Time Course of Symptoms in Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Registration
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
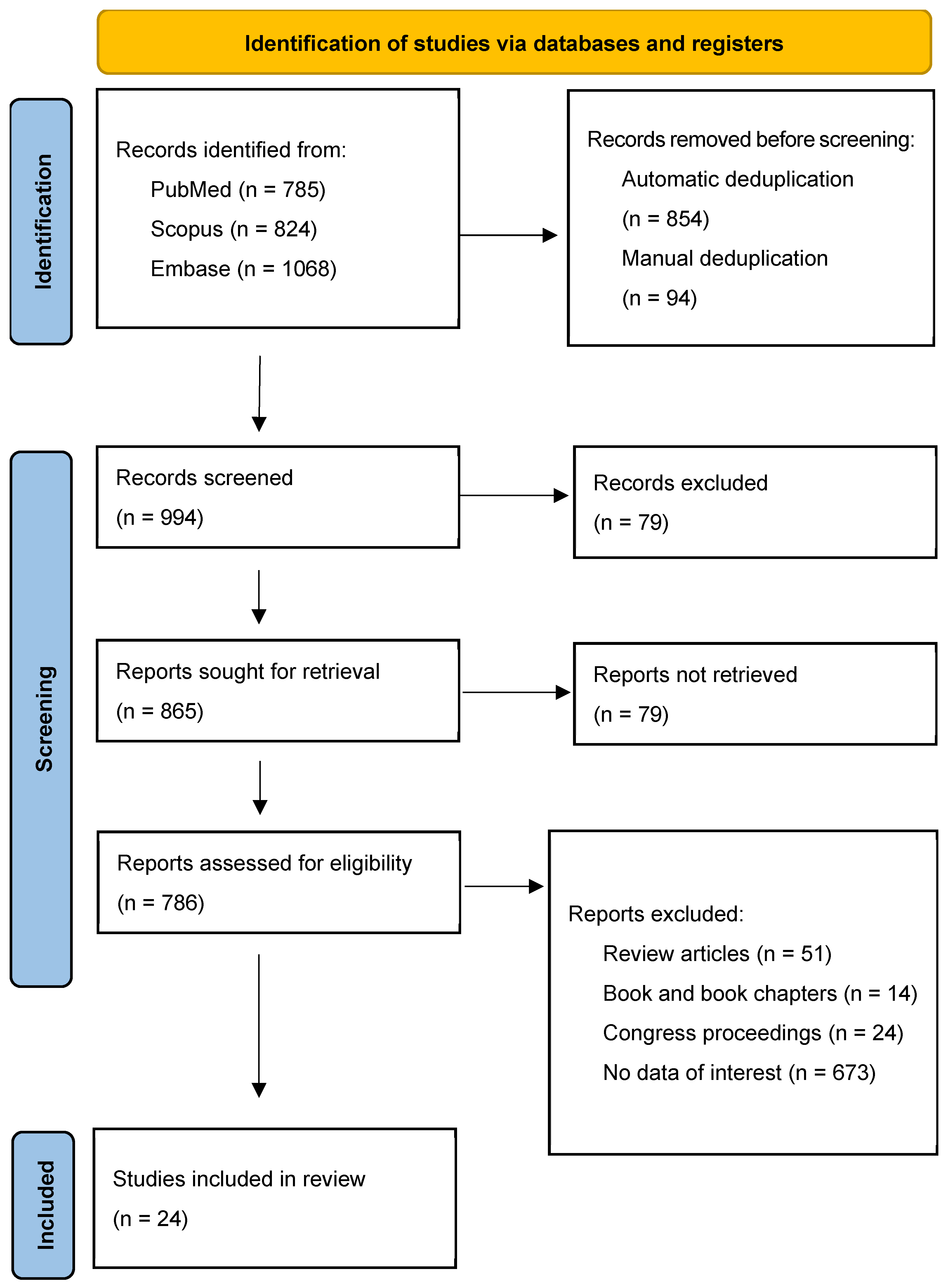
2.4. Study Selection
2.5. Data Extraction, Quality Assessment, and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sample Characteristics
3.2. Effects of Symptom Duration
3.3. Follow-Up and Clinical Outcome Data
3.4. Quality Assessment of Included Studies
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Section/Topic | # | Checklist Item | Reported on Page # |
| TITLE | |||
| Title | 1 | Identify the report as a systematic review, meta-analysis, or both. | 1 |
| ABSTRACT | |||
| Structured summary | 2 | Provide a structured summary including, as applicable: background; objectives; data sources; study eligibility criteria, participants, and interventions; study appraisal and synthesis methods; results; limitations; conclusions and implications of key findings; systematic review registration number. | 1 |
| Introduction | |||
| Rationale | 3 | Describe the rationale for the review in the context of what is already known. | 2 |
| Objectives | 4 | Provide an explicit statement of questions being addressed with reference to participants, interventions, comparisons, outcomes, and study design (PICOS). | 2 |
| Methods | |||
| Protocol and registration | 5 | Indicate if a review protocol exists, if and where it can be accessed (e.g., web address), and, if available, provide registration information including registration number. | 2 |
| Eligibility criteria | 6 | Specify study characteristics (e.g., PICOS, length of follow-up) and report characteristics (e.g., years considered, language, publication status) used as criteria for eligibility, giving rationale. | 2 |
| Information sources | 7 | Describe all information sources (e.g., databases with dates of coverage, contact with study authors to identify additional studies) in the search and date last searched. | 3 |
| Search | 8 | Present full electronic search strategy for at least one database, including any limits used, such that it could be repeated. | Appendix B |
| Study selection | 9 | State the process for selecting studies (i.e., screening, eligibility, included in systematic review, and, if applicable, included in the meta-analysis). | 3 |
| Data collection process | 10 | Describe method of data extraction from reports (e.g., piloted forms, independently, in duplicate) and any processes for obtaining and confirming data from investigators. | 3 |
| Data items | 11 | List and define all variables for which data were sought (e.g., PICOS, funding sources) and any assumptions and simplifications made. | 3 |
| Risk of bias in individual studies | 12 | Describe methods used for assessing risk of bias of individual studies (including specification of whether this was done at the study or outcome level), and how this information is to be used in any data synthesis. | N/A |
| Summary measures | 13 | State the principal summary measures (e.g., risk ratio, difference in means). | N/A |
| Synthesis of results | 14 | Describe the methods of handling data and combining results of studies, if done, including measures of consistency (e.g., I2) for each meta-analysis. | N/A |
| Risk of bias across studies | 15 | Specify any assessment of risk of bias that may affect the cumulative evidence (e.g., publication bias, selective reporting within studies). | Table 6 |
| Additional analyses | 16 | Describe methods of additional analyses (e.g., sensitivity or subgroup analyses, meta-regression), if done, indicating which were pre-specified. | N/A |
| Results | |||
