Diagnostic Criteria and Technical Evaluation of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Comprehensive Approaches to the Diagnosis of CRPS
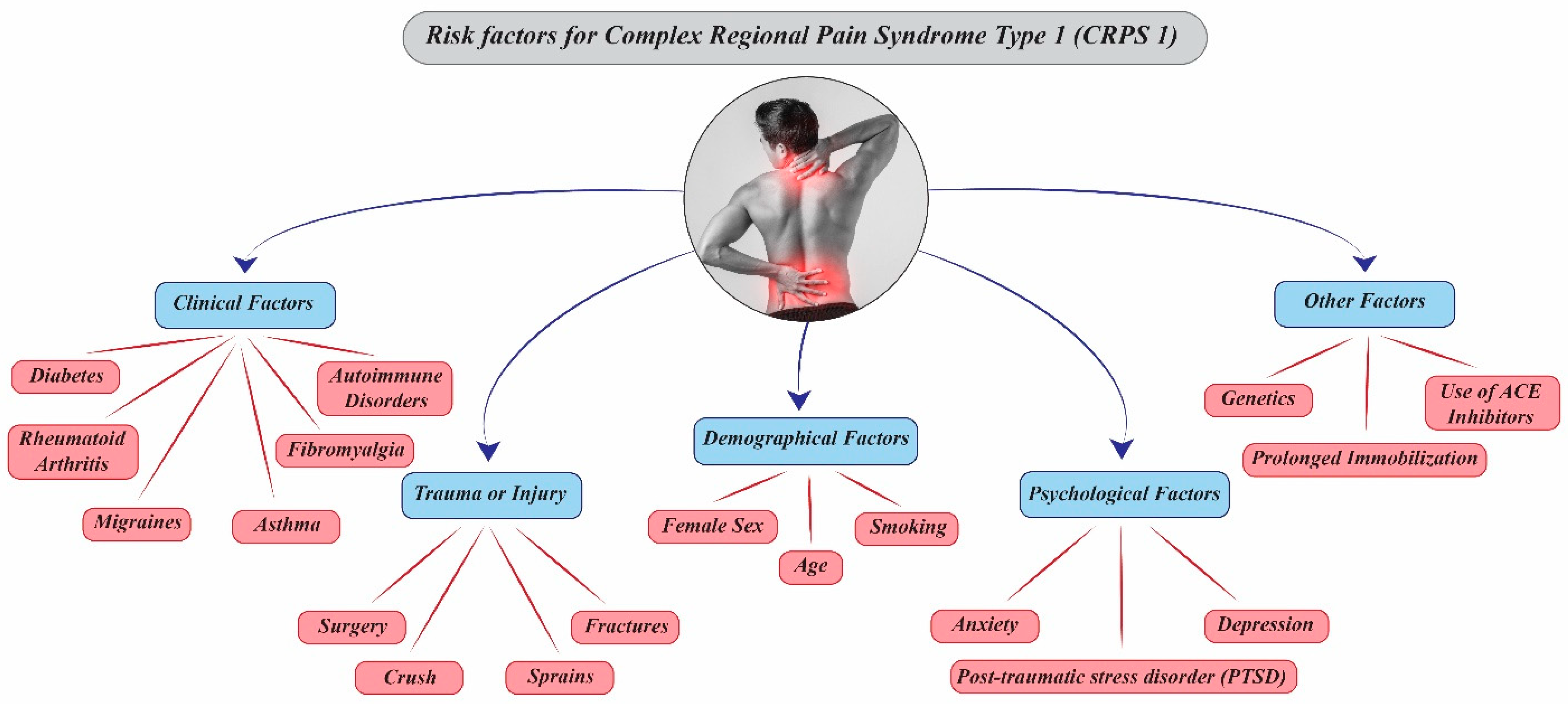
3.1. Potential Risk Factors for the Development of CRPS Type 1
3.1.1. Demographic Factors
3.1.2. Clinical and Traumatic Triggers
3.1.3. Psychological and Psychosocial Factors
3.2. Classification of Diagnostic Methods for CRPS
3.2.1. Patient-Reported Outcome Measures (PROMs)
3.2.2. Clinician-Reported Measures
3.2.3. Clinical Measures (Instrumental Tests)
- Motor Function: Grip strength (dynamometer), range of motion (goniometer), finger-to-palm distance (tape), wrist movement (wearables). Autonomic Abnormalities: Skin temperature, swelling/edema, limb photography, bone scintigraphy, sleep tracking, heart rate variability, and specialized nerve function tests [9].
- Cognitive Function: Computer-based cognitive tests [9].
- Sensory Function: Quantitative sensory tests including von Frey filaments, pinpricks, pressure pain thresholds, electrical thresholds, and dynamic allodynia [9].
- Electrophysiology: EEG and electroneurography (ENG) [9].
- Impairment Level Sum Score (ISS): Composite of pain, temperature, limb volume, and range of motion to quantify functional impairment [9].
- Advanced Assessments: These include skin biopsy, bone metabolism markers, cytokine profiling, microRNA analysis, and oxidative stress assays [9]. No single test confirms CRPS; therefore, combining PROMs, clinician-reported measures, and instrumental tests with standardized criteria provides the most accurate and comprehensive diagnostic evaluation [1,9].
3.3. Diagnostic Approach to Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS)
3.3.1. Clinical Assessment
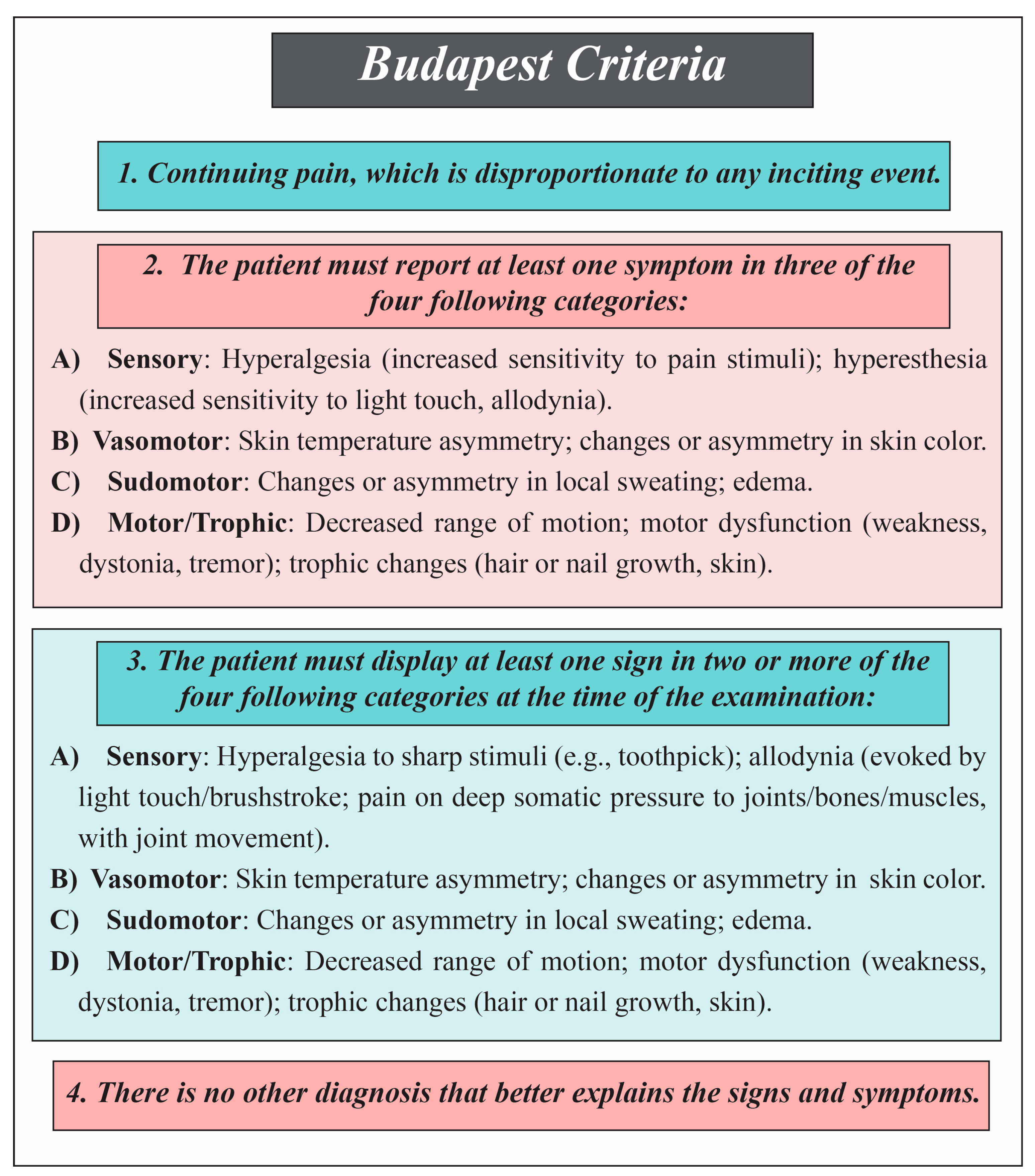
Diagnostic Criteria for Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS)
- (1)
- Budapest Criteria
- (2)
- Budapest Research Criteria
- (3)
- Veldman Criteria
- Unexplained diffuse pain;
- Skin color difference compared to the contralateral limb;
- Diffuse edema;
- Skin temperature difference relative to the opposite limb;
- Limited active range of motion.
