Diagnostic Value of EUS-FNA in the Differential Diagnosis of Esophageal Strictures Lacking Typical Malignant Features
Abstract
1. Introduction
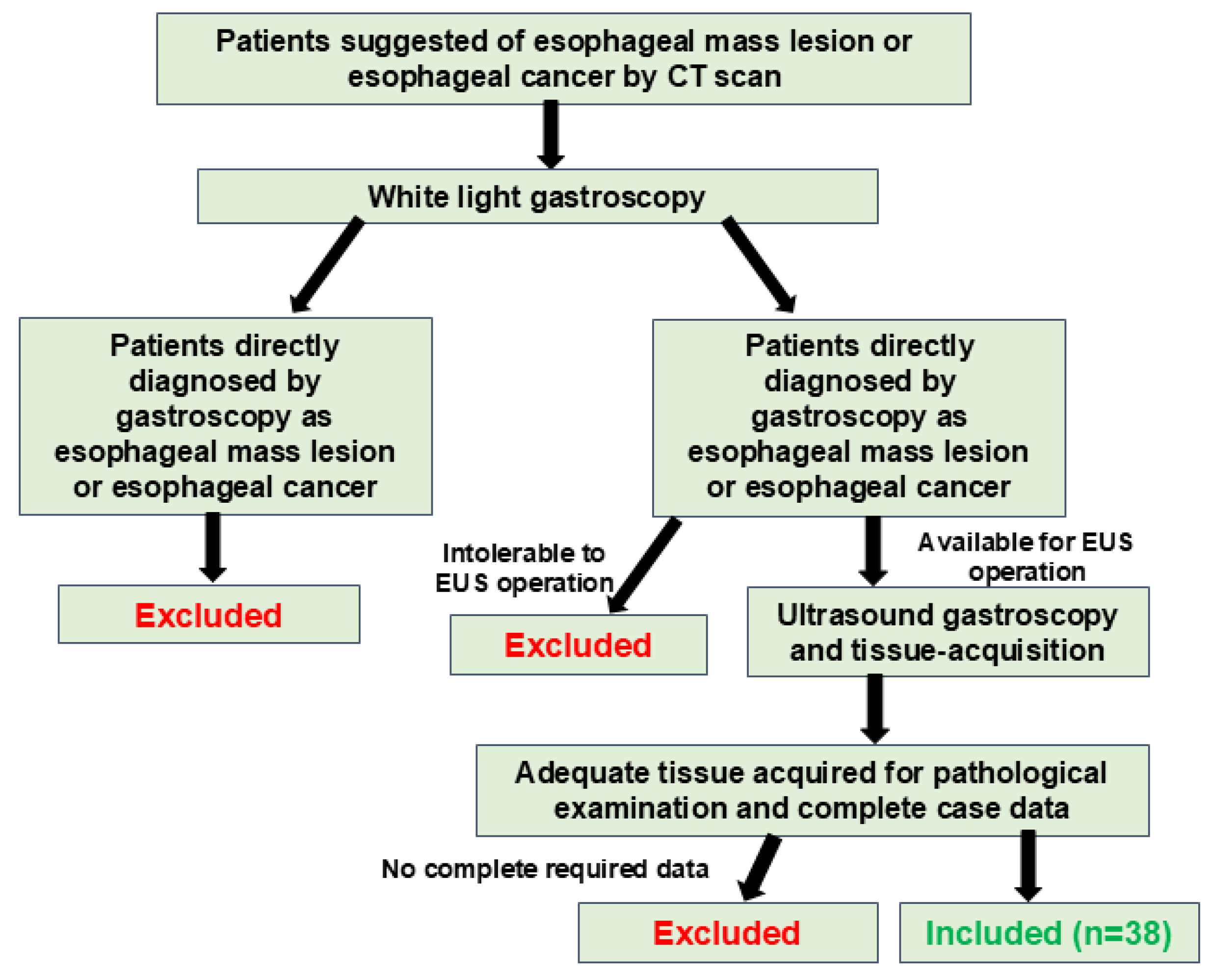
2. Methods
2.1. The Subjects
2.2. Endoscopic Gastroscopy and EUS-Guided Tissue Acquisition Process
2.3. Sample Processing
2.4. Postoperative Follow-Up of the Patients
2.5. Data Collection
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics of the Patients
3.2. CT Characteristics of the Patients
3.3. Different Characteristics of Mucosa in Benign and Malignant Diseases
3.4. Different Characteristics of the Mucosa in Different Types of Esophageal Cancer
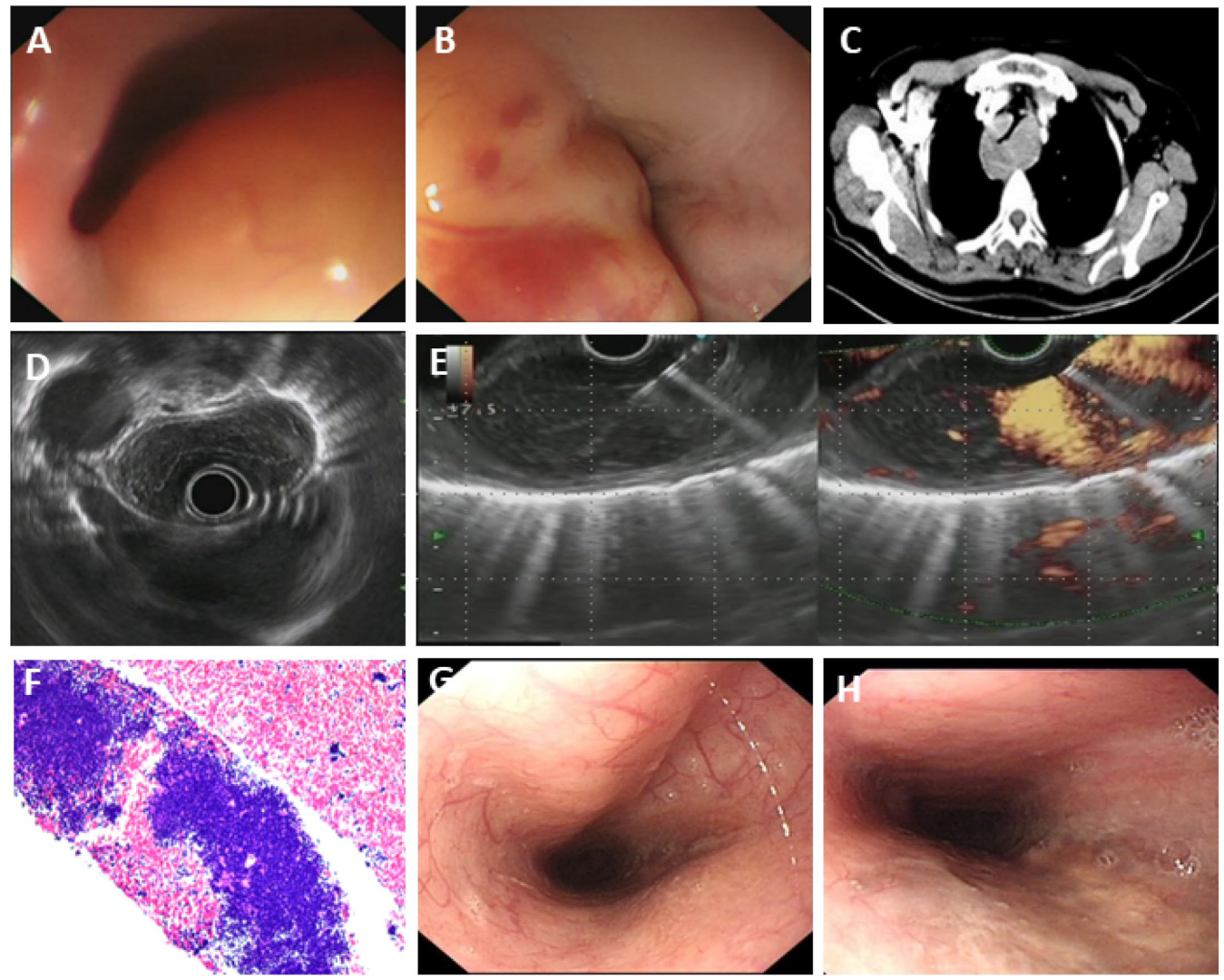
3.5. Rare Esophageal Diseases Characterized by Severe Esophageal Stenosis
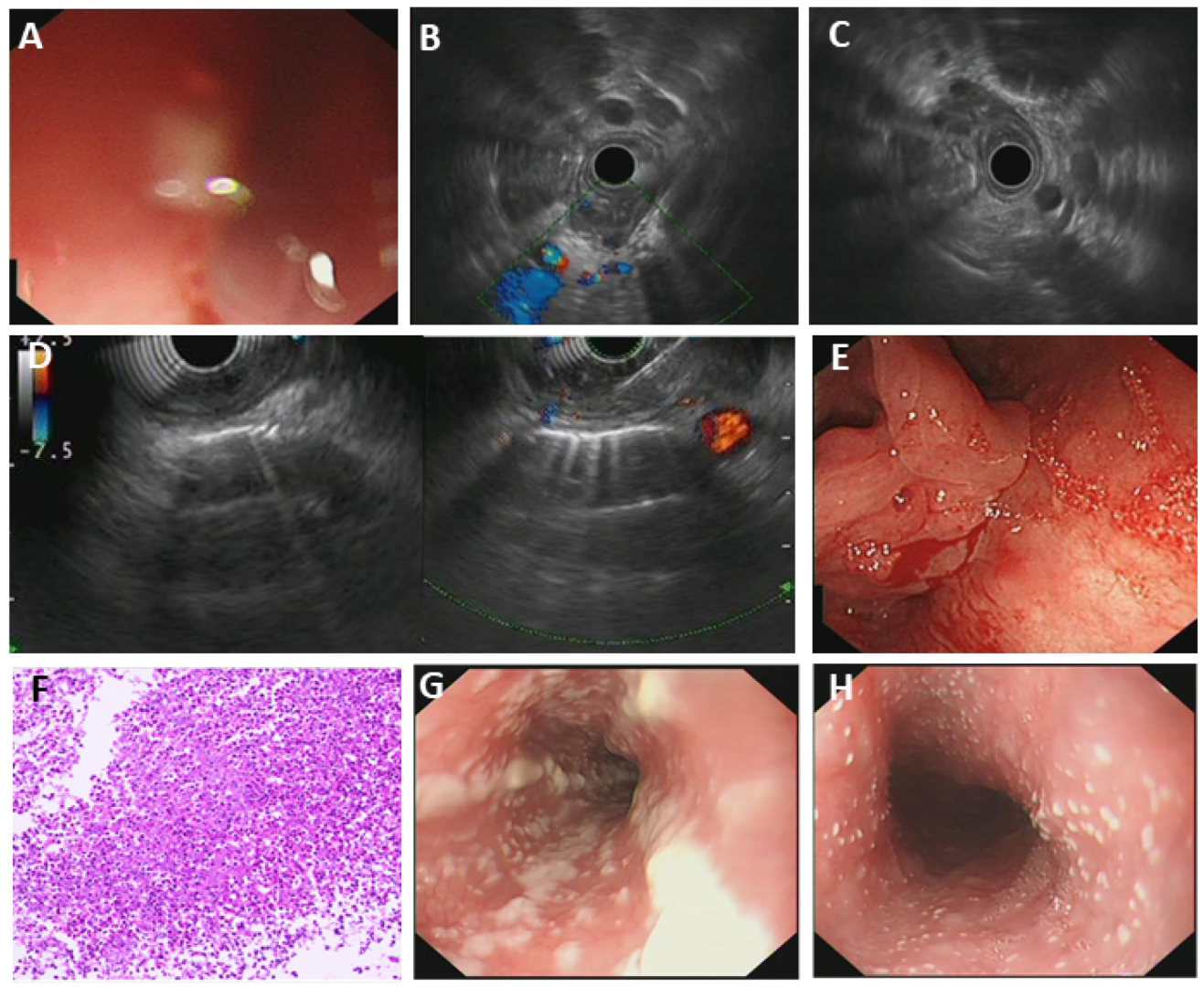
3.5.1. Fungal Esophagitis
3.5.2. Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE)
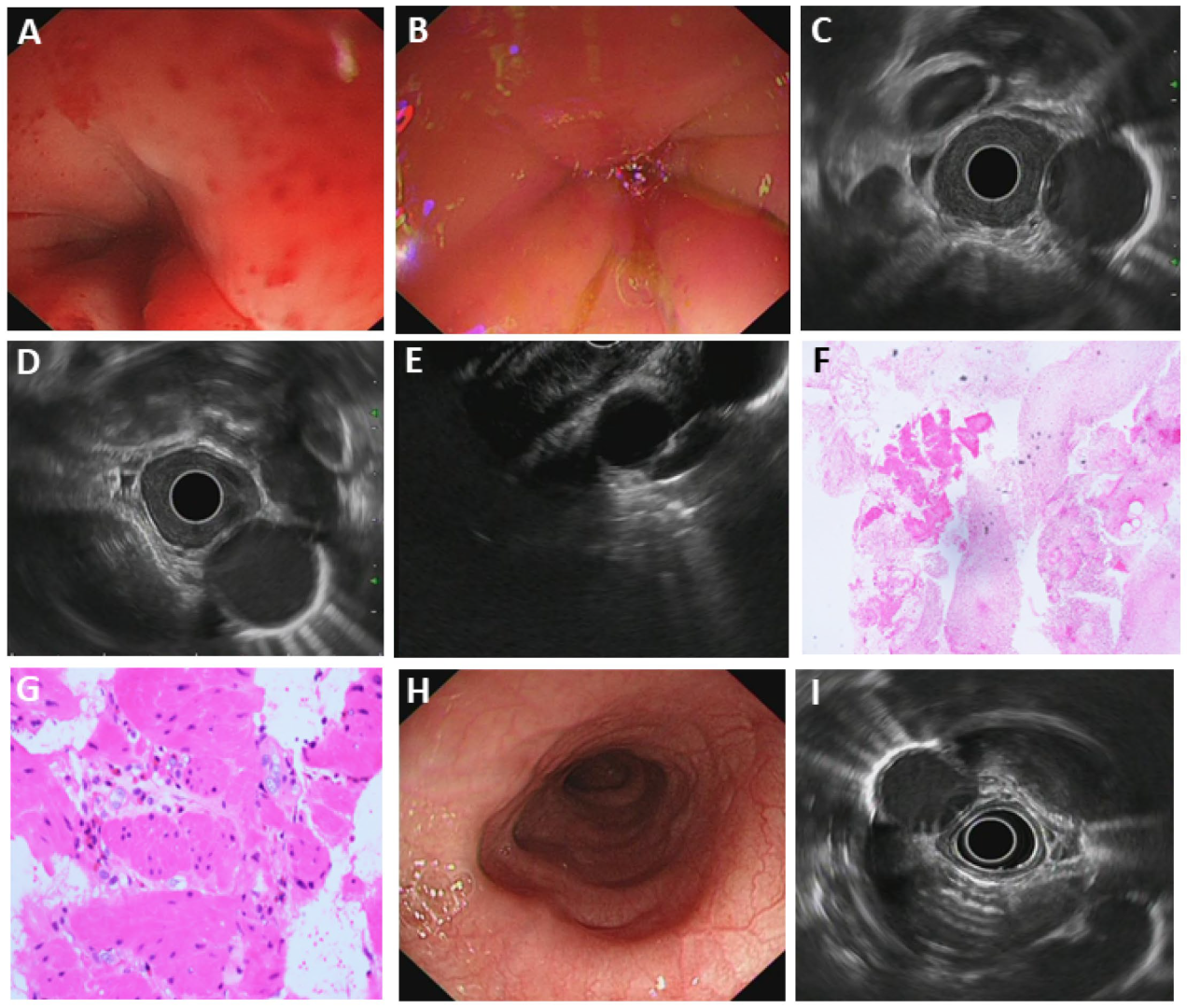
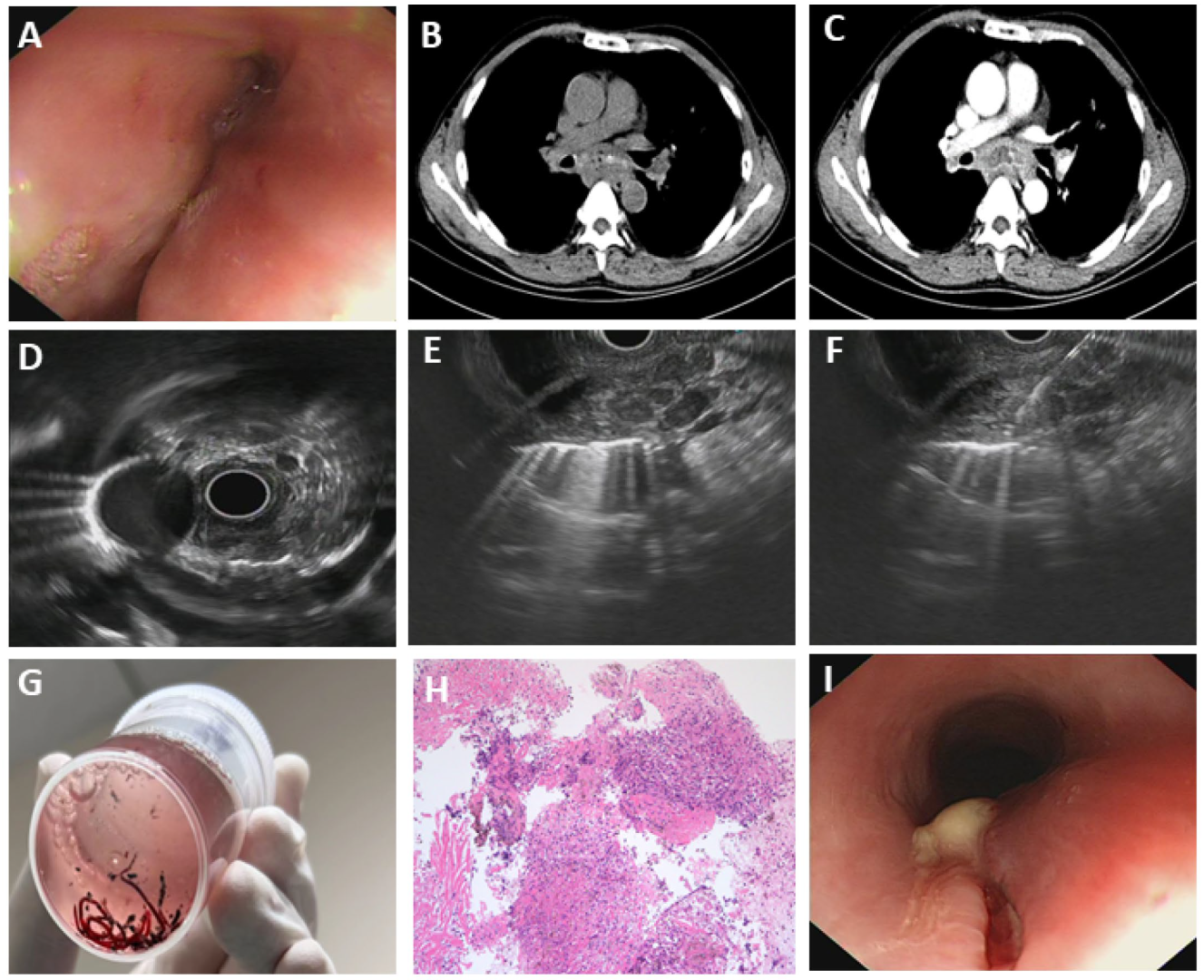
3.5.3. Esophageal Tuberculosis
3.5.4. Primary Esophageal MALT Lymphoma
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EC | Esophageal carcinoma |
| EUS | Endoscopic ultrasonography |
| ESCC | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma |
| EAC | Esophageal adenocarcinoma |
| FNA | Fine needle aspiration |
| ROSE | Rapid On-Site Evaluation |
| PLT | platelet |
| INR | International normalized ratio |
| ECG | Electrocardiogram |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| EoE | Eosinophilic esophagitis |
| ET | Esophageal tuberculosis |
| MALT | Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue |
References