| Study selection | 17 | Give numbers of studies screened, assessed for eligibility, and included in the review, with reasons for exclusions at each stage, ideally with a flow diagram. | Figure 1 |
| Study characteristics | 18 | For each study, present characteristics for which data were extracted (e.g., study size, PICOS, follow-up period) and provide the citations. | 3 |
| Risk of bias within studies | 19 | Present data on risk of bias of each study and, if available, any outcome level assessment (see item 12). | N/A |
| Results of individual studies | 20 | For all outcomes considered (benefits or harms), present, for each study: (a) simple summary data for each intervention group (b) effect estimates and confidence intervals, ideally with a forest plot. | Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3 |
| Synthesis of results | 21 | Present results of each meta-analysis done, including confidence intervals and measures of consistency. | N/A |
| Risk of bias across studies | 22 | Present results of any assessment of risk of bias across studies (see Item 15). | N/A |
| Additional analysis | 23 | Give results of additional analyses, if done (e.g., sensitivity or subgroup analyses, meta-regression [see Item 16]). | N/A |
| Discussion | |||
| Summary of evidence | 24 | Summarize the main findings including the strength of evidence for each main outcome; consider their relevance to key groups (e.g., healthcare providers, users, and policymakers). | 4–8 |
| Limitations | 25 | Discuss limitations at study and outcome level (e.g., risk of bias), and at review level (e.g., incomplete retrieval of identified research, reporting bias). | 10 |
| Conclusions | 26 | Provide a general interpretation of the results in the context of other evidence, and implications for future research. | 11 |
| Funding | |||
| Funding | 27 | Describe sources of funding for the systematic review and other support (e.g., supply of data); role of funders for the systematic review. | 11 |
Appendix B
| Database | Medline (PubMed) |
| Filter | None |
| Search details | (((((((((normal) AND pressure) AND hydrocephalus)) AND (((((hydrocephalus, normal pressure[MeSH Terms]) OR normal pressure hydrocephalus[MeSH Terms]) OR normal pressure hydrocephalus) OR mph normal pressure hydrocephalus[MeSH Terms]) OR mph))) AND (((((shunting) OR ventriculoperitoneal shunt) OR shunt, ventriculoperitoneal[MeSH Terms]) OR ventriculoperitoneal shunt[MeSH Terms]) OR ventriculoperitoneal))) AND (((adult[MeSH Terms]) OR aged[MeSH Terms]) OR adult)) AND English[lang].” Only studies published in the English language were selected. |
| Database | Scopus |
| Filter | None |
| Search details | (TITLE-ABS-KEY(normal AND pressure AND hydrocephalus) AND (TITLE-ABS-KEY(normal pressure hydrocephalus) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(mph normal pressure hydrocephalus)) AND (TITLE-ABS-KEY(shunting) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(ventriculoperitoneal shunt) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(ventriculoperitoneal)) AND (TITLE-ABS-KEY(adult) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY(aged)) AND (LIMIT-TO(LANGUAGE, “English”))) |
| Database | Embase |
| Filter | None |
| Search details | (normal AND pressure AND hydrocephalus) AND (“normal pressure hydrocephalus”/exp OR “mph normal pressure hydrocephalus”) AND (“shunting”/exp OR “ventriculoperitoneal shunt”/exp OR “ventriculoperitoneal”) AND (“adult”/exp OR “aged”/exp) AND [english]/lim |
References
