Diagnostic Properties of Different Serological Methods for Syphilis Testing in Brazil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Sample Collection
2.2. Sample Size Calculation
2.3. Treponemal Tests
2.3.1. The Point-of-Care (POC) Lateral Flow Treponemal Test
2.3.2. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.3.3. The Treponema Pallidum Hemagglutination Assay (TPHA)
2.4. Nontreponemal Tests
2.4.1. The Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL) Test
2.4.2. The Rapid Plasma Reagin (RPR) Test
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peeling, R.W.; Mabey, D.; Chen, X.S.; Garcia, P.J. Syphilis. Lancet 2023, 402, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Health Sector Strategies on, Respectively, HIV, Viral Hepatitis and Sexually Transmitted Infections for the Period 2022–2030, 1st ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022; ISBN 978-92-4-005377-9.
- Ministério da Saúde Boletim Epidemiológico de Sífilis—Número Especial | Out. 2023—Ministério Da Saúde. Available online: https://www.gov.br/saude/pt-br/centrais-de-conteudo/publicacoes/boletins/epidemiologicos/especiais/2023/boletim-epidemiologico-de-sifilis-numero-especial-out.2023/view (accessed on 28 March 2024).
- Sweitzer, S.; Duncan, J.A.; Seña, A.C. Update on syphilis diagnostics. Curr Opin Infect Dis 2025, 38, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manual Técnico Para o Diagnóstico Da Sífilis—Ministério Da Saúde. Available online: https://www.gov.br/saude/pt-br/assuntos/saude-de-a-a-z/s/sifilis/publicacoes/manual-tecnico-para-o-diagnostico-da-sifilis.pdf/view (accessed on 28 March 2024).
- Papp, J.R.; Park, I.U.; Fakile, Y.; Pereira, L.; Pillay, A.; Bolan, G.A. CDC Laboratory Recommendations for Syphilis Testing, United States, 2024. MMWR Recomm. Rep. 2024, 73, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendland, E.; de Oliveira, V.; Pedrotti, L.; Souza, F.; Pereira, G.; Gerbase, A. Health Information and Monitoring of Sexually Transmitted Infections (SIM Study): A Single-Center, Parallel, Three-Arm Randomized Controlled Trial Protocol for Enhancing Adherence to Syphilis Treatment and Follow-Up. Trials 2022, 23, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Liu, L.-L.; Guo, X.-J.; Xi, Y.; Lin, L.-R.; Zhang, H.-L.; Huang, S.-J.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Characterization of the Classical Biological False-Positive Reaction in the Serological Test for Syphilis in the Modern Era. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 20, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malm, K.; Andersson, S.; Fredlund, H.; Norrgren, H.; Biague, A.; Månsson, F.; Ballard, R.; Unemo, M. Analytical Evaluation of Nine Serological Assays for Diagnosis of Syphilis. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2015, 29, 2369–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negash, M.; Wondmagegn, T.; Geremew, D. Comparison of RPR and ELISA with TPHA for the Diagnosis of Syphilis: Implication for Updating Syphilis Point-of-Care Tests in Ethiopia. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 2978419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, R.B.; Mancuso, A.C.B.; Camey, S.A.; Leotti, V.B.; Hirakata, V.N.; Azambuja, G.S.; Castro, S.M.D.J. Power and Sample Size for Health Researchers: Uma Ferramenta Para Cálculo de Tamanho Amostral e Poder Do Teste Voltado a Pesquisadores Da Área Da Saúde. CBR Clin. Biomed. Res. 2020, 40, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The Measurement of Observer Agreement for Categorical Data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2022. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- Power, M.; Fell, G.; Wright, M. Principles for High-Quality, High-Value Testing. Evid. Based Med. 2013, 18, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syphilis Testing Algorithms Using Treponemal Tests for Initial Screening—Four Laboratories, New York City, 2005–2006. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm5732a2.htm (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Gupta, C.; Mittal, K.; Kaur, R.; Kaur, J.; Sood, T.; Kaur, G.; Kaur, P. Evaluation of Chemiluminescence Immunoassay as a Screening Test for Syphilis on Blood Donor Samples. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2023, 62, 103836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakkar, B.; Philip, J.; Mallhi, R.S. Comparative Evaluation of Rapid Plasma Reagin and ELISA with Treponema Pallidum Hemagglutination Assay for the Detection of Syphilis in Blood Donors: A Single Center Experience. Hematol. Transfus. Cell Ther. 2024, 46, S43–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, Â.A.O.; Lima, A.A.; Vasconcelos, L.D.C.M.; De Almeida, R.A.; De Freitas, N.E.M.; Habib, F.L.; Oliva, T.A.; Da Silva, M.F.D.C.R.; De Siqueira, I.C.; Santos, F.L.N. Performance Assessment of Treponemal and Nontreponemal Tests for the Diagnosis of Acquired Syphilis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2024, 110, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huh, H.J.; Chung, J.-W.; Park, S.Y.; Chae, S.L. Comparison of Automated Treponemal and Nontreponemal Test Algorithms as First-Line Syphilis Screening Assays. Ann. Lab. Med. 2016, 36, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, I.; Nakamachi, Y.; Ohji, G.; Yano, Y.; Saegusa, J. Comparison of 17 Serological Treponemal and Nontreponemal Assays for Syphilis: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Pract. Lab. Med. 2022, 32, e00302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for Syphilis Infection in Nonpregnant Adolescents and Adults: US Preventive Services Task Force Reaffirmation Recommendation Statement. JAMA 2022, 328, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshed, M.G.; Singh, A.E. Recent Trends in the Serologic Diagnosis of Syphilis. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2015, 22, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, H.; Wu, S.; Li, T.; Li, H.; Deng, L.; Sun, Z. Analysis of 2 Reverse Syphilis Testing Algorithms in Diagnosis of Syphilis: A Large-Cohort Prospective Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 67, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnicker, M.J. Which Algorithm Should Be Used to Screen for Syphilis? Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 25, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, M.-L.; Lin, L.-R.; Liu, L.-L.; Zhang, H.-L.; Huang, S.-J.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Guo, X.-J.; Xi, Y.; Liu, L.; Chen, F.-Y.; et al. Analysis of 3 Algorithms for Syphilis Serodiagnosis and Implications for Clinical Management. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 58, 1116–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Choi, W.; Shin, S.; Choi, J.; Kim, H.; Chung, H.-J.; Moon, H.-W.; Hur, M.; Yun, Y.-M. Strategy for Performing Treponemal Tests in Reverse-Sequence Algorithms of Syphilis Diagnosis. Clin. Biochem. 2019, 63, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, I.U.; Tran, A.; Pereira, L.; Fakile, Y. Sensitivity and Specificity of Treponemal-Specific Tests for the Diagnosis of Syphilis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, S13–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evren, K.; Berkem, R.; Yücel, M. Evaluation of the Diagnostic Algorithms for Serodiagnosis of Syphilis. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 75, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthias, J.; Klingler, E.J.; Schillinger, J.A.; Keller, G.; Wilson, C.; Peterman, T.A. Frequency and Characteristics of Biological False-Positive Test Results for Syphilis Reported in Florida and New York City, USA, 2013 to 2017. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, e00898-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smikle, M.F.; James, O.B.; Prabhakar, P. Biological False Positive Serological Tests for Syphilis in the Jamaican Population. Sex. Transm. Infect. 1990, 66, 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augenbraun, M.; French, A.; Glesby, M.; Sanchez-Keeland, L.; Young, M.; Greenblatt, R.; Sharma, A. Hepatitis C Virus Infection and Biological False-Positive Syphilis Tests. Sex. Transm. Infect. 