Ultrasonography Assessment of Neck Anatomy for Prediction of Difficult Mask Ventilation in Obese Patients: A Prospective Observational Study †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASA | American Society of Anesthesiologists |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| CT | Computer tomography |
| DMV | Difficult mask ventilation |
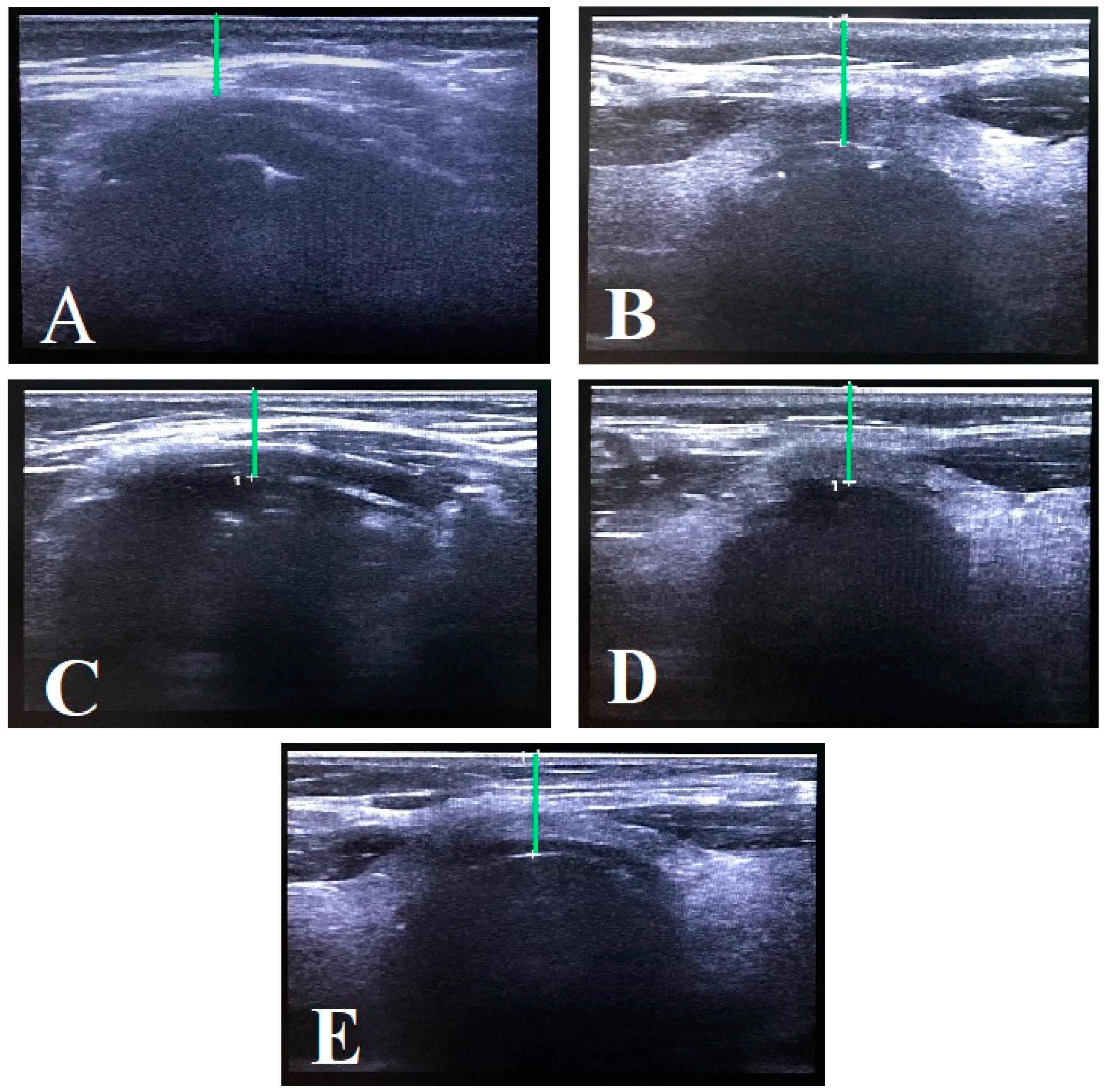
| DS | Distance of skin |
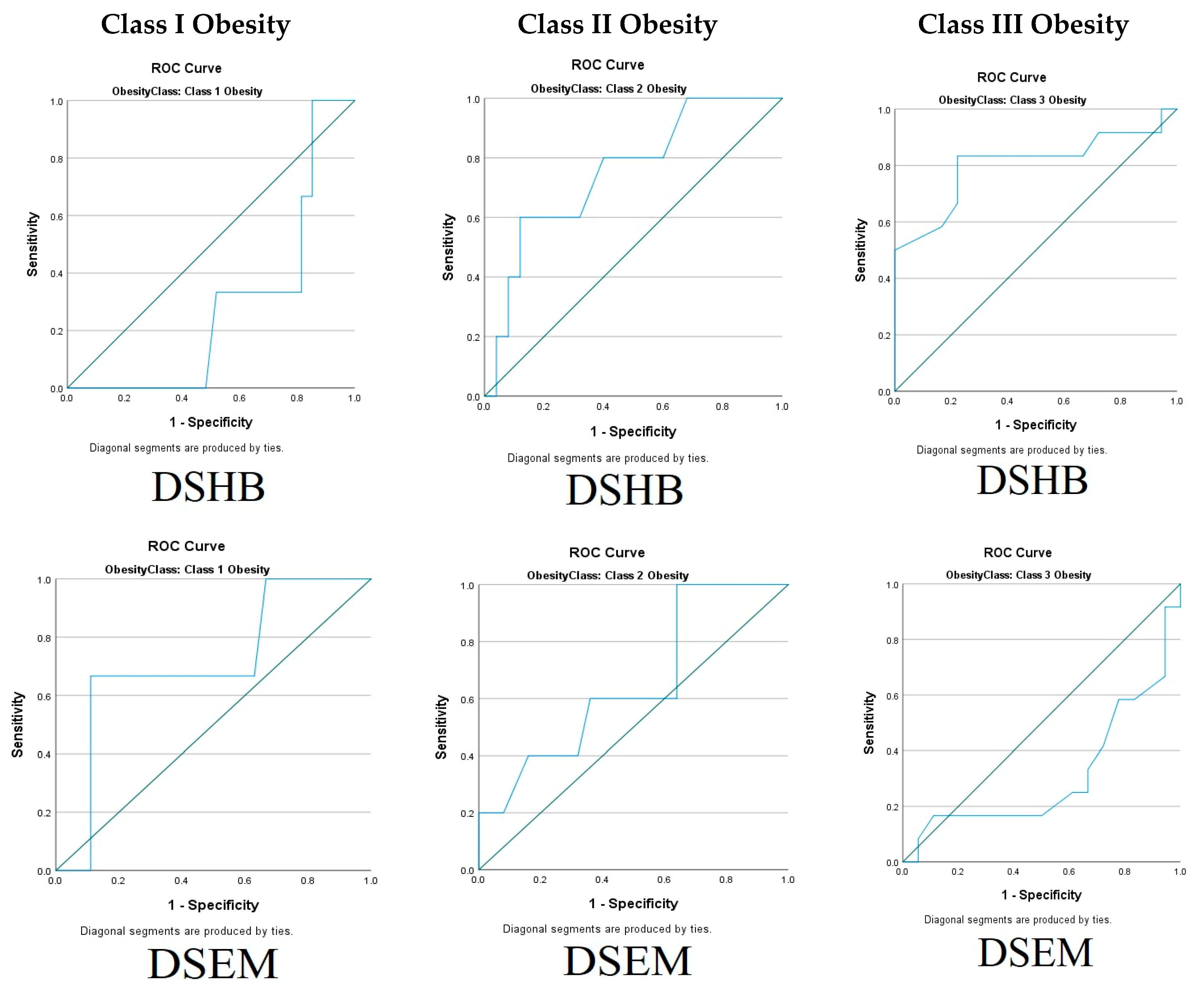
| DSHB | Distance from skin to hyoid bone |
| DSEM | Distance from skin to epiglottis |
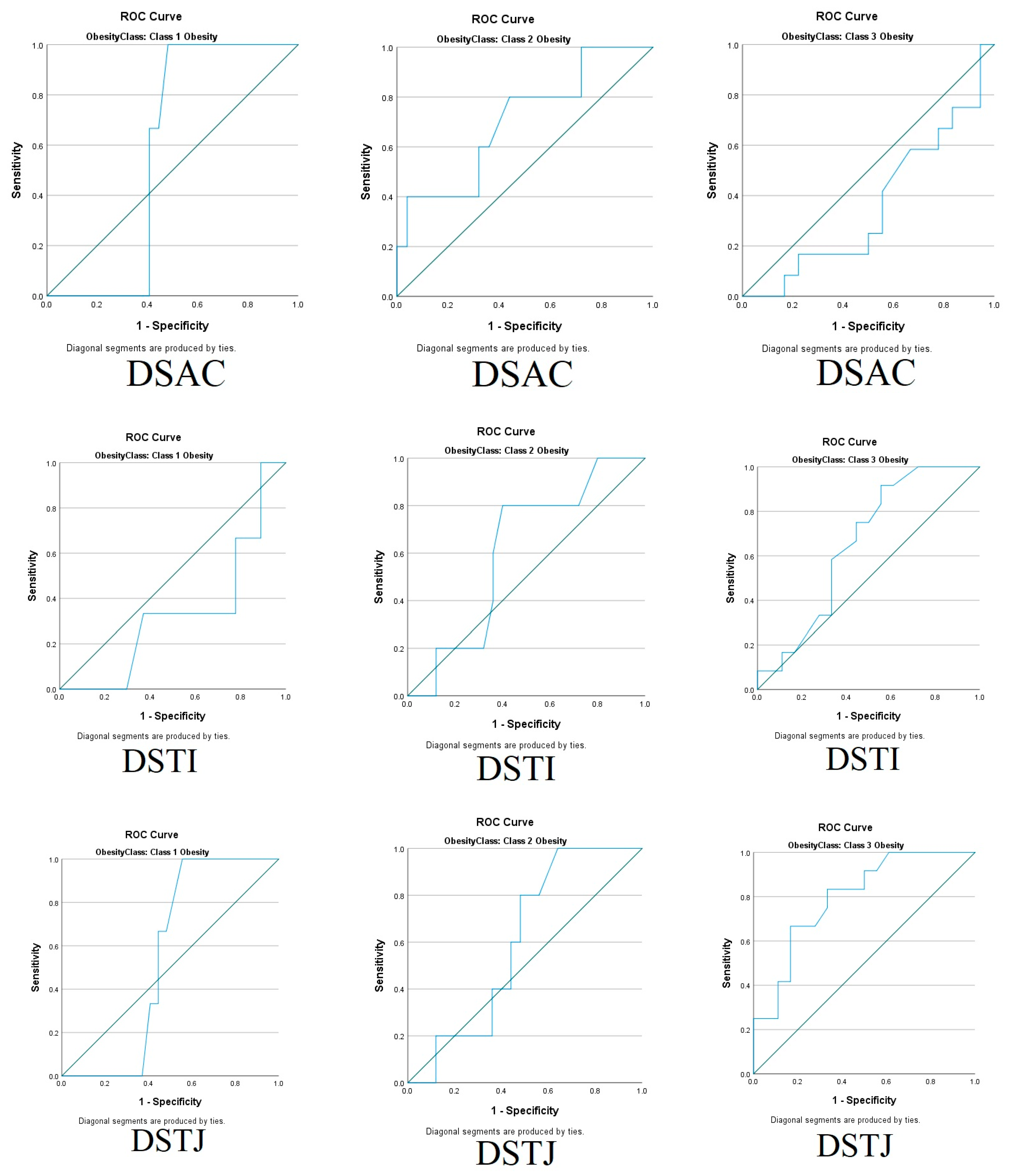
| DSAC | Distance from skin to anterior commissure of the vocal cords |
| DSTI | Distance from skin to thyroid isthmus |
| DSTJ | Distance from skin to trachea at the jugular notch level |
| DSTJ | Deep Soft Tissue at Junction |
| ROC | Receiver-operating characteristic |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| TMD | Thyromental distance |
| UKMMC | Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Centre |
