Digital Image Speckle Correlation (DISC): Facial Muscle Tracking for Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human Study Design
2.1.1. Control Groups
2.1.2. Patient 1 (Bell’s Palsy)
2.1.3. Patient 2 (Ketamine Therapy)
2.2. Video Recording Setup
2.3. Stimulus
2.4. DISC Algorithm
2.5. Active Muscle Regions
2.6. Reaction Time Measurements
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
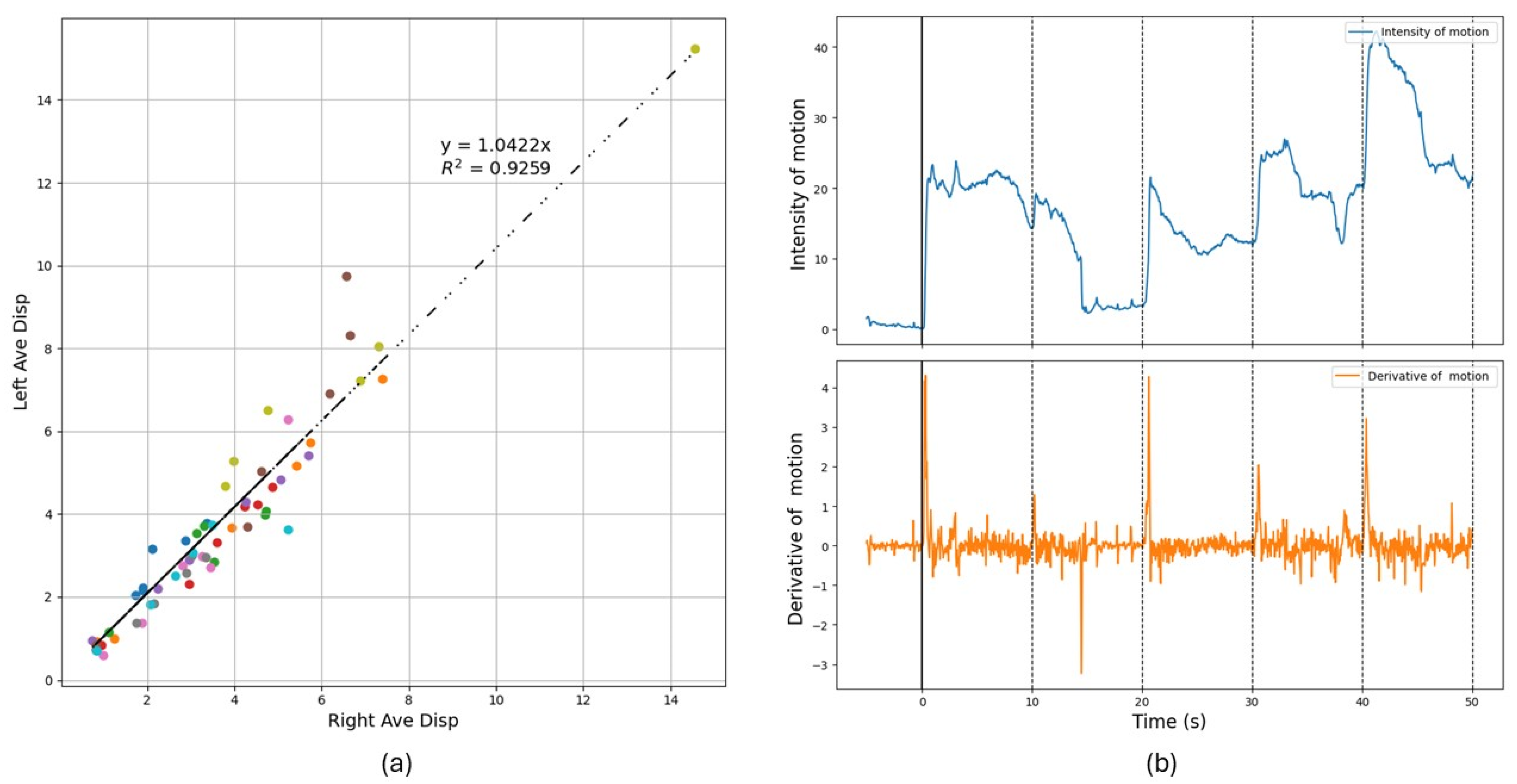
3.1. Control Group
3.2. Case Study 1: Patient Diagnosed with Bell’s Palsy
3.3. Case Study 2: Patient Undergoing Ketamine Treatment
4. Discussion
4.1. Facial Paralysis Evaluation
4.2. Psychiatric Evaluations
4.2.1. Reaction Time
4.2.2. Self-Reported Scores vs. DISC Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DISC | Digital Image Speckle Correlation |
| sEMG | Surface Electromyography |
| SMAS | Superficial Musculoaponeurotic System |
| TRD | Treatment-resistant Depression |
| IAPS | International Affective Picture System |
| VRT | Visual Reaction Time |
| DA | Degree of Asymmetry |
| PHQ-9 | Patient Depression Questionnaire-9 |
| QIDS-SR | Quick Inventory of Depressive Symptomatology Self-Report |
| BDI | Beck’s Depression Inventory |
| BAI | Beck Anxiety Inventory |
| GAD | Generalized Anxiety Disorder |
| PCL-5 | PTSD Checklist for DSM-5 |
References
- Cui, H.; Zhong, W.; Yang, Z.; Cao, X.; Dai, S.; Huang, X.; Hu, L.; Lan, K.; Li, G.; Yu, H. Comparison of Facial Muscle Activation Patterns Between Healthy and Bell’s Palsy Subjects Using High-Density Surface Electromyography. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 618985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popkirov, S.; Stone, J.; Buchan, A.M. Functional Neurological Disorder. Stroke 2020, 51, 1629–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertozzi, N.; Bianchi, B.; Salvagni, L.; Raposio, E. Activity Evaluation of Facial Muscles by Surface Electromyography. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2020, 8, e3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, R.; Ketko, I.; Scheinowitz, M.; Hanein, Y. Facial Electromyography during Exercise Using Soft Electrode Array: A Feasibility Study. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0298304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, E.A.Y. Reaction Time and EMG Measurement Applied to Human Control Modeling. Measurement 2010, 43, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Goodson, K.E. Subpixel Displacement and Deformation Gradient Measurement Using Digital Image/Speckle Correlation. Opt. Eng. 2001, 40, 1613–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, F.-P. Micro/Nano Speckle Method with Applications to Material, Tissue Engineering and Heart Mechanics. In Experimental Analysis of Nano and Engineering Materials and Structures, Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Experimental Mechanics, Alexandroupolis, Greece, 1–6 July 2007; Gdoutos, E.E., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 7–8. [Google Scholar]