- McGirt, M.J.; Woodworth, G.; Coon, A.L.; Thomas, G.; Williams, M.A.; Rigamonti, D. Diagnosis, treatment, and analysis of long-term outcomes in idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 2005, 57, 699–705; discussion 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Láez, R.; Caballero-Arzapalo, H.; López-Menéndez, L.Á.; Arango-Lasprilla, J.C.; Vázquez-Barquero, A. Epidemiology of Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: A Systematic Review of the Literature. World Neurosurg. 2015, 84, 2002–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Relkin, N.; Marmarou, A.; Klinge, P.; Bergsneider, M.; Black, P.M. Diagnosing idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 2005, 57 (Suppl. S3), S4–S16; discussion ii–v. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.A.; Malm, J. Diagnosis and Treatment of Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. Contin. Minneap. Minn. 2016, 22, 579–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, M.; Yamada, S.; Miyajima, M.; Ishii, K.; Kuriyama, N.; Kazui, H.; Kanemoto, H.; Suehiro, T.; Yoshiyama, K.; Kameda, M.; et al. Guidelines for Management of Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (Third Edition): Endorsed by the Japanese Society of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2021, 61, 63–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazui, H.; Miyajima, M.; Mori, E.; Ishikawa, M. SINPHONI-2 Investigators. Lumboperitoneal shunt surgery for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (SINPHONI-2): An open-label randomised trial. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrén, K.; Wikkelsø, C.; Tisell, M.; Hellström, P. Natural course of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2014, 85, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czosnyka, Z.; Owler, B.; Keong, N.; Santarius, T.; Baledent, O.; Pickard, J.D.; Czosnyka, M. Impact of duration of symptoms on CSF dynamics in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2011, 123, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakili, S.; Moran, D.; Hung, A.; Elder, B.D.; Jeon, L.; Fialho, H.; Sankey, E.W.; Jusué-Torres, I.; Goodwin, C.R.; Lu, J.; et al. Timing of surgical treatment for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: Association between treatment delay and reduced short-term benefit. Neurosurg. Focus 2016, 41, E2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinge, P.; Hellström, P.; Tans, J.; Wikkelsø, C. European iNPH Multicentre Study Group. One-year outcome in the European multicentre study on iNPH. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2012, 126, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisell, M.; Tullberg, M.; Hellström, P.; Edsbagge, M.; Högfeldt, M.; Wikkelsö, C. Shunt surgery in patients with hydrocephalus and white matter changes. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 114, 1432–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razay, G.; Vreugdenhil, A.; Liddell, J. A prospective study of ventriculo-peritoneal shunting for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. J. Clin. Neurosci. Off. J. Neurosurg. Soc. Australas. 2009, 16, 1180–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agerskov, S.; Hellström, P.; Andrén, K.; Kollén, L.; Wikkelsö, C.; Tullberg, M. The phenotype of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus-a single center study of 429 patients. J. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 391, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutowski, P.; Rot, S.; Fritsch, M.; Meier, U.; Gölz, L.; Lemcke, J. Secondary deterioration in patients with normal pressure hydrocephalus after ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement: A proposed algorithm of treatment. Fluids Barriers CNS 2020, 17, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidiac, C.; Sundström, N.; Tullberg, M.; Arvidsson, L.; Olivecrona, M. Waiting time for surgery influences the outcome in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus—A population-based study. Acta Neurochir. 