Drug-Induced Sarcoid-like Reactions Associated to Targeted Therapies and Biologic Agents
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Excessive immune response: Certain drugs can induce a significant and uncontrolled increase in immune activity, as observed with checkpoint inhibitors and BRAF inhibitors. These medications can lead to excessive activation of T cells, including Th1 and Th17, ultimately promoting granuloma formation [5,6].
- Paradoxical immune activation: Some anti-inflammatory medications can alter the immune profile, leading to the unexpected activation of pathways involved in granuloma formation. For example, despite their role in treating inflammatory conditions, both anti-TNF agents and Rituximab have been reported to induce granuloma development in some patients [7,8].
2. Materials and Methods
3. Targeted Therapies Associated with Drug-Induced Sarcoid-like Reaction
3.1. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
3.2. Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Antagonists
3.3. BRAF Inhibitors
3.4. Monoclonal Antibodies
3.5. Miscellaneous Drugs
4. Diagnosis
5. Management and Therapy
- The severity of the primary condition;
- The availability of other therapeutic options;
- The severity of DISR symptoms.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BAFF | B-cell-activating factor |
| BRAF | B-Raf proto-oncogene, serine/threonine kinase |
| CTLA-4 | Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 |
| DISRs | Drug-induced sarcoid-like reactions |
| ICIs | Immune checkpoint inhibitors |
| irAEs | Immune-related adverse events |
| IWOS | International Workshop on Ocular Sarcoidosis |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| PD-1 | Programmed death-1 |
| TNF-alfa | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
References
- Sakthivel, P.; Bruder, D. Mechanism of granuloma formation in sarcoidosis. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2017, 24, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broos, C.E.; Van Nimwegen, M.; Hoogsteden, H.C.; Hendriks, R.W.; Kool, M.; Van Den Blink, B. Granuloma Formation in Pulmonary Sarcoidosis. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chopra, A.; Nautiyal, A.; Kalkanis, A.; Judson, M.A. Drug-Induced Sarcoidosis-Like Reactions. Chest 2018, 154, 664–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danlos, F.-X.; Pagès, C.; Baroudjian, B.; Vercellino, L.; Battistella, M.; Mimoun, M.; Jebali, M.; Bagot, M.; Tazi, A.; Lebbé, C. Nivolumab-Induced Sarcoid-Like Granulomatous Reaction in a Patient with Advanced Melanoma. Chest 2016, 149, e133–e136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apalla, Z.; Kemanetzi, C.; Papageorgiou, C.; Bobos, M.; Manoli, M.; Fotiadou, C.; Hatzibougias, D.; Boukovinas, I.; Stergiou, E.; Levva, S.; et al. Challenges in sarcoidosis and sarcoid-like reactions associated to immune checkpoint inhibitors: A narrative review apropos of a case. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e14618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuske, M.; Westphal, D.; Wehner, R.; Schmitz, M.; Beissert, S.; Praetorius, C.; Meier, F. Immunomodulatory effects of BRAF and MEK inhibitors: Implications for Melanoma therapy. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 136, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galimberti, F.; Fernandez, A.P. Sarcoidosis following successful treatment of pemphigus vulgaris with rituximab: A rituximab-induced reaction further supporting B-cell contribution to sarcoidosis pathogenesis? Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2016, 41, 413–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amber, K.T.; Bloom, R.; Mrowietz, U.; Hertl, M. TNF-α: A treatment target or cause of sarcoidosis? J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2015, 29, 2104–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, A.; Wolchok, J.D. Cancer immunotherapy using checkpoint blockade. Science 2018, 359, 1350–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.C.; Duffy, C.R.; Allison, J.P. Fundamental Mechanisms of Immune Checkpoint Blockade Therapy. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 1069–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Casals, M.; Brahmer, J.R.; Callahan, M.K.; Flores-Chávez, A.; Keegan, N.; Khamashta, M.A.; Lambotte, O.; Mariette, X.; Prat, A.; Suárez-Almazor, M.E. Immune-related adverse events of checkpoint inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcoval, J.; Bauer-Alonso, A.; Fornons-Servent, R.; Jiménez-Colomo, L.; Sabaté-Llobera, A.; Penín, R.M. Subcutaneous sarcoidosis induced by pembrolizumab in a melanoma patient mimicking subcutaneous metastasis at 18F-FDG PET/CT. Rev. Esp. Med. Nucl. E Imagen Mol. Engl. Ed. 2021, 40, 255–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keukeleire, S.D.; Schwarze, J.; Awada, G.; Everaert, H.; Van Binst, A.M.; Cras, L.; Neyns, B.; Aspeslagh, S. An atypical sarcoid-like reaction during anti-protein death 1 treatment in a patient with metastatic melanoma. Melanoma Res. 2020, 30, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jespersen, H.; Bjursten, S.; Ny, L.; Levin, M. Checkpoint inhibitor-induced sarcoid reaction mimicking bone metastases. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, e327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambichler, T.; Philippou, S.; Scheel, C.H.; Susok, L. Development of thoracic sarcoid reactions associated with complete response to anti-PD-1 therapy in a patient with advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosse, A.; Grosse, C. Diagnostic yield of broncho-alveolar lavage for pembrolizumab induced sarcoid-like reaction of the lung. Cytopathology 2019, 30, 686–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y. FDG PET/CT Course of Pembrolizumab-Associated Multiorgan Sarcoidosis. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2019, 44, 167–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodbeck, R.; Metelitsa, A.I.; Naert, K.A. Granulomatous Tumoral Melanosis Associated with Pembrolizumab Therapy: A Mimicker of Disease Progression in Metastatic Melanoma. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2018, 40, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraki, T.; Hatanaka, M.; Arimura, A.; Kawahira, H.; Kirishima, M.; Kitazono, I.; Horinouchi, M.; Higashi, M.; Kanekura, T.; Tanimoto, A. Granulomatous/sarcoid-like reactions in the setting of programmed cell death-1 inhibition: A potential mimic of disease recurrence. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2020, 47, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keane, F.; Yogiaveetil, E.; Kezlarian, B.; Lagratta, M.; Segal, N.H.; Abou-Alfa, G.; O’Reilly, E.M.; Saltz, L.; El Dika, I. Immune checkpoint blockade induced sarcoid-like reaction mimicking progression of disease in a patient with microsatellite instable colorectal cancer: Case report and review of the literature. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2024, 15, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, A.; Mehrmal, S.; Chaudhry, S. Immunotherapy-induced exclusively cutaneous sarcoid-like reaction. BMJ Case Rep. 2023, 16, e252766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomax, A.J.; McGuire, H.M.; McNeil, C.; Choi, C.J.; Hersey, P.; Karikios, D.; Shannon, K.; Van Hal, S.; Carr, U.; Crotty, A.; et al. Immunotherapy-induced sarcoidosis in patients with melanoma treated with PD -1 checkpoint inhibitors: Case series and immunophenotypic analysis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 20, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chahin, M.; Stack, A.; Siddiqi, A.; Shaikh, M. Is it metastatic melanoma or is it sarcoidosis? Non-caseating granulomas due to pembrolizumab. BMJ Case Rep. 2020, 13, e240701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chau, B.T.C.; McKelvie, P.; Bazargan, A.; Mohamed, M. Pembrolizumab associated sarcoid-like lymphadenopathy mimicking progressive disease in Hodgkin lymphoma. Pathology 2021, 53, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirgi, Y.; Krochmal, R.; Fleury, C.M.; Holmes, M.; Dewitt, C.A.; Cardis, M.; Kim, C. Pembrolizumab-Associated Cutaneous and Pulmonary Sarcoidosis in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment. Clin. Lung Cancer 2022, 23, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousuf, H.; Mekki, R.; Khan, K.; Hussain, A. Pembrolizumab-Induced Sarcoid-Like Reaction in a Patient with Lung Cancer. Cureus 2020, 12, e12395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaty, S.; Bastian, C.M.; Ramirez-Cibes, I.; Shahlapour, M.; Dhillon, W. Pembrolizumab-Induced Sarcoid-Like Reaction: FDG-PET Scan Interpretation in the Era of Immunotherapy. Cureus 2020, 12, e9449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheshire, S.C.; Board, R.E.; Lewis, A.R.; Gudur, L.D.; Dobson, M.J. Pembrolizumab-induced Sarcoid-like Reactions during Treatment of Metastatic Melanoma. Radiology 2018, 289, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, M.C.; Molloy, K.; Crowther, S.; Feeney, J.; Gillis, A.; Connolly, M.; Kelleher, F. Pembrolizumab-Related Sarcoid-Like Reaction Presenting as Reactivation of Quiescent Scars. J. Oncol. Pract. 