Parotid Gland Magnetic Resonance Elastography Feasibility Study: Clinical Diagnostic Potential and Future Perspectives as a Radiological Palpation Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Imaging Protocol and MRE Technique
2.3. Image Postprocessing and ROI Analysis
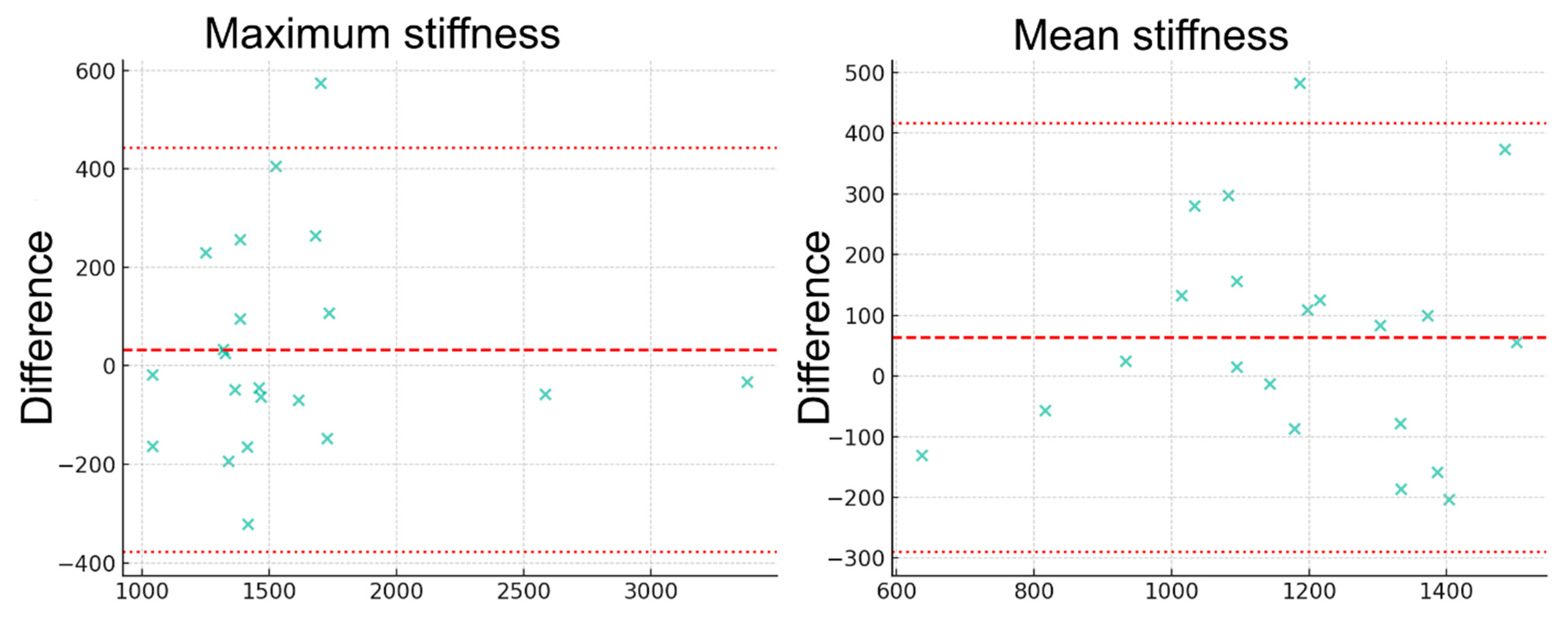
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Declaration of AI Use
References
- Thoeny, H.C. Imaging of salivary gland tumours. Cancer Imaging 2007, 7, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divi, V.; Fatt, M.A.; Teknos, T.N.; Mukherji, S.K. Use of cross-sectional imaging in predicting surgical location of parotid neoplasms. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2005, 29, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousem, D.M.; Kraut, M.A.; Chalian, A.A. Major salivary gland imaging. Radiology 2000, 216, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thoeny, H.C.; De Keyzer, F.; Boesch, C.; Hermans, R. Diffusion-weighted imaging of the parotid gland: Influence of the choice of b-values on the apparent diffusion coefficient value. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2004, 20, 786–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsholtz, F.H.J.; Reiter, R.; Garcia, S.R.M.; Braun, J.; Sack, I.; Hamm, B.; Schaafs, L.-A. Multifrequency magnetic resonance elastography-based tomoelastography of the parotid glands-feasibility and reference values. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2022, 51, 20210337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Savic, L.J.; Hillebrandt, K.H.; Sack, I. MR Elastography in Cancer. Investig. Radiol. 2023, 58, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.D.; Yeung, D.K.W.; Ahuja, A.T.; Tse, G.M.K.; Yuen, H.Y.; Wong, K.T.; van Hasselt, A.C. Salivary gland tumors at in vivo proton MR spectroscopy. Radiology 2005, 237, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, D.K.; Bhatia, K.S.; Lee, Y.Y.; King, A.D.; Garteiser, P.; Sinkus, R.; Ahuja, A.T. MR elastography of the head and neck: Driver design and initial results. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 31, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahn, M.M.; Brennan, M.D.; Bahn, R.S.; Dean, D.S.; Kugel, J.L.; Ehman, R.L. Development and application of magnetic resonance elastography of the normal and pathological thyroid gland in vivo. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2009, 30, 1151–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manduca, A.; Bayly, P.V.; Ehman, R.L.; Kolipaka, A.; Royston, T.J.; Sack, I.; Sinkus, R.; Van Beers, B.E. MR elastography: Principles, guidelines, and terminology. Magn. Reson. Med. 2021, 85, 2377–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atamaniuk, V.; Chen, J.; Obrzut, M.; Glaser, K.J.; Hańczyk, Ł.; Pozaruk, A.; Gutkowski, K.; Obrzut, B.; Domka, W.; Ehman, R.L.; et al. High-frequency shear wave MR elastography of parotid glands: Custom driver design and preliminary results. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunnetci, K.M.; Kaba, E.; Celiker, F.B.; Alkan, A. Deep Network-Based Comprehensive Parotid Gland Tumor Detection. Acad. Radiol. 2024, 31, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabuuchi, H.; Fukuya, T.; Tajima, T.; Hachitanda, Y.; Tomita, K.; Koga, M. Salivary gland tumors: Diagnostic value of gadolinium-enhanced dynamic MR imaging with histopathologic correlation. Radiology 2003, 226, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Takashima, S.; Takayama, F.; Kawakami, S.; Saito, A.; Matsushita, T.; Momose, M.; Ishiyama, T. Head and neck lesions: Characterization with diffusion-weighted echo-planar MR imaging. Radiology 2001, 220, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habermann, C.R.; Sinkus, R.; Albrecht, A.; Cramer, M.C.; Weiss, F.; Adam, G. MR-elastography of the parotid gland: Feasibility and first experiences. RöFo 2005, 177, A26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, Y.; Shirai, A.; Ogura, I. Shear Wave Elastography for Parotid Glands: Quantitative Analysis of Shear Elastic Modulus in Relation to Age, Gender, and Internal Architecture in Patients with Oral Cancer. J. Imaging 2025, 11, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökçe, E.; Beyhan, M. Diagnostic efficacy of diffusion-weighted imaging and semiquantitative and quantitative dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI in salivary gland tumors. World J. Radiol. 2023, 15, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantisani, V.; David, E.; Sidhu, P.S.; Sacconi, B.; Greco, A.; Pandolfi, F.; Tombolini, M.; Mele, L.L.; Calliada, F.; Brunese, L.; et al. Parotid Gland Lesions: Multiparametric Ultrasound and MRI Features. Ultraschall Med. 2016, 37, 454–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökçe, E.; Beyhan, M. Advanced magnetic resonance imaging findings in salivary gland tumors. World J. Radiol. 2022, 14, 256–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Chen, Y.; She, D.; Xing, Z.; Chen, T.; Cao, D. Diffusion kurtosis imaging and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI for the differentiation of parotid gland tumors. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 2748–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariappan, Y.K.; Glaser, K.J.; Ehman, R.L. Magnetic resonance elastography: A review. Clin. Anat. 2010, 23, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvi, S.; Chudek, D.; Limaiem, F. Parotid Cancer. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Xie, J.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Lin, Q.; Xu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Zheng, R.; Xu, B. Analysis of the Parotid Glands on an Energy Spectrum CT Iodine Map to Evaluate Irradiation-Induced Acute Xerostomia. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2024, 23, 15330338241256814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorino, C.; Rizzo, G.; Scalco, E.; Broggi, S.; Belli, M.L.; Dell’oca, I.; Dinapoli, N.; Ricchetti, F.; Rodriguez, A.M.; Di Muzio, N.; et al. Density variation of parotid glands during IMRT for head-neck cancer: Correlation with treatment and anatomical parameters. Radiother. Oncol. 2012, 104, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brook, I. Early side effects of radiation treatment for head and neck cancer. Cancer Radiother. 2021, 25, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsanie, I.; Rajab, S.; Cottom, H.; Adegun, O.; Agarwal, R.; Jay, A.; Graham, L.; James, J.; Barrett, A.W.; van Heerden, W.; et al. Distribution and Frequency of Salivary Gland Tumours: An International Multicenter Study. Head Neck Pathol. 2022, 16, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.-M.; Wen, M.-H.; Hsu, W.-L.; Chang, C.-M.; Hou, P.-Y.; Liao, L.-J. Ultrasonographic and elastographic biometry in adult major salivary glands: A preliminary case-control report. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, K.; Cho, C.C.; Tong, C.S.; Lee, Y.Y.; Yuen, E.H.; Ahuja, A.T. Shear wave elastography of focal salivary gland lesions: Preliminary experience in a routine head and neck US clinic. Eur. Radiol. 2012, 22, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atamaniuk, V.; Chen, J.; Glaser, K.; Pozaruk, A.; Obrzut, M.; Obrzut, B.; Domka, W.; Gutkowski, K.; Ehman, R.; Cholewa, M. Feasibility of High-Frequency Shear Wave MR Elastography of the Parotid Glands; ISMRM: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Gontarz, M.; Urbańska, M.; Bargiel, J.; Gąsiorowski, K.; Marecik, T.; Szczurowski, P.; Zapała, J.; Wyszyńska-Pawelec, G. Metastatic malignancies in the parotid gland: A retrospective study. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2024, 52, 1334–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

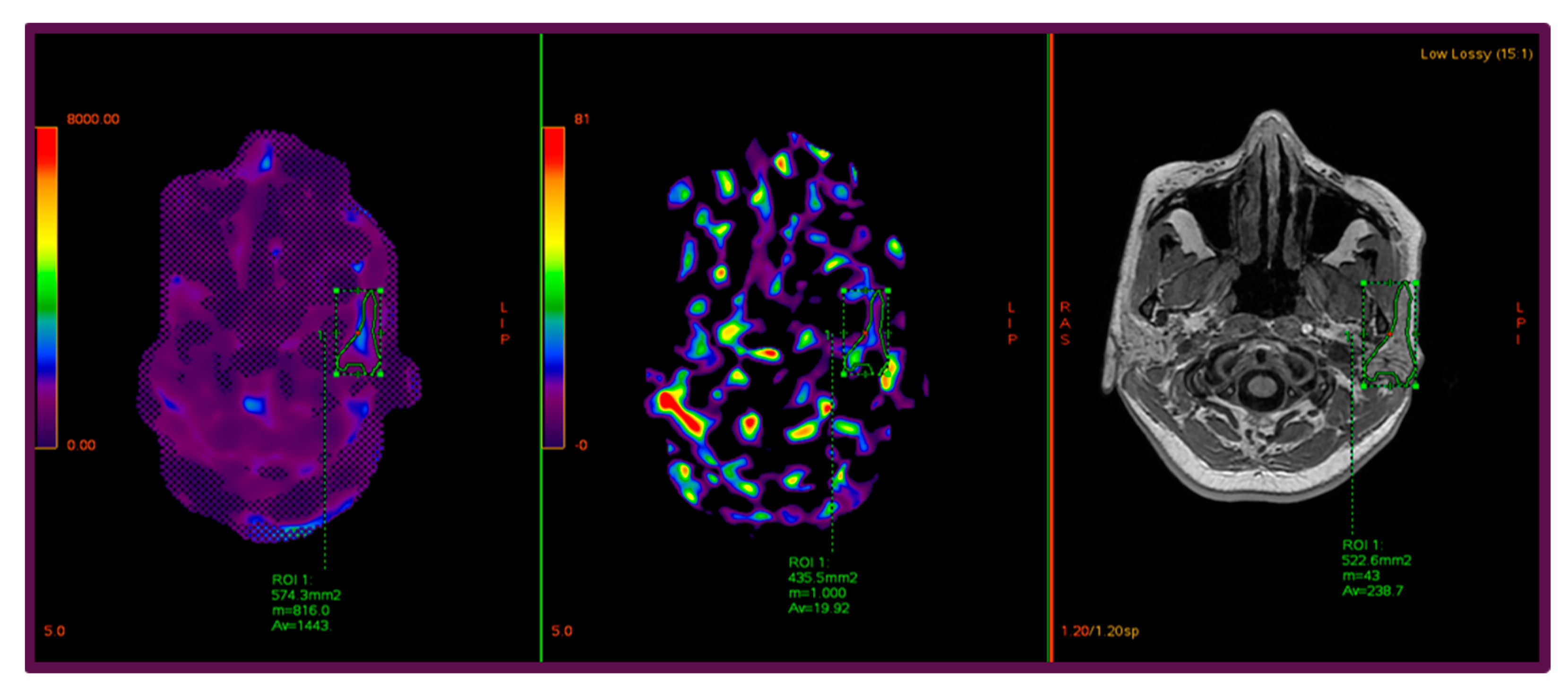
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Magnetic field strength | 3T |
| Sequence | GRE MRE |
| Orientation | Axial |
| Number of slices | 4 |
| Slice thickness | 10 mm |
| Field of view (FOV) | 420 mm |
| Phase FOV | 100% (420 mm) |
| Base resolution/Acquisition matrix | 256 × 64 |
| Phase resolution | 25% |
| Phase encoding direction | A–P |
| Acceleration factor (ASSET, SENSE, GRAPPA) | 2 |
| Echo time (TE) | Shortest (approx. 20 ms) |
| Repetition time (TR) | 50 ms |
| Flip angle (FA) | 20° |
| Number of breath-holds | 4 (end-expiration, one per slice) |
| R1_Max ± SD kPa | R1_Mean ± SD kPa | R2_Max ± SD kPa | R2_Mean ± SD kPa | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Left | 1.743 ± 0.721 | 1.356 ± 0.190 | 1.950 ± 0.469 | 1.272 ± 0.224 |
| Right | 1.401 ± 0.165 | 1.118 ± 0.167 | 1.363 ± 0.174 | 1.196 ± 0.146 |
| Localization | R1_Max ± SD kPa | R1_Mean ± SD kPa | R2_Max ± SD kPa | R2_Mean ± SD kPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Left | 2.354 ± 1.040 | 1.222 ± 0.205 | 2.350 ± 1.012 | 1.207 ± 0.034 |
| Right | 1.390 ± N/A | 1.153 ± N/A | 1.342 ± N/A | 1.278 ± N/A |
