Optimization of DNA Fragmentation Techniques to Maximize Coverage Uniformity of Clinically Relevant Genes Using Whole Genome Sequencing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Extraction
2.2. Cell Lines
2.3. Library Preparation and Sequencing
2.4. WGS Analysis and Normalized Coverage
2.5. TSO500 DNA Analysis Using CLC Workbench
2.6. Variant Performance
3. Results
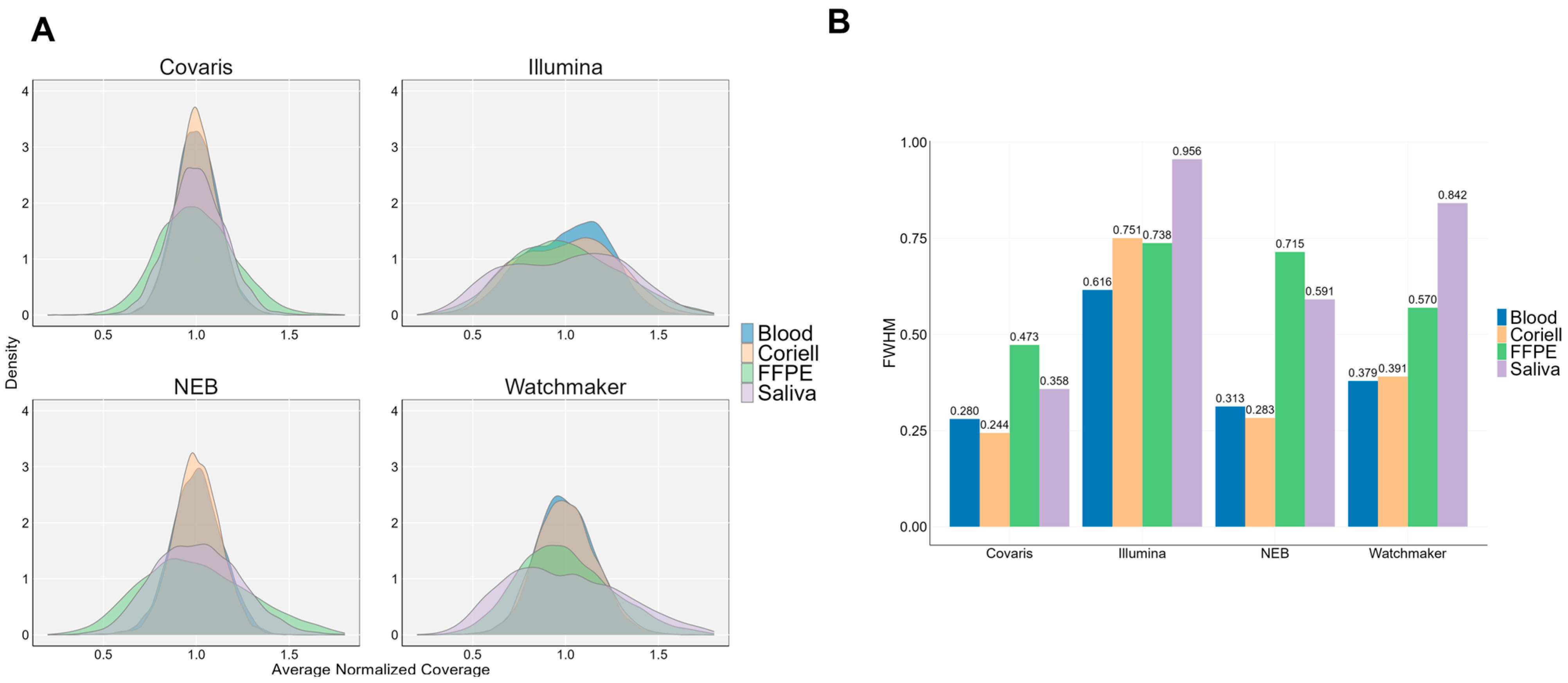
3.1. Sequencing Data Quality and Coverage
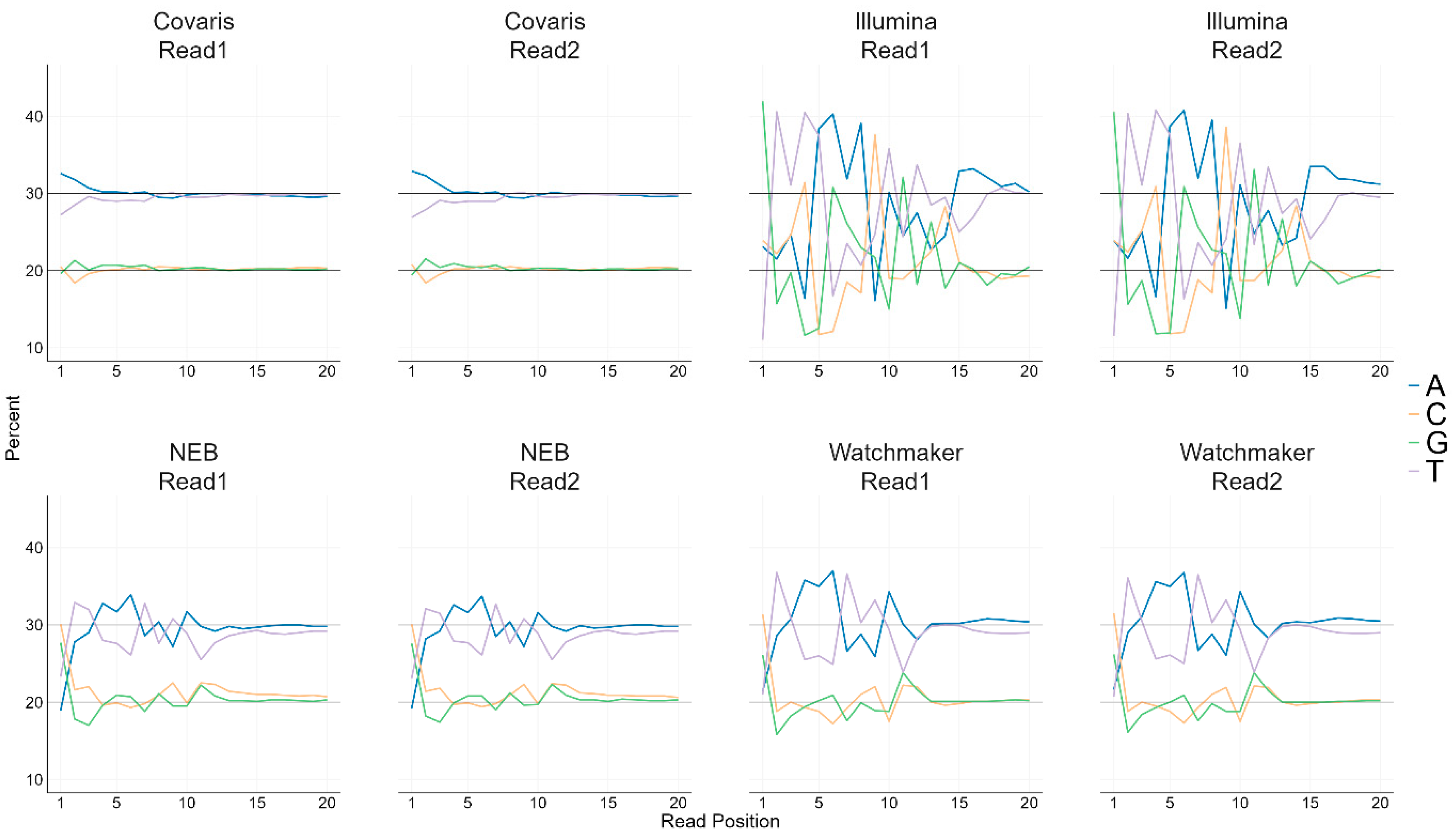
3.2. Base Bias in Sequencing Reads
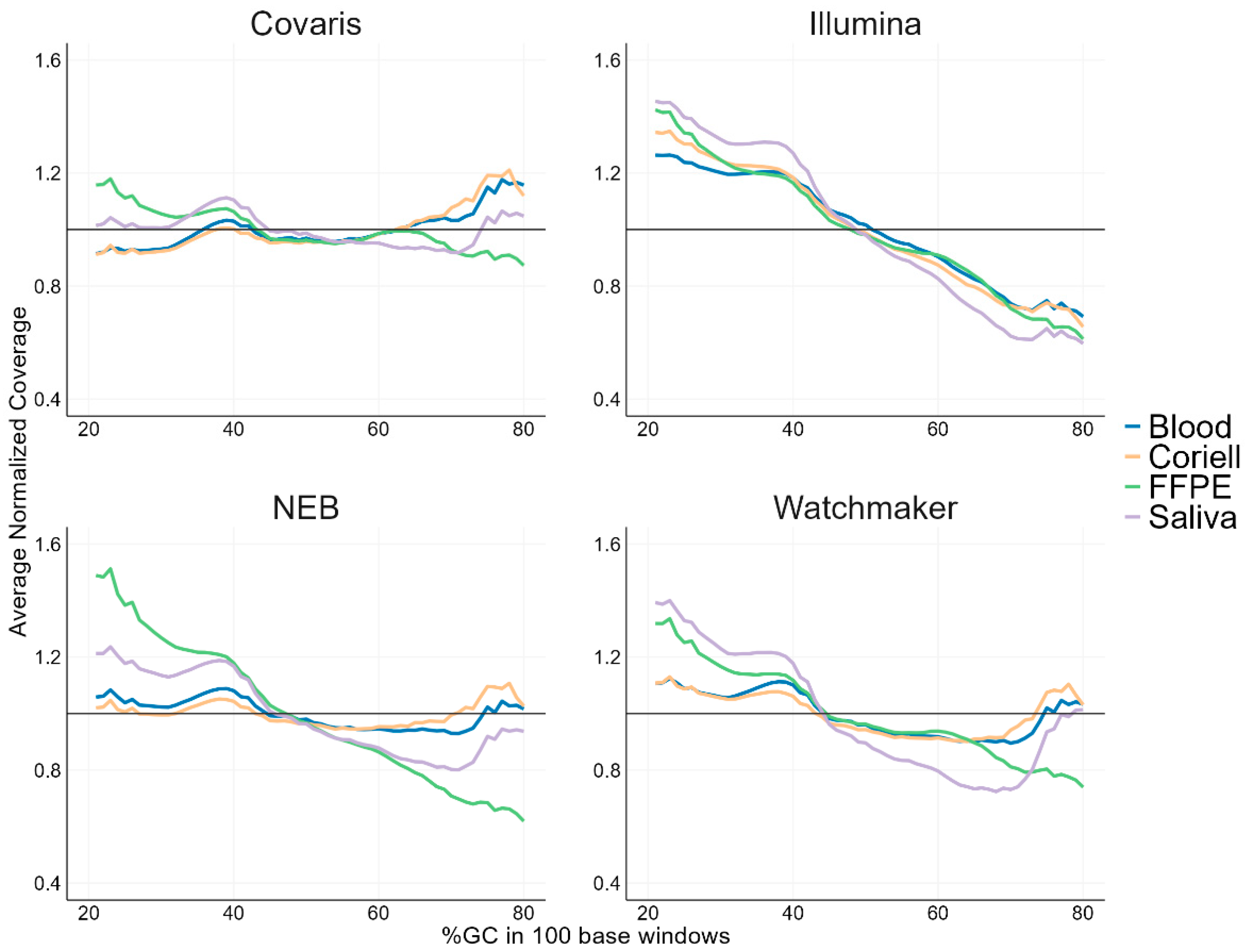
3.3. GC Bias Analysis
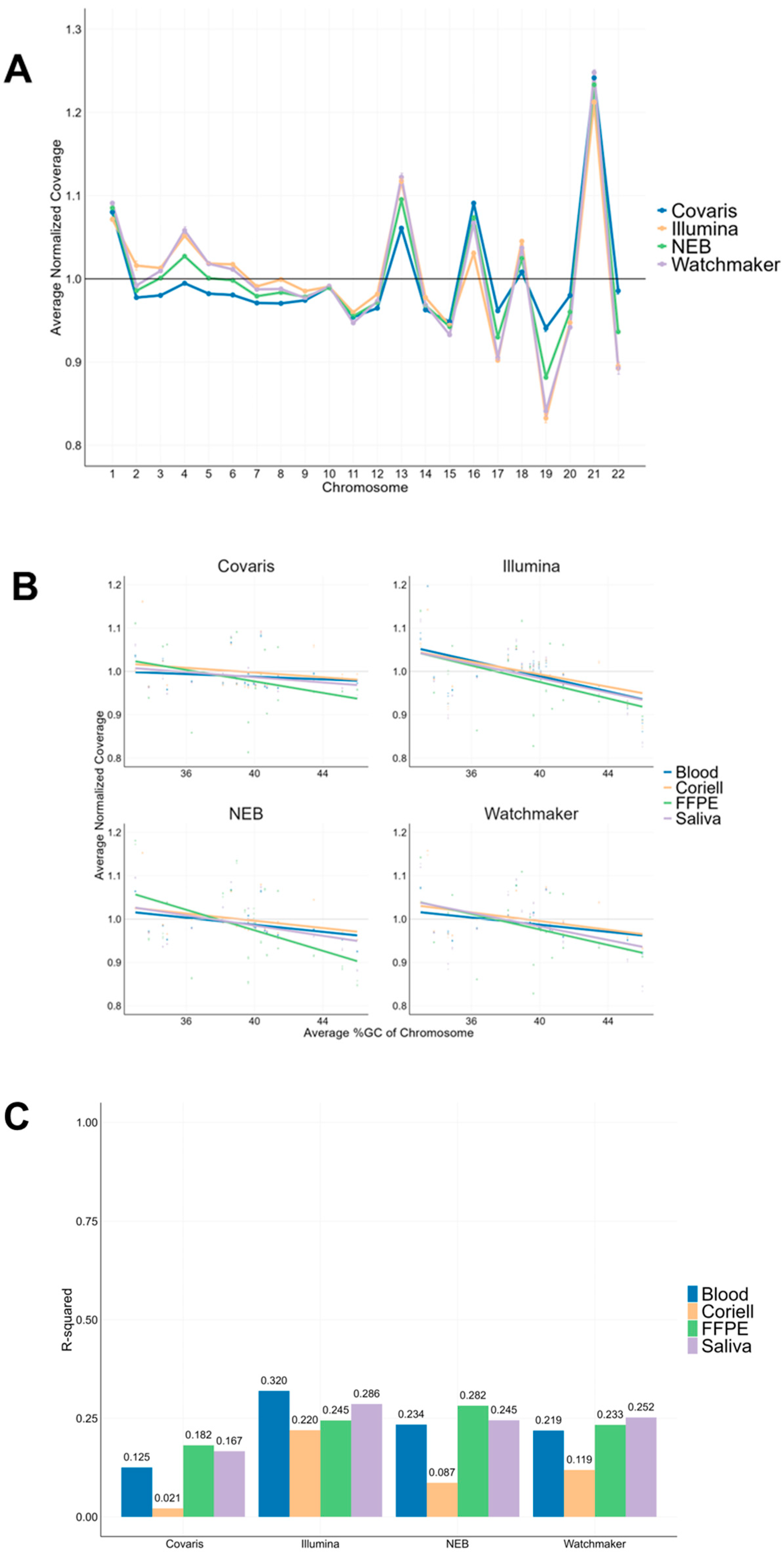
3.4. Chromosomal Coverage Uniformity Analysis
3.5. Uniformity Coverage Analysis of the TSO500 Regions
3.6. Variant Performance in TSO500 Regions
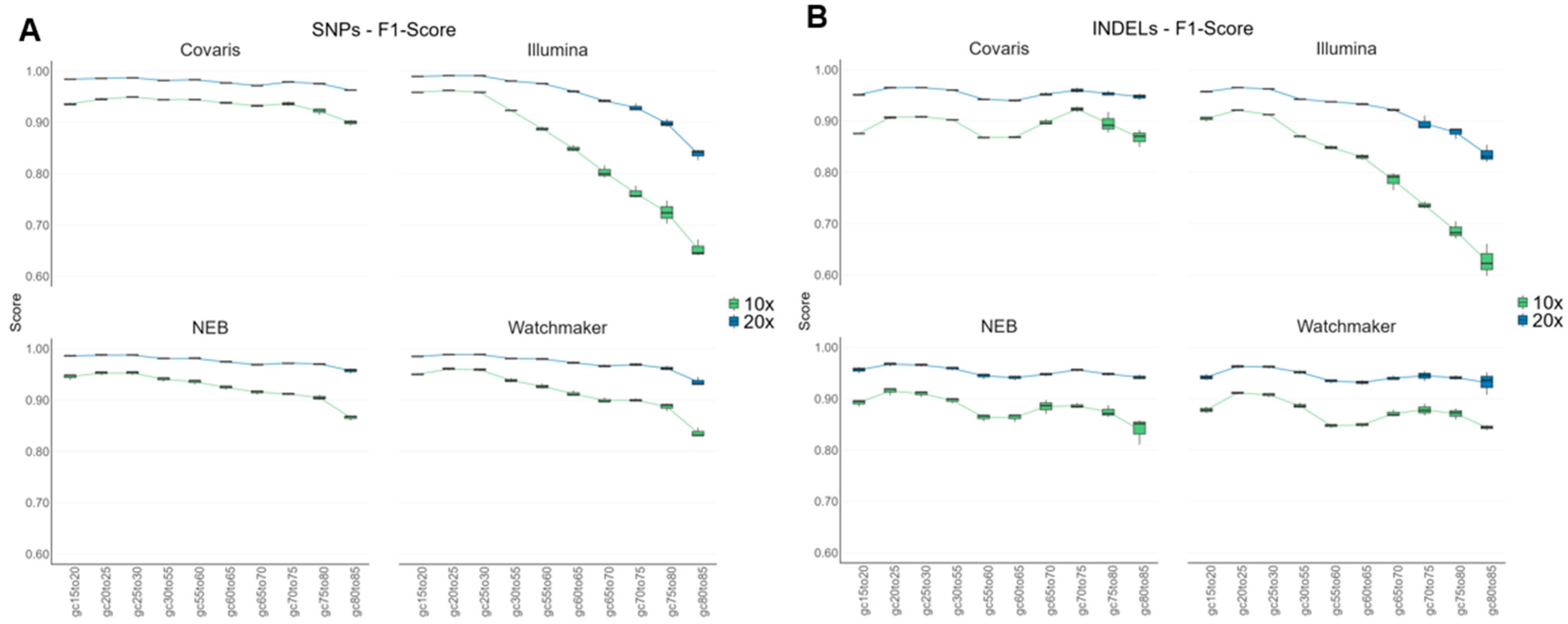
3.7. Variant Performance Across GC-Content Regions in the Human Genome
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brlek, P.; Bulić, L.; Bračić, M.; Projić, P.; Škaro, V.; Shah, N.; Shah, P.; Primorac, D. Implementing Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) in Clinical Practice: Advantages, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Cells 2024, 13, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satam, H.; Joshi, K.; Mangrolia, U.; Waghoo, S.; Zaidi, G.; Rawool, S.; Thakare, R.P.; Banday, S.; Mishra, A.K.; Das, G.; et al. Next-Generation Sequencing Technology: Current Trends and Advancements. Biology 2023, 12, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bick, D.; Ahmed, A.; Deen, D.; Ferlini, A.; Garnier, N.; Kasperaviciute, D.; Leblond, M.; Pichini, A.; Rendon, A.; Satija, A.; et al. Newborn Screening by Genomic Sequencing: Opportunities and Challenges. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2022, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisar, H.; Wajid, B.; Shahid, S.; Anwar, F.; Wajid, I.; Khatoon, A.; Sattar, M.U.; Sadaf, S. Whole-genome sequencing as a first-tier diagnostic framework for rare genetic diseases. Exp. Biol. Med. 2021, 246, 2610–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellingford, J.M.; Barton, S.; Bhaskar, S.; Williams, S.G.; Sergouniotis, P.I.; O’Sullivan, J.; Lamb, J.A.; Perveen, R.; Hall, G.; Newman, W.G.; et al. Whole Genome Sequencing Increases Molecular Diagnostic Yield Compared with Current Diagnostic Testing for Inherited Retinal Disease. Ophthalmology 2016, 123, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulding, R.; Dawes, D.; Price, M.; Wilkie, S.; Dawes, M. Genotype-guided drug prescribing: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized control trials. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 80, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qahwaji, R.; Ashankyty, I.; Sannan, N.S.; Hazzazi, M.S.; Basabrain, A.A.; Mobashir, M. Pharmacogenomics: A Genetic Approach to Drug Development and Therapy. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagger, F.O.; Borgwardt, L.; Jespersen, A.S.; Hansen, A.R.; Bertelsen, B.; Kodama, M.; Nielsen, F.C. Whole genome sequencing in clinical practice. BMC Med. Genom. 2024, 17, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenkovich, N.P.; Szymanski, J.J.; Earland, N.; Chauhan, P.S.; Pellini, B.; Chaudhuri, A.A. Genomic approaches to cancer and minimal residual disease detection using circulating tumor DNA. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e006284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, L.J.; Arcila, M.E.; Corless, C.; Kamel-Reid, S.; Lubin, I.M.; Pfeifer, J.; Temple-Smolkin, R.L.; Voelkerding, K.V.; Nikiforova, M.N. Guidelines for Validation of Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Oncology Panels: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the Association for Molecular Pathology and College of American Pathologists. J. Mol. Diagn. 2017, 19, 341–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Dobrinsky, J.; Tsoi, S.; Foxcroft, G.R.; Dixon, W.T.; Stothard, P.; Verstegen, J.; Dyck, M.K.; Nichols, J. Characterization of the altered gene expression profile in early porcine embryos generated from parthenogenesis and somatic cell chromatin transfer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shashikant, C.S.; Jensen, M.; Altman, N.S.; Girirajan, S. Novel metrics to measure coverage in whole exome sequencing datasets reveal local and global