Tumor Cell Proportion Assessment in Advanced Non-Squamous Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Tissue Samples in Real-World Settings in Japan: The ASTRAL Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Tissue Specimens
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Data Collection
2.3.1. Participating Study Sites
2.3.2. Central Pathology Committee
2.3.3. AI Algorithm
2.4. Endpoints
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients
3.2. Tissue Sampling
3.3. Pathological Findings
3.4. Tumor Cell Proportions
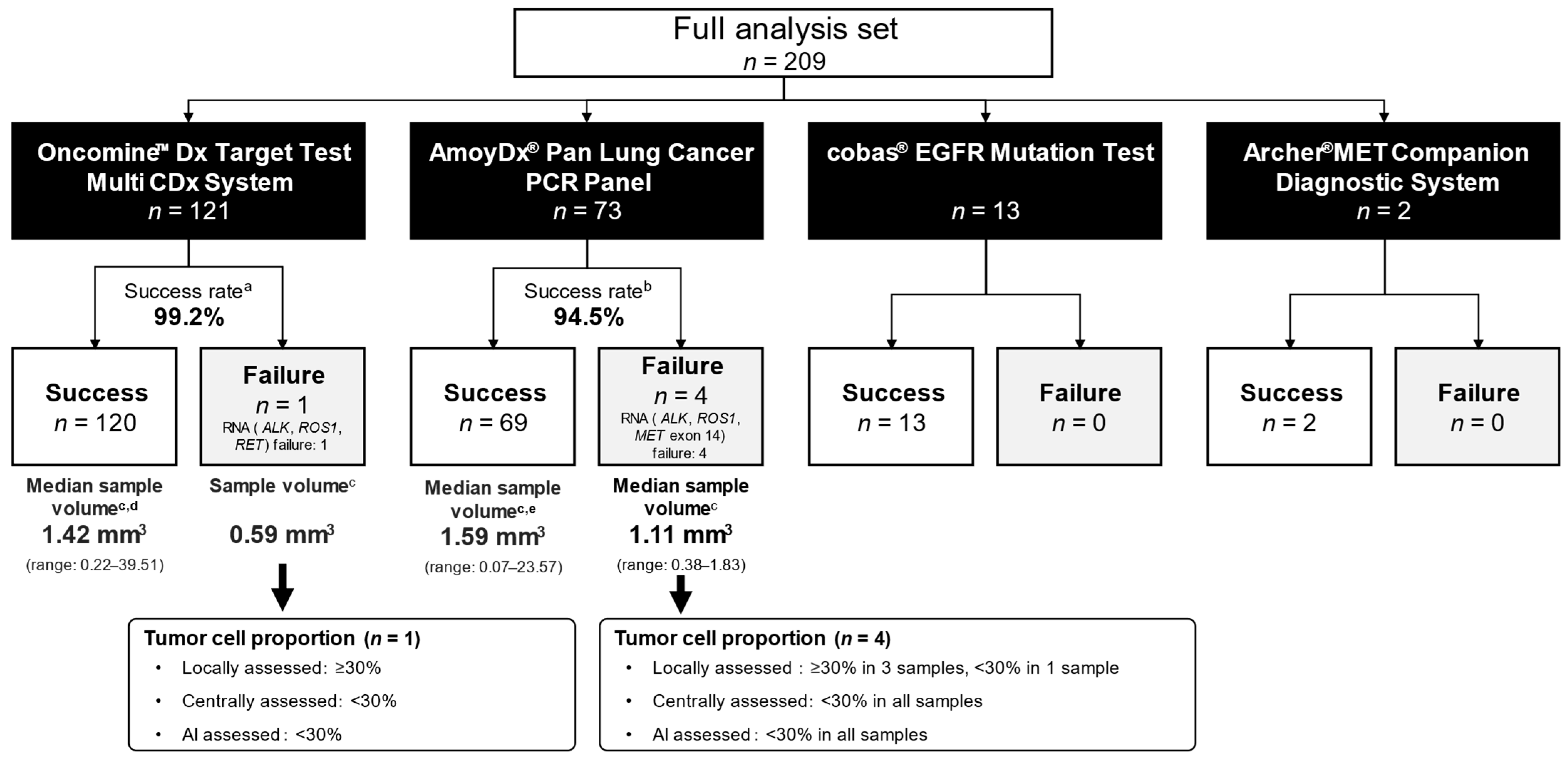
3.5. Biomarker Testing
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| ALK | Anaplastic lymphoma kinase |
| AmoyDx PLC | AmoyDx® Pan Lung Cancer PCR Panel |
| BRAF | V-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B1 |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| EBUS-GS | Endobronchial ultrasound using a guide sheath |
| EBUS-TBNA | Endobronchial ultrasound transbronchial needle aspiration |
| ECOG PS | Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| FAS | Full analysis set |
| FFPE | Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| HER2 | Human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 |
| ICC | Intraclass correlation coefficient |
| KRAS | V-Ki-ras2 Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog |
| MET | Mesenchymal–epithelial transition |
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung cancer |
| NTRK | Neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase |
| Oncomine DxTT | Oncomine™ Dx Target Test Multi CDx System |
| RET | Rearranged during transfection |
| ROS1 | ROS proto-oncogene 1 |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| TCP | Tumor cell proportion analysis set |
References
- NIH National Cancer Institute. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment (PDQ®)—Health Professional Version. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/types/lung/hp/non-small-cell-lung-treatment-pdq#_484856_toc (accessed on 18 April 2025).
