Novel Sonoguided Digital Palpation and Ultrasound-Guided Hydrodissection of the Long Thoracic Nerve for Managing Serratus Anterior Muscle Pain Syndrome: A Case Report with Technical Details
Abstract
1. Introduction
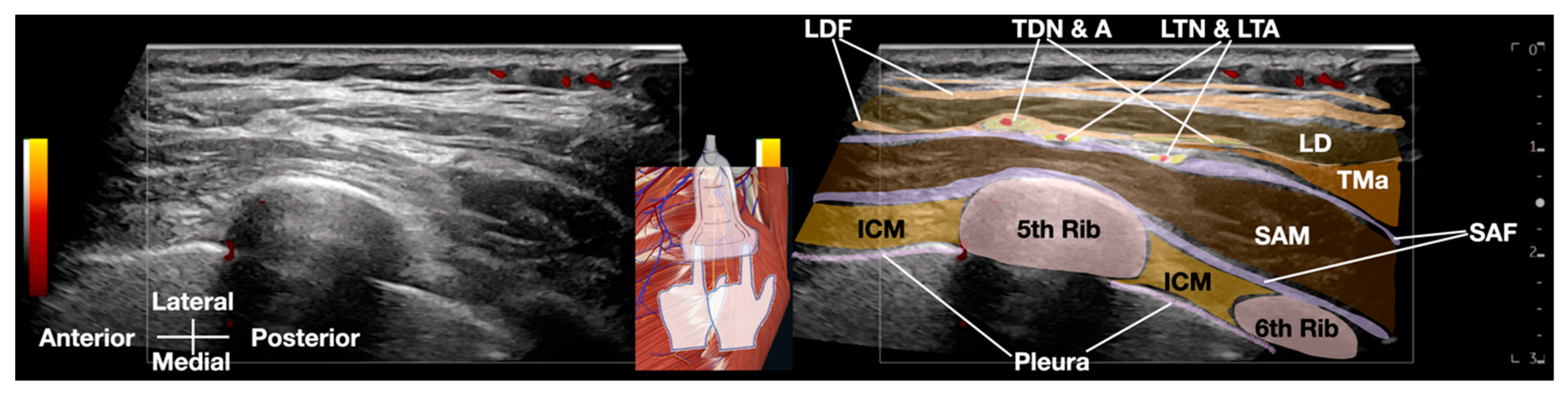
Anatomy of SAM and LTN
2. Case Presentation
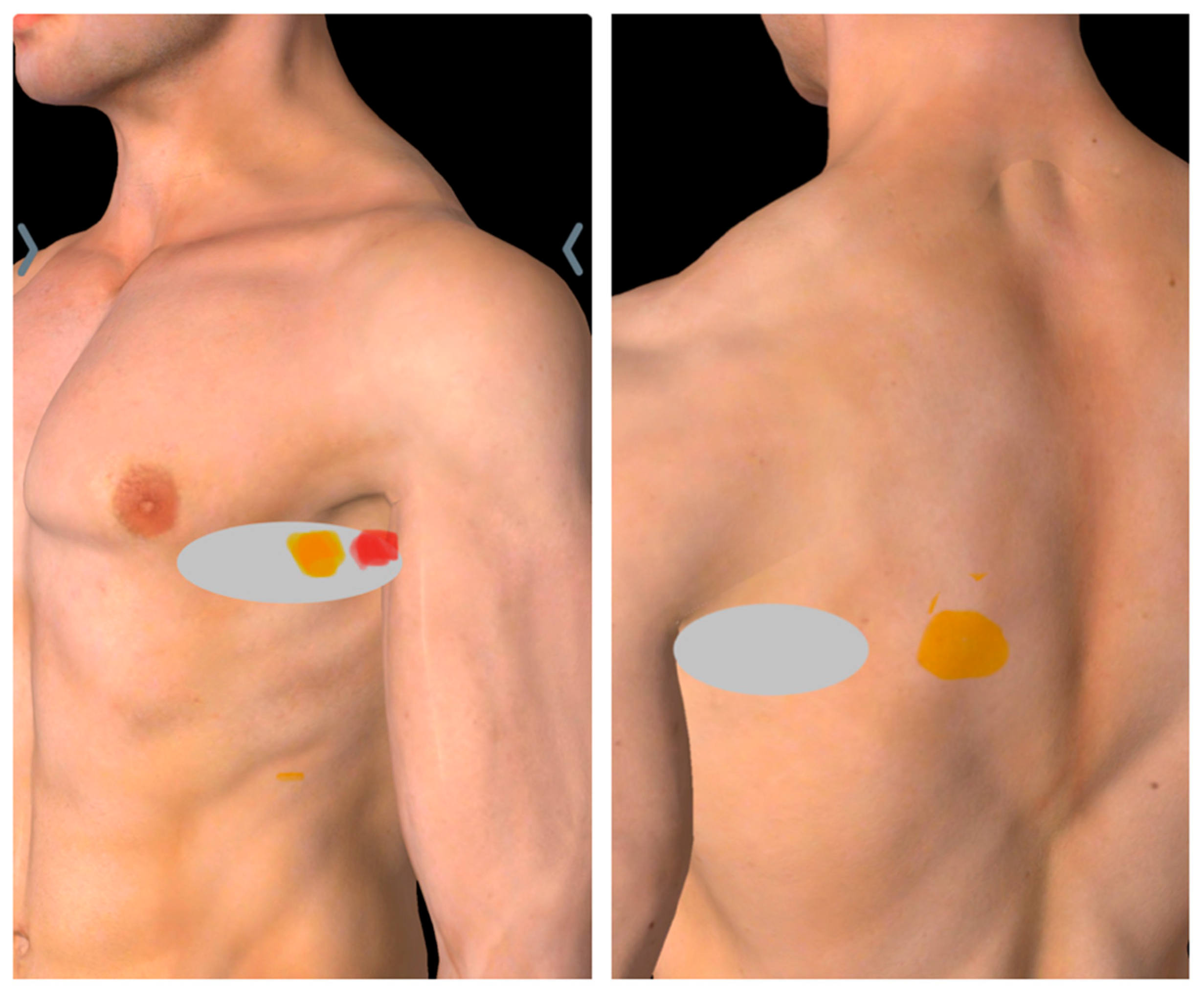
2.1. Diagnosis of SAMPS Using Sonoguided Digital Palpation
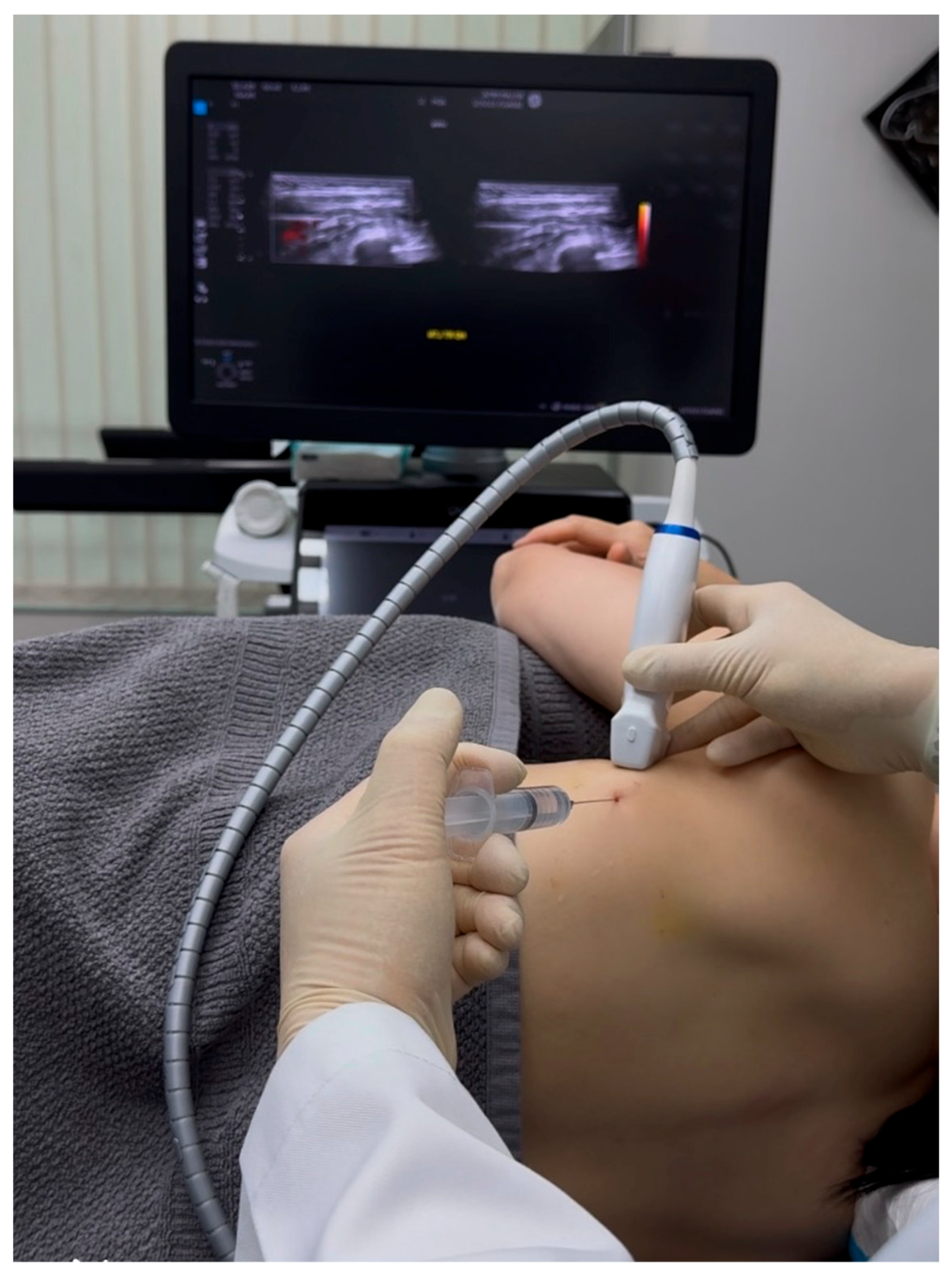
2.2. Ultrasound-Guided Hydrodissection of Long Thoracic Nerve: Methodology
3. Discussion
- Preserved neural feedback enables real-time procedural titration. By avoiding local anesthetic-induced blockade, clinicians maintain the ability to monitor patient-reported symptoms during needle advancement and fluid injection. This continuous feedback allows for immediate adjustment of injection parameters (e.g., volume, pressure, or needle positioning) based on pain reproduction or relief, ensuring optimal nerve decompression while minimizing iatrogenic irritation.
- Elimination of false-negative pain response assessment. Local anesthetics can mask incomplete nerve release by temporarily suppressing pain signals, potentially leading to premature termination of hydrodissection before full adhesiolysis is achieved. Without anesthetic interference, the persistence or resolution of symptoms during the procedure provides a more reliable indicator of therapeutic efficacy.
- Uncompromised post-procedural evaluation. The absence of anesthetic effects permits accurate functional assessment immediately following the intervention. Clinicians can distinguish between true therapeutic success (mechanical decompression) and transient analgesia (chemical blockade), facilitating more informed decisions about further management. This is particularly valuable when assessing early outcomes or planning staged procedures.