2022, 164, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benveniste, R.J.; Sur, S. Delayed symptom progression after ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement for normal pressure hydrocephalus. J. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 393, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, C.; Goertz, L.; Schulte, A.P.; Goldbrunner, R.; Krischek, B. Minimizing overdrainage with flow-regulated valves—Initial results of a prospective study on idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2018, 173, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eide, P.K. Intracranial pressure parameters in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus patients treated with ventriculo-peritoneal shunts. Acta Neurochir. 2006, 148, 21–29; discussion 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Yan, Z.; She, L.; Dong, J. The Clinical Effect of Postoperative Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: A Retrospective and Comparative Analysis of 61 Patients with Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt. World Neurosurg. 2017, 104, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tullberg, M.; Blennow, K.; Månsson, J.E.; Fredman, P.; Tisell, M.; Wikkelsö, C. Cerebrospinal fluid markers before and after shunting in patients with secondary and idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Cerebrospinal Fluid Res. 2008, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, G.A.S.; de Oliveira, M.F.; Pinto, F.C.G. The Timed Up and Go Test as a Diagnostic Criterion in Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. World Neurosurg. 2017, 105, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegelitz, D.; Arvidsson, J.; Hellström, P.; Tullberg, M.; Wikkelsø, C.; Starck, G. Pre-and postoperative cerebral blood flow changes in patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus measured by computed tomography (CT)-perfusion. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. Off. J. Int. Soc. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2016, 36, 1755–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringstad, G.; Emblem, K.E.; Eide, P.K. Phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging reveals net retrograde aqueductal flow in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. J. Neurosurg. 2016, 124, 1850–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurcoane, A.; Keil, F.; Szelenyi, A.; Pfeilschifter, W.; Singer, O.C.; Hattingen, E. Directional diffusion of corticospinal tract supports therapy decisions in idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Neuroradiology 2014, 56, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solana, E.; Sahuquillo, J.; Junqué, C.; Quintana, M.; Poca, M.A. Cognitive disturbances and neuropsychological changes after surgical treatment in a cohort of 185 patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. Off. J. Natl. Acad. Neuropsychol. 2012, 27, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundin, F.; Ledin, T.; Wikkelsø, C.; Leijon, G. Postural function in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus before and after shunt surgery: A controlled study using computerized dynamic posturography (EquiTest). Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2013, 115, 1626–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira MFde Saad, F.; Reis, R.C.; Rotta, J.M.; Pinto, F.C.G. Programmable valve represents an efficient and safe tool in the treatment of idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus patients. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2013, 71, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foss, T.; Eide, P.K.; Finset, A. Intracranial pressure parameters in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus patients with or without improvement of cognitive function after shunt treatment. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2007, 23, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundin, F.; Tisell, A.; Leijon, G.; Leinhard, O.D.; Davidsson, L.; Grönqvist, A.; Wikkelsø, C.; Lundberg, P. Preoperative and postoperative 1H-MR spectroscopy changes in frontal deep white matter and the thalamus in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2013, 84, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzen, H.; Ravdin, L.D.; Assuras, S.; Heros, R.; Kaplitt, M.; Schwartz, T.H.; Fink, M.; Levin, B.E.; Relkin, N.R. Postshunt cognitive and functional improvement in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 2011, 68, 416–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poca, M.A.; Mataró, M.; Del Mar Matarín, M.; Arikan, F.; Junqué, C.; Sahuquillo, J. Is the placement of shunts in patients with idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus worth the risk? Results of a study based on continuous monitoring of intracranial pressure. J. Neurosurg. 2004, 100, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, T.; Ouchi, Y.; Yoshikawa, E.; Sugihara, G.; Torizuka, T.; Tanaka, K. Striatal D2 receptor availability after shunting in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2007, 48, 1981–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illán-Gala, I.; Pérez-Lucas, J.; Martín-Montes, A.; Máñez-Miró, J.; Arpa, J.; Ruiz-Ares, G. Evolución a largo plazo de la hidrocefalia crónica del adulto idiopática tratada con válvula de derivación ventrículo-peritoneal. Neurología 2017, 32, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, U.; Miethke, C. Predictors of outcome in patients with normal-pressure hydrocephalus. J. Clin. Neurosci. Off. J. Neurosurg. Soc. Australas. 2003, 10, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegelitz, D.; Arvidsson, J.; Hellström, P.; Tullberg, M.; Wikkelsø, C.; Starck, G. In Patients with Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Postoperative Cerebral Perfusion Changes Measured by Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlate with Clinical Improvement. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2015, 39, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eide, P.K.; Brean, A. Intracranial pulse pressure amplitude levels determined during preoperative assessment of subjects with possible idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Acta Neurochir. 2006, 148, 1151–1156; discussion 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eide, P.K.; Sorteberg, W. Diagnostic intracranial pressure monitoring and surgical management in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: A 6-year review of 214 patients. Neurosurgery 2010, 66, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thavarajasingam, S.G.; El-Khatib, M.; Rea, M.; Russo, S.; Lemcke, J.; Al-Nusair, L.; Vajkoczy, P. Clinical predictors of shunt response in the diagnosis and treatment of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Neurochir. 