Ultrasound-Guided Hydrodissection with Needle Stabilization: An Innovative Nerve-Sparing Approach to Remove a Contraceptive Implant Causing Ulnar Neuropathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
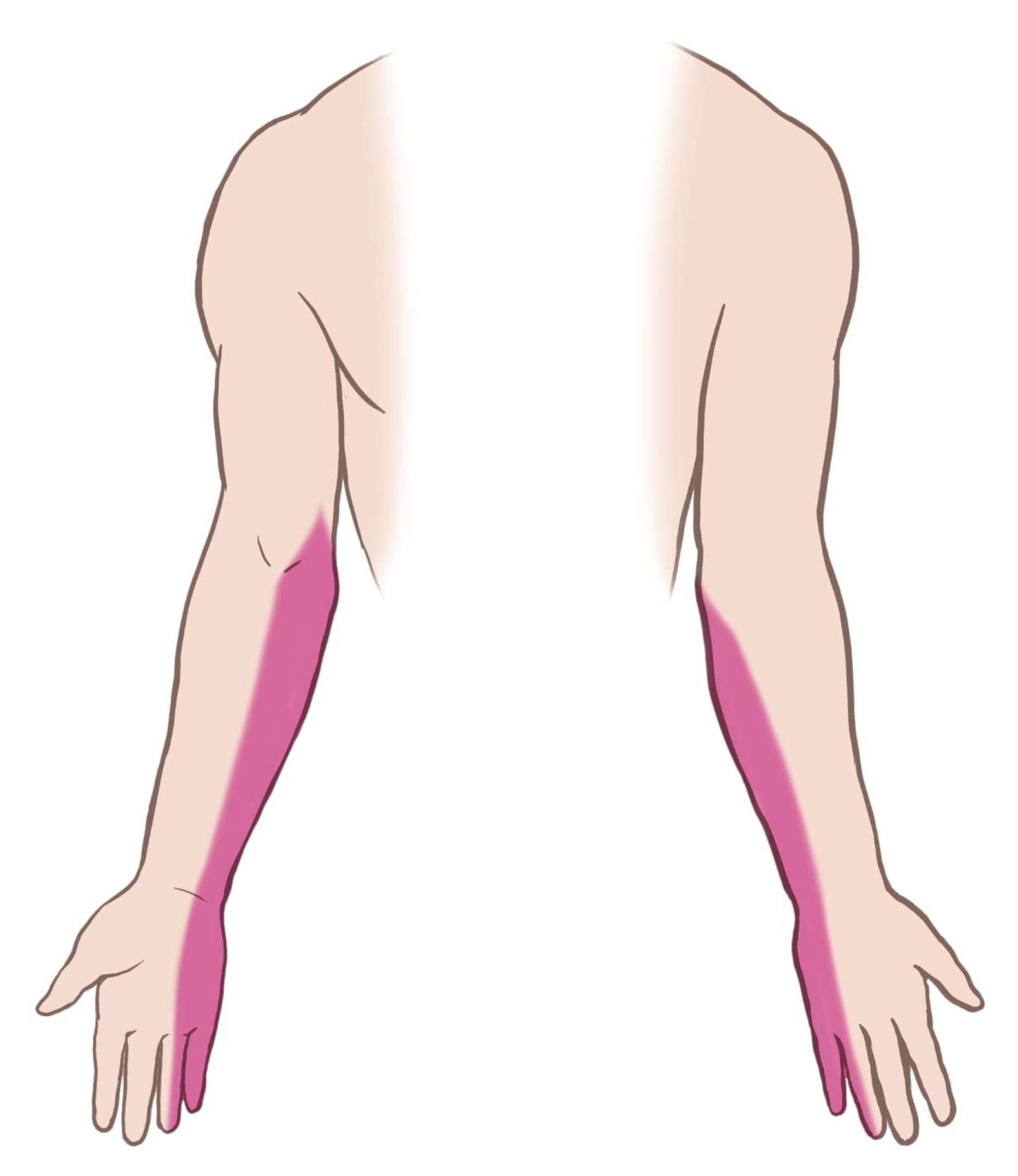
2. Case Presentation
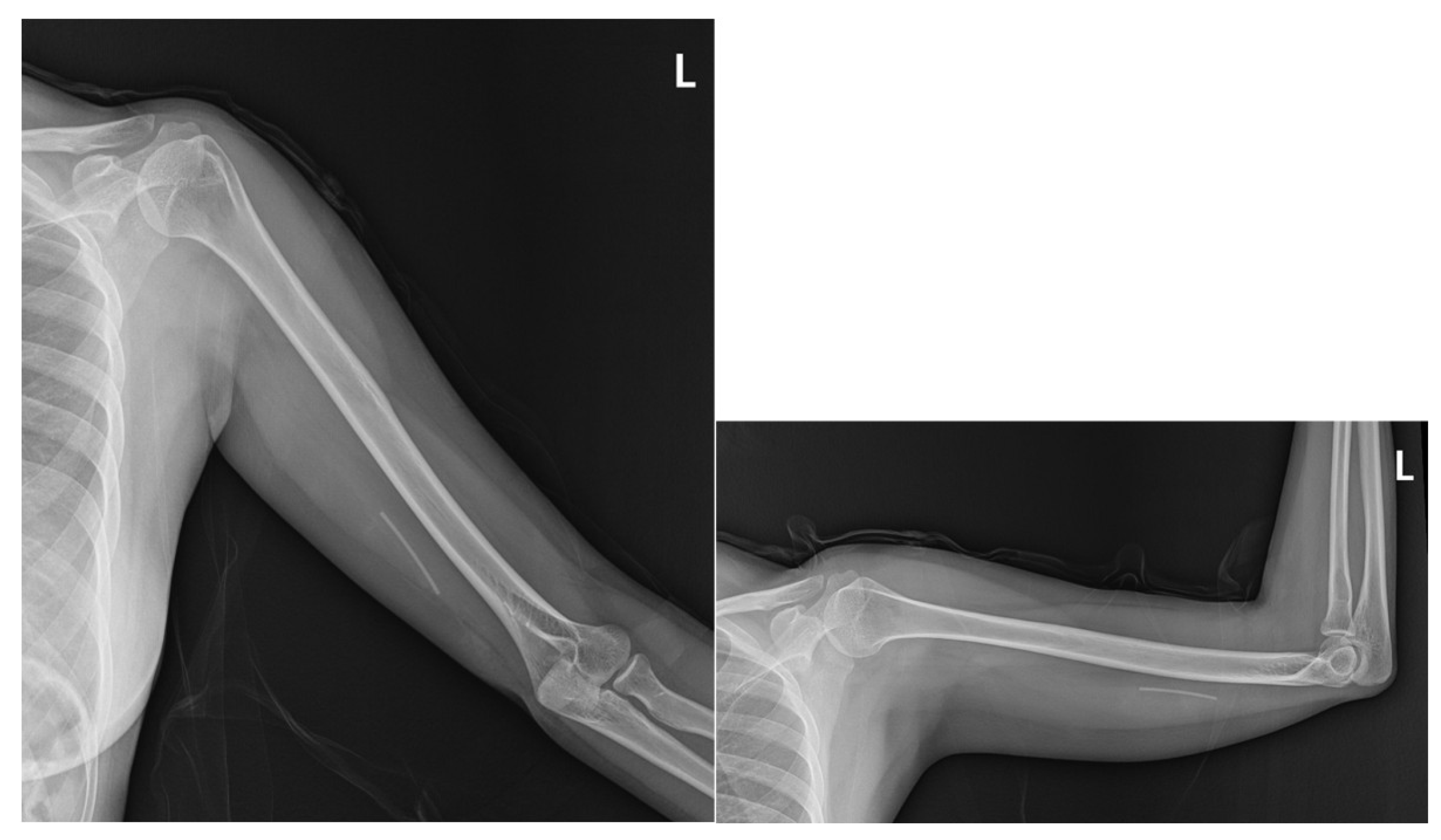
