Clinical Utility of Duplex Ultrasonography in the Recognition of Transplant Renal Artery Stenosis: A Single Center Experience
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
- Elevated serum creatinine (greater than or equal to 1.3 mg/dL);
- More than 50% renal artery stenosis on initial Duplex ultrasonography;
- Hypertension requiring two or more antihypertensive medications.
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACEIs | Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors |
| ARBs | angiotensin receptor blockers |
| BMI | body mass index |
| DSA | digital subtraction angiography |
| ESRD | end-stage renal disease |
| IR | interventional radiology |
| PSV | peak systolic velocity |
| PTA | percutaneous transluminal angioplasty |
| RI | resistance index |
| SPSS | Statistical Package for the Social Sciences |
| TRAS | transplant renal artery stenosis |
References
- Dimitroulis, D.; Bokos, J.; Zavos, G.; Nikiteas, N.; Karidis, N.P.; Katsaronis, P.; Kostakis, A. Vascular complications in renal transplantation: A single-center experience in 1367 renal transplantations and review of the literature. Transplant. Proc. 2009, 41, 1609–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pini, A.; Faggioli, G.; Pini, R.; Mauro, R.; Gallitto, E.; Mascoli, C.; Grandinetti, V.; Donati, G.; Odaldi, F.; Ravaioli, M.; et al. Assessment and Management of Transplant Renal Artery Stenosis. A Literature Review. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2022, 82, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safian, R.D. Transplant renal artery stenosis: What lessons should we learn? Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2011, 77, 294–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanhouche, G.; Santos, G.R.F.; Orellana, H.C.; Galhardo, A.; Faccinetto, A.C.B.; Barteczko, M.L.M.; Carvalho, L.S.F.d.; Taddeo, J.B.; Foresto, R.D.; Moises, V.A.; et al. Risk factors of transplant renal artery stenosis in kidney transplant recipients. Clinics 2022, 77, 100087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, H.J.; Jo, H.C.; Yang, J.H.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, H.J.; Choi, J.H.; Choi, S.H.; Song, B.G.; Choe, Y.H.; Choi, S.H.; et al. Flash Pulmonary Edema in a Patient with Unilateral Renal Artery Stenosis and Bilateral Functioning Kidneys. Korean Circ. J. 2010, 40, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fananapazir, G.; McGahan, J.P.; Corwin, M.T.; Stewart, S.L.; Vu, C.T.; Wright, L.; Troppmann, C. Screening for Transplant Renal Artery Stenosis: Ultrasound-Based Stenosis Probability Stratification. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2017, 209, 1064–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalili, J.; Khosroshahi, H.T.; Malekshoar, M.; Dehghan, M.; Akhgari, A.; Ghafouri Asbagh, A. Case report: Endovascular treatment of transplant renal artery stenosis in patient with normal color duplex ultrasound of the renal artery. Clin. Case Rep. 2024, 12, e8492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baird, D.P.; Williams, J.; Petrie, M.C.; Smith, J.R. Transplant Renal Artery Stenosis. Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 5, 2399–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Kayler, L.K.; Zand, M.S.; Muttana, R.; Chernyak, V.; DeBoccardo, G.O. Transplant renal artery stenosis: Clinical manifestations, diagnosis and therapy. Clin. Kidney J. 2015, 8, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, F.P.; Abbott, K.C.; Neff, R.T.; Elster, E.A.; Falta, E.M.; Lentine, K.L.; Agodoa, L.Y.; Jindal, R.M. Incidence, predictors and outcomes of transplant renal artery stenosis after kidney transplantation: Analysis of USRDS. Am. J. Nephrol. 2009, 30, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamara, F.; Fajar, J.K.; Gersom, C.; Wicaksono, R.S.; Tupamahu, A.R.; Huda, F.N.; Sari, F.R.; Dela, J.A.; Putri, I.E.; Sutrisno, M.A.; et al. Global prevalence and contributing factors of transplant renal artery stenosis in renal transplant recipients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Narra J. 2024, 4, e1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunawardena, T.; Sharma, H. Transplant Renal Artery Stenosis: Current Concepts. Exp. Clin. Transplant. 2022, 20, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; Han, Y.; Yu, T.; Chen, S.; Tang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. Diagnosis and Treatment of Renal Artery Stenosis in China in the Era of Donation After Cardiac Death. Ann. Transplant. 2020, 25, e918076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias-Cabrales, C.; Pérez-Sáez, M.J.; Redondo-Pachón, D.; Buxeda, A.; Burballa, C.; Bermejo, S.; Sierra, A.; Mir, M.; Burón, A.; Zapatero, A.; et al. Usefulness of the KDPI in Spain: A comparison with donor age and definition of standard/expanded criteria donor. Nefrología 2018, 38, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, A.J.; Machin, D.R.; Lesniewski, L.A. Mechanisms of Dysfunction in the Aging Vasculature and Role in Age-Related Disease. Circ. Res. 2018, 123, 825–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzas Montalvo, C.; Medina-Polo, J.; Miranda Utrera, N.R.; Juste Álvarez, S.; de la Calle Moreno, A.; Caro González, M.P.; de la Blanca, R.S.P.; Hernández Arroyo, M.; Peña Vallejo, E.; Teigell Tobar, J.; et al. Transplant renal artery stenosis: Study of incidence using doppler ultrasound, risk factors and analysis is effect in graft outcomes. Actas Urol. Esp. (Engl. Ed.) 2024, 48, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, H.A.; Suwaidi, J.A. Endothelial dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2007, 3, 853–876. [Google Scholar]
