Microstructural Analysis of Whole-Brain Changes Increases the Detection of Pediatric Focal Cortical Dysplasia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. MRI Protocol
2.3. Calculation of MRI Indicators
2.3.1. DTI and MTI Indicators Based on Lesions
2.3.2. Voxel-Based Morphometry (VBM) Indicators
2.3.3. TBSS Based on DTI
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Clinical Data and Lesion Distribution
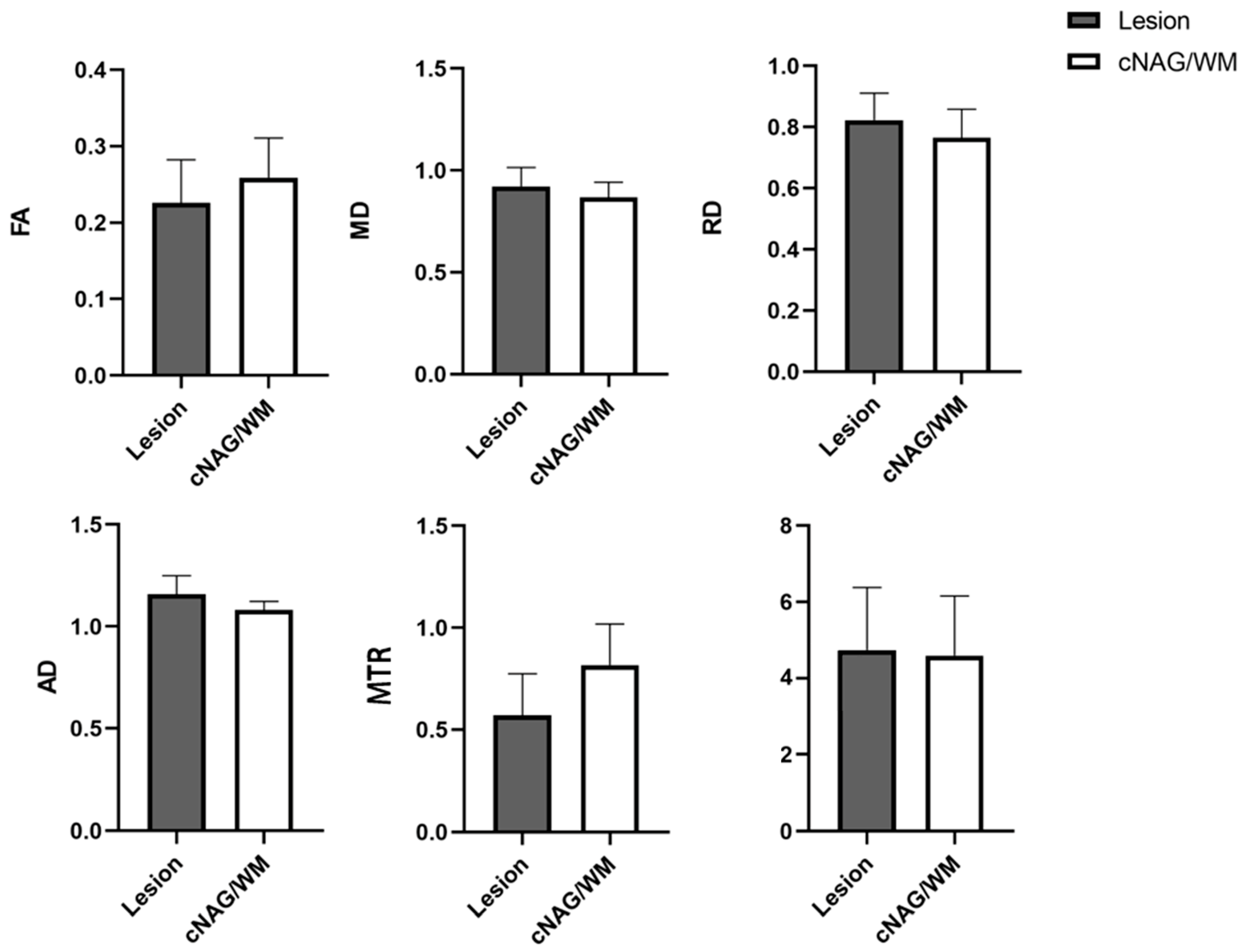
3.2. DTI and MTI Results Based on Lesions of Pediatric FCD
3.3. VBM Results Based on the Whole Brain of Pediatric FCD Patients
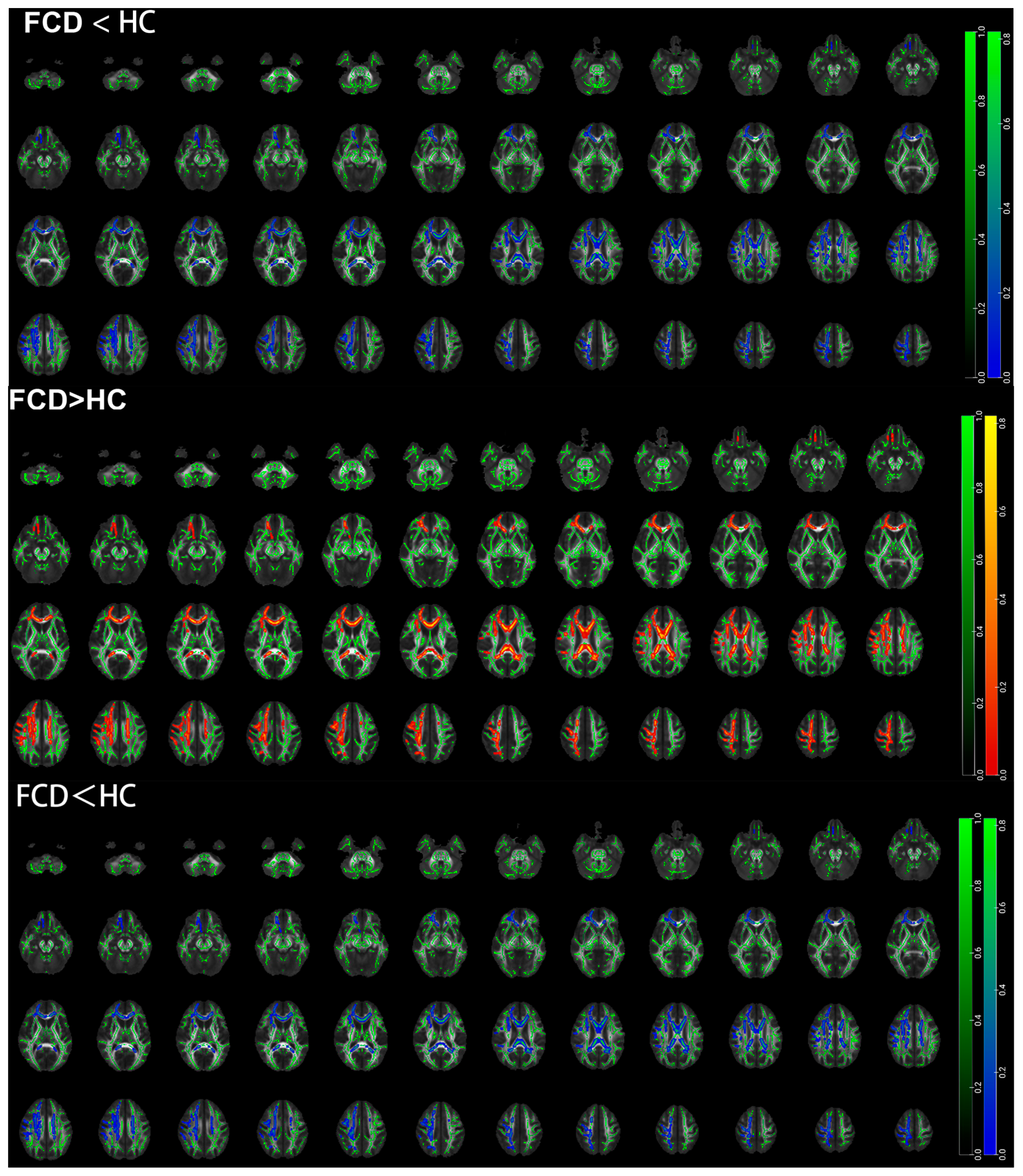
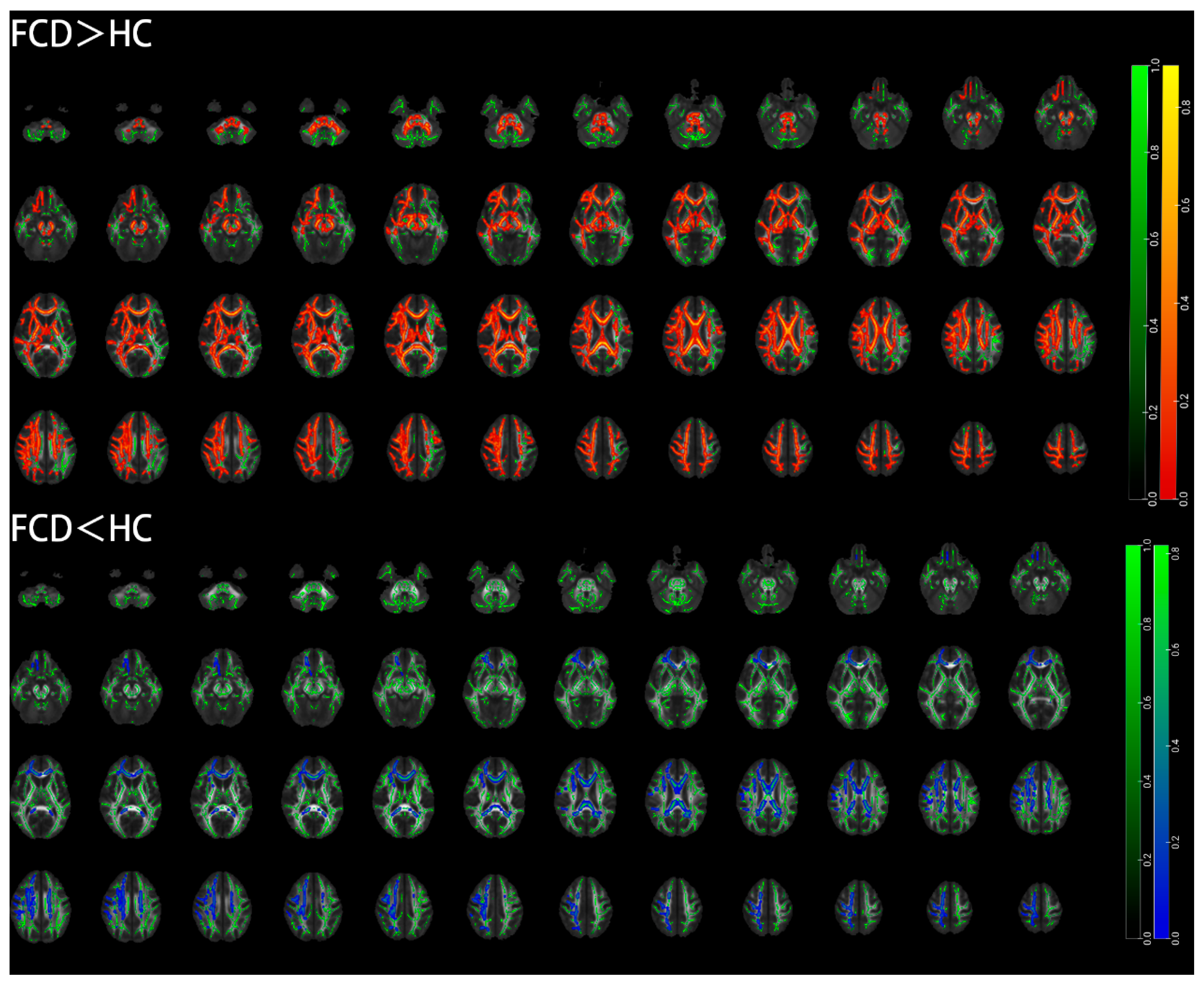
3.4. TBSS Results Based on the Whole Brain of Pediatric FCD Patients
4. Discussion
4.1. Lesion-Related Microstructural Damage in Individuals with FCD
4.2. Whole-Brain Cortical Volume Damage in Individuals with FCD
4.3. Whole-Brain WM Microstructural Damage in Individuals with FCD
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cohen, N.T.; Chang, P.; You, X.; Zhang, A.; Havens, K.A.; Oluigbo, C.O.; Whitehead, M.T.; Gholipour, T.; Gaillard, W.D. Prevalence and Risk Factors for Pharmacoresistance in Children With Focal Cortical Dysplasia-Related Epilepsy. Neurology 2022, 99, e2006–e2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumcke, I.; Coras, R.; Busch, R.M.; Morita-Sherman, M.; Lal, D.; Prayson, R.; Cendes, F.; Lopes-Cendes, I.; Rogerio, F.; Almeida, V.S.; et al. Toward a better definition of focal cortical dysplasia: An iterative histopathological and genetic agreement trial. Epilepsia 2021, 62, 1416–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernasconi, A.; Bernasconi, N.; Bernhardt, B.C.; Schrader, D. Advances in MRI for ‘cryptogenic’ epilepsies. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2011, 7, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrini, R.; Duchowny, M.; Jayakar, P.; Krsek, P.; Kahane, P.; Tassi, L.; Melani, F.; Polster, T.; Andre, V.M.; Cepeda, C.; et al. Diagnostic methods and treatment options for focal cortical dysplasia. Epilepsia 2015, 56, 1669–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, N.C.; Englot, D.J.; Cage, T.A.; Sughrue, M.E.; Barbaro, N.M.; Chang, E.F. A meta-analysis of predictors of seizure freedom in the surgical management of focal cortical dysplasia. J. Neurosurg. 2012, 116, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lin, Y.; Wang, S.; Jones, S.; Prayson, R.; Moosa, A.N.V.; McBride, A.; Gonzalez-Martinez, J.; Bingaman, W.; Najm, I.; et al. Voxel-based morphometric magnetic resonance imaging postprocessing in non-lesional pediatric epilepsy patients using pediatric normal databases. Eur. J. Neurol. 2019, 26, 969-e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Murillo, D.; Castro-Ospina, A.E.; Duque-Munoz, L.; Martinez-Vargas, J.D.; Suarez-Revelo, J.X.; Velez-Arango, J.M.; de la Iglesia-Vaya, M. Automatic Detection of Focal Cortical Dysplasia Using MRI: A Systematic Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 7072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krsek, P.; Pieper, T.; Karlmeier, A.; Hildebrandt, M.; Kolodziejczyk, D.; Winkler, P.; Pauli, E.; Blumcke, I.; Holthausen, H. Different presurgical characteristics and seizure outcomes in children with focal cortical dysplasia type I or II. Epilepsia 2009, 50, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Walderveen, M.A.; Truyen, L.; van Oosten, B.W.; Castelijns, J.A.; Lycklama a Nijeholt, G.J.; van Waesberghe, J.H.; Polman, C.; Barkhof, F. Development of hypointense lesions on T1-weighted spin-echo magnetic resonance images in multiple sclerosis: Relation to inflammatory activity. Arch. Neurol. 1999, 56, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dousset, V.; Grossman, R.I.; Ramer, K.N.; Schnall, M.D.; Young, L.H.; Gonzalez-Scarano, F.; Lavi, E.; Cohen, J.A. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis and multiple sclerosis: Lesion characterization with magnetization transfer imaging. Radiology 1992, 182, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, M.; Rocca, M.A. Magnetization transfer magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of neurological diseases. J. Neuroimaging 2004, 14, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca Vde, C.; Yasuda, C.L.; Tedeschi, G.G.; Betting, L.E.; Cendes, F. White matter abnormalities in patients with focal cortical dysplasia revealed by diffusion tensor imaging analysis in a voxelwise approach. Front. Neurol. 2012, 3, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.J.; Bernhardt, B.C.; Caldairou, B.; Hall, J.A.; Guiot, M.C.; Schrader, D.; Bernasconi, N.; Bernasconi, A. Multimodal MRI profiling of focal cortical dysplasia type II. Neurology 2017, 88, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, B.M.; Coan, A.C.; Beltramini, G.C.; Liu, M.; Yassuda, C.L.; Ghizoni, E.; Beaulieu, C.; Gross, D.W.; Cendes, F. White matter abnormalities associate with type and localization of focal epileptogenic lesions. Epilepsia 2015, 56, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M.; Jenkinson, M.; Johansen-Berg, H.; Rueckert, D.; Nichols, T.E.; Mackay, C.E.; Watkins, K.E.; Ciccarelli, O.; Cader, M.Z.; Matthews, P.M.; et al. Tract-based spatial statistics: Voxelwise analysis of multi-subject diffusion data. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 1487–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumcke, I.; Thom, M.; Aronica, E.; Armstrong, D.D.; Vinters, H.V.; Palmini, A.; Jacques, T.S.; Avanzini, G.; Barkovich, A.J.; Battaglia, G.; et al. The clinicopathologic spectrum of focal cortical dysplasias: A consensus classification proposed by an ad hoc Task Force of the ILAE Diagnostic Methods Commission. Epilepsia 2011, 52, 158–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Cabronero, J.; Williams, G.B.; Pengas, G.; Nestor, P.J. Absolute diffusivities define the landscape of white matter degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2010, 133 Pt 2, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, A.L.; Lee, J.E.; Lazar, M.; Field, A.S. Diffusion