2010, 86, 97–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.M.; Binnicker, M.J.; Campbell, S.; Carroll, K.C.; Chapin, K.C.; Gonzalez, M.D.; Harrington, A.; Jerris, R.C.; Kehl, S.C.; Leal, S.M.; et al. Guide to Utilization of the Microbiology Laboratory for Diagnosis of Infectious Diseases: 2024 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and the American Society for Microbiology (ASM). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2024, ciae104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuddenham, S.; Katz, S.S.; Ghanem, K.G. Syphilis Laboratory Guidelines: Performance Characteristics of Nontreponemal Antibody Tests. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71 (Suppl. 1), S21–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M.A.; Horberg, M.A.; Agwu, A.L.; Colasanti, J.A.; Jain, M.K.; Short, W.R.; Singh, T.; Aberg, J.A. Primary Care Guidance for Persons With Human Immunodeficiency Virus: 2020 Update by the HIV Medicine Association of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e3572–e3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu-Edusei, K.; Peterman, T.A.; Ballard, R.C. Serologic Testing for Syphilis in the United States: A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Two Screening Algorithms. Sex. Transm. Dis. 2011, 38, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.; Karapanagiotidis, T.; Nicholson, S.; Toma, H.; Vo, K.L.; Douros, C.; Azzato, F.; Edler, P.; Graham, M.; Towns, J.M.; et al. Alternative treponemal serology assays for diagnosis and confirmation of syphilis in a diagnostic laboratory: A retrospective evaluation of four agglutination assays and one ELISA. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2025, e01768-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

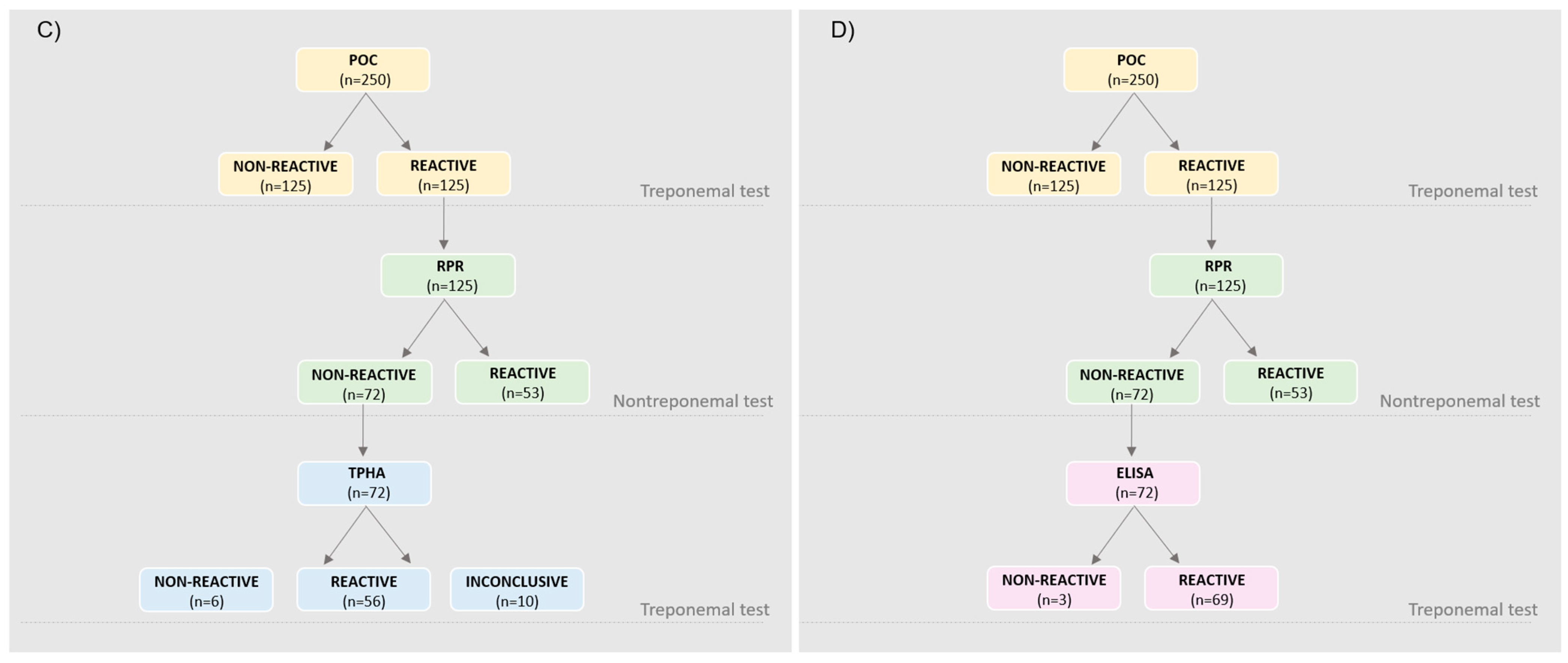
| Characteristics | Treponemal Test | Nontreponemal Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POC Test | ELISA | TPHA | VDRL Test | RPR Test | |
| Method | Immunochromatographic | Immunoassay | Hemagglutination | Agglutination | Agglutination |
| Specimen type | Whole blood | Serum | Serum | Serum | Serum |
| Specimen volume required | 10 µL | 5 µL | 10 µL | 100 µL * | 100 µL * |
| Dilution | NA | Manual dilution | Manual dilution | Manual dilution | Manual dilution |
| Time to test result ** | 20 min | 110 min | 90 min | 10 min | 14 min |
| Interpretation | Dependentobserver | Automated | Dependent observer | Dependent observer | Dependent observer |
| Manufacturer | Bioclin | Bioclin | ASI | Wiener | Laborclin |
| Characteristics | Total N (%) | POC+ N (%) | POC− N (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 123 (49.2) | 67 (54.47) | 56 (45.53) | 0.206 |
| Female | 127 (50.8) | 58 (45.67) | 69 (54.33) | |
| Age (years) | ||||
| 18–29 | 83 (33.2) | 36 (43.37) | 47 (56.63) | 0.282 |