- Uhlenhopp, D.J.; Then, E.O.; Sunkara, T.; Gaduputi, V. Epidemiology of esophageal cancer: Update in global trends, etiology and risk factors. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 1010–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.Q.; Ma, Y.L.; Qin, Q.; Wang, P.H.; Luo, Y.; Xu, P.F.; Cui, Y. Epidemiology of esophageal cancer in 2020 and projections to 2030 and 2040. Thorac. Cancer 2023, 14, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deboever, N.; Jones, C.M.; Yamashita, K.; Ajani, J.A.; Hofstetter, W.L. Advances in diagnosis and management of cancer of the esophagus. BMJ 2024, 385, e074962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Shu, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, S.; Jiang, W.; Liang, J.; Cheng, X.; Xu, Z. Burdens of stomach and esophageal cancer from 1990 to 2019 and projection to 2030 in China: Findings from the 2019 Global Burden of Disease Study. J. Glob. Health 2024, 14, 04025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, M.W.; Burgers, K.G.; Fry, V.T. Esophageal Cancer. Am. Fam. Physician 2017, 95, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, S.M.; Yeom, J.A.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, G.H.; Nam, K.J.; Jeong, Y.J. Findings of Endoscopic US and CT of Esophageal Disease. J. Korean Soc. Radiol. 2024, 85, 883–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaheen, N.J.; Falk, G.W.; Iyer, P.G.; Souza, R.F.; Yadlapati, R.H.; Sauer, B.G.; Wani, S. Diagnosis and Management of Barrett’s Esophagus: An Updated ACG Guideline. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 117, 559–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouw, R.E.; Barret, M.; Biermann, K.; Bisschops, R.; Czakó, L.; Gecse, K.B.; de Hertogh, G.; Hucl, T.; Iacucci, M.; Jansen, M.; et al. Endoscopic tissue sampling—Part 1: Upper gastrointestinal and hepatopancreatobiliary tracts. European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline. Endoscopy 2021, 53, 1174–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, B.C.; Bhatt, A.; Greer, K.B.; Lee, L.S.; Park, W.G.; Sauer, B.G.; Shami, V.M. ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Gastrointestinal Subepithelial Lesions. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 118, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennathur, A.; Gibson, M.K.; Jobe, B.A.; Luketich, J.D. Oesophageal carcinoma. Lancet 2013, 381, 400–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, A.; Falk, G.W. Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Review. JAMA 2021, 326, 1310–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, I.W.; Atkinson, A.E.; Liu, X.; Suriawinata, A.A.; Lefferts, J.A.; Lisovsky, M. Mucosal inflammation in Candida esophagitis has distinctive features that may be helpful diagnostically. Mod. Pathol. 2018, 31, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagundes, R.B.; Dalcin, R.P.; Rocha, M.P.; Moraes, C.C.; Carlotto, V.S.; Wink, M.O. Esophageal tuberculosis. Endoscopy 2007, 39 (Suppl. S1), E149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohli, D.R.; Faigel, D.O. Esophageal leiomyomas: Making mole hills out of mole hills? Gastrointest. Endosc. 2018, 87, 378–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.J.; Xu, A.P.; Xu, M.D. MALT Lymphoma of the Esophagus. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 22, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.; Narayan, J.; Angadi, S.; Shah, B.; Ingle, M.; Kiran, B.; Tyagi, U.; Kumar, L.; Wu, C.C.H.; Bhrugumalla, S.; et al. Role of endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition for the diagnosis of gastric wall thickening: A retrospective study with meta-analysis. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2023, 36, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, L.; Qing, Y.; Chu, Y.; Liang, C.; Lv, L.; Liu, D.; Tan, Y.; Zhou, Y. Role of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration (EUS-FNA) in the Diagnosis of Suspicious Malignant Esophageal Strictures. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordea, M.A.; Pîrvan, A.; Gheban, D.; Silaghi, C.; Lupan, I.; Samasca, G.; Pepelea, L.; Junie, L.M.; Costache, C. Infectious Esophagitis in Romanian Children: From Etiology and Risk Factors to Clinical Characteristics and Endoscopic Features. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioftsiou, S.; Faiz, M.; Malki, Z.; Mohammadi, M. Esophageal Tuberculosis Mimicking Malignancy in an Immunocompetent Patient: A Case Report. Cureus 2025, 17, e86606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellon, E.S.; Gonsalves, N.; Hirano, I.; Furuta, G.T.; Liacouras, C.A.; Katzka, D.A. ACG Clinical Guideline: Evidenced Based Approach to the Diagnosis and Management of Esophageal Eosinophilia and Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE). Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgouros, S.N.; Bergele, C.; Mantides, A. Eosinophilic esophagitis in adults: A systematic review. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 18, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellon, E.S.; Liacouras, C.A.; Molina-Infante, J.; Furuta, G.T.; Spergel, J.M.; Zevit, N.; Spechler, S.J.; Attwood, S.E.; Straumann, A.; Aceves, S.S.; et al. Updated International Consensus Diagnostic Criteria for Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Proceedings of the AGREE Conference. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1022–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.K.; Jain, S.; Jain, M.; Yaduvanshi, A. Esophageal tuberculosis: Is it so rare? Report of 12 cases and review of the literature. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 97, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Zhang, C.; Fang, S.G.; Zhong, P.; Zhu, X.F.; Lin, L.; Xiao, H.L. Primary esophageal mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma A case report and review of literature. Medicine 2017, 96, e6478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facciorusso, A.; Crinò, S.F.; Ramai, D.; Madhu, D.; Fugazza, A.; Carrara, S.; Spadaccini, M.; Mangiavillano, B.; Gkolfakis, P.; Mohan, B.P.; et al. Comparative diagnostic performance of different techniques for EUS-guided fine-needle biopsy sampling of solid pancreatic masses: A network meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2023, 97, 839–848.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facciorusso, A.; Arvanitakis, M.; Crinò, S.F.; Fabbri, C.; Fornelli, A.; Leeds, J.; Archibugi, L.; Carrara, S.; Dhar, J.; Gkolfakis, P.; et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue sampling: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Technical and Technology Review. Endoscopy 2025, 57, 390–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| No. | Sex * | Age | Lesion Location | Final Diagnosis | Presence and Location of Lymphadenopathy | Presence and Degree of Anemia ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F | 45 | Mid-thoracic | Lung-derived metastatic cancer | Bilateral cervical lymph nodes | - |
| 2 | M | 62 | Mid-thoracic | Lung-derived metastatic cancer | - | - |
| 3 | F | 72 | Lower thoracic | Esophageal adenocarcinoma | Bilateral axillary | Mild |
| 4 | M | 65 | Upper-thoracic | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Mediastinum and right hilar | - |
| 5 | M | 75 | Upper-thoracic | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Bilateral hilar | - |
| 6 | M | 47 | Mid-thoracic | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | - | Moderate |
| 7 | M | 63 | Mid-thoracic | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | - | - |
| 8 | M | 73 | Upper-thoracic | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Mediastinum | Mild |
| 9 | F | 52 | Mid-thoracic | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Right hilar | - |
| 10 | F | 52 | Mid-thoracic | Fungal esophagitis | Mediastinum | - |
| 11 | M | 52 | Mid-thoracic | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | - | Mild |
| 12 | M | 71 | Lower-thoracic | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Right hilar | Mild |
| 13 | M | 82 | Cervical | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | - | Mild |
| 14 | M | 63 | Upper-thoracic | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Bilateral supraclavicular | Mild |
| 15 | F | 43 | Upper-thoracic | Gastroesophagitis | - | - |
| 16 | M | 70 | Mid-thoracic | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Mediastinum | - |
| 17 | M | 75 | Upper-thoracic | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Mediastinum | Mild |
| 18 | M | 70 | Lower-thoracic | Esophageal adenocarcinoma | Peri-esophageal and mediastinum | Mild |
| 19 | M | 61 | Upper-thoracic | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Hepatogastric ligament | Mild |
| 20 | F | 37 | Cervical | Esophageal varices | - | - |
| 21 | M | 55 | Upper-thoracic | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Mediastinum | - |
| 22 | M | 52 | Mid-thoracic | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | - | Mild |
| 23 | M | 77 | Lower-thoracic | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Mediastinum and bilateral hilar | Mild |
| 24 | F | 55 | Mid-thoracic | Eosinophilic esophagitis | - | Mild |
| 25 | M | 62 | Mid-thoracic | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Mediastinum and bilateral hilar | Mild |
