Comparison of Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast and Arterial Spin Labeling MRI Perfusion in the Assessment of Stroke and Steno-Occlusive Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Procedure
2.2. Selection Criteria and Data Collection
2.3. Risk-of-Bias Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Image Quality
3. Results
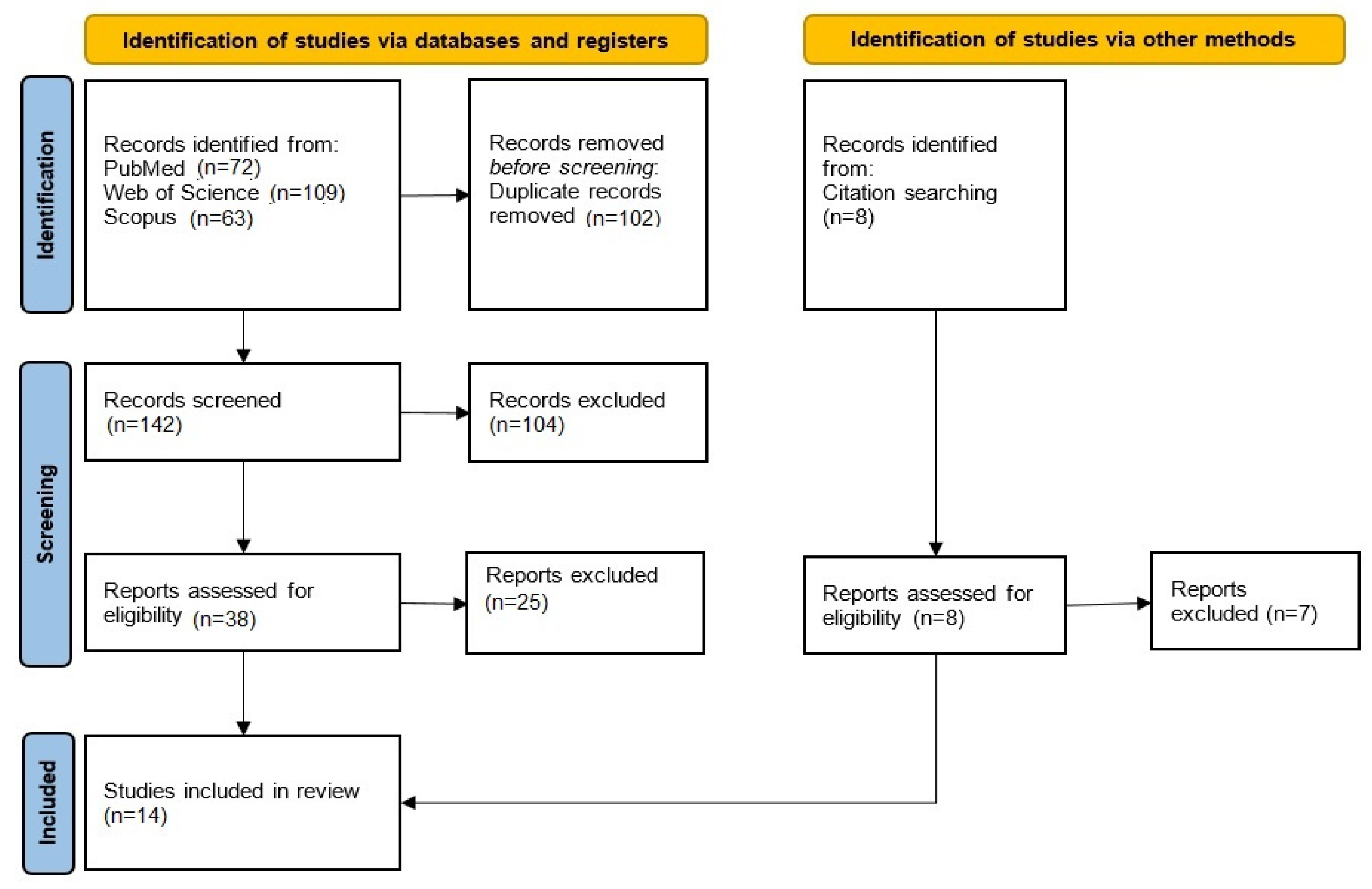
3.1. Literature Search
3.2. Bias Assessment
3.3. Quality Assessment
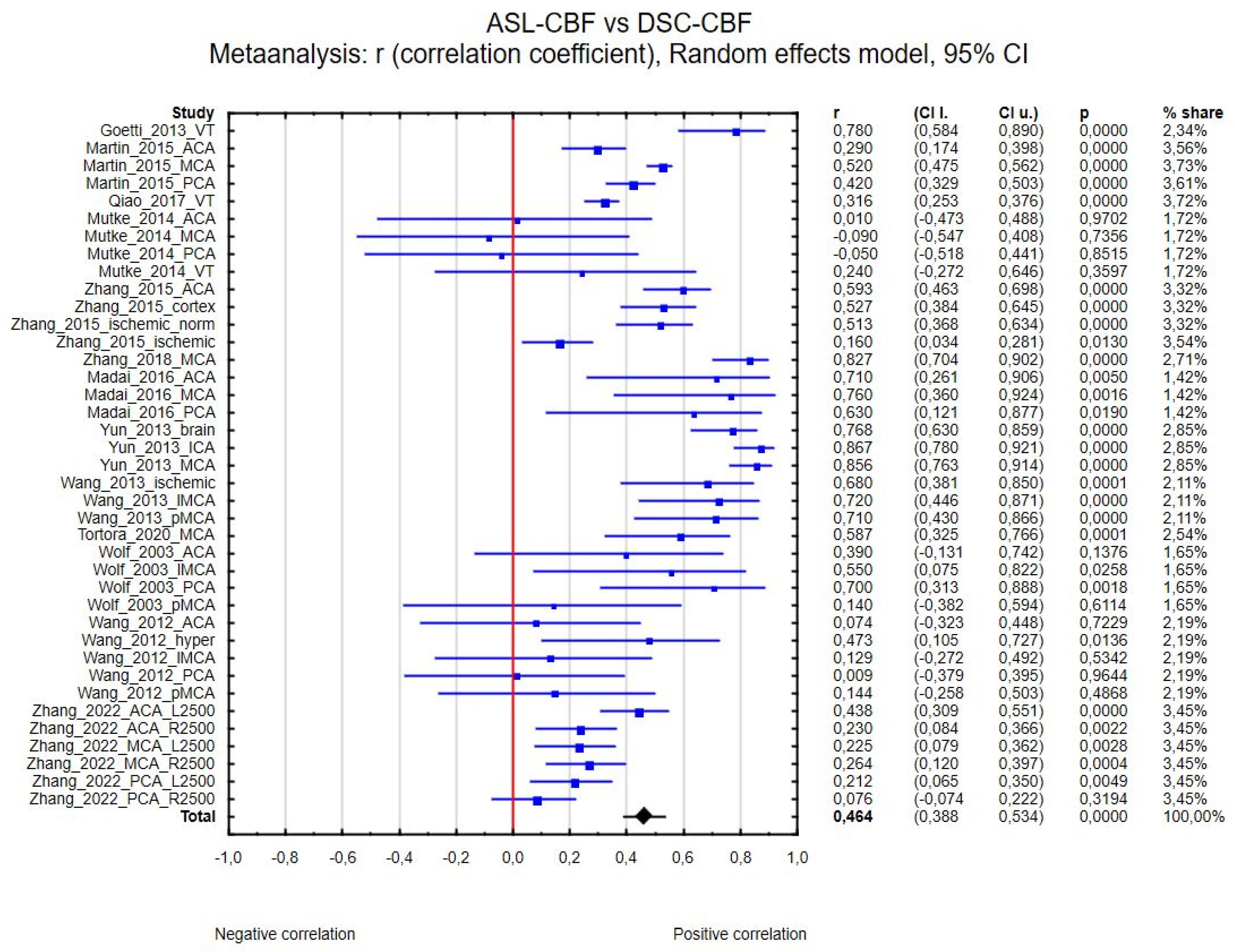
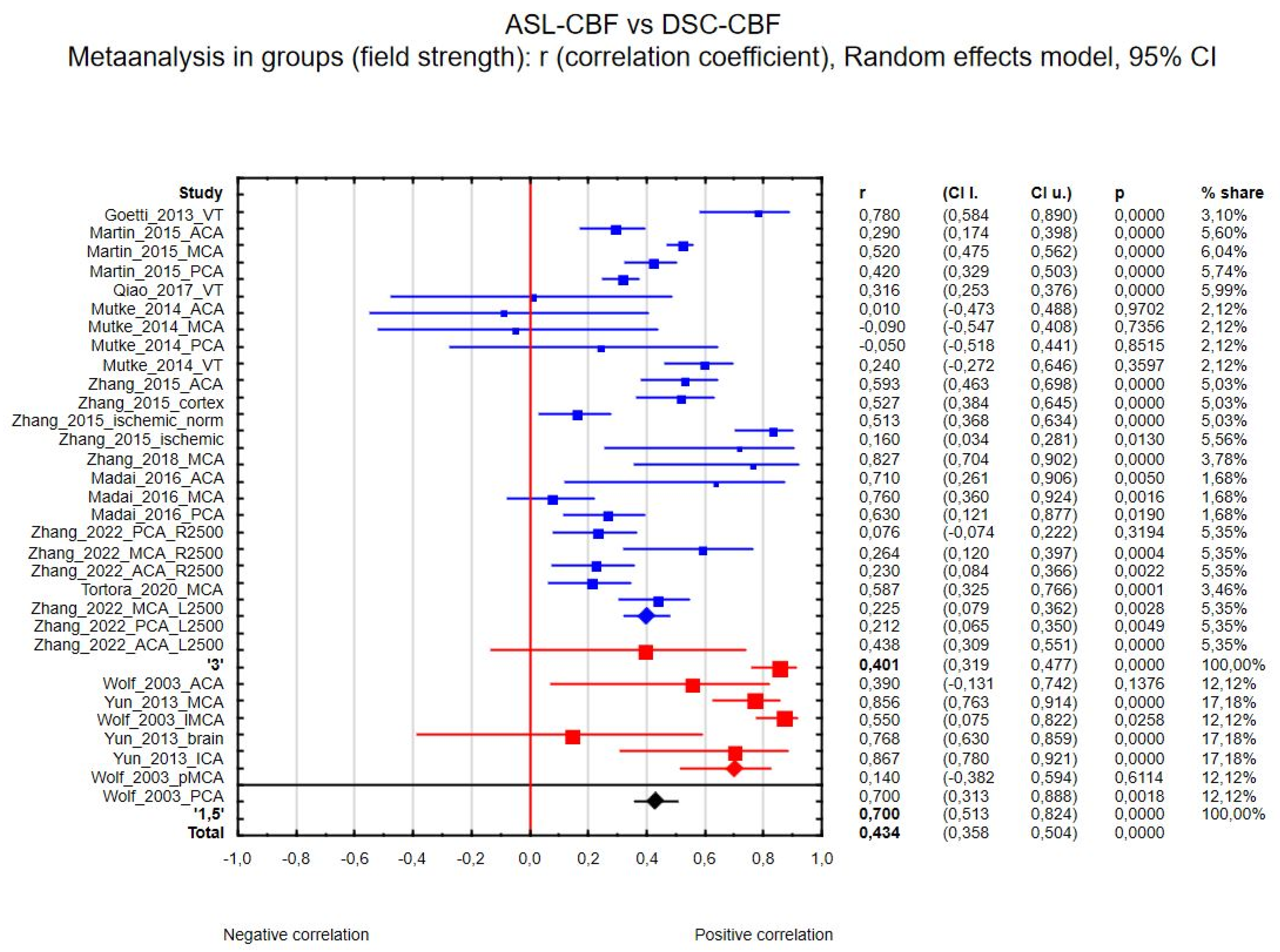
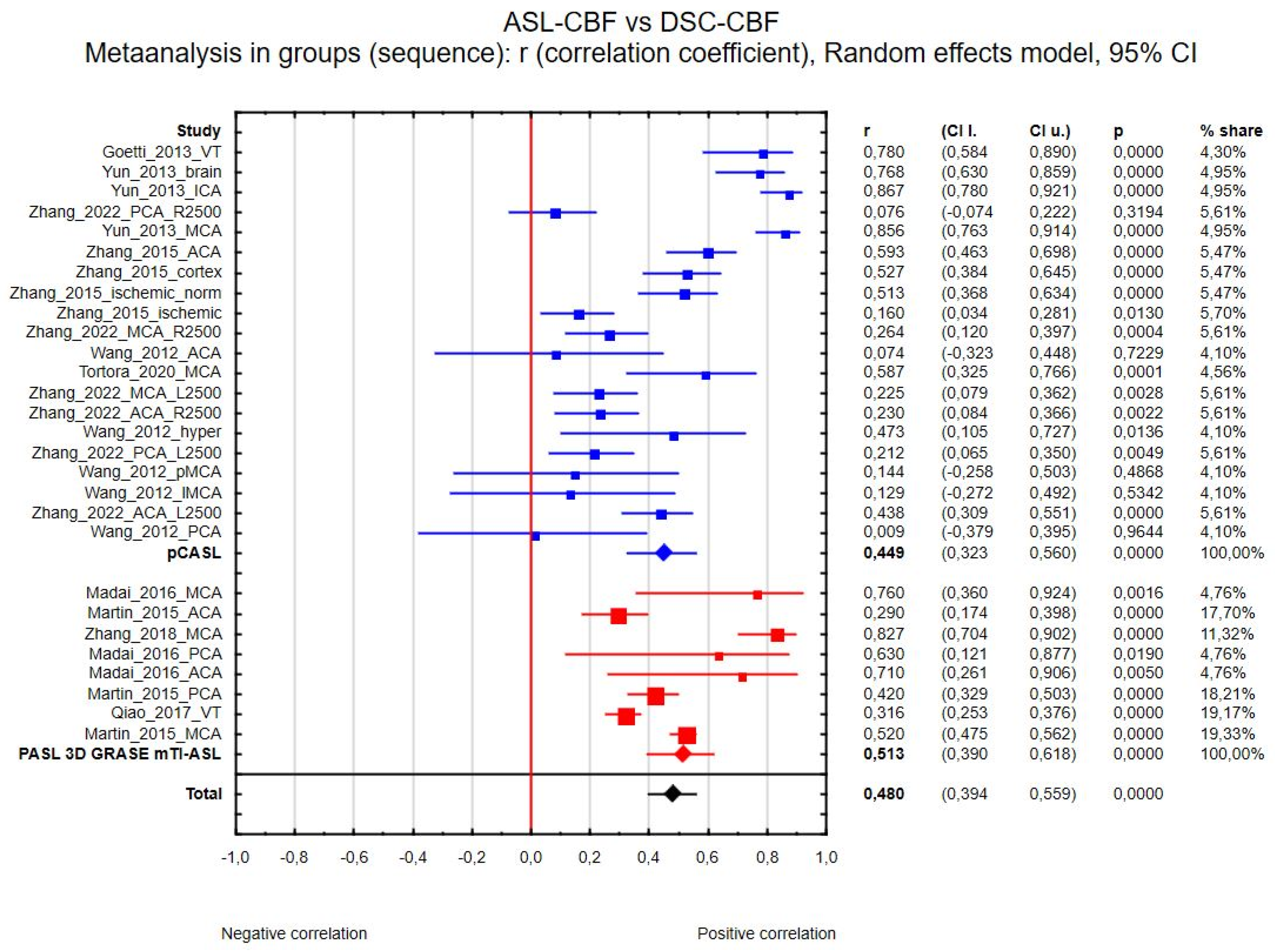
3.4. Data Analysis
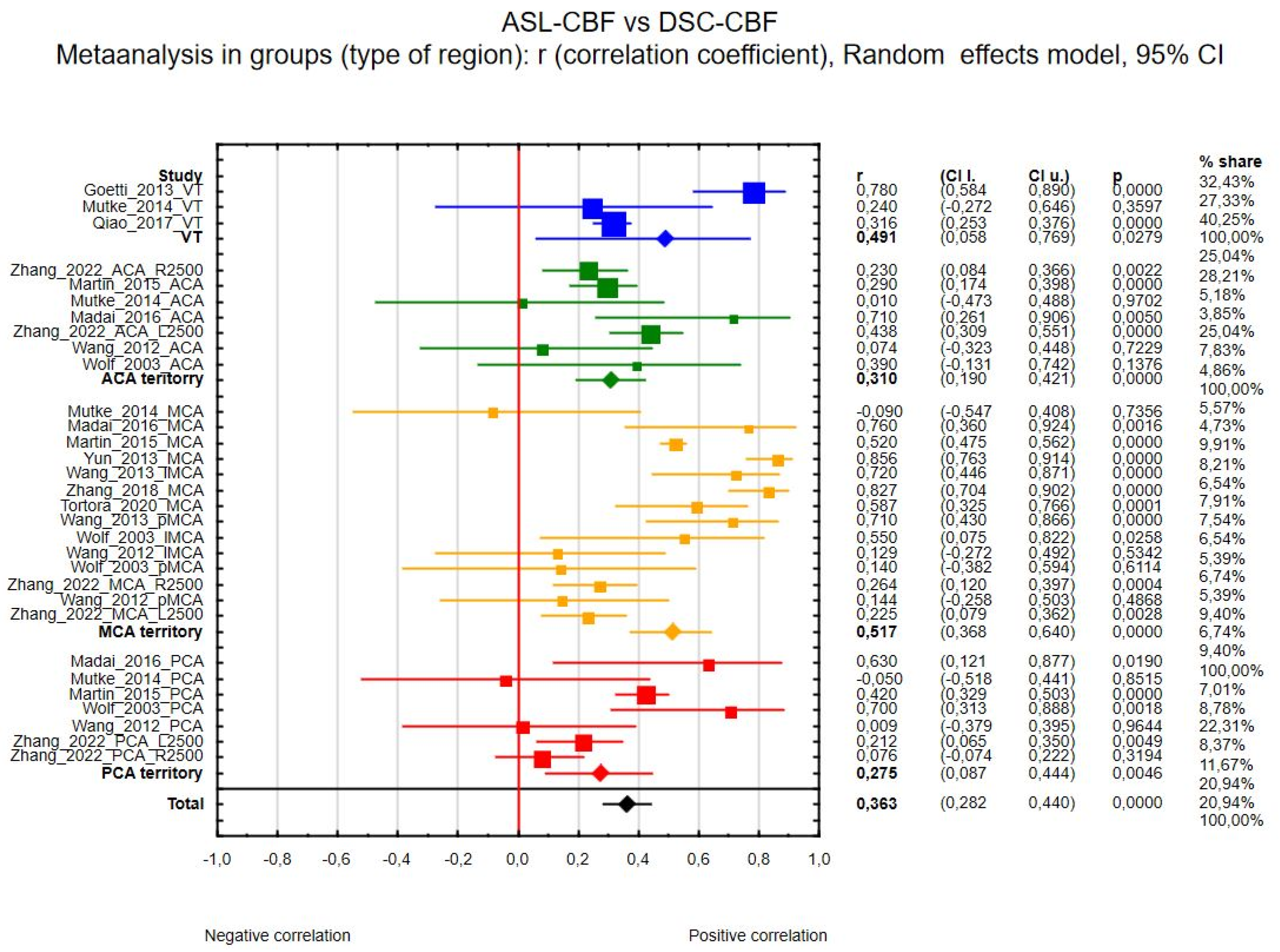
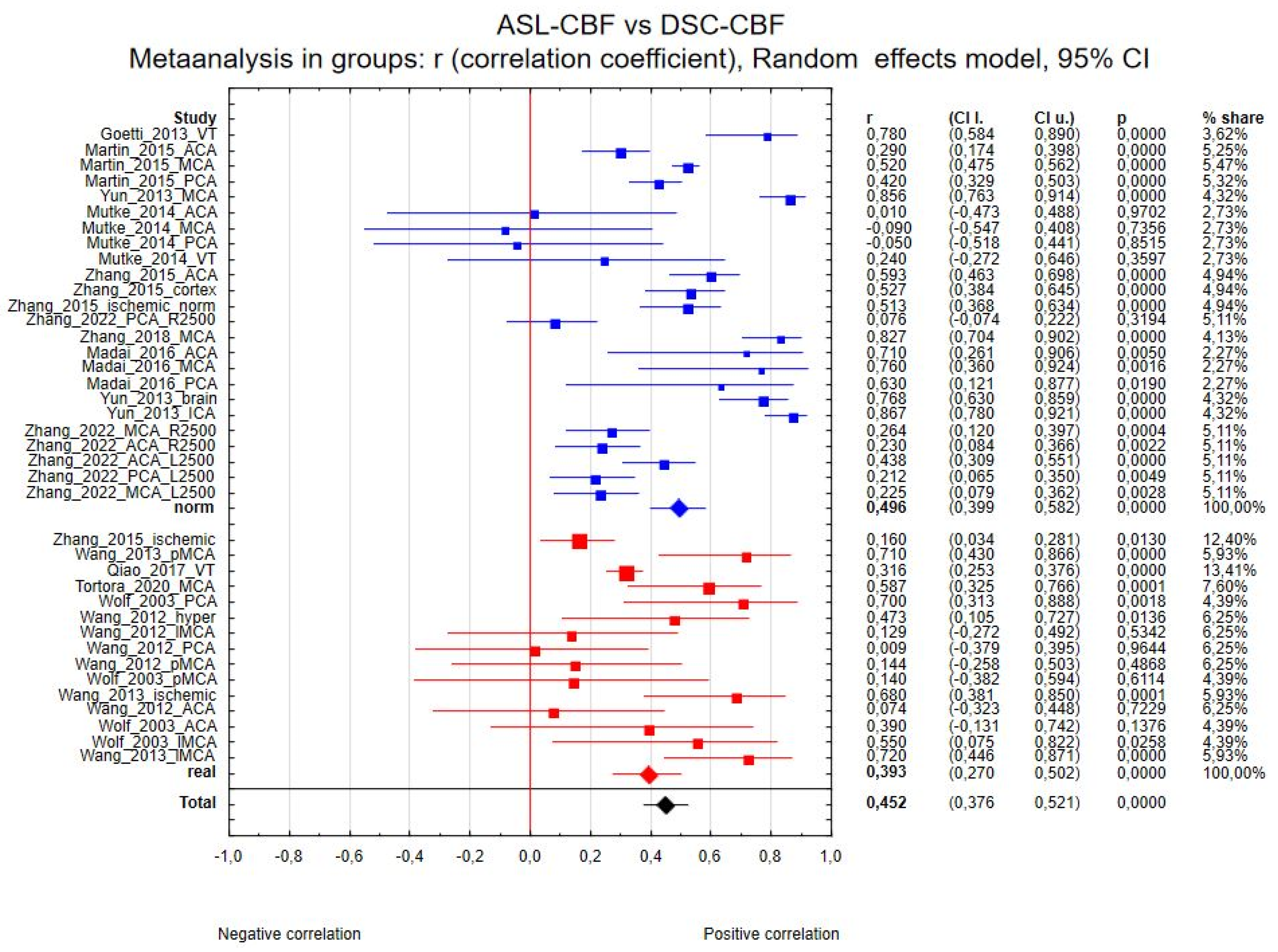
3.4.1. ASL-CBF vs. DSC-CBF
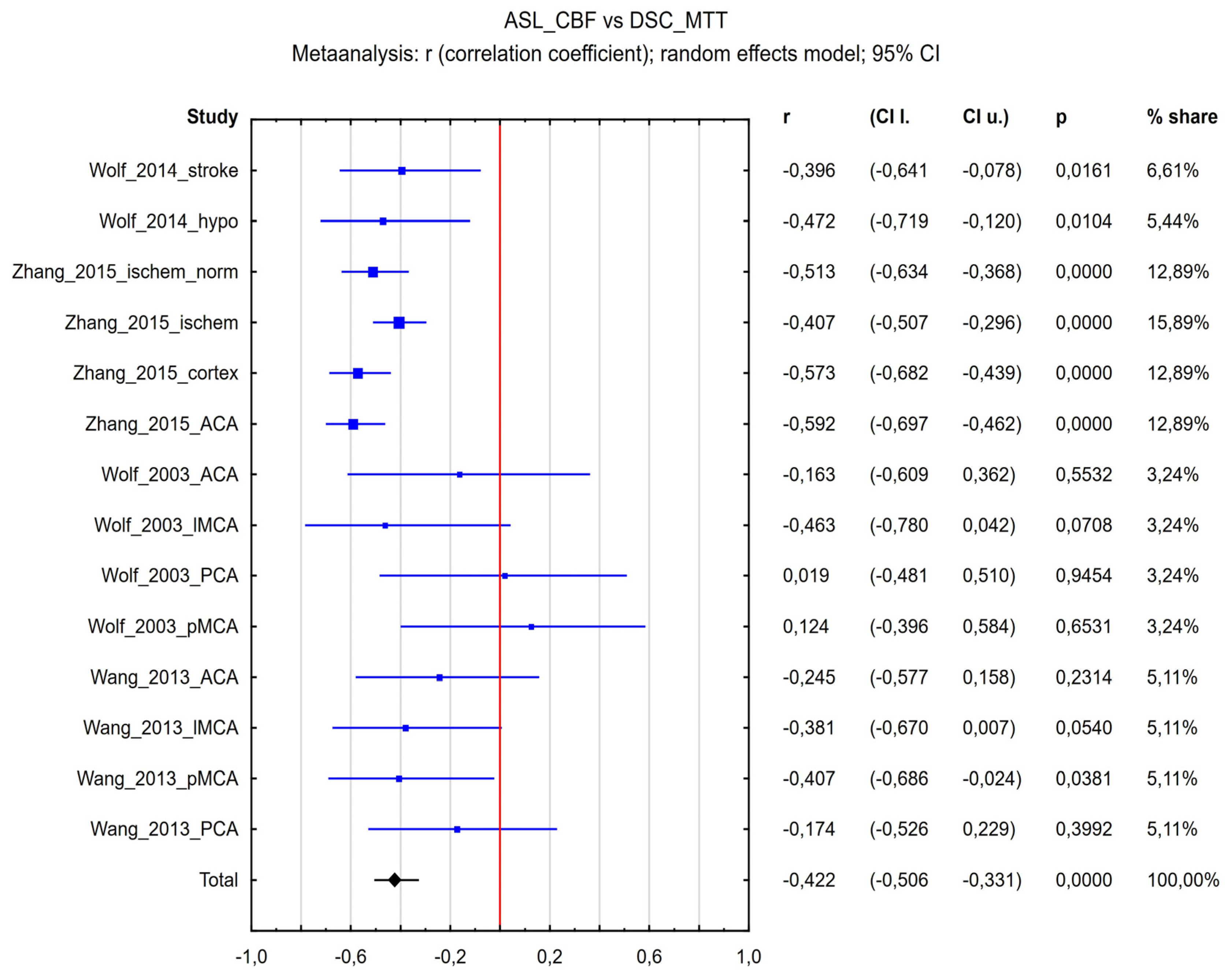
3.4.2. ASL-CBF vs. DSC-MTT
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASL | arterial spin labeling |
| DSC | dynamic susceptibility contrast |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| MTT | mean transit time |
| CBF | cerebral blood flow |
| rCBF | regional cerebral blood flow |
| CBV | cerebral blood volume |
| TTP | time to peak |
| SPECT | single-photon emission computed tomography |
| PET | positron emission tomography |
| PLD | post-labeling delay |
| ATT | arterial transit time |
| 3D-GRASE | three-dimensional gradient and spin echo |
| pCASL | pseudo-continuous arterial spin labeling |
| CASL | continuous arterial spin labeling |
| PASL | pulsed arterial spin labeling |
| mTI-ASL | multi-time inversion arterial spin labeling |
| ROI | region of interest |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| QUADAS | Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies |
| ASL-BAT | arterial spin labeling–bolus arrival time |
| ACA | anterior cerebral artery |
| MCA | middle cerebral artery |
| PCA | posterior cerebral artery |
| SNR | signal-to-noise ratio |
References
- Sourbron, S. Technical Aspects of MR Perfusion. Eur. J. Radiol. 2010, 76, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuutinen, J.; Liu, Y.; Laakso, M.P.; Karonen, J.O.; Vanninen, E.J.; Kuikka, J.T.; Aronen, H.J.; Vanninen, R.L. Perfusion Differences on SPECT and PWI in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke. Neuroradiology 2009, 51, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, R.J.; McDonald, J.S.; Kallmes, D.F.; Jentoft, M.E.; Murray, D.L.; Thielen, K.R.; Williamson, E.E.; Eckel, L.J. Intracranial Gadolinium Deposition after Contrast-Enhanced MR Imaging. Radiology 2015, 275, 772–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinreb, J.C.; Rodby, R.A.; Yee, J.; Wang, C.L.; Fine, D.; McDonald, R.J.; Perazella, M.A.; Dillman, J.R.; Davenport, M.S. Use of Intravenous Gadolinium-Based Contrast Media in Patients with Kidney Disease: Consensus Statements from the American College of Radiology and the National Kidney Foundation. Radiology 2021, 298, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, J.M.; Kaufman, M.J.; Ross, M.H.; Mendelson, J.H.; Maas, L.C.; Cohen, B.M.; Renshaw, P.F. Sequential Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast MR Experiments