Cytogenetic Profile of Chromosomal Aberrations in Leukemia Using the Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH) Method at a Tertiary Institution in Gauteng Province
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Sample Preparation Procedure and Laboratory Analysis
Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH) Procedure
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Distribution of Demographic Characteristics and Leukemia Subtypes Identified by FISH
| Demographic Characteristics | Total Population (n = 349) | ALL (n = 65) | AML (n = 109) | CLL (n = 36) | CML (n = 139) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age: Median (interquartile range) | 32 (16–51) | 12 (6–21) | 22 (13–40) | 68 (56–75) | 39 (29–46) | p < 0.001 |
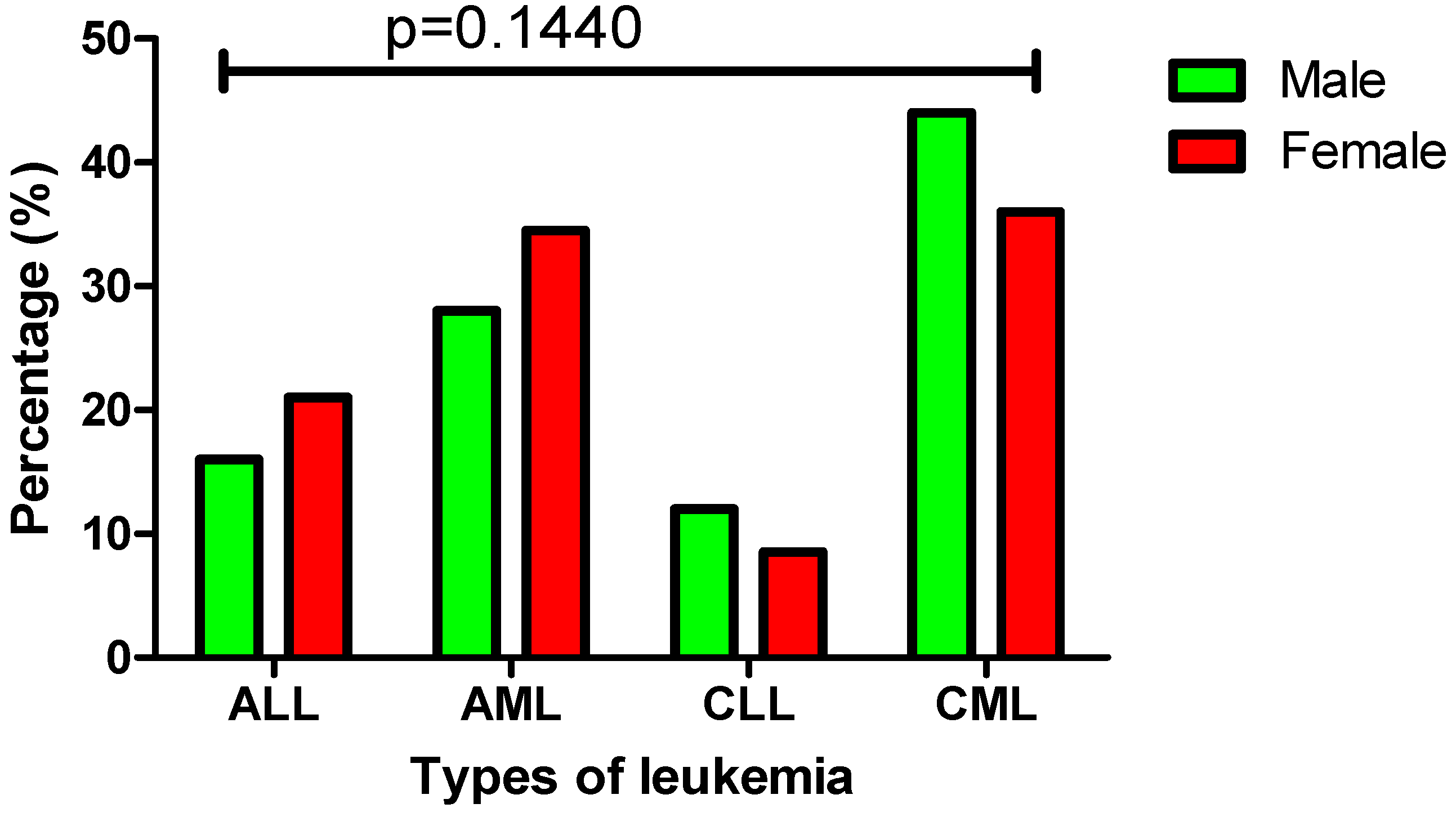
| Gender: | p = 0.1440 | |||||
| Male, n (%) | 173 (50%) | 28 (16%) | 48 (28%) | 21 (12%) | 76 (44%) | |
| Female, n (%) | 176 (50%) | 37 (21%) | 61 (34.5%) | 15 (8.5%) | 63 (36%) | |
| Ethnicity: | ||||||
| Black, n (%) | 349 (100%) | 65 (19%) | 109 (31%) | 36 (10%) | 139 (40%) |
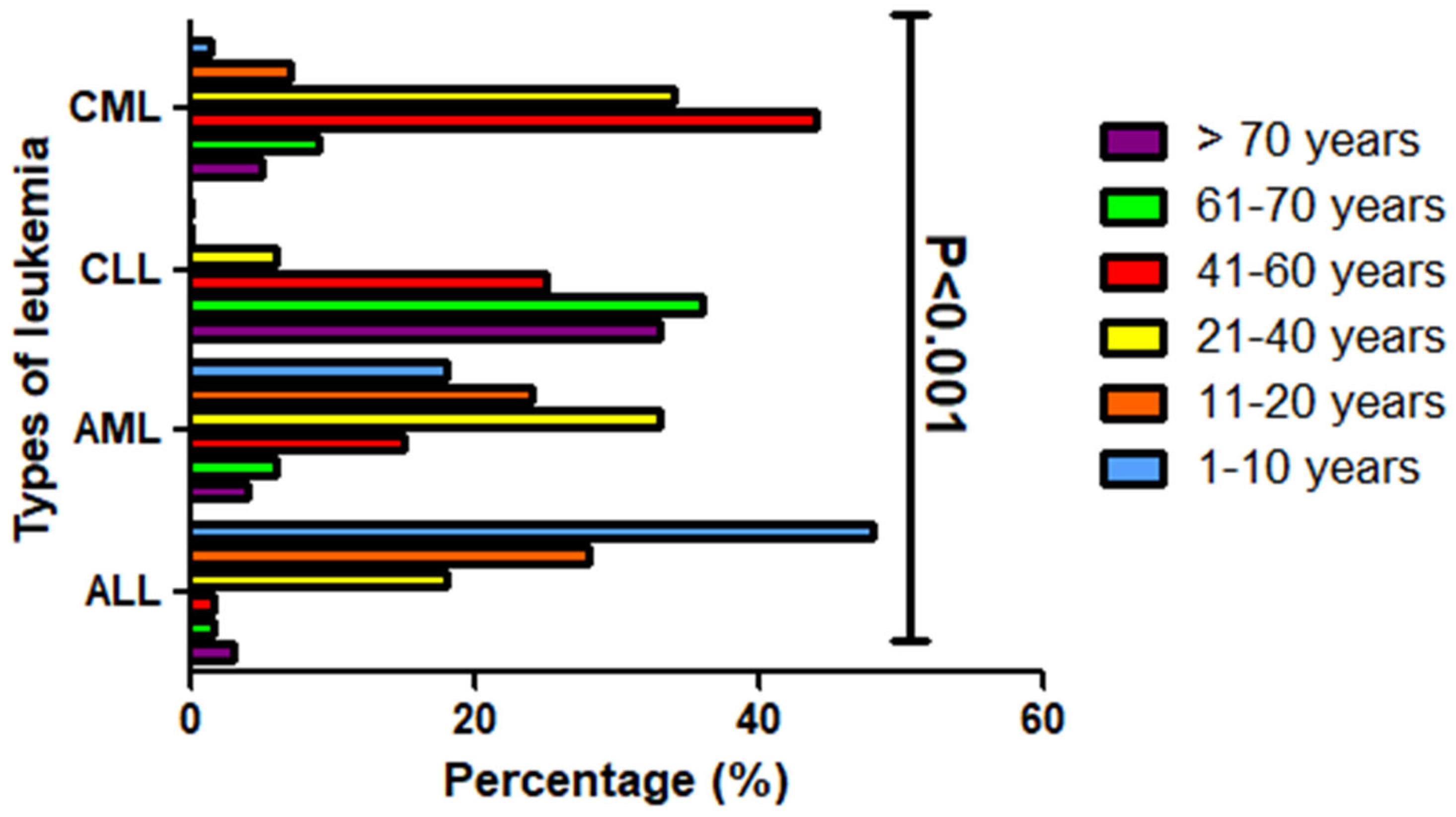
3.2. Age Distribution Patterns Across Four Main Leukemia Subtypes
3.3. Gender Distribution and Incidence Patterns of Leukemia Subtypes
3.4. Prevalence of Common Chromosomal Aberrations Detected by FISH in Leukemia Patients
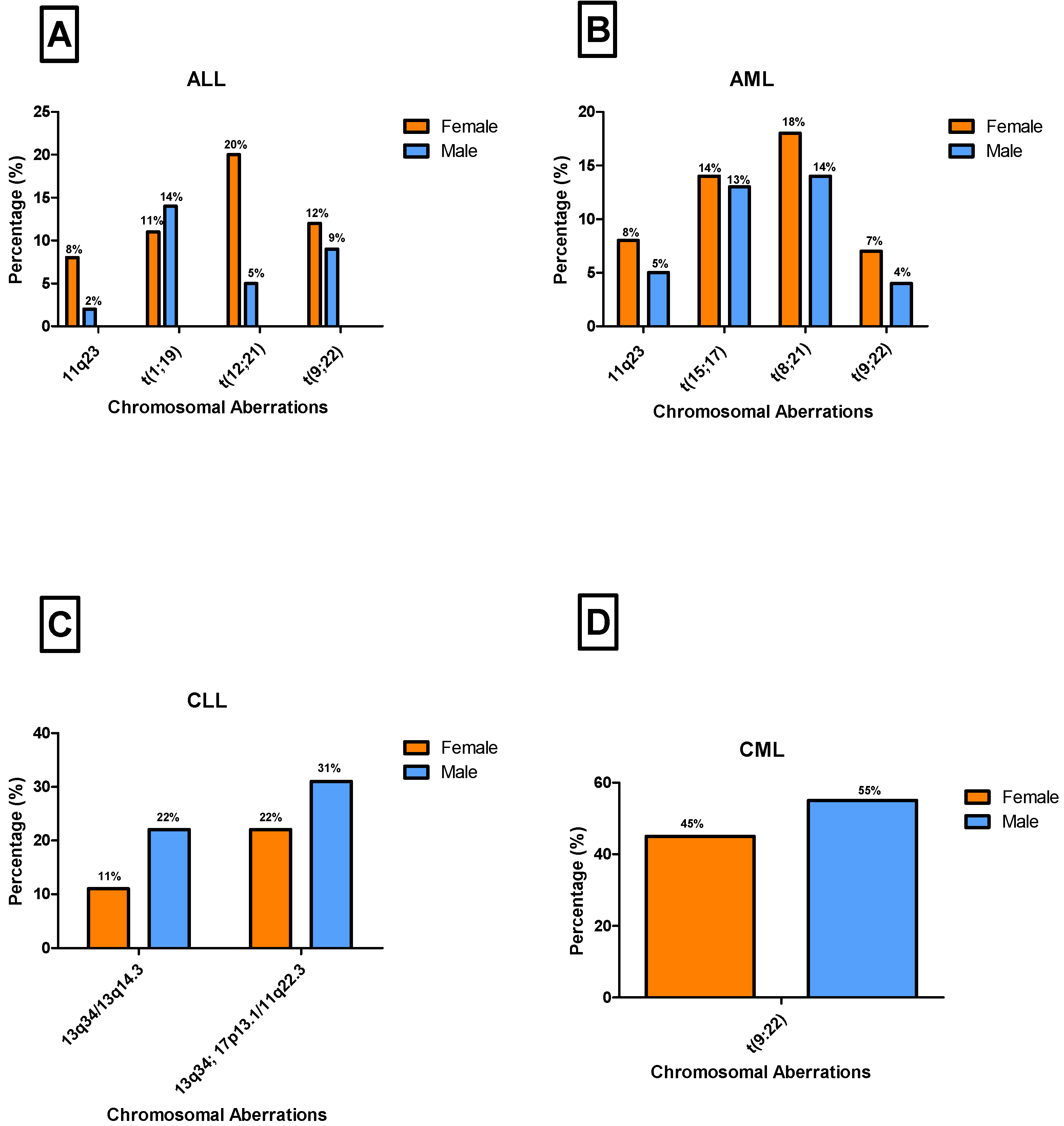
3.5. Gender-Specific Distribution and Prevalence of Chromosomal Aberrations Across Leukemia Subtypes
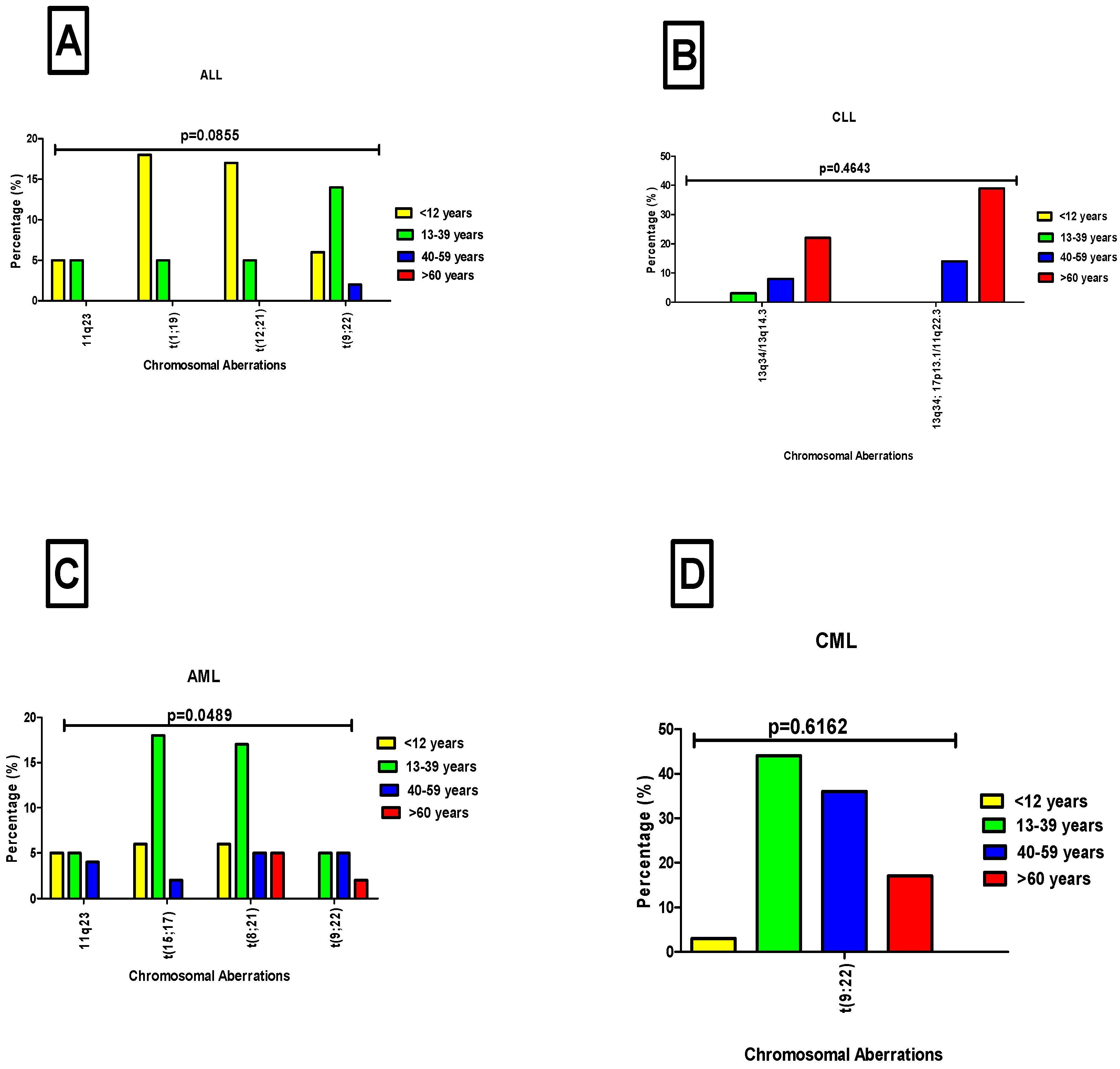
3.6. Distribution of Chromosomal Aberrations Across Age Groups in Leukemia Patients
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
7. Recommendation for Future Studies
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, J.; Chan, S.C.; Ngai, C.H.; Lok, V.; Zhang, L.; Lucero-Prisno, D.E., III; Xu, W.; Zheng, Z.J.; Elcarte, E.; Withers, M.; et al. Disease burden, risk factors, and trends of leukemia: A global analysis. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 904292. [Google Scholar]
- Amini, M.; Sharma, R.; Jani, C. Gender differences in leukemia outcomes based on health care expenditures using estimates from the GLOBOCAN 2020. Arch. Public Health 2023, 81, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkin, D.M.; Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Jemal, A. Cancer in Africa 2012. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2014, 23, 953–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, M. Fact Sheet on Acute Myelomonocytic Leukemia; Association of South Africa: Johannesburg, South Africa, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rugwizangoga, B.; Niyikora, N.; Musabyimana, A.; Izimukwiye, A.I.; Aurelius, J.; Martner, A.; Umubyeyi, A. Experience and Perception of Patients and Healthcare Professionals on Acute Leukemia in Rwanda: A Qualitative Study. Cancer Manag. Res. 2022, 14, 1923–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulled, N.; Singer, M. In the shadow of HIV & TB: A commentary on the COVID epidemic in South Africa. Glob. Public Health 2020, 15, 1231–1243. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ngwenya, N.; Gumede, D.; Shahmanesh, M.; McGrath, N.; Grant, A.; Seeley, J. Community perceptions of the socio-economic structural context influencing HIV and TB risk, prevention and treatment in a high prevalence area in the era of antiretroviral therapy. Afr. J. AIDS Res. 2018, 17, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viljoen, I.; Hendricks, C.; Mellet, J.; Pepper, M. Perspectives on establishing a public cord blood inventory in South Africa. Cytotherapy 2021, 23, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, H.C. Controversies in the surgical management of skeletal metastases. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 2005, 87, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obeagu, E.I.; Omar, D.M.; Bunu, U.O.; Obeagu, G.U.; Esther, U.; Alumand, P.C.; Ugwu, O. Leukaemia burden in Africa. Int. J. Curr. Res. Biol. Med. 2023, 8, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Lagunas-Rangel, F.A.; Chávez-Valencia, V.; Gómez-Guijosa, M.Á.; Cortes-Penagos, C. Acute myeloid leukemia—Genetic alterations and their clinical prognosis. Int. J. Hematol.-Oncol. Stem Cell Res. 2017, 11, 328. [Google Scholar]
- Taofeek, I.D.B.E.O.; Kwaifa, O.Y.A.I.K.; Isaac, F.O.A.B.I.; Oluwasayo, Z.B.A.H.B. Challenges associated with living with haematological malignancies in sub-Saharan Africa. Sokoto J. Med. Lab. Sci. 2023, 8, 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- Munung, N.S.; Ambele, M.A.; Moela, P. Advancing global equity in cancer genomics–challenges and opportunities in Sub-Saharan Africa. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2021, 66, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, W.; Rego, E. How to manage Philadelphia-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia in resource-constrained settings. Cancers 2023, 15, 5783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraha, D.M.; Ghirmay, E.; Gebresilassie, E.; Zerat, G.E.; Kokob, R.; Tesfazghi, A.; Negash, S.; Daniel, T.; Mohammed, S.; Mengistu, S.T.; et al. Incidence of leukemia in Eritrea: 11-year Laboratory-based retrospective analysis of nationally representative data. Res. Sq. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korubo, K.I.; Okoye, H.C.; Efobi, C.C. The economic burden of malignant and premalignant hematological diseases in Southern Nigeria. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2018, 21, 1396–1402. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Durosinmi, M.A.; Olarewaju, J.O.; Bolarinwa, R.A.A.; Akinyemi, P.A. A Review Article on Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia in Nigeria in the Era of Targeted Therapy. Niger. J. Haematol. 2023, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Mulatie, Z.; Berta, D.M.; Gedefie, A.; Ebrahim, H.; Eshetu, B.; Gessese, T.; Tilahun, M.; Ali, S.; Debash, H.; Kassa, Y.; et al. Prevalence of hematological malignancies in Africa: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 9471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodkinson, K.E.; Willem, P.; Moodley, M.; Engelbrecht, D.; Patel, P.; Wiggill, T.; Ketseoglou, I.; van Zijl, H.; Vaughan, J.; Chapanduka, Z.; et al. The genetic landscape of acute myeloid leukaemia in the South African public sector. S. Afr. J. Oncol. 2024, 8, a309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadhia, P.K.; Modi, P.Y.; Vaniawala, S.N. Prevalence of cytogenetic abnormalities in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Med. Clin. 2019, 3, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Khalid, K.; Padda, J.; Syam, M.; Moosa, A.; Kakani, V.; Sanka, S.; Zubair, U.; Padda, S.; Cooper, A.C.; Jean-Charles, G.; et al. 13q14 deletion and its effect on prognosis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cureus 2021, 13, e16839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durak Aras, B.; Isik, S.; Uskudar Teke, H.; Aslan, A.; Yavasoglu, F.; Gulbas, Z.; Demirkan, F.; Ozen, H.; Cilingir, O.; Inci, N.S.; et al. Which prognostic marker is responsible for the clinical heterogeneity in CLL with 13q deletion? Mol. Cytogenet. 2021, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehlmann, R. Chronic myeloid leukemia in 2020. Hemasphere 2020, 4, e468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaker, E.; Nouri, N.; Sorkhizadeh, S.; Ghasemirad, H.; Hajijafari, A.H.; Zare, F. The importance of personalized medicine in chronic myeloid leukemia management: A narrative review. Egypt. J. Med. Human Genet. 