Can We Determine Osteoarthritis Severity Based on Systemic Immuno-Inflammatory Index?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Selection of Study Population
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OA | Osteoarthritis |
| SII | Systemic Immune-Inflammatory Index |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| MMPs | Matrix Metalloproteinases |
| PGE2 | Prostaglandin-E2 |
| NO | Nitric Oxide |
| CRP | C-Reactive Protein |
| ESR | Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| CBC | Complete Blood Count |
| WBC | White Blood Cell Count |
| NLR | Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio |
| PLR | Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio |
| MLR | Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte Ratio |
| PDW | Platelet Distribution Width |
| RDW | Red Cell Distribution Width |
| RPR | Rapid Plasma Reagin |
| MPV | Mean Platelet Volume |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid |
| Hgb | Hemoglobin |
| SLE | Systemic Lupus Erythematosus |
| RA | Rheumatoid Arthritis |
| BMD | Bone Mineral Density |
| AS | Ankylosing Spondylitis |
| POP | Postoperative Pneumonia |
References
- Arden, N.; Nevitt, M.C. Osteoarthritis: Epidemiology. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2006, 20, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, J.N.; Arant, K.R.; Loeser, R.F. Diagnosis and Treatment of Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis. JAMA 2021, 325, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Clanche, S.; Bonnefont-Rousselot, D.; Sari-Ali, E.; Rannou, F.; Borderie, D. Inter-relations between osteoarthritis and metabolic syndrome: A common link? Biochimie 2016, 121, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldring, M.B.; Goldring, S.R. Osteoarthritis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2007, 213, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldring, M.B.; Otero, M. Inflammation in osteoarthritis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2011, 23, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellam, J.; Berenbaum, F. The role of synovitis in pathophysiology and clinical symptoms of osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2010, 6, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolove, J.; Lepus, C.M. Role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: Latest findings and interpretations. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2013, 5, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berenbaum, F. Osteoarthritis as an inflammatory disease (osteoarthritis is not osteoarthrosis!). Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2013, 21, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, M.J.; Veale, D.J.; FitzGerald, O.; van den Berg, W.B.; Bresnihan, B. Synovial tissue inflammation in early and late osteoarthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2005, 64, 1263–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, M.; Martel-Pelletier, J.; Lajeunesse, D.; Pelletier, J.P.; Fahmi, H. Role of proinflammatory cytokines in the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2011, 7, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livshits, G.; Zhai, G.; Hart, D.J.; Kato, B.S.; Wang, H.; Williams, F.M.K.; Spector, T.D. Interleukin-6 is a significant predictor of radiographic knee osteoarthritis: The Chingford study. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 2037–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spector, T.D.; Hart, D.J.; Nandra, D.; Doyle, D.V.; Mackillop, N.; Gallimore, J.R.; Pepys, M.B. Low-level increases in serum C-reactive protein are present in early osteoarthritis of the knee and predict progressive disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1997, 40, 723–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Ma, N.; Tang, Q.; Wei, T.; Yang, M.; Fu, H.; Hu, Z.; Liang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhong, R. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet to lymphocyte ratio (PLR) were useful markers in assessment of inflammatory response and disease activity in SLE patients. Mod. Rheumatol. 2016, 26, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, H.; Qin, B.; Hu, Z.; Ma, N.; Yang, M.; Wei, T.; Tang, Q. Neutrophil- and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratios are Correlated with Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clin. Lab. 2015, 61, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, C.D.; Parajuli, A.; Gale, H.J.; Bulteel, N.S.; Schuetz, P.; de Jager, C.P.C.; Loonen, A.J.; Merekoulias, G.I.; Baillie, J.K. The utility of peripheral blood leucocyte ratios as biomarkers in infectious diseases: A systematic review and metaanalysis. J. Infect. 2019, 78, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Wang, W.; Tang, W.; Lv, Q.; Ding, W. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), and systemic immune inflammation index (SII) to predict postoperative pneumonia in elderly hip fracture patients. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2023, 18, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilge, M.; Akilli, I.K.; Karaayvaz, E.B.; Yesilova, A.; Yasar, K.K. Comparison of systemic immune-inflammation index (SII), early warning score (ANDC) and prognostic nutritional index (PNI) in hospitalized patients with malignancy, and their influence on mortality from COVID-19. Infect. Agents Cancer 2021, 16, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, X.; Long, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.L.; Wen, W.; Guo, L.; Xia, W.; Zhang, W.W.; Lin, H.X. Prognostic Value of Preoperative Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index in Breast Cancer: A Propensity Score-Matching Study. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.L.; Wu, C.H.; Hsu, P.F.; Chen, S.C.; Huang, S.S.; Chan, W.L.; Lin, S.J.; Chou, C.Y.; Chen, J.W.; Pan, J.P.; et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) predicted clinical outcome in patients with coronary artery disease. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 50, e13230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Wang, C.; Luo, Y.; Ye, X.; Han, X.; Feng, Y.; Zhong, P.; Wu, D. Systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) but not platelet-albumin-bilirubin (PALBI) grade is associated with severity of acute ischemic stroke (AIS). Int. J. Neurosci. 2021, 131, 1203–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanacan, A.; Uyanik, E.; Unal, C.; Beksac, M.S. A cut-off value for systemic immune-inflammation index in the prediction of adverse neonatal outcomes in preterm premature rupture of the membranes. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2020, 46, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellgren, J.H.; Lawrence, J.S. Radiological Assessment of Osteo-Arthrosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1957, 16, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, R.C.; Felson, D.T.; Helmick, C.G.; Arnold, L.M.; Choi, H.; Deyo, R.A.; Gabriel, S.; Hirsch, R.; Hochberg, M.C.; Hunder, G.G.; et al. Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and other rheumatic conditions in the United States. Part II. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glyn-Jones, S.; Palmer, A.J.R.; Agricola, R.; Price, A.J.; Vincent, T.L.; Weinans, H.; Carr, A.J. Osteoarthritis. Lancet 2015, 386, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blagojevic, M.; Jinks, C.; Jeffery, A.; Jordan, K.P. Risk factors for onset of osteoarthritis of the knee in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2010, 18, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koonce, R.C.; Bravman, J.T. Obesity and osteoarthritis: More than just wear and tear. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2013, 21, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spector, T.D.; Cicuttini, F.; Baker, J.; Loughlin, J.; Hart, D. Genetic influences on osteoarthritis in women: A twin study. BMJ 1996, 312, 940–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felson, D.T.; Niu, J.; Gross, K.D.; Englund, M.; Sharma, L.; Cooke, T.D.V.; Guermazi, A.; Roemer, F.W.; Segal, N.; Goggins, J.M.; et al. Valgus malalignment is a risk factor for lateral knee osteoarthritis incidence and progression: Findings from the Multicenter Osteoarthritis Study and the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelber, A.C.; Hochberg, M.C.; Mead, L.A.; Wang, N.Y.; Wigley, F.M.; Klag, M.J. Joint injury in young adults and risk for subsequent knee and hip osteoarthritis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2000, 133, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Liu, Q.; Yin, H.; Wang, K.; Diao, N.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; Guo, A. Prevalence Trends of Site-Specific Osteoarthritis From 1990 to 2019: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 1172–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.D.; Triantafillou, S.; Parker, A.; Youssef, P.P.; Coleman, M. Synovial membrane inflammation and cytokine production in patients with early osteoarthritis. J. Rheumatol. 1997, 24, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hira, S.; Tamam, C. Hematologic indices and osteoarthritis. Cukurova Med. J. 2017, 42, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasoglu, O.; Boluk, H.; Onat, S.S.; Tasoglu, I.; Ozgırgın, N. Is blood neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio an independent predictor of knee osteoarthritis severity? Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 35, 1579–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Yan, L.; CHai, K. Systemic immune-inflammation index is associated with disease activity in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2021, 35, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.C.; Jiang, W.; Chen, X.; Yang, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.H. Systemic immune-inflammation index independently predicts poor survival of older adults with hip fracture: A prospective cohort study. BMC Geriatr. 2021, 21, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Xia, C.; Wu, L.; Li, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, J. Systemic Immune Inflammation Index (SII), System Inflammation Response Index (SIRI) and Risk of All-Cause Mortality and Cardiovascular Mortality: A 20-Year Follow-Up Cohort Study of 42,875 US Adults. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Xie, X.; Xue, J.; Xie, H.; Zhang, Y. Association of the systemic immune-inflammation index with all-cause mortality in patients with arteriosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 952953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Yao, C.; Xia, H.; Li, C. Postoperative Systemic Immune Inflammation Index (SII): A Superior Prognostic Factor of Endometrial Cancer. Front. Surg. 2021, 22, 704235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, B.W.; Yang, Y.F.; Yang, C.C.; Yan, L.J.; Ding, Z.N.; Liu, H.; Xue, J.S.; Dong, Z.R.; Chen, Z.Q.; Hong, J.G.; et al. Systemic Immune–Inflammation Index Predicts Prognosis of Cancer Immunotherapy: Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis. Immunotherapy 2022, 14, 1481–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldovan, F.; Ivanescu, A.D.; Fodor, P.; Moldovan, L.; Bataga, T. Correlation between Inflammatory Systemic Biomarkers and Surgical Trauma in Elderly Patients with Hip Fractures. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 6, 5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tian, S.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, R.; Yin, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Hou, Z.; Zhang, Y. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and fracture severity in young and middle-aged patients with tibial plateau fractures. Int. Orthop. 2020, 44, 2769–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
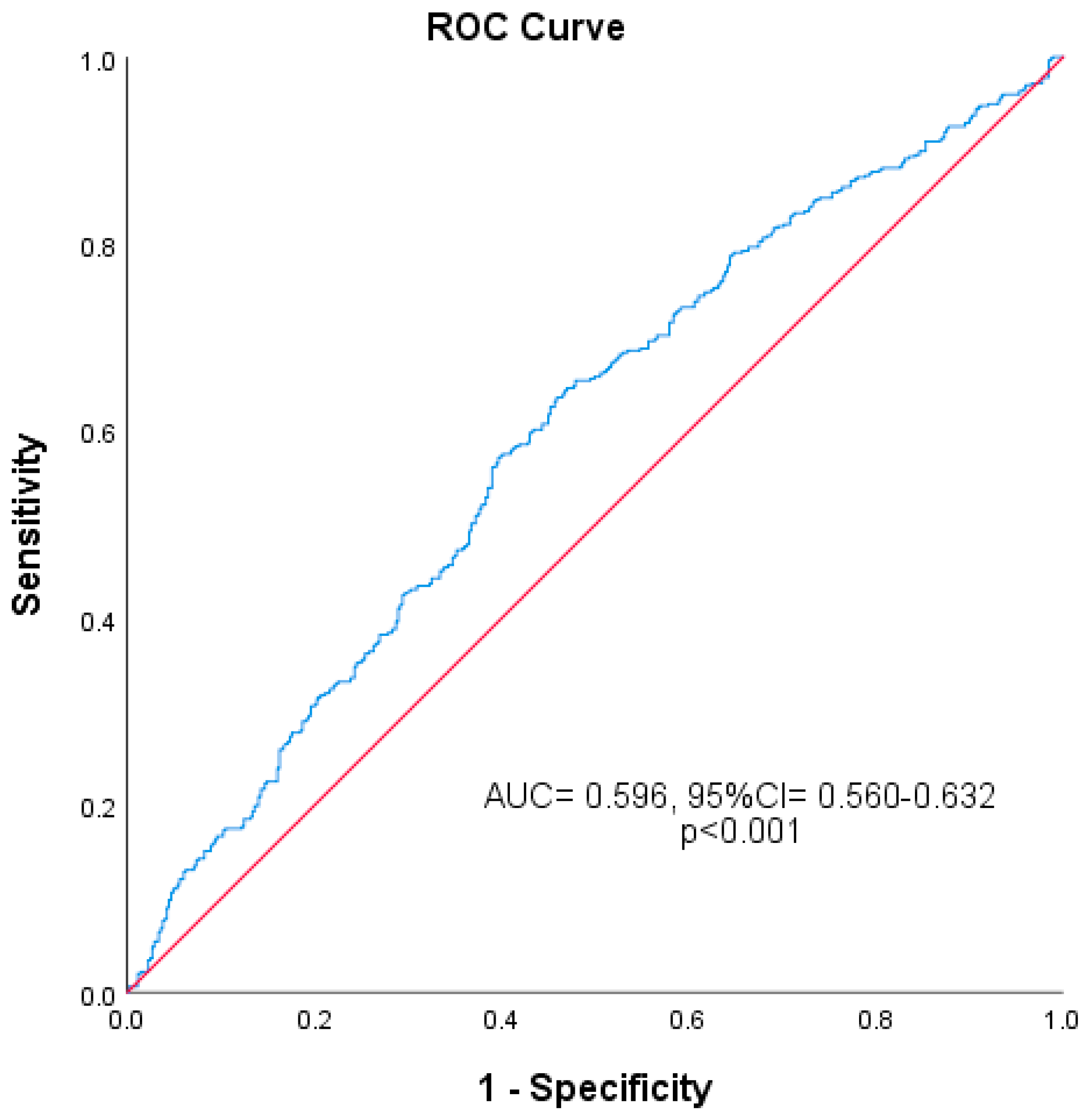
| Group I n = 449 (%47.5) | Group II n = 497 (%52.5) | Total Study Population n = 946 (%100) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 54.00 (47.00–62.00) | 66.00 (60.00–71.00) | 61.00 (53.00–68.00) | <0.001 |
| Gender | ||||
| Female | 302 (%67.3) | 398 (%80.1) | 700 (%74.0) | <0.001 |
| Male | 147 (%32.7) | 99 (%19.9) | 246 (%26.0) | <0.001 |
| WBC (×109/L) | 7.49 (6.31–8.82) | 7.43 (6.28–8.71) | 7.46 (6.29–8.73) | 0.65 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 13.70 (12.90–15.00) | 13.50 (12.60–14.60) | 13.70 (12.70–14.70) | 0.002 |
| Lymphocyte (×109/L) | 2.36 (1.91–2.87) | 2.07 (1.69–2.58) | 2.20 (1.78–2.73) | <0.001 |
| Neutrophil (×109/L) | 4.18 (3.35–5.25) | 4.50 (3.56–5.68) | 4.39 (3.46–5.50) | 0.03 |
| Platelet (×109/L) | 270.00 (234.00–314.00) | 279.00 (233.50–319.50) | 273.00 (234.00–318.00) | 0.295 |
| SII | 474.54 (359.29–677.25) | 578.14 (414.58–799.71) | 536.72 (381.56–745.75) | <0.001 |
| SII | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| <627.9 | >627.9 | <0.001 | |
| Group I (Mild–Moderate OA) | 317 (%52.6) | 132 (%38.5) | |
| Group II (Severe OA) | 286 (%47.4) | 211 (%61.5) | |
| Total | 603 (%100) | 343 (%100) | 946 |
| Univariate | Multivariate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | OR (%95 CI) | p Value | OR (%95 CI) | p Value |
| Age | 1.132 (1.112–1.153) | <0.001 | 1.131 (1.111–1.151) | <0.001 |
| Hemoglobin | 0.852 (0.786–0.924) | <0.001 | 0.920 (0.833–1.015) | 0.096 |
| SII | 1.772 (1.353–2.321) | <0.001 | 1.623 (1.182–2.229) | 0.003 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yilmaz, B.K.; Altin, R.; Sari, A. Can We Determine Osteoarthritis Severity Based on Systemic Immuno-Inflammatory Index? Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15121556
Yilmaz BK, Altin R, Sari A. Can We Determine Osteoarthritis Severity Based on Systemic Immuno-Inflammatory Index? Diagnostics. 2025; 15(12):1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15121556
Chicago/Turabian StyleYilmaz, Bilge Kagan, Recep Altin, and Alper Sari. 2025. "Can We Determine Osteoarthritis Severity Based on Systemic Immuno-Inflammatory Index?" Diagnostics 15, no. 12: 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15121556
APA StyleYilmaz, B. K., Altin, R., & Sari, A. (2025). Can We Determine Osteoarthritis Severity Based on Systemic Immuno-Inflammatory Index? Diagnostics, 15(12), 1556. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15121556