2021, 163, 2641–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrén, K.; Wikkelsø, C.; Hellström, P.; Tullberg, M.; Jaraj, D. Early shunt surgery improves survival in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Eur. J. Neurol. 2021, 28, 1153–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krahulik, D.; Vaverka, M.; Hrabalek, L.; Hampl, M.; Halaj, M.; Jablonsky, J.; Langova, K. Ventriculoperitoneal shunt in treating of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus-single-center study. Acta Neurochir. 2020, 162, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrén, K.; Wikkelsø, C.; Laurell, K.; Kollén, L.; Hellström, P.; Tullberg, M. Symptoms and signs did not predict outcome after surgery: A prospective study of 143 patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. J. Neurol. 2024, 271, 3215–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, S.; Kimura, T.; Jingami, N.; Masamichi, A.; Hirai, O.; Tokuda, T.; Miyajima, M.; Kazui, H.; Mori, E.; Ishikawa, M. Disability risk or unimproved symptoms following shunt surgery in patients with idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus: Post hoc analysis of SINPHONI-2. J. Neurosurg. 2016, 126, 2002–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, T.; Yajima, K. Long-term 4 Years Follow-up Study of 482 Patients Who Underwent Shunting for Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus-Course of Symptoms and Shunt Efficacy Rates Compared by Age Group. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2019, 59, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianconi, A.; Colonna, S.; Minardi, M.; Di Perna, G.; Ceroni, L.; Nico, E.; Garbossa, D.; Borgarello, S.; Cofano, F. Prognostic Factors in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Patients After Ventriculo-Peritoneal Shunt: Results from a Single-Institution Observational Cohort Study with Long Term Follow-Up. World Neurosurg. 2024, 187, e1089–e1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caneva, S.; Hamedani, M.; Pesaresi, A.; Mori, L.; Marzi, A.; Pellegrino, L.; Merciadri, P.; Bianconi, A.; Zona, G.; Pardini, M.; et al. Beyond early motor response: Longitudinal cognitive and gait assessments after extended lumbar drainage in normal pressure hydrocephalus. Eur. J. Neurol. 2025, 32, e16567, Erratum in Eur. J. Neurol. 2025, 32, e70204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Acronym | Search Strategy |
|---|---|
| P (population or problem) | Adults diagnosed with idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) |
| I (intervention) | Ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt surgery |
| C (comparison) | None |
| O (outcome) | None |
| S (study design) | Original research studies |
| Study | Year | n | Male (n) | Mean Age (Years) | Follow-Up Intervals (Months) | Country | Type of Study | Duration of Symptoms (Months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Razay G. et al. [12] | 2019 | 62 | 39 | 77.6 | 3, 6, 12, >12 months | Australia | Retrospective | 24 |
| Agerskov G. et al. [13] | 2018 | 429 | 266 | 71 | 3 and 6 | Sweden | Retrospective | 44 |
| Wetzel C. et al. [14] | 2018 | 32 | 21 | 71.2 | 3 and 6 | Germany | Prospective | 22.9 |
| Tullberg M. et al. [15] | 2008 | 18 | 11 | 68 | 3 | Sweden | Prospective | 40 |
| Yang L. et al. [16] | 2017 | 27 | 17 | 71.1 | 3 and 6 | China | Prospective | 12 |
| Yang L. et al. [16] | 2017 | 31 | 20 | 71.4 | 3 and 6 | China | Prospective | 12 |
| Mendes GAS et al. [17] | 2017 | 29 | 18 | 73.9 | 12 and more | Spain | Prospective | 19.9 |
| Mendes GAS et al. [17] | 2017 | 26 | 15 | 71.5 | 12 | Brazil | Prospective | 27.33 |
| Ziegelitz D. et al. [18] | 2015 | 5 | 4 | 69 | 3 | Sweden | Prospective | 22 |