- Japan Lung Cancer Society. Guidelines for Diagnosis and Treatment of Lung Cancer—Including Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma and Thymic Tumors 2024. Available online: https://www.haigan.gr.jp/publication/guideline/examination/2024/ (accessed on 18 April 2025). (In Japanese).
- Penault-Llorca, F.; Kerr, K.M.; Garrido, P.; Thunnissen, E.; Dequeker, E.; Normanno, N.; Patton, S.J.; Fairley, J.; Kapp, J.; de Ridder, D.; et al. Expert Opinion on NSCLC Small Specimen Biomarker Testing—Part 2: Analysis, Reporting, and Quality Assessment. Virchows Arch. 2022, 481, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatanaka, Y.; Kuwata, T.; Morii, E.; Kanai, Y.; Ichikawa, H.; Kubo, T.; Hatanaka, K.C.; Sakai, K.; Nishio, K.; Fujii, S.; et al. The Japanese Society of Pathology Practical Guidelines on the Handling of Pathological Tissue Samples for Cancer Genomic Medicine. Pathol. Int. 2021, 71, 725–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Biomarker Committee of The Japan Lung Cancer Society. The Guidance for Biomarker Testing in Lung Cancer Patients. September 2024. Available online: https://www.haigan.gr.jp/publication/guidance/inspection/ (accessed on 18 April 2025). (In Japanese).
- Smits, A.J.; Kummer, J.A.; de Bruin, P.C.; Bol, M.; van den Tweel, J.G.; Seldenrijk, K.A.; Willems, S.M.; Offerhaus, G.J.; de Weger, R.A.; van Diest, P.J.; et al. The Estimation of Tumor Cell Percentage for Molecular Testing by Pathologists Is Not Accurate. Mod. Pathol. 2014, 27, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viray, H.; Li, K.; Long, T.A.; Vasalos, P.; Bridge, J.A.; Jennings, L.J.; Halling, K.C.; Hameed, M.; Rimm, D.L. A Prospective, Multi-Institutional Diagnostic Trial to Determine Pathologist Accuracy in Estimation of Percentage of Malignant Cells. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2013, 137, 1545–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikubo, M.; Seto, K.; Kitamura, A.; Nakaguro, M.; Hattori, Y.; Maeda, N.; Miyazaki, T.; Watanabe, K.; Murakami, H.; Tsukamoto, T.; et al. Calculating the Tumor Nuclei Content for Comprehensive Cancer Panel Testing. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alowais, S.A.; Alghamdi, S.S.; Alsuhebany, N.; Alqahtani, T.; Alshaya, A.I.; Almohareb, S.N.; Aldairem, A.; Alrashed, M.; Bin Saleh, K.; Badreldin, H.A.; et al. Revolutionizing Healthcare: The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Clinical Practice. BMC Med. Educ. 2023, 23, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosatto, E.; Gerard, K.; Graf, H.P.; Ogura, M.; Kiyuna, T.; Hatanaka, K.C.; Matsuno, Y.; Hatanaka, Y. A Multi-Scale Conditional Deep Model for Tumor Cell Ratio Counting. In Proceedings of the SPIE Medical Imaging 2021: Digital Pathology, Online, 15 February 2021; Tomaszewski, J.E., Ward, A.D., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2021; Volume 11603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyuna, T.; Cosatto, E.; Hatanaka, K.C.; Yokose, T.; Tsuta, K.; Motoi, N.; Makita, K.; Shimizu, A.; Shinohara, T.; Suzuki, A.; et al. Evaluating Cellularity Estimation Methods: Comparing AI Counting with Pathologists’ Visual Estimates. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Japanese Society of Pathology; Japanese Society of Digital Pathology; Digital Pathology Technical Standard Review Committee. Digital Pathology System Technical Standard for Pathological Diagnosis, 3rd Edition. 2018. Available online: https://pathology.or.jp/news/pdf/kijjun-181222.pdf (accessed on 18 April 2025). (In Japanese).
