Genetic Variants Associated with Breast Cancer Are Detected by Whole-Exome Sequencing in Vietnamese Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
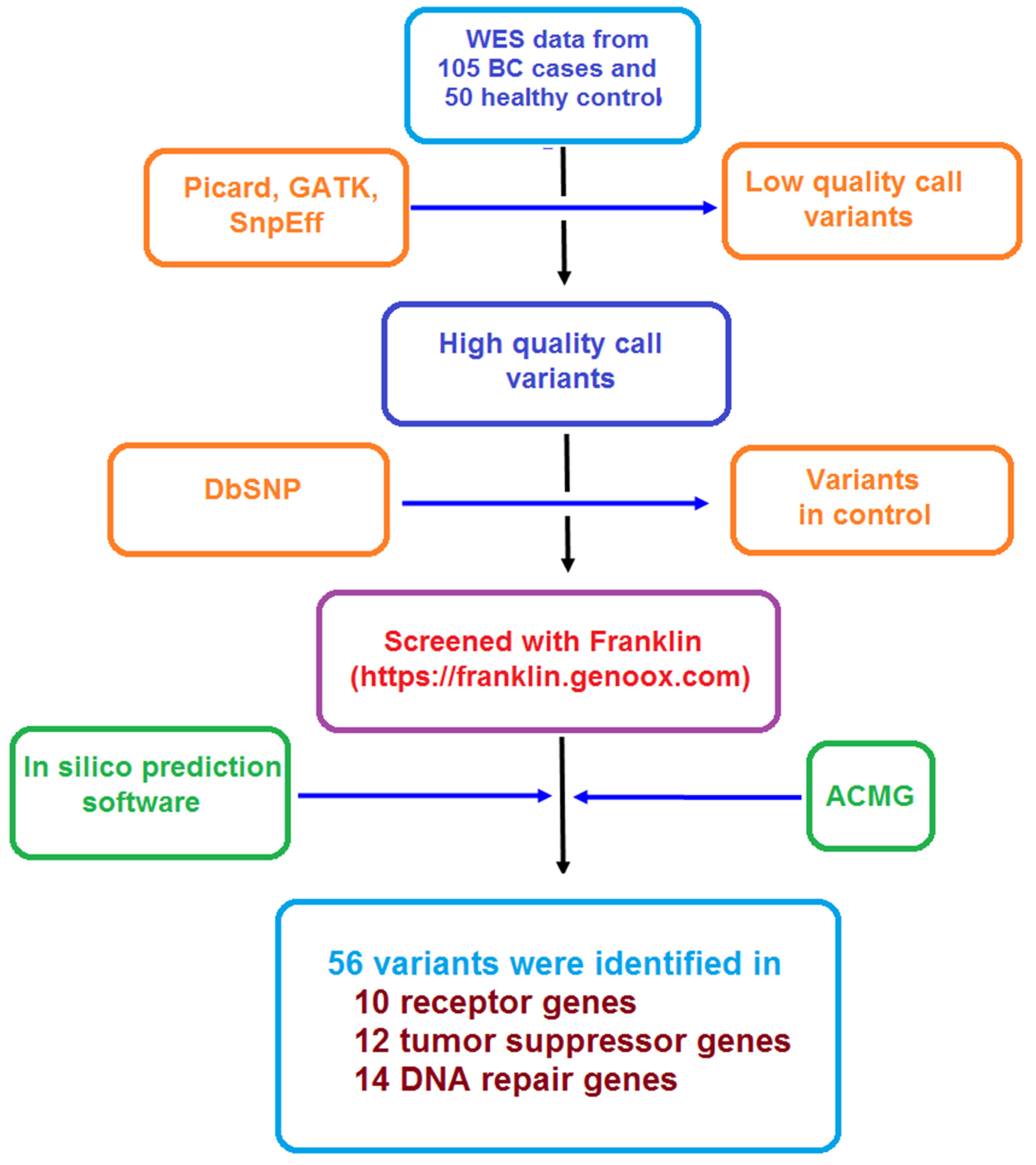
2. Materials and Methods
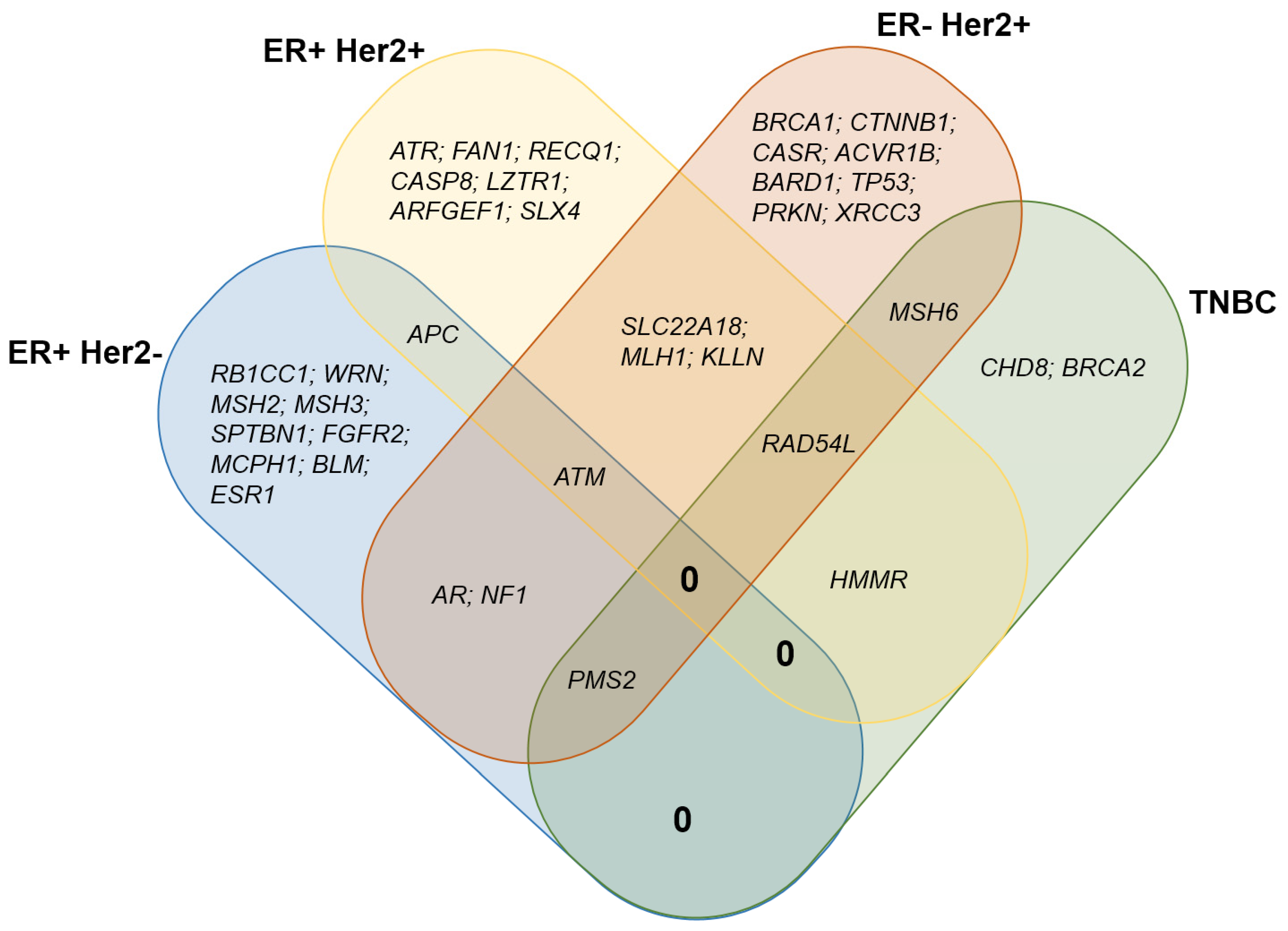
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Receptor Genes
4.2. Tumor-Suppressor Genes
4.3. DNA Repair Genes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginsburg, O.; Bray, F.; Coleman, M.; Vanderpuye, V.; Eniu, A.; Kotha, S.R.; Sarker, M.; Huong, T.T.; Allemani, C.; Dvaladze, A.; et al. The global burden of women’s cancers: A grand challenge in global health. Lancet 2016, 389, 847–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Ervik, M.; Lam, F.; Colombet, M.; Mery, L.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Soerjomataram, I.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Obser-Vatory: Cancer Today; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2020; Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today (accessed on 9 July 2021).
- Wong, F.Y.; Tham, W.Y.; Nei, W.L.; Lim, C.; Miao, H. Age exerts a continuous effect in the outcomes of Asian breast cancer patients treated with breastconserving therapy. Cancer Commun. 2018, 38, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuire, A.; Brown, J.A.L.; Malone, C.; McLaughlin, R.; Kerin, M.J. Effects of age on the detection and management of breast cancer. Cancers 2015, 7, 908–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harbeck, N.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Cortes, J.; Gnant, M.; Houssami, N.; Poortmans, P.; Ruddy, K.; Tsang, J.; Cardoso, F. Breast cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2019, 5, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M.; Das, D.; Pandey, M. Understanding genetic variations associated with familial breast cancer. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2024, 22, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Duan, J.J.; Bian, X.W.; Yu, S.C. Triple-negative breast cancer molecular subtyping and treatment progress. Breast Cancer Res. 2020, 22, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.X.; Gong, Y.; Ling, H.; Hu, X.; Shao, Z.M. Racial/ethnic differences in the outcomes of patients with metastatic breast cancer: Contributions of demographic, socioeconomic, tumor and metastatic characteristics. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 173, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiyanbola, O.O.; Arao, R.F.; Miglioretti, D.L.; Sprague, B.L.; Hampton, J.M.; Stout, N.K.; Kerlikowske, K.; Braithwaite, D.; Buist, D.S.; Egan, K.M.; et al. Emerging trends in family history of breast cancer and associated risk. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2017, 26, 1753–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglia, M.L.; Tang, M.T.C.; Malone, K.E.; Porter, P.; Li, C.I. Family history and risk of second primary breast cancer after in situ breast carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2018, 27, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Chen, S.; Liu, C.; Li, J.; Wei, X.; Jia, M.; Guo, J.; Jin, J.; Meng, D.; Zhi, X. SPTBN1 inhibits growth and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer by downregulating miR-21. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 909, 174401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrucelli, N.; Daly, M.B.; Pal, T. BRCA1- and BRCA2-Associated hereditary breast and ovarian cancer. In GeneReviews® [Internet]; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Couch, F.J.; Shimelis, H.; Hu, C.; Hart, S.N.; Polley, E.C.; Na, J.; Hallberg, E.; Moore, R.; Thomas, A.; Lilyquist, J.; et al. Associations between cancer predisposition testing panel genes and breast cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1190–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulkes, W.D. Inherited susceptibility to common cancers. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2143–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiovitz, S.; Korde, L.A. Genetics of breast cancer: A topic in evolution. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easton, D.F.; Pharoah, P.D.; Antoniou, A.C.; Tischkowitz, M.; Tavtigian, S.V.; Nathanson, K.L.; Devilee, P.; Foulkes, W.D. Gene-panel sequencing and the prediction of breast-cancer risk. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2243–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandler, M.R.; Bilgili, E.P.; Merner, N.D. A review of whole-exome sequencing efforts toward hereditary breast cancer susceptibility gene discovery. Hum. Mutat. 2016, 37, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolenko, A.P.; Suspitsin, E.N.; Kuligina, E.S.; Bizin, I.V.; Frishman, D.; Imyanitov, E.N. Identification of novel hereditary cancer genes by whole exome sequencing. Cancer Lett. 2015, 369, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, M.; Wang, S.; Ali, N. Advanced approaches to breast cancer classification and diagnosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 632079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Yu, H.; Hemminki, A.; Försti, A.; Sundquist, K.; Hemminki, K. Familial associations of female breast cancer with other cancers. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 141, 2253–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badr, L.K.; Bourdeanu, L.; Alatrash, M.; Bekarian, G. Breast cancer risk factors: A crosscultural comparison between the west and the east. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2018, 19, 2109–2116. [Google Scholar]
- Reiner, A.S.; Sisti, J.; John, E.M.; Lynch, C.F.; Brooks, J.D.; Mellemkjær, L.; Boice, J.D.; Knight, J.A.; Concannon, P.; Capanu, M.; et al. Breast cancer family history and contralateral breast cancer risk in young women: An update from the women’s environmental cancer and radiation epidemiology study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Wen, L.; Niu, M.; Zhao, L.; Guan, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, H. Activin receptors in human cancer: Functions, mechanisms, and potential clinical applications. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 222, 116061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anestis, A.; Zoi, I.; Papavassiliou, A.G.; Karamouzis, M.V. Androgen receptor in breast cancer—Clinical and preclinical research insights. Molecules 2020, 25, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barati Bagherabad, M.; Afzaljavan, F.; Vahednia, E.; Rivandi, M.; Vakili, F.; Hashemi Sadr, S.; Homaei Shandiz, F.; Pasdar, A. Association of Caspase 8 promoter variants and haplotypes with the risk of breast cancer and molecular profile in Iranian population: A case—Control study. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 16435–16444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahednia, E.; Homaei Shandiz, F.; Barati Bagherabad, M.; Moezzi, A.; Afzaljavan, F.; Tajbakhsh, A.; Kooshyar, M.M.; Pasdar, A. The impact of CASP8 rs10931936 and rs1045485 polymorphisms as well as the haplotypes on breast cancer risk: A casecontrol study. Clin. Breast Cancer 2019, 19, e563–e577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afzaljavan, F.; Vahednia, E.; Barati Bagherabad, M.; Vakili, F.; Moezzi, A.; Hosseini, A.; Homaei Shandiz, F.; Mahdi Kooshyar, M.; Nassiri, M.; Pasdar, A. Genetic contribution of caspase-8 variants and haplotypes to breast cancer risk and prognosis: A case-control study in Iran. BMC Med. Genom. 2023, 16, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Clézardin, P.; Kamel, S.; Brazier, M.; Mentaverri, R. The CaSR in pathogenesis of breast cancer: A new target for early stage bone metastases. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Xu, H.; Cheng, Y.; Lin, X.; Zeng, J.; Sun, Y. Calcium-sensing receptor, a potential biomarker revealed by large-scale public databases and experimental verification in metastatic breast cancer. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2024, 23, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, G. PTCH1 and CTNNB1 emerge as pivotal predictors of resistance to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in ER +/HER2- breast cancer. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1216438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altiparmak-Ulbegi, G.; Hasbal-Celikok, G.; Aksoy-Sagirli, P. AKT1 and CTNNB1 mutations as drivers of paclitaxel resistance in breast cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2025, 30, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandarlapaty, S.; Chen, D.; He, W.; Sung, P.; Samoila, A.; You, D.; Bhatt, T.; Patel, P.; Voi, M.; Gnant, M.; et al. Prevalence of ESR1 mutations in cell-free DNA and outcomes in metastatic breast cancer: A secondary analysis of the BOLERO-2 clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 1310–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fribbens, C.; O’Leary, B.; Kilburn, L.; Hrebien, S.; Garcia-Murillas, I.; Beaney, M.; Cristofanilli, M.; Andre, F.; Loi, S.; Loibl, S.; et al. Plasma ESR1 mutations and the treatment of estrogen receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2961–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, P.; Chang, M.T.; Xu, G.; Bandlamudi, C.; Ross, D.S.; Vasan, N.; Cai, Y.; Bielski, C.M.; Donoghue, M.T.A.; Jonsson, P.; et al. The genomic landscape of endocrine-resistant advanced breast cancers. Cancer Cell 2018, 34, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dustin, D.; Gu, G.; Fuqua, S.A.W. ESR1 mutations in breast cancer. Cancer 2019, 125, 3714–3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brett, J.O.; Spring, L.M.; Bardia, A.; Wander, S.A. ESR1 mutation as an emerging clinical biomarker in metastatic hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2021, 23, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fievet, A.; Mouret-Fourme, E.; Colas, C.; de Pauw, A.; Stoppa-Lyonnet, D.; Buecher, B. Prevalence of pathogenic variants of FAN1 in more than 5000 patients assessed for genetic predisposition to colorectal, breast, ovarian, or other cancers. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1919–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, M. Cancer genomics and genetics of FGFR2. Int. J. Oncol. 2008, 33, 233–237. [Google Scholar]
- Wahabi, K.; Perwez, A.; Kamarudheen, S.; Bhat, Z.I.; Mehta, A.; Moshahid, M.; Rizvi, A. Parkin gene mutations are not common, but its epigenetic inactivation is a frequent event and predicts poor survival in advanced breast cancer patients. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.E.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, K.Y.; Park, J.H.; Roh, H.; Park, H.Y.; Kim, W.S. High prevalence of the MLH1 V384D germline mutation in patients with HER2-positive luminal B breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsolami, M.; Aboalola, D.; Malibari, D.; Alghamdi, T.; Alshekhi, W.; Jad, H.; Rumbold-Hall, R.; Altowairqi, A.S.; Bell, S.M.; Alsiary, R.A. The emerging role of MCPH1/BRIT1 in carcinogenesis. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1047588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Brakeleer, S.; De Grève, J.; Desmedt, C.; Joris, S.; Sotiriou, C.; Piccart, M.; Pauwels, I.; Teugels, E. Frequent incidence of BARD1-truncating mutations in germline DNA from triple-negative breast cancer patients. Clin. Genet. 2016, 89, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ye, F.; Liang, Y.; Yang, Q. Breast cancer brain metastasis: Insight into molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 125, 1056–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabir, A.; Qayoom, H.; Haq, B.U.; Abo Mansoor, A.; Abdelrahim, A.; Ahmad, I.; Almilabairy, A.; Ahmad, F.; Mir, M.A. Exploring HMMR as a therapeutic frontier in breast cancer treatment, its interaction with various cell cycle genes, and targeting its overexpression through specific inhibitors. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1361424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankunny, M.; Eng, C. KLLN-mediated DNA damage-induced apoptosis is associated with regulation of p53 phosphorylation and acetylation in breast cancer cells. Cell Death Discovery 2018, 4, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieleba, I.; Smolen, P.; Czukiewska, E.; Szczesniak, D.; Filip, A.A. LZTR1: C.1260+1del variant as a significant predictor of early-age breast cancer development: Case report combined with in silico analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uusitalo, E.; Rantanen, M.; Kallionpaa, R.A.; Poyhonen, M.; Leppavirta, J.; Yla-Outinen, H.; Riccardi, V.M.; Pukkala, E.; Pitkäniemi, J.; Peltonen, S.; et al. Distinctive cancer associations in patients with neurofibromatosis type 1. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 1978–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffith, O.L.; Spies, N.C.; Anurag, M.; Griffith, M.; Luo, J.; Tu, D.; Yeo, B.; Kunisaki, J.; Miller, C.A.; Krysiak, K.; et al. The prognostic effects of somatic mutations in ER-positive breast cancer. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, D.G.R.; Kallionpää, R.A.; Clementi, M.; Trevisson, E.; Mautner, V.F.; Howell, S.J.; Lewis, L.; Zehou, O.; Peltonen, S.; Brunello, A.; et al. Breast cancer in neurofibromatosis 1: Survival and risk of contralateral breast cancer in a five country cohort study. Genet. Med. 2020, 22, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, A.; Proszek, P.; Pascual, J.; Fribbens, C.; Shamsher, M.K.; Kingston, B.; O’Leary, B.; Herrera-Abreu, M.T.; Cutts, R.J.; Garcia-Murillas, I.; et al. Inactivating NF1 mutations are enriched in advanced breast cancer and contribute to endocrine therapy resistance. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 608–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Gao, Y.; Heller, S.L. Breast cancer screening utilization and outcomes in women with neurofibromatosis type 1. Clin. Breast Cancer 2023, 23, e200–e205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Xu, C.; Zhao, Z.; Qin, X.; Xu, H.; Zhang, H. Low expression of SLC22A18 predicts poor survival outcome in patients with breast cancer after surgery. Cancer Epidemiol. 2011, 35, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakker, J.L.; van Mil, S.E.; Crossan, G.; Sabbaghian, N.; De Leeneer, K.; Poppe, B.; Adank, M.; Gille, H.; Verheul, H.; Meijers-Heijboer, H.; et al. Analysis of the novel fanconi anemia gene SLX4/FANCP in familial breast cancer cases. Hum. Mutat. 2013, 34, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, A.M.; Ryan, A.J. ATM and ATR as therapeutic targets in cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 149, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ansari, M.M.; Al-Saif, M.; Arafah, M.; Eldali, A.M.; Tulbah, A.; Al-Tweigeri, T.; Semlali, A.; Khabar, K.S.; Aboussekhra, A. Clinical and functional significance of tumor/stromal ATR expression in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. 2020, 22, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, C.G. Relationship between polymorphisms in homologous recombination repair genes RAD51 G172T, XRCC2 & XRCC3 and risk of breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1047336. [Google Scholar]
