Atypical Lipomatous Tumours vs. Lipomas: A Multimodal Diagnostic Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Data Collection and Prediction Models
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Univariate Analysis of Relevant Parameters Distinguishing Lipomas and ALTs
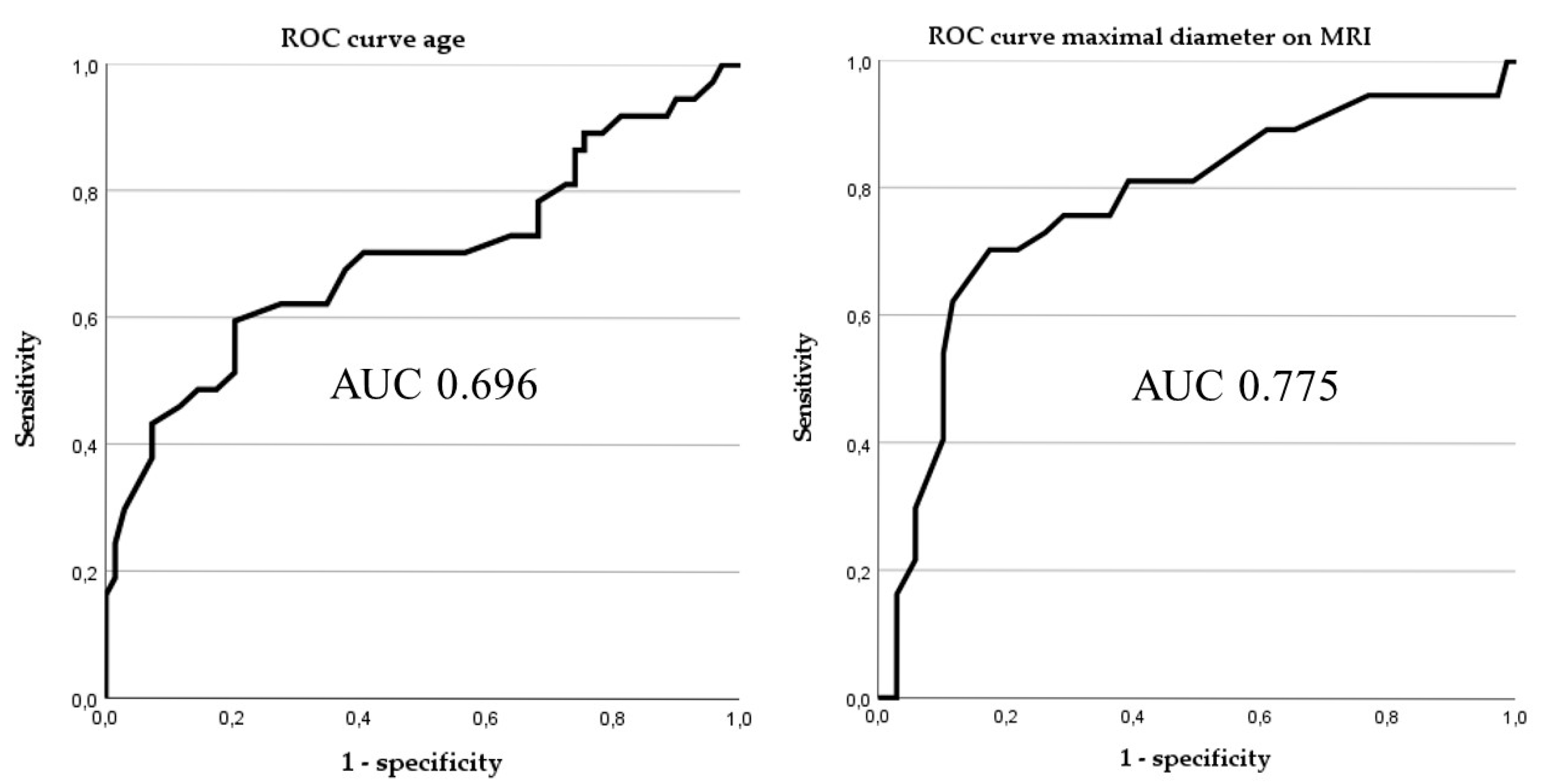
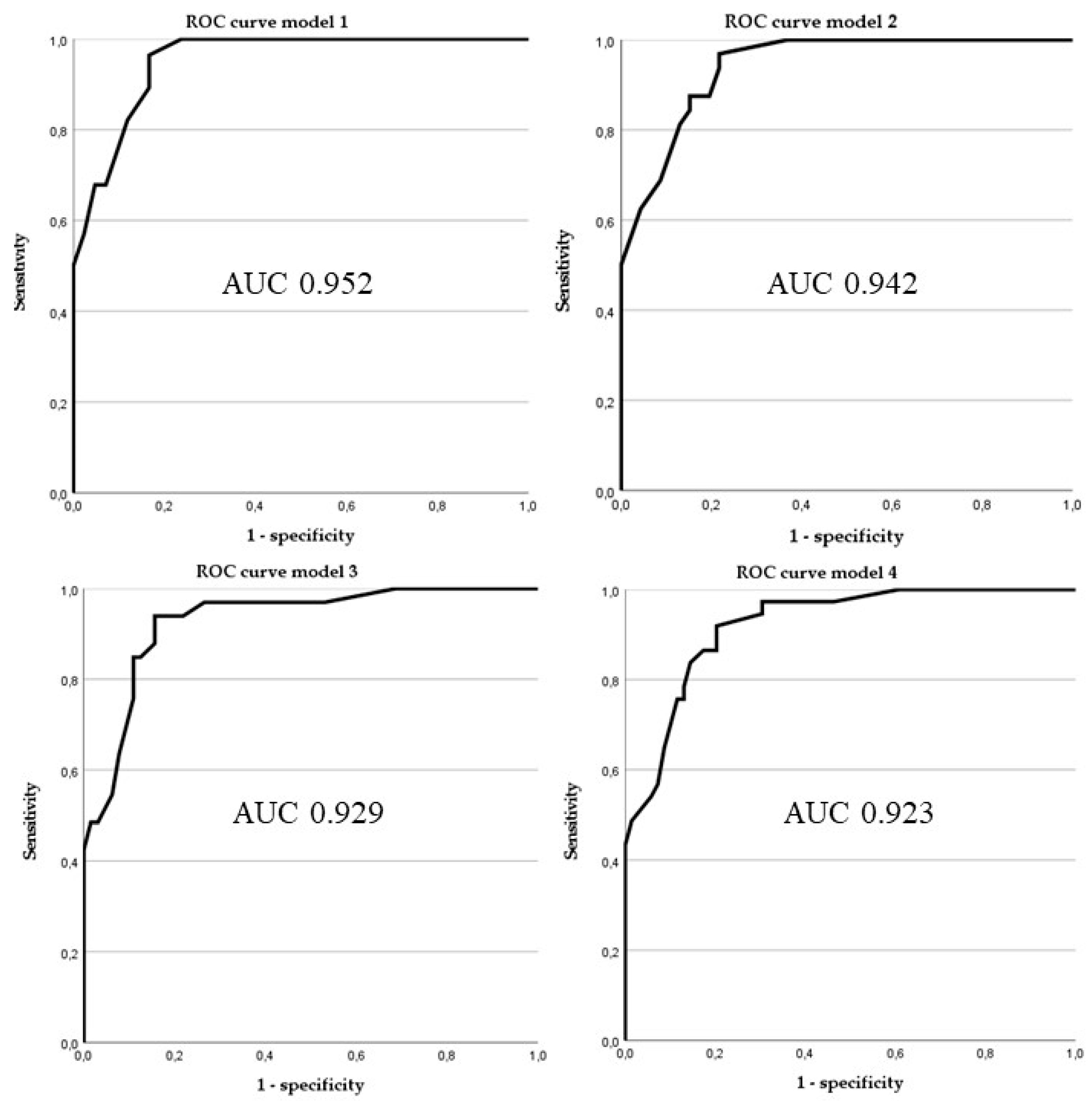
3.3. Predictive Accuracy of Different Prediction Tools
3.4. Assessment of Remaining 82 “Lipomas” Without Molecular Pathology Testing
3.5. Risk Calculator
4. Discussion
Strength and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| ALT | Atypical lipomatous tumour |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| CDK4 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 |
| CEUS | Contrast Enhanced Ultra-Sound |
| CISH | Chromogenic in situ hybridization |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| FISH | Fluorescence in situ hybridization |
| IQR | Inter quartile range |
| MDM2 | Murine Double Minute 2 |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| NPV | Negative Predictive Value |
| PPV | Positive Predictive Value |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristics |
| SISH | Silver-enhanced in situ hybridization |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Le Nail, L.R.; Crenn, V.; Rosset, P.; Ropars, M. Management of adipose tumors in the limbs. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2022, 108, 103162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gronchi, A.; Miah, A.B.; Dei Tos, A.P.; Abecassis, N.; Bajpai, J.; Bauer, S.; Biagini, R.; Bielack, S.; Blay, J.Y.; Bolle, S.; et al. Soft tissue and visceral sarcomas: ESMO-EURACAN-GENTURIS Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 1348–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, E.J.; Stewart, C.L.; Clay, M.R.; McCarter, M.M. Lipoma and Its Doppelganger: The Atypical Lipomatous Tumor/Well-Differentiated Liposarcoma. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 102, 637–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gitto, S.; Interlenghi, M.; Cuocolo, R.; Salvatore, C.; Giannetta, V.; Badalyan, J.; Gallazzi, E.; Spinelli, M.S.; Gallazzi, M.; Serpi, F.; et al. MRI radiomics-based machine learning for classification of deep-seated lipoma and atypical lipomatous tumor of the extremities. Radiol. Med. 2023, 128, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkaduhimi, H.; van der Linde, J.A.; Flipsen, M.; van Deurzen, D.F.P.; van den Bekerom, M.P.J. A systematic and technical guide on how to reduce a shoulder dislocation. Turk. J. Emerg. Med. 2016, 16, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clay, M.R.; Martinez, A.P.; Weiss, S.W.; Edgar, M.A. MDM2 and CDK4 Immunohistochemistry: Should It Be Used in Problematic Differentiated Lipomatous Tumors?: A New Perspective. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2016, 40, 1647–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thway, K.; Wang, J.; Swansbury, J.; Min, T.; Fisher, C. Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization for MDM2 Amplification as a Routine Ancillary Diagnostic Tool for Suspected Well-Differentiated and Dedifferentiated Liposarcomas: Experience at a Tertiary Center. Sarcoma 2015, 2015, 812089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clay, M.R.; Martinez, A.P.; Weiss, S.W.; Edgar, M.A. MDM2 Amplification in Problematic Lipomatous Tumors: Analysis of FISH Testing Criteria. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2015, 39, 1433–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Erickson-Johnson, M.; Wang, X.; Oliveira, J.L.; Nascimento, A.G.; Sim, F.H.; Wenger, D.E.; Zamolyi, R.Q.; Pannain, V.L.; Oliveira, A.M. Molecular testing for lipomatous tumors: Critical analysis and test recommendations based on the analysis of 405 extremity-based tumors. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2010, 34, 1304–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardo, L.; Abdelhafez, Y.G.; Acquafredda, F.; Schirò, S.; Wong, A.L.; Sarohia, D.; Maroldi, R.; Darrow, M.A.; Guindani, M.; Lee, S.; et al. Qualitative evaluation of MRI features of lipoma and atypical lipomatous tumor: Results from a multicenter study. Skelet. Radiol. 2020, 49, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, S.; Yokouchi, M.; Setoguchi, T.; Ishidou, Y.; Sasaki, H.; Shimada, H.; Komiya, S. Differentiation of lipoma and atypical lipomatous tumor by a scoring system: Implication of increased vascularity on pathogenesis of liposarcoma. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2015, 16, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mick, P.; Seeberger, A.; Renkawitz, T.; Lehner, B.; Hariri, M.; Fischer, C.; Doll, J. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound reveals perfusion differences between benign lipoma and semi-malignant atypical lipomatous tumors: A prospective clinical study. Ultraschall Med. 2024, 45, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farshid, G.; Otto, S.; Collis, M.; Napper, S.; Nicola, M. Silver In Situ Hybridization for the Rapid Assessment of MDM2 Amplification in Soft Tissue and Bone Tumors. Validation Based on an Audit of 192 Consecutive Cases Evaluated by Silver In Situ Hybridization and Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2023, 31, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardekian, S.K.; Solomides, C.C.; Gong, J.Z.; Peiper, S.C.; Wang, Z.X.; Bajaj, R. Comparison of Chromogenic In Situ Hybridization and Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization for the Evaluation of MDM2 Amplification in Adipocytic Tumors. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2015, 29, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Q.; Hsu, A.T.Y.W.; Goytain, A.; Ng, T.L.T.; Nielsen, T.O. A Rapid and Cost-Effective Gene Expression Assay for the Diagnosis of Well-Differentiated and Dedifferentiated Liposarcomas. J. Mol. Diagn. 2021, 23, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Mutiso, F.; Tian, L. Joint hypothesis testing of the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve and the Youden index. Pharm. Stat. 2021, 20, 657–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballhause, T.M.; Korthaus, A.; Jahnke, M.; Frosch, K.H.; Yamamura, J.; Dust, T.; Schlickewei, C.W.; Priemel, M.H. Lipomatous Tumors: A Comparison of MRI-Reported Diagnosis with Histological Diagnosis. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisson, M.; Kashima, T.; Delaney, D.; Tirabosco, R.; Clarke, A.; Cro, S.; Flanagan, A.M.; O’Donnell, P. MRI characteristics of lipoma and atypical lipomatous tumor/well-differentiated liposarcoma: Retrospective comparison with histology and MDM2 gene amplification. Skelet. Radiol. 2013, 42, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Ko, A.T.; Huang, J.H.; Lee, B.C.; Yang, R.S.; Liang, C.W.; Tai, H.C.; Cheng, N.C. Developing a clinical scoring system to differentiate deep-seated atypical lipomatous tumor from lipoma of soft tissue. Asian J. Surg. 2019, 42, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cay, N.; Mendi, B.A.R.; Batur, H.; Erdogan, F. Discrimination of lipoma from atypical lipomatous tumor/well-differentiated liposarcoma using magnetic resonance imaging radiomics combined with machine learning. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2022, 40, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donners, R.; Krieg, A.H.; Baumhoer, D.; Boll, D.T.; Harder, D. Quantitative signal intensity ratios to distinguish between subfascial lipoma and atypical lipomatous tumor/well-differentiated liposarcoma using short-tau inversion recovery (STIR) MRI. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2020, 101, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhnen, C.; Mentzel, T.; Lehnhardt, M.; Homann, H.H.; Sciot, R.; Debiec-Rychter, M. Lipoma and atypical lipomatous tumor within the same neoplasia: Evidence for a continuous transition. Pathologe 2010, 31, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Lipoma n = 69 | Atypical Lipomatous Tumour (ALT) n = 37 | p-Values | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender, male | 45 | 22 | 0.56 |
| Gender, female | 24 | 15 | |
| Age, in years | 60 (48–67) | 69 (56–78) | <0.01 |
| History of increasing size of lesion | 0.15 | ||
| - yes | 47 | 22 | |
| - no | 13 | 2 | |