- Staloff, I.A.; Guan, E.; Katz, S.; Rafailovitch, M.; Sokolov, A.; Sokolov, S. An in Vivo Study of the Mechanical Properties of Facial Skin and Influence of Aging Using Digital Image Speckle Correlation. Skin Res. Technol. 2008, 14, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitney, Z.B.; Jain, M.; Zito, P.M. Anatomy, Skin, Superficial Musculoaponeurotic System (SMAS) Fascia. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Pamudurthy, S.; Guan, E.; Mueller, K.; Rafailovich, M. Dynamic Approach for Face Recognition Using Digital Image Skin Correlation. In Audio- and Video-Based Biometric Person Authentication; Kanade, T., Jain, A., Ratha, N.K., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; Volume 3546, pp. 1010–1018. ISBN 978-3-540-27887-0. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatnagar, D.; Conkling, N.; Rafailovich, M.; Phillips, B.T.; Bui, D.T.; Khan, S.U.; Dagum, A.B. An In Vivo Analysis of the Effect and Duration of Treatment with Botulinum Toxin Type A Using Digital Image Speckle Correlation. Skin Res. Technol. 2013, 19, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.; Klein, G.; Xu, Y.; Rafailovich, M.; Gilbert Fernandez, J.J.; Khan, S.U.; Bui, D.T.; Dagum, A.B. Digital Image Speckle Correlation to Optimize Botulinum Toxin Type A Injection: A Prospective, Randomized, Crossover Trial. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 143, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadon, J.R.; Yang, F.; Burgert, R.; Mohammad, S.; Gammel, T.; Sepe, M.; Rafailovich, M.; Mikell, C.B.; Polak, P.; Mofakham, S. Real-Time Emotion Detection by Quantitative Facial Motion Analysis. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0282730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, D. Influence of Deformable Substrates on Macroscopic and Microscopic Phenomenon of Tissue. Ph.D. Thesis, State University of New York at Stony Brook, New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, P.J.; Bradley, M.M.; Cuthbert, B.N. International Affective Picture System (IAPS) [Database record]. APA PsycTests 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, C.; Wang, J.; Opristescu, D.; Volk, W. Implementation and Evaluation of Optical Flow Methods for Two-Dimensional Deformation Measurement in Comparison to Digital Image Correlation. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2018, 107, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecompte, D.; Smits, A.; Bossuyt, S.; Sol, H.; Vantomme, J.; Van Hemelrijck, D.; Habraken, A.M. Quality Assessment of Speckle Patterns for Digital Image Correlation. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2006, 44, 1132–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Meurer, M.; Zhang, X.-M.; Bergs, T.; Ding, H. Understanding Kinematics of the Orthogonal Cutting Using Digital Image Correlation—Measurement and Analysis. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2021, 144, 031008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleet, D.; Weiss, Y. Optical Flow Estimation. In Handbook of Mathematical Models in Computer Vision; Paragios, N., Chen, Y., Faugeras, O., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2006; pp. 237–257. ISBN 978-0-387-28831-4. [Google Scholar]
- House, J.W.; Brackmann, D.E. Facial Nerve Grading System. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 1985, 93, 146–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, A.; Polechoński, J.; Polechoński, P.; Cholewa, J. Ruler Drop Method in Virtual Reality as an Accurate and Reliable Tool for Evaluation of Reaction Time of Mixed Martial Artists. Sustainability 2023, 15, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, B.T.; Cruickshank, A.G.; Flavell, J.C.; Bennett, S.J.; Buckley, J.G.; Harris, J.M.; Scally, A.J. Faster Visual Reaction Times in Elite Athletes Are Not Linked to Better Gaze Stability. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Bansal, R.; Kumar, A.; Singh, K. A Comparative Study of Visual and Auditory Reaction Times on the Basis of Gender and Physical Activity Levels of Medical First Year Students. Int. J. Appl. Basic Med. Res. 2015, 5, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrough, J.W.; Wan, L.-B.; Iacoviello, B.; Collins, K.A.; Solon, C.; Glicksberg, B.; Perez, A.M.; Mathew, S.J.; Charney, D.S.; Iosifescu, D.V.; et al. Neurocognitive Effects of Ketamine in Treatment-Resistant Major Depression: Association with Antidepressant Response. Psychopharmacology 2013, 231, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Cho, S.; Lee, J.-H. The Effects of Long-Term Ketamine Treatment on Cognitive Function in Complex Regional Pain Syndrome: A Preliminary Study. Pain Med. 2016, 17, 1447–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strous, J.F.M.; Weeland, C.J.; van der Draai, F.A.; Daams, J.G.; Denys, D.; Lok, A.; Schoevers, R.A.; Figee, M. Brain Changes Associated with Long-Term Ketamine Abuse, A Systematic Review. Front. Neuroanat. 2022, 16, 795231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coull, J.T.; Morgan, H.; Cambridge, V.C.; Moore, J.W.; Giorlando, F.; Adapa, R.; Corlett, P.R.; Fletcher, P.C. Ketamine Perturbs Perception of the Flow of Time in Healthy Volunteers. Psychopharmacology 2011, 218, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tully, J.L.; Dahlén, A.D.; Haggarty, C.J.; Schiöth, H.B.; Brooks, S. Ketamine Treatment for Refractory Anxiety: A Systematic Review. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 88, 4412–4426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edinoff, A.N.; Sall, S.; Koontz, C.B.; Williams, A.K.; Drumgo, D.; Mouhaffel, A.; Cornett, E.M.; Murnane, K.S.; Kaye, A.D. Ketamine Evolving Clinical Roles and Potential Effects with Cognitive, Motor and Driving Ability. Neurol. Int. 2023, 15, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daini, R.; Comparetti, C.M.; Ricciardelli, P. Behavioral Dissociation between Emotional and Non-Emotional Facial Expressions in Congenital Prosopagnosia. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, P.J.; Enticott, P.G.; Mayes, A.K.; Hoy, K.E.; Herring, S.E.; Fitzgerald, P.B. Symptom Correlates of Static and Dynamic Facial Affect Processing in Schizophrenia: Evidence of a Double Dissociation? Schizophr. Bull. 2010, 36, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiñaga, A.R.; Hernandez, D.E.; Quezada, A.; Calvillo Téllez, A. Emotion Recognition by Correlating Facial Expressions and EEG Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowski, G.M.; Ghosh-Hajra, S.; Fickling, S.D.; Liu, C.C.; Song, X.; Robinovitch, S.; Doesburg, S.M.; D’Arcy, R.C.N. Brain Vital Signs: Expanding from the Auditory to Visual Modality. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffaryazdi, N.; Wasim, S.T.; Dileep, K.; Nia, A.F.; Nanayakkara, S.; Broadbent, E.; Billinghurst, M. Using Facial Micro-Expressions in Combination with EEG and Physiological Signals for Emotion Recognition. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 864047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddharth, S.; Jung, T.-P.; Sejnowski, T.J. Impact of Affective Multimedia Content on the Electroencephalogram and Facial Expressions. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, M.L.; Attwood, A.S.; Penton-Voak, I.S.; Munafò, M.R. The Role of State and Trait Anxiety in the Processing of Facial Expressions of Emotion. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2022, 9, 210056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, K.-S.; Lee, W.H.; Kim, S.; Shin, D.-W.; Shin, Y.-C.; Lim, S.-W. Impaired Facial Expression Recognition in Patients with Social Anxiety Disorder: A Case-Control Study. Cognit. Neuropsychiatry 2018, 23, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Sequence | Topic | IAPS ID | Valence (std) | Arousal (std) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Treatment | 1 | Kittens | 1463 | 7.81 (1.96) | 5.11 (2.17) |
| 2 | Children | 2347 | 8.35 (0.98) | 5.88 (2.53) | |
| 3 | Bride | 2209 | 7.95 (1.46) | 5.91 (2.40) | |
| 4 | Fireworks | 5910 | 8.16 (1.15) | 5.80 (2.75) | |
| 5 | Sailing | 8080 | 7.73 (1.43) | 6.25 (2.34) | |
| After Treatment | 1 | Puppies | 1710 | 8.59 (0.99) | 5.31 (2.54) |
| 2 | Baby | 2045 | 8.17 (1.21) | 6.02 (2.29) | |
| 3 | Wedding | 4626 | 7.80 (1.76) | 6.06 (2.51) | |
| 4 | Castle | 7502 | 8.15 (1.25) | 6.07 (2.58) | |
| 5 | Gymnast | 8470 | 7.94 (1.31) | 5.98 (2.20) |
| 1st Visit | 2nd Visit | 3rd Visit | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Self-reporting scores prior to ketamine administration | ||||
| PHQ-9: Patient Health Questionaire | 8 | 6 | 8 | |
| QIDS-SR: Quick Inventory of Depressive Symptomatology-Self-Report | 6 | 5 | 6 | |
| BDI: Beck Depression Inventory | 12 | 10 | 15 | |
| BAI: Beck Anxiety Inventory | 19 | 21 | 26 | |
| GAD: Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD-7) | 5 | 7 | 6 | |
| PCL-5: Posttraumatic Stress Disorder | 29 | 30 | 31 | |
| Number of images for which the patient dissociated | ||||
| Before Treatment | 2 | 0 | 1 | |
| After Treatment | 2 | 1 | 2 | |
| Visual reaction time(milliseconds): Mean (std) | ||||
| Before Treatment | 534 (118) | 485 (86) | 439 (77) | |
| After Treatment | 564 (161) | 573 (74) | 512 (42) | |
| Average Intensity of muscular motion in response to the stimulus | ||||
| Before Treatment | 9.20 | 8.05 | 6.60 | |
| After Treatment | 6.74 | 9.02 | 7.34 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, S.; Polak, P.; Fiore, S.; Passman, J.N.; Davis, R.; Manu, L.M.; Rafailovich, M. Digital Image Speckle Correlation (DISC): Facial Muscle Tracking for Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1574. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131574
Fu S, Polak P, Fiore S, Passman JN, Davis R, Manu LM, Rafailovich M. Digital Image Speckle Correlation (DISC): Facial Muscle Tracking for Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(13):1574. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131574
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Shi, Pawel Polak, Susan Fiore, Justin N. Passman, Raphael Davis, Lucian M. Manu, and Miriam Rafailovich. 2025. "Digital Image Speckle Correlation (DISC): Facial Muscle Tracking for Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders" Diagnostics 15, no. 13: 1574. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131574
APA StyleFu, S., Polak, P., Fiore, S., Passman, J. N., Davis, R., Manu, L. M., & Rafailovich, M. (2025). Digital Image Speckle Correlation (DISC): Facial Muscle Tracking for Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders. Diagnostics, 15(13), 1574. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15131574







