right lobe | 26 (52.0%) |
| Isthmus | 6 (12.0%) |
| Nodule component | |
| Solid | 32 (64.0%) |
| Predominantly solid | 12 (24.0%) |
| Predominantly cystic | 6 (12.0%) |
| Vascularization | |
| Present | 23 (46.0%) |
| Absent | 27 (54.0%) |
| Time | Mean Volume ± SD (mL) | Mean VRR (%) ± SD |
|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 19.16 ± 15.67 | – |
| 1 Month | 9.82 ± 9.15 | 48.16 ± 19.13 |
| 3 Month | 7.17 ± 7.19 | 61.64 ± 17.38 |
| 6 Month | 5.28 ± 6.36 | 73.11 ± 17.40 |
| Variable | Pearson r—3rd Month | Pearson r—6th Months |
|---|---|---|
| ADC Mean | −0.525 (p < 0.001) * | −0.564 (p < 0.001) * |
| Age | −0.159 (p = 0.270) * | −0.003 (p = 0.980) * |
| Nodule Volume | 0.066 (p = 0.650) * | −0.049 (p = 0.730) * |
| Ablation Duration | −0.034 (p = 0.810) * | −0.168 (p = 0.240) * |
| Variable | Mean VRR (3 Months) | Mean VRR (6 Months) |
|---|---|---|
| Gender (F/M) | 64.8%/57.4% (p = 0.116) * | 76.0%/69.1% (p = 0.275) * |
| Vascularity (Yes/No) | 63.7%/60.0% (p = 0.465) * | 77.9%/69.0% (p = 0.108) * |
| Variable | β Coefficient | Standard Error | p-Value | 95% CI (Lower–Upper) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constant | 109.83 | 10.74 | <0.001 | 88.78 to 130.87 |
| ADC Mean | −19.52 | 5.13 | 0.0004 | −29.58 to −9.46 |
| Nodule Volume | 0.10 | 0.31 | 0.749 | −0.51 to 0.71 |
| Ablation Duration | −0.71 | 0.94 | 0.455 | −2.56 to 1.14 |
| Vascularity | 1.92 | 4.58 | 0.677 | −7.06 to 10.89 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Demir, M.; Yasar, Y. Apparent Diffusion Coefficient as a Predictor of Microwave Ablation Response in Thyroid Nodules: A Prospective Study. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2538. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192538
Demir M, Yasar Y. Apparent Diffusion Coefficient as a Predictor of Microwave Ablation Response in Thyroid Nodules: A Prospective Study. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(19):2538. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192538
Chicago/Turabian StyleDemir, Mustafa, and Yunus Yasar. 2025. "Apparent Diffusion Coefficient as a Predictor of Microwave Ablation Response in Thyroid Nodules: A Prospective Study" Diagnostics 15, no. 19: 2538. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192538
APA StyleDemir, M., & Yasar, Y. (2025). Apparent Diffusion Coefficient as a Predictor of Microwave Ablation Response in Thyroid Nodules: A Prospective Study. Diagnostics, 15(19), 2538. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192538






