Additive Value of EBUS-TBNA for Staging Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in Patients Evaluated for Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
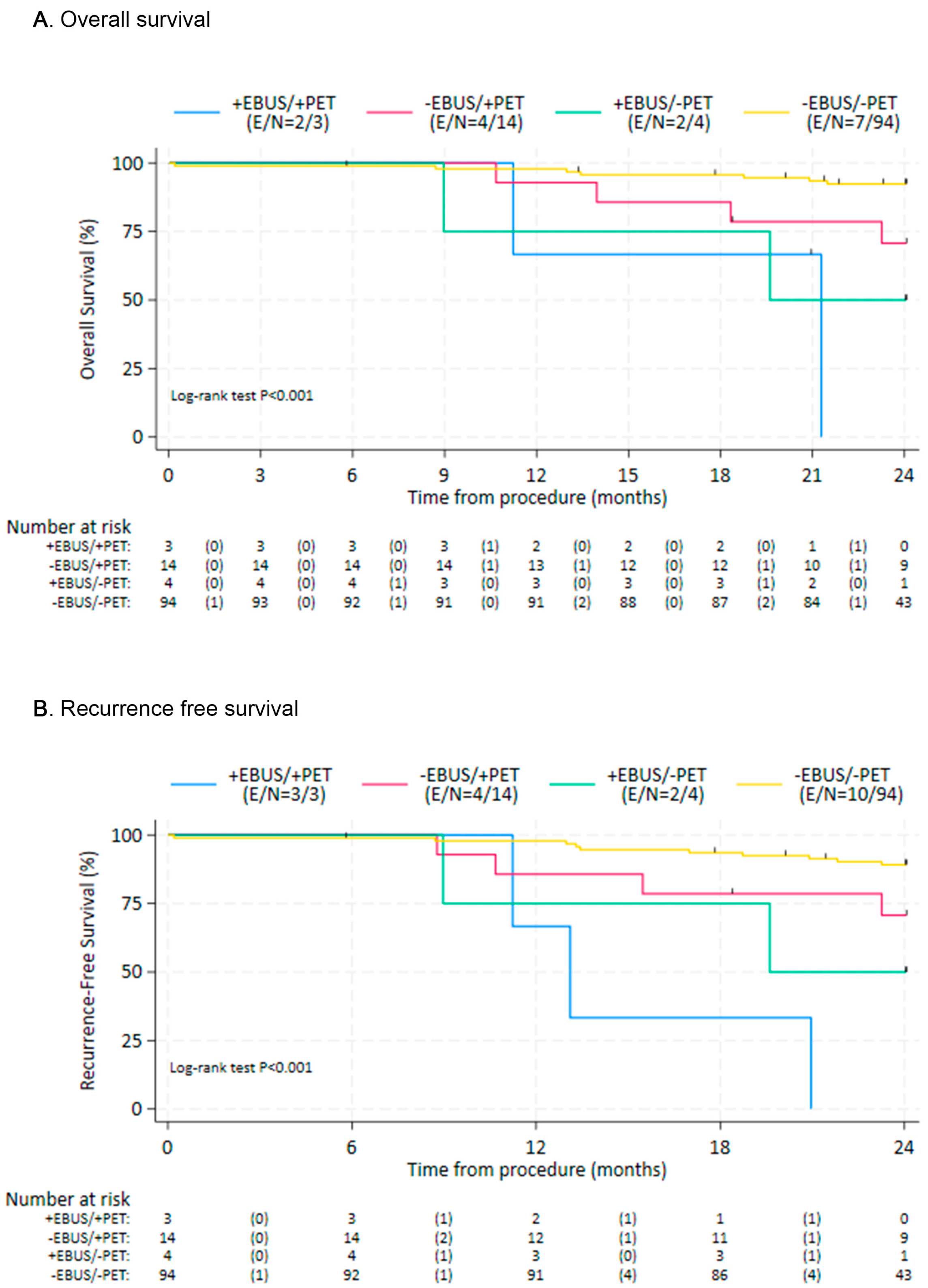
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung cancer |
| SBRT | Stereotactic body radiation therapy |
| PET/CT | Positron emission tomography/computed tomography |
| EBUS-TBNA | Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration |
| PPV | Positive predictive value |
| NPV | Negative predictive value |
| IRB | Institutional Review Board |
| IACUC | Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee |
| DFS | Disease-free survival |
| AJCC | American Joint Commission on Cancer |
| SUV | Standardized uptake value |
| FDG | Fluorodeoxyglucose |
| ROSE | Rapid onsite cytologic evaluation |
| Gy | Gray |
| OS | Overall survival |
| RFS | Recurrence-free survival |
| HR | Hazard ratio |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| cm | Centimeters |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| ECOG | Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group |
| FEV1 | Forced expiratory volume in 1 s |
| DLCO | Diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide |
| NR | Not reached |
| NE | Not estimable |
References
- Timmerman, R.; Paulus, R.; Galvin, J.; Michalski, J.; Straube, W.; Bradley, J.; Fakiris, A.; Bezjak, A.; Videtic, G.; Johnstone, D.; et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for inoperable early stage lung cancer. JAMA 2010, 303, 1070–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, P.; Nyman, J.; Hoyer, M.; Wennberg, B.; Gagliardi, G.; Lax, I.; Drugge, N.; Ekberg, L.; Friesland, S.; Johansson, K.-A.; et al. Outcome in a prospective phase II trial of medically inoperable stage I non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 3290–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, L.L.v.D.; Klinkenberg, T.J.; Groen, H.J.; Widder, J. Patterns of recurrence and survival after surgery or stereotactic radiotherapy for early stage NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senthi, S.; Lagerwaard, F.J.; Haasbeek, C.J.; Slotman, B.J.; Senan, S. Patterns of disease recurrence after stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for early stage non-small-cell lung cancer: A retrospective analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 802–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, P.; Grosu, H.; Eapen, G.A.; Rodriguez, M.; Lazarus, D.; Ost, D.; Jimenez, C.A.; Morice, R.; Bandi, V.; Tamara, L.; et al. Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration for systematic nodal staging of lung cancer in patients with N0 disease by computed tomography and integrated positron emission tomography-computed tomography. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2015, 12, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasufuku, K.; Nakajima, T.; Waddell, T.; Keshavjee, S.; Yoshino, I. Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration for differentiating N0 versus N1 lung cancer. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2013, 96, 1756–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, M.; Yang, X.; Ma, Q.; He, Y. Retrospective analysis for the false positive diagnosis of PET-CT scan in lung cancer patients. Medicine 2017, 96, e7415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moloney, F.; Ryan, D.; McCarthy, L.; McCarthy, J.; Burke, L.; Henry, M.; Kennedy, M.; Hinchion, J.; McSweeney, S.; Maher, M.; et al. Increasing the accuracy of 18F-FDG PET/CT interpretation of “mildly positive” mediastinal nodes in the staging of non-small cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Radiol. 2014, 83, 843–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tournoy, K.G.; Maddens, S.; Gosselin, R.; Van Maele, G.; van Meerbeeck, J.P.; Kelles, A. Integrated FDG-PET/CT does not make invasive staging of the intrathoracic lymph nodes in non-small cell lung cancer redundant: A prospective study. Thorax 2007, 62, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edge, S.B.; Compton, C.C. The American Joint Committee on Cancer: The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging manual and the future of TNM. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 17, 1471–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusch, V.W.; Asamura, H.; Watanabe, H.; Giroux, D.J.; Rami-Porta, R.; Goldstraw, P. The IASLC lung cancer staging project: A proposal for a new international lymph node map in the forthcoming seventh edition of the TNM classification for lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2009, 4, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vial, M.R.; Khan, K.A.; O’cOnnell, O.; Peng, S.A.; Gomez, D.R.; Chang, J.Y.; Rice, D.C.; Mehran, R.; Jimenez, C.J.; Grosu, H.B.; et al. Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration in the nodal staging of stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy patients. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2017, 103, 1600–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Xing, L.; Ma, H.; Xie, P.; Zhang, L.; Xu, X.; Yue, J.; Sun, X.; Hu, X.; et al. Mediastinal lymph nodes staging by 18F-FDG PET/CT for early stage non-small cell lung cancer: A multicenter study. Radiother. Oncol. 2012, 102, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwangbo, B.; Park, E.Y.; Yang, B.; Lee, G.K.; Kim, T.S.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, J.M. Long-term survival according to N stage diagnosed by endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration in non-small cell lung cancer. Chest 2022, 161, 1382–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball, D.; Mai, G.T.; Vinod, S.; Babington, S.; Ruben, J.; Kron, T.; Chesson, B.; Herschtal, A.; Vanevski, M.; Rezo, A.; et al. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy versus standard radiotherapy in stage 1 non-small-cell lung cancer (TROG 09.02 CHISEL): A phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Saynak, M.; Veeramachaneni, N.K.; Fried, D.V.; Jagtap, M.R.; Chiu, W.K.; Higginson, D.S.; Lawrence, M.V.; Khandani, A.H.; Qaqish, B.F.; et al. Non-small cell lung cancer: Prognostic importance of positive FDG PET findings in the mediastinum for patients with N0-N1 disease at pathologic analysis. Radiology 2011, 261, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, V.; Coleman, R.E.; Herndon, J.; Patz, E.F., Jr. The prognostic significance of fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography imaging for patients with nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Cancer 1998, 83, 918–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Age (years), mean ± SD | 72.3 ± 7.6 |