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015, Part III of the 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Navab, N., Hornegger, J., Wells, W., Frangi, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonett, D.G. Sample Size Requirements for Estimating Intraclass Correlations with Desired Precision. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1331–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGraw, K.O.; Wong, S.P. Forming Inferences About Some Intraclass Correlation Coefficients. Psychol. Methods 1996, 1, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazdal, D.; Rempel, E.; Oliveira, C.; Allgäuer, M.; Harms, A.; Singer, K.; Kohlwes, E.; Ormanns, S.; Fink, L.; Kriegsmann, J.; et al. Conventional and Semi-Automatic Histopathological Analysis of Tumor Cell Content for Multigene Sequencing of Lung Adenocarcinoma. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 1666–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carretero-Barrio, I.; Pijuan, L.; Illarramendi, A.; Curto, D.; López-Ríos, F.; Estébanez-Gallo, Á.; Castellvi, J.; Granados-Aparici, S.; Compañ-Quilis, D.; Noguera, R.; et al. Concordance in the Estimation of Tumor Percentage in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Using Digital Pathology. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stankovic, B.; Bjørhovde, H.A.K.; Skarshaug, R.; Aamodt, H.; Frafjord, A.; Müller, E.; Hammarström, C.; Beraki, K.; Bækkevold, E.S.; Woldbæk, P.R.; et al. Immune Cell Composition in Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2019, 9, 3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeyasu, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Motoi, N.; Teishikata, T.; Tanaka, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Shinno, Y.; Okuma, Y.; Goto, Y.; Horinouchi, H.; et al. Feasibility of Next-Generation Sequencing (Oncomine™ DX Target Test) for the Screening of Oncogenic Mutations in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 51, 1114–1122, Erratum in Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 51, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemoto, D.; Yokose, T.; Katayama, K.; Murakami, S.; Kato, T.; Saito, H.; Suzuki, M.; Eriguchi, D.; Samejima, J.; Nagashima, T.; et