Molar Pregnancy: Early Diagnosis, Clinical Management, and the Role of Referral Centers
Abstract
1. Introduction
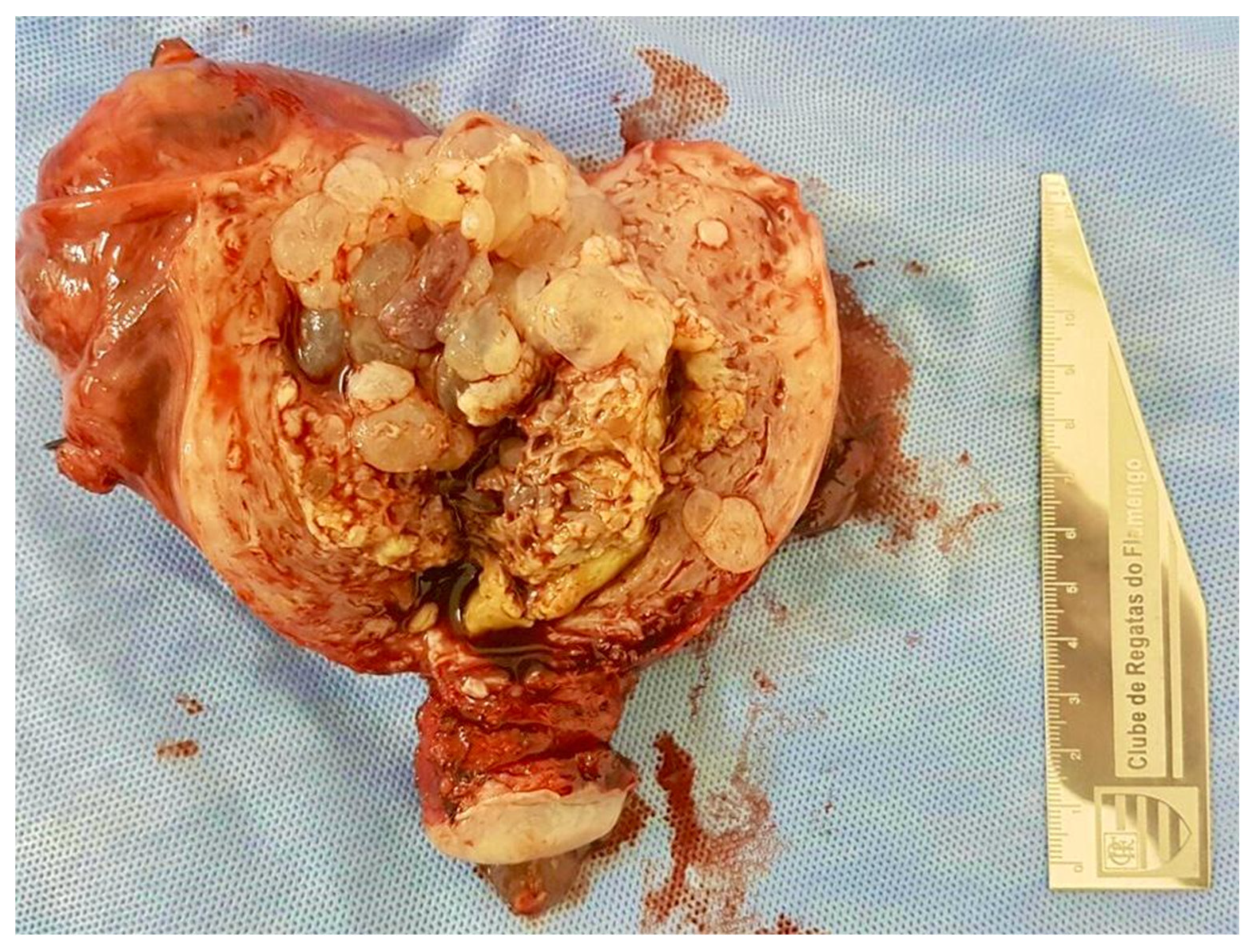
2. Diagnosis of Molar Pregnancy
3. Diagnosis and Treatment of Clinical Complications of Molar Pregnancy
3.1. Uterine Hemorrhage
3.2. Early-Onset Preeclampsia (Before 20 Weeks’ Gestation)
3.3. Hyperthyroidism
- -
- Beta-blockade: propranolol 40–80 mg orally every 6 h or 1–2 mg IV every 10 min until heart rate is controlled;
- -
- Inhibition of hormone synthesis: propylthiouracil 500–1000 mg orally as a loading dose, then 250 mg every 6 h;
- -
- Inhibition of hormone release: potassium iodide, 5 drops orally every 6 h, administered 1 h after propylthiouracil;
- -
- Reduction of peripheral T4-to-T3 conversion: hydrocortisone 100 mg IV every 8 h.