Appendix A
| Classification | Description |
|---|---|
| Grade 1 | Ventilated by mask |
| Grade 2 | Ventilated by mask with oral airway/adjuvant |
| Grade 3 | Difficult mask ventilation (inadequate, unstable, or requiring two practitioners) |
| Grade 4 | Unable to mask-ventilate |
References
- Cattano, D.; Killoran, P.V.; Cai, C.; Katsiampoura, A.D.; Corso, R.M.; Hagberg, C.A. Difficult Mask Ventilation in General Surgical Population: Observation of Risk Factors and Predictors. F1000Research 2014, 3, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Orbany, M.; Woehlck, H.J. Difficult Mask Ventilation. Anesth. Analg. 2009, 109, 1870–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundstrøm, L.H.; Rosenstock, C.V.; Wetterslev, J.; Nørskov, A.K. The DIFFMASK Score for Predicting Difficult Facemask Ventilation: A Cohort Study of 46,804 Patients. Anaesthesia 2019, 74, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saddawi-Konefka, D.; Hung, S.L.; Kacmarek, R.M.; Jiang, Y. Optimizing Mask Ventilation: Literature Review and Development of a Conceptual Framework. Respir. Care 2015, 60, 1834–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apfelbaum, J.L.; Hagberg, C.A.; Caplan, R.A.; Blitt, C.D.; Connis, R.T.; Nickinovich, D.G.; Hagberg, C.A.; Caplan, R.A.; Benumof, J.L.; Berry, F.A.; et al. Practice Guidelines for Management of the Difficult Airway. Anesthesiology 2013, 118, 251–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Tremper, K.K.; Kheterpal, S.; O’Reilly, M. Grading Scale for Mask Ventilation. Anesthesiology 2004, 101, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, T.M.; Woodall, N.; Frerk, C. Major Complications of Airway Management in the UK: Results of the Fourth National Audit Project of the Royal College of Anaesthetists and the Difficult Airway Society. Part 1: Anaesthesia. Br. J. Anaesth. 2011, 106, 617–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.; Wong, D.T. Airway Management and Oxygenation in Obese Patients. Can. J. Anesth./J. Can. D’anesthésie 2013, 60, 929–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manno, E.; Navarra, M.; Faccio, L.; Motevallian, M.; Bertolaccini, L.; Mfochivè, A.; Pesce, M.; Evangelista, A. Deep Impact of Ultrasound in the Intensive Care Unit. Anesthesiology 2012, 117, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandri, F.; Antenucci, G.; Piervincenzi, E.; Buonopane, C.; Bellucci, R.; Andreoli, C.; Alunni Fegatelli, D.; Ranieri, M.V.; Bilotta, F. Ultrasound as a New Tool in the Assessment of Airway Difficulties. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2019, 36, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parameswaran, K.; Todd, D.C.; Soth, M. Altered Respiratory Physiology in Obesity. Can. Respir. J. 2006, 13, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, I.S.; Bebakar, W.M.W.; Kamaruddin, N.A. Clinical Practice Guidelines on Management of Obesity 2004; Ministry of Health: Putrajaya, Malaysia, 2004.