al. Tissue Surface Area and Tumor Cell Count Affect the Success Rate of the Oncomine Dx Target Test in the Analysis of Biopsy Tissue Samples. Thorac. Cancer 2021, 12, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, S.; Yokose, T.; Nemoto, D.; Suzuki, M.; Usui, R.; Nakahara, Y.; Kondo, T.; Kato, T.; Saito, H. Suitability of Bronchoscopic Biopsy Tissue Samples for Next-Generation Sequencing. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariyasu, R.; Uchibori, K.; Ninomiya, H.; Ogusu, S.; Tsugitomi, R.; Manabe, R.; Sakamaoto, H.; Tozuka, T.; Yoshida, H.; Amino, Y.; et al. Feasibility of Next-Generation Sequencing Test for Patients with Advanced NSCLC in Clinical Practice. Thorac. Cancer 2021, 12, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, S.; Otsubo, K.; Yoshida, H.; Ito, K.; Nakamura, A.; Teraoka, S.; Matsumoto, N.; Shiraishi, Y.; Haratani, K.; Tamiya, M.; et al. Real-World Data on NGS Using the Oncomine DxTT for Detecting Genetic Alterations in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: WJOG13019L. Cancer Sci. 2022, 113, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwama, E.; Yamamoto, H.; Okubo, F.; Ijichi, K.; Ibusuki, R.; Shiaraishi, Y.; Yoneshima, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Oda, Y.; Okamoto, I. Evaluation of Appropriate Conditions for Oncomine DxTT Testing of FFPE Specimens for Driver Gene Alterations in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Thorac. Cancer 2023, 14, 2288–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunimasa, K.; Matsumoto, S.; Kawamura, T.; Inoue, T.; Tamiya, M.; Kanzaki, R.; Maniwa, T.; Okami, J.; Honma, K.; Goto, K.; et al. Clinical Application of the AMOY 9-in-1 Panel to Lung Cancer Patients. Lung Cancer 2023, 179, 107190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midha, A.; Dearden, S.; McCormack, R. EGFR Mutation Incidence in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer of Adenocarcinoma Histology: A Systematic Review and Global Map by Ethnicity (mutMapII). Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 2892–2911. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, J.; Masago, K.; Saito, H.; Nishino, K.; Kurata, T.; Itoh, Y.; Yoshimura, Y.; Yabuki, Y.; Dosaka-Akita, H. Biomarker Testing for Personalized, First-Line Therapy in Advanced Nonsquamous Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients in the Real World Setting in Japan: A Retrospective, Multicenter, Observational Study (the BRAVE Study). Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2020, 12, 1758835920904522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, T.; Matsubara, T.; Takahama, T.; Yokoyama, T.; Nakamura, A.; Tokito, T.; Okamoto, T.; Akamatsu, H.; Oki, M.; Sato, Y.; et al. Biomarker Testing in Patients with Unresectable Advanced or Recurrent Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2347700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
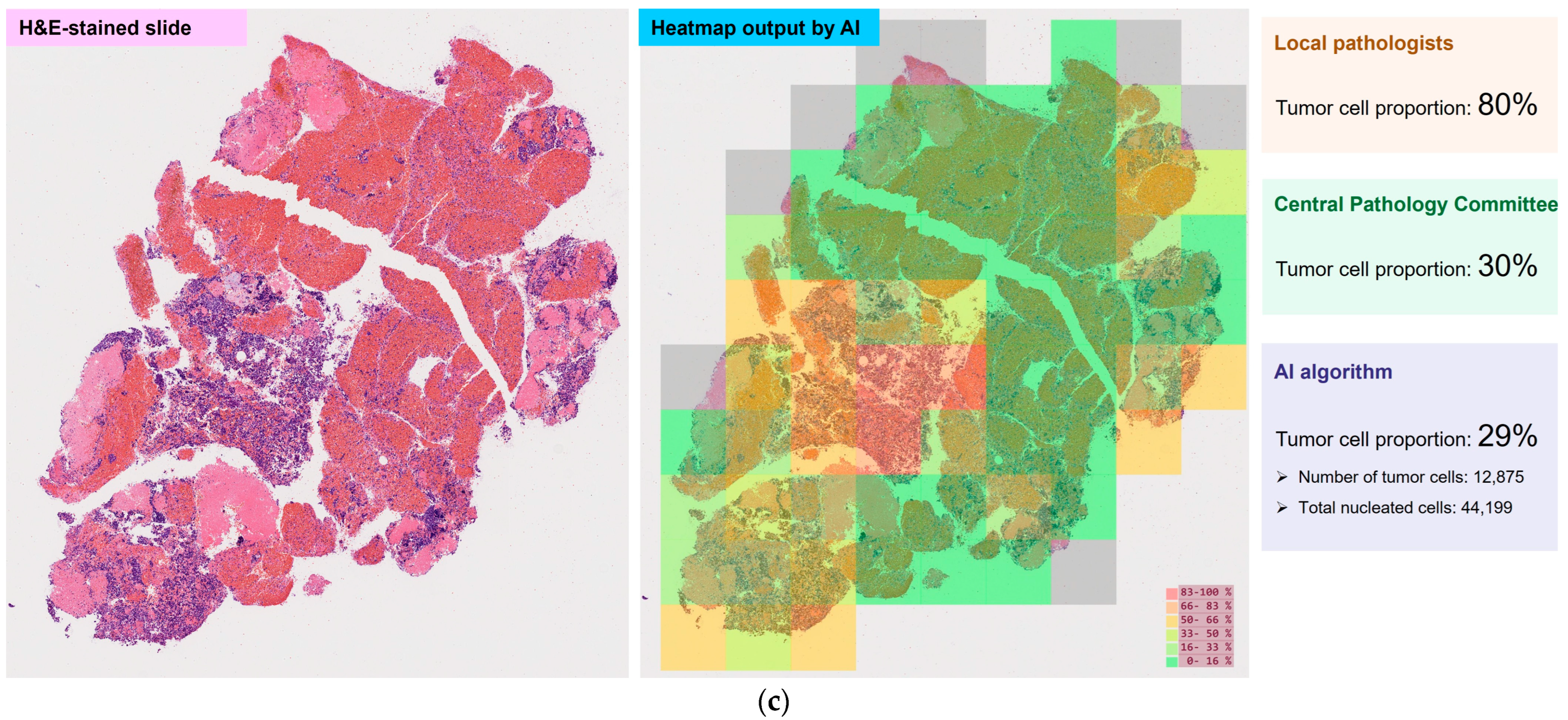

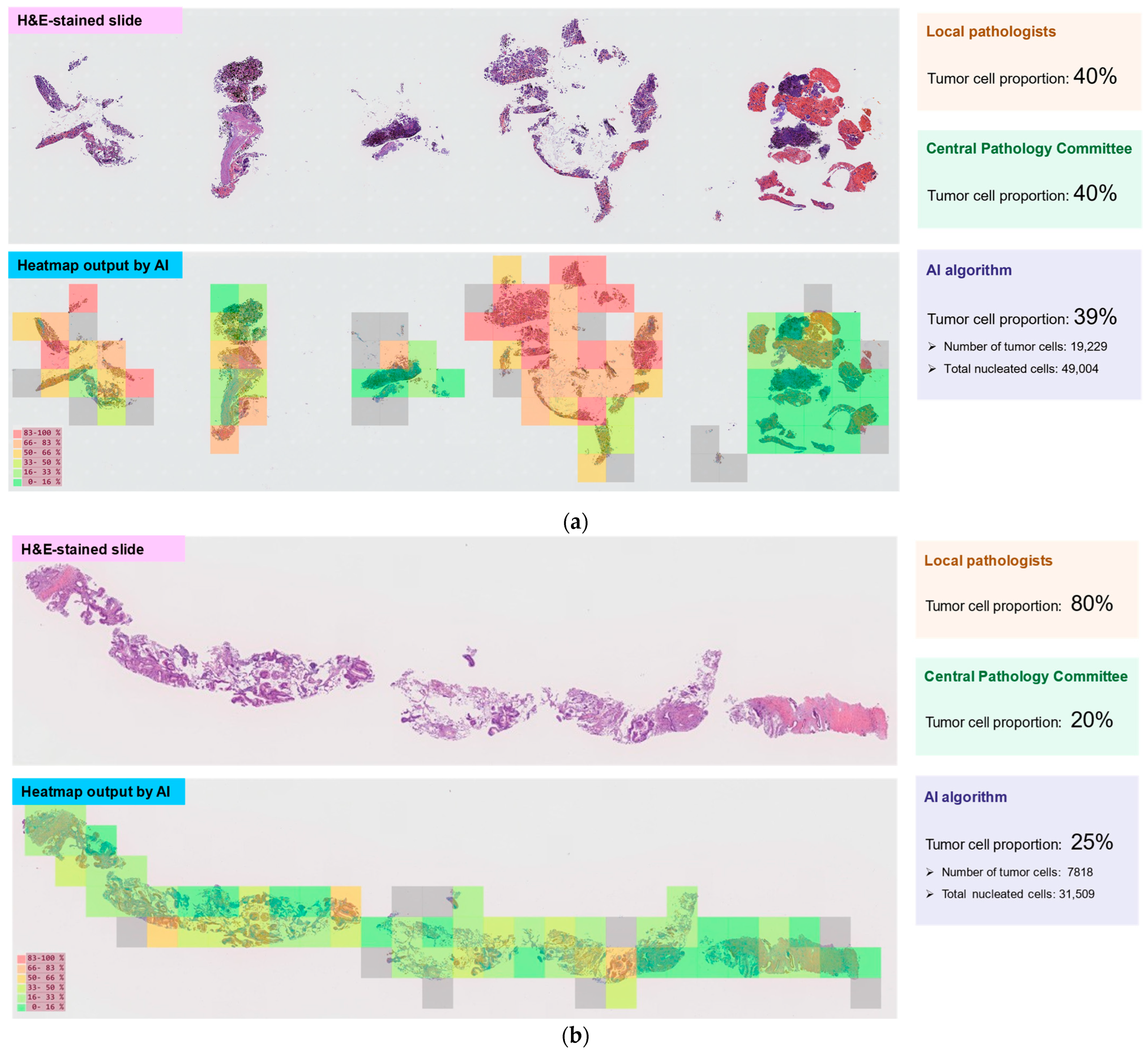

| Full Analysis Set n = 209 | Tumor Cell Proportion Analysis Set n = 204 | |
|---|---|---|
| Age, median (range), y | 70.0 (36.0–90.0) | 70.0 (36.0–90.0) |
| Sex | ||
| Male | 136 (65.1) | 131 (64.2) |
| Female | 73 (34.9) | 73 (35.8) |
| Smoking status | ||
| Current | 35 (16.7) | 34 (16.7) |
| Former | 117 (56.0) | 113 (55.4) |
| Never | 57 (27.3) | 57 (27.9) |
| Histologic type | ||
| Adenocarcinoma | 189 (90.4) | 184 (90.2) |
| Other | 20 (9.6) | 20 (9.8) |
| ECOG PS | ||
| 0 | 83 (39.7) | 82 (40.2) |
| 1 | 106 (50.7) | 103 (50.5) |
| 2 | 15 (7.2) | 14 (6.9) |
| 3 | 3 (1.4) | 3 (1.5) |
| 4 | 2 (1.0) | 2 (1.0) |
| Clinical stage | ||
| IIIB | 3 (1.4) | 3 (1.5) |
| IIIC | 0 | 0 |
| IVA | 67 (32.1) | 66 (32.4) |
| IVB | 119 (56.9) | 117 (57.4) |
| Post-operative recurrence | 20 (9.6) | 18 (8.8) |
| Tumor Cell Proportion Analysis Set n = 204 | |
|---|---|
| Sampling location, n (%) | |
| Primary tumor | 153 (75.0) |
| Lymph node | 38 (18.6) |
| Intrathoracic | 32 |
| Extrathoracic | 6 |
| Metastatic lesion | 13 (6.4) |
| Bone | 5 |
| Brain | 2 |
| Lung | 2 |
| Pleural nodule | 2 |
| Liver | 1 |
| Adrenal gland | 1 |
| Sampling method, n (%) | |
| Surgical resection | 28 (13.7) |
| Bronchoscope biopsy | 157 (77.0) |
| EBUS-GS | 48 |
| EBUS-TBNA | 43 |
| Transbronchial lung biopsy | 43 |
| Endobronchial biopsy | 23 |
| Computed tomography-guided needle biopsy | 16 (7.8) |
| Echo-guided needle biopsy | 2 (1.0) |