| Ringstad G. et al. [19] | 2015 | 17 | 9 | 74 | 12 | Norway | Prospective | 24 |
| Ziegelitz D. et al. [20] | 2015 | 15 | 8 | 71 | 3 | Sweden | Prospective | 36 |
| Jurcoane A. et al. [21] | 2014 | 12 | 9 | 74 | 24 | Germany | Prospective | 25 |
| Lundin F. et al. [22] | 2013 | 20 | 73 | 3 | Sweden | Prospective | 36 | |
| Oliveira MF et al. [23] | 2012 | 24 | 13 | 77.1 | 12 | Brazil | Prospective | 27.3 |
| Lundin F. et al. [24] | 2012 | 14 | 8 | 74 | 3 | Sweden | Prospective | 37 |
| Solana E. et al. [25] | 2012 | 185 | 111 | 73.96 | 6 | Spain | Prospective | 24 |
| Katzen H. et al. [26] | 2011 | 12 | 4 | 74.92 | 6 | USA | Prospective | 26.96 |
| Tisell M. et al. [11] | 2011 | 7 | 75 | 3 and 6 | Sweden | Prospective | 36 | |
| Razay G. et al. [12] | 2008 | 18 | 9 | 76.4 | 3 to 4 | Australia | Prospective | 55 |
| Nakayama T. et al. [27] | 2007 | 8 | 5 | 74.9 | 1 | Japan | Prospective | 27.6 |
| Foss T. et al. [28] | 2006 | 27 | 8 | 72 | 6 and 9 | Norway | Prospective | 30 |
| Eide PK et Brean A. [29] | 2006 | 40 | 21 | 75 | 12 | Norway | Prospective | 24 |
| Eide PK [30] | 2005 | 39 | 14 | 71 | 12 | Norway | Retrospective | 27.6 |
| Poca MA et al. [31] | 2005 | 12 | 8 | 74.08 | 6 | Spain | Prospective | 40 |
| Eide PK et Sorteberg [32] | 2005 | 19 | 8 | 68 | 12 | Norway | Prospective | 30 |
| Poca MA et al. [31] | 2004 | 43 | 30 | 71.1 | 6 | Spain | Prospective | 35.6 |
| Study | n | Duration of Symptoms (Months) | MMSE (0 m, 3 m, 6 m, 12 m) | TUG (s) (0 m, 3 m, 6 m, 12 m) | TUGs (Steps) (0 m, 3 m, 6 m, 12 m) |
| Agerskov G. et al. [13] | 429 | 44 | 0 m: 25; 3 m: 27.2 | 0 m: 17; 3 m: 12 | N/A |
| Wetzel C. et al. [14] | 32 | 22.9 | 0 m: 24.5; 3 m: 26.1; 6 m: 26.8 | N/A | N/A |
| Oliveira MF et al. [27] | 24 | 27.3 | 0 m: 19 | 0 m: 21; 3 m: 41 | 0 m: 35.77 |
| I.Illán-Gala I. et al. [33] | 29 | 19.9 | 0 m: 25 | 3 m: 25.3 | N/A |
| Lundin F. et al. [29] | 20 | 36 | 0 m: 27; 3 m: 27 | 0 m: 20; 3 m: 13.5 | 6 m: 26.5; 12 m: 19 |
| Lundin F. et al. [29] | 14 | 37 | 0 m: 28 | 0 m: 19.5; 3 m: 12 | 6 m: 29.5; 12 m: 17 |
| Solana E. et al. [25] | 185 | 24 | 0 m: 24; 6 m: 25 | N/A | N/A |
| Katzen H. et al. [30] | 12 | 26.96 | 0 m: 24.5; 6 m: 25.58 | N/A | N/A |
| Razay G. et al. [12] | 18 | 54 | 0 m: 23.5; 6 m: 28 | 0 m: 17; 3 m: 13 | N/A |
| Tisell M. et al. [11] | 18 | 40 | 0 m: 23.3; 6 m: 25.9 | N/A | N/A |
| Foss T. et al. [28] | 27 | 30 | 0 m: 25; 6 m: 26+ | N/A | N/A |
| Poca MA et al. [25] | 43 | 35.6 | 0 m: 21.33; 6 m: 22.56 | N/A | N/A |
| Jurcoane A. et al. [24] | 12 | 25 | 0 m: 26.3; 6 m: 27.6 | N/A | N/A |
| Tisell M. et al. [11] | 7 | 36 | 0 m: 22.5 | 0 m: 33.6; 3 m: 18; 6 m: 22 | N/A |
| Poca MA et al. [31] | 12 | 40 | 0 m: 19.83; 6 m: 22.42 | N/A | N/A |
| Mendes GAS et al. [21] | 26 | 27.33 | 0 m: 20 | 0 m: 22; 3 m: 38.7 | 6 m: 27.6 |
| Nakayama T. et al. [32] | 8 | 27.6 | 0 m: 21.3; 1 m: 21.8 | N/A | N/A |
| Study | n | Duration of Symptoms (Months) | 10 m (s) (0 m, 3 m, 6 m, 12 m) | 10 m (Steps) (0 m, 3 m, 6 m, 12 m) | EVANS Index (0 m, 3 m, 6 m, 12 m) |
| Lundin F. et al. [26] | 20 | 36 | 0 m: 16.5 | 0 m: 11.5 | - |
| Lundin F. et al. [29] | 14 | 37 | 0 m: 15 | 0 m: 9 | 0 m: 0.38; 3 m: 0.37 |
| Ringstad G. et al. [23] | 18 | 54 | 0 m: 17.4 | 0 m: 14.2 | N/A |
| Tullberg M. et al. [20] | 18 | 40 | 0 m: 23.4 | 0 m: 12.6 | N/A |
| Jurcoane A. et al. [24] | 12 | 25 | 0 m: 9.4 | 6 m: 8.4 | N/A |
| Tisell M. et al. [11] | 7 | 36 | 0 m: 25.3; 3 m: 33 | N/A | N/A |
| Oliveira MF et al. [27] | 24 | 27.3 | N/A | N/A | 0 m: 0.37; 12 m: 0.33 |
| Ziegelitz D. et al. [22] | 15 | 36 | N/A | N/A | 0 m: 0.4; 3 m: 0.37 |
| Ziegelitz D. et al. [35] | 5 | 22 | N/A | N/A | 0 m: 0.42; 3 m: 0.41 |