| Localization | R1_Max ± SD kPa | R1_Mean ± SD kPa | R2_Max ± SD kPa | R2_Mean ± SD kPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Left | 1.689 ± 0.385 | 1.359 ± 0.174 | 1.832 ± 0.337 | 1.343 ± 0.133 |
| Right | 1.326 ± 0.159 | 1.099 ± 0.173 | 1.359 ± 0.189 | 1.133 ± 0.158 |
| Statistic | R1-Max | R1-Mean | R2-Max | R2-Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | 0.021 kPa | 0.021 kPa | 0.021 kPa | 0.021 kPa |
| Mean | 1.595 kPa | 1.210 kPa | 1.563 kPa | 1.147 kPa |
| Std | 0.532 kPa | 0.241 kPa | 0.529 kPa | 0.234 kPa |
| Min | 0.959 kPa | 0.571 kPa | 1.051 kPa | 0.701 kPa |
| Max | 3.362 kPa | 1.671 kPa | 3.395 kPa | 1.505 kPa |
| Median | 1.436 kPa | 1.241 kPa | 1.438 kPa | 1.149 kPa |
| Study (Year) | Participants/Patients | Organ/Region | Method/Equipment/Driver | Frequency | Measured Parameters | Mean Stiffness/Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elsholtz et al., 2022 [5] | 20 healthy volunteers | Parotid | 3T MRI, multifrequency tomoelastography | 25–50 Hz | SWS, φ | SWS mean: 0.97 m/s, φ mean: 0.59 rad |
| Yeung et al., 2013 [8] | 10 healthy volunteers | Parotid | 3T MRI, adaptive driver for parotid | 25–50 Hz | G’ (shear modulus) | 1.12 ± 0.48 kPa |
| Atamaniuk et al., 2024 [11] | 10 healthy volunteers | Parotid | 3T MRI, high-frequency passive driver | 50–100 Hz | Shear modulus | 1.25 ± 0.20 kPa |
| Habermann et al., 2005 [15] | 5 healthy volunteers | Parotid | 3T MRI, mechanical driver directly on gland | 50 Hz | Shear modulus | 1.29 ± 0.08 kPa |
| Tanabe et al., 2025 [16] | 124 parotid glands | Parotid | 2D-SWE | - | Shear wave elastography | 11.32 ± 1.91 kPa (SWE) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Solak, M.; Kaba, E.; Beyazal, M.; Çeliker, M.; Çeliker, F.B. Parotid Gland Magnetic Resonance Elastography Feasibility Study: Clinical Diagnostic Potential and Future Perspectives as a Radiological Palpation Method. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2351. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182351
Solak M, Kaba E, Beyazal M, Çeliker M, Çeliker FB. Parotid Gland Magnetic Resonance Elastography Feasibility Study: Clinical Diagnostic Potential and Future Perspectives as a Radiological Palpation Method. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(18):2351. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182351
Chicago/Turabian StyleSolak, Merve, Esat Kaba, Mehmet Beyazal, Metin Çeliker, and Fatma Beyazal Çeliker. 2025. "Parotid Gland Magnetic Resonance Elastography Feasibility Study: Clinical Diagnostic Potential and Future Perspectives as a Radiological Palpation Method" Diagnostics 15, no. 18: 2351. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182351
APA StyleSolak, M., Kaba, E., Beyazal, M., Çeliker, M., & Çeliker, F. B. (2025). Parotid Gland Magnetic Resonance Elastography Feasibility Study: Clinical Diagnostic Potential and Future Perspectives as a Radiological Palpation Method. Diagnostics, 15(18), 2351. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182351