- Weigelt, B.; Bi, R.; Kumar, R.; Blecua, P.; Mandelker, D.L.; Geyer, F.C.; Pareja, F.; James, P.A. The landscape of somatic genetic alterations in breast cancers from ATM germline mutation carriers. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 110, 1030–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluzniak, W.; Wokołorczyk, D.; Rusak, B.; Huzarski, T.; Kashyap, A.; Stempa, K.; Rudnicka, H.; Jakubowska, A.; Szwiec, M.; Morawska, S.; et al. Inherited variants in BLM and the risk and clinical characteristics of breast cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Gao, L.; Yin, H.; Jiang, M. BLM mutation is associated with increased tumor mutation burden and improved survival after immunotherapy across multiple cancers. Cancer Med. 2024, 13, e6716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, M.; Lazarus, K.; Santolla, M.F.; Pensa, S.; Williams, E.; Siu, A.J.Q.; Mohammed, H.; Mohorianu, I.; Maggiolini, M.; Carroll, J.; et al. CHD8 interacts with BCL11A to induce oncogenic transcription in triple negative breast cancer. EMBO J. 2025, 44, 3448–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, A.A. The chromodomain helicase DNA-binding chromatin remodelers: Family traits that protect from and promote cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Prespect. Med. 2017, 7, a026450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, M.E.; Jackson, S.A.; Susswein, L.R.; Zeinomar, N.; Ma, X.; Marshall, M.L.; Stettner, A.R.; Milewski, B.; Xu, Z.; Solomon, B.D.; et al. MSH6 and PMS2 germ-line pathogenic variants implicated in Lynch syndrome are associated with breast cancer. Genet. Med. 2018, 20, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cybulski, C.; Carrot-Zhang, J.; Kluźniak, W.; Rivera, B.; Kashyap, A.; Wokołorczyk, D.; Giroux, S.; Nadaf, J.; Hamel, N.; Zhang, S.; et al. Germline RECQL mutations are associated with breast cancer susceptibility. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 643–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helgadottir, H.T.; Thutkawkorapin, J.; Lagerstedt-Robinson, K.; Lindblom, A. Sequencing for germline mutations in Swedish breast cancer families reveals novel breast cancer risk genes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, K.; Chen, Y. Germline RECQL gene mutations in Chinese patients with breast cancer. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1366769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patient Characteristic | Clinical Breast Cancer Pathology Subtypes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Luminal A ER+/Her2- | Luminal B ER+/Her2+ | HER2-Enriched ER-/Her2+ | TNBC | |
| Patient No. (n = 105) | Average age is 49.3 ± 9.7 years old (range of age: 29–73) | |||
| Mean age (SD), y (n) | 50.1 ± 8.9 (n = 26) | 51.8 ± 9.1 (n = 32) | 50.9 ± 8.9 (n = 29) | 43.9 ± 8.1 (n = 18) |
| Range of age at diagnosis of breast cancer (y) | 31–67 | 37–73 | 33–68 | 29–60 |
| Age of patient | Number of patients with/without variant | |||
| <30 | 1 (0/1) | |||
| 31–40 | 4 (1/3) | 5 (4/1) | 6 (3/3) | 6 (3/3) |
| 41–50 | 10 (6/4) | 8 (0/8) | 9 (4/5) | 8 (1/7) |
| 51–60 | 9 (2/7) | 12 (3/9) | 10 (5/5) | 3 (0/3) |
| >60 | 3 (0/3) | 7 (0/7) | 4 (1/3) | |
| Total number of patients with variants (%) | 9 (34.6) | 7 (24.1) | 13 (44.8) | 4 (22.2) |
| Ovarian cancer | 1 | |||
| Thyroid cancer | 1 | |||
| Skin cancer | 1 | |||
| Family history, no. (%) | ||||
| Breast cancer | 5 (19.3) | 4 (12.5) | 2 (6.7) | 4 (22.2) |
| Ovarian cancer | 1 (3.8) | 1 (3.1) | 2 (11.1) | |
| Lung cancer | 3 (11.6) | 4 (12.5) | ||
| Colorectal cancer | 1 (3.8) | 1 (3.1) | 1 (3.4) | |
| Endometrial cancer | 1 (3.8) | 1 (3.1) | 2 (6.7) | 1 (5.6) |
| Other cancer | 1 (3.8) | 3 (9.4) | 4 (13.8) | |
| No cancer family history | 14 (53.9) | 18 (56.3) | 20 (69.4) | 11 (61.1) |
| Patient | Age of Onset/ Subtype | Gene | cDNA/Protein | dbSNP/ClinVar/ACMG | Family History |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UK1 | 45 TNBC | CHD8 | c.6472C>T p.Arg2158Cys | rs371915075/ VUS (PM2, PP2) | - |
| UK2 | 43 ER-/Her2+ | KLLN | c.438delC p.Pro146fs | rs1405023663/ VUS (PM2) | - |
| UK3 | 37 ER+/Her2+ | SLX4 | c.4204C>T p.Gln1402* | Novel/ LP (PVS1) | breast |
| ATM | c.5888A>G p.Asp1963Gly | rs1555110484/ VUS (PM2, PP3) | |||
| UK5 | 60 ER+/Her2+ | RECQL | c.820delT p.Cys274fs | Novel/ LP (PVS1, PM2) | - |
| LZTR1 | c.1646A>G p.Asp549Gly | rs762315626/ VUS (PM2, PP3) | |||
| UK6 | 33 ER-/Her2+ | NF1 | c.4451C>G p.Ser1484Cys | Novel/ VUS (PM2, PP2) | - |
| UK12 | 53 ER+/Her2- | WRN | c.2977C>T p.Arg993Cys | rs749330842/ VUS (PM2) | - |