3.4. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome/Trophoblastic Embolization
4. Primary Treatment of Molar Pregnancy
5. Postmolar Follow-Up
6. Diagnosis of Postmolar Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia
- -
- Plateaued hCG levels (variation < 10%) across four consecutive weekly measurements over 3 weeks;
- -
- Rising hCG values (increase of ≥10%) across three consecutive weekly measurements over at least 2 weeks;
- -
- Histopathological diagnosis of choriocarcinoma, placental site trophoblastic tumor, or epithelioid trophoblastic tumor.
7. Importance of Referral Centers for Gestational Trophoblastic Disease
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soper, J.T. Gestational Trophoblastic Disease: Current Evaluation and Management. Obstet. Gynecol. 2021, 137, 355–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, C.; van Trommel, N.; Braicu, E.I.; Planchamp, F.; Berkowitz, R.; Seckl, M.; EOTTD-ESGO-GCIG-ISSTD Guideline Committee. Practical Guidelines for the Treatment of Gestational Trophoblastic Disease: Collaboration of the European Organisation for the Treatment of Trophoblastic Disease (EOTTD)-European Society of Gynaecologic Oncology (ESGO)-Gynecologic Cancer InterGroup (GCIG)-International Society for the Study of Trophoblastic Diseases (ISSTD). J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43, 2119–2128. [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz, N.S.; Eskander, R.N.; Adelman, M.R.; Burke, W. Epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment of gestational trophoblastic disease: A Society of Gynecologic Oncology evidenced-based review and recommendation. Gynecol. Oncol. 2021, 163, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joneborg, U. Epidemiology of Gestational Trophoblastic Disease. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2024, 38, 1173–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, B. Pathology of Gestational Trophoblastic Disease (GTD). Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2024, 38, 1191–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lok, C.; Frijstein, M.; van Trommel, N. Clinical presentation and diagnosis of Gestational Trophoblastic Disease. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2021, 74, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangili, G.; Garavaglia, E.; Cavoretto, P.; Gentile, C.; Scarfone, G.; Rabaiotti, E. Clinical presentation of hydatidiform mole in northern Italy: Has it changed in the last 20 years? Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2008, 198, e1–e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.Y.; Goldstein, D.P.; Bernstein, M.R.; Horowitz, N.S.; Mattar, R.; Maesta, I.; Braga, A.; Berkowitz, R.S. Maternal Near Miss According to World Health Organization Classification Among Women with a Hydatidiform Mole: Experience at the New England Trophoblastic Disease Center, 1994–2013. J. Reprod. Med. 2016, 61, 210–214. [Google Scholar]
- Mitric, C.; Yang, K.; Bhat, G.; Lheureux, S.; Laframboise, S.; Li, X.; Bouchard-Fortier, G. Gestational trophoblastic neoplasia: Does centralization of care impact clinical management? Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2023, 33, 1724–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albright, B.B.; Ellett, T.; Knochenhauer, H.E.; Goins, E.C.; Monuszko, K.A.; Kaplan, S.J.; Previs, R.A.; Moss, H.A.; Havrilesky, L.J.; Davidson, B.A. Treatments and outcomes in high-risk gestational trophoblastic neoplasia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2023, 130, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, C.; van Trommel, N.; Massuger, L.; Golfier, F.; Seckl, M.; Clinical Working Party of the EOTTD. Practical clinical guidelines of the EOTTD for treatment and referral of gestational trophoblastic disease. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 130, 228–240. [Google Scholar]
- Aiob, A.; Naskovica, K.; Amdur Zilberfarb, I.; Sharon, A.; Bornstein, J.; Lowenstein, L. Changes in diagnostic sensitivity, incidence and presentation of complete and partial hydatidiform mole over the years. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2022, 274, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newhouse, I.; Spacey, A.; Scragg, B.; Szczepura, K. The diagnostic value and accuracy of ultrasound in diagnosing hydatidiform mole: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature. Radiography 2022, 28, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, J.L.; Maturen, K.E.; Mowers, E.L.; Pasque, K.B.; Wasnik, A.P.; Dalton, V.K.; Bell, J.D. Sonographic diagnosis of partial versus complete molar pregnancy: A reappraisal. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2017, 45, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngu, S.F.; Ngan, H.Y.S. Surgery including fertility-sparing treatment of GTD. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2021, 74, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurain, J.R. Gestational trophoblastic disease I: Epidemiology, pathology, clinical presentation and diagnosis of gestational trophoblastic disease, and management of hydatidiform mole. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 203, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Management of Gestational Trophoblastic Disease: Green-top Guideline No 38-June 2020. BJOG 2021, 128, e1–e27.
- Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Pan, J.; Chen, J.; Shi, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W.; Yang, N.; Jin, Z.; Xiang, Y. Bleeding from gestational trophoblastic neoplasia: Embolotherapy efficacy and tumour response to chemotherapy. Clin. Radiol. 2017, 72, 992.e7–992.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Lu, Y.; Huang, W.; Tong, B.; Lu, W. Total hysterectomy versus uterine evacuation for preventing post-molar gestational trophoblastic neoplasia in patients who are at least 40 years old: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 202: Gestational Hypertension and Preeclampsia. Obstet. Gynecol. 2019, 133, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, M.M.; Maesta, I.; Costa, R.A.d.A.; Mazeto, G.M.; Horowitz, N.S.; Elias, K.M.; Braga, A.; Berkowitz, R.S. Clinical characteristics and thyroid function in complete hydatidiform mole complicated by hyperthyroidism. Gynecol. Oncol. 2022, 165, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.-X.; Xiang, Y.; Feng, F.-Z.; Ren, T.; Yang, J.-J.; Zhao, J.; Wan, X.-R. Pulmonary deportation of hydatidiform mole: A 12-year, single tertiary center experience in China. Chin. Med. J. 2020, 133, 1930–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, T.; Sutin, K.; Carreno, C.A.; Hibbett, E.; Funai, E.F. Central hemodynamic monitoring in a woman with acute respiratory insufficiency after evacuation of a complete molar pregnancy. A case report. J. Reprod. Med. 2001, 46, 916–922. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lima, L.d.L.A.; Parente, R.C.M.; Maestá, I.; Junior, J.A.; Filho, J.F.d.R.; Montenegro, C.A.B.; Braga, A. Clinical and radiological correlations in patients with gestational trophoblastic disease. Radiol. Bras. 2016, 49, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padrón, L.; Rezende-Filho, J.; Amim-Junior, J.; Sun, S.Y.; Charry, R.C.; Maestá, I.; Elias, K.M.; Horowitz, N.; Braga, A.; Berkowitz, R.S. Manual Compared With Electric Vacuum Aspiration for Treatment of Molar Pregnancy. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 131, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmar, F.T.C.; Braga, A.; Rezende-Filho, J.; Villas-Boas, J.M.S.; Charry, R.C.; Maesta, I. Uterine artery Doppler flow velocimetry parameters for predicting gestational trophoblastic neoplasia after complete hydatidiform mole, a prospective cohort study. Clinics 2017, 72, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, A.; Padrón, L.; Rezende-Filho, J.; Elias, K.; Horowitz, N.; Berkowitz, R. Treatment of hydatidiform mole using manual vacuum aspiration: Technical and tactical aspects. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2021, 31, 1299–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagey, J.M.; Drury, K.E.; Kaplan, S.; Davidson, B.A.; Morse, J.E. Contraceptive use following gestational trophoblastic disease: A systematic review. Contraception 2024, 137, 110488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, H.L.; Doyle, P. Influence of oral contraceptives in the development of post-molar trophoblastic neoplasia—A systematic review. Gynecol. Oncol. 2006, 100, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, J.M.Q.; Braga, A.; Santos, R.S.; Ramos, M.M.; Cortés-Charry, R.; Maestá, I. Comparison of 2 Human Chorionic Gonadotropin Immunoassays Commercially Available for Monitoring Patients With Gestational Trophoblastic Disease. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2017, 27, 1494–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madi, J.M.; Paganella, M.P.; Litvin, I.E.; Viggiano, M.; Wendland, E.M.; Elias, K.M.; Horowitz, N.S.; Braga, A.; Berkowitz, R.S. Perinatal outcomes of first pregnancy after chemotherapy for gestational trophoblastic neoplasia: A systematic review of observational studies and meta-analysis. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2022, 226, 633–645.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, L.; Maher, G.J.; Joyce, C.; Niemann, I.; Fisher, R.; Sunde, L. When to Consult a Geneticist Specialising in Gestational Trophoblastic Disease. Gynecol. Obstet. Investig. 2024, 89, 198–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalogiannidis, I.; Kalinderi, K.; Kalinderis, M.; Miliaras, D.; Tarlatzis, B.; Athanasiadis, A. Recurrent complete hydatidiform mole: Where we are, is there a safe gestational horizon? Opinion and mini-review. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2018, 35, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngan, H.Y.S.; Seckl, M.J.; Berkowitz, R.S.; Xiang, Y.; Golfier, F.; Sekharan, P.K.; Braga, A.; Garrett, A. Diagnosis and management of gestational trophoblastic disease: 2021 update. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2021, 155 (Suppl. S1), 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strickland, A.L.; Gwin, K. Gestational trophoblastic disease- rare, sometimes dramatic, and what we know so far. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2022, 39, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Assis, R.T.; de Morais, L.R.; de Freitas, A.C.F.S.; FIlho, R.C.S.; de Carvalho, L.R.B.; Parreira, B.E.; Yamachi, C.Y.; Braga, A.; Sun, S.Y. Telemedicine in post-molar follow-up: Is it a useful tool? Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2022, 32, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- França, A.C.G.; Uberti, E.M.H.; Muller, K.P.; Cardoso, R.B.; Giguer, F.; El Beitune, P.; Braga, A. Emotional and Clinical Aspects Observed in Women with Gestational Trophoblastic Disease: A Multidisciplinary Action. Rev. Bras. Ginecol. Obstet. 2022, 44, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, A.; Lopes, R.; Campos, V.; Freitas, F.; Maestá, I.; Sun, S.Y.; Pedrotti, L.G.; Bessel, M.; de Sousa, C.B.; Leal, E.; et al. The impact of the distance traveled between residence and gestational trophoblastic neoplasia reference center and clinical outcomes in Brazilian women. Gynecol. Oncol. 2023, 176, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Feature | Complete Hydatidiform Mole | Partial Hydatidiform Mole |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical presentation | Vaginal bleeding; uterus larger than gestational age; markedly elevated β-hCG; absent fetal parts | Vaginal bleeding; uterus appropriate or slightly enlarged; mildly elevated β-hCG; fetal parts may be present |
| Ultrasound findings | “Snowstorm” or “cluster of grapes” appearance; no embryo or fetus | Cystic, thickened placenta; abnormal fetus may be present; “Swiss cheese” appearance |
| Histopathology | Diffusely hydropic villi with central cisterns; circumferential and diffuse trophoblastic hyperplasia; absence of fetal tissue | Mixed villous population with scalloped hydropic villi; trophoblastic inclusions; focal, mild trophoblastic hyperplasia; fetal tissue often present |
| p57Kip2 immunostaining | Negative in cytotrophoblasts and villous stromal cells | Positive nuclear staining in cytotrophoblasts and stromal cells |
| Ki-67 immunostaining | High proliferation index; strong nuclear positivity in cytotrophoblasts and syncytiotrophoblasts | Moderate proliferation index; mainly in cytotrophoblasts; lower than CHM |
| p53 immunostaining | Strong and diffuse nuclear expression, mainly in cytotrophoblasts (3+) | Weak and focal nuclear staining, mainly in cytotrophoblasts (1+) |
| Cytogenetic profile | Diploid, androgenetic (46,XX or 46,XY; entirely paternal) | Triploid, diandric (69,XXY; 69,XXX; 69,XYY; two paternal, one maternal genome) |
| Risk of postmolar GTN | 15–20% | <5% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Braga, A.; Coutinho, L.; Chagas, M.; Soares, J.P.; Callado, G.Y.; Alevato, R.; Lozoya, C.; Sun, S.Y.; Araujo Júnior, E.; Rezende-Filho, J. Molar Pregnancy: Early Diagnosis, Clinical Management, and the Role of Referral Centers. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1953. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15151953
Braga A, Coutinho L, Chagas M, Soares JP, Callado GY, Alevato R, Lozoya C, Sun SY, Araujo Júnior E, Rezende-Filho J. Molar Pregnancy: Early Diagnosis, Clinical Management, and the Role of Referral Centers. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(15):1953. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15151953
Chicago/Turabian StyleBraga, Antônio, Lohayne Coutinho, Marcela Chagas, Juliana Pereira Soares, Gustavo Yano Callado, Raphael Alevato, Consuelo Lozoya, Sue Yazaki Sun, Edward Araujo Júnior, and Jorge Rezende-Filho. 2025. "Molar Pregnancy: Early Diagnosis, Clinical Management, and the Role of Referral Centers" Diagnostics 15, no. 15: 1953. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15151953
APA StyleBraga, A., Coutinho, L., Chagas, M., Soares, J. P., Callado, G. Y., Alevato, R., Lozoya, C., Sun, S. Y., Araujo Júnior, E., & Rezende-Filho, J. (2025). Molar Pregnancy: Early Diagnosis, Clinical Management, and the Role of Referral Centers. Diagnostics, 15(15), 1953. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15151953









