In Vivo Confocal Microscopy of the Cornea in Diagnosing Small Fibre Neuropathy: A Cross-Sectional Observational Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Ethical Statement
2.3. Questionnaires
2.4. Skin Biopsy
2.5. Ophthalmological Examination
2.6. Corneal In Vivo Confocal Microscopy
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
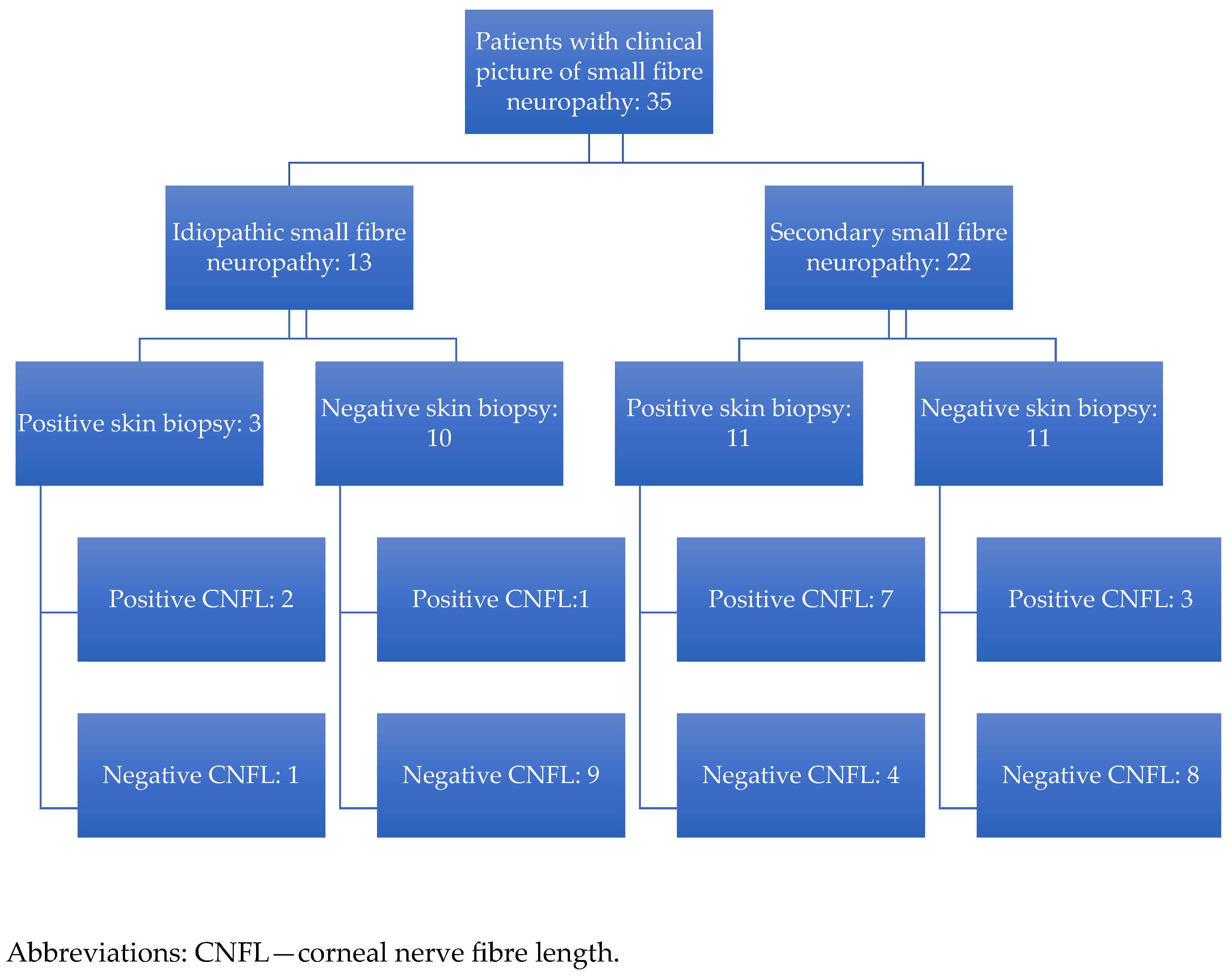
3.1. Skin Biopsy and In Vivo Confocal Microscopy of the Cornea
3.2. Comparison of Skin Biopsy Results to IVCM Corneal Measurements
3.3. Ophthalmological Exam Findings and IVCM Results
3.4. Clinical Characteristics Compared to IVCM and Skin Biopsy Results
3.5. Questionnaire Results in Comparison to IVCM and Skin Biopsy Outcomes
3.6. Comparison of IVCM and Skin Biopsy Results in Secondary and Idiopathic SFN
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CDT | Cold detection threshold |
| CNBD | Corneal nerve branch density |
| CNFD | Corneal nerve fibre density |
| CNFL | Corneal nerve fibre length |
| HRT3RCM | Heidelberg Retinal Tomograph 3 Rostock cornea module |
| IENFD | Intraepidermal nerve fibre density |
| IVCM | In vivo confocal microscopy |
| NPS | Neuropathic pain score |
| NPV | Negative predictive value |
| OHQ | Orthostatic Hypotension Questionnaire |
| PGP | Protein gene product |
| PPV | Positive predictive value |
| QSART | Quantitative sudomotor axon reflex test |
| QST | Quantitative sensory testing |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SFN | Small fibre neuropathy |
| TBUT | Tear break-up time |
References
- Terkelsen, A.J.; Karlsson, P.; Lauria, G.; Freeman, R.; Finnerup, N.B.; Jensen, T.S. The diagnostic challenge of small fibre neuropathy: Clinical presentations, evaluations, and causes. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 934–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, B.A.; Bakkers, M.; Hoeijmakers, J.G.; Faber, C.G.; Merkies, I.S. Improving assessment in small fiber neuropathy. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2015, 20, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhad, K.; Traub, R.; Ruzhansky, K.M.; Brannagan, T.H. Causes of neuropathy in patients referred as “idiopathic neuropathy”. Muscle Nerve 2016, 53, 856–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, M.J.; Bakkers, M.; Merkies, I.S.; Hoeijmakers, J.G.; van Raak, E.P.; Faber, C.G. Incidence and prevalence of small-fiber neuropathy: A survey in the Netherlands. Neurology 2013, 8, 1356–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, R.; Gewandter, J.S.; Faber, C.G.; Gibbons, C.; Haroutounian, S.; Lauria, G.; Levine, T.; Malik, R.A.; Singleton, J.R.; Smith, A.G.; et al. Idiopathic distal sensory polyneuropathy: ACTTION diagnostic criteria. Neurology 2020, 95, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauria, G.; Hsieh, S.T.; Johansson, O.; Kennedy, W.R.; Leger, J.M.; Mellgren, S.I.; Nolano, M.; Merkies, I.S.; Polydefkis, M.; Smith, A.G.; et al. European Federation of Neurological Societies/Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline on the use of skin biopsy in the diagnosis of small fiber neuropathy. Report of a joint task force of the European Federation of Neurological Societies and the Peripheral Nerve Society. Eur. J. Neurol. 