ViSwNeXtNet Deep Patch-Wise Ensemble of Vision Transformers and ConvNeXt for Robust Binary Histopathology Classification
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Literature Review
1.2. Novelties and Contributions
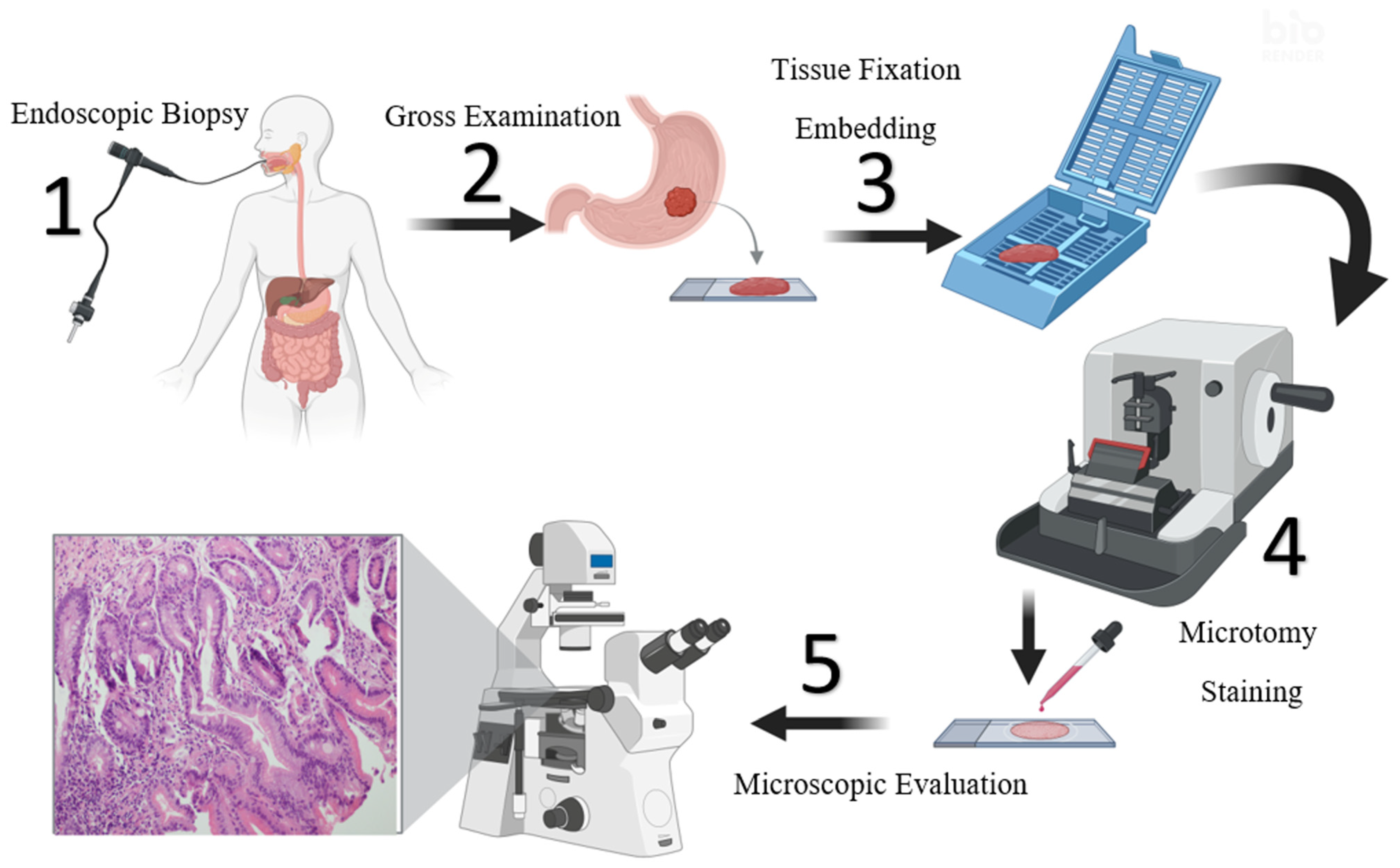
2. Materials
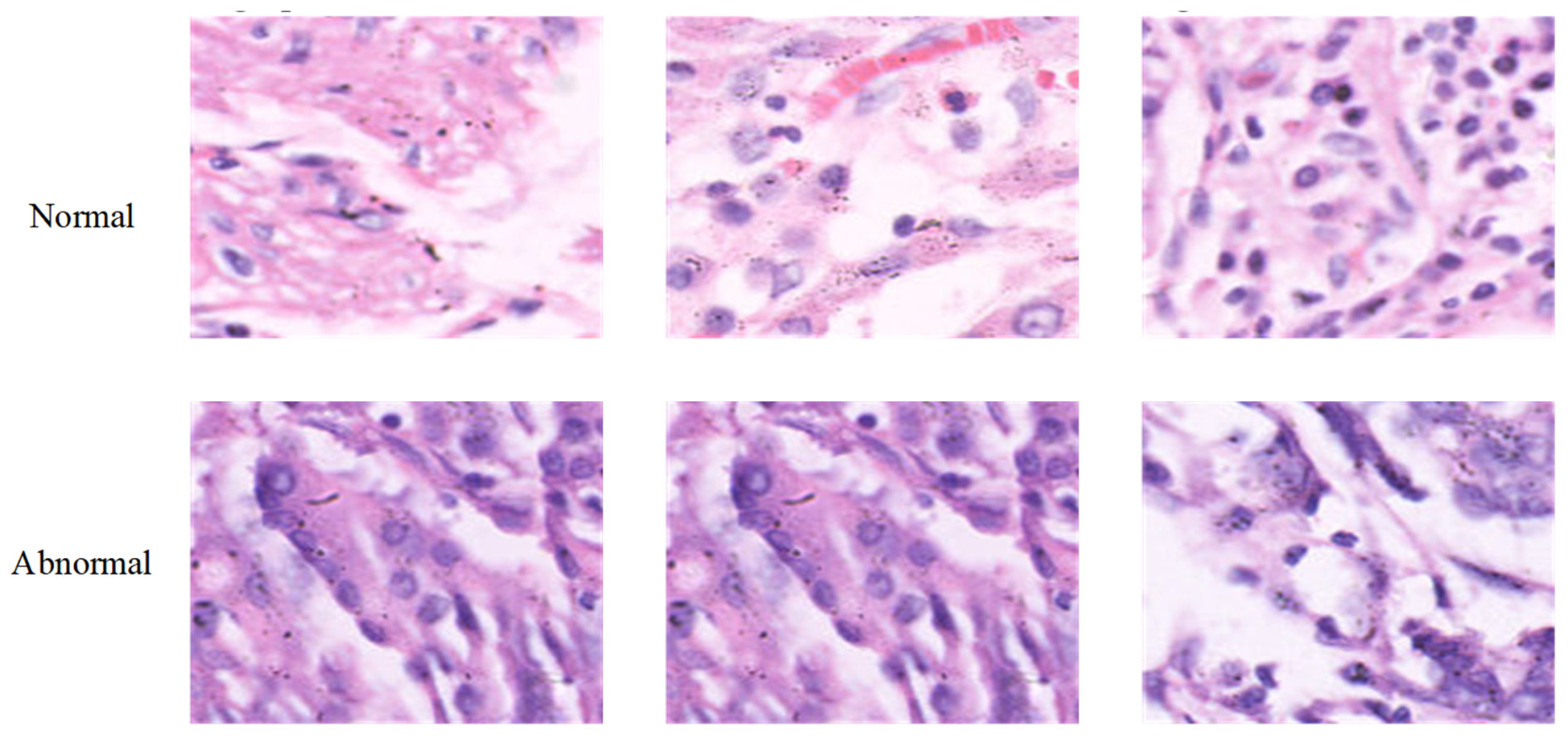
2.1. Collected Dataset
2.2. GasHisSDB Dataset
3. Our Proposals
3.1. ConvNeXt-Tiny
3.2. Swin-Tiny
3.3. ViT Base
4. Experimental Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Drnovsek, J.; Homan, M.; Zidar, N.; Smid, L.M. Pathogenesis and potential reversibility of intestinal metaplasia—A milestone in gastric carcinogenesis. Radiol. Oncol. 2024, 58, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, A.R.; Goldenring, J.R. Injury, repair, inflammation and metaplasia in the stomach. J. Physiol. 2018, 596, 3861–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Yang, Y.; Fang, S.; Guo, S.; Xu, C.; Zhang, P.; Wei, W. Gastric cancer risk of intestinal metaplasia subtypes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2021, 12, e00402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tziatzios, G.; Ziogas, D.Ι.; Gkolfakis, P.; Papadopoulos, V.; Papaefthymiou, A.; Mathou, N.; Giannakopoulos, A.; Gerasimatos, G.; Paraskeva, K.D.; Triantafyllou, K. Endoscopic Grading and Sampling of Gastric Precancerous Lesions: A Comprehensive Literature Review. Curr. Oncol. 2024, 31, 3923–3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genta, R.M.; Turner, K.O.; Robiou, C.; Singhal, A.; Rugge, M. Incomplete intestinal metaplasia is rare in autoimmune gastritis. Dig. Dis. 2023, 41, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laohawetwanit, T.; Wanpiyarat, N.; Lerttanatum, N.; Apornvirat, S.; Kantasiripitak, C.; Atiroj, N.; Pisutpunya, A.; Phairintr, P.; Suttichan, K.; Poungmeechai, N. Histopathologic evaluation of gastric intestinal metaplasia in non-neoplastic biopsy specimens: Accuracy and interobserver reliability among general pathologists and pathology residents. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2024, 70, 152284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ye, T.; Rong, L.; Peng, H.; Tong, J.; Xiao, X.; Wan, X.; Guo, J. GATA4 forms a positive feedback loop with CDX2 to transactivate MUC2 in bile acids-induced gastric intestinal metaplasia. Gut Liver 2023, 18, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaaleh, S.; Alomari, M.; Rashid, M.U.; Castaneda, D.; Castro, F.J. Gastric intestinal metaplasia and gastric cancer prevention: Watchful waiting. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2024, 91, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.J.; Choi, H.S.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, S.H.; Yoon, J.H.; Keum, B.; Kim, H.J.; Chun, H.J.; Park, Y.H. Gastric cancer and intestinal metaplasia: Differential metabolic landscapes and new pathways to diagnosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiliçarslan, A.; Varli, G. Should Special Staining (AB/PAS) be Routinely Performed in Gastric Biopsies for the Detection of Intestinal Metaplasia? Int. J. Surg. Pathol. 2024, 32, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Gu, J.; Liu, S.; Xu, S.; Zhao, Q. MSFA-Net: Multi-scale feature aggregation and attention-enhanced U-Net for microscopic hyperspectral pathology images segmentation. Opt. Laser Technol. 2025, 187, 112652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Gao, H.; Qin, T.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, P.; Xu, P. Boundary aware microscopic hyperspectral pathology image segmentation network guided by information entropy weight. Front. Oncol. 2025, 15, 1549544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, A.; Quek, S.X.X.; Zailani, N.; Wee, J.S.; Yong, D.; Ahn, B.Y.; Ho, K.Y.; Chung, H. Machine learning classification and biochemical characteristics in the real-time diagnosis of gastric adenocarcinoma using Raman spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 2469. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, S.; Liu, Z.; Qiu, Q.; Tang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Kuang, Z.; Du, X.; Xiao, S.; Liu, Y.; Luo, Y. Diagnosing and grading gastric atrophy and intestinal metaplasia using semi-supervised deep learning on pathological images: Development and validation study. Gastric Cancer 2024, 27, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwaya, M.; Hayashi, Y.; Sakai, Y.; Yoshizawa, A.; Iwaya, Y.; Uehara, T.; Kitagawa, M.; Fukayama, M.; Mori, K.; Ota, H. Artificial intelligence for evaluating the risk of gastric cancer: Reliable detection and scoring of intestinal metaplasia with deep learning algorithms. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2023, 98, 925–933.e921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braatz, J.; Rajpurkar, P.; Zhang, S.; Ng, A.Y.; Shen, J. Deep learning-based sparse whole-slide image analysis for the diagnosis of gastric intestinal metaplasia. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.01449. [Google Scholar]
- Barmpoutis, P.; Waddingham, W.; Yuan, J.; Ross, C.; Kayhanian, H.; Stathaki, T.; Alexander, D.C.; Jansen, M. A digital pathology workflow for the segmentation and classification of gastric glands: Study of gastric atrophy and intestinal metaplasia cases. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0275232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Yao, J.; Chen, B.; Song, J.; Yang, X. Localizing and identifying intestinal metaplasia based on deep learning in oesophagoscope. In Proceedings of the 2019 8th International Symposium on Next Generation Electronics (ISNE), Zhengzhou, China, 9–10 October 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Siripoppohn, V.; Pittayanon, R.; Tiankanon, K.; Faknak, N.; Sanpavat, A.; Klaikaew, N.; Vateekul, P.; Rerknimitr, R. Real-time semantic segmentation of gastric intestinal metaplasia using a deep learning approach. Clin. Endosc. 2022, 55, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Rahaman, M.M.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, W.; Sun, C.; Yao, Y. GasHisSDB: A new gastric histopathology image dataset for computer aided diagnosis of gastric cancer. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 142, 105207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Mao, H.; Wu, C.-Y.; Feichtenhofer, C.; Darrell, T.; Xie, S. A convnet for the 2020s. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 11976–11986. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Wang, K.; Zuo, W. Neighborhood component feature selection for high-dimensional data. J. Comput. 2012, 7, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncer, T.; Dogan, S.; Özyurt, F.; Belhaouari, S.B.; Bensmail, H. Novel multi center and threshold ternary pattern based method for disease detection method using voice. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 84532–84540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taşcı, B. Multilevel hybrid handcrafted feature extraction based depression recognition method using speech. J. Affect. Disord. 2024, 364, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]
- Tasci, B.; Tasci, I. Deep feature extraction based brain image classification model using preprocessed images: PDRNet. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2022, 78, 103948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taşcı, B. Attention deep feature extraction from brain MRIs in explainable mode: DGXAINet. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudavadkar, G.R.; Deng, M.; Al-Heejawi, S.M.A.; Arora, I.H.; Breggia, A.; Ahmad, B.; Christman, R.; Ryan, S.T.; Amal, S. Gastric cancer detection with ensemble learning on digital pathology: Use case of gastric cancer on gashissdb dataset. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, C.; Wang, G.; Li, X.; Rahaman, M.M.; Sun, H.; Hu, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Sun, C. GasHis-Transformer: A multi-scale visual transformer approach for gastric histopathological image detection. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 130, 108827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Zou, S.; Zhou, W.; Huang, Y.; Shao, L.; Yuan, J.; Gou, X.; Jin, W.