| UK16 | 47 ER+/Her2- | MSH2 | c.2197G>A p.Ala733Thr | rs772662439/ VUS (PM2, PP3) | breast |
| UB3 | 39 TNBC | RAD54L | c.788G>A p.Gly263Glu | rs186059216/ VUS (PM2, PP3) | uterus |
| UB4 | 40 ER+/Her2+ | FAN1 | c.1822dupG p.Ala608fs | Novel/ LP (PVS1, PM2) | breast |
| UB6 | 54 ER-/Her2+ | CTNNB1 | c.1345C>T p.Arg449Cys | rs771596917/ VUS (PM2, PP2) | - |
| UB7 | 50 ER-/Her2+ | BARD1 | c.1620A>T p.Lys540Asn | rs747076015/ VUS (PM2) | - |
| MSH6 | c.944C>G p.Ser315Cys | rs63750491/ VUS (PM2) | |||
| UB12 | 56 ER+/Her2+ | ATR | c.4352G>A p.Arg1451Gln | rs371919176/ VUS (PM2, PP2) | other |
| UB16 | 73 ER+/Her2+ | KLLN | c.250G>C p.Gly84Arg | rs3758479/ VUS (PM2) | other |
| UB17 | 54 ER+/Her2+ | MLH1 | c.776T>C p.Leu259Ser | rs56250509/ Pathogenic VUS (PM2, PP3) | other |
| UB18 | 64 ER-/Her2+ | TP53 | c.1024C>G p.Arg342Gly | Novel/ VUS (PM2) | - |
| UB19 | 51 ER+/Her2+ | RAD54L | c.866G>A p.Ser289Asn | rs371268995/ VUS (PM2) | - |
| UB21 | 44 ER+/Her2- | SPTBN1 | c.109+1G>T | Novel/ VUS (PM2) | ovary |
| NF1 | c.888+5G>A | rs556444929/ VUS (PM2) | |||
| UB23 | 55 ER+/Her2- | NF1 | c.888+5G>A | rs556444929/ VUS (PM2) | - |
| Patient | Age of Onset/ Subtype | Gene | cDNA/Protein | dbSNP/ACMG | Family History |
| UB25 | 53 TNBC | SLC22A18 | c.604A>G p.Ile202Val | rs758404808/ VUS (PM2) | breast |
| UB26 | 62 ER+/Her2+ | APC | c.5290C>G p.Gln1764Glu | rs529543591/ VUS (PM2) | - |
| UB29 | 49 ER-/Her2+ | ATM | c.3190A>G p.Met1064Val | rs79431304/ VUS (BP4) | other |
| UB30 | 62 ER+/Her2+ | HMMR | c.146-4G>A | rs199936654/ VUS (PM2) | uterus |
| UB33 | 49 ER+/Her2- | RB1CC1 | c.4394C>T p.Thr1465Ile | Novel/ VUS (PM2, PP3) | other |
| ATM | c.1683A>T p.Gln561His | Novel/ VUS (PM2) | |||
| APC | c.5105G>A p.Gly1702Glu | rs769273526/ VUS (PM2) | |||
| UB35 | 57 TNBC | PMS2 | c.746_753del p.Asp249Valfs*2 | rs587782710/ P (PVS1, PS4, PM2) | - |
| MSH6 | c.1159G>A p.Asp387Asn | rs746532720/ VUS (PM2) | |||
| HMMR | c.1642C>A p.Gln548Lys | Novel/ VUS (PM2) | |||
| UB36 | 59 ER-/Her2+ | CASR | c.1190G>A p.Gly397Glu | rs1210105383/ LP (PM, PM5, PP, PP3) | ovary |
| UB43 | 39 ER+/Her2+ | CASP8 | c.268C>T p.Pro90Ser | rs1559350009/ VUS (PM2) | ovary |
| HMMR | c.104C>T p.Pro35Leu | rs568662551/ VUS (PM2) | |||
| UB44 | 50 ER-/Her2+ | SLC22A18 | c.28A>C p.Asn10His | rs575087578/ VUS (PM2) | - |
| UB48 | 56 ER+/Her2+ | ATM | c.2838+9C>T | rs370160823/ VUS | - |
| UB49 | 46 TNBC | BRCA2 | c.3861_3864del p.Asn1287Lysfs*5 | rs886040500/ P (PVS1,PS4, PM2) | breast |
| UB52 | 37 ER+/Her2- | ESR1 | c.433G>A p.Gly145Ser | rs201617046/ VUS (PM2) | - |
| UB53 | 35 ER-/Her2+ | ATM | c.8805G>A p.Met2935Ile | rs772621438/ VUS (PP3) | - |
| MLH1 | c.776T>C p.Leu259Ser | rs56250509/ Pathogenic VUS (PM2, PP3) | |||
| UB54 | 45 ER-/Her2+ | ACVR1B | c.899G>C p.Gly300Ala | Novel/ VUS (PM2, PP2) | - |
| AR | c.1009G>C p.Gly337Arg | rs1363782162/ VUS (PM2, PP3) | |||
| UB55 | 56 ER-/Her2+ | XRCC3 | c.85C>T p.His29Tyr | rs546983534/ VUS (PM2) | - |
| UB59 | 49 ER+/Her2- | BLM | c.3558+3A>G | rs766386042/ VUS | - |
| MSH3 | c.3302+4A>C | rs779568504/ VUS | |||
| UB60 | 41 ER+/Her2- | MCPH1 | c.2257G>A p.Gly753Arg | rs587783737/ VUS (PM2) | breast |
| UB62 | 60 ER+/Her2- | FGFR2 | c.1763A>G p.Tyr588Cys | rs770827652/ VUS (PM2, PP2) | other |
| PMS2 | c.229G>A p.Glu77Lys | rs751235177/ VUS (PM2) | |||
| UB63 | 45 ER+/Her2- | AR | c.2182A>G p.Asn728Asp | Novel/ LP (PM1, PM2, PM5, PP2) | uterus |
| UB70 | 40 ER+/Her2+ | ARFGEF1 | c.2699-1G>A | rs200901179/ P (PVS1, PS4) | - |
| MLH1 | c.761A>G p.Lys254Arg | rs786202528/ VUS (PM2, PP3) | |||
| UB76 | 59 ER-/Her2+ | RAD54L | c.788G>A p.Gly263Glu | rs186059216/ VUS (PM2, PP3) | uterus |
| UB77 | 56 ER-/Her2+ | PRKN | c.850G>C p.Gly284Arg | rs751037529/ P (PP1, PP3, PS3, PM2, PM3) | - |
| BRCA1 | c.3083G>A p.Arg1028His | rs80357459/ VUS (BP6) | |||
| UB79 | 37 ER-/Her2+ | BRCA1 | c.1544_1550del p.Glu515Valfs*15 | Novel/ P (PVS1, PS4, PM2) | - |