non-uniformity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggs, E.R.; Andersen, E.F.; Cherry, A.M.; Kantarci, S.; Kearney, H.; Patel, A.; Raca, G.; Ritter, D.I.; South, S.T.; Thorland, E.C. Technical standards for the interpretation and reporting of constitutional copy-number variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) and the Clinical Genome Resource (ClinGen). Genet. Med. 2021, 23, 2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, R.L.; Brand, H.; Karczewski, K.J.; Zhao, X.; Alföldi, J.; Francioli, L.C.; Khera, A.V.; Lowther, C. A structural variation reference for medical and population genetics. Nature 2021, 590, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holesova, Z.; Pös, O.; Gazdarica, J.; Kucharik, M.; Budis, J.; Hyblova, M.; Minarik, G.; Szemes, T. Understanding genetic variability: Exploring large-scale copy number variants through non-invasive prenatal testing in European populations. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudmant, P.H.; Rausch, T.; Gardner, E.J.; Handsaker, R.E.; Abyzov, A.; Huddleston, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, K.; Jun, G.; Fritz, M.H.-Y.; et al. An integrated map of structural variation in 2504 human genomes. Nature 2015, 526, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.W.; Asri, M.; Ebler, J.; Doerr, D.; Haukness, M.; Hickey, G.; Lu, S.; Lucas, J.K.; Monlong, J.; Abel, H.J.; et al. A draft human pangenome reference. Nature 2023, 617, 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adey, A.; Morrison, H.G.; Asan; Xun, X.; Kitzman, J.O.; Turner, E.H.; Stackhouse, B.; MacKenzie, A.P.; Caruccio, N.C.; Zhang, X.; et al. Rapid, low-input, low-bias construction of shotgun fragment libraries by high-density in vitro transposition. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribarska, T.; Bjornstad, P.M.; Sundaram, A.Y.M.; Gilfillan, G.D. Optimization of enzymatic fragmentation is crucial to maximize genome coverage: A comparison of library preparation methods for Illumina sequencing. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krusche, P.; Trigg, L.; Boutros, P.C.; Mason, C.E.; De La Vega, F.M.; Moore, B.L.; Gonzalez-Porta, M.; Eberle, M.A.; Tezak, Z.; Lababidi, S.; et al. Best practices for benchmarking germline small-variant calls in human genomes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.A.; Akinrinade, O.; Chaix, M.; Mital, S. Quality of whole genome sequencing from blood versus saliva derived DNA in cardiac patients. BMC Med. Genom. 2020, 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwarshuis, N.; Kalra, D.; McDaniel, J.; Sanio, P.; Alvarez Jerez, P.; Jadhav, B.; Huang, W.; Mondal, R.; Busby, B.; Olson, N.D.; et al. The GIAB genomic stratifications resource for human reference genomes. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sims, D.; Sudbery, I.; Ilott, N.E.; Heger, A.; Ponting, C.P. Sequencing depth and coverage: Key considerations in genomic analyses. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbitoff, Y.A.; Polev, D.E.; Glotov, A.S.; Serebryakova, E.A.; Shcherbakova, I.V.; Kiselev, A.M.; Kostareva, A.A.; Glotov, O.S.; Predeus, A.V. Systematic dissection of biases in whole-exome and whole-genome sequencing reveals major determinants of coding sequence coverage. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonarakis, S.E. Short arms of human acrocentric chromosomes and the completion of the human genome sequence. Genome Res. 2022, 32, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Library Prep Kit | Sample | Average Insert Size (bp) | Average of Reads (M) | Mapped Reads (%) | Average Coverage (X) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Covaris | Blood | 389 | 308.8 | 99.5 | 25.5 |
| Coriell | 389 | 339.6 | 99.5 | 28.3 | |
| FFPE | 348 | 301.9 | 99.5 | 19.7 | |
| Saliva | 378 | 335.9 | 71.0 | 24.9 | |
| Illumina | Blood | 376 | 372.9 | 99.1 | 30.6 |
| Coriell | 348 | 303.8 | 99.2 | 24.9 | |
| FFPE | 329 | 335.0 | 98.6 | 21.6 | |
| Saliva | 336 | 402.6 | 65.9 | 26.8 | |
| NEB | Blood | 407 | 313.7 | 99.3 | 25.9 |
| Coriell | 404 | 361.2 | 99.5 | 29.9 | |
| FFPE | 336 | 223.1 | 99.3 | 14.9 | |
| Saliva | 368 | 258.4 | 69.6 | 18.3 | |
| Watchmaker | Blood | 442 | 302.1 | 99.4 | 25.6 |
| Coriell | 429 | 295.6 | 99.5 | 25.3 | |
| FFPE | 408 | 280.6 | 99.4 | 14.6 | |