2018, 14, 200–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honigman, A.D.; Lai, F.; Elakis, J.; Prall, O.; Goh, M.; McCormack, C. Pembrolizumab-induced sarcoid granulomatous panniculitis and bullous pemphigoid in a single patient. Clin. Case Rep. 2019, 7, 773–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.J.; Mitchell, T.C.; Chu, E.Y. Pembrolizumab-induced sarcoidal infusion site reaction. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2018, 45, 727–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhri, G.; Akel, R.; Salem, Z.; Tawil, A.; Tfayli, A. Pulmonary Sarcoidosis Activation following Neoadjuvant Pembrolizumab plus Chemotherapy Combination Therapy in a Patient with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Case Report. Case Rep. Oncol. 2017, 10, 1070–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cousin, S.; Toulmonde, M.; Kind, M.; Cazeau, A.-L.; Bechade, D.; Coindre, J.-M.; Italiano, A. Pulmonary sarcoidosis induced by the anti-PD1 monoclonal antibody pembrolizumab. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1178–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-D.; Kim, M.-S.; Han, M.-H.; Kim, Y.-J.; Jung, H.-Y.; Choi, J.-Y.; Cho, J.-H.; Park, S.-H.; Kim, C.-D.; Kim, Y.-L.; et al. Renal Sarcoidosis-like Reaction Induced by PD-1 Inhibitor Treatment in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Case Report and Literature Review. Medicina 2023, 59, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrateh, O.N.; Abugharbieh, Y.; Asbeh, Y.A.; Hour, H.; Awad, I.; Bannoura, S. Sarcoid-like reaction and hypothyroidism induced by PD-1 inhibitor treatment in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A case report and literature review. BMC Pulm. Med. 2024, 24, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitriou, F.; Frauchiger, A.L.; Urosevic-Maiwald, M.; Naegeli, M.C.; Goldinger, S.M.; Barysch, M.; Franzen, D.; Kamarachev, J.; Braun, R.; Dummer, R.; et al. Sarcoid-like reactions in patients receiving modern melanoma treatment. Melanoma Res. 2018, 28, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamori, S.; Furubayashi, N.; Taguchi, K.; Matsubara, T.; Fujishita, T.; Ito, K.; Yamaguchi, M.; Toyozawa, R.; Seto, T.; Negishi, T.; et al. Sarcoid-like reaction of the extrathoracic lymph node in a patient with lung adenocarcinoma treated with pembrolizumab. Thorac. Cancer 2021, 12, 2122–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, F.; Torre-Sada, L.F.; Mott, F.E.; Kim, S.T.; Nurieva, R.; Nagarajan, P.; Guo, M.; Shannon, V.R.; Faiz, S.A.; Casal, R.F.; et al. Sarcoidosis and Airway Disease After Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy: Case Study and Review of the Literature. J. Immunother. Precis. Oncol. 2023, 6, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatim, N.; Mateus, C.; Charles, P. Sarcoidosis post-anti-PD-1 therapy, mimicking relapse of metastatic melanoma in a patient undergoing complete remission. Rev. Médecine Interne 2018, 39, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayá García-Manso, I.; García Ródenas, M.D.M.; Barroso Medel, M.E.; Illán Gambín, F.J. Sarcoidosis-Like Granulomatous Reaction Associated with Pembrolizumab Immunotherapy. Arch. Bronconeumol. Engl. Ed. 2018, 54, 592–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, M.; Liu, H.; Ma, D.; Lin, Y.; Wang, M.; Xu, Y. Sarcoidosis-like reaction after neoadjuvant pembrolizumab combined with chemotherapy mimicking disease progression of NSCLC induced encouraging discovery of pathological complete response. Thorac. Cancer 2021, 12, 3433–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L.; Patel, G.; Chiesa-Fuxench, Z.C.; McGettigan, S.; Schuchter, L.; Mitchell, T.C.; Ming, M.E.; Chu, E.Y. Timing of Onset of Adverse Cutaneous Reactions Associated with Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 Inhibitor Therapy. JAMA Dermatol. 2018, 154, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tetzlaff, M.T.; Nelson, K.C.; Diab, A.; Staerkel, G.A.; Nagarajan, P.; Torres-Cabala, C.A.; Chasen, B.A.; Wargo, J.A.; Prieto, V.G.; Amaria, R.N.; et al. Granulomatous/sarcoid-like lesions associated with checkpoint inhibitors: A marker of therapy response in a subset of melanoma patients. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firwana, B.; Ravilla, R.; Raval, M.; Hutchins, L.; Mahmoud, F. Sarcoidosis-like syndrome and lymphadenopathy due to checkpoint inhibitors. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2017, 23, 620–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, E.F.; Lipson, E.; Suresh, K.; Cappelli, L.C.; Monaco, S.E.; Maleki, Z. Immune checkpoint blocker-related sarcoid-like granulomatous inflammation: A rare adverse event detected in lymph node aspiration cytology of patients treated for advanced malignant melanoma. Hum. Pathol. 2019, 91, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthod, G.; Lazor, R.; Letovanec, I.; Romano, E.; Noirez, L.; Mazza Stalder, J.; Speiser, D.E.; Peters, S.; Michielin, O. Pulmonary Sarcoid-Like Granulomatosis Induced by Ipilimumab. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, e156–e159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, A.; Schoeffler, A.; Dalle, S.; Phan, A.; Kiakouama, L.; Thomas, L. Anti-CTLA4 Monoclonal Antibody Induced Sarcoidosis in a Metastatic Melanoma Patient. Dermatology 2009, 218, 69–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reule, R.B.; North, J.P. Cutaneous and pulmonary sarcoidosis-like reaction associated with ipilimumab. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 69, e272–e273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Leboráns, L.; Esteve Martínez, A.; Victoria Martínez, A.M.; Alegre De Miquel, V.; Berrocal Jaime, A. Cutaneous sarcoidosis in a melanoma patient under Ipilimumab therapy: Sarcoidosis induced by Ipilimumab therapy. Dermatol. Ther. 2016, 29, 306–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobini, N.; Dhillon, R.; Dickey, J.; Spoon, J.; Sadrolashrafi, K. Exclusive Cutaneous and Subcutaneous Sarcoidal Granulomatous Inflammation due to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: Report of Two Cases with Unusual Manifestations and Review of the Literature. Case Rep. Dermatol. Med. 2019, 2019, 6702870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes, J.; Rosen, A.; Dehesa, L.; Dickinson, G.; Alonso-Llamazares, J. Granulomatous Reaction in a Patient with Metastatic Melanoma Treated with Ipilimumab: First Case Reported with Isolated Cutaneous Findings. Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas Engl. Ed. 2019, 110, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, W.V.; Guislain, A.; Kvistborg, P.; Schumacher, T.N.M.; Haanen, J.B.A.G.; Blank, C.U. Ipilimumab-Induced Sarcoidosis in a Patient with Metastatic Melanoma Undergoing Complete Remission. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, e7–e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, R.; Nørgaard, P.; Al-Jailawi, M.K.M.; Svane, I.M. Late development of splenic sarcoidosis-like lesions in a patient with metastatic melanoma and long-lasting clinical response to ipilimumab. OncoImmunology 2014, 3, e954506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- González-Cruz, C.; Bodet, D.; Muñoz-Couselo, E.; García-Patos, V. Mediastinal FDG-positive lymph nodes simulating melanoma progression: Drug-induced sarcoidosis like/lymphadenopathy related to ipilimumab. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, e237310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.P.; Kennedy, M.P.; Barry, J.E.; O’Regan, K.N.; Power, D.G. New-Onset Mediastinal and Central Nervous System Sarcoidosis in a Patient with Metastatic Melanoma Undergoing CTLA4 Monoclonal Antibody Treatment. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2014, 37, 351–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tissot, C.; Carsin, A.; Freymond, N.; Pacheco, Y.; Devouassoux, G. Sarcoidosis complicating anti-cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 monoclonal antibody biotherapy. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 41, 246–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, S.B.; Possick, J.D.; Kluger, H.M.; Galan, A.; Han, D. Sarcoidosis Following Anti-PD-1 and Anti-CTLA-4 Therapy for Metastatic Melanoma. J. Immunother. 2017, 40, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilgenhof, S.; Morlion, V.; Seghers, A.C.; Vandenbroucke, F.; Everaert, H.; Neyns, B. Sarcoidosis in a Patient with Metastatic Melanoma Sequentially Treated with Anti-CTLA-4 Monoclonal Antibody and Selective BRAF Inhibitor. Anticancer Res. 2012, 32, 1355–1359. [Google Scholar]