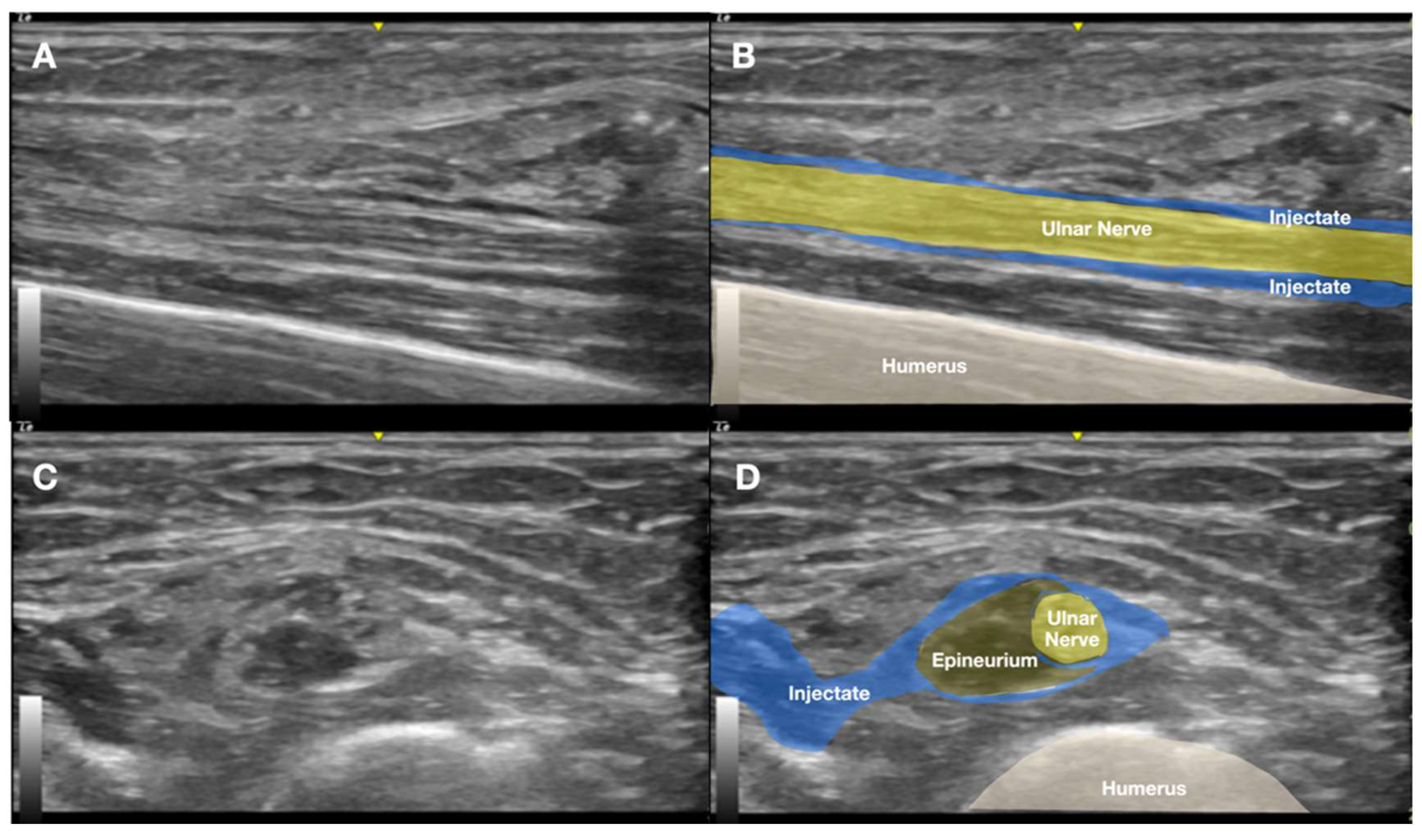
2.1. Prior Imaging Included Radiography (Figure 3), Which Confirmed the Implant’s Location, and Ultrasound (Figure 4), Which Demonstrated Its Proximity to the Ulnar Nerve

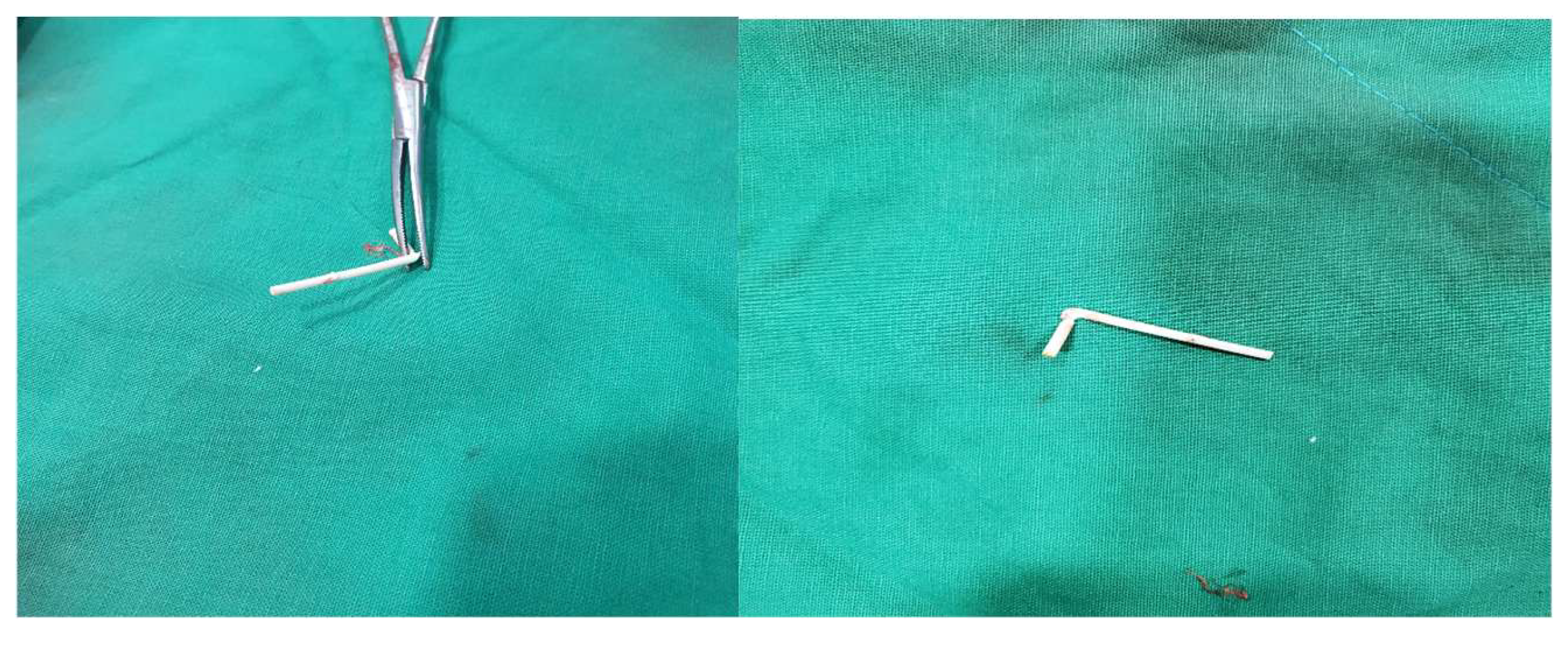
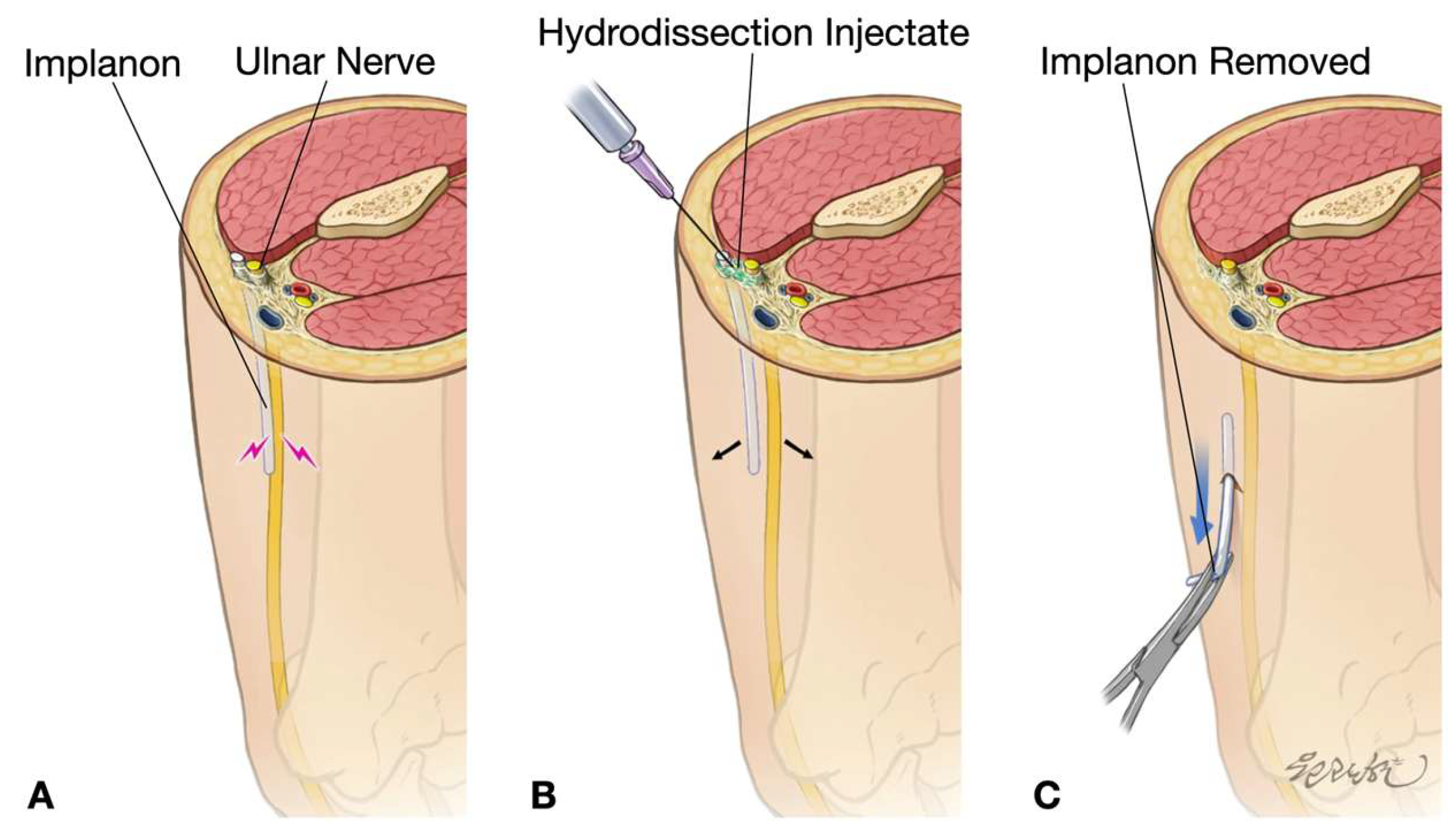
2.2. The Procedure
2.3. Follow-Up and Long-Term Outcomes
3. Discussion
Management Strategies for Non-Palpable or Deeply Placed Implants
4. Conclusions
- Early imaging evaluation: Prompt imaging is essential for non-palpable implants associated with neurological symptoms.
- Specialized technical skills: Proficiency in needle stabilization and HD techniques is crucial for achieving optimal outcomes.
- Centralized referral pathways: Referral systems should be established for complex cases.
Key Lessons
- Prevention potential: Proper insertion technique and post-placement palpation can prevent most migration-related complications [21].
- Technique triad: The combination of (a) 5% dextrose HD, (b) 25G needle stabilization, and (c) real-time US visualization enables successful percutaneous removal of nerve-adherent implants.
- Research priorities: Multicenter registries should track (a) optimal HD volumes, (b) long-term nerve outcomes, and (c) cost–benefit analyses compared to surgery [6].
