Radix Entomolaris and Complex Incisor Anatomy in a Saudi Cohort: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
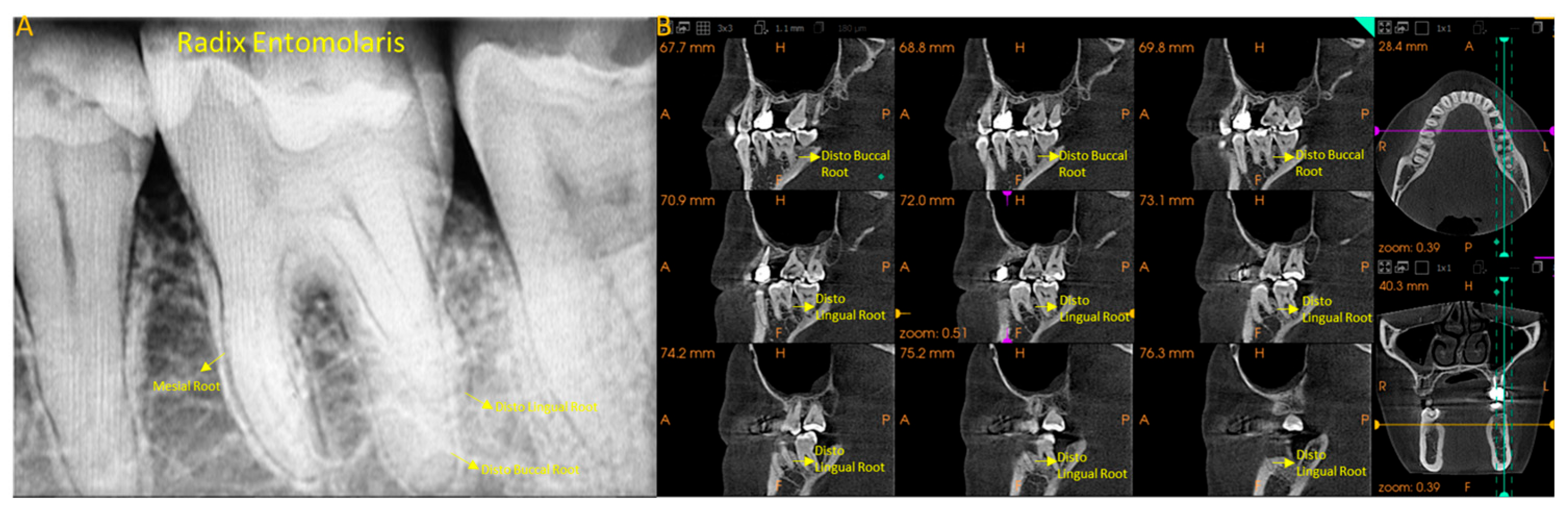
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Sample
2.3. CBCT Unit and Evaluation
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Data
3.2. Root Canal Classification of the MI
3.3. Prevalence of DLR in MFM (Radix)
3.3.1. Gender
3.3.2. Age
3.3.3. Site
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Costa, F.F.N.P.; Pacheco-Yanes, J.; Siqueira, J.F., Jr.; Oliveira, A.C.S.; Gazzaneo, I.; Amorim, C.A.; Santos, P.H.B.; Alveset, F.R.F. Association between missed canals and apical periodontitis. Int. Endod. J. 2019, 52, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, K.; Teoh, Y.Y.; Walsh, L.J. Root canal cleaning in roots with complex canals using agitated irrigation fluids. Aust. Endod. J. 2023, 49, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.; Brown, J.; Pimentel, T.; Kelly, R.D.; Abella, F.; Durack, C. Cone beam computed tomography in Endodontics—A review of the literature. Int. Endod. J. 2019, 52, 1138–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, A.W.K.; Harper, B.; Zhang, C.; Neelakantan, P.; Bornstein, M.M. Do different cone beam computed tomography exposure protocols influence subjective image quality before and after root canal treatment? Clin. Oral Investig. 2021, 25, 2119–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, A.W.K.; Jacobs, R.; Bornstein, M.M. Novel low-dose protocols using cone beam computed tomography in dental medicine: A review focusing on indications, limitations, and future possibilities. Clin. Oral Investig. 2019, 23, 2573–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.M.A.; Rossi-Fedele, G.; Dummer, P.M.H. Critical analysis of a new system to classify root and canal morphology—A systematic review. Aust. Endod. J. 2023, 49, 750–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, M.B.; Gufran, K.; Alhabib, O.; Alafraa, O.; Alzahrani, F.; Abuelqomsan, M.S.; Karobari, M.I.; Alnajei, A.; Afroz, M.M.; Akram, S.M.; et al. CBCT based study to analyze and classify root canal morphology of maxillary molars—A retrospective study. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 26, 6550–6560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karobari, M.I.; Noorani, T.Y.; Halim, M.S.; Ahmed, H.M.A. Root and canal morphology of the anterior permanent dentition in Malaysian population using two classification systems: A CBCT clinical study. Aust. Endod. J. 2021, 47, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhumaidi, A.M.; Mirza, M.B.; Karobari, M.I.; Abuelqomsan, M.A.; Hashem, Q.; Aldaijy, M.T.; Albarr, N.Y.; Aldaijy, R.T.; Moaleem, M.A. Classifying the internal anatomy of anterior teeth in the Yemeni population using two systems: A retrospective CBCT study. Odontology 2025, 113, 416–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.N.R.; Ensinas, P.; Chan, F.; Babayeva, N.; von Zuben, M.; Berti, L.; Lam, E.W.N.; Antúnez, M.; Pei, F.; de la Espriella, C.M.; et al. Worldwide Prevalence of the Lingual Canal in Mandibular Incisors: A Multicenter Cross-sectional Study with Meta-analysis. J. Endod. 2023, 49, 819–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayaoglu, G.; Peker, I.; Gumusok, M.; Sarikir, C.; Kayadugun, A.; Ucok, O. Root and canal symmetry in the mandibular anterior teeth of patients attending a dental clinic: CBCT study. Braz. Oral Res. 2015, 29, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhengyan, Y.; Keke, L.; Fei, W.; Yueheng, L.; Zhi, Z. Cone-beam computed tomography study of the root and canal morphology of mandibular permanent anterior teeth in a Chongqing population. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2015, 12, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, M.; Chan, S.; Ku, J. Relative frequency of teeth needing conventional and surgical endodontic treatment in patients treated at a graduate endodontic clinic—A Penn Endo database study. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2008, 106, e62–e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duman, S.B.; Duman, S.; Bayrakdar, I.S.; Yasa, Y.; Gumussoy, I. Evaluation of radix entomolaris in mandibular first and second molars using cone-beam computed tomography and review of the literature. Oral Radiol. 2020, 36, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Guo, Q.; Tan, B.K.; Huang, D.; Zhou, X.; Shen, Y.; Gao, Y.; Haapasalo, M. Geometric analysis of the distolingual root and canal in mandibular first molars: A micro-computed tomographic study. J. Endod. 2021, 47, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.C.; Cheng, W.C.; Chung, M.P.; Su, C.C.; Weng, P.W.; Tsai, Y.W.C.; Chiang, H.S.; Yeh, H.W.; Chung, C.H.; Shieh, Y.S.; et al. Complicated root canal morphology of mandibular lateral incisors is associated with the presence of distolingual root in mandibular first molars: A cone beam computed tomographic study in a Taiwanese population. J. Endod. 2018, 44, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.B.; Seo, M.S. Mandibular incisors with two canals are associated with the presence of the distolingual root in mandibular first molars: A cone-beam computed tomographic study. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-C.; Cheng, W.-C.; Weng, P.-W.; Chung, M.-P.; Su, C.-C.; Chiang, H.-S.; Tsai, Y.-W.C.; Chung, C.-H.; Shieh, Y.-S.; Huang, R.-Y. The presence of distolingual root in mandibular first molars is correlated with complicated root canal morphology of mandibular central incisors: A cone beam computed tomographic study in a Taiwanese population. J. Endod. 2018, 44, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Chen, M.; Zeng, J.; Wu, B. Vertucci’s root canal configuration of 11,376 mandibular anteriors and its relationship with distolingual roots in mandibular first molars in a Cantonese population: A cone-beam computed tomography study. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, K.; Banga, K.S.; Pawar, A.; Wahjuningrum, D.A.; Karobari, M.I. Distolingual root prevalence in mandibular first molar and complex root canal morphology in incisors: A CBCT analysis in Indian population. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rammahi, H.M.; Chai, W.L.; Nabhan, M.S.; Ahmed, H.M.A. Root and canal anatomy of mandibular first molars using micro computed tomography: A systematic review. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshayban, M.; Abughosh, T.; Almalki, W.; Alrasheed, M. Cone-beam computed tomographic evaluation of root canal morphology of mandibular anterior teeth in a Saudi subpopulation, retrospective In-Vivo study. Saudi Dent. J. 2022, 34, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashyakhy, M. Anatomical analysis of permanent mandibular incisors in a Saudi Arabian population: An in vivo cone-beam computed tomography study. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2019, 22, 1611–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomaszewska, I.M.; Skinningsrud, B.; Jarzebska, A.; Pekala, J.R.; Tarasiuk, J.; Iwanaga, J. Internal and external morphology of mandibular molars: An original micro CT study and meta-analysis with review of implications for endodontic therapy. Clin. Anat. 2018, 31, 797–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.N.; Nole, C.; Ounsi, H.F.; Parashos, P.; Plotino, G.; Ragnarsson, M.F.; Aguilar, R.R.; Santiago, F.; Seedat, H.C.; Vargas, W.; et al. Worldwide assessment of the mandibular first molar second distal root and root canal: A cross-sectional study with meta-analysis. J. Endod. 