- Garanzini, E.M.; Scaramuzza, D.; Spadarella, G.; Di Guardo, L.; Marchianò, A. Sarcoidosis-like disease mimicking metastases during adjuvant ipilimumab therapy in advanced melanoma patient: CT scan and MRI help in managing difficult clinical decision. BJRcase Rep. 2020, 6, 20190065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelzer, V.H.; Rothschild, S.I.; Zihler, D.; Wicki, A.; Willi, B.; Willi, N.; Voegeli, M.; Cathomas, G.; Zippelius, A.; Mertz, K.D. Systemic inflammation in a melanoma patient treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors—An autopsy study. J. Immunother. Cancer 2016, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagiri, A.; Yamazaki, H.; Ikeda, T. A case of sarcoidosis-like reaction associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. IJU Case Rep. 2022, 5, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Yue, D.; Qian, J.; Zhang, L.; Song, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, C.; Sun, L.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. Case Report: Sarcoid-Like Reactions and Tertiary Lymphoid Structures Following Dual Checkpoint Inhibition in a Patient with Early-Stage Lung Adenocarcinoma. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 794217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, J.P.; Star, P.; Wong, S.; Damian, D.L.; Saw, R.P.M.; Whitfeld, M.J.; Menzies, A.M.; Joshua, A.M.; Smith, A. Cutaneous Sarcoidosis Due to Immune-Checkpoint Inhibition and Exacerbated by a Novel BRAF Dimerization Inhibitor. Skin. Health Dis. 2021, 1, e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, I.; Malinzak, M.; Salama, A.K.S. Delayed onset of neurosarcoidosis after concurrent ipilimumab/nivolumab therapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagawa, T.; Sato, Y.; Nagashima, H.; Takada, K.; Takahashi, M.; Hirakawa, M.; Hamaguchi, K.; Tamura, F.; Fujikawa, K.; Okamoto, K.; et al. Hilar/mediastinal and cutaneous drug-induced sarcoidosis-like reaction associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors in metastatic colorectal cancer: A case report. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1203621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charkviani, M.; Herrmann, S.M. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor–Associated Sarcoidosis Reaction in the Kidney: Case Report. Kidney Med. 2023, 5, 100626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suozzi, K.C.; Stahl, M.; Ko, C.J.; Chiang, A.; Gettinger, S.N.; Siegel, M.D.; Bunick, C.G. Immune-related sarcoidosis observed in combination ipilimumab and nivolumab therapy. JAAD Case Rep. 2016, 2, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasin, H.; Yadala, V.; Khan, N.A.J.; Graffeo, V.; Denning, K.; Lebowicz, Y. Immunotherapy-Induced Sarcoid-Like Reaction: A Shrewd Imitator. J. Investig. Med. High Impact Case Rep. 2021, 9, 23247096211009400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuss, J.E.; Kunk, P.R.; Stowman, A.M.; Gru, A.A.; Slingluff, C.L.; Gaughan, E.M. Sarcoidosis in the setting of combination ipilimumab and nivolumab immunotherapy: A case report & review of the literature. J. Immunother. Cancer 2016, 4, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Zurita, A.; Vázquez-Montero, L.; Gallego-López, L.; Mediano-Rambla, M.D.; De La Cruz-Merino, L. Sarcoidosis-like reaction induced by immune checkpoint inhibitor in a patient with hepatocellular carcinoma: A case report. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1150128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, V.; Preti, B.; Fernandes, R. Suspected immune checkpoint inhibitor-induced pulmonary sarcoid reaction in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Case Rep. 2022, 10, e5960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Gao, J.; Shannon, V.R.; Siefker-Radtke, A. Systemic sarcoidosis first manifesting in a tattoo in the setting of immune checkpoint inhibition. BMJ Case Rep. 2016, 2016, bcr2016216217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeCarli, K.; Masel, R.; Hsu, A.; Lopresti, M. Treatment-induced sarcoidosis in a patient with metastatic clear cell ovarian cancer. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, e247278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J.; Hebroni, F.; Bedayat, A.; Pourzand, L. Case 286: Sarcoidlike Granulomatosis and Lymphadenopathy—Thoracic Manifestations of Nivolumab Drug Toxicity. Radiology 2021, 298, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ung, C.; Gragoudas, E. Checkpoint inhibitor-induced sarcoid choroidal granulomas. Am. J. Ophthalmol. Case Rep. 2020, 18, 100652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrego-Callejas, T.; Sandoval-Álvarez, S.; Gómez-Wolff, R.; Vásquez, G. Cutaneous and Pulmonary Sarcoid-Like Reaction Induced by Nivolumab: Case Report and Brief Literature Review. JCR J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 27, S460–S464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laroche, A.; Alarcon Chinchilla, E.; Bourgeault, E.; Doré, M.-A. Erythema Nodosum as the Initial Presentation of Nivolumab-Induced Sarcoidosis-Like Reaction. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2018, 22, 627–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lainez, S.; Tissot, C.; Cottier, M.; Vergnon, J.-M. EBUS-TBNA Can Distinguish Sarcoid-Like Side Effect of Nivolumab Treatment from Tumor Progression in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Respiration 2017, 94, 518–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Perez, J.A.; Beveridge, M.G.; Victor, T.A.; Cibull, T.L. Granulomatous and lichenoid dermatitis after IgG4 anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody therapy for advanced cancer. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2018, 45, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.V.; Squires, C.; Gasparri, M.; Sheinin, Y. Nivolumab induced pulmonary sarcoid-like granulomas with a concurrent pleural schwannoma: A pathologic-radiologic correlation of a rare condition mimicking metastatic melanoma. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2022, 57, 151880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulbah, R.I.; Rowe, S.P.; Solnes, L.B.; Javadi, M.S. Nivolumab-Associated Pulmonary and Bone Sarcoidosis in a Patient with Melanoma of Unknown Primary. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2019, 44, e519–e521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Schembri, G. Nivolumab-Induced Development of Pulmonary Sarcoidosis in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2017, 42, 728–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnbaum, M.R.; Ma, M.W.; Fleisig, S.; Packer, S.; Amin, B.D.; Jacobson, M.; McLellan, B.N. Nivolumab-related cutaneous sarcoidosis in a patient with lung adenocarcinoma. JAAD Case Rep. 2017, 3, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, L.; Hochmair, M.; Kifjak, D.; Haug, A.R.; Prayer, F.; Mayerhoefer, M.E.; Herold, C.; Prosch, H. Particular findings on lung CT in patients undergoing immunotherapy for bronchogenic carcinoma. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2020, 132, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T.; Ishitsuka, Y.; Iwamoto, K.; Koguchi-Yoshioka, H.; Tanaka, R.; Watanabe, R.; Fujisawa, Y.; Fujimoto, M. Programmed cell death 1 blockade-induced cutaneous sarcoid-like epithelioid granulomas in advanced melanoma: A case report. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018, 32, pe260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montaudié, H.; Pradelli, J.; Passeron, T.; Lacour, J.-P.; Leroy, S. Pulmonary sarcoid-like granulomatosis induced by nivolumab. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 176, 1060–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, S.; Kawachi, H.; Yoshida, H.; Fukao, A.; Terashita, S.; Ikeue, T.; Horikawa, S.; Sugita, T. Sarcoid-Like Granulomatosis Induced by Nivolumab Treatment in a Lung Cancer Patient. Case Rep. Oncol. 2018, 11, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuchi, K.; Hikawa, M.; Sano, Y.; Kasuya, A.; Aoshima, M.; Tatsuno, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Kosugi, I.; Tokura, Y. Sarcoid-like reaction and vitiligo occurring after nivolumab therapy in a patient with metastatic melanoma. J. Dermatol. 2019, 46, E359–E360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolini, L.; Poli, C.; Blanchard, S.; Urban, T.; Croué, A.; Rousselet, M.-C.; Le Roux, S.; Labarrière, N.; Jeannin, P.; Hureaux, J. Thoracic and cutaneous sarcoid-like reaction associated with anti-PD-1 therapy: Longitudinal monitoring of PD-1 and PD-L1 expression after stopping treatment. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.A.; Hogan, K.; Amjadi, K. Atezolizumab-Induced Sarcoid-Like Granulomatous Reaction in a Patient with Urothelial Cell Carcinoma. Immunotherapy 2018, 10, 1189–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunoda, A.; Mizuno, T.; Iida, S.; Uchida, K.; Yamashita, M.; Sukeno, K.; Oka, H.; Tono, Y.; Ishihara, M.; Saito, K.; et al. Atezolizumab-Induced Sarcoidosis-Like Reaction in a Patient with Metastatic Breast Cancer. Case Rep. Oncol. Med. 2022, 2022, 2709062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, K.; Wallace, M.; Mulrennan, S. Recommencement of atezolizumab with associated pulmonary sarcoid-like reaction. Respirol. Case Rep. 2024, 12, e01363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafon, M.; Blaye, C.; Kind, M.; Bechade, D.; Chassaigne, F.; Italiano, A.; Grellety, T. Sarcoidosis-like reaction in metastatic triple negative breast cancer treated by anti-PD-L1. Breast J. 2019, 25, 971–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balestra, R.; Benzaquen, S.; Wang, J. Sarcoidosis-like Granulomatous Lung Reaction Associated with Anti–Programmed Death Receptor-1 Ligand Therapy. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2017, 14, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanderson, E.; Wimaleswaran, H.; Senko, C.; White, S.; McDonald, C.F. Durvalumab induced sarcoid-like pulmonary lymphadenopathy. Respirol. Case Rep. 2020, 8, e00542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, S.; Yasuoka, H.; Shoshihara, N.; Ishida, D.; Sakamaki, Y. Sarcoid-Like Granulomatosis of the Lung Related to Durvalumab After Chemoradiation for Pulmonary Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Med. Cases 2023, 14, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantarotto, M.; Barata, R.; Coelho, R.; Carvalheiro, C.; Rolim, I.; Garrido, P.; GIl, N.; Duarte-Ramos, F.; Stumpf Tonin, F.S. The Meaning of Lymphadenopathies During Adjuvant Durvalumab After Chemoradiotherapy for Lung Cancer: Thinking Beyond Disease Progression. Cureus 2022, 14, e26729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Mu, F.; Zou, B.; Wang, L. Pulmonary sarcoidosis-like reactions induced by sintilimab in esophageal cancer: A case report. Medicine 2023, 102, e34432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udalova, I.; Monaco, C.; Nanchahal, J.; Feldmann, M. Anti-TNF Therapy. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, S.B.; Furst, D.E. Problems encountered during anti-tumour necrosis factor therapy. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2006, 20, 757–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzeni, F.; Gianturco, L.; Talotta, R.; Varisco, V.; Ditto, M.C.; Turiel, M.; Sarzi-Puttini, P. Investigating the Potential Side Effects of Anti-TNF Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis: Cause for Concern? Immunotherapy 2015, 7, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoni, C.; Braun, J. Side effects of anti-TNF therapy: Current knowledge. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2002, 20, S152. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dalbeth, N.; Perez-Ruiz, F.; Edwards, N.L.; Schlesinger, N. In Defense of Research into the Crystal Induced Arthropathies. J. Rheumatol. 2008, 35, 2278–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Akiyama, M.; Kaneko, Y.; Hanaoka, H.; Kuwana, M.; Takeuchi, T. Acute Kidney Injury due to Renal Sarcoidosis during Etanercept Therapy: A Case Report and Literature Review. Intern. Med. 2015, 54, 1131–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lamrock, E.; Brown, P. Development of cutaneous sarcoidosis during treatment with tumour necrosis alpha factor antagonists. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2012, 53, e87–e90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, M.A.H.B.; Saraiva, M.I.R.; Silva, L.K.L.D.; Fraga, R.C.; Kakizaki, P.; Valente, N.Y.S. Development of exclusively cutaneous sarcoidosis in patient with rheumatoid arthritis during treatment with etanercept. Rev. Assoc. Médica Bras. 2016, 62, 718–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyagi, R.; Ideguchi, H.; Soga, T.; Yamakawa, Y.; Otsuki, H.; Niino, H.; Shiina, T.; Ueda, A.; Ishigatsubo, Y. Development of pulmonary and cardiac sarcoidosis during etanercept therapy. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 17, 810–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-López, M.A.; Blanco, R.; González-vela, M.C.; Fernández-llaca, H.; Rodríguez-valverde, V. Development of sarcoidosis during etanercept therapy. Arthritis Care Res. 2006, 55, 817–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiguro, T.; Takayanagi, N.; Kurashima, K.; Matsushita, A.; Harasawa, K.; Yoneda, K.; Tsuchiya, N.; Miyahara, Y.; Yamaguchi, S.; Yano, R.; et al. Development of Sarcoidosis during Etanercept Therapy. Intern. Med. 2008, 47, 1021–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Skoie, I.M.; Wildhagen, K.; Omdal, R. Development of sarcoidosis following etanercept treatment: A report of three cases. Rheumatol. Int. 2012, 32, 1049–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verschueren, K.; Van Essche, E.; Verschueren, P.; Taelman, V.; Westhovens, R. Development of sarcoidosis in etanercept-treated rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin. Rheumatol. 2007, 26, 1969–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, A.M.; Green, P.J.; Pasternak, S. Etanercept-induced cutaneous and pulmonary sarcoid-like granulomas resolving with adalimumab. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2012, 39, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, K.; Weinblatt, M. Granulomatous lung disease occurring during etanercept treatment. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 53, 618–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifee, M.; Bansal, A.; Bever, G.J.; Stewart, J.M. Late-onset Etanercept-associated Ocular Sarcoidosis with Profound Vision Loss. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2022, 30, 2055–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peno-Green, L.; Lluberas, G.; Kingsley, T.; Brantley, S. Lung Injury Linked to Etanercept Therapy. Chest 2002, 122, 1858–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongpooswan, S.; Abrudescu, A. Lung Sarcoidosis in Etanercept Treated Rheumatoid Arthritis Patient: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Case Rep. Rheumatol. 2014, 2014, 358567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichhoff, G. Management with secukinumab of tumour necrosis factor inhibitor-induced pulmonary sarcoidosis-like reaction in a patient with psoriasis. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2020, 45, 455–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoufack, C.; Semerano, L.; Podglajen, I.; Bruneval, P.; Meune, C.; Valeyre, D.; Dhote, R.; Boissier, M.-C.; Saidenberg-Kermanac’h, N. Mitral valve granulomatosis: A paradoxical reaction complicating etanercept treatment in rheumatoid arthritis. A case report. Jt. Bone Spine 2021, 88, 105183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendling, D.; Nueffer, J.-P. Muscular sarcoidosis under anti-TNF treatment in ankylosing spondylitis. Jt. Bone Spine 2018, 85, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, D.; Manolios, N.; Howe, G.; Spencer, D. New onset sarcoid-like granulomatosis developing during anti-TNF therapy: An under-recognised complication. Intern. Med. J. 2012, 42, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübscher, O.; Re, R.; Iotti, R. Pulmonary rheumatoid nodules in an etanercept-treated patient. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 2077–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farah, R.E.; Shay, M.D. Pulmonary Sarcoidosis Associated with Etanercept Therapy. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2007, 27, 1446–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhamra, K.; Stevens, R. Pulmonary Sarcoidosis following Etanercept Treatment. Case Rep. Rheumatol. 2012, 2012, 724013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Majjad, A.; Bezza, A.; Biyi, A.; El Ochi, M.R.; El Maghraoui, A. Pulmonary Sarcoidosis following Etanercept Treatment for Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Case Rep. Rheumatol. 2018, 2018, 9867248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louie, G.H.; Chitkara, P.; Ward, M.M. Relapse of sarcoidosis upon treatment with etanercept. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 896–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daien, C.I.; Monnier, A.; Claudepierre, P.; Constantin, A.; Eschard, J.-P.; Houvenagel, E.; Samimi, M.; Pavy, S.; Pertuiset, E.; Toussirot, E.; et al. Sarcoid-like granulomatosis in patients treated with tumor necrosis factor blockers: 10 cases. Rheumatology 2009, 48, 883–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashkes, P.J.; Shajrawi, I. Sarcoid-related uveitis occuring during etanercept therapy. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2003, 21, 645–646. [Google Scholar]
- Massara, A.; Cavazzini, L.; La Corte, R.; Trotta, F. Sarcoidosis Appearing During Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor α Therapy: A New “Class Effect” Paradoxical Phenomenon. Two Case Reports and Literature Review. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 39, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toussirot, E.; Pertuiset, E.; Kantelip, B.; Wendling, D. Sarcoidosis occuring during anti-TNF-alpha treatment for inflammatory rheumatic diseases: Report of two cases. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2008, 26, 471–475. [Google Scholar]
- Unterstell, N.; Bressan, A.L.; Serpa, L.A.; Castro, P.P.D.F.E.; Gripp, A.C. Systemic sarcoidosis induced by etanercept: First Brazilian case report. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2013, 88, 197–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-K.; Hwang, P.-H.; Yun, S.-K.; Kim, H.-U.; Park, J. Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Blocker-Induced Erythrodermic Sarcoidosis in with Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Ann. Dermatol. 2017, 29, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobolewska, B.; Baglivo, E.; Edwards, A.O.; Kramer, M.; Miserocchi, E.; Palestine, A.G.; Schwab, I.R.; Zamir, E.; Doycheva, D.; Zierhut, M. Drug-induced Sarcoid Uveitis with Biologics. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2022, 30, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Stoep, D.; Braunstahl, G.-J.; Van Zeben, J.; Wouters, J. Sarcoidosis During Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Therapy: No Relapse After Rechallenge. J. Rheumatol. 2009, 36, 2847–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bewley, A.P.; Maleki, S. Systemic sarcoidosis reactions as a result of tumour necrosis factor-alpha treatment for patients with psoriasis. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 46, 1548–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theunssens, X.; Bricman, L.; Dierckx, S.; Sapart, E.; Sokolova, T.; Avramovska, A.; Durez, P. Anti-TNF Induced Sarcoidosis-Like Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: Review Cases from the RA UCLouvain Brussels Cohort. Rheumatol. Ther. 2022, 9, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatierra, J.; Magro-Checa, C.; Rosales-Alexander, J.L.; Raya-Alvarez, E. Acute sarcoidosis as parotid fever in rheumatoid arthritis under anti-tumor necrosis factor-α therapy. Rheumatology 2011, 50, 1346–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, S.; Perlman, D.M.; Allen, T.L.; Ritter, J.H.; Bhargava, M. Adalimumab induced pulmonary sarcoid reaction. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2013, 10, 53–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metyas, S.K.; Tadros, R.M.; Arkfeld, D.G. Adalimumab-induced noncaseating granuloma in the bone marrow of a patient being treated for rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol. Int. 2009, 29, 437–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues-Fernandes, C.I.; Migliorati, C.A.; Gueiros, L.A.M.; De Lima Morais, T.M.; Vargas, P.A.; De Almeida, O.P.; Lopes, M.A.; Santos-Silva, A.R. Adalimumab-induced sarcoidosis-like reaction involving oral cavity in rheumatoid arthritis: A case-based review. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 3833–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcella, S.; Welsh, B.; Foley, P. Development of sarcoidosis during adalimumab therapy for chronic plaque psoriasis: TNF antagonist-associated sarcoidosis. Australas. J. Dermatol. 2011, 52, e8–e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsten, P.; Sweiss, N.J.; Nagorsnik, U.; Niewold, T.B.; Gröne, H.-J.; Gross, O.; Müller, G.A. Drug-Induced Granulomatous Interstitial Nephritis in a Patient with Ankylosing Spondylitis During Therapy with Adalimumab. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2010, 56, e17–e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turkowski, Y.; Konnikov, N.; Mahalingam, M. Necrotizing Granulomas in a Patient with Psoriasis and Sarcoidosis After Adalimumab—Medication-Induced Reaction or Reactivation of Latent Disease? Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2019, 41, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wladis, E.J.; Tarasen, A.J.; Roth, Z.J.; Farber, M.G.; Ross, J.; Michaels, V.M. Orbital Sarcoid-Like Granulomatosis After Inhibition of Tumor Necrosis Factor-α. Ophthal. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 32, e30–e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korta, D.Z.; Ochieng, P.; Fishman, D.; Katz, S.E. Pulmonary sarcoidosis and latent tuberculosis in a patient with psoriasis treated with adalimumab. Dermatol. Online J. 2015; 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, E.; Yamamoto, Y.; Okuda, Y.; Sakaguchi, K.; Suzuki, K.; Kai, Y.; Takeda, M.; Hontsu, S.; Yamauchi, M.; Yoshikawa, M.; et al. Pulmonary sarcoidosis with a cavitary lesion in the lung caused by a TNF-α inhibitor: A case report. Respirol. Case Rep. 2022, 10, e01065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgane, V.; Jean-Charles, C.; Nicolas, M.; Jocelyne, M.; Nicole, P.; Bruno, B.; Philippe, Z.; Pierre-Louis, C. Renal sarcoid-like granulomatosis during anti-TNF therapy. Kidney Int. 2014, 86, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, C.S.; Ashourian, K.T.; Sobol, E.K.; Fink, M.; Saltzman, B.; Teich, S. Sarcoid-Associated Bilateral Multifocal Choroiditis Secondary to Adalimumab. J. Curr. Ophthalmol. 2021, 33, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanellopoulou, T.; Filiotou, A.; Kranidioti, H.; Dourakis, S.P. Sarcoid-like granulomatosis in patients treated with anti-TNFα factors. A case report and review of the literature. Clin. Rheumatol. 2011, 30, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leventaki, V.; Flerlage, J. Sarcoid-like granulomatosis in a patient receiving anti-TNFα for psoriasis. Am. J. Hematol. 2018, 93, 722–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotze, P.G.; De Barcelos, I.F.; Da Silva Kotze, L.M. Sarcoidosis during therapy with adalimumab in a Crohn’s disease patient: A paradoxical effect. J. Crohns Colitis 2013, 7, e599–e600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoforidou, A.; Goudakos, J.; Bobos, M.; Lefkaditis, E.; Vital, V.; Markou, K. Sarcoidosis-like granulomatosis of the hypopharynx as a complication of anti-TNF therapy. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2013, 34, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decock, A.; Van Assche, G.; Vermeire, S.; Wuyts, W.; Ferrante, M. Sarcoidosis-Like Lesions: Another Paradoxical Reaction to Anti-TNF Therapy? J. Crohns Colitis 2016, 11, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhaille, F.; Viseux, V.; Caudron, A.; Dadban, A.; Tribout, C.; Boumier, P.; Clabaut, A.; Lok, C. Cutaneous Sarcoidosis Occurring during Anti-TNF-Alpha Treatment: Report of Two Cases. Dermatology 2010, 220, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashima, S.; Moriichi, K.; Ando, K.; Ueno, N.; Tanabe, H.; Yuzawa, S.; Fujiya, M. Development of pulmonary sarcoidosis in Crohn’s disease patient under infliximab biosimilar treatment after long-term original infliximab treatment: A case report and literature review. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021, 21, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numakura, T.; Tamada, T.; Nara, M.; Muramatsu, S.; Murakami, K.; Kikuchi, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Muroi, M.; Okazaki, T.; Takagi, S.; et al. Simultaneous development of sarcoidosis and cutaneous vasculitis in a patient with refractory Crohn’s disease during infliximab therapy. BMC Pulm. Med. 2016, 16, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes-Valenzuela, E.; Navarro Cañadas, C.; Oyarzún Bahamonde, E.; Moreta Rodriguez, M.; Barrio, J. Severe sarcoidosis-like reaction in a patient with Crohn’s Disease treated with infliximab. Any relationship? Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2021, 45, 101696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gîlcă, G.-E.; Diaconescu, S.; Bălan, G.G.; Timofte, O.; Ştefănescu, G. Sarcoidosis associated with infliximab therapy in ulcerative colitis: A case report. Medicine 2017, 96, e6156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robicheaux Clementine, R.; Lyman, J.; Zakem, J.; Mallepalli, J.; Lindsey, S.; Quinet, R. Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Antagonist-Induced Sarcoidosis. JCR J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2010, 16, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’shea, F.D.; Marras, T.K.; Inman, R.D. Pulmonary sarcoidosis developing during infliximab therapy. Arthritis Care Res. 2006, 55, 978–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josse, S.; Klemmer, N.; Moreno-Swirc, S.; Goëb, V.; Lequerré, T.; Vittecoq, O. Infliximab induced skin and pulmonary sarcoidosis in a rheumatoid arthritis patient. Jt. Bone Spine 2009, 76, 718–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, A.; Gilson, B.; Lafontaine, S.; Pautot, J.-X.; Bindi, P. Sarcoïdose pneumo-rénale apparue sous anti-TNFα. Rev. Médecine Interne 2012, 33, e25–e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Kaneta, K.; Honma, M.; Ishida-Yamamoto, A.; Ashida, T.; Kohgo, Y.; Ohsaki, Y.; Iizuka, H. Sarcoidosis during infliximab therapy for Crohn’s disease. J. Dermatol. 2010, 37, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fok, K.C.; Ng, W.W.S.; Henderson, C.J.A.; Connor, S.J. Cutaneous sarcoidosis in a patient with ulcerative colitis on infliximab. J. Crohns Colitis 2012, 6, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almodovar, R.; Izquierdo, M.; Zarco, P.; Quirós, F.J.; Mazzucchelli, R.; Steen, B. Pulmonary sarcoidosis in a patient with ankylosing spondylitis treated with infliximab. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2007, 25, 99. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Massara, A.; Cavazzini, L.; La Corte, R.; Trotta, F. Comment on: Sarcoid-like granulomatosis in patients treated with tumour necrosis factor blockers: 10 cases. Rheumatology 2010, 49, 1019–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, H.; Nomura, W.; Sugawara, M. Certolizumab Pegol-Induced Folliculitis-Like Lichenoid Sarcoidosis in a Patient with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Case Rep. Dermatol. 2017, 9, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulikakos, P.I.; Sullivan, R.J.; Yaeger, R. Molecular Pathways and Mechanisms of BRAF in Cancer Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 4618–4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, R.; Zhou, S.; Zhong, W.; Rong, S.; Cong, Z.; Li, Y.; Xie, Q.; Chen, H.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; et al. Therapeutic efficacy of combined BRAF and MEK inhibition in metastatic melanoma: A comprehensive network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 28502–28512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaherty, K.T.; Infante, J.R.; Daud, A.; Gonzalez, R.; Kefford, R.F.; Sosman, J.; Hamid, O.; Schuchter, L.; Cebon, J.; Ibrahim, N.; et al. Combined BRAF and MEK Inhibition in Melanoma with BRAF V600 Mutations. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1694–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacouture, M.; Sibaud, V. Toxic Side Effects of Targeted Therapies and Immunotherapies Affecting the Skin, Oral Mucosa, Hair, and Nails. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2018, 19, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.T.C.; Garnett, M.J.; Roe, S.M.; Lee, S.; Niculescu-Duvaz, D.; Good, V.M.; Project, C.G.; Jones, C.M.; Marshall, C.J.; Springer, C.J.; et al. Mechanism of Activation of the RAF-ERK Signaling Pathway by Oncogenic Mutations of B-RAF. Cell 2004, 116, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assan, F.; Schlemmer, F.; Assie, J.-B.; Mahevas, M.; Sustronck, P.; Ortonne, N.; Velter, C.; Fardet, L.; Zehou, O. Atypical systemic sarcoid-like granulomatosis in two patients treated with BRAF and MEK inhibitors. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2019, 29, 556–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, J.P.; Star, P.; Phan, K.; Loh, Y.; Joshua, A.M.; Smith, A. BRAF inhibition and the spectrum of granulomatous reactions. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2022, 87, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui Ong, E.L.; Sinha, R.; Jmor, S.; Fearfield, L. BRAF Inhibitor–Associated Granulomatous Dermatitis: A Report of 3 Cases. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2019, 41, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutros, A.; Schiavi, C.; Cecchi, F.; Spagnolo, F.; Guadagno, A.; Tanda, E.T.; Giusti, F.; Murdaca, G.; Queirolo, P. Case Report: Immune-Related Toxicity During Adjuvant Treatment with BRAF Plus MEK Inhibitors in a Melanoma Patient. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 579523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.J.; Hawryluk, E.B.; Tahan, S.R.; Flaherty, K.; Kim, C.C. Cutaneous Granulomatous Eruption and Successful Response to Potent Topical Steroids in Patients Undergoing Targeted BRAF Inhibitor Treatment for Metastatic Melanoma. JAMA Dermatol. 2014, 150, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Leal, L.; Agut-Busquet, E.; Romani, J.; Sabat, M.; Yebenes, M.; Saez, A.; Luelmo, J. Cutaneous granulomatous panniculitis and sarcoidal granulomatous papular eruption in a patient with metastatic melanoma treated with a BRAF inhibitor. J. Dermatol. 2016, 43, 715–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, S.; Lheure, C.; Franck, N.; Goldman-Lévy, G.; Aractingi, S.; Dupin, N.; Kramkimel, N.; Guégan, S. Induced sarcoid-like reactions in patients with metastatic melanoma treated with dabrafenib and trametinib: A monocentric retrospective study. Melanoma Res. 2020, 30, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bala, V.-M.; Mitsogianni, M.; Laschos, K.; Pliakou, E.; Lazaridi, E.; Lampropoulou, D.-I.; Aravantinos, G. Mediastinal and hilar sarcoid-like reaction in a patient treated with dabrafenib and trametinib for metastatic melanoma: A case report and review of the literature. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 16, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, J.S.; Norris, D.A.; Wisell, J. Novel cutaneous effects of combination chemotherapy with BRAF and MEK inhibitors: A report of two cases. Br. J. Dermatol. 2013, 169, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgese, F.; Cognigni, V.; Scortichini, L.; Ranallo, N.; Lunerti, V.; Migliore, A.; Tronconi, F.; Berardi, R. Potential immune-related adverse events during dabrafenib and trametinib treatment: A case series of patients with BRAF V600E melanoma. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 18, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eser Öztürk, H.; Süllü, Y. Sarcoid-like Granulomatous Intraocular Inflammation Caused by Vemurafenib Treatment for Metastatic Melanoma. Turk. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 50, 50–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.; Wilhelmsson, M.; Foo, J.C.; Yeung, R.S.M.; Krtizinger, F.; McKeown, T.; Coblentz, A.; Ertl-Wagner, B.; Tabori, U.; Bartels, U. Sarcoid-like reaction in a child following prolonged therapeutic exposure to dabrafenib and trametinib for BRAF V600E mutated hypothalamic/chiasmatic glioma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer, 2023; epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, A.; Thomas, L.; Bories, N.; Zaharia, D.; Balme, B.; Freymond, N.; Dalle, S. Sarcoidosis associated with vemurafenib. Br. J. Dermatol. 