2023, 24, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladikou, E.E.; Kassi, E. The emerging role of estrogen in B cell malignancies. Leuk. Lymphoma 2017, 58, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samulowitz, A.; Gremyr, I.; Eriksson, E.; Hensing, G. “Brave men” and “emotional women”: A theory-guided literature review on gender bias in health care and gendered norms towards patients with chronic pain. Pain. Res. Manag. 2018, 2018, 6358624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, G.C.; Ravandi, F.; DiNardo, C.D.; Jabbour, E.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Andreeff, M. Therapeutic implications of menin inhibition in acute leukemias. Leukemia 2021, 35, 2482–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, H.; Disteche, C.M.; Berletch, J.B. X inactivation and escape: Epigenetic and structural features. Frontiers in cell and developmental biology. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radivoyevitch, T.; Jankovic, G.M.; Tiu, R.V.; Saunthararajah, Y.; Jackson, R.C.; Hlatky, L.R.; Gale, R.P.; Sachs, R.K. Sex differences in the incidence of chronic myeloid leukemia. Radiat. Environ. Biophys 2014, 53, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukkamalla, S.K.R.; Taneja, A.; Malipeddi, D.; Master, S.R. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Jephcote, C.; Brown, D.; Verbeek, T.; Mah, A. A systematic review and meta-analysis of haematological malignancies in residents living near petrochemical facilities. Environ. Health 2020, 19, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stabellini, N.; Tomlinson, B.; Cullen, J.; Shanahan, J.; Waite, K.; Montero, A.J.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S.; Hamerschlak, N. Sex differences in adults with acute myeloid leukemia and the impact of sex on overall survival. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 6711–6721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuan, J.W.; Su, A.T.; Sim, S.P.; Tay, S.P. Higher prevalence of harbouring BCR::ABL1 in first-degree relatives of chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) patients compared to normal population. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daltveit, D.S.; Morgan, E.; Colombet, M.; Steliarova-Foucher, E.; Bendahhou, K.; Marcos-Gragera, R.; Rongshou, Z.; Smith, A.; Wei, H.; Soerjomataram, I. Global patterns of leukemia by subtype, age, and sex in 185 countries in 2022. Leukemia 2025, 39, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Tang, X.; Hu, J.; He, G.