in Human Brain: Residual Contrast Agent Effect, Steady State, and Hemodynamic Perturbation. Magn. Reson. Med. 1995, 34, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grade, M.; Hernandez Tamames, J.A.; Pizzini, F.B.; Achten, E.; Golay, X.; Smits, M. A Neuroradiologist’s Guide to Arterial Spin Labeling MRI in Clinical Practice. Neuroradiology 2015, 57, 1181–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, E.C. An Introduction to ASL Labeling Techniques. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2014, 40, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsop, D.C.; Detre, J.A.; Golay, X.; Günther, M.; Hendrikse, J.; Hernandez-Garcia, L.; Lu, H.; Macintosh, B.J.; Parkes, L.M.; Smits, M.; et al. Recommended Implementation of Arterial Spin-Labeled Perfusion Mri for Clinical Applications: A Consensus of the ISMRM Perfusion Study Group and the European Consortium for ASL in Dementia. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 73, 102–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, C.H.; Kim, H.S.; Jung, S.C.; Choi, C.G.; Kim, S.J. Perfusion MRI as a Diagnostic Biomarker for Differentiating Glioma from Brain Metastasis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 3819–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wang, Q.; Shao, A.; Xu, B.; Zhang, J. The Performance of MR Perfusion-Weighted Imaging for the Differentiation of High-Grade Glioma from Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourdias, T.; Rodrigo, S.; Oppenheim, C.; Naggara, O.; Varlet, P.; Amoussa, S.; Calmon, G.; Roux, F.X.; Meder, J.F. Pulsed Arterial Spin Labeling Applications in Brain Tumors: Practical Review. J. Neuroradiol. 2008, 35, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, J.; Wu, M.; Wang, X.; Qiao, L.; Guo, G.; Zhang, C. The Diagnostic Value of Quantitative Analysis of ASL, DSC-MRI and DKI in the Grading of Cerebral Gliomas: A Meta-Analysis. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 15, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, C.H.; Kim, H.S.; Jung, S.C.; Park, J.E.; Choi, C.G.; Kim, S.J. MRI as a Diagnostic Biomarker for Differentiating Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma from Glioblastoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 50, 560–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.Y.; Hu, X.Q.; Xu, J.F.; Zhu, W.J.; Wu, H.Y.; Dong, F.J. Diagnostic Accuracy of Arterial Spin-Labeling MR Imaging in Detecting the Epileptogenic Zone: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2021, 42, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F. Magnetic Resonance Diffusion-Perfusion Mismatch in Acute Ischemic Stroke: An Update. World J. Radiol. 2012, 4, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiting, P.F.; Rutjes, A.W.S.; Westwood, M.E.; Mallett, S.; Deeks, J.J.; Reitsma, J.B.; Leeflang, M.M.G.; Sterne, J.A.C.; Bossuyt, P.M.M. Quadas-2: A Revised Tool for the Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupinski, M.T.; Dunlap, W.P. Approximating Pearson Product-Moment Correlations from Kendall’s Tau and Spearman’s Rho. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1996, 56, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetti, R.; O’Gorman, R.; Khan, N.; Kellenberger, C.J.; Scheer, I. Arterial Spin Labelling MRI for Assessment of Cerebral Perfusion in Children with Moyamoya Disease: Comparison with Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast MRI. Neuroradiology 2013, 55, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.Z.; Madai, V.I.; Von Samson-Himmelstjerna, F.C.; Mutke, M.A.; Bauer, M.; Herzig, C.X.; Hetzer, S.; Günther, M.; Sobesky, J. 3D GRASE Pulsed Arterial Spin Labeling at Multiple Inflow Times in Patients with Long Arterial Transit Times: Comparison with Dynamic Susceptibility-Weighted Contrast-Enhanced MRI at 3 Tesla. J. Perinatol. 2015, 35, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, M.E.; Layer, V.; Gregori, J.; Griebe, M.; Szabo, K.; Gass, A.; Hennerici, M.G.; Günther, M.; Kern, R. Assessment of Perfusion Deficits in Ischemic Stroke Using 3D-GRASE Arterial Spin Labeling Magnetic Resonance Imaging with Multiple Inflow Times. J. Neuroimaging 2014, 24, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, P.G.; Han, C.; Zuo, Z.W.; Wang, Y.T.; Pfeuffer, J.; Duan, L.; Qian, T.; Li, G.J. Clinical Assessment of Cerebral Hemodynamics in Moyamoya Disease via Multiple Inversion Time Arterial Spin Labeling and Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast-Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Comparative Study. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 44, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutke, M.A.; Madai, V.I.; von Samson-Himmelstjerna, F.C.; Zaro Weber, O.; Revankar, G.S.; Martin, S.Z.; Stengl, K.L.; Bauer, M.; Hetzer, S.; Günther, M.; et al. Clinical Evaluation of an Arterial-Spin-Labeling Product Sequence in Steno-Occlusive Disease of the Brain. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.X.; Yao, Y.H.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, W.J.; Tang, X.Y.; Qin, Y.Y.; Zhao, L.Y.; Liu, C.X.; Zhu, W.Z. zhen Comparative Study of DSC-PWI and 3D-ASL in Ischemic Stroke Patients. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. Med. Sci. 2015, 35, 923–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Xia, C.; Liu, Y.; Qian, W.; Peng, W.; Liu, K.; Li, L.; Zhao, F.; Li, Z. Comparative Study of MR MTI-ASL and DSC-PWI in Evaluating Cerebral Hemodynamics of Patients with Moyamoya Disease. Medicine 2018, 97, e12768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madai, V.I.; Martin, S.Z.; von Samson-Himmelstjerna, F.C.; Herzig, C.X.; Mutke, M.A.; Wood, C.N.; Thamm, T.; Zweynert, S.; Bauer, M.; Hetzer, S.; et al. Correction for Susceptibility Distortions Increases the Performance of Arterial Spin Labeling in Patients with Cerebrovascular Disease. J. Neuroimaging 2016, 26, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, T.J.; Sohn, C.H.; Han, M.H.; Kang, H.S.; Kim, J.E.; Yoon, B.W.; Paeng, J.C.; Choi, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Song, I.C.; et al. Effect of Delayed Transit Time on Arterial Spin Labeling: Correlation with Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast Perfusion Magnetic Resonance in Moyamoya Disease. Invest. Radiol. 