2010, 17, 903–912. [Google Scholar]
- Backonja, M.M.; Attal, N.; Baron, R.; Bouhassira, D.; Drangholt, M.; Dyck, P.J.; Edwards, R.R.; Freeman, R.; Gracely, R.; Haanpaa, M.H.; et al. Value of quantitative sensory testing in neurological and pain disorders: NeuPSIG consensus. Pain 2013, 154, 1807–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devigili, G.; Rinaldo, S.; Lombardi, R.; Cazzato, D.; Marchi, M.; Salvi, E.; Eleopra, R.; Lauria, G. Diagnostic criteria for small fibre neuropathy in clinical practice and research. Brain 2019, 142, 3728–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provitera, V.; Gibbons, C.H.; Wendelschafer-Crabb, G.; Donadio, V.; Vitale, D.F.; Stancanelli, A.; Caporaso, G.; Liguori, R.; Wang, N.; Santoro, L.; et al. A multi-center, multinational age- and genderadjusted normative dataset for immunofluorescent intraepidermal nerve fiber density at the distal leg. Eur. J. Neurol. 2016, 23, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørnkaer, A.; Gaist, L.M.; Holbech, J.V.; Gaist, D.; Wirenfeldt, M.; Sindrup, S.H.; Krøigård, T. Corneal confocal microscopy in small and mixed fiber neuropathy-Comparison with skin biopsy and cold detection in a large prospective cohort. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2023, 28, 664–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falco, P.; Galosi, E.; Di Stefano, G.; Leone, C.; Di Pietro, G.; Tramontana, L.; De Stefano, G.; Litewczuk, D.; Esposito, N.; Truini, A. Autonomic Small-Fiber Pathology in Patients With Fibromyalgia. J. Pain 2024, 25, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, D.; Papanas, N.; Zhivov, A.; Allgeier, S.; Winter, K.; Ziegler, I.; Brüggemann, J.; Strom, A.; Peschel, S.; Köhler, B.; et al. Early detection of nerve fiber loss by corneal confocal microscopy and skin biopsy in recently diagnosed type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2014, 63, 2454–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruzat, A.; Qazi, Y.; Hamrah, P. In Vivo Confocal Microscopy of Corneal Nerves in Health and Disease. Ocul. Surf. 2017, 15, 15–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulton, E.A.; Borsook, D. C-Fiber Assays in the Cornea vs. Skin. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalteniece, A.; Ferdousi, M.; Azmi, S.; Mubita, W.M.; Marshall, A.; Lauria, G.; Faber, C.G.; Soran, H.; Malik, R.A. Corneal confocal microscopy detects small nerve fibre damage in patients with painful diabetic neuropathy. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, U.; Jeziorska, M.; Petropoulos, I.N.; Asghar, O.; Fadavi, H.; Ponirakis, G.; Marshall, A.; Tavakoli, M.; Boulton, A.J.M.; Efron, N.; et al. Diagnostic utility of corneal confocal microscopy and intra-epidermal nerve fibre density in diabetic neuropathy. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Franca, B.; Yaïci, R.; Matuszewska-Iwanicka, A.; Nandrean, S.; Gutzmer, R.; Hettlich, H.J. Bilateral In Vivo Confocal Microscopic Changes of the Corneal Subbasal Nerve Plexus in Patients with Acute Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus. Ophthalmol. Ther. 2025, 14, 941–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, E.; Ivarsen, A.; Hjortdal, J. Signs of long-term corneal nerve deterioration after uneventful cataract surgery. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2022, 48, 372–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikmetas, O.; Kocabeyoglu, S.; Mocan, M.C.; Karahan, S.; İrkec, M. The relationship between corneal subbasal nerve density and corneal sensitivity in patients with Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 69, 1730–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouheraoua, N.; Hrarat, L.; Parsa, C.F.; Akesbi, J.; Sandali, O.; Goemaere, I.; Hamiche, T.; Laroche, L.; Borderie, V. Decreased Corneal Sensation and Subbasal Nerve Density, and Thinned Corneal Epithelium as a Result of 360-Degree Laser Retinopexy. Ophthalmology 2015, 122, 2095–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israilevich, R.N.; Syed, Z.A.; Xu, D.; Kaiser, R.S.; Garg, S.J.; Spirn, M.J.; Mehta, S.; Gupta, O.P.; Ho, A.C.; Kuriyan, A.E.; et al. Neurotrophic keratopathy following rhegmatogenous retinal detachment surgery. Can. J. Ophtalmol. 2024, 59, e321–e326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galer, B.S.; Jensen, M.P. Development and preliminary validation of a pain measure specific to neuropathic pain: The Neuropathic Pain Scale. Neurology 1997, 48, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, H.; Malamut, R.; Norcliffe-Kaufmann, L.; Rosa, K.; Freeman, R. The Orthostatic Hypotension Questionnaire (OHQ): Validation of a novel symptom assessment scale. Clin. Auton. Res. 2012, 22, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauria, G.; Cornblath, D.R.; Johansson, O.; McArthur, J.C.; Mellgren, S.I.; Nolano, M.; Rosenberg, N.; Sommer, C.; European Federation of Neurological Societies. EFNS guidelines on the use of skin biopsy in the diagnosis of peripheral neuropathy. Eur. J. Neurol. 2005, 12, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauria, G.; Bakkers, M.; Schmitz, C.; Lombardi, R.; Penza, P.; Devigili, G.; Smith, A.G.; Hsieh, S.T.; Mellgren, S.I.; Umapathi, T.; et al. Intraepidermal nerve fiber density at the distal leg: A worldwide normative reference study. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2010, 15, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bron, A.J.; Evans, V.E.; Smith, J.A. Grading of corneal and conjunctival staining in the context of other dry eye tests. Cornea 2003, 22, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, M.; Ferdousi, M.; Petropoulos, I.N.; Morris, J.; Pritchard, N.; Zhivov, A.; Ziegler, D.; Pacaud, D.; Romanchuk, K.; Perkins, B.A. Normative values for corneal nerve morphology assessed using corneal confocal microscopy: A multinational normative data set. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulos, I.N.; Alam, U.; Fadavi, H.; Marshall, A.; Asghar, O.; Dabbah, M.A.; Chen, X.; Graham, J.; Ponirakis, G.; Boulton, A.J.; et al. Rapid automated diagnosis of diabetic peripheral neuropathy with in vivo corneal confocal microscopy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 2071–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Moreno, A.; Baudouin, C.; Melik Parsadaniantz, S.; Réaux-Le Goazigo, A. Morphological and Functional Changes of Corneal Nerves and Their Contribution to Peripheral and Central Sensory Abnormalities. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 610342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Lozano, R.E.; Hernandez-Camarena, J.C.; Loya-Garcia, D.; Merayo-Lloves, J.; Rodriguez-Garcia, A. The molecular basis of neurotrophic keratopathy: Diagnostic and therapeutic implications. A review. Ocul. Surf. 2021, 19, 224–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheirkhah, A.; Muller, R.; Mikolajczak, J.; Ren, A.; Kadas, E.M.; Zimmermann, H.; Pruess, H.; Paul, F.; Brandt, A.U.; Hamrah, P. Comparison of standard versus wide-field composite images of the corneal subbasal layer by in vivo confocal microscopy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 5801–5807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vagenas, D.; Pritchard, N.; Edwards, K.; Shahidi, A.M.; Sampson, G.P.; Russell, A.W.; Malik, R.A.; Efron, N. Optimal image sample size for corneal nerve morphometry. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2012, 89, 812–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkins, B.A.; Lovblom, L.E.; Bril, V.; Scarr, D.; Ostrovski, I.; Orszag, A.; Edwards, K.; Pritchard, N.; Russell, A.; Dehghani, C.; et al. Corneal confocal microscopy for identification of diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy: A pooled multinational consortium study. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 1856–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azmi, S.; Ferdousi, M.; Petropoulos, I.N.; Fadavi, H.; Tavakoli, M.; Alam, U.; Jones, W.; Marshall, A.; Jeziorska, M.; Boulton, A.J.; et al. Corneal confocal microscopy shows an improvement in small-fiber neuropathy in subjects with type 1 diabetes on continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion compared with multiple daily injection. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, e3–e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantyh, W.G.; Dyck, P.J.; Dyck, P.J.; Engelstad, J.K.; Litchy, W.J.; Sandroni, P.; Davis, M.D.P. Epidermal nerve fiber quantification in patients with erythromelalgia. JAMA Dermatol. 2017, 153, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Yang, Y.; de Greef, B.T.; Hoeijmakers, J.G.; Gerrits, M.M.; Verhamme, C.; Qu, J.; Lauria, G.; Merkies, I.S.; Faber, C.G.; et al. The domain II S4-S5 linker in Nav1.9: A missense mutation enhances activation, impairs fast inactivation, and produces human painful neuropathy. Neuromolecular. Med. 2015, 17, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shy, M.E.; Frohman, E.M.; So, Y.T.; Arezzo, J.C.; Cornblath, D.R.; Giuliani, M.J.; Kincaid, J.C.; Ochoa, J.L.; Parry, G.J.; Weimer, L.H. Quantitative sensory testing: Report of the Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2003, 60, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galosi, E.; Leonardi, L.; Falco, P.; Di Pietro, G.; Fasolino, A.; Esposito, N.; Leone, C.; Di Stefano, G.; Inghilleri, M.; Luigetti, M.; et al. Functional and morphometric assessment of small-fibre damage in late-onset hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis with polyneuropathy: The controversial relation between small-fibre-related symptoms and diagnostic test findings. Amyloid 2023, 30, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfaye, S.; Boulton, A.J.; Dyck, P.J.; Freeman, R.; Horowitz, M.; Kempler, P.; Lauria, G.; Malik, R.A.; Spallone, V.; Vinik, A.; et al. Diabetic neuropathies: Update on definitions, diagnostic criteria, estimation of severity, and treatments. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 2285–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, B.C. Quantitative sudomotor axon reflex test (QSART) as a diagnostic tool of small fiber neuropathy. Ann. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2022, 24, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackmore, D.; Siddiqi, Z.A. Diagnostic criteria for small fiber neuropathy. J. Clin. Neuromusc. Dis. 2017, 18, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvarajah, D.; Cash, T.; Davies, J.; Sankar, A.; Rao, G.; Grieg, M.; Pallai, S.; Gandhi, R.; Wilkinson, I.D.; Tesfaye, S. SUDOSCAN: A simple, rapid, and objective method with potential for screening for diabetic peripheral neuropathy. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieger, S.M.; Reimann, M.; Haase, R.; Henkel, E.; Hanefeld, M.; Ziemssen, T. Sudomotor Testing of Diabetes Polyneuropathy. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riveline, J.P.; Mallone, R.; Tiercelin, C.; Yaker, F.; Alexandre-Heymann, L.; Khelifaoui, L.; Travert, F.; Fertichon, C.; Julla, J.B.; Vidal-Trecan, T.; et al. Validation of the Body Scan®, a new device to detect small fiber neuropathy by assessment of the sudomotor function: Agreement with the Sudoscan®. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1256984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, M.; Marshall, A.; Pitceathly, R.; Fadavi, H.; Gow, D.; Roberts, M.E.; Efron, N.; Boulton, A.J.; Malik, R.A. Corneal confocal microscopy: A novel means to detect nerve fibre damage in idiopathic small fibre neuropathy. Exp. Neurol. 2010, 223, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucher, F.; Schneider, C.; Blau, T.; Cursiefen, C.; Fink, G.R.; Lehmann, H.C.; Heindl, L.M. Small-fiber neuropathy is associated with corneal nerve and dendritic cell alterations: An in vivo confocal microscopy study. Cornea 2015, 34, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basantsova, N.Y.; Starshinova, A.A.; Dori, A.; Zinchenko, Y.S.; Yablonskiy, P.K.; Shoenfeld, Y. Small-fiber neuropathy definition, diagnosis, and treatment. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 40, 1343–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geerts, M.; Hoeijmakers, J.G.J.; Gorissen-Brouwers, C.M.L.; Faber, C.G.; Merkies, I.S.J. Small Fiber Neuropathy: A Clinical and Practical Approach. J. Nurs. Pract. 2023, 19, 104547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efron, N.; Edwards, K.; Roper, N.; Pritchard, N.; Sampson, G.P.; Shahidi, A.M.; Vagenas, D.; Russell, A.; Graham, J.; Dabbah, M.A.; et al. Repeatability of measuring corneal subbasal nerve fiber length in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Eye Contact Lens 2010, 36, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudejans, L.C.; Niesters, M.; Brines, M.; Dahan, A.; van Velzen, M. Quantification of small fiber pathology in patients with sarcoidosis and chronic pain using cornea confocal microscopy and skin biopsies. J. Pain Res. 2017, 10, 2057–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.G.; Singleton, J.R. Obesity and hyperlipidemia are risk factors for early diabetic neuropathy. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2013, 27, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmi, S.; Ferdousi, M.; Liu, Y.; Adam, S.; Siahmansur, T.; Ponirakis, G.; Marshall, A.; Petropoulos, I.N.; Ho, J.H.; Syed, A.A.; et al. The role of abnormalities of lipoproteins and HDL functionality in small fibre dysfunction in people with severe obesity. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, B.; Pasha, R.; Kamath, A.; Malik, R.A.; Ferdousi, M.; Soran, H. Small nerve fibre damage and cardiac autonomic dysfunction in patients with hypertriglyceridaemia. Atherosclerosis 2025, 405, 119186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.G.; Rose, K.; Singleton, J.R. Idiopathic neuropathy patients are at high risk for metabolic syndrome. J. Neurol. Sci. 2008, 273, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haroutounian, S.; Todorovic, M.S.; Leinders, M.; Campagnolo, M.; Gewandter, J.S.; Dworkin, R.H.; Freeman, R. Diagnostic criteria for idiopathic small fiber neuropathy. A systematic review. Muscle Nerve 2021, 63, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
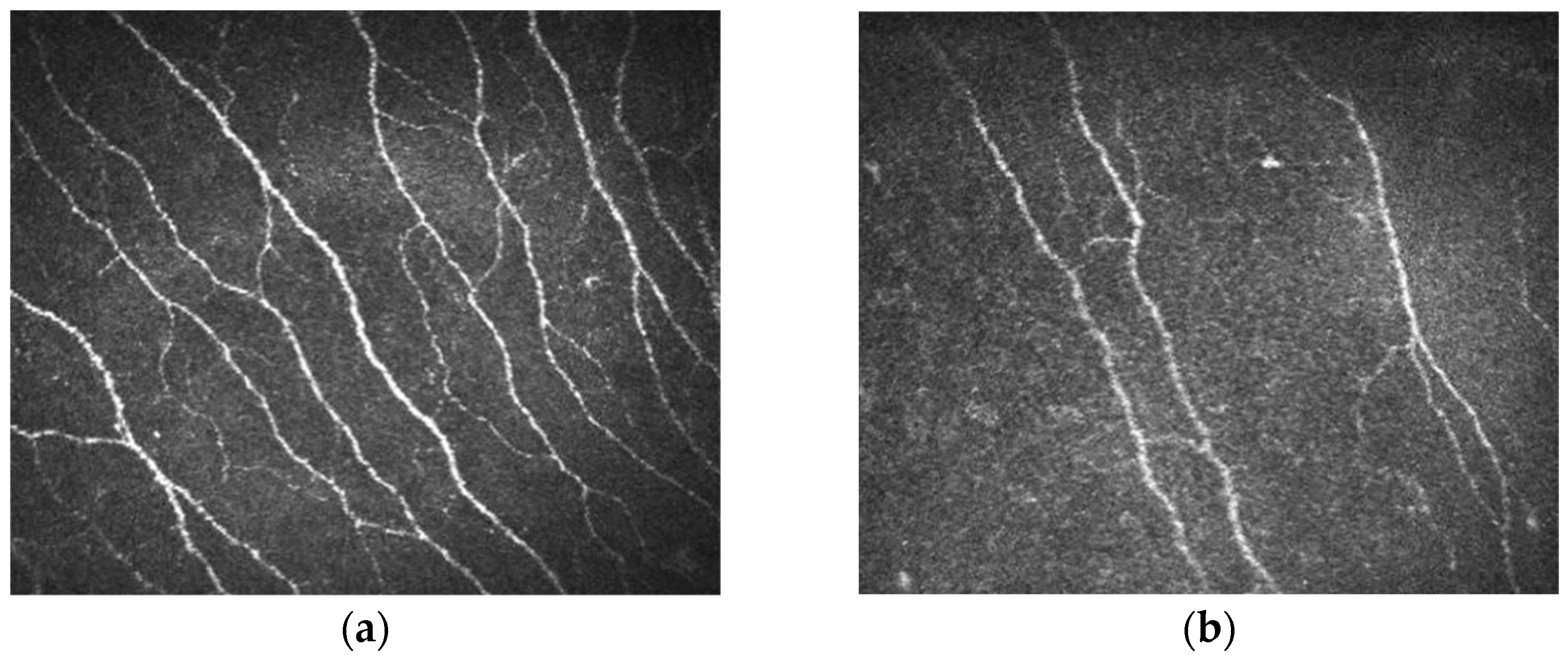
| Intra-Epidermal Nerve Fibre Density (mm/mm2), Increasing Below the 5th Percentile in Bold | Sex | Age (Years) | CNFL—Corneal Nerve Fibre Length (Nerve Fibres mm/mm2), Below 5th Percentile in Bold |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | m | 39 | 14.3 |
| 0.5 | m | 69 | 10.2 |
| 1.2 | m | 48 | 11.1 |
| 1.2 | f | 57 | 14.8 |
| 1.6 | m | 53 | 12.9 |
| 2.1 | f | 75 | 8.8 |
| 2.8 | f | 51 | 20.0 |
| 2.8 | f | 74 | 14.9 |
| 2.9 | f | 68 | 15.8 |
| 3.1 | f | 70 | 11.6 |
| 3.5 | f | 50 | 11.9 |
| 3.9 | f | 77 | 12.9 |
| 4.0 | f | 76 | 13.5 |
| 4.3 | m | 76 | 22.1 |
| 4.3 | f | 30 | 13.2 |
| 4.9 | f | 74 | 12.9 |
| 5.0 | m | 75 | 11.8 |
| 5.8 | f | 51 | 11.4 |
| 8.2 | f | 66 | 12.2 |
| Group 1, Positive Skin Biopsy (N = 14) | Group 2, Negative Skin Biopsy (N = 21) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CNFL (mm/mm2) | 13.667 ± 2.994 | 16.272 ± 3.544 | p = 0.030 |
| CNFL below 5th percentile | 9 (64.3%) | 4 (19%) | p = 0.007 |
| CNBD (branches/mm2) | 36.676 ± 14.681 | 48.812 ± 17.830 | p = 0.042 |
| CNBD below 5th percentile | 0 | 3 (14.3%) | p = 0.259 |
| CNFD (main fibres/mm2) | 18.472 ± 3.8 | 19.719 ± 2.584 | p = 0.255 |
| CNFD below 5th percentile | 1 (7.1%) | 0 | p = 0.400 |
| CNFL Below the 5th Percentile (N = 13) | CNFL Above the 5th Percentile (N = 22) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Reduced corneal sensitivity | 5 (38.5%) | 3 (13.6%) | p = 0.116 |
| Positive Schirmer | 5 (38.5%) | 9 (40.9%) | p = 0.886 |
| Normal TBUT | 2 (15.4%) | 3 (13.6%) | p = 1.000 |
| Positive Oxford | 3 (23.1%) | 5 (22.7%) | p = 1.000 |
| Endothelial cell density (cells/mm2) | 2496.2 ± 305.5 | 2460.5 ± 314.8 | p = 0.746 |
| Group 1, Positive Skin Biopsy (N = 14) | Group 2, Negative Skin Biopsy (N = 21) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 59.4 ± 13.5 | 63.8 ± 13.5 | p = 0.359 |
| Gender | p = 1 | ||
| Male | 4 (28.6%) | 7 (33.3%) | |
| Female | 10 (71.4%) | 14 (66.7%) | |
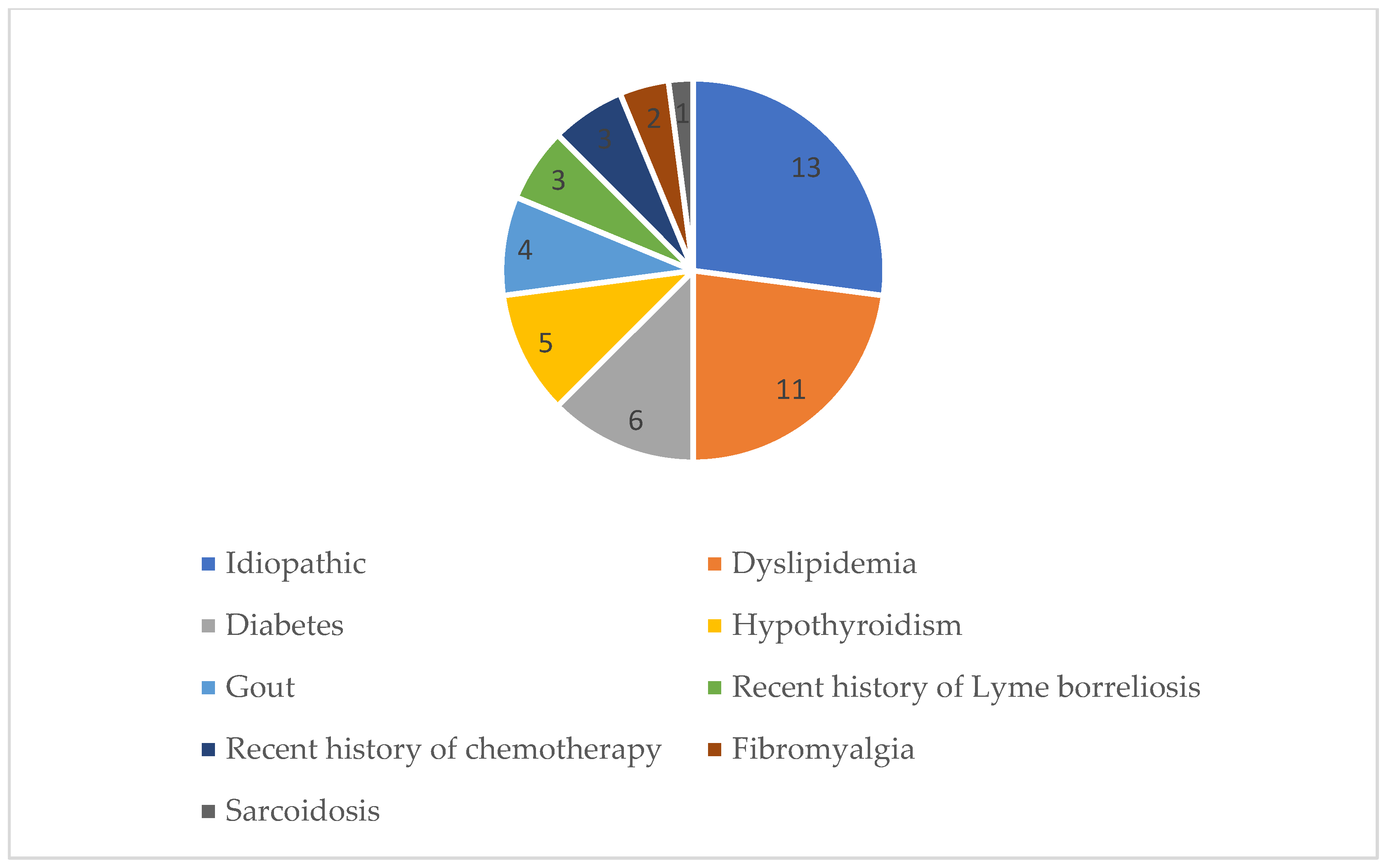
| Diabetes | 4 (28.6%) | 2 (9.5%) | p = 0.191 |
| Dyslipidaemia | 8 (57.1%) | 3 (14.3%) | p = 0.012 |
| Length-dependent symptoms | 11 (78.6%) | 20 (95.8%) | p = 0.132 |
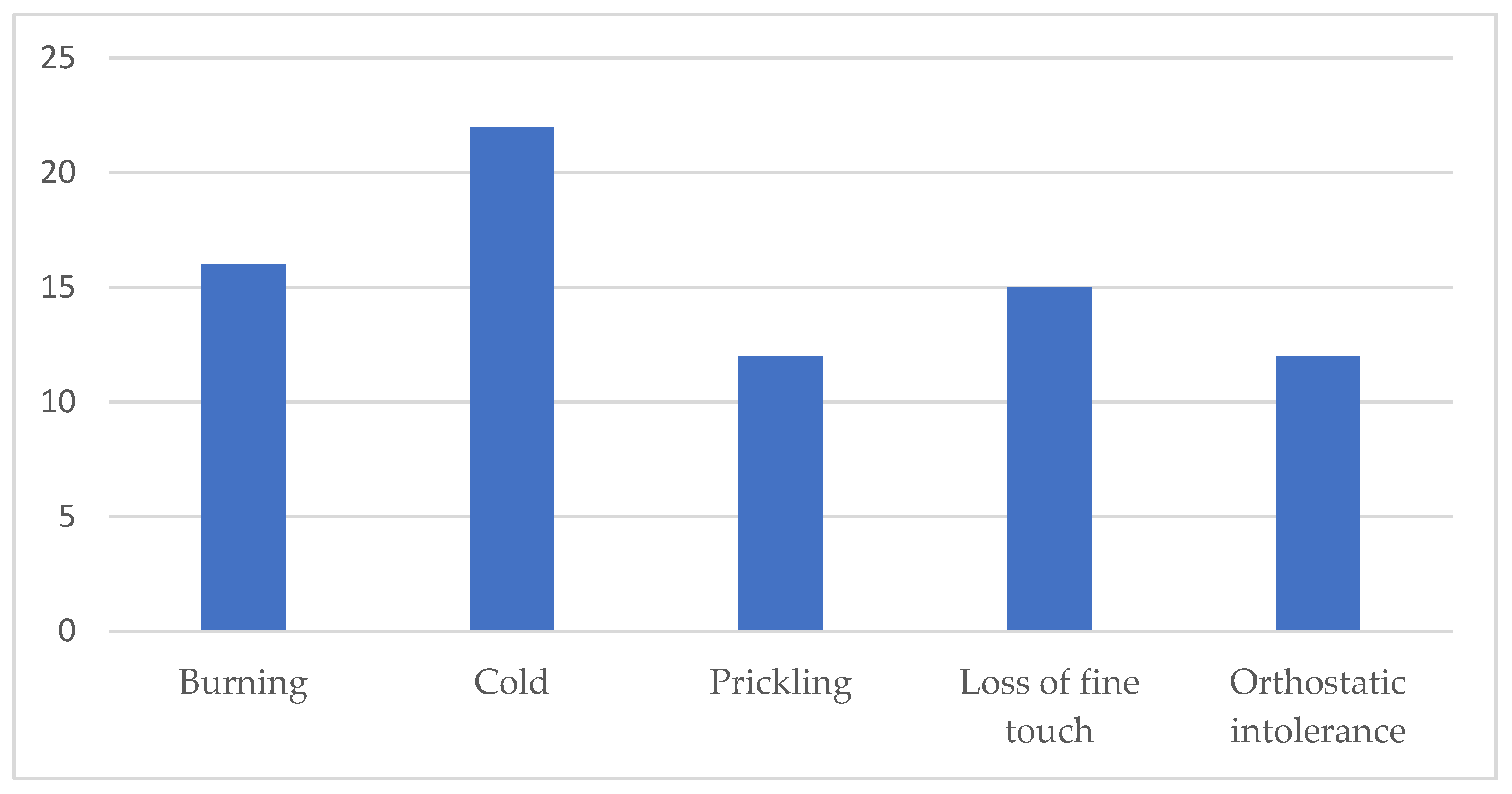
| Burning | 7 (50%) | 10 (47.6%) | p = 0.890 |
| Cold | 9 (64.3%) | 13 (61.9%) | p = 0.886 |
| Prickling | 4 (28.6%) | 9 (42.9%) | p = 0.488 |
| Fine touch | 5 35.7%) | 10 (47.6%) | p = 0.486 |