tensor imaging of the brain. Neurotherapeutics 2007, 4, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.K.; Sun, S.W.; Ramsbottom, M.J.; Chang, C.; Russell, J.; Cross, A.H. Dysmyelination revealed through MRI as increased radial (but unchanged axial) diffusion of water. Neuroimage 2002, 17, 1429–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lexa, F.J.; Grossman, R.I.; Rosenquist, A.C. Dyke Award paper. MR of wallerian degeneration in the feline visual system: Characterization by magnetization transfer rate with histopathologic correlation. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1994, 15, 201–212. [Google Scholar]
- Bohbot, V.D.; Kalina, M.; Stepankova, K.; Spackova, N.; Petrides, M.; Nadel, L. Spatial memory deficits in patients with lesions to the right hippocampus and to the right parahippocampal cortex. Neuropsychologia 1998, 36, 1217–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, U.; Carmant, L.; Mikati, M.A. Electroencephalographic discharges of temporal lobe seizures in children and young adults. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1998, 107, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieb, J.P.; Dasheiff, R.M.; Engel, J., Jr. Role of the frontal lobes in the propagation of mesial temporal lobe seizures. Epilepsia 1991, 32, 822–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isnard, J.; Guenot, M.; Ostrowsky, K.; Sindou, M.; Mauguiere, F. The role of the insular cortex in temporal lobe epilepsy. Ann. Neurol. 2000, 48, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, C.; Saint-Hilaire, J.M.; Richer, F. Temporal and spatial characteristics of intracerebral seizure propagation: Predictive value in surgery for temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 1994, 35, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harroud, A.; Boucher, O.; Tran, T.P.Y.; Harris, L.; Hall, J.; Dubeau, F.; Mohamed, I.; Bouthillier, A.; Nguyen, D.K. Precuneal epilepsy: Clinical features and surgical outcome. Epilepsy Behav. 