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, B. Investigation on combined copy number variation sequencing and cytogenetic karyotyping for prenatal diagnosis. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2021, 21, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughan, J.; Bouwer, N.; Willem, P.; Wiggill, T.; Hodkinson, K. The translocation t(1;19)(q23; p13)(TCF3/PBX1 fusion) is the most common recurrent genetic abnormality detected amongst patients with B-cell lymphoblastic leukaemia in Johannesburg, South Africa. SA J. Oncol. 2021, 5, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, M.; Liu, K.; Tirado, C.A. The t(12;21)(p13; q22) in Pediatric B-Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: An Update. J. Assoc. Genet. Technol. 2017, 43, 99. [Google Scholar]
- Inaba, H.; Pui, C.H. Advances in the diagnosis and treatment of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porazzi, P.; De Dominici, M.; Salvino, J.; Calabretta, B. Targeting the CDK6 dependence of Ph+ acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Genes 2021, 12, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulczycka, M.; Derlatka, K.; Tasior, J.; Sygacz, M.; Lejman, M.; Zawitkowska, J. Infant Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia-New Therapeutic Opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona, S.; Bor, J.; Nattey, C.; Maughan-Brown, B.; Maskew, M.; Fox, M.P.; Glencross, D.K.; Ford, N.; MacLeod, W.B. Persistent high burden of advanced HIV disease among patients seeking care in South Africa’s national HIV program: Data from a nationwide laboratory cohort. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 66 (Suppl. 2), S111–S117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opie, J.; Verburgh, E.; Bailly, J.; Mayne, E.; Louw, V. Hematological Complications of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Infection: An Update From an HIV-Endemic Setting. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2024, 11, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pemmaraju, N.; Kantarjian, H.; Ravandi, F.; Nogueras-Gonzalez, G.M.; Huang, X.; O’Brien, S.; Wierda, W.