2013, 169, 206–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lheure, C.; Kramkimel, N.; Franck, N.; Laurent-Roussel, S.; Carlotti, A.; Queant, A.; Goldwasser, F.; Avril, M.-F.; Dupin, N. Sarcoidosis in Patients Treated with Vemurafenib for Metastatic Melanoma: A Paradoxical Autoimmune Activation. Dermatology 2015, 231, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Rivas, M.; Moreira, C.; Marcoval, J. Sarcoidosis related to checkpoint and BRAF/MEK inhibitors in melanoma. Autoimmun. Rev. 2020, 19, 102587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastasopoulou, A.; Diamantopoulos, P.T.; Skalioti, C.; Liapis, G.; Psychogiou, E.; Ziogas, D.C.; Gogas, H. The diagnosis and management of sarcoid-like reactions in patients with melanoma treated with BRAF and MEK inhibitors. A case series and review of the literature. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2021, 13, 17588359211047349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durcan, R.; Heffron, C.; Sweeney, B. Natalizumab induced cutaneous sarcoidosis-like reaction. J. Neuroimmunol. 2019, 333, 476955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisinos, C.A.; Lees, C.W.; Wallace, W.A.H.; Satsangi, J. Sarcoidosis complicating treatment with natalizumab for Crohn’s disease. Thorax 2011, 66, 1109–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shono, Y.; Kamata, M.; Takeoka, S.; Ikawa, T.; Tateishi, M.; Fukaya, S.; Hayashi, K.; Fukuyasu, A.; Tanaka, T.; Ishikawa, T.; et al. Cutaneous sarcoidosis in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis receiving tocilizumab. J. Dermatol. 2018, 45, e217–e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, N.; Hansen, I.; El Moussaoui, M.; Giot, J.; Vercheval, C.; Lommers, É.; Somja, J.; Moutschen, M.; Maquet, P. Lung and liver sarcoidosis-like reaction induced by tocilizumab. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 87, 4848–4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Giorno, R.; Iodice, A.; Mangas, C.; Gabutti, L. New-onset cutaneous sarcoidosis under tocilizumab treatment for giant cell arteritis: A quasi-paradoxical adverse drug reaction. Case report and literature review. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2019, 11, 1759720X19841796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamente, L.; Buscot, M.; Marquette, C.-H.; Roux, C. Sarcoidosis and tocilizumab: Is there a link? Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2017, 35, 716. [Google Scholar]
- Nutz, A.; Pernet, C.; Combe, B.; Cohen, J.-D. Sarcoidosis Induced by Tocilizumab: A Paradoxical Event? J. Rheumatol. 2013, 40, 1773–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodosiou, G.; Luu, H.; Svensson, Å. Tocilizumab-induced sarcoidosis-like reaction in a patient with giant cell arteritis. Clinical implications of a paradoxical phenomenon. Int. J. Dermatol. 2020, 59, 888–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glanowski, C.; Clouzeau, A.; Bialé, L.; Banal, F.; Lechevalier, D. Une sarcoïdose sous tocilizumab: À propos d’un cas. Rev. Médecine Interne 2018, 39, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pescitelli, L.; Emmi, G.; Tripo, L.; Lazzeri, L.; Urban, M.L.; Silvesri, E.; Vannucchi, M.; Prignano, F. Cutaneous sarcoidosis during rituximab treatment for microscopic polyangiitis: An uncommon adverse effect? Eur. J. Dermatol. 2017, 27, 667–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, R.A.; De Oliveira, J.L.; Ferraciolli, S.F.; Guedes, L.K.N.; Pasoto, S.G. Neurosarcoidosis during the treatment of primary Sjögren’s syndrome: Is it a paradoxical effect of rituximab? Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2022, 40, 2464–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornacker, M.; Kraemer, A.; Leo, E.; Ho, A. Occurrence of sarcoidosis subsequent to chemotherapy for non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: Report of two cases. Ann. Hematol. 2002, 81, 103–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakih, O.; Verhoeven, F.; Prati, C.; Wendling, D. Paradoxical Löfgren’s syndrome in a patient treated with rituximab: Interferon is not the key. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 1181–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrabet, S.; Dahmene, R.; Fradi, A.; Jaziri, A.; Boukadida, R.; Azzebi, A.; Sahtout, W.; Ben Aicha, N.; Zellama, D.; Achour, A.; et al. Sarcoid-Like Reaction in the Kidney Following Rituximab for Mantle Lymphoma in a 60-Year-Old Man. Am. J. Mens Health 2023, 17, 15579883231159343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, O.; Eskazan, A.E.; Ar, M.C.; Beköz, H.; Tabak, F.; Ongen, G.; Ferhanoglu, B. Sarcoidosis mimicking lymphoma on positron emission tomography-computed tomography in two patients treated for lymphoma: Two case reports. J. Med. Case Rep. 2009, 3, 7306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Holdeman, K.; Laurini, J.A.; Bierman, P.J.; Vose, J.M.; Bociek, R.G.; Armitage, J.O. Sarcoidosis mimicking recurrent lymphoma. Am. J. Hematol. 2012, 87, 711–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- London, J.; Grados, A.; Fermé, C.; Charmillon, A.; Maurier, F.; Deau, B.; Crickx, E.; Brice, P.; Chapelon-Abric, C.; Haioun, C.; et al. Sarcoidosis Occurring After Lymphoma: Report of 14 Patients and Review of the Literature. Medicine 2014, 93, e121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesely, N.C.; Thomas, R.M.; Rudnick, E.; Longo, M.I. Scar sarcoidosis following rituximab therapy. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e13693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choo, S.P.; Lim, D.W.T.; Lo, C.P.L.; Koong, H.N.; Tao, M.; Lim, C.H. Variable Problems in Lymphomas: CASE 1. Burkitt’s Lymphoma Presenting with Central Airway Obstruction. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 8112–8113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, J.B.; Matthews, P.; Rattehalli, R.; Woodhead, F.; Perkins, P.; Powell, G.; Szczecinska, W.; Gach, J.E. Acute systemic sarcoidosis complicating ustekinumab therapy for chronic plaque psoriasis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2015, 172, 834–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, M.M.; Bazarbashi, N.; Kaur, M.; Gupta, A. Sarcoid- like Phenomenon—Ustekinumab induced granulomatous reaction mimicking diffuse metastatic disease: A case report and review of the literature. J. Med. Case Rep. 2019, 13, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobak, S.; Semiz, H. Ustekinumab-induced Sarcoidosis in a Patient with Psoriatic Arthritis. Curr. Drug Saf. 2020, 15, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogan, D.; Newton, K.; Pineda, E.; Evans, A.; Guo, H.; Azumi, N.; Cohen, P.; Reichner, C.; Anderson, E. A Case of Trastuzumab-Induced Pulmonary Sarcoidosis. Chest 2012, 142, 1037A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotidis, E.; Paschali, A.; Andreadou, A.; Chatzipavlidou, V. HER-2 breast cancer treatment induced mediastinal sarcoid like reaction depicted on 18F-FDG PET/CT. Hell. J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 24, 159–160. [Google Scholar]