| Orthostatic intolerance | 4 (28.6%) | 9 (42.9%) | p = 0.488 |
| Reduced corneal sensitivity | 4 (28.6%) | 4 (19%) | p = 0.685 |
| CNFL Below the 5th Percentile (N = 13) | CNFL Above the 5th Percentile (N = 22) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 62.6 ± 14.7 | 61.7 ± 13.05 | p = 0.846 |
| Gender | p = 1.000 | ||
| Male | 4 (30.8%) | 7 (31.8%) | |
| Female | 9 (69.2%) | 15 (68.2%) | |
| Diabetes | 4 (30.8%) | 2 (9.1%) | p = 0.166 |
| Dyslipidaemia | 5 (38.5%) | 6 (27.3%) | p = 0.475 |
| Length-dependent symptoms | 12 (92.3%) | 19 (86.3%) | p = 1.000 |
| Burning | 4 (30.8%) | 13 (59.1%) | p = 0.164 |
| Cold | 9 (69.2%) | 13 (59.1%) | p = 0.721 |
| Prickling | 4 (30.8%) | 9 (40.9%) | p = 0.721 |
| Fine touch | 3 (23.1%) | 12 (54.5%) | p = 0.089 |
| Orthostatic intolerance | 3 (23.1%) | 10 (47.6%) | p = 0.282 |
| Reduced corneal sensitivity | 5 (38.5%) | 3 (13.6%) | p = 0.116 |
| Group 1, Positive Skin Biopsy (n = 14) | Group 2, Negative Skin Biopsy (n = 21) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Neuropathic Pain Scale questionnaire | 38.57 ± 15.84 | 35.48 ± 18.16 | p = 0.607 |
| Orthostatic Hypotension Questionnaire | 21.64 ± 23.38 | 25 ± 22.46 | p = 0.607 |
| CNFL Below the 5th Percentile (N = 13) | CNFL Above the 5th Percentile (N = 22) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Neuropathic Pain Scale questionnaire | 37.62 ± 16.07 | 36.18 ± 18.03 | p = 0.810 |
| Orthostatic Hypotension Questionnaire | 19.38 ± 22.68 | 26.18 ± 22.61 | p = 0.397 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petrovič, D.; Mujnović, A.; Hammami, A.; Krašovec, T.; Kirbiš, M.; Stunf Pukl, S. In Vivo Confocal Microscopy of the Cornea in Diagnosing Small Fibre Neuropathy: A Cross-Sectional Observational Study. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2207. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172207
Petrovič D, Mujnović A, Hammami A, Krašovec T, Kirbiš M, Stunf Pukl S. In Vivo Confocal Microscopy of the Cornea in Diagnosing Small Fibre Neuropathy: A Cross-Sectional Observational Study. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(17):2207. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172207
Chicago/Turabian StylePetrovič, David, Ajla Mujnović, Adela Hammami, Tjaša Krašovec, Mojca Kirbiš, and Spela Stunf Pukl. 2025. "In Vivo Confocal Microscopy of the Cornea in Diagnosing Small Fibre Neuropathy: A Cross-Sectional Observational Study" Diagnostics 15, no. 17: 2207. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172207
APA StylePetrovič, D., Mujnović, A., Hammami, A., Krašovec, T., Kirbiš, M., & Stunf Pukl, S. (2025). In Vivo Confocal Microscopy of the Cornea in Diagnosing Small Fibre Neuropathy: A Cross-Sectional Observational Study. Diagnostics, 15(17), 2207. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172207