| 26 | F | 57 | Lower-thoracic | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Mediastinum and bilateral hilar | - |
| 27 | F | 62 | Lower-thoracic | Esophageal leiomyoma | Hepatogastric ligament | - |
| 28 | F | 39 | Lower-thoracic | Esophageal leiomyoma | Mediastinum and bilateral axillary | - |
| 29 | M | 47 | Mid-thoracic | Esophageal tuberculosis | - | - |
| 30 | F | 63 | Mid-thoracic | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | - | Mild |
| 31 | M | 62 | Full-length | Esophageal lymphoma | - | - |
| 32 | M | 65 | Upper-thoracic | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | - | Mild |
| 33 | F | 69 | Lower-thoracic | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Left hilar and mediastinum | Mild |
| 34 | M | 68 | Full-length | Achalasia | Mediastinum | - |
| 35 | M | 65 | Mid-thoracic | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | - | Mild |
| 36 | M | 77 | Mid-thoracic | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Mediastinum | Mild |
| 37 | M | 63 | Cervical | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Mediastinum | - |
| 38 | M | 67 | Lower-thoracic | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | Mediastinum | Moderate |
| Final Diagnosis | Contrast-Enhanced CT Enhancement Feature * | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Uneven Enhancement | Even Enhancement | No Significant Enhancement | |
| Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) | 13/25 (52%) | 7/25 (28%) | 5/25 (20%) |
| Esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) | 0/2 (0%) | 1/2 (50%) | 1/2 (50%) |
| Metastatic cancer | 2/2 (100%) | 0/2 (0%) | 0/2 (0%) |
| Fungal esophagitis | 1/1 (100%) | 0/1 (0%) | 0/1 (0%) |
| Gastroesophagitis | 0/1 (0%) | 1/1 (100%) | 0/1 (0%) |
| Eosinophilic esophagitis | 0/1 (0%) | 0/1 (0%) | 1/1 (100%) |
| Achalasia | 0/1 (0%) | 0/1 (0%) | 1/1 (100%) |