2022, 48, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, N.M.; Myin, K.K. Three-Rooted Permanent Mandibular First Molars: A Meta-Analysis of Prevalence. Int. J. Dent. 2022, 2022, 9411076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, M.-G.; Huang, H.-L.; Hsue, S.-S.; Hsu, J.-T.; Chen, S.-Y.; Jou, M.-J.; Tsai, C.-C. Detection of permanent three-rooted mandibular first molars by cone-beam computed tomography imaging in Taiwanese individuals. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Lu, Q.; Wang, H.; Ding, Y.; Wang, P.; Ni, L. Root canal morphology of permanent three-rooted mandibular first molars—Part I: Pulp floor and root canal system. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 990–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Alawi, H.; Al-Nazhan, S.; Al-Maflehi, N.; Aldosimani, M.A.; Zahid, M.N.; Shihabi, G.N. The prevalence of radix molaris in the mandibular first molars of a Saudi subpopulation based on cone-beam computed tomography. Restor. Dent. Endod. 2019, 45, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riyahi, A.M.; Alssum, K.; Hadadi, H.; Alsayyari, A.; Alebrah, T.; Aljarbou, F. Prevalence of three-rooted mandibular permanent first and second molars in the Saudi population. Saudi Dent. J. 2019, 31, 492–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, M.Q.; Srivastava, S.; Alotaibi, B.B.R.; Bhatti, U.A.; Abulhamael, A.M.; Habib, S.R. A Cone Beam Computed Tomography-Based Investigation of the Frequency and Pattern of Radix Entomolaris in the Saudi Arabian Population. Medicina 2023, 59, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, C.T.; de Oliveira-Santos, C.; Bernardineli, N.; Duarte, M.A.H.; Bramante, C.M.; Minotti-Bonfante, P.G.; Ordinola-Zapata, R. Prevalence and morphometric analysis of three-rooted mandibular first molars in a Brazilian subpopulation. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2016, 24, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimi, S.; Mokhtari, H.; Ranjkesh, B.; Johari, M.; Reyhani, M.F.; Shahi, S.; Reyhani, S.S. Prevalence of Extra Roots in Permanent Mandibular First Molars in Iranian Population: A CBCT Analysis. Iran. Endod. J. 2017, 12, 70–73. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.Y.; Yang, S.E. Cone beam computed tomography study of incidence of distolingual root and distance from distolingual canal to buccal cortical bone of mandibular first molars in a Korean population. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.R.; Moon, Y.M.; Seo, M.S. Prevalence and features of distolingual roots in mandibular molars analyzed by cone beam computed tomography. Imaging Sci. Dent. 2015, 45, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, J.N.; Ordinola-Zapata, R.; Marques, D.; Francisco, H.; Carames, J. Differences in root canal configuration in human permanent teeth within different age groups. Int. Endod. J. 2018, 51, 931–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Choi, M.R.; Yoo, J.J. Concurrent relationship between additional canals of mandibular first molars and maxillary first molars using cone beam computed tomography. Oral Radiol. 2013, 29, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.C.; Su, C.C.; Tsai, Y.C.; Cheng, W.C.; Chung, M.P.; Chiang, H.S.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Chung, C.H.; Shieh, Y.S.; Huang, R.Y. Complicated root canal configuration of mandibular first premolars is correlated with the presence of the distolingual root in mandibular first molars: A cone beam computed tomographic study in Taiwanese individuals. J. Endod. 2017, 43, 1064–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papic, M.; Papic, M.; Vuletic, M.; Zdravkovic, D.; Misic, A.; Zivanovic, S. Complicated root canal morphology of permanent mandibular lateral incisors is associated with the presence of a second mesiobuccal canal in permanent maxillary first molars. Serb. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2019, 23, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Classification System | Mandibular Incisors (n = 2248) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central Incisors n = 1124 | Lateral Incisors n = 1124 | Chi-Square Test | ||||