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HD | Hydrodissection |
| LA | Local anesthetic |
| NPRS | Numeric pain rating scale |
| QuickDASH | Quick Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand |
| US | Ultrasound |
References
- Adler, R.S.; Sofka, C.M. Percutaneous ultrasound-guided injections in the musculoskeletal system. Ultrasound Q. 2003, 19, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatt, D.L.; Charalambous, C.P. Ultrasound-guided barbotage for calcific tendonitis of the shoulder: A systematic review including 908 patients. Arthroscopy 2014, 30, 1166–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.; Mansour, D.; Richardson, D. Location and removal of non-palpable Implanon implants with the aid of ultrasound guidance. BMJ Sex. Reprod. Health 2006, 32, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, F.; Bianciotto, A. Contraceptive subcutaneous device migration: What does an orthopaedic surgeon need to know? A case report and literature review. Acta Bio Medica: Atenei Parm. 2020, 91, 232–237. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UNDESA). Contraceptive Use by Method, Data Booklet 2019. Available online: https://www.un.org/en/development/desa/population/publications/pdf/family/ContraceptiveUseByMethodDataBooklet2019.pdf (accessed on 17 August 2025).
- Soler-Perromat, J.C.; Isern-Kebschull, J.; Del Amo, M.; Bartolomé-Solanas, Á.; Ríos, J.; de Guirior, C.; Carmona, F.; García-Diez, A.-I.; Porta-Vilaró, M.; Tomás, X. Ultrasound-guided minimally invasive removal of deep contraceptive implants: Outcomes and challenges. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2024, 14, 7791–7802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matulich, M.C.; Chen, M.J.; Schimmoeller, N.R.; Hsia, J.K.; Uhm, S.; Wilson, M.D.; Creinin, M.D. Referral Center Experience With Nonpalpable Contraceptive Implant Removals. Obstet. Gynecol. 2019, 134, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques, T.; Brienne, C.; Henry, S.; Baffet, H.; Giraudet, G.; Demondion, X.; Cotten, A. Minimally invasive removal of deep contraceptive implants under continuous ultrasound guidance is effective, quick, and safe. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 1718–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaad, S.K.; Salih, N.M.; Hassan, M.N.; Abid, M.S.; Hamid, H.F.; Ameen Ahmed, N.H.; Muhammad, H.M.; Ghafoor, A.K.; Othman, S.; Kakamad, F.H. Contraceptive implant migration to the ulnar nerve: A case report with literature review. Clin. Case Rep. 2024, 12, e9420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, K.H.S.; Hung, C.Y.; Chiang, Y.P.; Onishi, K.; Su, D.C.J.; Clark, T.B.; Reeves, K.D. Ultrasound-Guided Nerve Hydrodissection for Pain Management: Rationale, Methods, Current Literature, and Theoretical Mechanisms. J. Pain Res. 2020, 13, 1957–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugroho, N.; Lam, K.H.S.; Tandiono, T.; Suryadi, T.; Suhaimi, A.; Ratnawati, W.; Su, D.C.-J.; Yoon, Y.; Reeves, K.D. Novel Sonoguided Digital Palpation and Ultrasound-Guided Hydrodissection of the Long Thoracic Nerve for Managing Serratus Anterior Muscle Pain Syndrome: A Case Report with Technical Details. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.W.; Hwang, J.; Park, C.; Lee, M.; Yoon, Y.; Seo, Y.-S.; Yu, H.; Park, R.; Shim, J.; Ann, J.; et al. Confirming the Presence of Neurapraxia and Its Potential for Immediate Reversal by Novel Diagnostic and Therapeutic Ultrasound-Guided Hydrodissection Using 5% Dextrose in Water Without Local Anesthetics: Application in a Case of Acute Radial Nerve Palsy. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, D.C.J.; Chang, K.V.; Lam, S.K.H. Shear Wave Elastography to Guide Perineural Hydrodissection: Two Case Reports. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, H.; Kyriazis, M.; Reeves, K.D.; Lyftogt, J.; Rabago, D. Topical mannitol reduces capsaicin-induced pain: Results of a pilot-level, double-blind, randomized controlled trial. PM&R 2015, 7, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Wang, W.; Zhao, S.; Chen, S.; Chen, H.