Performance of Ultra-High-Frequency Ultrasound in the Evaluation of Skin Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis: A Cross-Sectional Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Assessment
2.2. Ultrasound Assessment
- Face: longitudinal, 1 cm inferior to the zygomatic arcus on the right cheek.
- Chest: longitudinal, 5 cm caudal to the clavicula on the mid-clavicular line.
- Abdomen: longitudinal, 5 cm above the umbilicus.
- Upper arms (left and right): transverse, at the distance halfway between the epicondylus lateralis and the acromion.
- Forearms (left and right): transverse, dorsal side at the distance two-thirds between the ulnar styloid process and the epicondylus lateralis.
- Hands (left and right): transverse, dorsal side of the third metacarpal bone.
- Fingers (left and right): longitudinal, dorsal side of the basic phalanx of the third finger.
- Thighs (left and right): longitudinal in the middle of the thigh.
- Lower legs (left and right): longitudinal, lateral at distance halfway between the head of the fibula and the lateral malleolus.
- Feet (left and right): longitudinal, over the third metatarsal bone.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Time Requirement for Ultrasound Assessments
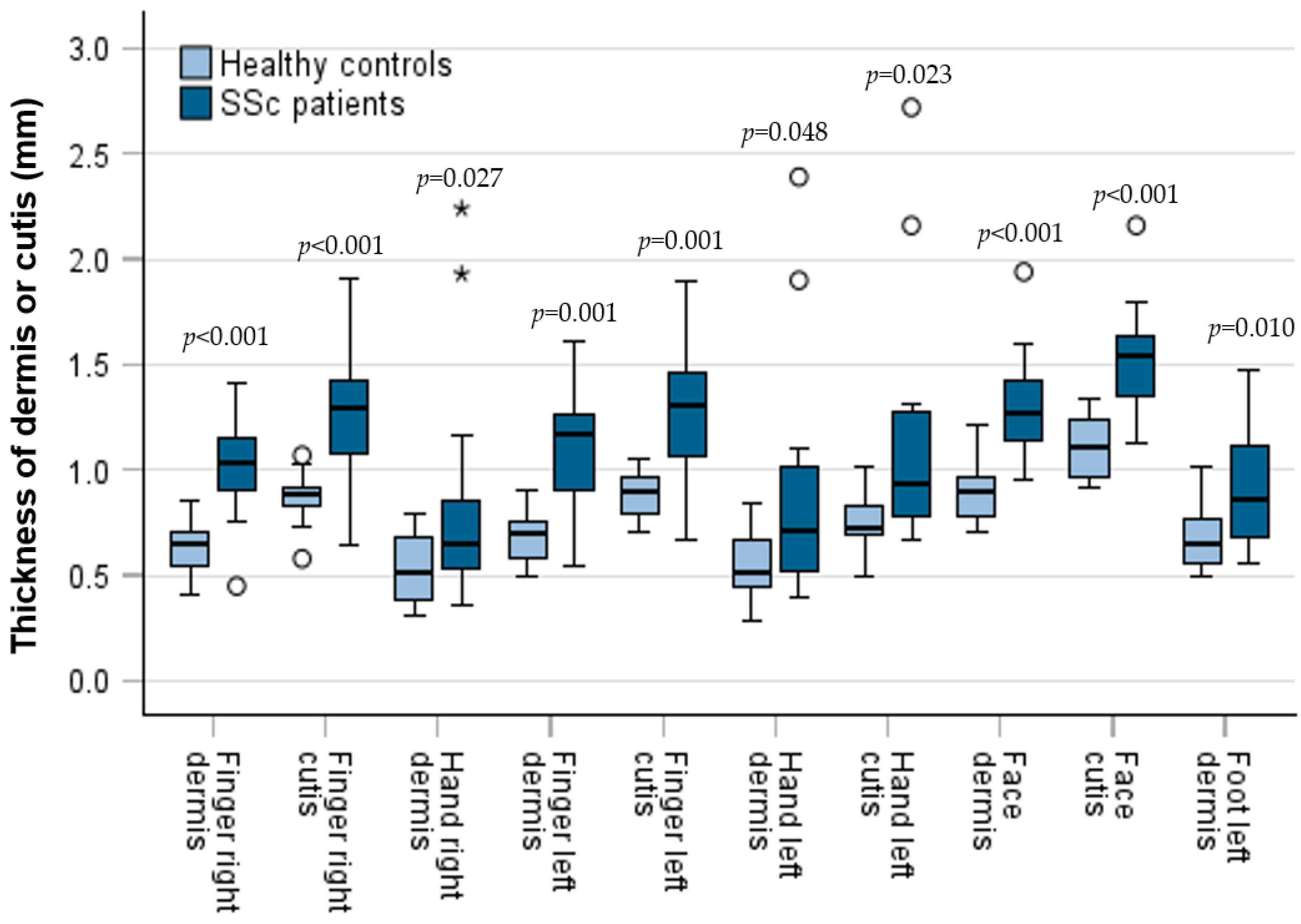
3.3. Comparison of Skin Thickness Between Patients and Controls
3.4. Patients with Diffuse Cutaneous Disease
3.5. Comparison of Clinical (mRSS) and UHF-US Assessment
3.6. Interobserver Reliability
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| UHF-US | Ultra-high-frequency ultrasound |
| ICC | Intraclass correlation coefficient |
| SSc | Systemic sclerosis |
| lcSSc | Limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis |
| dcSSc | Diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis |
| mRSS | Modified Rodnan skin score |
References
- Di Battista, M.; Barsotti, S.; Orlandi, M.; Lepri, G.; Codullo, V.; Della Rossa, A.; Guiducci, S.; Del Galdo, F. One year in review 2021: Systemic sclerosis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2021, 39 (Suppl. S130), 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Oria, M.; Gandin, I.; Riccardo, P.; Hughes, M.; Lepidi, S.; Salton, F.; Confalonieri, P.; Confalonieri, M.; Tavano, S.; Ruaro, B. Correlation between Microvascular Damage and Internal Organ Involvement in Scleroderma: Focus on Lung Damage and Endothelial Dysfunction. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, J.; Trojanowska, M.; Kuwana, M. Pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis: Recent insights of molecular and cellular mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. J. Scleroderma Relat. Disord. 2017, 2, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czirják, L.; Földvari, I.; Müller-Ladner, U. Skin involvement in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology 2008, 47 (Suppl. S5), v44–v45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, D.; Furst, D.E.; Clements, P.J.; Allanore, Y.; Baron, M.; Czirják, L.; Distler, O.; Foeldvari, I.; Kuwana, M.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; et al. Standardization of the Modified Rodnan Skin Score for use in clinical trials of systemic sclerosis. J. Scleroderma Relat. Disord. 