| Time between first symptoms and presentation, in months | 24 (6–72) | 11 (6–33) | 0.19 |
| Location | <0.01 | ||
| - upper limb | 29 | 2 | |
| - lower limb | 17 | 30 | |
| - pelvis/trunk | 23 | 5 | |
| Location in relation to fascia | <0.01 | ||
| - superficial | 25 | 2 | |
| - deep | 44 | 35 | |
| Location within limb | 0.03 | ||
| - proximal | 34 | 30 | |
| - distal | 12 | 2 | |
| Homogeneity on T1 and STIR on MRI | <0.01 | ||
| - yes | 45 | 11 | |
| - no | 24 | 26 | |
| Any contrast enhancement on MRI | <0.01 | ||
| - yes | 32 | 26 | |
| - no | 32 | 7 | |
| Largest diameter on MRI, in cm | 9 (7–14) | 18 (12–22) | <0.01 |
| Largest diameter of pathological specimen, in cm | 10 (7–12) | 15 (10–21) | <0.01 |
| Histologically proven atypia | <0.01 | ||
| - yes | 2 | 16 | |
| - no | 67 | 21 | |
| Result of MDM2 amplification | <0.01 | ||
| - positive | 0 | 30 | |
| - negative | 69 | 1 |
| Model | Sensitivity | Specificity | Positive Predictive Value | Negative Predictive Value | Missed Atypical Lipomatous Tumours * | False Positive Lipomas * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1a | 0.964 | 0.833 | 0.794 | 0.972 | 1/28 | 7/42 |
| Model 1b | 1 | 0.762 | 0.737 | 1 | 0/28 | 10/42 |
| Model 2 | 0.969 | 0.783 | 0.756 | 0.973 | 1/32 | 10/46 |
| Model 3 | 0.939 | 0.844 | 0.756 | 0.964 | 2/33 | 10/64 |
| Model 4 | 0.919 | 0.797 | 0.708 | 0.948 | 3/37 | 14/69 |
| Histological atypia | 0.432 | 0.971 | 0.889 | 0.761 | 21/37 | 2/69 |
| MDM2 amplification | 0.970 | 1 | 1 | 0.986 | 1/33 | 0/69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weschenfelder, W.; Koeglmeier, K.L.; Weschenfelder, F.; Spiegel, C.; Malouhi, A.; Gassler, N.; Hofmann, G.O. Atypical Lipomatous Tumours vs. Lipomas: A Multimodal Diagnostic Approach. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1538. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15121538
Weschenfelder W, Koeglmeier KL, Weschenfelder F, Spiegel C, Malouhi A, Gassler N, Hofmann GO. Atypical Lipomatous Tumours vs. Lipomas: A Multimodal Diagnostic Approach. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(12):1538. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15121538
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeschenfelder, Wolfram, Katharina Lucia Koeglmeier, Friederike Weschenfelder, Christian Spiegel, Amer Malouhi, Nikolaus Gassler, and Gunther Olaf Hofmann. 2025. "Atypical Lipomatous Tumours vs. Lipomas: A Multimodal Diagnostic Approach" Diagnostics 15, no. 12: 1538. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15121538
APA StyleWeschenfelder, W., Koeglmeier, K. L., Weschenfelder, F., Spiegel, C., Malouhi, A., Gassler, N., & Hofmann, G. O. (2025). Atypical Lipomatous Tumours vs. Lipomas: A Multimodal Diagnostic Approach. Diagnostics, 15(12), 1538. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15121538