- (4)
- IASP Criteria
- (5)
- CRPS Severity Score (CSS) in Disease Monitoring
- (6)
- Atkins Criteria
- Assess the pain. Determine if the pain appears to be burning, neuropathic, or non-dermatomal. Identify signs of abnormal sensitivity, such as allodynia (pain from non-painful stimuli) and hyperpathia (exaggerated pain response).
- Check vasomotor and sweating patterns. Compare limb temperatures and identify abnormal sweating that signals vasomotor instability.
- Observe swelling. Note any swelling in the affected limb as a key sign.
- Evaluate joint mobility and soft tissue condition. Identify reduced joint movement, soft-tissue contractures, and trophic signs such as skin thinning, hair loss, or nail changes.
- Exclude other diagnoses. Confirm that no other disorder accounts for the symptoms and functional impairment.
Clinical and Laboratory Assessment
3.3.2. Functional and Paraclinical Approach
Electrophysiological Studies
Sensory and Autonomic Testing
- Warm CRPS: early, often resolves within six months.
- Cold CRPS: chronic, associated with long-term disease.
Quantitative and Non-Invasive Techniques
- (1)
- Laser Doppler Imaging (LDI)
- (2)
- Electrochemical Skin Conductance (ESC)
- (3)
- Quantitative Sensory Testing (QST)
- (4)
- Temperature Assessment Using Thermography and Infrared Techniques
3.3.3. Imaging Evaluations
Skeletal Muscle Imaging
- (1)
- Skeletal Muscle MRI
- (2)
- High-Resolution Peripheral Quantitative Computed Tomography (HR-pQCT)
- (3)
- Three-Phase Bone Scintigraphy (TPBS)
- (4)
- Fascia-Related Imaging Advances
Neuroimaging Techniques
- (1)
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Functional MRI (FMRI)
- (2)
- Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI)
- (3)
- Positron Emission Tomography–Computed Tomography (PET-CT)
- (4)
- Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS)
3.3.4. Sympathetic Nerve Block
3.3.5. Biomarkers in the Diagnosis of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS)
Systemic Inflammatory Markers
Autoantibodies and Immune-Related Markers
Local and Skin Biomarkers
Other Diagnostic Biomarkers
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) as Diagnostic Biomarker in CRPS
3.4. Delayed Diagnosis in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS)
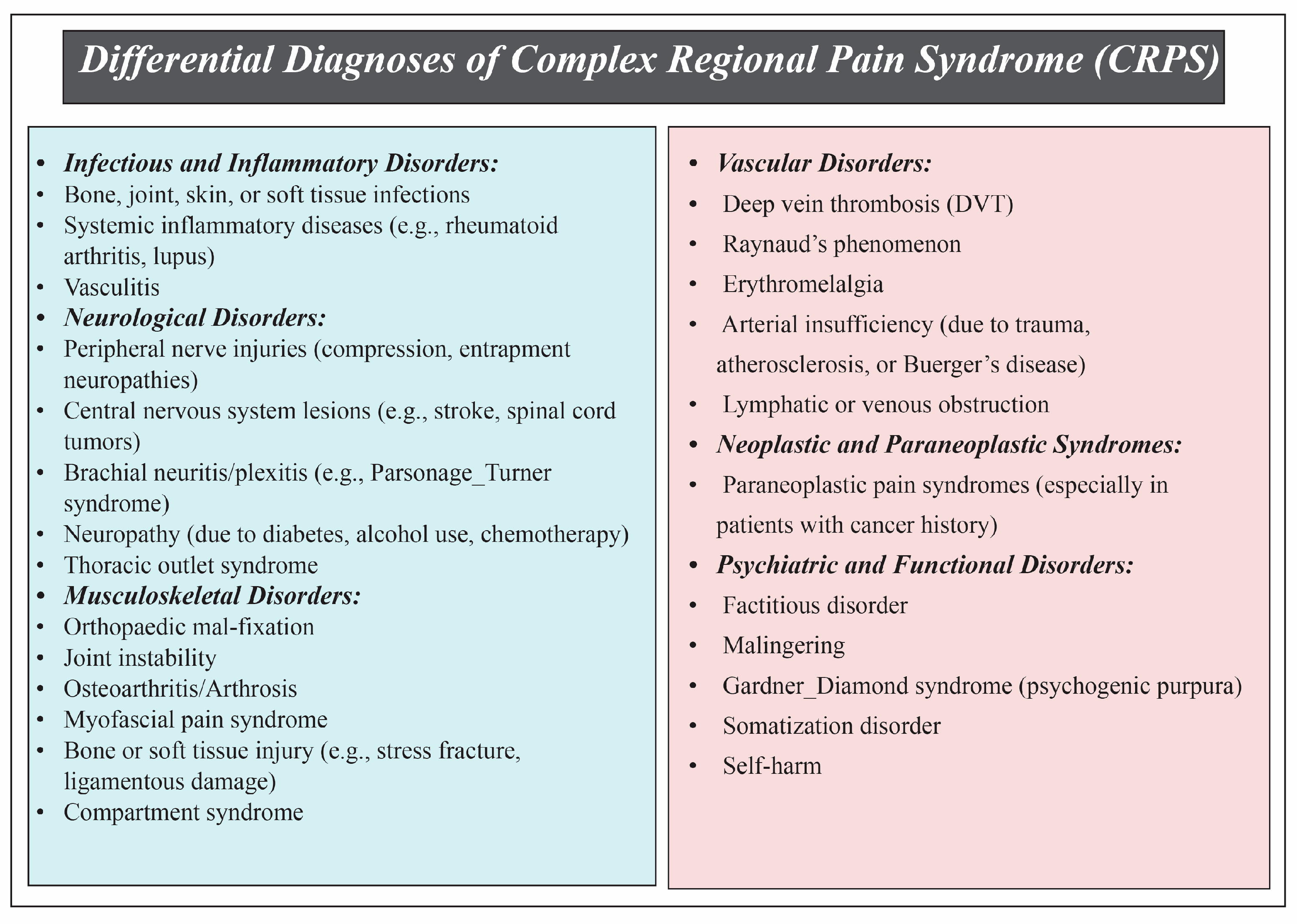
3.5. Differential Diagnoses
3.6. Challenges in the Diagnosis of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS)
3.7. Complex Regional Pain Syndrome in Children
3.8. Future Directions in the Diagnosis and Management of CRPS
3.8.1. Standardization and Validation of Diagnostic Criteria
3.8.2. Biomarkers
3.8.3. Genetic and Autoimmune Contributions
3.8.4. Advanced Imaging and Fascial Studies
4. Discussion
Limitations of Current Diagnostic Standards for Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
- Redefinition of CRPS Type 2: The updated criteria require signs extending beyond the injured nerve territory, providing a more precise definition of CRPS Type 2.