- Frerk, C.; Mitchell, V.S.; McNarry, A.F.; Mendonca, C.; Bhagrath, R.; Patel, A.; O’Sullivan, E.P.; Woodall, N.M.; Ahmad, I. Difficult Airway Society 2015 Guidelines for Management of Unanticipated Difficult Intubation in Adults. Br. J. Anaesth. 2015, 115, 827–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruopp, M.D.; Perkins, N.J.; Whitcomb, B.W.; Schisterman, E.F. Youden Index and Optimal Cut-Point Estimated from Observations Affected by a Lower Limit of Detection. Biom. J. 2008, 50, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, D.; Pace, N.L.; Lee, A.; Hovhannisyan, K.; Warenits, A.-M.; Arrich, J.; Herkner, H. Airway Physical Examination Tests for Detection of Difficult Airway Management in Apparently Normal Adult Patients. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; Kawakami, Y.; Sugita, M.; Yoshikawa, K.; Fukunaga, T. Use of B-Mode Ultrasound for Visceral Fat Mass Evaluation: Comparisons with Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Appl. Hum. Sci. 1995, 14, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.; Yu, E.; Wong, D.T.; Karkhanis, R.; Gullane, P.; Chan, V.W.S. Comparison of Sonography and Computed Tomography as Imaging Tools for Assessment of Airway Structures. J. Ultrasound Med. 2011, 30, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, S.M.; Sampangiramaiah, S.; Mathew, M. Cross Sectional Observational Study Performed to See for Relation of Mallampati Score and Extended Mallampati Score with Body Mass Index. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2017, 11, UG01–UG03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheterpal, S.; Martin, L.; Shanks, A.M.; Tremper, K.K. Prediction and Outcomes of Impossible Mask Ventilation. Anesthesiology 2009, 110, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shailaja, S.; Nichelle, S.M.; Shetty, A.K.; Hegde, B.R. Comparing Ease of Intubation in Obese and Lean Patients Using Intubation Difficulty Scale. Anesth. Essays Res. 2014, 8, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, T.S.; Fox, P.E.; Somasundaram, A.; Minhajuddin, A.; Gonzales, M.X.; Pak, T.J.; Ogunnaike, B. The Influence of Morbid Obesity on Difficult Intubation and Difficult Mask Ventilation. J. Anesth. 2019, 33, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, T.S.; Solak, M.; Toker, K. The Incidence and Risk Factors of Difficult Mask Ventilation. J. Anesth. 2005, 19, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.-Y.; Tzeng, I.-S.; Hsieh, Y.-L.; Kao, M.-C.; Huang, Y.-C. Submental Ultrasound Is Effective in Predicting Difficult Mask Ventilation but Not in Difficult Laryngoscopy. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2021, 47, 2243–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padhy, S.; Padhy, N.; Patro, A.; Kar, A.K.; Jonnavithula, N.; Durga, P. Submental Ultrasound for Assessment of Difficult Mask Ventilation in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnoea Posted for Surgery under General Anaesthesia. A Prospective Observational Study. Trends Anaesth. Crit. Care 2021, 41, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adi, O.; Kok, M.S.; Abdull Wahab, S.F. Focused Airway Ultrasound: An Armamentarium in Future Airway Management. J. Emerg. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 3, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Obesity | p Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class I (n = 30) | Class II (n = 30) | Class III (n = 30) | ||
| Age | 55.80 ± 14.5 | 50.80 ± 16.50 | 48.10 ± 16.60 | 0.169 |
| Gender | 0.873 | |||
| Male | 12 (40.00) | 13 (43.30) | 14 (46.70) | |
| Female | 18 (60.00) | 17 (56.70) | 16 (53.30) | |
| ASA physical status | 0.121 | |||
| I | 4 (13.30) | 8 (26.70) | 2 (6.70) | |