2017, 2, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Praet, J.T.; Smith, V.; Haspeslagh, M.; Degryse, N.; Elewaut, D.; de Keyser, F. Histopathological cutaneous alterations in systemic sclerosis: A clinicopathological study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13, R35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrecchia, F.; Laboureau, J.; Verola, O.; Roos, N.; Porcher, R.; Bruneval, P.; Ertault, M.; Tiev, K.; Michel, L.; Mauviel, A.; et al. Skin involvement in scleroderma—Where histological and clinical scores meet. Rheumatology 2007, 46, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhaecke, A.; Cutolo, M.; Heeman, L.; Vilela, V.; Deschepper, E.; Melsens, K.; Smith, V. High-frequency ultrasonography: Reliable tool to measure skin fibrosis in SSC? A systematic literature review and additional pilot study. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furst, D.; Khanna, D.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Clements, P.; Steen, V.; Pope, J.; Merkel, P.; Foeldvari, I.; Seibold, J.; Pittrow, D.; et al. Systemic sclerosis—Continuing progress in developing clinical measures of response. J. Rheumatol. 2007, 34, 1194–1200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lepri, G.; Hughes, M.; Allanore, Y.; Denton, C.P.; Furst, D.E.; Wang, Y.; Santiago, T.; Galetti, I.; Del Galdo, F.; Khanna, D.; et al. The role of skin ultrasound in systemic sclerosis: Looking below the surface to understand disease evolution. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023, 5, 422–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, T.; Santos, E.J.F.; Ruaro, B.; Lepri, G.; Green, L.; Wild, M.; Watanabe, S.; Lescoat, A.; Hesselstrand, R.; del Galdo, F.; et al. Recommendations for the execution and reporting of skin ultrasound in systemic sclerosis: An international collaboration under the WSF skin ultrasound group. RMD Open 2022, 8, e002371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago, T.; Benfaremo, D.; Moroncini, G. Skin ultrasound in systemic sclerosis: Past, present and exciting future. Rheumatol. Adv. Pract. 2024, 8, rkae012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naredo, E.; Pascau, J.; Damjanov, N.; Lepri, G.; Gordaliza, P.M.; Janta, I.; Ovalles-Bonilla, J.G.; López-Longo, F.J.; Matucci-Cerinic, M. Performance of ultra-high-frequency ultrasound in the evaluation of skin involvement in systemic sclerosis: A preliminary report. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 1671–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Battista, M.; Barsotti, S.; Vitali, S.; Palma, M.; Granieri, G.; Oranges, T.; Aringhieri, G.; Dini, V.; Della Rossa, A.; Neri, E.; et al. Multiparametric skin assessment in a monocentric cohort of systemic sclerosis patients: Is there a role for ultra-high frequency ultrasound? Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, R.H. On the use of a pilot sample for sample size determination. Stat. Med. 1995, 14, 1933–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teare, M.D.; Dimairo, M.; Shephard, N.; Hayman, A.; Whitehead, A.; Walters, S.J. Sample size requirements to estimate key design parameters from external pilot randomised controlled trials: A simulation study. Trials 2014, 15, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julious, S.A. Sample size of 12 per group rule of thumb for a pilot study. Pharm. Stat. 2005, 4, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Cheng, Y.; Zhu, X.; Cai, Y.; Xue, Y.; Kong, N.; Yu, Y.; Xua, D.; Zhen, S.; Yang, X.; et al. Ultrasound assessment of skin thickness and stiffness: Correlation with histology and clinical score in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeRoy, E.C.; Black, C.; Fleischmajer, R.; Jablonska, S.; Krieg, T.; Medsger, T.A.; Rowell, N.; Wollheim, F. Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis): Classification, subsets and pathogenesis. J. Rheumatol. 1988, 15, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cicchetti, D.V. Guidelines, criteria, and rules of thumb for evaluating normed and standardized assessment instruments in psychology. Psychol. Assess. 1994, 6, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzetti, R.; Vitali, S.; Aringhieri, G.; Nisi, M.; Oranges, T.; Dini, V.; Ferro, F.; Baldini, C.; Romanelli, M.; Caramella, D.; et al. Ultra-high frequency ultrasound, a promising diagnostic technique: Review of the literature and single-center experience. Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. 2021, 72, 418–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bierig, S.M.; Jones, A. Accuracy and cost comparison of ultrasound versus alternative imaging modalities, including CT, MR, PET, and angiography. J. Diagn. Med. Sonogr. 2009, 25, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beiu, C.; Popa, L.G.; Bălăceanu-Gurău, B.; Iliescu, C.A.; Racoviță, A.; Popescu, M.N.; Mihai, M.M. Personalization of Minimally-Invasive Aesthetic Procedures with the Use of Ultrasound Compared to Alternative Imaging Modalities. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago, T.; Santos, E.; Ruaro, B.; Lepri, G.; Green, L.; Wildt, M.; Watanabe, S.; Lescoat, A.; Hesselstrand, R.; Del Galdo, F.; et al. Ultrasound and elastography in the assessment of skin involvement in systemic sclerosis: A systematic literature review focusing on validation and standardization—WSF Skin Ultrasound Group. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2022, 52, 151954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manetti, M.; Romano, E.; Rosa, I.; Guiducci, S.; Bellando-Randone, S.; De Paulis, A.; Ibba-Manneschi, L.; Matucci-Cerinic, M. Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition contributes to endothelial dysfunction and dermal fibrosis in systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 924–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutolo, M.; Soldano, S.; Smith, V. Pathophysiology of systemic sclerosis: Current understanding and new insights. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 15, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkmann, E.R.; Andréasson, K.; Smith, V. Systemic sclerosis. Lancet 2023, 401, 304–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulli, A.; Ruaro, B.; Smith, V.; Paolino, S.; Pizzorni, C.; Pesce, G. Subclinical dermal involvement is detectable by high-frequency ultrasound even in patients with limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, T.L.; Lunt, M.; McManus, B.; Anderson, M.E.; Herrick, A.L. Seventeen-point dermal ultrasound scoring system—A reliable measure of skin thickness in patients with systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology 2003, 42, 1559–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.; Berghen, N.; Hysa, E.; Vanhaecke, A.; Wallaert, S.; Gotelli, E.; Cutolo, M. Ultrasound for day-to-day clinical use: Construction of a simple discriminator between healthy skin and thickened systemic sclerosis skin. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2024, 42 (Suppl. S146), S00. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flower, V.A.; Barratt, S.L.; Hart, D.; Mackenzie, A.; Shipley, J.A.; Ward, S.; Pauling, J.D. High-frequency ultrasound assessment of systemic sclerosis skin involvement: Intraobserver repeatability and relationship with clinician assessment and dermal collagen content. J. Rheumatol. 2021, 48, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, R.; Khachemoune, A. Ultrasound utility in the management of morphea: A comprehensive review. Indian. Dermatol. Online J. 2024, 15, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Cappellari, A.; Lan, B.; Abayazid, M.; Stramigioli, S.; Niu, K. Automatic Robotic Ultrasound for 3D Musculoskeletal Reconstruction: A Comprehensive Framework. Technologies 2025, 13, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Salcudean, S.E.; Navab, N. Robotic ultrasound imaging: State-of-the-art and future perspectives. Med. Image Anal. 2023, 89, 102878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| SSc N = 14 | HC N = 14 | |
|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 68.4 (14.8) | 67.6 (11.5) |
| Sex | ||
| Female | 12 (85.7) | 12 (85.7) |
| Male | 2 (14.3) | 2 (14.3) |
| Disease duration, years | 8.6 (5.2) | - |
| Skin involvement | ||
| Diffuse (dc) | 4 (28.6) | - |
| Limited (lc) | 10 (71.4) | - |
| mRSS, points | 14.9 (13.2) | 0 |
| Antibodies | ||
| Anti-centromere | 10 (71.1) | - |
| Anti-Scl-70 | 3 (21.4) | - |
| No specific | 1 (2.1) | - |
| Disease manifestations | ||
| Raynaud’s phenomenon | 13 (92.9) | - |
| Puffy fingers | 1 (7.1) | - |
| Digital ulcers | 9 (64.3) | - |
| Interstitial lung disease | 7 (50) | - |
| Pulmonary hypertension | 2 (14.3) | - |
| Gastrointestinal involvement | 8 (57.1) | - |
| Immunosuppresant therapy | 10 (71.4) | - |
| Mycophenolat mofetil | 6 (42.9) | - |
| Methotrexate | 3 (21.4) | - |
| Cyclophosphamid i.v. | 1 (7.4) | - |
| Low-dose oral GCs | 2 (14.3) | - |
| (≤5 mg prednisone/day) | 1 (2.1) | - |
| Dermal Thickness, mm | mRSS 0 or 1 | mRSS 2 or 3 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right finger | min | 0.45 | 0.76 | |
| max | 1.15 | 1.41 | ||
| mean | 0.93 | 1.15 | 0.200 | |
| SD | 0.21 | 0.24 | ||
| Left finger | min | 0.54 | 0.99 | |
| max | 1.27 | 1.61 | ||
| mean | 0.90 | 1.28 | 0.025 | |
| SD | 0.26 | 0.19 | ||
| Right hand | min | 0.36 | 0.80 | |
| max | 1.17 | 2.24 | ||
| mean | 0.64 | 1.46 | 0.032 | |
| SD | 0.22 | 0.64 | ||
| Left hand | min | 0.40 | 0.77 | |
| max | 1.10 | 2.39 | ||
| mean | 0.66 | 1.49 | 0.023 | |
| SD | 0.22 | 0.68 |
| Location | Correlation Coefficient | 95% CI Lower; Upper | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Right finger | 0.76 | 0.53; 0.89 | p < 0.001 |