- Introduction of CRPS Not Otherwise Specified (NOS): A new category for patients who meet previous criteria but do not conform to the updated definitions, allowing better classification of atypical cases.
- Greater Flexibility in Symptom Requirements: The new guidelines allow for more flexibility in the number of symptoms necessary for diagnosis, accommodating clinical variability.
- Emphasis on Subgroup Identification: Recognition of subtypes such as warm versus cold CRPS is highlighted, which is essential for targeted treatment planning.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harden, N.R.; Bruehl, S.; Perez, R.; Birklein, F.; Marinus, J.; Maihofner, C.; Lubenow, T.; Buvanendran, A.; Mackey, S.; Graciosa, J.; et al. Validation of proposed diagnostic criteria (the “Budapest Criteria”) for Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. J. Pain 2010, 150, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryskalin, L.; Ghelarducci, G.; Marinelli, C.; Morucci, G.; Soldani, P.; Bertozzi, N.; Annoscia, P.; Poggetti, A.; Gesi, M. Effectiveness of decision support to treat complex regional pain syndrome. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebel, A.; Birklein, F.; Brunner, F.; Clark, J.D.; Gierthmühlen, J.; Harden, N.; Huygen, F.; Knudsen, L.; McCabe, C.; Lewis, J.; et al. The Valencia consensus-based adaptation of the IASP complex regional pain syndrome diagnostic criteria. Pain 2021, 162, 2346–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.E.; Moon, J.Y.; Shin, J.Y.; Kim, Y.C. Analysis of quantitative sudomotor axon reflex test patterns in patients with complex regional pain syndrome diagnosed using the Budapest criteria. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2019. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorodkin, R.; Herrick, A.L.; Murray, A.K. Microvascular Response in Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome as Measured by Laser Doppler Imaging. Microcirculation 2016, 23, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birklein, F.; Riedl, B.; Claus, D.; Neundörfer, B. Pattern of autonomic dysfunction in time course of complex regional pain syndrome. Clin. Auton. Res. 1998, 8, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnik, M.A.; Kesselring, P.; Ott, A.; Urman, R.D.; Luedi, M.M. Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) and the Value of Early Detection. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2023, 27, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesaroli, G.; Hundert, A.; Birnie, K.A.; Campbell, F.; Stinson, J. Screening and diagnostic tools for complex regional pain syndrome: A systematic review. Pain 2021, 162, 1295–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalewski, A.; Andreieva, I.; Wiśniowska, J.; Tarnacka, B.; Gromadzka, G. Clinical and Molecular Barriers to Understanding the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pons, T.; Shipton, E.A.; Williman, J.; Mulder, R.T. Potential risk factors for the onset of complex regional pain syndrome type 1: A systematic literature review. Anesthesiol. Res. Pract. 2015, 2015, 956539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchalski, P.; Zyluk, A. Complex regional pain syndrome type 1 after fractures of the distal radius: A prospective study of the role of psychological factors. J. Hand Surg. Br. 2005, 30, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, P.U.; Groothoff, J.W.; ten Duis, H.J.; Geertzen, J.H. Incidence of complex regional pain syndrome type I after fractures of the distal radius. Eur. J. Pain. 2003, 7, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Mos, M.; de Bruijn, A.G.; Huygen, F.J.; Dieleman, J.P.; Stricker, B.H.; Sturkenboom, M.C. The incidence of complex regional pain syndrome: A population-based study. J. Pain 2007, 129, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duman, I.; Dincer, U.; Taskaynatan, M.A.; Cakar, E.; Tugcu, I.; Dincer, K. Reflex sympathetic dystrophy: A retrospective epidemiological study of 168 patients. Clin. Rheumatol. 2007, 26, 1433–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, G.; Galer, B.S.; Schwartz, L. Epidemiology of complex regional pain syndrome: A retrospective chart review of 134 patients. Pain 1999, 80, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.J.; Fallat, L.M. Complex regional pain syndrome of the lower extremity: A retrospective study of 33 patients. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 1999, 38, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moseley, G.L.; Herbert, R.D.; Parsons, T.; Lucas, S.; Van Hilten, J.J.; Marinus, J. Intense pain soon after wrist fracture strongly predicts who will develop complex regional pain syndrome: Prospective cohort study. J. Pain 2014, 15, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rijn, M.A.; Marinus, J.; Putter, H.; van Hilten, J.J. Onset and progression of dystonia in complex regional pain syndrome. J. Pain 2007, 130, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandroni, P.; Benrud-Larson, L.M.; McClelland, R.L.; Low, P.A. Complex regional pain syndrome type I: Incidence and prevalence in Olmsted county, a population-based study. Pain 2003, 103, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beerthuizen, A.; Stronks, D.L.; Van’t Spijker, A.; Yaksh, A.; Hanraets, B.M.; Klein, J.; Huygen, F. Demographic and medical parameters in the development of complex regional pain syndrome type 1 (CRPS1): Prospective study on 596 patients with a fracture. J. Pain 2012, 153, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellad, A.; Salah, S.; Ben Salah Frih, Z. Complex regional pain syndrome type I: Incidence and risk factors in patients with fracture of the distal radius. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 95, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savaş, S.; İnal, E.E.; Yavuz, D.D.; Uslusoy, F.; Altuntaş, S.H.; Aydın, M.A. Risk factors for complex regional pain syndrome in patients with surgically treated traumatic injuries attending hand therapy. J. Hand Ther. 2018, 31, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monti, D.A.; Herring, C.L.; Schwartzman, R.J.; Marchese, M. Personality assessment of patients with complex regional pain syndrome type I. Clin. J. Pain 1998, 14, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feliu, M.H.; Edwards, C.L. Psychologic factors in the development of complex regional pain syndrome: History, myth, and evidence. Clin. J. Pain 2010, 26, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollack, H.J.; Neumann, R.; Pollack, E. [Sudeck’s disease and the psyche]. Beitr. Orthop. Traumatol. 1980, 27, 463–468. [Google Scholar]
- van der Windt, D.A.; Kuijpers, T.; Jellema, P.; van der Heijden, G.J.; Bouter, L.M. Do psychological factors predict outcome in both low-back pain and shoulder pain? Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2007, 66, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanton-Hicks, M.; Jänig, W.; Hassenbusch, S.; Haddox, J.D.; Boas, R.; Wilson, P. Reflex sympathetic dystrophy: Changing concepts and taxonomy. Pain 1995, 63, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harden, R.N.; Bruehl, S.; Stanton-Hicks, M.; Wilson, P.R. Proposed new diagnostic criteria for complex regional pain syndrome. Pain. Med. 2007, 8, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harden, R.N.; Bruehl, S.; Galer, B.S.; Saltz, S.; Bertram, M.; Backonja, M.; Gayles, R.; Rudin, N.; Bhugra, M.K.; Stanton-Hicks, M. Complex regional pain syndrome: Are the IASP diagnostic criteria valid and sufficiently comprehensive? Pain 1999, 83, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, P.; Low, P.; Bedder, M.; Covington, E.; Rauck, R. Diagnostic algorithm for complex regional pain syndromes. Progress Pain Res. Manag. 1996, 6, 93–105. [Google Scholar]