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X. Clinically applicable histopathological diagnosis system for gastric cancer detection using deep learning. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Li, Q. A hyperspectral dataset of precancerous lesions in gastric cancer and benchmarks for pathological diagnosis. J. Biophotonics 2022, 15, e202200163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


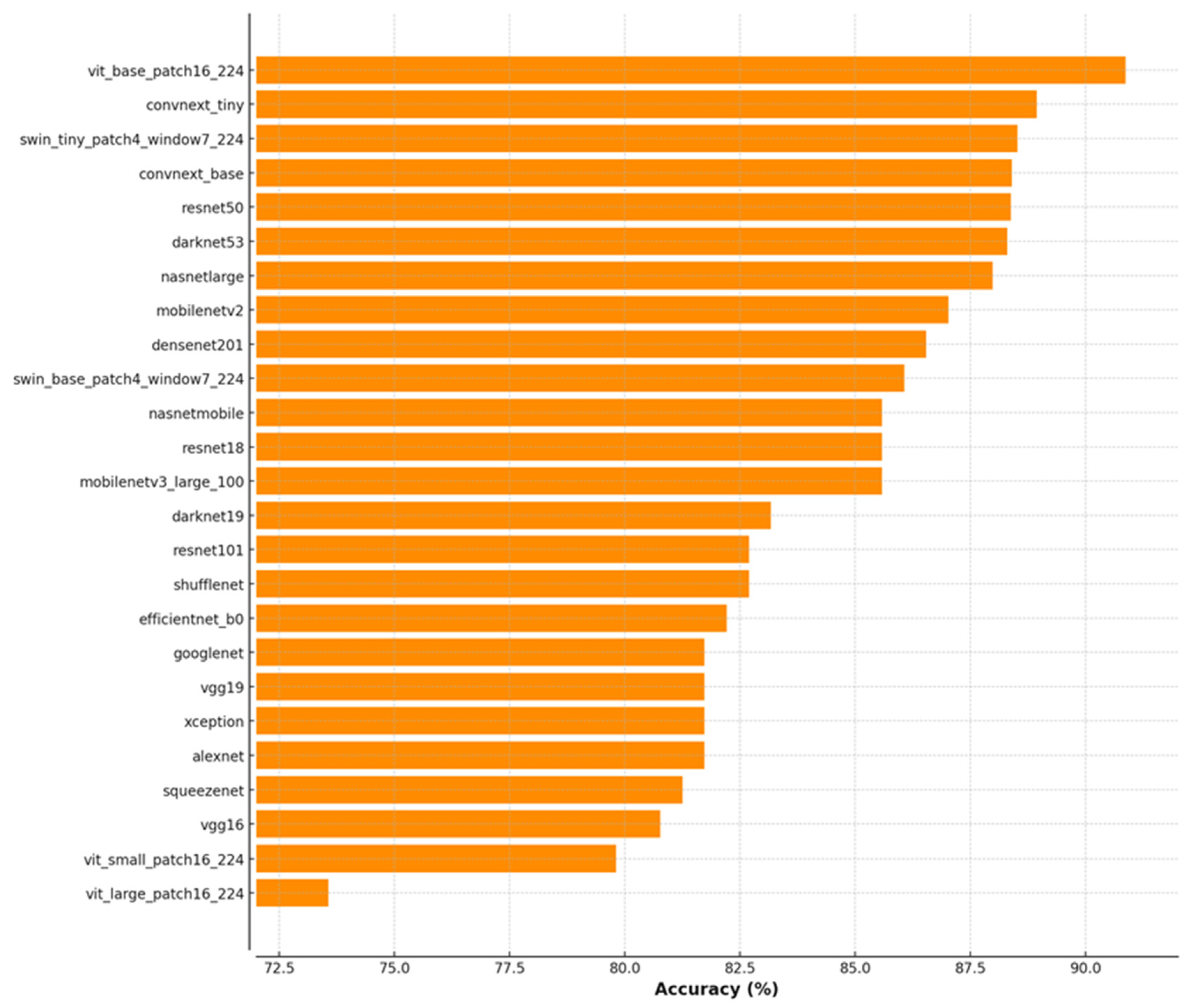



| Model | Class | Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Precision (%) | F1 Score (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Swin-Tiny | Control | 88.62 | 87.72 | 89.53 | 89.43 | 88.57 |
| IM | 89.53 | 87.72 | 87.83 | 88.68 | ||
| ConvNeXt-Tiny | Control | 91.90 | 91.55 | 92.25 | 92.26 | 91.91 |
| IM | 92.25 | 91.55 | 91.54 | 91.89 | ||
| ViT Base | Control | 93.83 | 92.71 | 94.96 | 94.89 | 93.79 |
| IM | 94.96 | 92.71 | 92.80 | 93.87 | ||
| INCA + Combined | Control | 94.41 | 94.63 | 94.19 | 94.26 | 94.44 |
| IM | 94.19 | 94.63 | 94.55 | 94.37 |
| Model | Class | Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Precision (%) | F1 Score (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Swin-Tiny | Normal | 96.1 | 96.84 | 94.97 | 96.73 | 96.79 |
| Abnormal | 94.97 | 96.84 | 95.14 | 95.05 | ||
| ConvNeXt-Tiny | Normal | 95.65 | 96.48 | 94.37 | 96.34 | 96.41 |
| Abnormal | 94.37 | 96.48 | 94.59 | 94.48 | ||
| ViT Base | Normal | 97.83 | 98.29 | 97.12 | 98.13 | 98.21 |
| Abnormal | 97.12 | 98.29 | 97.37 | 97.25 | ||
| INCA + Combined | Normal | 99.2 | 99.39 | 98.91 | 99.3 | 99.34 |
| Abnormal | 98.91 | 99.39 | 99.05 | 98.98 |
| Study | Dataset | Method | Number of Classes | Limitation | Result (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hu et al. (2022) [20] | GasHisSDB (245,196 images) | ML (RF, SVM), DL (VGG16, ResNet50, ViT) | 2 (normal/ abnormal) | Classical ML models perform poorly; ViT underperforms without enough epochs | ResNet50: 96.09%, VGG16: 96.47%, ViT: up to 94.59% |