2017, 73, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanna, A.E.; Trimble, M.R. The precuneus: A review of its functional anatomy and behavioural correlates. Brain 2006, 129 Pt 3, 564–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennari, A.G.; Cserpan, D.; Stefanos-Yakoub, I.; Kottke, R.; O’Gorman Tuura, R.; Ramantani, G. Diffusion tensor imaging discriminates focal cortical dysplasia from normal brain parenchyma and differentiates between focal cortical dysplasia types. Insights Imaging 2023, 14, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleichgerrcht, E.; Greenblatt, A.S.; Kellermann, T.S.; Rowland, N.; Vandergrift, W.A.; Edwards, J.; Davis, K.A.; Bonilha, L. Patterns of seizure spread in temporal lobe epilepsy are associated with distinct white matter tracts. Epilepsy Res. 2021, 171, 106571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urquia-Osorio, H.; Pimentel-Silva, L.R.; Rezende, T.J.R.; Almendares-Bonilla, E.; Yasuda, C.L.; Concha, L.; Cendes, F. Superficial and deep white matter diffusion abnormalities in focal epilepsies. Epilepsia 2022, 63, 2312–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concha, L.; Beaulieu, C.; Wheatley, B.M.; Gross, D.W. Bilateral white matter diffusion changes persist after epilepsy surgery. Epilepsia 2007, 48, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; An, D.; Tong, X.; Liu, W.; Xiao, F.; Ren, J.; Niu, R.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, B.; Lei, D.; et al. Different patterns of white matter changes after successful surgery of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuroimage Clin. 2019, 21, 101631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, D.W.; Concha, L.; Beaulieu, C. Extratemporal white matter abnormalities in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy demonstrated with diffusion tensor imaging. Epilepsia 2006, 47, 1360–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scanlon, C.; Mueller, S.G.; Cheong, I.; Hartig, M.; Weiner, M.W.; Laxer, K.D. Grey and white matter abnormalities in temporal lobe epilepsy with and without mesial temporal sclerosis. J. Neurol. 