- Galer, B.S.; Butler, S.; Jensen, M.P. Case reports and hypothesis: A neglect-like syndrome may be responsible for the motor disturbance in reflex sympathetic dystrophy (Complex Regional Pain Syndrome-1). J. Pain Symptom Manag. 1995, 10, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartzman, R.J.; Kerrigan, J. The movement disorder of reflex sympathetic dystrophy. Neurology 1990, 40, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozin, F.; Ryan, L.M.; Carerra, G.F.; Soin, J.S.; Wortmann, R.L. The reflex sympathetic dystrophy syndrome (RSDS). III. Scintigraphic studies, further evidence for the therapeutic efficacy of systemic corticosteroids, and proposed diagnostic criteria. Am. J. Med. 1981, 70, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbons, J.J.; Wilson, P.R. RSD score: Criteria for the diagnosis of reflex sympathetic dystrophy and causalgia. Clin. J. Pain 1992, 8, 260–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruehl, S.; Harden, R.N.; Galer, B.S.; Saltz, S.; Bertram, M.; Backonja, M.; Gayles, R.; Rudin, N.; Bhugra, M.K.; Stanton-Hicks, M. External validation of IASP diagnostic criteria for Complex Regional Pain Syndrome and proposed research diagnostic criteria. International Association for the Study of Pain. Pain 1999, 81, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.A. Reflex sympathetic dystrophy. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 1946, 26, 780–790. [Google Scholar]
- Yim, K.H.; Park, S.Y.; Yim, J.Y.; Kim, Y.C.; Lee, S.C.; Nahm, F.S. Proposing a scoring system for the research criteria of complex regional pain syndrome. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2011, 26, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumitani, M.; Shibata, M.; Sakaue, G.; Mashimo, T. Development of comprehensive diagnostic criteria for complex regional pain syndrome in the Japanese population. J. Pain 2010, 150, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, S.; Maihöfner, C. Signs and Symptoms in 1,043 Patients with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. J. Pain 2018, 19, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harden, N.R.; Bruehl, S.; Perez, R.; Birklein, F.; Marinus, J.; Maihofner, C.; Lubenow, T.; Buvanendran, A.; Mackey, S.; Graciosa, J.; et al. Development of a severity score for CRPS. J. Pain 2010, 151, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumova, E.K.; Frettlöh, J.; Klauenberg, S.; Richter, H.; Wasner, G.; Maier, C. Long-term skin temperature measurements—A practical diagnostic tool in complex regional pain syndrome. J. Pain 2008, 140, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldman, P.H.; Reynen, H.M.; Arntz, I.E.; Goris, R.J. Signs and symptoms of reflex sympathetic dystrophy: Prospective study of 829 patients. Lancet 1993, 342, 1012–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, R.S.; Burm, P.E.; Zuurmond, W.W.; Bezemer, P.D.; Brink, H.E.; de Lange, J.J. Physicians’ assessments versus measured symptoms of complex regional pain syndrome type 1: Presence and severity. Clin. J. Pain 2005, 21, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oerlemans, H.M.; Oostendorp, R.A.; de Boo, T.; Perez, R.S.; Goris, R.J. Signs and symptoms in complex regional pain syndrome type I/reflex sympathetic dystrophy: Judgment of the physician versus objective measurement. Clin. J. Pain 1999, 15, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, R.S.; Burm, P.E.; Zuurmond, W.W.; Giezeman, M.J.; van Dasselaar, N.T.; Vranken, J.; de Lange, J.J. Interrater reliability of diagnosing complex regional pain syndrome type I. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2002, 46, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, R.S.; Collins, S.; Marinus, J.; Zuurmond, W.W.; de Lange, J.J. Diagnostic criteria for CRPS I: Differences between patient profiles using three different diagnostic sets. Eur. J. Pain 2007, 11, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.W.; Choi, S.U.; Park, M.; Shin, J.H. Validity of the Budapest Criteria For Poststroke Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Clin. J. Pain 2019, 35, 831–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galer, B.S.; Bruehl, S.; Harden, R.N. IASP diagnostic criteria for complex regional pain syndrome: A preliminary empirical validation study. International Association for the Study of Pain. Clin. J. Pain 1998, 14, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Vusse, A.C.; Stomp-van den Berg, S.G.; de Vet, H.C.; Weber, W.E. Interobserver reliability of diagnosis in patients with complex regional pain syndrome. Eur. J. Pain 2003, 7, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harden, R.N.; Maihofner, C.; Abousaad, E.; Vatine, J.J.; Kirsling, A.; Perez, R.; Kuroda, M.; Brunner, F.; Stanton-Hicks, M.; Marinus, J.; et al. A prospective, multisite, international validation of the Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Severity Score. Pain 2017, 158, 1430–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebel, A.; Turner-Stokes, L.F. Complex Regional Pain Syndrome in Adults: UK Guidelines for Diagnosis, Referral and Management in Primary and Secondary Care; The Royal College of Physicians: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Reinders, M.F.; Geertzen, J.H.; Dijkstra, P.U. Complex regional pain syndrome type I: Use of the International Association for the Study of Pain diagnostic criteria defined in 1994. Clin. J. Pain 2002, 18, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melf-Marzi, A.; Böhringer, B.; Wiehle, M.; Hausteiner-Wiehle, C. Modern Principles of Diagnosis and Treatment in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2022, 119, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birklein, F.; Sittl, R.; Spitzer, A.; Claus, D.; Neundörfer, B.; Handwerker, H.O. Sudomotor function in sympathetic reflex dystrophy. Pain 1997, 69, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benzon, H.; Raja, S.N.; Fishman, S.E.; Liu, S.S.; Cohen, S.P. Essentials of Pain Medicine E-Book; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lubkowska, A.; Pluta, W. Infrared thermography as a non-invasive tool in musculoskeletal disease rehabilitation—The control variables in applicability—A systematic review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Guzmán, S.; Nava-Obregón, T.A.; Palacios-Ríos, D.; Estrada-Cortinas, J.Á.; González-García, M.; Mendez-Guerra, J.F.; González-Santiago, O. Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS), a review. Med. Univ. 2015, 17, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, L.F.; Terkelsen, A.J.; Drummond, P.D.; Birklein, F. Complex regional pain syndrome: A focus on the autonomic nervous system. Clin. Auton. Res. 2019, 29, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David Clark, J.; Tawfik, V.L.; Tajerian, M.; Kingery, W.S. Autoinflammatory and autoimmune contributions to complex regional pain syndrome. Mol. Pain 2018, 14, 1744806918799127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruehl, S.; Maihöfner, C.; Stanton-Hicks, M.; Perez, R.S.; Vatine, J.J.; Brunner, F.; Birklein, F.; Schlereth, T.; Mackey, S.; Mailis-Gagnon, A.; et al. Complex regional pain syndrome: Evidence for warm and cold subtypes in a large prospective clinical sample. Pain 2016, 157, 1674–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorodkin, R.; Moore, T.; Herrick, A. Assessment of endothelial function in complex regional pain syndrome type I using iontophoresis and laser Doppler imaging. Rheumatology 2004, 43, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Littlejohn, G. Neurogenic neuroinflammation in fibromyalgia and complex regional pain syndrome. Nat. Rev. Rheumatology 2015, 11, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, A.K.; Gorodkin, R.E.; Moore, T.L.; Gush, R.J.; Herrick, A.L.; King, T.A. Comparison of red and green laser doppler imaging of blood flow. Lasers Surg. Med. 2004, 35, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heerschap, A.; den Hollander, J.A.; Reynen, H.; Goris, R.J. Metabolic changes in reflex sympathetic dystrophy: A 31P NMR spectroscopy study. Muscle Nerve 1993, 16, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhatt, S.; Krauss, E.M.; Winston, P. The Role of FLIR ONE Thermography in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Case Series. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2021, 100, e48–e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelimsky, T.C.; Low, P.A.; Naessens, J.M.; Wilson, P.R.; Amadio, P.C.; O’Brien, P.C. Value of autonomic testing in reflex sympathetic dystrophy. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1995, 70, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, V.A.; Sandroni, P.; Fealey, R.D.; Low, P.A. Detection of small-fiber neuropathy by sudomotor testing. Muscle Nerve 2006, 34, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandroni, P.; Low, P.A.; Ferrer, T.; Opfer-Gehrking, T.L.; Willner, C.L.; Wilson, P.R. Complex regional pain syndrome I (CRPS I): Prospective study and laboratory evaluation. Clin. J. Pain 1998, 14, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvarajah, D.; Cash, T.; Davies, J.; Sankar, A.; Rao, G.; Grieg, M.; Pallai, S.; Gandhi, R.; Wilkinson, I.D.; Tesfaye, S. SUDOSCAN: A Simple, Rapid, and Objective Method with Potential for Screening for Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, J.; Miranda, B.; Castro, I.; de Carvalho, M.; Conceição, I. The diagnostic accuracy of Sudoscan in transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 127, 2222–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harden, R.N.; Oaklander, A.L.; Burton, A.W.; Perez, R.S.; Richardson, K.; Swan, M.; Barthel, J.; Costa, B.; Graciosa, J.R.; Bruehl, S. Complex regional pain syndrome: Practical diagnostic and treatment guidelines, 4th edition. Pain Med. 2013, 14, 180–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oaklander, A.L.; Horowitz, S.H. The complex regional pain syndrome. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2015, 131, 481–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, I.; Dauphin, M.; Naumann, M.; Flachenecker, P.; Müllges, W.; Koltzenburg, M.; Sommer, C. Selective degeneration of sudomotor fibers in Ross syndrome and successful treatment of compensatory hyperhidrosis with botulinum toxin. Muscle Nerve 1998, 21, 1790–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oaklander, A.L.; Rissmiller, J.G.; Gelman, L.B.; Zheng, L.; Chang, Y.; Gott, R. Evidence of focal small-fiber axonal degeneration in complex regional pain syndrome-I (reflex sympathetic dystrophy). J. Pain 2006, 120, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bussa, M.; Guttilla, D.; Lucia, M.; Mascaro, A.; Rinaldi, S. Complex regional pain syndrome type I: A comprehensive review. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2015, 59, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niehof, S.P.; Huygen, F.J.; Van der Weerd, R.W.; Westra, M.; Zijlstra, F.J. Thermography imaging during static and controlled thermoregulation in complex regional pain syndrome type 1: Diagnostic value and involvement of the central sympathetic system. Biomed. Eng. Online 2006, 5, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.W.; Nahm, F.S.; Choi, E.; Lee, P.-B.; Jang, I.-K.; Lee, C.J.; Kim, Y.C.; Lee, S.C. Multicenter study on the asymmetry of skin temperature in complex regional pain syndrome: An examination of temperature distribution and symptom duration. Medicine 2016, 95, e5548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammer, K.; Ring, F. The Thermal Human Body: A Practical Guide to Thermal Imaging; Jenny Stanford Publishing: Singapore, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cañada-Soriano, M.; Priego-Quesada, J.I.; Bovaira, M.; Garcia-Vitoria, C.; Salvador Palmer, R.; Cibrian Ortiz de Anda, R.; Moratal, D. Quantitative analysis of real-time infrared thermography for the assessment of lumbar sympathetic blocks: A preliminary study. Sensors 2021, 21, 3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringer, R.; Wertli, M.; Bachmann, L.M.; Buck, F.M.; Brunner, F. Concordance of qualitative bone scintigraphy results with presence of clinical complex regional pain syndrome 1: Meta-analysis of test accuracy studies. Eur. J. Pain 2012, 16, 1347–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, Y.; Saito, Y.; Yokota, T.; Kanda, T.; Mizusawa, H. Skeletal muscle MRI in complex regional pain syndrome. Intern. Med. 2009, 48, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussawy, H.; Schmidt, T.; Rolvien, T.; Rüther, W.; Amling, M. Evaluation of bone microstructure in CRPS-affected upper limbs by HR-pQCT. Clin. Cases Miner. Bone Metab. 2017, 14, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, M.; Kang, H.J.; Do, K.H.; Yang, H.S.; Han, E.J.; Yoo, J. Diagnostic performance of three-phase bone scintigraphy and digital infrared thermography imaging for chronic post-traumatic complex regional pain syndrome. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, S.J.; Chinthagada, M.; Hoppenstehdt, D.; Kijowski, R.; Fareed, J. Role of neuropeptides in pathogenesis of reflex sympathetic dystrophy. Acta Orthop. Belg. 1998, 64, 448–451. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goldsmith, D.P.; Vivino, F.B.; Eichenfield, A.H.; Athreya, B.H.; Heyman, S. Nuclear imaging and clinical features of childhood reflex neurovascular dystrophy: Comparison with adults. Arthritis Rheum. 1989, 32, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner-Stokes, L.; Goebel, A. Complex regional pain syndrome in adults: Concise guidance. Clin. Med. 2011, 11, 596–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.H.; Kim, S.J. Bone scintigraphy in patients with pain. Korean J. Pain 2017, 30, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wertli, M.M.; Brunner, F.; Steurer, J.; Held, U. Usefulness of bone scintigraphy for the diagnosis of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome 1: A systematic review and Bayesian meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forero, M.; Kamel, R.A.; Chan, P.L.; Maida, E. Two years follow-up of continuous erector spinae plane block in a patient with upper extremity complex regional pain syndrome type I. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2022, 47, 434–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirri, C.; Stecco, A.; Stecco, C.; Özçakar, L. Ultrasound imaging and Fascial Manipulation® for rigid retinacula in two cases of complex regional pain syndrome. Med. Ultrason. 2022, 24, 372–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schranz, K.; Meitz, D.; Powers, B.; Ables, A. Treating Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Using Counterstrain: A Novel Approach. Cureus 2020, 12, e10948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkli, B.; Ansoanuur, G.; Hernandez, N. Case Report: Treatment of Refractory Post-Surgical Neuralgia With Erector Spinae Plane Block. Pain Pract. 2020, 20, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, S.; Choi, J.; Kim, E.D. A high thoracic erector spinae plane block used for sympathetic block in patients with upper extremity complex regional pain syndrome. J. Clin. Anesth. 2020, 60, 99–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sintzoff, S.; Sintzoff, S., Jr.; Stallenberg, B.; Matos, C. Imaging in reflex sympathetic dystrophy. Hand Clin. 1997, 13, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruehl, S.; Harden, R.N.; Galer, B.S.; Saltz, S.; Backonja, M.; Stanton-Hicks, M. Complex regional pain syndrome: Are there distinct subtypes and sequential stages of the syndrome? Pain 2002, 95, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotta, J.; Saari, J.; Koskinen, M.; Hlushchuk, Y.; Forss, N.; Hari, R. Abnormal brain responses to action observation in complex regional pain syndrome. J. Pain 2017, 18, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geha, P.Y.; Baliki, M.N.; Harden, R.N.; Bauer, W.R.; Parrish, T.B.; Apkarian, A.V. The brain in chronic CRPS pain: Abnormal gray-white matter interactions in emotional and autonomic regions. Neuron 2008, 60, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bingel, U.; Gläscher, J.; Weiller, C.; Büchel, C. Somatotopic representation of nociceptive information in the putamen: An event-related fMRI study. Cereb. Cortex 2004, 14, 1340–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Fierro, B.; De Tommaso, M.; Giglia, F.; Giglia, G.; Palermo, A.; Brighina, F. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) during capsaicin-induced pain: Modulatory effects on motor cortex excitability. Exp. Brain Res. 2010, 203, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Cui, R.; Zhang, X. The link between depression and chronic pain: Neural mechanisms in the brain. Neural Plast. 2017, 2017, 9724371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pietro, F.; Lee, B.; Henderson, L.A. Altered resting activity patterns and connectivity in individuals with complex regional pain syndrome. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2020, 41, 3781–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotta, J.; Zhou, G.; Harno, H.; Forss, N.; Hari, R. Complex regional pain syndrome: The matter of white matter? Brain Behav. 