| Gen | cDNA | Protein | Varity | Mutation Assesor | Mutation Taster | SIFT | Polyphen2 | DANN | Meta | Primate AI | Bayes Del | Geno Canyon | Fit Con | Prediction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHD8 | c.6472C>T | p.Arg2158Cys | D (0.73) | M (2.10) | D (1) | D (0.00) | D (0.84) | D (1) | D (0.91) | D (0.90) | D (0.5) | D (1) | D (0.7) | Pathogenic |
| ATM | c.5888A>G | p.Asp1963Gly | D (0.75) | M (2.52) | D (1) | D (0.01) | - | - | B (0.02) | U (0.57) | U (0.5) | D (1) | D (0.7) | Pathogenic |
| LZTR1 | c.1646A>G | p.Asp549Gly | D (0.73) | M (2.16) | D (1) | D (0.01) | D (1) | - | U (0.50) | D (0.80) | D (0.2) | D (1) | D (0.7) | Pathogenic |
| NF1 | c.4451C>G | p.Ser1484Cys | D (0.68) | M (0.02) | D (1) | D (0.01) | - | - | D (0.59) | U (0.78) | U (0.0) | D (0.97) | D (0.6) | Pathogenic |
| WRN | c.2977C>T | p.Arg993Cys | D (0.85) | H (3.80) | D (1) | D (0.00) | D (1) | D (1) | B (0.31) | B (0.41) | U (0.1) | D (1) | D (0.7) | Pathogenic |
| MSH2 | c.2197G>A | p.Ala733Thr | D (0.87) | H (3.60) | D (1) | D (0.01) | D (0.96) | D (1) | D (0.81) | U (0.76) | D (0.2) | D (1) | D (0.7) | Pathogenic |
| RAD54L | c.788G>A | p.Gly263Glu | D (0.72) | M (2.32) | D (1) | D (0.01) | D (0.84) | D (1) | D (0.81) | U (0.63) | D (0.3) | D (1) | D (0.7) | Pathogenic |
| CTNNB1 | c.1345C>T | p.Arg449Cys | D (0.72) | M (2.50) | D (1) | U (0.05) | D (0.64) | D (1) | D (0.56) | D (0.94) | D (0.2) | - | D (0.6) | Pathogenic |
| BARD1 | c.1620A>T | p.Lys540Asn | D (0.42) | M (2.36) | D (0.97) | D (0.00) | D (0.97) | D (0.9) | D (0.64) | B (0.43) | B (−0.33) | B (0) | D (0.7) | Pathogenic |
| MSH6 | c.944C>G | p.Ser315Cys | B (0.09) | L (1.61) | B (0.13) | U (0.04) | D (0.61) | D (0.9) | D (0.54) | B (0.27) | B (−0.21) | D (1) | D (0.6) | Conflict |
| ATR | c.4352G>A | p.Arg1451Gln | B (0.07) | N (−0.95) | D (1) | B (1) | B (0.01) | D (1) | B (0.01) | B (0.36) | B (−0.68) | D (1) | D (0.7) | B |
| KLLN | c.250G>C | p.Gly84Arg | B (0.11) | N (0) | B (0) | B (0.59) | U (0.27) | D (0.8) | B (0.04) | B (0.31) | B (−0.53) | - | B (0.0) | B |
| MLH1 | c.776T>C | p.Leu259Ser | D (0.92) | L (1.84) | D (1) | D (0) | D (1) | D (1) | B (0.29) | U (0.67) | D (0.2) | D (1) | D (0.7) | Pathogenic |
| TP53 | c.1024C>G | p.Arg342Gly | D (0.81) | M (2.40) | B (0) | U (0.05) | - | D (1) | D (0.77) | B (0.27) | U (−0.08) | B (0) | D (0.7) | Conflict |
| RAD54L | c.866G>A | p.Ser289Asn | B (0.06) | N (0.56) | D (0.74) | B (0.21) | B (0.01) | D (0.9) | D (0.55) | B (0.44) | B (−0.37) | B (0) | D (0.7) | Conflict |
| SLC22A18 | c.604A>G | p.Ile202Val | B (0.06) | M (2.16) | B (0.43) | B (0.12) | U (0.25) | D (0.9) | B (0.33) | B (0.45) | B (−0.41) | B (0.34) | D (0.7) | B |
| APC | c.5290C>G | p.Gln1764Glu | B (0.1) | L (0.81) | B (0) | D (0.01) | B (0.29) | D (0.9) | B (0.49) | B (0.37) | B (−0.21) | D (1) | D (0.7) | B |
| ATM | c.3190A>G | p.Met1064Val | B (0.21) | M (2.14) | B (0) | U (0.07) | B (0) | B (0.4) | B (0.16) | B (0.27) | B (−0.40) | B (0) | D (0.6) | B |
| RB1CC1 | c.4394C>T | p.Thr1465Ile | D (0.47) | N (0) | D (1) | D (0.00) | - | D (1) | B (0.06) | D (0.79) | B (−0.34) | D (1) | D (0.7) | Pathogenic |
| ATM | c.1683A>T | p.Gln561His | B (0.04) | L (1.60) | B (0) | B (0.33) | - | D (0.9) | B (0.13) | B (0.33) | B (−0.45) | D (0.60) | D (0.7) | B |
| APC | c.5105G>A | p.Gly1702Glu | B (0.09) | N (0) | B (0) | B (0.44) | B (0) | D (0.9) | B (0.39) | B (0.33) | B (−0.32) | B (0) | D (0.7) | B |
| MSH6 | c.1159G>A | p.Asp387Asn | B (0.21) | N (0.63) | D (1) | B (0.27) | - | D (0.9) | B (0.40) | B (0.32) | B (−0.38) | D (1) | D (0.6) | Conflict |
| HMMR | c.1642C>A | p.Gln548Lys | B (0.06) | L (1.52) | B (0.08) | B (0.12) | - | D (0.8) | B (0.02) | B (0.37) | B (−0.62) | D (0.97) | D (0.7) | B |
| CASP8 | c.268C>T | p.Pro90Ser | B (0.28) | M (2.02) | B (0.46) | D (0.01) | - | D (1) | D (0.69) | B (0.41) | U (−0.14) | D (1) | D (0.7) | Conflict |
| HMMR | c.104C>T | p.Pro35Leu | B (0.16) | M (2.56) | D (1) | U (0.09) | D (1) | D (1) | B (0.07) | U (0.52) | B (−0.36) | D (1) | D (0.7) | Conflict |