- Gallo, G.; Volpe, M.; Savoia, C. Endothelial Dysfunction in Hypertension: Current Concepts and Clinical Implications. Front. Med. 2022, 8, 798958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garland, S.; Pullerits, K.; Chukwu, C.A.; Chinnadurai, R.; Middleton, R.; Kalra, P.A. The effect of primary renal disease upon outcomes after renal transplant. Clin. Transplant. 2024, 38, e15216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, M.L.; Yong, C.; Trotter, P.B.; Grant, L.; Hosgood, S.A. Risk factors for transplant renal artery stenosis after live donor transplantation. Br. J. Surg. 2019, 106, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, D.; Vijayvergiya, R.; Kishore, K.; Subramani, V.N.; Banoth, M.; Reddy Perugu, S.P.; Mandwar, M.; Bamaniya, B.; Panjathia, A.; Gupta, P.; et al. Vascular Reconstruction of Multiple Renal Arteries—A Risk Factor for Transplant Renal Artery Stenosis: Insight From a Matched Case-Control Study. Transpl. Int. 2024, 37, 13298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, G.; Li, H.; Zuo, X.; Wang, C.; Xiao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X. Oscillatory shear stress promotes vein graft intimal hyperplasia via NADPH oxidase-related pathways. Front. Surg. 2023, 10, 1073557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Cao, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Y. The Etiology and Molecular Mechanism Underlying Smooth Muscle Phenotype Switching in Intimal Hyperplasia of Vein Graft and the Regulatory Role of microRNAs. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 935054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muske, S.; Aralapuram, K.; Jayaprakash, S.; Gurusiddaiah, S.C.; Nagesh, C.M.; Shankar, M. Transplant Renal Artery Stenosis with Varied Clinical Presentations. J. Indian Coll. Cardiol. 2024, 14, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.; Ademola, B.L.; Yusuf, L.; Abdulmalik, M.A. Renal Arterial Doppler Velocimetric Indices Among Healthy Subjcts in North West Nigeria. J. West Afr. Coll. Surg. 2018, 8, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qi, R.; Qi, G.; Zhu, D.; Wang, J. Diagnosis and Treatment of Early Transplant Renal Artery Stenosis: Experience From a Center in Eastern China. Transplant. Proc. 2020, 52, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, G.M.; Ireland, H.; Moss, J.G.; Harden, P.N.; Junor, B.J.; Rodger, R.S.; Briggs, J.D. Colour Doppler ultrasound in renal transplant artery stenosis: Which Doppler index? Clin. Radiol. 1995, 50, 618–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tublin, M.E.; Bude, R.O.; Platt, J.F. The Resistive Index in Renal Doppler Sonography: Where Do We Stand? Am. J. Roentgenol. 2003, 180, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khulaifat, S. Evaluation of a Transplanted Kidney by Doppler Ultrasound. Saudi J. Kidney Dis. Transplant. 2008, 19, 730. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, D.S.; He, W.; Shin, M.H.; Choi, N.K. Resistive index as a predictor of early failure of kidney transplantation. Korean J. Transplant. 2019, 33, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buturović-Ponikvar, J. Renal transplant artery stenosis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2003, 18, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosa Barrios, R.H.; Burguera Vion, V.; Casillas Sagrado, E.; Villa Hurtado, D.; Jiménez Álvaro, S.; Martín Capón, I.; Fernández Lucas, M.; Rivera Gorrín, M.E. Renal Transplant Artery Stenosis and Kinking: An Unusual Association. J. Point Care Ultrasound 2023, 8, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Hentel, K.; Zhu, Q.; Ma, T.; Shih, G.; Mennitt, K.; Min, R. Doppler angle correction in the measurement of intrarenal parameters. Int. J. Nephrol. Renov. Dis. 2011, 4, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Darabont, R.; Mihalcea, D.; Vinereanu, D. Current Insights into the Significance of the Renal Resistive Index in Kidney and Cardiovascular Disease. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macchini, M.; Mokrane, T.; Darcourt, J.; Bellière, J.; Kamar, N.; Candelari, R.; Rousseau, H.; Meyrignac, O. Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty alone versus stent placement for the treatment of transplant renal artery stenosis. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2019, 100, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
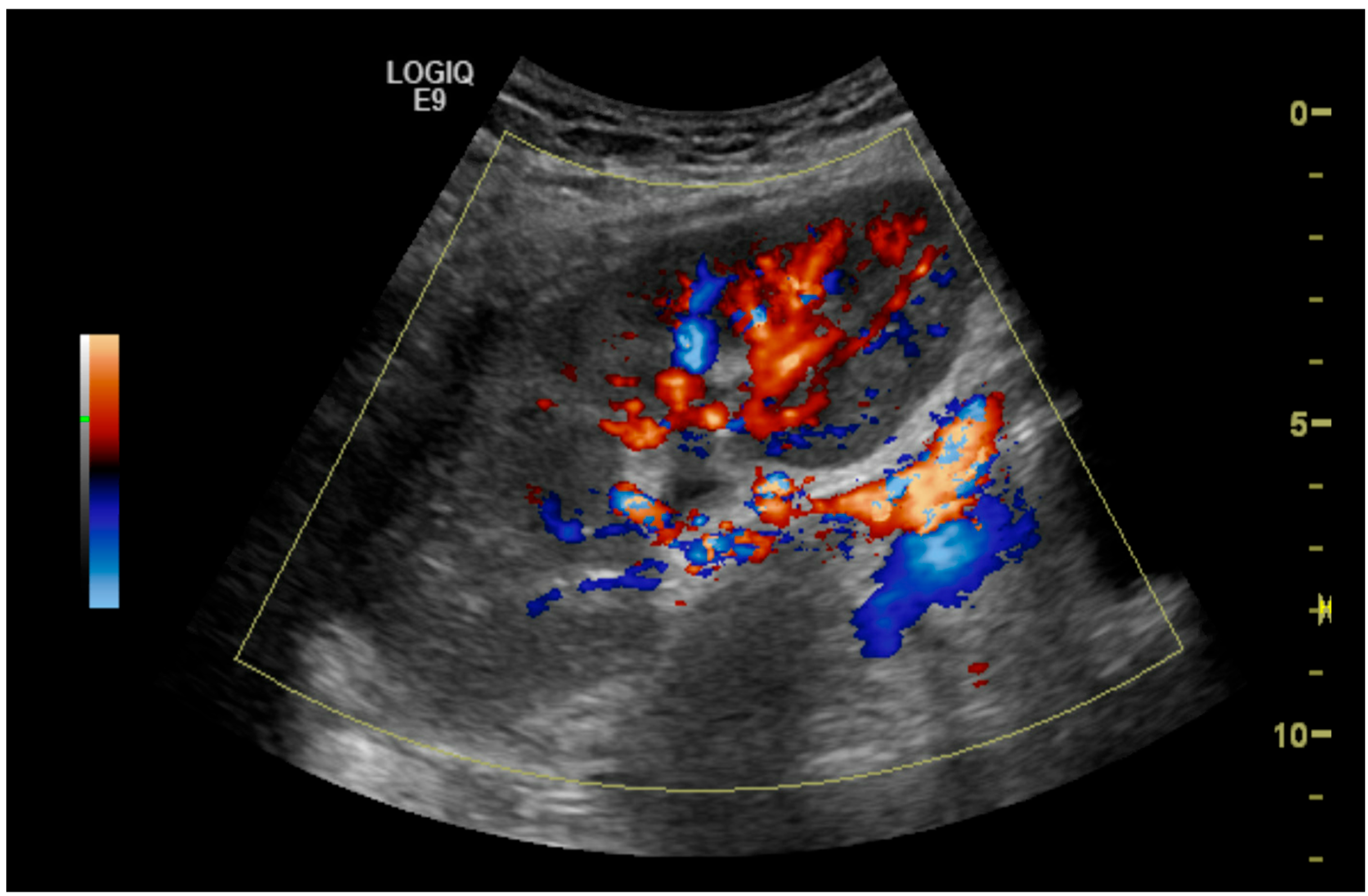


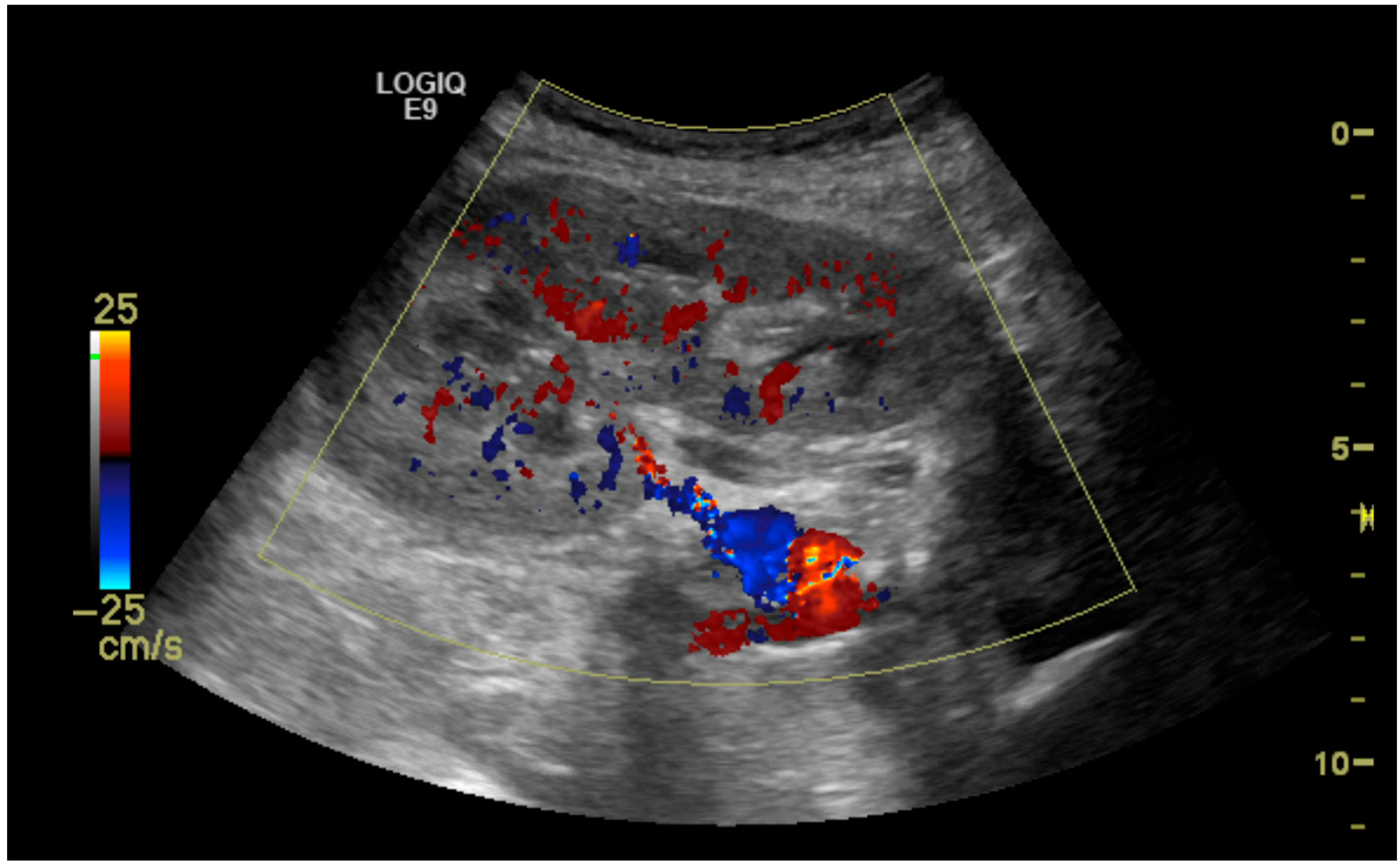
| Mean (Range) | |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 36 (6–60) |
| KDPI score | 41 (2–90) |
| Cold ischemia time (hours) | 23 (12.5–40.2) |
| Frequency (n) | Percentage (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Mean age (years) | 55.8 (27 to 71) | - |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 29.51 (20 to 37.9) | - |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 17 | 60.7 |
| Female | 11 | 39.3 |
| Race | ||
| African American | 21 | 75 |
| Caucasian | 5 | 18 |
| Hispanic | 2 | 7 |
| Comorbidity | ||
| Hypertension | 16 | 57 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 9 | 32 |
| Interstitial nephritis | 2 | 7 |
| Autoimmune nephropathies | 1 | 4 |
| ASA score | ||
| 3 | 23 | 82 |
| 4 | 5 | 18 |
| Mean (Range) | |
|---|---|
| Time from transplant to RAS diagnosis (months) | 4.9 (0.4–17) |
| BP systolic (mmHg) | 151 (99–213) |
| BP diastolic (mmHg) | 76 (55–120) |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 2.43 (1.28–6.38) |
| Prescribed antihypertensive medications | 3 (2–5) |
| Case No. | Resistive Indices | Peak Systolic Velocity (cm/s) | Location | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper | Mid | Lower | |||
| 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 548 | Anastomosis |