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 1st HD | First step of the hydrodissection, transducer and needle direction |
| 2nd HD | Second step of hydrodissection, transducer and needle direction |
| 3rd HD | Third step of hydrodis-section, transducer and needle direction |
| D5W | 5% Dextrose in Water |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| EMG | Electromyography |
| HD | Hydrodissection |
| LA | Local Anesthetic |
| LDF | Latissimus Dorsi Fascia |
| LTN | Long Thoracic Nerve |
| LTA | Lateral Thoracic Artery |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| NRS | Numeric Rating Scale |
| NSAIDs | Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs |
| PCI | Percutaneous Coronary Intervention |
| PRP | Platelet-Rich Plasma |
| PSFS | Patient-Specific Functional Scale |
| SAM | Serratus Anterior Muscle |
| SAMPS | Serratus Anterior Muscle Pain Syndrome |
| SAF | Serratus Anterior Fascia |
| SDP | Sonoguided Digital Palpation |
| SPADI | Shoulder Pain and Disability Index |
| TDN | Thoracodorsal Nerve |
| TMa | Teres Major Muscle |
| US | Ultrasound |
References
- Bautista, A.; Webb, C.; Rosenquist, R. Serratus Anterior Muscle Pain Syndrome: A Diagnostic Conundrum. Pain Med. 2017, 18, 1600–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldman, S.D. Atlas of Uncommon Pain Syndromes; Saunders/Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bordoni, B.; Myers, T. A Review of the Theoretical Fascial Models: Biotensegrity, Fascintegrity, and Myofascial Chains. Cureus 2020, 12, e7092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Standring, S. A brief history of topographical anatomy. J. Anat. 2016, 229, 32–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinnatamby, C.S. Last’s Anatomy: Regional and Applied; Churchill Livingstone: Edinburgh, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pathak, A.; Wilson, R.; Sharma, S.; Pryymachenko, Y.; Ribeiro, D.C.; Chua, J.; Abbott, J.H. Measurement Properties of the Patient-Specific Functional Scale and Its Current Uses: An Updated Systematic Review of 57 Studies Using COSMIN Guidelines. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2022, 52, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, K.K.; Jennings, S.; Richardson, G.; van Vliet, D.; Hefford, C.; Abbott, J.H. The patient-specific functional scale: Psychometrics, clinimetrics, and application as a clinical outcome measure. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2012, 42, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, H.H. Addition of Osteopathic Visceral Manipulation to OMT for Low Back Pain Decreases Pain and Increases Quality of Life. J. Am. Osteopat. Assoc. 2017, 117, 333–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Eguaras, N.; Rodríguez-López, E.S.; Lopez-Dicastillo, O.; Franco-Sierra, M.Á.; Ricard, F.; Oliva-Pascual-Vaca, Á. Effects of Osteopathic Visceral Treatment in Patients with Gastroesophageal Reflux: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaud, A.; Darbois, N.; Monvoisin, R.; Pinsault, N. Reliability of diagnosis and clinical efficacy of visceral osteopathy: A systematic review. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seffinger, M.A. Foundations of Osteopathic Medicine: Philosophy, Science, Clinical Applications, and Research, 4th ed.; Wolters Kluwer: Hong Kong, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mologne, M.S.; Randall, Z.D.; Olafsen, N.P.; Brogan, D.M.M.; Dy, C.J.M. Correlation of Ultrasound and Electrodiagnostic Evaluation in Ballistic Peripheral Nerve Injuries. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2025, 13, e6846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijntjes, J.; Borchert, A.; van Alfen, N. Nerve Ultrasound in Traumatic and Iatrogenic Peripheral Nerve Injury. Diagnostics 2020, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toia, F.; Gagliardo, A.; D’Arpa, S.; Gagliardo, C.; Gagliardo, G.; Cordova, A. Preoperative evaluation of peripheral nerve injuries: What is the place for ultrasound? J. Neurosurg. 2016, 125, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, L.B.E.; Iyer, V.G.; Zhang, Y.P.; Shields, C.B. Iatrogenic median and ulnar nerve injuries during carpal tunnel release: Clinical, electrodiagnostic, and ultrasound features in 12 patients. Patient series. J. Neurosurg. Case Lessons 2023, 5, CASE22543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, K.H.S.; Hung, C.