2013, 48, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.J.J.; Alger, J.R.; Qiao, J.X.; Gunther, M.; Pope, W.B.; Saver, J.L.; Salamon, N.; Liebeskind, D.S. Multi-Delay Multi-Parametric Arterial Spin-Labeled Perfusion MRI in Acute Ischemic Stroke - Comparison with Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast Enhanced Perfusion Imaging. Neuroimage Clin. 2013, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortora, D.; Scavetta, C.; Rebella, G.; Bertamino, M.; Scala, M.; Giacomini, T.; Morana, G.; Pavanello, M.; Rossi, A.; Severino, M. Spatial Coefficient of Variation Applied to Arterial Spin Labeling MRI May Contribute to Predict Surgical Revascularization Outcomes in Pediatric Moyamoya Vasculopathy. Neuroradiology 2020, 62, 1003–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, R.L.; Alsop, D.C.; McGarvey, M.L.; Maldjian, J.A.; Wang, J.; Detre, J.A. Susceptibility Contrast and Arterial Spin Labeled Perfusion MRI in Cerebrovascular Disease. J. Neuroimaging 2003, 13, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.J.J.; Alger, J.R.; Qiao, J.X.; Hao, Q.; Hou, S.; Fiaz, R.; Gunther, M.; Pope, W.B.; Saver, J.L.; Salamon, N.; et al. The Value of Arterial Spin-Labeled Perfusion Imaging in Acute Ischemic Stroke: Comparison with Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast-Enhanced MRI. Stroke 2012, 43, 1018–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Lu, M.; Liu, S.; Liu, D.; Shen, X.; Sheng, F.; Han, C.; Cai, J. The Value of 3D Pseudo-Continuousarterial Spin Labeling Perfusion Imaging in Moyamoya Disease—Comparison with Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast Perfusion Imaging. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 944246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huck, S.; Kerl, H.U.; Al-Zghloul, M.; Groden, C.; Nölte, I. Arterial Spin Labeling at 3.0 Tesla in Subacute Ischemia: Comparison to Dynamic Susceptibility Perfusion. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2012, 22, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, D.A.; Bokkers, R.P.H.; Mirasol, R.V.; Luby, M.; Henning, E.C.; Merino, J.G.; Warach, S.; Latour, L.L. Pseudocontinuous Arterial Spin Labeling Quantifies Relative Cerebral Blood Flow in Acute Stroke. Stroke 2012, 43, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokkers, R.P.H.; Hernandez, D.A.; Merino, J.G.; Mirasol, R.V.; Van Osch, M.J.; Hendrikse, J.; Warach, S.; Latour, L.L. Whole-Brain Arterial Spin Labeling Perfusion MRI in Patients with Acute Stroke. Stroke 2012, 43, 1290–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lin, C.; Minuti, A.; Lipton, M. Arterial Spin Labeling Compared to Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast MR Perfusion Imaging for Assessment of Ischemic Penumbra: A Systematic Review. J. Neuroimaging 2021, 31, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essig, M.; Shiroishi, M.S.; Nguyen, T.B.; Saake, M.; Provenzale, J.M.; Enterline, D.; Anzalone, N.; Dörfler, A.; Rovira, À.; Wintermark, M.; et al. Perfusion MRI: The Five Most Frequently Asked Technical Questions. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2013, 200, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calamante, F.; Gadian, D.G.; Connelly, A. Delay and Dispersion Effects in Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast MRI: Simulations Using Singular Value Decomposition. Magn. Reson. Med. 2000, 44, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibaraki, M.; Shimosegawa, E.; Toyoshima, H.; Takahashi, K.; Miura, S.; Kanno, I. Tracer Delay Correction of Cerebral Blood Flow with Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast-Enhanced MRI. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2005, 25, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibaraki, M.; Shimosegawa, E.; Toyoshima, H.; Ishigame, K.; Ito, H.; Takahashi, K.; Miura, S.; Kanno, I. Effect of Regional Tracer Delay on CBF in Healthy Subjects Measured with Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast-Enhanced MRI: Comparison with 15O-PET. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2005, 4, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrikse, J.; van Osch, M.J.P.; Rutgers, D.R.; Bakker, C.J.G.; Kappelle, L.J.; Golay, X.; van der Grond, J. Internal Carotid Artery Occlusion Assessed at Pulsed Arterial Spin-Labeling Perfusion MR Imaging at Multiple Delay Times. Radiology 2004, 233, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deibler, A.R.; Pollock, J.M.; Kraft, R.A.; Tan, H.; Burdette, J.H.; Maldjian, J.A. Arterial Spin-Labeling in Routine Clinical Practice, Part 3: Hyperperfusion Patterns. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2008, 29, 1428–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detre, J.A.; Alsop, B.C.; Vives, L.R.; Maccotta, L.; Teener, J.W.; Raps, E.C. Noninvasive MRI Evaluation of Cerebral Blood Flow in Cerebrovascular Disease. Neurology 1998, 50, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, A.P.; Guo, J.; Khalighi, M.M.; Gulaka, P.K.; Shen, B.; Park, J.H.; Gandhi, H.; Holley, D.; Rutledge, O.; Singh, P.; et al. Long-Delay Arterial Spin Labeling Provides More Accurate Cerebral Blood Flow Measurements in Moyamoya Patients: A Simultaneous Positron Emission Tomography/MRI Study. Stroke 2017, 48, 2441–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujikawa, T.; Kimura, H.; Matsuda, T.; Fujiwara, Y.; Isozaki, M.; Kikuta, K.I.; Okazawa, H. Arterial Transit Time Mapping Obtained by Pulsed Continuous 3D ASL Imaging with Multiple Post-Label Delay Acquisitions: Comparative Study with PET-CBF in Patients with Chronic Occlusive Cerebrovascular Disease. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iutaka, T.; de Freitas, M.B.; Omar, S.S.; Scortegagna, F.A.; Nael, K.; Nunes, R.H.; Pacheco, F.T.; Maia Júnior, A.C.M.; Do Amaral, L.L.F.; da Rocha, A.J. Arterial Spin Labeling: Techniques, Clinical Applications, and Interpretation. Radiographics 2023, 43, e220088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacIntosh, B.J.; Lindsay, A.C.; Kylintireas, I.; Kuker, W.; Günther, M.; Robson, M.D.; Kennedy, J.; Choudhury, R.P.; Jezzard, P. Multiple Inflow Pulsed Arterial Spin-Labeling Reveals Delays in the Arterial Arrival Time in Minor Stroke and Transient Ischemic Attack. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2010, 31, 1892–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmer, M.D.; Giese, A.K.; Fotiadis, P.; Etherton, M.R.; Cloonan, L.; Viswanathan, A.; Greenberg, S.M.; Wu, O.; Rost, N.S. Spatial Signature of White Matter Hyperintensities in Stroke Patients. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.F.; Hsu, J.; Xu, X.; Kim, G.; Sheppard, S.M.; Meier, E.L.; Miller, M.I.; Hillis, A.E.; Faria, A.V. Digital 3D Brain MRI Arterial Territories Atlas. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Alsop, D.C.; Li, L.; Listerud, J.; Gonzalez-At, J.B.; Schnall, M.D.; Detre, J.A. Comparison of Quantitative Perfusion Imaging Using Arterial Spin Labeling at 1.5 and 4.0 Tesla. Magn. Reson. Med. 2002, 48, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patients | Field Strength (T) | ASL Type | PLD or mTI (ms) | Number of Patients | Number of ROIs Analyzed | Correlation Type (P—Pearson; S—Spearman) | r | Perfusion Parameters | Region (m—Manual; a—Automatic) | Normalization with Reference Zone (1) or Real Values (0) | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSC | ASL | ||||||||||||
| Goetti 2013 | Moyamoya disease | 3.0 | pCASL | 1500 | 10 | 30 | P | 0.79 | CBF | CBF | ACA + MCA + PCA (m) | 1 (cerebellum) | [19] |
| Martin 2015 | Steno-occlusive disease | 3.0 | 3D GRASE mTI-PASL | 15× TI, 300–3100, 200 increment | 43 | 258 | S | 0.29 | CBF | CBF | ACA (m) | 1 (contralateral) | [20] |
| 1075 | S | 0.52 | CBF | CBF | MCA (m) | 1 (contralateral) | |||||||
| 344 | S | 0.42 | CBF | CBF | PCA (m) | 1 (contralateral) | |||||||
| Wolf 2014 | Ischemic stroke | 1.5 | 3D GRASE mTI-PASL | 10× TI, 250–2500, | 36 | 36 | P | −0.41 | MTT | CBF | Ischemic hemisphere (m) | 1 (contralateral) | [21] |
| 28 | P | −0.49 | MTT | CBF | Hypoperfusion ROI (m) | 1 (contralateral) | |||||||
| Qiao 2017 | Moyamoya disease | 3.0 | 3D GRASE mTI-PASL | 16× TI, 480–4080, | 41 | 824 | S | 0.32 | CBF | CBF | MCA + ACA (m) | 0 | [22] |
| Mutke 2014 | Steno-occlusive disease | 3.0 | PASL | 1800 | 17 | 17 | S | 0.24 | CBF | CBF | ACA + MCA + PCA (m) | 1 (contralateral) | [23] |
| 17 | S | 0.01 | CBF | CBF | ACA territory GM (m) | 1 (contralateral) | |||||||
| 17 | S | −0.09 | CBF | CBF | MCA territory GM (m) | 1 (contralateral) | |||||||
| 17 | S | −0.05 | CBF | CBF | PCA territory GM (m) | 1 (contralateral) | |||||||
| Zhang 2015 | Ischemic stroke | 3.0 | pCASL | 1525 | 30 | 120 | P | 0.53 | CBF | CBF | Ischemic hemisphere (m) | 1 (contralateral) | [24] |
| 240 | P | 0.17 | CBF | CBF | Ischemic hemisphere (m) | 0 | |||||||
| 120 | P | 0.55 | CBF | CBF | Cortex (m) | 1 (contralateral) | |||||||
| 120 | P | 0.611 | CBF | CBF | Anterior circulation (m) | 1 (contralateral) | |||||||
| 120 | P | −0.53 | MTT | CBF | Ischemic hemisphere (m) | 1 (contralateral) | |||||||
| 240 | P | −0.42 | MTT | CBF | Ischemic hemisphere (m) | 0 | |||||||
