B-Cell Epitope Mapping of the Treponema pallidum Tp0435 Immunodominant Lipoprotein for Peptide-Based Syphilis Diagnostics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Study Sites and Population
2.3. Rabbit Infection and Sera Collection
2.4. Recombinant Tp0435 Expression and Purification
2.5. ELISAs with Overlapping Synthetic Peptides and Recombinant Tp0435
3. Results
3.1. Reactivity of Patient Sera to Tp0435 Peptides
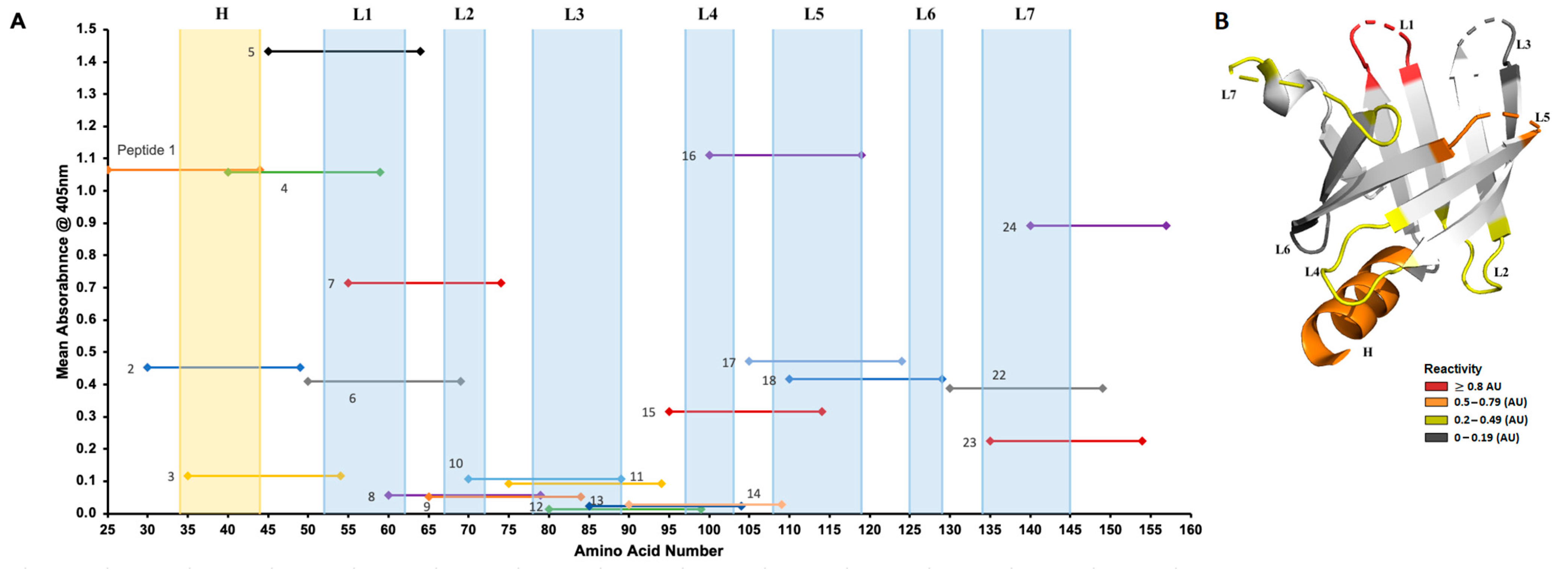
3.2. Reactivity of Rabbit Sera to Tp0435 Peptides
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Radolf, J.D.; Lukehart, S.A. (Eds.) Pathogenic Treponema: Molecular and Cellular Biology; Caister Academic Press: Norfolk, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. World Health Organization. Syphilis. 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/syphilis (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- ECDC. Syphilis. In Annual Epidemiological Report for 2022; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Wan, B.; Wang, M.; Lin, S.; Wu, Y.; Huang, J. Evaluating the global, regional, and national impact of syphilis: Results from the global burden of disease study 2019. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC. Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI) Surveillance, 2023; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2024.