-Y.; Chiang, Y.-P.; Onishi, K.; Su, D.C.J.; Clark, T.B.; Reeves, K.D. Ultrasound-Guided Nerve Hydrodissection for Pain Management: Rationale, Methods, Current Literature, and Theoretical Mechanisms. J. Pain Res. 2020, 13, 1957–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Goh, D.; Cho, S.; Noh, Y.; Hwang, B. Serratus anterior plane block with ultrasound-guided hydrodissection for lateral thoracic pain caused by long thoracic nerve neuropathy—A case report. Anesth. Pain Med. 2022, 17, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Schaffer, G.; Nowakowsky, M.; Eghtesadi, M.; Cogan, J. Ultrasound-Guided Trigger Point Injection for Serratus Anterior Muscle Pain Syndrome: Description of Technique and Case Series. A A Case Rep. 2015, 5, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.K.H.; Reeves, K.D.; Cheng, A.L. Transition from deep regional blocks toward deep nerve hydrodissection in the upper body and torso: Method description and results from a retrospective chart review of the analgesic effect of 5% dextrose water as the primary hydrodissection injectate to enhance safety. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 7920438. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, K.H.S.; Su, D.C.-J.; Wu, Y.-T.; Varrassi, G.; Suryadi, T.; Reeves, K.D.; Tsan, Y. A Novel Ultrasound-Guided Bilateral Vagal Nerve Hydrodissection With 5% Dextrose Without Local Anesthetic for Recalcitrant Chronic Multisite Pain and Autonomic Dysfunction. Cureus 2024, 16, e63609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, K.D.; Shaw, J.; McAdam, R.; Lam, K.H.S.; Mulvaney, S.W.; Rabago, D. A Novel Somatic Treatment for Post-traumatic Stress Disorder: A Case Report of Hydrodissection of the Cervical Plexus Using 5% Dextrose. Cureus 2022, 14, e23909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, R.A.; Lackner, J.B.; Steilen-Matias, D.; Harris, D.K. A Systematic Review of Dextrose Prolotherapy for Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain. Clin. Med. Insights Arthritis Musculoskelet. Disord. 2016, 9, 139–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elders, L.A.; Van der Meche, F.G.; Burdorf, A. Serratus anterior paralysis as an occupational injury in scaffolders: Two case reports. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2001, 40, 710–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travell, J.G.; Simons, D. Myofascial Pain and Dysfunction the Trigger Point Manual (Vol. 1 and 2); Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1992; p. 626. [Google Scholar]
- Lavelle, E.D.; Lavelle, W.; Smith, H.S. Myofascial trigger points. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2007, 91, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagcier, F.; Yurdakul, O.V. A myofascial trigger point of the serratus anterior muscle that could mimic a heart attack: A dry needling treatment protocol. Acupunct. Med. 2021, 39, 563–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buntragulpoontawee, M.; Chang, K.-V.; Vitoonpong, T.; Pornjaksawan, S.; Kitisak, K.; Saokaew, S.; Kanchanasurakit, S. The Effectiveness and Safety of Commonly Used Injectates for Ultrasound-Guided Hydrodissection Treatment of Peripheral Nerve Entrapment Syndromes: A Systematic Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 621150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, D.C.; Hung, C.Y.; Lam, K.H.S. Ultrasound Evaluation and Guided Injection of the Subscapularis and Serratus Anterior Muscles Between the Scapula and the Thoracic Cage: A Technical Note. J. Ultrasound Med. 2024, 43, 1353–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.-T.; Liu, I.-C.; Syu, W.-T.; Kuo, P.-L.; Wu, C.-H. Effect of Perineural Injection with Different Dextrose Volumes on Median Nerve Size, Elasticity and Mobility in Hands with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.T.; Liao, C.-L.; Hsiao, M.-Y.; Hsueh, H.-W.; Chao, C.-C.; Wu, C.-H. Volume Matters in Ultrasound-Guided Perineural Dextrose Injection for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Randomized, Double-Blinded, Three-Arm Trial. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 625830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liza Maniquis-Smigel, K.D.R.; Rosen, H.J.; Lyftogt, J.; Graham-Coleman, C.; Cheng, A.-L.; Rabago, D. Analgesic Effect of Caudal 5% Dextrose in Water in Chronic Low Back Pain. A Randomized Controlled Trial of Epidural Injection. Anesthesiol. Pain Med. 2016, 96, e103. [Google Scholar]