| 30–45 | 88 (35.2) | 46 (52.27) | 42 (47.73) | |
| 46–59 | 40 (16.0) | 19 (47.50) | 21 (52.50) | |
| 60+ | 39 (15.6) | 24 (61.54) | 15 (38.46) | |
| Ethnicity | ||||
| White | 148 (60.16) | 64 (43.24) | 84 (56.76) | 0.036 |
| Black | 43 (17.48) | 26 (60.47) | 17 (39.53) | |
| Brown | 52 (21.14) | 29 (55.77) | 23 (44.23) | |
| Others | 3 (1.22) | 3 (100.00) | 0 (0.00) | |
| Education Level | ||||
| Elementary | 65 (26.0) | 46 (70.77) | 19 (29.23) | <0.001 |
| Secondary | 90 (36.0) | 43 (47.78) | 47 (52.22) | |
| University | 95 (38.0) | 36 (37.89) | 59 (62.11) |
| True Positive (n) | True Negative (n) | False Positive (n) | False Negative (n) | Sensitivity % (95% CI) | Specificity % (95% CI) | PPV % (95% CI) | NPV % (95% CI) | KAPPA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POC test vs. TPHA | 107 | 123 | 7 | 2 | 98.0 (94.0–100.0) | 95.0 (89.0–98.0) | 94.0 (88.0–97.0) | 98.0 (94.0–100.0) | 0.85 |
| ELISA vs. TPHA | 106 | 119 | 9 | 3 | 97.0 (92.0–99.0) | 93.0 (87.0- 97.0) | 92.0 (86.0–96.0) | 98.0 (93.0–99.0) | 0.81 |
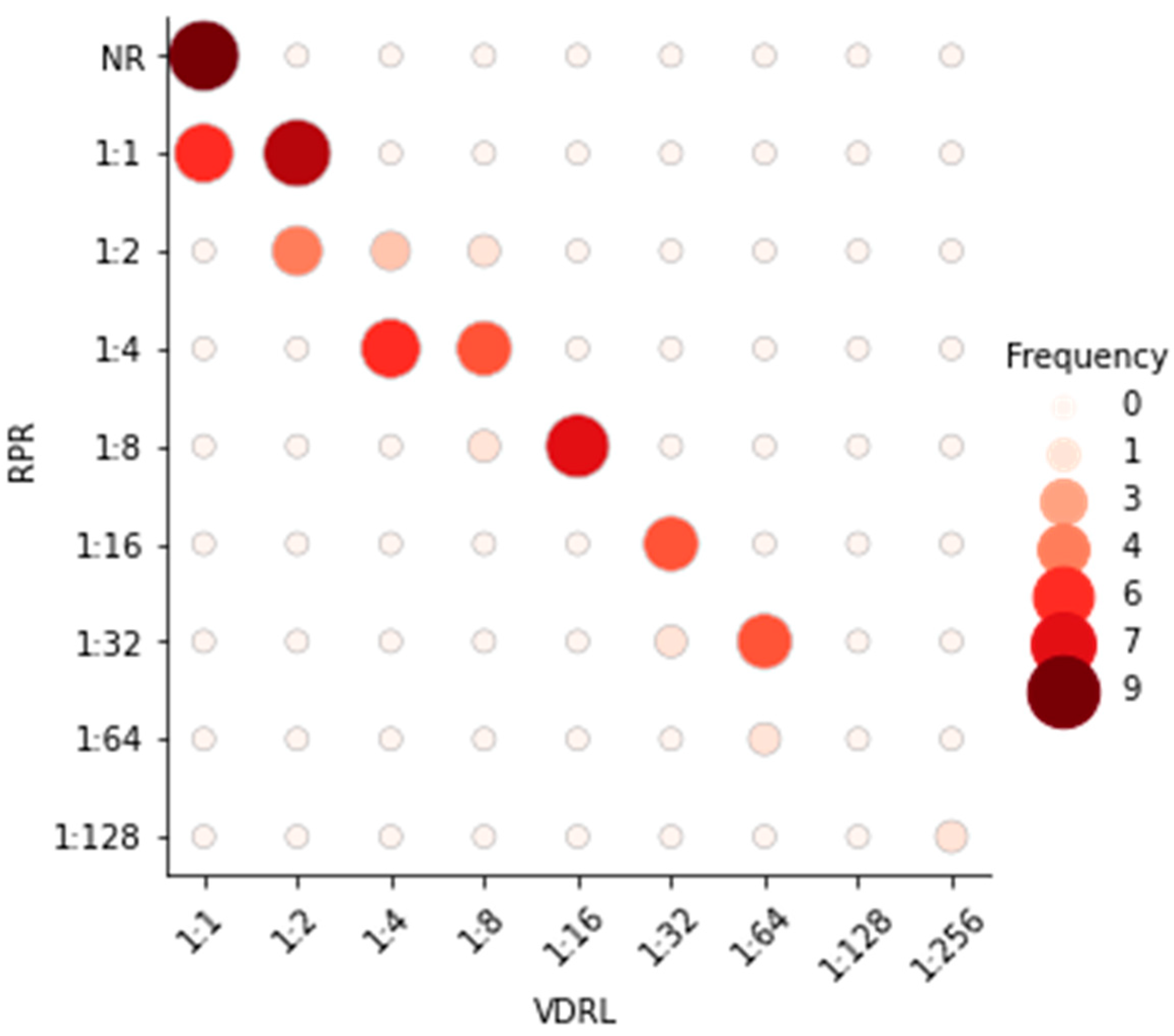
| VDRL test vs. RPR test | 53 | 187 | 9 | 1 | 98.0 (90.0–100.0) | 95.0 (91.0–98.0) | 85.0 (74.0–93.0) | 99.0 (97.0–100.0) | 0.89 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Basgalupp, S.; Dornelles, T.; Pedrotti, L.; dos Santos, A.; de Oliveira, C.; dos Santos, G.; de Brito, E.; Pinheiro, B.H.; Philippus, A.C.; Bigolin, Á.; et al. Diagnostic Properties of Different Serological Methods for Syphilis Testing in Brazil. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15121448
Basgalupp S, Dornelles T, Pedrotti L, dos Santos A, de Oliveira C, dos Santos G, de Brito E, Pinheiro BH, Philippus AC, Bigolin Á, et al. Diagnostic Properties of Different Serological Methods for Syphilis Testing in Brazil. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(12):1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15121448
Chicago/Turabian StyleBasgalupp, Suelen, Thayane Dornelles, Luana Pedrotti, Aniúsca dos Santos, Cáren de Oliveira, Giovana dos Santos, Emerson de Brito, Ben Hur Pinheiro, Ana Cláudia Philippus, Álisson Bigolin, and et al. 2025. "Diagnostic Properties of Different Serological Methods for Syphilis Testing in Brazil" Diagnostics 15, no. 12: 1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15121448
APA StyleBasgalupp, S., Dornelles, T., Pedrotti, L., dos Santos, A., de Oliveira, C., dos Santos, G., de Brito, E., Pinheiro, B. H., Philippus, A. C., Bigolin, Á., Gaspar, P. C., Moreno, F., Pereira, G., Tonini, M. L., & Wendland, E. (2025). Diagnostic Properties of Different Serological Methods for Syphilis Testing in Brazil. Diagnostics, 15(12), 1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15121448