2017, 7, e00647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, J.J.; Kim, J.; Jeong, H.; Oh, J.K.; Lee, S.; Lyoo, I.K.; Chung, Y.A.; Yoon, S. Prefrontal White Matter Abnormalities Associated With Pain Catastrophizing in Patients With Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2021, 102, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loggia, M.L.; Chonde, D.B.; Akeju, O.; Arabasz, G.; Catana, C.; Edwards, R.R.; Hill, E.; Hsu, S.; Izquierdo-Garcia, D.; Ji, R.R.; et al. Evidence for brain glial activation in chronic pain patients. Brain 2015, 138, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauveau, F.; Boutin, H.; Van Camp, N.; Dollé, F.; Tavitian, B. Nuclear imaging of neuroinflammation: A comprehensive review of [11C]PK11195 challengers. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2008, 35, 2304–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.Y.; Seo, S.; Lee, J.S.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, D.H.; Jung, Y.H.; Song, M.K.; Lee, K.J.; Kim, Y.C.; Kwon, H.W.; et al. [11C]-(R)-PK11195 positron emission tomography in patients with complex regional pain syndrome: A pilot study. Medicine 2017, 96, e5735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.H.; Kim, H.; Jeon, S.Y.; Kwon, J.M.; Lee, D.; Choi, S.H.; Kang, D.H. Aberrant interactions of peripheral measures and neurometabolites with lipids in complex regional pain syndrome using magnetic resonance spectroscopy: A pilot study. Mol. Pain 2018, 14, 1744806917751323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.H.; Kim, H.; Jeon, S.Y.; Kwon, J.M.; Lee, W.J.; Kim, Y.C.; Jang, J.H.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Kang, D.H. Brain Metabolites and Peripheral Biomarkers Associated with Neuroinflammation in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Using [11C]-(R)-PK11195 Positron Emission Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy: A Pilot Study. Pain Med. 2019, 20, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, D.D.; Long, S.; Wilsey, B.; Rafii, A. Analysis of peak magnitude and duration of analgesia produced by local anesthetics injected into sympathetic ganglia of complex regional pain syndrome patients. Clin. J. Pain 1998, 14, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchikanti, L. The role of radiofrequency in the management of complex regional pain syndrome. Curr. Rev. Pain 2000, 4, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlan, A.D.; Lui, P.W.; Mailis, A. Chemical sympathectomy for neuropathic pain: Does it work? Case report and systematic literature review. Clin. J. Pain 2001, 17, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biomarkers and surrogate endpoints: Preferred definitions and conceptual framework. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 69, 89–95. [CrossRef]
- Birklein, F.; Schlereth, T. Complex regional pain syndrome-significant progress in understanding. Pain 2015, 156 (Suppl. S1), S94–S103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharwani, K.D.; Dik, W.A. Highlighting the Role of Biomarkers of Inflammation in the Diagnosis and Management of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2019, 23, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenz, M.; Üçeyler, N.; Frettlöh, J.; Höffken, O.; Krumova, E.K.; Lissek, S.; Reinersmann, A.; Sommer, C.; Stude, P.; Waaga-Gasser, A.M.; et al. Local cytokine changes in complex regional pain syndrome type I (CRPS I) resolve after 6 months. J. Pain 2013, 154, 2142–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krämer, H.H.; Eberle, T.; Üçeyler, N.; Wagner, I.; Klonschinsky, T.; Müller, L.P.; Sommer, C.; Birklein, F. TNF-α in CRPS and ‘normal’ trauma—Significant differences between tissue and serum. J. Pain 2011, 152, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huygen, F.J.; De Bruijn, A.G.; De Bruin, M.T.; Groeneweg, J.G.; Klein, J.; Zijlstra, F.J. Evidence for local inflammation in complex regional pain syndrome type 1. Mediat. Inflamm. 2002, 11, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkitny, L.; McAuley, J.H.; Di Pietro, F.; Stanton, T.R.; O’Connell, N.E.; Marinus, J.; van Hilten, J.J.; Moseley, G.L. Inflammation in complex regional pain syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurology 2013, 80, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huygen, F.J.; Ramdhani, N.; van Toorenenbergen, A.; Klein, J.; Zijlstra, F.J. Mast cells are involved in inflammatory reactions during Complex Regional Pain Syndrome type 1. Immunol. Lett. 2004, 91, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritz, B.W.; Alexander, G.M.; Nogusa, S.; Perreault, M.J.; Peterlin, B.L.; Grothusen, J.R.; Schwartzman, R.J. Elevated blood levels of inflammatory monocytes (CD14+ CD16+) in patients with complex regional pain syndrome. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2011, 164, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankenberger, M.; Sternsdorf, T.; Pechumer, H.; Pforte, A.; Ziegler-Heitbrock, H.W. Differential cytokine expression in human blood monocyte subpopulations: A polymerase chain reaction analysis. Blood 1996, 87, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharwani, K.D.; Dirckx, M. Elevated Plasma Levels of sIL-2R in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Pathogenic Role for T-Lymphocytes? Mediators Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 2764261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohr, D.; Singh, P.; Tschernatsch, M.; Kaps, M.; Pouokam, E.; Diener, M.; Kummer, W.; Birklein, F.; Vincent, A.; Goebel, A.; et al. Autoimmunity against the β2 adrenergic receptor and muscarinic-2 receptor in complex regional pain syndrome. J. Pain 2011, 152, 2690–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaes, F.; Schmitz, K.; Tschernatsch, M.; Kaps, M.; Krasenbrink, I.; Hempelmann, G.; Bräu, M.E. Autoimmune etiology of complex regional pain syndrome (M. Sudeck). Neurology 2004, 63, 1734–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohr, D.; Tschernatsch, M.; Schmitz, K.; Singh, P.; Kaps, M.; Schäfer, K.H.; Diener, M.; Mathies, J.; Matz, O.; Kummer, W.; et al. Autoantibodies in complex regional pain syndrome bind to a differentiation-dependent neuronal surface autoantigen. J. Pain 2009, 143, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirckx, M.; Schreurs, M.W.; de Mos, M.; Stronks, D.L.; Huygen, F.J. The prevalence of autoantibodies in complex regional pain syndrome type I. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 718201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubuis, E.; Thompson, V.; Leite, M.I.; Blaes, F.; Maihöfner, C.; Greensmith, D.; Vincent, A.; Shenker, N.; Kuttikat, A.; Leuwer, M.; et al. Longstanding complex regional pain syndrome is associated with activating autoantibodies against alpha-1a adrenoceptors. J. Pain 2014, 155, 2408–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goebel, A.; Leite, M.I.; Yang, L.; Deacon, R.; Cendan, C.M.; Fox-Lewis, A.; Vincent, A. The passive transfer of immunoglobulin G serum antibodies from patients with longstanding Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. Eur. J. Pain 2011, 15, 504.e1–504.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrickson, J.E.; Hendrickson, E.T.; Gehrie, E.A.; Sidhu, D.; Wallukat, G.; Schimke, I.; Tormey, C.A. Complex regional pain syndrome and dysautonomia in a 14-year-old girl responsive to therapeutic plasma exchange. J. Clin. Apher. 2016, 31, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tékus, V.; Hajna, Z.; Borbély, É.; Markovics, A.; Bagoly, T.; Szolcsányi, J.; Thompson, V.; Kemény, Á.; Helyes, Z.; Goebel, A. A CRPS-IgG-transfer-trauma model reproducing inflammatory and positive sensory signs associated with complex regional pain syndrome. J. Pain 2014, 155, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, J.M.; Dharmalingam, B.; Marsh, S.J.; Thompson, V.; Goebel, A.; Brown, D.A. Effects of serum immunoglobulins from patients with complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) on depolarisation-induced calcium transients in isolated dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons. Exp. Neurol. 