- Maniquis-Smigel, L.; Reeves, K.D.; Rosen, H.J.; Lyftogt, J.; Graham-Coleman, C.; Cheng, A.-L.; Rabago, D. Short term analgesic effects of 5% dextrose epidural injections for chronic low back pain: A randomized controlled trial. Anesthesiol. Pain Med. 2017, 7, e42550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topol, G.A.; Pestalardo, I.G.; Reeves, K.D.; Elias, F.; Steinmetz, N.J.; Cheng, A.-L.; Rabago, D. Dextrose Prolotherapy for Symptomatic Grade IV Knee Osteoarthritis: A Pilot Study of Early and Longer-Term Analgesia and Pain-Specific Cytokine Concentrations. Clin. Pract. 2022, 12, 926–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.T.; Chen, Y.-P.; Lam, K.H.S.; Reeves, K.D.; Lin, J.-A.; Kuo, C.-Y. Mechanism of Glucose Water as a Neural Injection: A Perspective on Neuroinflammation. Life 2022, 12, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherng, J.H.; Chang, S.-J.; Tsai, H.-D.; Chun, C.-F.; Fan, G.-Y.; Reeves, K.D.; Lam, K.H.S.; Wu, Y.-T. The Potential of Glucose Treatment to Reduce Reactive Oxygen Species Production and Apoptosis of Inflamed Neural Cells In Vitro. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Feature | Bautista [1] 2017 | Kim 2022 [17] | Current Study |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Intervention | (LA + Steroid) Trigger-point injection | Nerve block (LA + steroid) | D5W without LA hydrodissection |
| Diagnostic Method | Clinical palpation | Physical examination, diagnostic trigger points injection, then EMG to diagnose LTN neuropathy | Quantitative SDP |
| Therapeutic Target | Muscle trigger points | Anesthetic dispersion | Fascial adhesions + hydrodissecting LTN |
| Volume/Extent | 2 mL of Bupivacaine 0.25% and Triamcinolone 4 mg/mL to each trigger points, total volume not mentioned | 20 mL of bupivacaine 0.125% with 20 mg Triamcinolone in the plane between the serratus anterior and latissimus dorsi | 20–30 mL D5W without LA (circumferential to the LTN and the fascial plane between the serratus anterior and latissiumus dorsi) |
| Mechanistic Rationale | Symptom suppression | Temporary analgesia | Biomechanical + anti-neurogenic inflammatory |
| Durability | Transient relief, two injections in five-month period | Need to repeat the block 7 days later, reviewed up to 3 months | 12 months sustained |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nugroho, N.; Lam, K.H.S.; Tandiono, T.; Suryadi, T.; Suhaimi, A.; Ratnawati, W.; Su, D.C.-J.; Yoon, Y.; Reeves, K.D. Novel Sonoguided Digital Palpation and Ultrasound-Guided Hydrodissection of the Long Thoracic Nerve for Managing Serratus Anterior Muscle Pain Syndrome: A Case Report with Technical Details. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15151891
Nugroho N, Lam KHS, Tandiono T, Suryadi T, Suhaimi A, Ratnawati W, Su DC-J, Yoon Y, Reeves KD. Novel Sonoguided Digital Palpation and Ultrasound-Guided Hydrodissection of the Long Thoracic Nerve for Managing Serratus Anterior Muscle Pain Syndrome: A Case Report with Technical Details. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(15):1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15151891
Chicago/Turabian StyleNugroho, Nunung, King Hei Stanley Lam, Theodore Tandiono, Teinny Suryadi, Anwar Suhaimi, Wahida Ratnawati, Daniel Chiung-Jui Su, Yonghyun Yoon, and Kenneth Dean Reeves. 2025. "Novel Sonoguided Digital Palpation and Ultrasound-Guided Hydrodissection of the Long Thoracic Nerve for Managing Serratus Anterior Muscle Pain Syndrome: A Case Report with Technical Details" Diagnostics 15, no. 15: 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15151891
APA StyleNugroho, N., Lam, K. H. S., Tandiono, T., Suryadi, T., Suhaimi, A., Ratnawati, W., Su, D. C.-J., Yoon, Y., & Reeves, K. D. (2025). Novel Sonoguided Digital Palpation and Ultrasound-Guided Hydrodissection of the Long Thoracic Nerve for Managing Serratus Anterior Muscle Pain Syndrome: A Case Report with Technical Details. Diagnostics, 15(15), 1891. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15151891