| ESR1 | c.433G>A | p.Gly145Ser | B (0.12) | L (0.26) | D (0.96) | B (0.24) | D (0.87) | D (0.9) | B (0.02) | U (0.55) | B (−0.47) | D (1) | B (0.4) | B |
| ATM | c.8805G>A | p.Met2935Ile | D (0.54) | M (2.69) | D (1) | U (0.05) | D (0.90) | D (0.9) | D (0.66) | U (0.69) | B (−0.07) | D (1) | D (0.7) | Pathogenic |
| MLH1 | c.776T>C | p.Leu259Ser | D (0.92) | L (1.84) | D (1) | D (0) | D (0.97) | D (0.9) | B (0.29) | U (0.67) | D (0.2) | D (1) | D (0.7) | Pathogenic |
| ACVR1B | c.899G>C | p.Gly300Ala | - | - | - | D (0) | - | B (0.5) | D (0.52) | B (0.44) | B (−0.37) | D (1) | D (0.5) | Conflict |
| AR | c.1009G>C | p.Gly337Arg | B (0.15) | - | B (0.2) | B (0.17) | - | D (1) | D (0.92) | U (0.60) | D (0.46) | D (1) | - | Conflict |
| XRCC3 | c.85C>T | p.His29Tyr | B (0.04) | M (1.94) | B (0) | B (0.11) | U (0.21) | D (0.8) | B (0.08) | B (0.22) | B (−0.41) | D (1) | - | B |
| MCPH1 | c.2257G>A | p.Gly753Arg | B (0.25) | M (2.35) | D (0.98) | U (0.06) | D (1) | D (1) | B (0.05) | B (0.45) | B (−0.29) | D (1) | D (0.7) | Conflict |
| FGFR2 | c.1763A>G | p.Tyr588Cys | D (0.68) | L (1.78) | D (1) | D (0.00) | - | D (0.9) | D (0.58) | D (0.82) | U (0.02) | D (1) | D (0.7) | Pathogenic |
| PMS2 | c.229G>A | p.Glu77Lys | D (0.72) | L (1.14) | D (1) | D (0.00) | D (0.98) | D (0.9) | B (0.33) | U (0.58) | U (0.00) | D (1) | D (0.7) | Pathogenic |
| MLH1 | c.761A>G | p.Lys254Arg | D (0.58) | L (1.77) | D (1) | U (0.03) | - | D (1) | B (0.33) | U (0.60) | U (0.13) | D (1) | D (0.7) | Pathogenic |
| RAD54L | c.788G>A | p.Gly263Glu | D (0.72) | M (2.32) | D (1) | D (0.00) | D (0.84) | D (1) | D (0.81) | U (0.63) | D (0.39) | D (1) | D (0.7) | Pathogenic |
| BRCA1 | c.3083G>A | p.Arg1028His | B (0.01) | N (−1.15) | D (0.65) | B (0.29) | B (0) | D (0.8) | B (0.06) | B (0.18) | B (−0.31) | D (1) | D (0.7) | B |
| ID | Gene | Variant | HSF (%) | MaxEnt (%) | Prediction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UB21 | SPTBN1 | c.109+1G>T | −28.00 | −83.27 | Broken donor site |
| NF1 | c.888+5G>A | - | - | - | |
| UB23 | NF1 | c.888+5G>A | - | - | - |
| UB30 | HMMR | c.146-4G>A | - | - | - |
| UB48 | ATM | c.2838+9C>T | - | - | - |
| UB59 | BLM | c.3558+3A>G | −22.92 | −74.69 | Broken donor site |
| MSH3 | c.3302+4A>C | −12.16 | −44.85 | Broken donor site |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Van Tung, N.; Lien, N.T.K.; Huan, L.D.; Phuong, P.C.; Mai, B.B.; Mai, N.T.H.; Huong, T.T.T.; Huyen, P.T.; Van Chu, N.; Van Dung, T.; et al. Genetic Variants Associated with Breast Cancer Are Detected by Whole-Exome Sequencing in Vietnamese Patients. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2187. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172187
Van Tung N, Lien NTK, Huan LD, Phuong PC, Mai BB, Mai NTH, Huong TTT, Huyen PT, Van Chu N, Van Dung T, et al. Genetic Variants Associated with Breast Cancer Are Detected by Whole-Exome Sequencing in Vietnamese Patients. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(17):2187. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172187
Chicago/Turabian StyleVan Tung, Nguyen, Nguyen Thi Kim Lien, Le Duc Huan, Pham Cam Phuong, Bui Bich Mai, Nguyen Thi Hoa Mai, Tran Thi Thanh Huong, Phung Thi Huyen, Nguyen Van Chu, Tran Van Dung, and et al. 2025. "Genetic Variants Associated with Breast Cancer Are Detected by Whole-Exome Sequencing in Vietnamese Patients" Diagnostics 15, no. 17: 2187. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172187
APA StyleVan Tung, N., Lien, N. T. K., Huan, L. D., Phuong, P. C., Mai, B. B., Mai, N. T. H., Huong, T. T. T., Huyen, P. T., Van Chu, N., Van Dung, T., Huy, L. H., Kien, D. C., Manh, D. V., Long, D. M., Lan, N. N., Hien, N. T., Hanh, H. H., & Hoang, N. H. (2025). Genetic Variants Associated with Breast Cancer Are Detected by Whole-Exome Sequencing in Vietnamese Patients. Diagnostics, 15(17), 2187. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172187