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Qian, H.; Tian, X. Discovery of first-in-class highly selective TRPV1 antagonists with dual analgesic and hypoglycemic effects. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2024, 107, 117750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherng, J.H.; Chang, S.J.; Tsai, H.D.; Chun, C.F.; Fan, G.Y.; Reeves, K.D.; Lam, K.H.S.; Wu, Y.T. The Potential of Glucose Treatment to Reduce Reactive Oxygen Species Production and Apoptosis of Inflamed Neural Cells In Vitro. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.T.; Chen, Y.P.; Lam, K.H.S.; Reeves, K.D.; Lin, J.A.; Kuo, C.Y. Mechanism of Glucose Water as a Neural Injection: A Perspective on Neuroinflammation. Life 2022, 12, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei-Ghazani, A.; Moradnia, S.; Azar, M.; Forogh, B.; Ahadi, T.; Chaibakhsh, S.; Khodabandeh, M.; Eftekharsadat, B. Ultrasound-guided 5% dextrose prolotherapy versus corticosteroid injection in carpal tunnel syndrome: A randomized, controlled clinical trial. Pain Manag. 2022, 12, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topol, G.A.; Pestalardo, I.G.; Reeves, K.D.; Elias, F.; Steinmetz, N.J.; Cheng, A.L.; Rabago, D. Dextrose Prolotherapy for Symptomatic Grade IV Knee Osteoarthritis: A Pilot Study of Early and Longer-Term Analgesia and Pain-Specific Cytokine Concentrations. Clin. Pract. 2022, 12, 926–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, A.; Narayan, N.; Pandya, A. Contraceptive Implant-Related Acute Ulnar Neuropathy: Prompt Diagnosis, Early Referral, and Management Are Key. Eplasty 2018, 18, e28. [Google Scholar]
- Mansour, D.; Fraser, I.S.; Walling, M.; Glenn, D.; Graesslin, O.; Egarter, C.; Herbst, J. Methods of accurate localisation of non-palpable subdermal contraceptive implants. J. Fam. Plan. Reprod. Health Care 2008, 34, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, B.C.; Kropelin, B. The electrophysiological effect of dextrose 5% in water on single-shot peripheral nerve stimulation. Anesth. Analg. 2005, 100, 1837–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, K.; Sakura, S.; Bollen, A.W.; Ciriales, R.; Drasner, K. Comparative toxicity of glucose and lidocaine administered intrathecally in the rat. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 1998, 23, 444–450. [Google Scholar]
- Dufour, E.; Donat, N.; Jaziri, S.; Kurdi, O.; Couturier, C.; Dreyfus, J.F.; Fischler, M. Ultrasound-guided perineural circumferential median nerve block with and without prior dextrose 5% hydrodissection: A prospective randomized double-blinded noninferiority trial. Anesth. Analg. 2012, 115, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buntragulpoontawee, M.; Chang, K.V.; Vitoonpong, T.; Pornjaksawan, S.; Kitisak, K.; Saokaew, S.; Kanchanasurakit, S. The Effectiveness and Safety of Commonly Used Injectates for Ultrasound-Guided Hydrodissection Treatment of Peripheral Nerve Entrapment Syndromes: A Systematic Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 621150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.T.; Wu, C.H.; Lin, J.A.; Su, D.C.J.; Hung, C.Y.; Lam, S.K. Efficacy of 5% Dextrose Water Injection for Peripheral Entrapment Neuropathy: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, K.H.S.; Wu, Y.T.; Reeves, K.D.; Galluccio, F.; Allam, A.E.S.; Peng, P.W. Ultrasound-Guided Interventions for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.T.; Lam, K.H.S.; Lai, C.Y.; Chen, S.R.; Shen, Y.P.; Su, Y.C.; Li, T.Y.; Wu, C.H. Novel Motor-Sparing Ultrasound-Guided Neural Injection in Severe Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Comparison of Four Injectates. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 9745322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.P.; Chen, J.; Chang, K.V.; Wu, W.T.; Özçakar, L. Utility of ultrasound elastography in evaluation of carpal tunnel syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2019, 45, 2855–2865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.T.; Ke, M.J.; Ho, T.Y.; Li, T.Y.; Shen, Y.P.; Chen, L.C. Randomized double-blinded clinical trial of 5% dextrose versus triamcinolone injection for carpal tunnel syndrome patients. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 84, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Ho, T.Y.; Shen, Y.P.; Su, Y.C.; Li, T.Y.; Tsai, C.K.; Wu, Y.T. Perineural Dextrose and Corticosteroid Injections for Ulnar Neuropathy at the Elbow: A Randomized Double-blind Trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2020, 101, 1296–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.R.; Herrera, S.R.; Lee, T.G.; Galdamez, F.M.; Vincent, K.L. The Feasibility of In-Clinic Ultrasound-Guided Removal of Contraceptive Implants: A Case Series. J. Clin. Gynecol. Obstet. 2014, 3, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Persaud, T.; Walling, M.; Geoghegan, T.; Buckley, O.; Stunell, H.; Torreggiani, W.C. Ultrasound-guided removal of Implanon devices. Eur. Radiol. 2008, 18, 2582–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques, T.; Henry, S.; Giraudet, G.; Demondion, X.; Cotten, A. Minimally-invasive fully ultrasound-guided removal of nonpalpable single-rod contraceptive implant: Case report and technical description. Contraception 2020, 101, 338–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Characteristic | Open Removal | US-Guided Removal | US-Guided HD + Stabilization + Removal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Target Indications | Excessively difficult implants | Deep implants (no mention of proximity to nearby nerves in the literature) | Nerve-adjacent or impinging implants |
| Operation Time | Long (>2 h) | Short (<30 min) | Moderate (30 to 60 min) |
| Scar Size | Large incision | Small incision | Small incision |
| Nerve Injury Risk | Possible | Possible | Minimal |
| Soft Tissue Damage | Extensive | Moderate | Minimal |
| Migration Risk | Negligible | Possible | Reduced |
| Conversion to Open Surgery | N/A | Possible | Rare |
| Learning Curve | Low | Moderate | High |
| Complication Rate | Higher | Lower | Minimal |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seo, Y.-S.; Lee, H.; Hwang, J.; Park, C.; Lee, M.; Yoon, Y.; Yu, H.; Choi, J.; Ko, G.; Su, D.C.-J.; et al. Ultrasound-Guided Hydrodissection with Needle Stabilization: An Innovative Nerve-Sparing Approach to Remove a Contraceptive Implant Causing Ulnar Neuropathy. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 2106. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15162106
Seo Y-S, Lee H, Hwang J, Park C, Lee M, Yoon Y, Yu H, Choi J, Ko G, Su DC-J, et al. Ultrasound-Guided Hydrodissection with Needle Stabilization: An Innovative Nerve-Sparing Approach to Remove a Contraceptive Implant Causing Ulnar Neuropathy. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(16):2106. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15162106
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeo, Yeui-Seok, HoWon Lee, Jihyo Hwang, Chanwool Park, MinJae Lee, Yonghyun Yoon, HyeMi Yu, Jaeik Choi, Gyungseog Ko, Daniel Chiung-Jui Su, and et al. 2025. "Ultrasound-Guided Hydrodissection with Needle Stabilization: An Innovative Nerve-Sparing Approach to Remove a Contraceptive Implant Causing Ulnar Neuropathy" Diagnostics 15, no. 16: 2106. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15162106
APA StyleSeo, Y.-S., Lee, H., Hwang, J., Park, C., Lee, M., Yoon, Y., Yu, H., Choi, J., Ko, G., Su, D. C.-J., Reeves, K. D., Suryadi, T., Suhaimi, A., & Lam, K. H. S. (2025). Ultrasound-Guided Hydrodissection with Needle Stabilization: An Innovative Nerve-Sparing Approach to Remove a Contraceptive Implant Causing Ulnar Neuropathy. Diagnostics, 15(16), 2106. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15162106