| Saliva | 380 | 264.8 | 66.4 | 23.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Process, V.; Ambavaram, M.M.R.; Vasantgadkar, S.; Khanal, S.; Werner, M.; Berkeley, M.A.; Herbert, Z.T.; Endress, G.; Thomann, U.; Daviso, E. Optimization of DNA Fragmentation Techniques to Maximize Coverage Uniformity of Clinically Relevant Genes Using Whole Genome Sequencing. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2294. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182294
Process V, Ambavaram MMR, Vasantgadkar S, Khanal S, Werner M, Berkeley MA, Herbert ZT, Endress G, Thomann U, Daviso E. Optimization of DNA Fragmentation Techniques to Maximize Coverage Uniformity of Clinically Relevant Genes Using Whole Genome Sequencing. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(18):2294. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182294
Chicago/Turabian StyleProcess, Vanessa, Madana M.R. Ambavaram, Sameer Vasantgadkar, Sushant Khanal, Martina Werner, Maura A. Berkeley, Zachary T. Herbert, Greg Endress, Ulrich Thomann, and Eugenio Daviso. 2025. "Optimization of DNA Fragmentation Techniques to Maximize Coverage Uniformity of Clinically Relevant Genes Using Whole Genome Sequencing" Diagnostics 15, no. 18: 2294. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182294
APA StyleProcess, V., Ambavaram, M. M. R., Vasantgadkar, S., Khanal, S., Werner, M., Berkeley, M. A., Herbert, Z. T., Endress, G., Thomann, U., & Daviso, E. (2025). Optimization of DNA Fragmentation Techniques to Maximize Coverage Uniformity of Clinically Relevant Genes Using Whole Genome Sequencing. Diagnostics, 15(18), 2294. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15182294