2016, 277, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.Z.; Wei, T.; Li, W.W.; Li, X.Q.; Clark, J.D.; Kingery, W.S. Immobilization contributes to exaggerated neuropeptide signaling, inflammatory changes, and nociceptive sensitization after fracture in rats. J. Pain 2014, 15, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, P.D.; Drummond, E.S.; Dawson, L.F.; Mitchell, V.; Finch, P.M.; Vaughan, C.W.; Phillips, J.K. Upregulation of α1-adrenoceptors on cutaneous nerve fibres after partial sciatic nerve ligation and in complex regional pain syndrome type II. J. Pain 2014, 155, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, P.D.; Morellini, N.; Finch, P.M.; Birklein, F.; Knudsen, L.F. Complex regional pain syndrome: Intradermal injection of phenylephrine evokes pain and hyperalgesia in a subgroup of patients with upregulated α1-adrenoceptors on dermal nerves. Pain 2018, 159, 2296–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijaya, L.K.; Morici, M.V.; Stumbles, P.A.; Finch, P.M.; Drummond, P.D. Stimulation of alpha-1 adrenoceptors may intensify cutaneous inflammation in complex regional pain syndrome. Pain 2023, 164, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munnikes, R.J.; Muis, C.; Boersma, M.; Heijmans-Antonissen, C.; Zijlstra, F.J.; Huygen, F.J. Intermediate stage complex regional pain syndrome type 1 is unrelated to proinflammatory cytokines. Mediat. Inflamm. 2005, 2005, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heijmans-Antonissen, C.; Wesseldijk, F.; Munnikes, R.J.; Huygen, F.J.; van der Meijden, P.; Hop, W.C.; Hooijkaas, H.; Zijlstra, F.J. Multiplex bead array assay for detection of 25 soluble cytokines in blister fluid of patients with complex regional pain syndrome type 1. Mediat. Inflamm. 2006, 2006, 28398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesseldijk, F.; Huygen, F.J.; Heijmans-Antonissen, C.; Niehof, S.P.; Zijlstra, F.J. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 are not correlated with the characteristics of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome type 1 in 66 patients. Eur. J. Pain 2008, 12, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, K.; Mehta, H.; Drevets, D.A.; Coggeshall, K.M. IL-6 increases B-cell IgG production in a feed-forward proinflammatory mechanism to skew hematopoiesis and elevate myeloid production. Blood 2010, 115, 4699–4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Lutz, I.; Railton, P.; Wiley, J.P.; McAllister, J.; Powell, J.; Krawetz, R.J. Serum and synovial fluid cytokine profiling in hip osteoarthritis: Distinct from knee osteoarthritis and correlated with pain. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2018, 19, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchida, A.I.; Beekhuizen, M.; t Hart, M.C.; Radstake, T.R.; Dhert, W.J.; Saris, D.B.; van Osch, G.J.; Creemers, L.B. Cytokine profiles in the joint depend on pathology, but are different between synovial fluid, cartilage tissue and cultured chondrocytes. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, S.; Farrell, J.; Dearman, R.J.; MacIver, K.; Naisbitt, D.J.; Moots, R.J.; Edwards, S.W.; Goebel, A. Cutaneous immunopathology of long-standing complex regional pain syndrome. Eur. J. Pain 2015, 19, 1516–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birklein, F.; Drummond, P.D.; Li, W.; Schlereth, T.; Albrecht, N.; Finch, P.M.; Dawson, L.F.; Clark, J.D.; Kingery, W.S. Activation of cutaneous immune responses in complex regional pain syndrome. J. Pain 2014, 15, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andronic, D.; Andronic, O. Skin biomarkers associated with complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) Type I: A systematic review. Rheumatol. Int. 2022, 42, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlova, I.A.; Alexander, G.M.; Qureshi, R.A.; Sacan, A.; Graziano, A.; Barrett, J.E.; Schwartzman, R.J.; Ajit, S.K. MicroRNA modulation in complex regional pain syndrome. J. Transl. Med. 2011, 9, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhold, A.K.; Kindl, G.K.; Dietz, C.; Scheu, N.; Mehling, K.; Brack, A.; Birklein, F.; Rittner, H.L. Molecular and clinical markers of pain relief in complex regional pain syndrome: An observational study. Eur. J. Pain 2023, 27, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietz, C.; Müller, M.; Reinhold, A.K.; Karch, L.; Schwab, B.; Forer, L.; Vlckova, E.; Brede, E.M.; Jakubietz, R.; Üçeyler, N.; et al. What is normal trauma healing and what is complex regional pain syndrome I? An analysis of clinical and experimental biomarkers. Pain 2019, 160, 2278–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, M.K.; Ramanathan, S.; Touati, A.; Zhou, Y.; Thanawala, R.U.; Alexander, G.M.; Sacan, A.; Ajit, S.K. Regulation of proinflammatory genes by the circulating microRNA hsa-miR-939. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Che, Y.; Zheng, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, X.; Shi, F. miR-223: An Immune Regulator in Infectious Disorders. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 781815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, P.J.; Hines, S.; Eisenberg, E.; Pud, D.; Finlay, D.R.; Connolly, K.M.; Paré, M.; Davar, G.; Rice, F.L. Pathologic alterations of cutaneous innervation and vasculature in affected limbs from patients with complex regional pain syndrome. J. Pain 2006, 120, 244–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yu, J. circCUL3 drives malignant progression of cervical cancer by activating autophagy through sponge miR-223-3p upregulation of ATG7. Gene 2024, 925, 148572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowal, J.; Tkach, M.; Théry, C. Biogenesis and secretion of exosomes. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2014, 29, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Andaloussi, S.; Lakhal, S.; Mäger, I.; Wood, M.J. Exosomes for targeted siRNA delivery across biological barriers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liang, H.; Zhang, J.; Zen, K.; Zhang, C.Y. Secreted microRNAs: A new form of intercellular communication. Trends Cell Biol. 2012, 22, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, E.H.; Zhang, E.; Ko, Y.; Sim, W.S.; Moon, D.E.; Yoon, K.J.; Hong, J.H.; Lee, W.H. Genome-wide expression profiling of complex regional pain syndrome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janicki, P.K.; Alexander, G.M.; Eckert, J.; Postula, M.; Schwartzman, R.J. Analysis of Common Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: Genome Wide Association Study Approach and Pooled DNA Strategy. Pain Med. 2016, 17, 2344–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birklein, F.; Ajit, S.K.; Goebel, A.; Perez, R.; Sommer, C. Complex regional pain syndrome—Phenotypic characteristics and potential biomarkers. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirckx, M.; Stronks, D.L.; van Bodegraven-Hof, E.A.; Wesseldijk, F.; Groeneweg, J.G.; Huygen, F.J. Inflammation in cold complex regional pain syndrome. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2015, 59, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dommerholt, J. Complex regional pain syndrome—1: History, diagnostic criteria and etiology. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2004, 8, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson McBride, A.R.; Barnett, A.J.; Livingstone, J.A.; Atkins, R.M. Complex regional pain syndrome (type 1): A comparison of 2 diagnostic criteria methods. Clin. J. Pain 2008, 24, 637–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmoush, A.J. Causalgia: Redefinition as a clinical pain syndrome. Pain 1981, 10, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunden, L.K.; Kleggetveit, I.P.; Jørum, E. Delayed diagnosis and worsening of pain following orthopedic surgery in patients with complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS). Scand. J. Pain 2016, 11, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunden, L.K.; Jorum, E. The challenge of recognizing severe pain and autonomic abnormalities for early diagnosis of CRPS. Scand. J. Pain 2021, 21, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, G.S.; Thompson, B.L.; Snell, D.L.; Dunn, J.A. Experiences of diagnosis and treatment for upper limb Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A qualitative analysis. Pain Med. 2023, 24, 1355–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja, S.N.; Buvanendran, A. Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Comprehensive Qualitative Research Study on Unmet Needs in the “Patient Journey”. J. Pain Res. 2021, 14, 2391–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Øien, A.M.; Dragesund, T. Identifying contrasting embodied voices of identity: A qualitative meta-synthesis of experiences of change among patients with chronic musculoskeletal pain in long-term physiotherapy. Physiother. Theory Pract. 2024, 40, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, R.; Turner, L. Using Communities of Practice Theory to Understand the Crisis of Identity in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/Myalgic Encephalomyelitis (CFS/ME). Chronic Illn. 2023, 19, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnerup, N.B.; Attal, N.; Haroutounian, S.; McNicol, E.; Baron, R.; Dworkin, R.H.; Gilron, I.; Haanpää, M.; Hansson, P.; Jensen, T.S.; et al. Pharmacotherapy for neuropathic pain in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima Pessôa, B.; Netto, J.G.M.; Adolphsson, L.; Longo, L.; Hauwanga, W.N.; McBenedict, B. Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: Diagnosis, Pathophysiology, and Treatment Approaches. Cureus 2024, 16, e76324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadivelu, N.; Urman, R.D.; Hines, R.L. Essentials of Pain Management; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lörincz, M.L.; Geall, F.; Bao, Y.; Crunelli, V.; Hughes, S.W. ATP-dependent infra-slow (<0.1 Hz) oscillations in thalamic networks. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissmann, R.; Uziel, Y. Pediatric complex regional pain syndrome: A review. Pediatr. Rheumatol. Online J. 2016, 14, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozin, F.; Haughton, V.; Ryan, L. The reflex sympathetic dystrophy syndrome in a child. J. Pediatr. 1977, 90, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, B.H.; Singsen, B.H.; Kent, J.T.; Kornreich, H.; King, K.; Hicks, R.; Hanson, V. Reflex neurovascular dystrophy in childhood. J. Pediatr. 1978, 93, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Gao, R.; Zhou, R.; Chen, H.; Liu, C.; Zhu, T.; Chen, C. The emerging power and promise of non-coding RNAs in chronic pain. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 1037929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.L.; Wang, H.C.; Chunag, Y.T.; Chou, C.W.; Lin, I.L.; Lai, C.S.; Chang, L.L.; Cheng, K.I. miRNA Expression Change in Dorsal Root Ganglia After Peripheral Nerve Injury. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 61, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, S.R.; Shenoda, B.B.; Qureshi, R.A.; Sacan, A.; Alexander, G.M.; Perreault, M.; Barrett, J.E.; Aradillas-Lopez, E.; Schwartzman, R.J.; Ajit, S.K. Analgesic Response to Intravenous Ketamine Is Linked to a Circulating microRNA Signature in Female Patients With Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. J. Pain 2015, 16, 814–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pande, R.; Parikh, A.; Shenoda, B.; Ramanathan, S.; Alexander, G.M.; Schwartzman, R.J.; Ajit, S.K. Hsa-miR-605 regulates the proinflammatory chemokine CXCL5 in complex regional pain syndrome. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 140, 111788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollmann, G.; Wertli, M.M. The role of the bone in complex regional pain syndrome 1-A systematic review. Eur. J. Pain 2023, 27, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varenna, M.; Orsini, F.; Di Taranto, R.; Zucchi, F.; Adami, G.; Gatti, D.; Crotti, C. Bone Turnover Markers and Wnt Signaling Modulators in Early Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. A Pre-specified Observational Study. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2024, 115, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krämer, H.H.; Hofbauer, L.C.; Szalay, G.; Breimhorst, M.; Eberle, T.; Zieschang, K.; Rauner, M.; Schlereth, T.; Schreckenberger, M.; Birklein, F. Osteoprotegerin: A new biomarker for impaired bone metabolism in complex regional pain syndrome? J. Pain 2014, 155, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.A.; Georgius, P.; Pires, A.S.; Heng, B.; Allwright, M.; Guennewig, B.; Santarelli, D.M.; Bailey, D.; Fiore, N.T.; Tan, V.X.; et al. Novel immune biomarkers in complex regional pain syndrome. J. Neuroimmunol. 2020, 347, 577330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baerlecken, N.; Gaulke, R.; Pursche, N.; Witte, T.; Karst, M.; Bernateck, M. Autoantibodies against P29ING4 are associated with complex regional pain syndrome. Immunol. Res. 2019, 67, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajerian, M.; Hung, V.; Khan, H.; Lahey, L.J.; Sun, Y.; Birklein, F.; Krämer, H.H.; Robinson, W.H.; Kingery, W.S.; Clark, J.D. Identification of KRT16 as a target of an autoantibody response in complex regional pain syndrome. Exp. Neurol. 2017, 287, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rooij, A.M.; Florencia Gosso, M.; Haasnoot, G.W.; Marinus, J.; Verduijn, W.; Claas, F.H.; van den Maagdenberg, A.M.; van Hilten, J.J. HLA-B62 and HLA-DQ8 are associated with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome with fixed dystonia. J. Pain 2009, 145, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rooijen, D.E.; Roelen, D.L.; Verduijn, W.; Haasnoot, G.W.; Huygen, F.J.; Perez, R.S.; Claas, F.H.; Marinus, J.; van Hilten, J.J.; van den Maagdenberg, A.M. Genetic HLA associations in complex regional pain syndrome with and without dystonia. J. Pain 2012, 13, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Rooij, A.M.; de Mos, M.; Sturkenboom, M.C.; Marinus, J.; van den Maagdenberg, A.M.; van Hilten, J.J. Familial occurrence of complex regional pain syndrome. Eur. J. Pain 2009, 13, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, S.S.; Goebel, A.; Lee, M.C.; Nahorski, M.S.; Shenker, N.; Pamela, Y.; Drissi, I.; Brown, C.; Ison, G.; Shaikh, M.F.; et al. Evidence of a genetic background predisposing to complex regional pain syndrome type 1. J. Med. Genet. 2024, 61, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guthmiller, K.B.; Dua, A.; Dey, S.; Varacallo, M.A. Complex Regional Pain Syndrome. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, W.; Song, Y.; Mo, C.; Jiang, S.; Wang, Z. Analysis of gene expression profile microarray data in complex regional pain syndrome. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 3371–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebel, A.; Blaes, F. Complex regional pain syndrome, prototype of a novel kind of autoimmune disease. Autoimmun. Rev. 2013, 12, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirri, C.; Pirri, N.; Petrelli, L.; Fede, C. An Emerging Perspective on the Role of Fascia in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elsayed, A.; Stark, C.W.; Topoluk, N.; Isaamullah, M.; Uzodinma, P.; Viswanath, O.; Gyorfi, M.J.; Fattouh, O.; Schlidt, K.C.; Dyara, O. A brief review of complex regional pain syndrome and current management. Ann. Med. 2024, 56, 2334398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fooladi, S.; Hasoon, J.; Kaye, A.D.; Abd-Elsayed, A. Diagnostic Criteria and Technical Evaluation of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Narrative Review. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2281. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172281
Fooladi S, Hasoon J, Kaye AD, Abd-Elsayed A. Diagnostic Criteria and Technical Evaluation of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Narrative Review. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(17):2281. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172281
Chicago/Turabian StyleFooladi, Shahnaz, Jamal Hasoon, Alan D. Kaye, and Alaa Abd-Elsayed. 2025. "Diagnostic Criteria and Technical Evaluation of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Narrative Review" Diagnostics 15, no. 17: 2281. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172281
APA StyleFooladi, S., Hasoon, J., Kaye, A. D., & Abd-Elsayed, A. (2025). Diagnostic Criteria and Technical Evaluation of Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Narrative Review. Diagnostics, 15(17), 2281. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172281