2013, 260, 2320–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Concha, L.; Beaulieu, C.; Collins, D.L.; Gross, D.W. White-matter diffusion abnormalities in temporal-lobe epilepsy with and without mesial temporal sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2009, 80, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| FCD (n = 28) | Healthy Controls (n = 34) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (male/female) | 14/14 | 21/13 | 0.999 |
| Age | 8 (5, 11.5) | 6 (4.75, 7) | 0.999 |
| Age of seizure onset | 7 (5, 9.75) | NA | |
| Family history | 15 (54%) | NA | |
| Right-handed | 23 (82%) | 30 (88%) | 0.999 |
| Distribution of lesions (by brain lobe) | NA | ||
| Frontal lobe | 11 (39%) | ||
| Parietal lobe | 9 (33%) | ||
| Occipital lobe | 3 (11%) | ||
| Temporal lobe | 3 (11%) | ||
| Insula | 2 (7%) |
| FCD | cNAG/WM | t | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lesion volume (mm3) | 4.737 ± 1.638 | 4.588 ± 1.567 | 0.316 | 0.753 |
| FA | 0.226 ± 0.056 | 0.259 ± 0.052 | −2.114 | 0.040 * |
| MD | 0.922 ± 0.092 | 0.868 ± 0.074 | 2.191 | 0.034 * |
| RD | 0.823 ± 0.088 | 0.765 ± 0.094 | 2.160 | 0.036 * |
| AD | 1.160 ± 0.089 | 1.080 ± 0.043 | 3.906 | 0.000 * |
| MTR | 0.570 ± 0.205 | 0.817 ± 0.201 | −4.130 | 0.000 * |
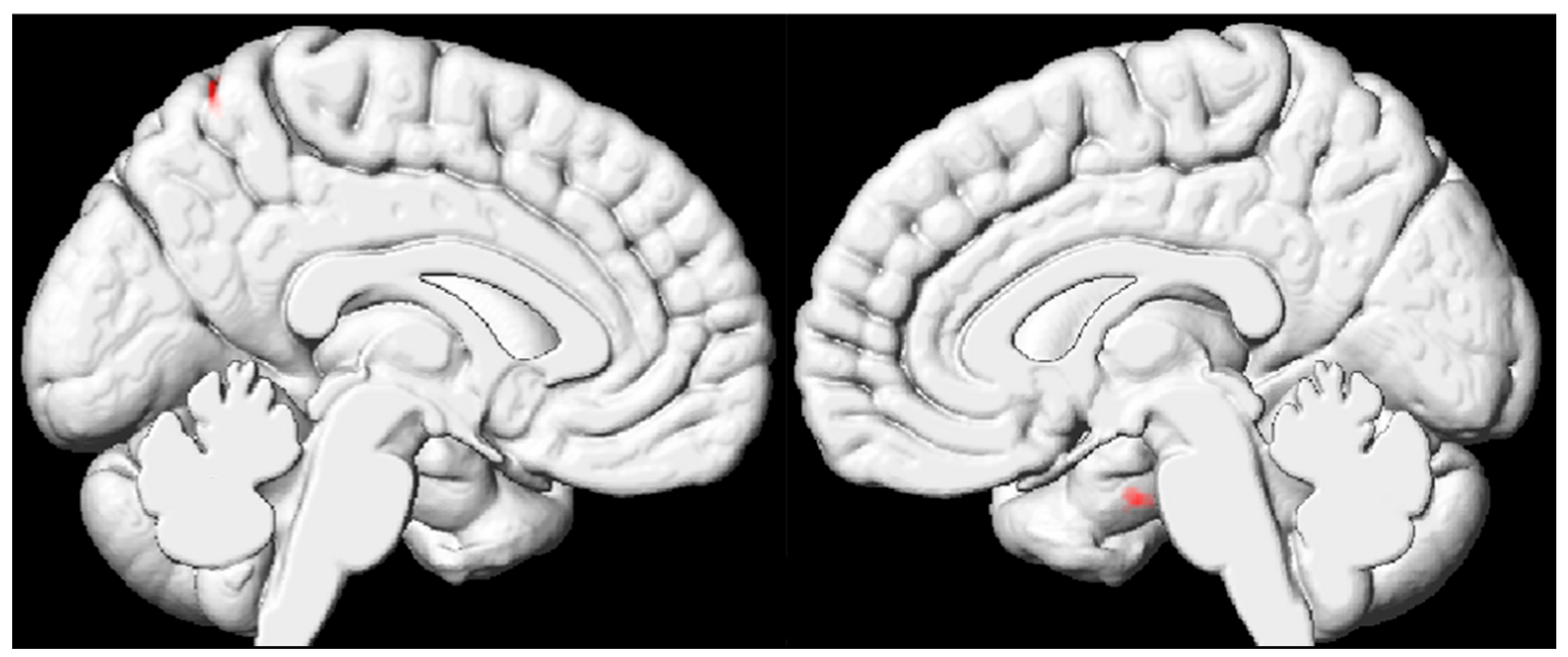
| Brain Region (AAL) | Cluster Size (Voxel) | Peak MNI Coordinates | t Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | |||
| FCD < HC | |||||
| Cluster 1 | |||||
| Right hippocampus | 26 | 19.5 | −9 | 33 | −4.4148 |
| Cluster 2 | |||||
| Left precentral gyrus | 20 | −13.5 | −61.5 | −64.5 | −5.1828 |
| Brain Region (AAL) | Cluster Size (Voxel) | Peak MNI Coordinates | t Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | ||||
| FCD < HC | ||||||
| Middle cerebellar peduncle | 115 | 24.3 | −60.4 | −38.8 | 0.965 | |
| Cingulum (cingulate gyrus) | L | 50 | −7.46 | 19.7 | 25.1 | 0.971 |