| Other a | 1 (0.5) |
| Type of fixing solution, n (%) | |
| 10% neutral buffered formalin solution | 202 (99.0) |
| Other b | 2 (1.0) |
| Fixation time, n (%) | |
| <6 h | 4 (2.0) |
| 6–<12 h | 14 (6.9) |
| 12–<24 h | 177 (86.8) |
| 24–<48 h | 7 (3.4) |
| 48–72 h | 1 (0.5) |
| Unknown | 1 (0.5) |
| Thickness of FFPE sections, mean (SD), μm | 5.00 (0.666) |
| Number of slides submitted for biomarker testing, median (range) | 10.0 (4.0–30.0) |
| Estimated sample volume c, median (range), mm3 | 1.39 (0.06–39.51) |
| Tumor Cell Proportion Analysis Set n = 204 | |
|---|---|
| Inflammatory cells a | |
| None or mild | 37 (18.1) |
| Moderate | 135 (66.2) |
| Severe | 32 (15.7) |
| Fibrosis b | |
| None or mild | 142 (69.6) |
| Moderate | 56 (27.5) |
| Severe | 6 (2.9) |
| Mucus b | |
| None or mild | 199 (97.5) |
| Moderate | 4 (2.0) |
| Severe | 1 (0.5) |
| Necrosis b | |
| None or mild | 192 (94.1) |
| Moderate | 8 (3.9) |
| Severe | 4 (2.0) |
| Crush c | |
| None or mild | 182 (89.2) |
| Moderate | 18 (8.8) |
| Severe | 4 (2.0) |
| Tumor Cell Proportion Analysis Set n = 204 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Local Pathologists vs. Central Pathology Committee | AI Algorithm vs. Central Pathology Committee | AI Algorithm vs. Local Pathologists | |
| Surgical resection (n = 28) | 0.534 (0.217, 0.751) | 0.642 (0.357, 0.817) | 0.330 (0.000, 0.617) |
| Bronchoscope biopsy (n = 157) | 0.603 (0.489, 0.697) | 0.643 (0.500, 0.744) | 0.485 (0.252, 0.644) |
| Computed tomography-guided needle biopsy (n = 16) | 0.558 (0.087, 0.821) | 0.621 (0.205, 0.848) | 0.415 (0.000, 0.750) |
| Tumor Cell Proportion Analysis Set n = 204 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| No or Slight Difference | Moderate Difference | Considerable Difference | |
| Local pathologists vs. Central Pathology Committee | 125 (61.3) | 38 (18.6) | 41 (20.1) |
| AI algorithm vs. Central Pathology Committee | 134 (65.7) | 35 (17.2) | 35 (17.2) |
| AI algorithm vs. local pathologists | 115 (56.4) | 44 (21.6) | 45 (22.1) |
| Oncomine™ Dx Target Test Multi CDx System | AmoyDx® Pan Lung Cancer PCR Panel | cobas® EGFR Mutation Test | Archer®MET Companion Diagnostic System | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EGFR mutation | 35/121 (28.9) | 21/73 (28.8) | 5/13 (38.5) | - |