| II | 15 (50.00) | 16 (53.30) | 14 (46.70) | |
| III | 11 (36.70) | 6 (20.00) | 14 (46.70) | |
| Mallampati score | ||||
| I | 7 (23.30) | 1 (3.30) | 0 (0.00) | 0.005 * |
| II | 23 (76.70) | 29 (96.70) | 30 (100.00) | |
| Thyromental distance | ||||
| >6 cm | 22 (73.30) | 26 (86.70) | 19 (63.30) | 0.115 |
| <6 cm | 8 (26.70) | 4 (13.30) | 11 (36.70) | |
| Mouth opening | 0.540 | |||
| (inter-incisor gap) | ||||
| >3 cm | 30 (100.00) | 28 (93.30) | 28 (93.30) | |
| <3 cm | 0 (0.00) | 2 (6.70) | 2 (6.70) | |
| Ultrasound distances | ||||
| DSHB | 1.05 (0.22) | 1.06 (0.11) | 1.30 (0.16) | 0.045 * |
| DSEM | 1.43 (0.24) | 1.32 (0.24) | 1.64 (0.11) | 0.038 * |
| DSAC | 1.08 (0.28) | 0.99 (0.16) | 1.26 (0.15) | 0.575 |
| DSTI | 0.77 (0.20) | 0.80 (0.08) | 0.79 (0.16) | 0.175 |
| DSTJ | 0.99 (0.19) | 0.94 (0.18) | 1.19 (0.13) | 0.207 |
| Obesity | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Class I (n = 30) | Class II (n = 30) | Class III (n = 30) | |
| Han Grade 1 | 9 (30.0) | 9 (30.0) | - |
| Han Grade 2 | 18 (60.0) | 16 (53.3) | 18 (60.0) |
| Han Grade 3 | 3 (10.0) | 5 (16.7) | 10 (33.3) |
| Han Grade 4 | - | - | 2 (6.7) |
| Obesity | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class I (n = 30) | Class II (n = 30) | Class III (n = 30) | ||||
| Easy (n = 27) | Difficult (n = 3) | Easy (n = 25) | Difficult (n = 5) | Easy (n = 18) | Difficult (n = 12) | |
| DSHB | 1.06 ± 0.220 | 0.92 ± 0.130 | 1.05 ± 0.110 | 1.15 ± 0.130 | 1.26 ± 0.18 | 1.36 ± 0.11 |
| p = 0.934, r 0.012 | * p= 0.002, r 0.464 | * p= 0.002, r 0.475 | ||||
| DSEM | 1.42 ± 0.240 | 1.56 ± 0.210 | 1.29 ± 0.180 | 1.49 ± 0.430 | 1.67 ± 0.08 | 1.60 ± 1.13 |
| p = 0.375, r 0.133 | p = 0.082, r 0.264 | p = 0.196, r 0.197 | ||||
| DSAC | 1.08 ± 0.240 | 1.07 ± 0.030 | 0.98 ± 0.140 | 1.12 ± 0.210 | 1.29 ± 0.18 | 1.22 ± 0.11 |
| p = 0.885, r 0.022 | p = 0.106, r 0.244 | p = 0.436, r 0.118 | ||||
| DSTI | 0.79 ± 0.210 | 0.67 ± 0.140 | 0.80 ± 0.090 | 0.81 ± 0.050 | 0.76 ± 0.13 | 0.84 ± 0.19 |
| p = 0.665, r 0.065 | p = 0.594, r 0.082 | p = 0.119, r 0.237 | ||||
| DSTJ | 0.99 + 0.200 | 0.99 ± 0.020 | 0.94 ± 0.200 | 0.95 ± 0.100 | 1.13 ± 0.11 | 1.27 ± 0.12 |
| p = 0.984, r 0.003 | p = 0.473, r 0.109 | p = 0.101, r 0.248 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsun-Hong, I.W.; Izaham, A.; Masri, S.N.N.S.; Maaya, M.; Mahdi, S.N.M.; Kader, K.N.A.; Budiman, M.; Yaacob, Y. Ultrasonography Assessment of Neck Anatomy for Prediction of Difficult Mask Ventilation in Obese Patients: A Prospective Observational Study. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131615
Hsun-Hong IW, Izaham A, Masri SNNS, Maaya M, Mahdi SNM, Kader KNA, Budiman M, Yaacob Y. Ultrasonography Assessment of Neck Anatomy for Prediction of Difficult Mask Ventilation in Obese Patients: A Prospective Observational Study. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(13):1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131615
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsun-Hong, Ignatius Wong, Azarinah Izaham, Syarifah Noor Nazihah Sayed Masri, Muhammad Maaya, Siti Nidzwani Mohamad Mahdi, Khazrul Nizar Abd Kader, Maryam Budiman, and Yazmin Yaacob. 2025. "Ultrasonography Assessment of Neck Anatomy for Prediction of Difficult Mask Ventilation in Obese Patients: A Prospective Observational Study" Diagnostics 15, no. 13: 1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131615
APA StyleHsun-Hong, I. W., Izaham, A., Masri, S. N. N. S., Maaya, M., Mahdi, S. N. M., Kader, K. N. A., Budiman, M., & Yaacob, Y. (2025). Ultrasonography Assessment of Neck Anatomy for Prediction of Difficult Mask Ventilation in Obese Patients: A Prospective Observational Study. Diagnostics, 15(13), 1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131615