| Esophageal lymphoma | 0/1 (0%) | 1/1 (100%) | 0/1 (0%) |
| Esophageal tuberculosis | 0/1 (0%) | 0/1 (0%) | 1/1 (100%) |
| Esophageal varices | 1/1 (100%) | 0/1 (0%) | 0/1 (0%) |
| Esophageal leiomyoma | 1/2 (50%) | 0/2 (0%) | 1/2 (50%) |
| Texture of Mucosa * | Coarse | Smooth |
|---|---|---|
| Benign diseases | 1/8 (12.5%) | 7/8 (87.5%) |
| Malignant diseases | 15/30 (50%) | 15/30 (50%) |
| Coarse Mucosa | Smooth Mucosa | |
|---|---|---|
| Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) | 17/25 (68%) | 8/25 (32%) |
| Esophageal Adenocarcinoma (EAC) | 0/2 (0%) | 2/2 (100%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, K.; He, Q.; Jin, Y.; Duan, C.; Liu, J.; Han, C.; Lin, R. Diagnostic Value of EUS-FNA in the Differential Diagnosis of Esophageal Strictures Lacking Typical Malignant Features. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2470. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192470
Zhang K, He Q, Jin Y, Duan C, Liu J, Han C, Lin R. Diagnostic Value of EUS-FNA in the Differential Diagnosis of Esophageal Strictures Lacking Typical Malignant Features. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(19):2470. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192470
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Keyi, Qi He, Yu Jin, Caihan Duan, Jun Liu, Chaoqun Han, and Rong Lin. 2025. "Diagnostic Value of EUS-FNA in the Differential Diagnosis of Esophageal Strictures Lacking Typical Malignant Features" Diagnostics 15, no. 19: 2470. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192470
APA StyleZhang, K., He, Q., Jin, Y., Duan, C., Liu, J., Han, C., & Lin, R. (2025). Diagnostic Value of EUS-FNA in the Differential Diagnosis of Esophageal Strictures Lacking Typical Malignant Features. Diagnostics, 15(19), 2470. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192470