| 120 | P | −0.59 | MTT | CBF | Cortex (m) | 1 (contralateral) | |||||||
| 120 | P | −0.61 | MTT | CBF | Anterior circulation (m) | 1 (contralateral) | |||||||
| Zhang 2018 | Moyamoya disease | 3.0 | 3D GRASE mTI-PASL | 16× TI, 480–4080, | 45 | 45 | P | 0.84 | CBF | CBF | Lateral MCA territories and basal ganglia (m) | 1 (cerebellum) | [25] |
| Madai 2016 | Steno-occlusive disease | 3.0 | 3D GRASE mTI-PASL | 15× TI, 300–3100, 200 increment | 13 | 13 | S | −0.22 | CBF | CBF | ACA (a) | 1 (contralateral) | [26] |
| 13 | S | 0.58 | CBF | CBF | MCA (a) | 1 (contralateral) | |||||||
| 13 | S | 0.58 | CBF | CBF | PCA (a) | 1 (contralateral) | |||||||
| Yun 2013 | Moyamoya disease | 1.5 | pCASL | 1500 | 54 | 54 | P | 0.87 | CBF | CBF | MCA (a) | 1 (cerebellum) | [27] |
| 54 | P | 0.88 | CBF | CBF | ICA (a) | 1 (cerebellum) | |||||||
| 54 | P | 0.78 | CBF | CBF | Anatomical structure-based ROIs (a) | 1 (cerebellum) | |||||||
| Wang 2013 | Acute stroke of MCA | 1.5/3.0 | 3D GRASE mTI-pCASL | 4× PLD, 1500–3000, 500 increment | 24 | 24 | P | 0.74 | CBF | CBF | Leptomeningeal MCA (a) | 0 | [28] |
| 24 | P | 0.73 | CBF | CBF | Perforator MCA (a) | 0 | |||||||
| 24 | P | 0.7 | CBF | CBF | Infarct ROI (a) | 0 | |||||||
| Tortora 2020 | Moyamoya disease | 3.0 | pCASL | 2000 | 37 | 37 | S | 0.59 | CBF | CBF | MCA (a) | 0 | [29] |
| Wolf 2003 | Acute and/or chronic cerebrovascular disease | 1.5 | CASL | 1500 | 8 | 16 | P | 0.41 | CBF | CBF | ACA (a) | 0 | [30] |
| 16 | P | 0.57 | CBF | CBF | Leptomeningeal MCA (a) | 0 | |||||||
| 16 | P | 0.72 | CBF | CBF | PCA (a) | 0 | |||||||
| 16 | P | 0.78 | CBF | CBF | Perforator MCA (a) | 0 | |||||||
| 16 | P | −0.17 | MTT | CBF | ACA (a) | 0 | |||||||
| 16 | P | −0.48 | MTT | CBF | Leptomeningeal MCA (a) | 0 | |||||||
| 16 | P | 0.02 | MTT | CBF | PCA (a) | 0 | |||||||
| 16 | P | 0.13 | MTT | CBF | Perforator MCA (a) | 0 | |||||||
| Wang 2012 | Acute ischemic stroke | 1.5/3.0 | pCASL | 2000 | 26 | 26 | S | 0.07 | CBF | CBF | ACA (a) | 0 | [31] |
| 26 | S | 0.13 | CBF | CBF | Leptomeningeal MCA (a) | 0 | |||||||
| 26 | S | 0.14 | CBF | CBF | Perforator MCA (a) | 0 | |||||||
| 26 | S | 0.01 | CBF | CBF | PCA (a) | 0 | |||||||
| 26 | S | 0.47 | CBF | CBF | Hypoperfusion lesion (a) | 0 | |||||||
| 26 | S | −0.24 | MTT | CBF | ACA (a) | 0 | |||||||
| 26 | S | −0.38 | MTT | CBF | Leptomeningeal MCA (a) | 0 | |||||||
| 26 | S | −0.41 | MTT | CBF | Perforator MCA (a) | 0 | |||||||
| 26 | S | −0.17 | MTT | CBF | PCA (a) | 0 | |||||||
| Zhang 2022 | Moyamoya disease | 3.0 | pCASL | 2500 | 174 | 174 | S | 0.438 | CBF | CBF | ACA (left) (a) | 1 (cerebellum) | [32] |
| 174 | S | 0.23 | CBF | CBF | ACA (right) (a) | 1 (cerebellum) | |||||||
| 174 | S | 0.225 | CBF | CBF | MCA (left) (a) | 1 (cerebellum) | |||||||
| 174 | S | 0.264 | CBF | CBF | MCA (right) (a) | 1 (cerebellum) | |||||||
| 174 | S | 0.212 | CBF | CBF | PCA (left) (a) | 1 (cerebellum) | |||||||
| 174 | S | 0.076 | CBF | CBF | PCA (right) (a) | 1 (cerebellum) | |||||||