- Halabi, R.; Grossman, C. Trastuzumab Induced Sarcoidosis Mimicking Metastatic Carcinoma. Chest 2011, 140, 56A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitos, S.; Niederauer, L.C.; Albert I Gracenea, P.; Mueller, J.; Straube, A.; Von Baumgarten, L. Case Report: Drug-Induced (Neuro) Sarcoidosis-Like Lesion Under IL4 Receptor Blockade with Dupilumab. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 881144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belhomme, N.; Gaignon, T.; Jouneau, S.; Misery, L.; Abasq-Thomas, C.; Cador, B.; Lecureur, V.; Cadiou, S.; Ballerie, A.; Polard, E.; et al. Drug-induced granulomatosis: Is dupilumab the new kid on the block? J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, e312–e313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, S.; Shimizu, M.; Miyashita, R.; Inoue, T.; Nagano, A.; Kunugi, S.; Hatori, T.; Okano, T.; Seike, M. Successful immunosuppressant-free treatment of a drug-induced sarcoidosis-like reaction caused by dupilumab. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2023, 44, 101883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, L.; Müller, L.J.; Volkers, S.M.; Heinrich, F.; Mashreghi, M.-F.; Ruppert, C.; Sander, L.E.; Hutloff, A. Follicular Helper–like T Cells in the Lung Highlight a Novel Role of B Cells in Sarcoidosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 204, 1403–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleue, C.A.; Shah, K.; Wentworth, A.; Bridges, A. Cutaneous sarcoid-like drug reaction caused by an anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitor. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2021, 48, 425–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facchinetti, F.; Gnetti, L.; Balestra, V.; Silva, M.; Silini, E.M.; Ventura, L.; Majori, M.; Bordi, P.; Tiseo, M. Sarcoid-like reaction mimicking disease progression in an ALK-positive lung cancer patient receiving lorlatinib. Investig. New Drugs 2019, 37, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, C.; Villeneuve, T.; Norkowski, E.; Rosencher, L.; Cadranel, J.; Mazières, J. Sarcoid-like reaction related to ALK-ROS inhibitors in lung cancer patients. Respir. Med. Res. 2024, 86, 101138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, D.L.; Patel, A. Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) immunotherapy for bladder cancer: Review of complications and their treatment. Aust. N. Z. J. Surg. 1998, 68, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Diego, A.; Rogado, M.C.; Prieto, M.; Nauffal, D.; Perpiñá, M. Disseminated Pulmonary Granulomas after Intravesical Bacillus Calmette-Guérin Immunotherapy. Respiration 1997, 64, 304–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, G.W. Methotrexate pulmonary toxicity. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 1997, 23, 917–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imokawa, S.; Colby, T.V.; Leslie, K.O.; Helmers, R.A. Methotrexate pneumonitis: Review of the literature and histopathological findings in nine patients. Eur. Respir. J. 2000, 15, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zisman , D.A.; McCune, W.J.; Tino, G.; Lynch, J.P. Drug-induced pneumonitis: The role of methotrexate. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2001, 18, 243–252. [Google Scholar]
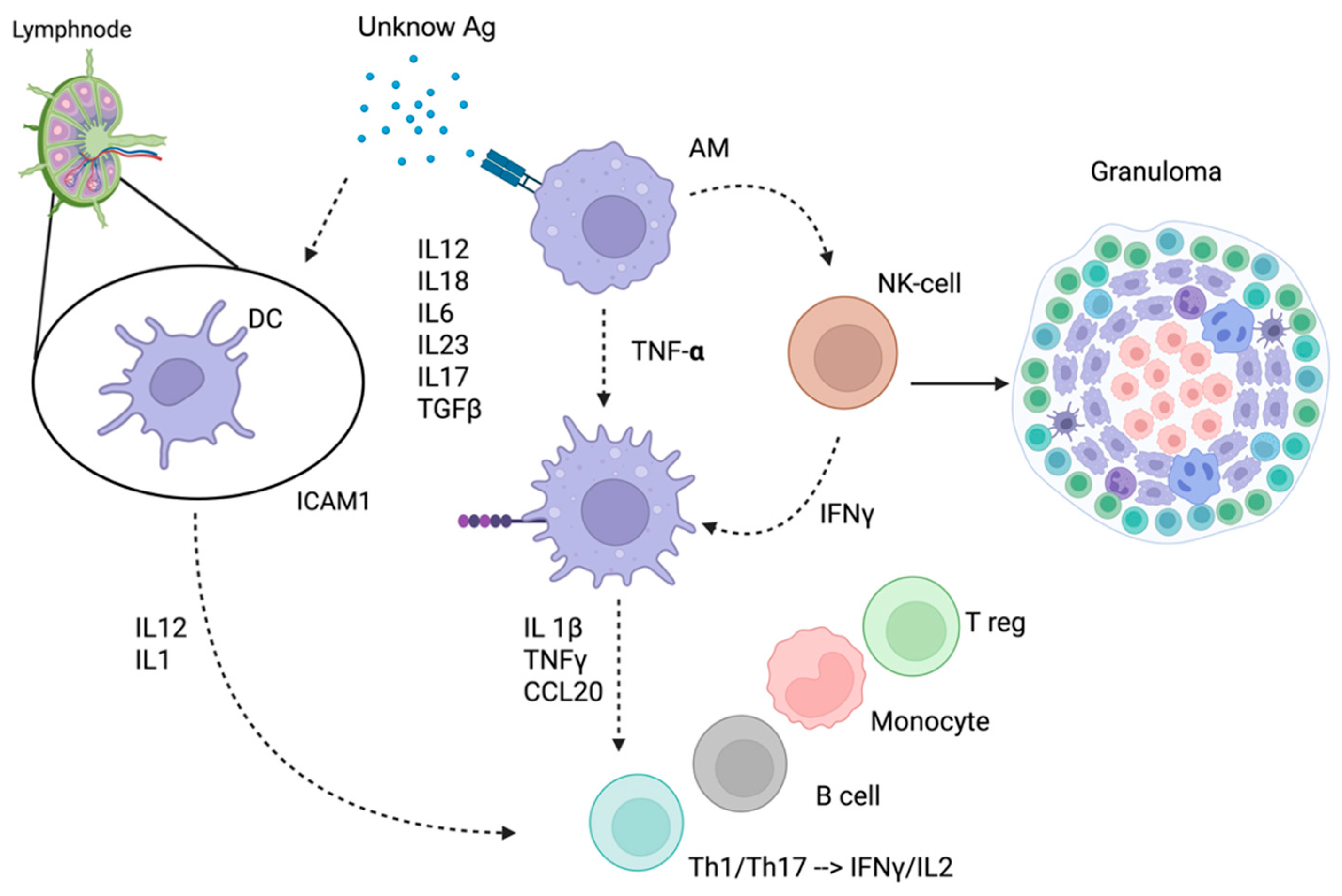
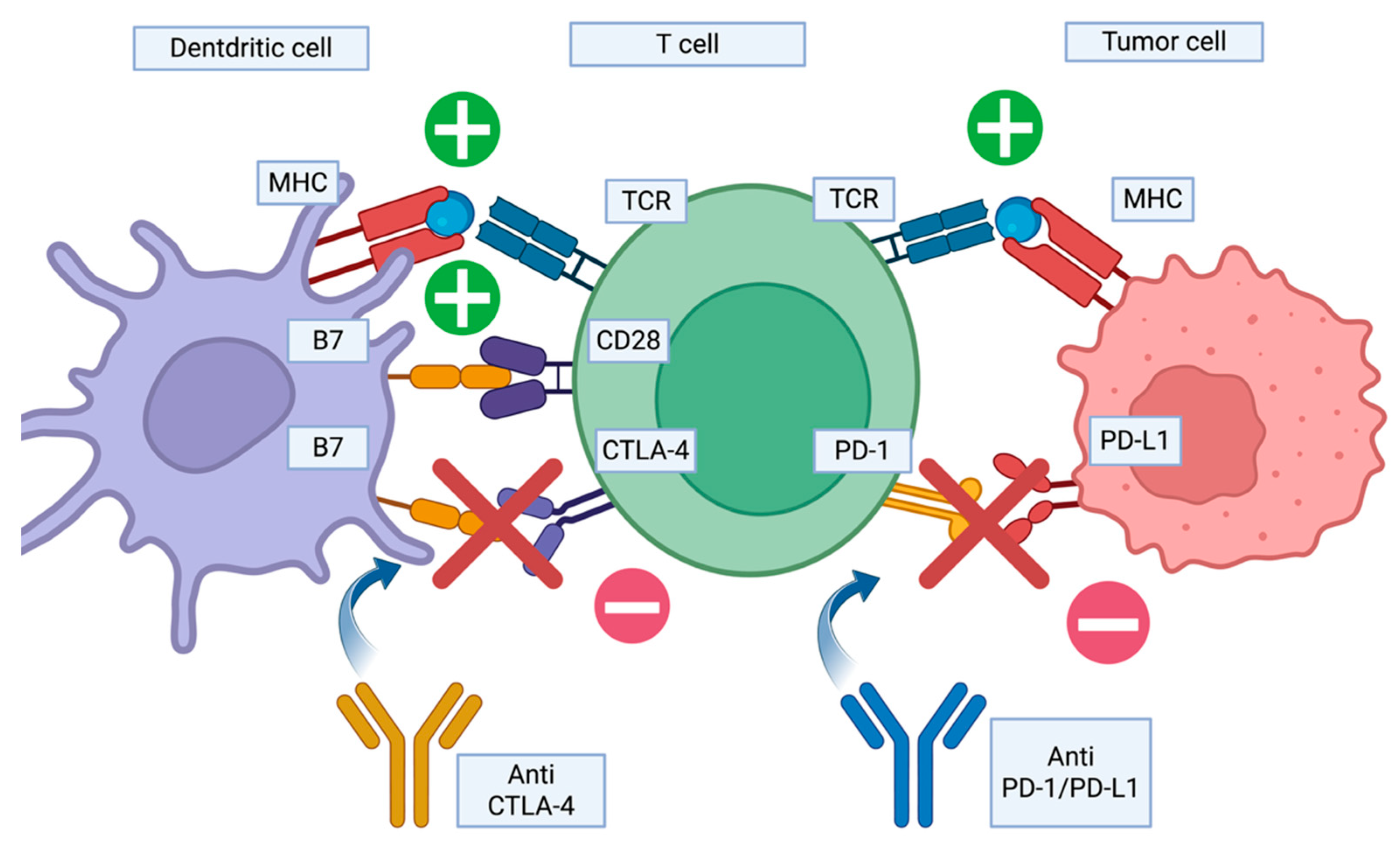
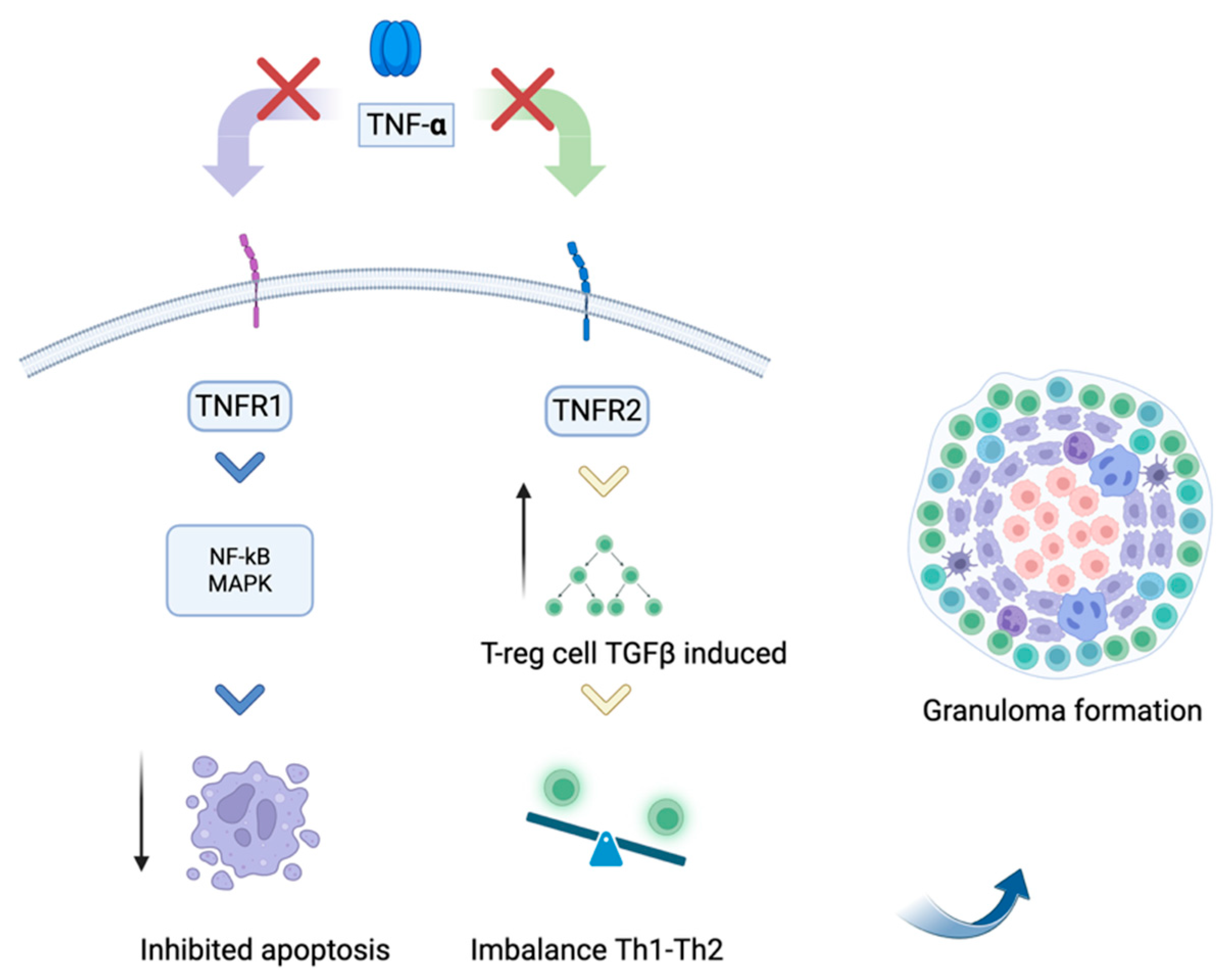

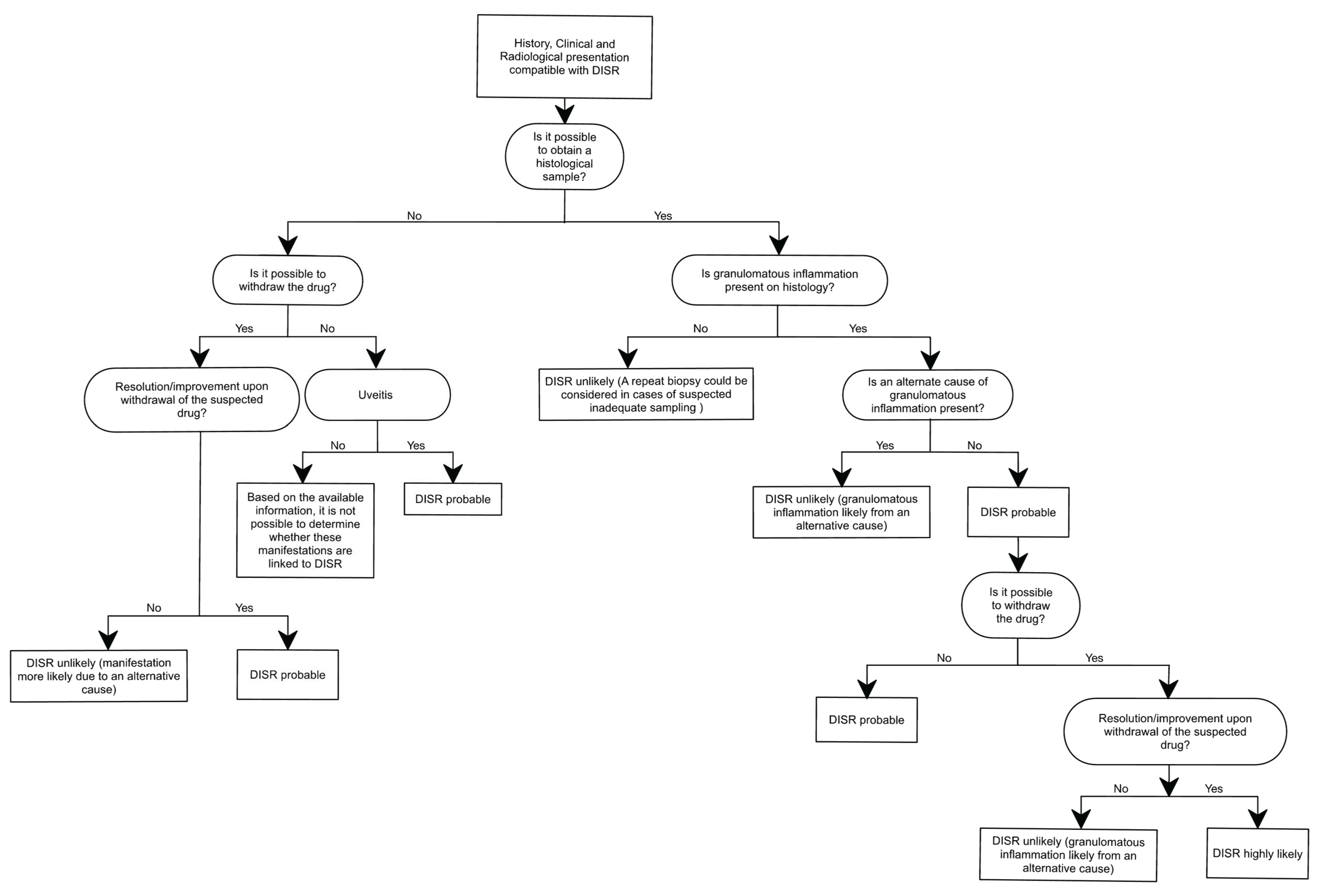
| Drug | Mechanism of Action | Treatment Indication | DISR Cases (n) | Median Time of Onset (months) | Number of Patients | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| With Signs and Symptoms | Requiring Drug Discontinuation | Requiring Treatment | Showing Resolution | |||||
| Pembrolizumab | Targets and blocks PD-1 ligand | BCA, ccRCC, CRC, cSCC, EAC, NPC, NSCLC, MM, NHL, SARC, UC, ULMS | 42 | 7.32 | 23 1 NR | 17 8 NR | 9 8 NR | 26 8 NR |
| Nivolumab | Targets and blocks PD-1 ligand | ccRCC, EM, GBM, MM, NSCLC, OM, PC | 21 | 3.9 | 13 4 NR | 10 | 10 | 13 4 NR |
| Ipilumab | Inhibits CTLA-4 pathway | MM | 20 | 6.37 | 15 1 NR | 13 2 NR | 9 2 NR | 18 1 NR |
| Nivolumab + Ipilumab | CCOC, ccRCC, CRC, HCC, NSCLC, MM, RCC, UC | 16 | 4.15 | 12 3 NR | 5 1 NR | 11 1 NR | 14 1 NR | |
| Atezolizumab | Binds PDL-1 ligand, targeting PD-1 pathway | BCA, HCC, UC | 4 | 3.45 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 4 |
| Durvalumab | Binds PDL-1 ligand, targeting PD-1 pathway | NSCLC | 3 | NS | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 |
| Avelumab | Binds PD-L1 and B7-1 receptors on T cells | OM | 1 | NS | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Sintilimab | Targets and blocks PD-1 ligand | ESCC | 1 | NS | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Drug | Mechanism of Action | Treatment Indication | DISR Cases (n) | Median Time of Onset (months) | Number of Patients | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| With Signs and Symptoms | Requiring Drug Discontinuation | Requiring Treatment | Showing Resolution | |||||
| Etanercept | Binds TNFR2 (p75) | AS, RA, CPP, JIA, JRA, PsA, SS | 48 1 (+ ADA) 1 (+ IFX) 1 (+ MTX) 6 (+ PDN) | 30 | 54 | 36 5 * 2 ** 1 (+ IFX) 1 NR | 42 1 NR | 55 |
| Adalimumab | Blocks TNF-α–TNFR1/2 interaction | RA, AS, BD, CD, CPP, JIA, JRA, PsA, PSO, SAPHO, UC | 30 1 (+ ETN) | 15.24 | 28 | 28 1 *** | 27 | 31 |
| Infliximab | Binds to soluble and transmembrane forms of TNF-α | RA, AS, CD, PsA, UC, UP | 21 | 41 | 17 2 NR | 15 | 13 2 NR | 21 |
| Golimumab | Binds and inhibits soluble and transmembrane form of TNF-α | AS | 1 | NS | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Certolizumab | Target the activation of TNF-α | RA | 1 | NS | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Drug | Mechanism of Action | Treatment Indication | DISR Cases (n) | Median Time of Onset (months) | Number of Patients | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| With Signs and Symptoms | Requiring Drug Discontinuation | Requiring Treatment | Showing Resolution | |||||
| (A) BRAF inhibitors | ||||||||
| Vemurafenib | Competitive inhibitor of BRAF V600E mutation | MM, LCH | 8 | 9 | 6 | 3 1 ** | 4 | 7 |
| Dabrafenib | Selective BRAF inhibitor targeting ATP-binding site | MM | 2 | NS | 2 | 1 ** | 1 | 2 |
| (B) BRAF inhibitors and MEK inhibitors | ||||||||
| Vemurafenib + Cobimetinib | Inhibition of MAPK pathways * | MM | 3 | NS | 3 | 2 ** | 2 | 3 |
| Dabrafenib + Trametinib | Inhibition of MAPK pathways * | MM, CG | 22 | 8.9 | 16 | 3 2 ** | 12 | 20 |
| Encorafenib + Binimetinib | Inhibition of MAPK pathways * | MM | 1 | NS | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Drug | Mechanism of Action | Treatment Indication | DISR Cases (n) | Median Time of Onset (months) | Number of Patients | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| With Signs and Symptoms | Requiring Drug Discontinuation | Requiring Treatment | Showing Resolution | |||||
| Natalizumab | Targets the lymphocyte adhesion molecule a4 integrin | CD, MS | 3 | NS | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Rituximab | Targets CD20 on B lymphocyte cell surface | MCL, CML, DLBCL, NHL, SS, RA, PV, RMPA | 16 | 14 | 9 | 0 | 8 | 16 |
| Ustekinumab | Blocks IL-12 and IL-23 | Ps | 3 | NS | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 |
| Tocilizumab | Blocks IL-6 | GCA, RA | 7 | 13 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 6 |
| Dupilumab | Blocks IL-4 and IL-13 | AD, ERS | 3 | NS | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| Trastuzumab | HER2 receptor inhibitor | Breast cancer | 3 | NS | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Drug | Mechanism of Action | Treatment Indication | DISR Cases (n) | Median Time of Onset (months) | Number of Patients | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| With Signs and Symptoms | Requiring Drug Discontinuation | Requiring Treatment | Showing Resolution | |||||
| (A) Interleukin inhibitor | ||||||||
| Abatacept | Binds to CD80/D86 on antigen-presenting cells, attenuating T-cell activation | RA | 1 | NS | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| (B) Tyrosine Kinase inhibitor | ||||||||
| Lorlatinib | Blocks ALK and ROS1 proteins | NSCLC with ALK mutation | 2 | NS | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andolfi, F.; Caffarri, L.; Neviani, M.; Rubini, S.; Andrisani, D.; Gozzi, F.; Beghé, B.; Clini, E.; Tonelli, R.; Cerri, S. Drug-Induced Sarcoid-like Reactions Associated to Targeted Therapies and Biologic Agents. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1658. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131658
Andolfi F, Caffarri L, Neviani M, Rubini S, Andrisani D, Gozzi F, Beghé B, Clini E, Tonelli R, Cerri S. Drug-Induced Sarcoid-like Reactions Associated to Targeted Therapies and Biologic Agents. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(13):1658. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131658
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndolfi, Federica, Luca Caffarri, Matilde Neviani, Silvia Rubini, Dario Andrisani, Filippo Gozzi, Bianca Beghé, Enrico Clini, Roberto Tonelli, and Stefania Cerri. 2025. "Drug-Induced Sarcoid-like Reactions Associated to Targeted Therapies and Biologic Agents" Diagnostics 15, no. 13: 1658. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131658
APA StyleAndolfi, F., Caffarri, L., Neviani, M., Rubini, S., Andrisani, D., Gozzi, F., Beghé, B., Clini, E., Tonelli, R., & Cerri, S. (2025). Drug-Induced Sarcoid-like Reactions Associated to Targeted Therapies and Biologic Agents. Diagnostics, 15(13), 1658. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131658