| Superior corona radiata | L | 10 | −28.4 | −0.197 | 19.2 | 0.971 |
| Brain Region (AAL) | Cluster Size (Voxel) | Peak MNI Coordinates | t Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | ||||
| FCD > HC | ||||||
| Middle cerebellar peduncle | 95 | −12.2 | −22.1 | −28.4 | 2.1 | |
| Internal capsule | R | 75 | 36.2 | −37 | 8.62 | 1.98 |
| Posterior thalamic radiation | R | 57 | 35.2 | −55.6 | 0.364 | 1.82 |
| Medial lemniscus | L | 42 | −4.15 | −34.8 | −40.3 | 2.43 |
| External capsule | L | 34 | 35.5 | −56.9 | 13.7 | 1.87 |
| Superior longitudinal fasciculus | R | 26 | 40.7 | −40.8 | 17 | 1.54 |
| Cerebral peduncle | L | 25 | −11.2 | −26.5 | −17.8 | 2.12 |
| Posterior thalamic radiation | L | 25 | −31.2 | −67 | 7.41 | 2.22 |
| Medial lemniscus | R | 16 | 4.51 | −37.1 | −34.9 | 1.92 |
| Superior corona radiata | R | 15 | 27.4 | −23.2 | 33.2 | 2.06 |
| Fornix | L | 14 | −25.7 | −33.2 | 7.25 | 1.98 |
| External capsule | R | 11 | 35.1 | −2.74 | −11.6 | 1.67 |
| Superior corona radiata | L | 10 | −21 | −14.6 | 35.5 | 1.37 |
| Superior longitudinal fasciculus | L | 10 | −35.9 | 0.816 | 26 | 1.4 |
| Cingulum (cingulate gyrus) | L | 10 | −6.44 | −9.68 | 35.9 | 1.8 |
| Brain Region (AAL) | Cluster Size (Voxel) | Peak MNI Coordinates | t Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | ||||
| FCD > HC | ||||||
| Cingulum (hippocampus) | L | 27 | −22.4 | −29.6 | −16.7 | 1.76 |
| Superior corona radiata | L | 20 | −31.4 | −10.2 | 23.1 | 1.64 |
| Superior corona radiata | R | 14 | 27.4 | −23.2 | 33.2 | 3.14 |
| Anterior corona radiata | L | 12 | −20.9 | 28.1 | 21.3 | 1.77 |
| Cingulum (cingulate gyrus) | L | 12 | −8 | 32.6 | 14.1 | 2.64 |
| Cingulum (hippocampus) | R | 11 | 26.1 | −20.3 | −26.5 | 1.29 |
| Splenium of corpus callosum | 11 | 15.5 | −45.2 | 28.6 | 2.36 | |
| FCD < HC | ||||||
| Middle cerebellar peduncle | 38 | −22.6 | −62 | −11.2 | 2.2 | |
| Anterior corona radiata | L | 18 | −17.6 | 28 | −11.2 | 1.4 |
| Fornix | L | 23 | −30.8 | −28.1 | −2.82 | 1.48 |
| Genu of corpus callosum | 13 | −12 | 21.2 | −6.51 | 1.93 | |