| Mudavadkar et al. (2024) [31] | GasHisSDB | Ensemble (ResNet, VGG, EfficientNet, etc.) | 2 | DL models limited in visual extraction individually | Acc: 93–98% |
| Chen et al. (2022) [32] | Public H&E dataset (280) + 620 images | GasHis Transformer | 2 | Small dataset; generalizability across stains not fully resolved | Acc: 98.0%, Prec: 98.0%, Recall: 100.0%, F1: 96.0% |
| Song et al. (2020) [33] | 2123 WSIs + 3212 real world test slides | ResNet 50, Inception v3, DenseNet | 2 | Private dataset; specificity moderate (80.6%) | Sens: ~100%, Spec: 80.6%, Acc: 87.3% |
| Zhang et al. (2022) [34] | 924 hyperspectral scenes | Symmetrically deep network | 2 | Traditional pathology tedious; limited early GC detection | Acc: 96.59% |
| Our Study | 1037 custom dataset + GasHisSDB (160 × 160) | ViSwNeXtNet (ConvNeXt + Swin + ViT ensemble + INCA) | 2 (IM, Normal) | Collected Dataset Acc: 94.41% Sens: 94.63% F1 Score: 94.40% GasHisSDB Acc: 99.20% Sens: 99.39% F1 Score: 99.16% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Solmaz, Ö.A.; Tasci, B. ViSwNeXtNet Deep Patch-Wise Ensemble of Vision Transformers and ConvNeXt for Robust Binary Histopathology Classification. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1507. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15121507
Solmaz ÖA, Tasci B. ViSwNeXtNet Deep Patch-Wise Ensemble of Vision Transformers and ConvNeXt for Robust Binary Histopathology Classification. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(12):1507. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15121507
Chicago/Turabian StyleSolmaz, Özgen Arslan, and Burak Tasci. 2025. "ViSwNeXtNet Deep Patch-Wise Ensemble of Vision Transformers and ConvNeXt for Robust Binary Histopathology Classification" Diagnostics 15, no. 12: 1507. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15121507
APA StyleSolmaz, Ö. A., & Tasci, B. (2025). ViSwNeXtNet Deep Patch-Wise Ensemble of Vision Transformers and ConvNeXt for Robust Binary Histopathology Classification. Diagnostics, 15(12), 1507. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15121507