| Patients | Field Strength (T) | ASL Type | Number of Patients | Original Scale | Original Results | Normalized Results (Values Between 0 and 1: 0—Poor Quality; 1—Excellent Quality) | Reference | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASL-CBF | DSC-CBF | ASL-BAT | DSC-TTP | ||||||||
| Martin 2015 | Steno-occlusive disease | 3.0 | 3D GRASE mTI-PASL | 43 | 1—very good 2—good 3—sufficient 4—uninterpretable | Mean score ASL-CBF: 2.0 DSC-CBF: 1.8 ASL-BAT: 3.0 DSC-TTP: 2.1 | 0.667 | 0.733 | 0.333 | 0.633 | [20] |
| Huck 2012 | Subacute ischemia | 3.0 | pASL | 15 | 0—poor 1—weak 2—moderate 3—good 4—excellent | Mean score ASL-CBF: 0.8 DSC-TTP: 2.53 | 0.200 | - | - | 0.633 | [33] |
| Mutke 2014 | Steno-occlusive disease | 3.0 | pASL | 28 | Good Medium Sufficient Uninterpretable | Number of each answer good/medium/sufficient/uninterpretable ASL-CBF 0/4/13/11 DSC-CBF 13/15/0/0 DSC-TTP 13/12/2/1 | 0.250 | 0.821 | - | 0.774 | [23] |
| Madai 2016 | Steno-occlusive disease | 3.0 | 3D GRASE mTI-PASL | 13 | 1—very good 2—good 3—sufficient 4—uninterpretable | mean score ASL-BAT—2.8 DSC-TTP—1.9 ASL-CBF—2.7 DSC-CBF—2.0 | 0.433 | 0.667 | 0.400 | 0.700 | [26] |
| Hernandez 2012 | Acute ischemic stroke | 3.0 | pCASL | 28 | Good to excellent Fair Poor Uninterpretable | Percent of each answer Good to excellent/fair/poor/uninterpretable ASL-CBF: 82.1%/7.1%/10.7%/0% DSC-TTP: 78.6%/7.1%/14.3%/0% | 0.905 | - | - | 0.881 | [34] |
| Wang 2012 | Acute ischemic stroke | 1.5/3.0 | pCASL | 26 | 0–3 | Mean score ASL-CBF—2.44 DSC-CBF—2.39 | 0.813 | 0.797 | - | - | [31] |
| Bokkers 2012 | Acute ischemic stroke | 3.0 | pCASL | 105 | Good Fair Poor Uninterpretable | Number of each answer good/fair/poor/uninterpretable DSC 75/15/10/5 ASL 76/17/9/3 | 0.860 | 0.841 | - | - | [35] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sabisz, A.; Brzeska, B.; Szurowska, E.; Szarmach, A. Comparison of Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast and Arterial Spin Labeling MRI Perfusion in the Assessment of Stroke and Steno-Occlusive Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131578
Sabisz A, Brzeska B, Szurowska E, Szarmach A. Comparison of Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast and Arterial Spin Labeling MRI Perfusion in the Assessment of Stroke and Steno-Occlusive Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(13):1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131578
Chicago/Turabian StyleSabisz, Agnieszka, Beata Brzeska, Edyta Szurowska, and Arkadiusz Szarmach. 2025. "Comparison of Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast and Arterial Spin Labeling MRI Perfusion in the Assessment of Stroke and Steno-Occlusive Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Diagnostics 15, no. 13: 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131578
APA StyleSabisz, A., Brzeska, B., Szurowska, E., & Szarmach, A. (2025). Comparison of Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast and Arterial Spin Labeling MRI Perfusion in the Assessment of Stroke and Steno-Occlusive Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics, 15(13), 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131578