| Cerebral peduncle | R | 12 | 12 | −23.8 | −10 | 1.6 |
| Sagittal stratum | L | 11 | −35.5 | −19.5 | −6 | 1.02 |
| External capsule | R | 10 | 35 | 4 | −3 | 1.07 |
| External capsule | L | 10 | −34 | −1 | −2 | 1.07 |
| Brain Region (AAL) | Cluster Size (Voxel) | Peak MNI Coordinates | t Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | ||||
| FCD < HC | ||||||
| Anterior corona radiata | L | 32 | −20.9 | 28.1 | 21.3 | 1.77 |
| Cingulum (hippocampus | L | 27 | −22.4 | −29.6 | −16.7 | 1,76 |
| Superior corona radiata | R | 14 | 27.4 | −23.2 | 33.2 | 3.14 |
| Cingulum (cingulate gyrus) | L | 12 | −8 | 32.6 | 14.1 | 2.64 |
| Cingulum (hippocampus) | R | 11 | 26.1 | −20.3 | −26.5 | 1.29 |
| Splenium of corpus callosum | 11 | 15.5 | −45.2 | 28.6 | 2.36 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Ding, S.; Peng, S.; Tang, W.; Gao, Y.; Huang, Z.; Cai, J. Microstructural Analysis of Whole-Brain Changes Increases the Detection of Pediatric Focal Cortical Dysplasia. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2311. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182311
Yang X, Ding S, Peng S, Tang W, Gao Y, Huang Z, Cai J. Microstructural Analysis of Whole-Brain Changes Increases the Detection of Pediatric Focal Cortical Dysplasia. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(18):2311. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182311
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xinyi, Shuang Ding, Song Peng, Wei Tang, Yali Gao, Zhongxin Huang, and Jinhua Cai. 2025. "Microstructural Analysis of Whole-Brain Changes Increases the Detection of Pediatric Focal Cortical Dysplasia" Diagnostics 15, no. 18: 2311. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182311
APA StyleYang, X., Ding, S., Peng, S., Tang, W., Gao, Y., Huang, Z., & Cai, J. (2025). Microstructural Analysis of Whole-Brain Changes Increases the Detection of Pediatric Focal Cortical Dysplasia. Diagnostics, 15(18), 2311. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182311