| ALK fusion | 2/120 (1.7) | 3/69 (4.3) | - | - |
| ROS1 fusion | 0/120 (0.0) | 1/69 (1.4) | - | - |
| BRAF mutation | 0/121 (0.0) | 2/73 (2.7) | - | - |
| RET fusion | 1/120 (0.8) | 0/64 (0.0) | - | - |
| MET exon 14 skipping | 7/114 (6.1) | 1/69 (1.4) | - | 0/2 (0.0) |
| KRAS mutation | 6/115 (5.2) | 6/68 (8.8) | - | - |
| HER2 mutation | 2/115 (1.7) | 1/65 (1.5) | - | - |
| NTRK fusion | 0/114 (0.0) | 0/64 (0.0) | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hatanaka, K.C.; Nishino, K.; Yokose, T.; Tanaka, H.; Motoi, N.; Taguchi, K.; Tamai, Y.; Hirai, T.; Yabuki, Y.; Hatanaka, Y. Tumor Cell Proportion Assessment in Advanced Non-Squamous Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Tissue Samples in Real-World Settings in Japan: The ASTRAL Study. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2165. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172165
Hatanaka KC, Nishino K, Yokose T, Tanaka H, Motoi N, Taguchi K, Tamai Y, Hirai T, Yabuki Y, Hatanaka Y. Tumor Cell Proportion Assessment in Advanced Non-Squamous Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Tissue Samples in Real-World Settings in Japan: The ASTRAL Study. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(17):2165. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172165
Chicago/Turabian StyleHatanaka, Kanako C., Kazumi Nishino, Tomoyuki Yokose, Hiroshi Tanaka, Noriko Motoi, Kenichi Taguchi, Yoichi Tamai, Takehiro Hirai, Yutaka Yabuki, and Yutaka Hatanaka. 2025. "Tumor Cell Proportion Assessment in Advanced Non-Squamous Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Tissue Samples in Real-World Settings in Japan: The ASTRAL Study" Diagnostics 15, no. 17: 2165. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172165
APA StyleHatanaka, K. C., Nishino, K., Yokose, T., Tanaka, H., Motoi, N., Taguchi, K., Tamai, Y., Hirai, T., Yabuki, Y., & Hatanaka, Y. (2025). Tumor Cell Proportion Assessment in Advanced Non-Squamous Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Tissue Samples in Real-World Settings in Japan: The ASTRAL Study. Diagnostics, 15(17), 2165. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172165