| Poca MA et al. [31] | 12 | 40 | N/A | N/A | 0 m: 0.38; 12 m: 0.33 |
| Mendes GAS et al. [21] | 26 | 27.33 | N/A | N/A | 0 m: 0.38; 12 m: 0.34 |
| Study | n | Duration of Symptoms (Months) | NPH Score (0 m, 3 m, 6 m, 12 m) |
| Yang L. et al. [19] | 27 | 27 | 0 m: 10.15; 3 m: 11.56; 6 m: 11.93 |
| Yang L. et al. [19] | 31 | 12 | 0 m: 10.39; 3 m: 11.84; 6 m: 12.58 |
| Ringstad G. et al. [23] | 17 | 24 | 0 m: 10; 12 m: 12 |
| Ziegelitz D. et al. [22] | 15 | 36 | 0 m: 48; 3 m: 68 |
| Ziegelitz D. et al. [35] | 5 | 22 | 0 m: 65; 3 m: 62 |
| Eide PK et Brean A. [36] | 40 | 24 | 0 m: 10; 12 m: 12 |
| Eide PK [18] | 39 | 27.6 | 0 m: 9; 12 m: 12 |
| Poca MA et al. [31] | 43 | 35.6 | 0 m: 9.21; 6 m: 12.42 |
| Poca MA et al. [31] | 12 | 40 | 0 m: 8.75; 6 m: 12.67 |
| Eide PK et Sorteberg [37] | 19 | 30 | 0 m: 9; 12 m: 11 |
| Study (Author, Year, Reference) | Selection | Comparability | Outcome | Total | Risk of Bias |
| Razay G. et al. [12] | 3 | 1 | 2 | 6 | Moderate risk |
| Agerskov G. et al. [13] | 4 | 2 | 2 | 8 | Low risk |
| Wetzel C. et al. [17] | 3 | 1 | 2 | 6 | Moderate risk |
| Tullberg M. et al. [20] | 3 | 1 | 2 | 6 | Moderate risk |
| Yang L. et al. [19] | 3 | 1 | 2 | 6 | Moderate risk |
| Mendes GAS et al. [21] | 3 | 1 | 2 | 6 | Moderate risk |
| Ziegelitz D. et al. [21] | 3 | 1 | 2 | 6 | Moderate risk |
| Ringstad G. et al. [23] | 3 | 1 | 2 | 6 | Moderate risk |
| Jurcoane A.et al. [24] | 3 | 1 | 2 | 6 | Moderate risk |
| Lundin F. et al. [26] | 3 | 1 | 2 | 6 | Moderate risk |
| Oliveira MF et al. [27] | 3 | 1 | 2 | 6 | Moderate risk |
| Solana E. et al. [25] | 3 | 1 | 2 | 6 | Moderate risk |
| Katzen H. et al. [30] | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | Moderate risk |
| Tisell M. et al. [11] | 2 | 1 | 2 | 5 | Moderate risk |
| Nakayama T. et al. [32] | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | Moderate risk |
| Foss T. et al. [28] | 2 | 1 | 2 | 5 | Moderate risk |
| Eide PK et Brean A. [36] | 3 | 1 | 2 | 6 | Moderate risk |
| Eide PK [18] | 2 | 1 | 2 | 5 | Moderate risk |
| Poca MA et al. [31] | 3 | 1 | 2 | 6 | Moderate risk |
| Eide PK et Sorteberg [37] | 2 | 1 | 2 | 5 | Moderate risk |
| Illán-Gala I. et al. [33] | 3 | 1 | 2 | 6 | Moderate risk |
| Ziegelitz D. et al. [22] | 3 | 1 | 2 | 6 | Moderate risk |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rovčanin, B.; Omerhodžić, I.; Nuhović, A.; Begagić, E.; Mahmutbegović, N.; Bečulić, H.; Sefo, H.; Mehmedika-Suljić, E.; Džurlić, A.; Pojskić, M. Time Course of Symptoms in Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1778. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15141778
Rovčanin B, Omerhodžić I, Nuhović A, Begagić E, Mahmutbegović N, Bečulić H, Sefo H, Mehmedika-Suljić E, Džurlić A, Pojskić M. Time Course of Symptoms in Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(14):1778. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15141778
Chicago/Turabian StyleRovčanin, Bekir, Ibrahim Omerhodžić, Adem Nuhović, Emir Begagić, Nevena Mahmutbegović, Hakija Bečulić, Haso Sefo, Enra Mehmedika-Suljić, Almir Džurlić, and Mirza Pojskić. 2025. "Time Course of Symptoms in Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus: A Systematic Review" Diagnostics 15, no. 14: 1778. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15141778
APA StyleRovčanin, B., Omerhodžić, I., Nuhović, A., Begagić, E., Mahmutbegović, N., Bečulić, H., Sefo, H., Mehmedika-Suljić, E., Džurlić, A., & Pojskić, M. (2025). Time Course of Symptoms in Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics, 15(14), 1778. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15141778