| Vertucci | Ahmed et al. | 41 (%) | 31 (%) | 42 (%) | 32 (%) | |
| I | 1TN1 | 402 (71.5) | 398 (70.8) | 367 (65.4) | 362 (64.4) | X2 52.44 p <0.001 ** |
| 71.1% | 64.9% | |||||
| II | 1TN2−1 | 0 | 0 | 22 (3.9) | 17 (3) | |
| 3.4% | ||||||
| III | 1TN1−2−1 | 92 (16.4) | 90 (16) | 116 (20.6) | 118 (21) | |
| 16.2% | 20.8% | |||||
| V | 1TN1−2 | 68 (12.1) | 74 (13.2) | 57 (10.1) | 65 (11.6) | |
| 12.7% | 10.9% | |||||
| n | Canal | Total | Right Central | Left Central | Right Lateral | Left Lateral | Chi-Square |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2248 Incisors | Simple | 1529 68% | 402 71.5% | 398 70.8% | 367 65.3% | 362 64.4% | X2 10.475 p 0.014 * |
| 71.1% | 64.9 | ||||||
| Complex | 719 32% | 160 28.5% | 164 29.2% | 195 34.7% | 200 35.6% | ||
| 28.85% | 35.15% | ||||||
| Teeth | Type | Gender | Chi-Square Test | Age | Chi-Square Test | Site | Chi-Square Test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | 20–39 | 40–59 | >60 | Right | Left | |||||
| 39 | 20 | 38 | 17 | 4 | 34 | 25 | |||||
| 3.5% | 1.8% | 3.4% | 1.5% | 0.4% | 3% | 2.2% | |||||
| Central incisors | I | 9 | 7 | X2 | 7 | 6 | 3 | X2 | 10 | 6 | X2 |
| 0.8% | 0.6% | 0.95 | 0.6% | 0.5% | 0.3% | 6.66 | 0.9% | 0.5% | 0.21 | ||
| III | 30 | 13 | p | 31 | 11 | 1 | p | 24 | 19 | p | |
| 2.7% | 1.2% | 0.33 ns | 2.8% | 1% | 0.1% | 0.035 * | 2.1% | 1.7% | 0.644 ns | ||
| Lateral incisors | I | 10 | 6 | X2 | 9 | 5 | 2 | X2 | 11 | 5 | X2 |
| 0.9% | 0.5% | 0.12 | 0.8% | 0.4% | 0.2% | 1.33 | 1% | 0.4% | 1.112 | ||
| III | 29 | 14 | p | 29 | 12 | 2 | p | 23 | 20 | p | |
| 2.6% | 1.3% | 0.72 ns | 2.6% | 1.1% | 0.2% | 0.51 ns | 2% | 1.9% | 0.29 ns | ||
| Quadrant | Tooth | Canal | Without DLR | DLR | Total | X2 | p | Odds Ratio | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right | Central Incisor | Simple | 392 | 10 | 402 | ||||
| 69.75% | 1.78% | 71.53% | 31.52 | <0.001 ** | 6.92 | 3.22–14.83 | |||
| Complex | 136 | 24 | 160 | ||||||
| 24.19% | 4.27% | 28.46% | |||||||
| Lateral Incisor | Simple | 356 | 11 | 367 | 17.34 | ||||
| 63.34% | 1.96% | 65.30% | <0.001 ** | 4.33 | 2.06–9.08 | ||||
| Complex | 172 | 23 | 195 | ||||||
| 30.60% | 4.09% | 34.69% | |||||||
| Left | Central Incisor | Simple | 392 | 6 | 398 | 27.75 | |||
| 69.75% | 1.06% | 70.81% | <0.001 ** | 8.56 | 3.35–21.85 | ||||
| Complex | 145 | 19 | 164 | ||||||
| 25.80% | 3.38% | 29.18% | |||||||
| Lateral Incisor | Simple | 357 | 5 | 362 | 22.514 | ||||
| 63.52% | 0.88% | 64.41% | <0.001 ** | 7.93 | 2.92–21.48 | ||||
| Complex | 180 | 20 | 200 | ||||||
| 32.08% | 3.55% | 35.58% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mirza, M.B. Radix Entomolaris and Complex Incisor Anatomy in a Saudi Cohort: A Retrospective Study. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1721. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131721
Mirza MB. Radix Entomolaris and Complex Incisor Anatomy in a Saudi Cohort: A Retrospective Study. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(13):1721. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131721
Chicago/Turabian StyleMirza, Mubashir Baig. 2025. "Radix Entomolaris and Complex Incisor Anatomy in a Saudi Cohort: A Retrospective Study" Diagnostics 15, no. 13: 1721. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131721
APA StyleMirza, M. B. (2025). Radix Entomolaris and Complex Incisor Anatomy in a Saudi Cohort: A Retrospective Study. Diagnostics, 15(13), 1721. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131721