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Thomas, D.; Pierce, S.; et al. Patient characteristics and outcomes in adolescents and young adults (AYA) with acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2016, 16, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duployez, N.; Willekens, C.; Marceau-Renaut, A.; Boudry-Labis, E.; Preudhomme, C. Prognosis and monitoring of core-binding factor acute myeloid leukemia: Current and emerging factors. Expert. Rev. Hematol. 2015, 8, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustun, C.; Morgan, E.; Moodie, E.E.M.; Pullarkat, S.; Yeung, C.; Broesby-Olsen, S.; Ohgami, R.; Kim, Y.; Sperr, W.; Vestergaard, H.; et al. Core-binding factor acute myeloid leukemia with t(8;21): Risk factors and a novel scoring system (I-CBFit). Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 4447–4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, J.J.; Chale, R.S.; Abad, A.C.; Schally, A.V. Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL): A review of the literature. Oncotarget 2020, 11, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balgobind, B.V.; Raimondi, S.C.; Harbott, J.; Zimmermann, M.; Alonzo, T.A.; Auvrignon, A.; Beverloo, H.B.; Chang, M.; Creutzig, U.; Dworzak, M.N.; et al. Novel prognostic subgroups in childhood 11q23/MLL-rearranged acute myeloid leukemia: Results of an international retrospective study. Blood 2009, 114, 2489–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strickland, S.A.; Vey, N. Diagnosis and treatment of therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2022, 171, 103607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Tineh, M.; Ali, E.A.; Alshurafa, A.; Nashwan, A.J.; Albsheer, K.; Ahmed, A.; Hailan, Y.; Rozi, W.; Aljaloudi, E.; Yassin, M.A. The Impact of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors on Fatherhood in Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Mixed-Method Study. Cureus 2023, 15, e33407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, L.; Hu, C.; Lu, P.; Que, Y.; Zhu, X.; Li, D. Trends in disease burden of chronic myeloid leukemia at the global, regional, and national levels: A population-based epidemiologic study. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, T.; Delgado, J.; Santacruz, R.; Martínez-Trillos, A.; Royo, C.; Navarro, A.; Pinyol, M.; Rozman, M.; Pereira, A.; Villamor, N.; et al. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia in the elderly: Clinico-biological features, outcomes, and proposal of a prognostic model. Haematologica 2014, 99, 1599–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stauder, R.; Eichhorst, B.; Hamaker, M.E.; Kaplanov, K.; Morrison, V.A.; Österborg, A.; Poddubnaya, I.; Woyach, J.A.; Shanafelt, T.; Smolej, L.; et al. Management of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in the elderly: A position paper from an international Society of Geriatric Oncology (SIOG) Task Force. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weide, R.; Feiten, S.; Chakupurakal, G.; Friesenhahn, V.; Kleboth, K.; Köppler, H.; Heymanns, J. Survival improvement of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in routine care 1995–2017. Leuk. Lymphoma 2019, 61, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyani, P.; Christodoulou, R.; Vassiliou, E. Immunosenescence: Aging and Immune System Decline. Vaccines 2024, 12, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravandi, F.; O’Brien, S. Immune defects in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2006, 55, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobczyńska-Konefał, A.; Jasek, M.; Karabon, L.; Jaskuła, E. Insights into genetic aberrations and signalling pathway interactions in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: From pathogenesis to treatment strategies. Biomark. Res. 2024, 12, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Leukemia Subtype | Probe | Target | Fluorophore Colour |
|---|---|---|---|
| CML, ALL, AML | BCR::ABL1 Dual fusion | t(9;22) | Green (BCR), orange (ABL1) |
| AML | RUNX1T1::RUNX1 (ETO::AML1) | t(8;21) | Orange (RUNX1T1), green (RUNX1) |
| AML | PML::RARA | t(15;17) | Orange (PML), green (RARA) |
| AML | RARA breaks apart | RARA | Orange/green (split signal for break apart) |
| AML | CBFB breaks apart | Inv(16:/t(16;16) | Orange/green (split signal for break apart) |
| ALL, AML | KMT2A (MLL) | 11q23 | Orange/green (split signal for break apart) |
| ALL | ETV6::RUNX1 (TEL/AML1) | t(12;21) | Orange (ETV6), green (RUNX1) |
| ALL | TCF3::PBX1 (E2A::PBX1) | t(1;19) | Orange (TCF3), green (PBX1) |
| CLL | TP53 ATM | 17p13.1/11q22.3 deletion | Orange (TP53), green (ATM) |
| CLL | D13S319::13q34 CEP12 | 13q14.3 deletion/trisomy 12 | Orange (D13S319), aqua (13q34), green (CEP12) |
| Age Groups | ALL (n = 65) | AML (n = 109) | CLL (n = 36) | CML (n = 139) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1–10 years (n, %) | 31 (48%) | 20 (18%) | 0 | 2 (1.4%) |
| 11–20 years (n, %) | 18 (28%) | 26 (24%) | 0 | 10 (7%) |
| 21–40 years (n, %) | 12 (18%) | 36 (33%) | 2 (6%) | 47 (34%) |
| 41–60 years (n, %) | 1 (1.5%) | 16 (15%) | 9 (25%) | 61 (44%) |