| 2 | 0.68 | 0.67 | 0.67 | 434 | Anastomosis |
| 3 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 669 | Anastomosis |
| 4 | 0.73 | 0.67 | 0.69 | 494 | Proximal |
| 5 | 0.45 | 0.43 | 0.47 | 535 | Anastomosis |
| 6 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 420 | Proximal |
| 7 | 0.63 | 0.69 | 0.59 | 679 | Proximal |
| 8 | 1 | 1 | 0.82 | 450 | Proximal |
| 9 | 0.58 | 0.63 | 0.54 | 348 | Anastomosis |
| 10 | 0.71 | 0.69 | 0.7 | 228 | Anastomosis |
| 11 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 293 | Mid |
| 12 | 0.76 | 0.78 | 0.74 | 324 | Proximal |
| 13 | 0.74 | 0.73 | 0.64 | 462 | Anastomosis |
| 14 | 0.67 | 0.7 | 1 | 604 | Hilum |
| 15 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 544 | Anastomosis |
| 16 | 0.59 | 0.56 | 0.43 | 319 | Mid |
| 17 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 853 | Anastomosis |
| 18 | 0.83 | 0.86 | 0.77 | 481 | Anastomosis |
| 19 | 0.43 | 0.57 | 0.61 | 713 | Proximal |
| 20 | 0.77 | 0.78 | 1 | 465 | Anastomosis |
| 21 | 0.75 | 0.7 | 0.77 | 403 | Proximal |
| 22 | 0.68 | 1 | 1 | 770 | Mid |
| 23 | 0.54 | 0.36 | 0.29 | 450 | Hilum |
| 24 | 0.7 | 0.77 | 0.73 | 304 | Proximal |
| 25 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 285 | Proximal |
| 26 | 0.49 | 0.63 | 0.62 | 234 | Proximal |
| 27 | 0.70 | 1.0 | 0.61 | 235 | Mid |
| 28 | 0.58 | 0.57 | 0.43 | 408 | Proximal |
| Mean | Standard Deviation | p-Value | 95% Confidence Interval | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resistive Index | Upper pole | 0.71 | 0.17 | 0.338 | 0.64–0.77 |
| Mid Pole | 0.73 | 0.19 | 0.66–0.80 | ||
| Lower Pole | 0.71 | 0.21 | 0.63–0.79 | ||
| Peak systolic velocity (cm/s) | 462.57 | 166.28 | - | 400.98–524.16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mirza, A.; Baig, U.; Khan, M.; Beigh, S.; Gani, I. Clinical Utility of Duplex Ultrasonography in the Recognition of Transplant Renal Artery Stenosis: A Single Center Experience. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15141766
Mirza A, Baig U, Khan M, Beigh S, Gani I. Clinical Utility of Duplex Ultrasonography in the Recognition of Transplant Renal Artery Stenosis: A Single Center Experience. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(14):1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15141766
Chicago/Turabian StyleMirza, Ahmad, Usman Baig, Munazza Khan, Shameem Beigh, and Imran Gani. 2025. "Clinical Utility of Duplex Ultrasonography in the Recognition of Transplant Renal Artery Stenosis: A Single Center Experience" Diagnostics 15, no. 14: 1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15141766
APA StyleMirza, A., Baig, U., Khan, M., Beigh, S., & Gani, I. (2025). Clinical Utility of Duplex Ultrasonography in the Recognition of Transplant Renal Artery Stenosis: A Single Center Experience. Diagnostics, 15(14), 1766. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15141766