| Left finger | 0.85 | 0.71; 0.91 | p < 0.001 |
| Right hand | 0.64 | 0.37; 0.83 | p < 0.001 |
| Left hand | 0.61 | 0.27; 0.83 | p < 0.001 |
| Upper right arm | 0.56 | p = 0.002 | |
| Upper left arm | 0.56 | p = 0.002 | |
| Right forearm | 0.67 | 0.39; 0.84 | p < 0.001 |
| Left forearm | 0.61 | p < 0.001 | |
| Face | 0.52 | 0.23; 0.74 | p = 0.005 |
| Chest | 0.02 | p = 0.902 | |
| Abdomen | 0.50 | p = 0.001 | |
| Right thigh | 0.39 | p = 0.040 | |
| Left thigh | 0.42 | p = 0.025 | |
| Lower right leg | 0.44 | 0.11; 0.70 | p = 0.020 |
| Lower left leg | 0.55 | 0.20; 0.77 | p = 0.003 |
| Right foot | 0.49 | 0.09; 0.76 | p = 0.009 |
| Left foot | 0.63 | 0.26; 0.83 | p < 0.001 |
| Location | ICC Dermis | 95% CI Lower; Upper | ICC Cutis | 95% CI Lower; Upper |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right finger | 0.80 | 0.53; 0.93 | 0.80 | 0.53; 0.93 |
| Left finger | 0.75 | 0.42; 0.91 | 0.80 | 0.51; 0.93 |
| Right hand | 0.84 | 0.61; 0.95 | 0.87 | 0.67; 0.95 |
| Left hand | 0.76 | 0.40; 0.92 | 0.82 | 0.56; 0.94 |
| Upper right arm | 0.91 | 0.78; 0.97 | 0.87 | 0.67; 0.95 |
| Upper left arm | 0.94 | 0.85; 0.98 | 0.94 | 0.85; 0.98 |
| Right forearm | 0.87 | 0.68; 0.96 | 0.88 | 0.70; 0.96 |
| Left forearm | 0.90 | 0.75; 0.96 | 0.91 | 0.78; 0.97 |
| Face | 0.56 | 0.05; 0.83 | 0.47 | 0.09; 0.80 |
| Chest | 0.87 | 0.68; 0.96 | 0.89 | 0.74; 0.96 |
| Abdomen | 0.84 | 0.60; 0.94 | 0.88 | 0.70; 0.96 |
| Right thigh | 0.93 | 0.83; 0.98 | 0.93 | 0.82; 0.97 |
| Left thigh | 0.92 | 0.80; 0.97 | 0.90 | 0.76; 0.96 |
| Lower right leg | 0.87 | 0.69; 0.96 | 0.89 | 0.73; 0.96 |
| Lower left leg | 0.92 | 0.82; 0.97 | 0.92 | 0.81; 0.97 |
| Right foot | 0.72 | 0.33; 0.94 | 0.72 | 0.35; 0.90 |
| Left foot | 0.89 | 0.73; 0.96 | 0.85 | 0.62; 0.95 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krammer, O.B.; Fleck, M.; Ehrenstein, B.; Hartung, W.; Günther, F. Performance of Ultra-High-Frequency Ultrasound in the Evaluation of Skin Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis: A Cross-Sectional Pilot Study. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131600
Krammer OB, Fleck M, Ehrenstein B, Hartung W, Günther F. Performance of Ultra-High-Frequency Ultrasound in the Evaluation of Skin Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis: A Cross-Sectional Pilot Study. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(13):1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131600
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrammer, Olga Barbara, Martin Fleck, Boris Ehrenstein, Wolfgang Hartung, and Florian Günther. 2025. "Performance of Ultra-High-Frequency Ultrasound in the Evaluation of Skin Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis: A Cross-Sectional Pilot Study" Diagnostics 15, no. 13: 1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131600
APA StyleKrammer, O. B., Fleck, M., Ehrenstein, B., Hartung, W., & Günther, F. (2025). Performance of Ultra-High-Frequency Ultrasound in the Evaluation of Skin Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis: A Cross-Sectional Pilot Study. Diagnostics, 15(13), 1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131600