| 61–70 years (n, %) | 1 (1.5%) | 7 (6%) | 13 (36%) | 12 (9%) |
| >70 years (n, %) | 2 (3%) | 4 (4%) | 12 (33%) | 7 (5%) |
| Chromosomal Aberrations | Probe/Gene | ALL (n = 65), % | AML (n = 109), % | CLL (n = 36), % | CML (n = 139), % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t(1;19) | TCF3::PBX1 | 16 (25%) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| t(12;21) | ETO::RUNX1 | 16 (25%) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| t(8;21) | RUNX1::RUNX1T1 | 0 | 35 (33%) | 0 | 0 |
| t(15;17) | PML::PARA | 0 | 29 (27%) | 0 | 0 |
| t(9;22) | BCR::ABL1 | 14 (22%) | 12 (11%) | 0 | 139 (100%) |
| 11q23 | KMT2A | 6 (9%) | 14 (13%) | 0 | 0 |
| 13q34/13q14.3; 17p13.1/11q22.3 | CEP12; TP53::ATM | 0 | 0 | 19 (53%) | 0 |
| 13q34/13q14.3 | CEP12 | 0 | 0 | 12 (33%) | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duma, Z.; Matsepane, K.C.; Nkoana, K.; Pheeha, S.M.; Mbele, B.; Simela-Tshabalala, T.; Tanyanyiwa, D.M. Cytogenetic Profile of Chromosomal Aberrations in Leukemia Using the Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH) Method at a Tertiary Institution in Gauteng Province. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2429. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192429
Duma Z, Matsepane KC, Nkoana K, Pheeha SM, Mbele B, Simela-Tshabalala T, Tanyanyiwa DM. Cytogenetic Profile of Chromosomal Aberrations in Leukemia Using the Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH) Method at a Tertiary Institution in Gauteng Province. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(19):2429. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192429
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuma, Zamathombeni, Karabo C. Matsepane, Koketso Nkoana, Sara M. Pheeha, Bathabile Mbele, Tandekile Simela-Tshabalala, and Donald M. Tanyanyiwa. 2025. "Cytogenetic Profile of Chromosomal Aberrations in Leukemia Using the Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH) Method at a Tertiary Institution in Gauteng Province" Diagnostics 15, no. 19: 2429. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192429
APA StyleDuma, Z., Matsepane, K. C., Nkoana, K., Pheeha, S. M., Mbele, B., Simela-Tshabalala, T., & Tanyanyiwa, D. M. (2025). Cytogenetic Profile of Chromosomal Aberrations in Leukemia Using the Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH) Method at a Tertiary Institution in Gauteng Province. Diagnostics, 15(19), 2429. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15192429