| Gender (n. %) | |
| F | 51 (44.3%) |
| M | 64 (55.7%) |
| Race (n. %) | |
| White | 103 (89.6%) |
| Non-white | 12 (10.4%) |
| Smoking hx (n. %) | |
| Never smoked | 1 (0.9%) |
| Former smoker | 106 (92.2%) |
| Current smoker | 8 (6.9%) |
| ECOG (n. %) | |
| 0 | 54 (47.0%) |
| 1 | 54 (47.0%) |
| >2 | 7 (6.0%) |
| Pulmonary function tests (mean ± SD) | |
| FEV1% | 79.2 ± 24.8 |
| DLCO | 80.7 ± 24.5 |
| Tumor Size (cm), mean ± SD | 2.1 ± 0.9 |
| Tumor centrality (n. %) | |
| Peripheral | 89 (77.4%) |
| Central | 26 (22.6%) |
| Tumor Histology (n. %) | |
| Adenocarcinoma | 86 (74.8%) |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 22 (19.1%) |
| Other malignancies | 7 (6.1%) |
| Tumor FDG Avidity (n. %) | |
| SUV < 2.5 | 23 (20.0%) |
| SUV ≥ 2.5 | 92 (80.0%) |
| EBUS Positive | EBUS Negative | Total | Concordance Rate (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PET/CT Positive | 3 (2.6%) | 14 (12.2%) | 17 | 84.3% (76.4%−90.4%) |
| PET/CT Negative | 4 (3.5%) | 94 (81.7%) | 98 | |
| Total | 7 | 108 | 115 |
| Cohort | N; (Deaths) | Median (95%CI) | HR(95%CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 3 (2) | 21.29 (11.24, NE) | ||
| B | 14 (4) | NR (18.33, NE) | 4.25 (1.24, 14.53) | 0.021 |
| C | 4 (2) | 19.61 (8.97, NE) | ||
| D | 94 (7) | NR | Ref. |
| Cohort | N; (Events) | Median (95%CI) | HR(95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 3 (3) | 13.11 (11.24, NE) | ||
| B | 14 (4) | NR (15.47, NE) | 3.06 (0.96, 9.76) | 0.059 |
| C | 4 (2) | 19.61 (8.97, NE) | ||
| D | 94 (10) | NR | Ref. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boster, J.M.; Goertzen, S.M.; Sainz, P.V.; Vial, M.R.; Zaveri-Desai, J.K.; Luna, L.D.; Waqar, A.; Grosu, H.B.; Casal, R.F.; Jimenez, C.A.; et al. Additive Value of EBUS-TBNA for Staging Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in Patients Evaluated for Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2136. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172136
Boster JM, Goertzen SM, Sainz PV, Vial MR, Zaveri-Desai JK, Luna LD, Waqar A, Grosu HB, Casal RF, Jimenez CA, et al. Additive Value of EBUS-TBNA for Staging Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in Patients Evaluated for Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(17):2136. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172136
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoster, Joshua M., S. Michael Goertzen, Paula V. Sainz, Macarena R. Vial, Jhankruti K. Zaveri-Desai, Luis D. Luna, Anum Waqar, Horiana B. Grosu, Roberto F. Casal, Carlos A. Jimenez, and et al. 2025. "Additive Value of EBUS-TBNA for Staging Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in Patients Evaluated for Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy" Diagnostics 15, no. 17: 2136. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172136
APA StyleBoster, J. M., Goertzen, S. M., Sainz, P. V., Vial, M. R., Zaveri-Desai, J. K., Luna, L. D., Waqar, A., Grosu, H. B., Casal, R. F., Jimenez, C. A., Ost, D. E., Sabath, B. F., Lin, J., Hernandez, M., & Eapen, G. A. (2025). Additive Value of EBUS-TBNA for Staging Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in Patients Evaluated for Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy. Diagnostics, 15(17), 2136. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15172136