- Tsuboi, M.; Evans, J.; Davies, E.P.; Rowley, J.; Korenromp, E.L.; Clayton, T.; Taylor, M.M.; Mabey, D.; Chico, R.M. Prevalence of syphilis among men who have sex with men: A global systematic review and meta-analysis from 2000–2020. Lancet Glob. Health 2021, 9, e1110–e1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moseley, P.; Bamford, A.; Eisen, S.; Lyall, H.; Kingston, M.; Thorne, C.; Piñera, C.; Rabie, H.; Prendergast, A.J.; Kadambari, S. Resurgence of congenital syphilis: New strategies against an old foe. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, e24–e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmour, L.S.; Walls, T. Congenital Syphilis: A Review of Global Epidemiology. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2023, 36, e0012622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, A.M.; Giacani, L.; Mayans, M.V.; Ubals, M.; Nieto, C.; Pérez-Mañá, C.; Quintó, L.; Romeis, E.; Mitjà, O. Efficacy of linezolid on Treponema pallidum, the syphilis agent: A preclinical study. EBioMedicine 2021, 65, 103281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukehart, S.A.; Molini, B.; Gomez, A.; Godornes, C.; Hof, R.; Fernandez, M.C.; Pitner, R.A.; Gray, S.A.; Carter, D.; Giacani, L.; et al. Immunization with a tri-antigen syphilis vaccine significantly attenuates chancre development, reduces bacterial load, and inhibits dissemination of Treponema pallidum. Vaccine 2022, 40, 7676–7692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towns, J.M.; Leslie, D.E.; Denham, I.; Azzato, F.; Fairley, C.K.; Chen, M. Painful and multiple anogenital lesions are common in men with Treponema pallidum PCR-positive primary syphilis without herpes simplex virus coinfection: A cross-sectional clinic-based study. Sex. Transm. Infect. 2016, 92, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golden, M.R.; Marra, C.M.; Holmes, K.K. Update on syphilis: Resurgence of an old problem. JAMA 2003, 290, 1510–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Duan, J.; Zhao, F. PCR detection for syphilis diagnosis: Status and prospects. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2019, 33, e22890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theel, E.S.; Katz, S.S.; Pillay, A. Molecular and Direct Detection Tests for Treponema pallidum Subspecies pallidum: A Review of the Literature, 1964–2017. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, S4–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, G.; Giammanco, A.; Virruso, R.; Fasciana, T. Current and Future Trends in the Laboratory Diagnosis of Sexually Transmitted Infections. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gratzer, B.; Pohl, D.; Hotton, A.L. Evaluation of diagnostic serological results in cases of suspected primary syphilis infection. Sex. Transm. Dis. 2014, 41, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wende, R.D.; Mudd, R.L.; Knox, J.M.; Holder, W.R. The VDRL slide test in 322 cases of darkfield positive primary syphilis. South. Med. J. 1971, 64, 633–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creegan, L.; Bauer, H.M.; Samuel, M.C.; Klausner, J.; Liska, S.; Bolan, G. An evaluation of the relative sensitivities of the venereal disease research laboratory test and the Treponema pallidum particle agglutination test among patients diagnosed with primary syphilis. Sex. Transm. Dis. 2007, 34, 1016–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparling, P.F. Diagnosis and treatment of syphilis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1971, 284, 642–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiumara, N.J. Posttreatment serological response of biologic false-positive reactors. JAMA 1982, 247, 817–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salle, R.; Delaleu, J.; Herms, F.; Louison, J.B.; Dauendorffer, J.N.; Bagot, M.; Bouaziz, J.D.; Fouéré, S. Epidemiological and serological characteristics of patients with late syphilis: A retrospective cohort of 76 patients. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2023, 37, e796–e797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seña, A.C.; Wolff, M.; Martin, D.H.; Behets, F.; Van Damme, K.; Leone, P.; Langley, C.; McNeil, L.; Hook, E.W. Predictors of serological cure and Serofast State after treatment in HIV-negative persons with early syphilis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 53, 1092–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, S.A. Manual of Tests for Syphilis, 9th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, E.H.; Klausner, J.D.; Caguin-Grygiel, G.; Madayag, C.; Barber, K.O.; Qiu, J.S.; Liska, S.; Pandori, M.W. Evaluation of an IgM/IgG sensitive enzyme immunoassay and the utility of index values for the screening of syphilis infection in a high-risk population. Sex. Transm. Dis. 2011, 38, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieberman, N.A.P.; Lin, M.J.; Xie, H.; Shrestha, L.; Nguyen, T.; Huang, M.L.; Haynes, A.M.; Romeis, E.; Wang, Q.Q.; Zhang, R.L.; et al. Treponema pallidum genome sequencing from six continents reveals variability in vaccine candidate genes and dominance of Nichols clade strains in Madagascar. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0010063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brautigam, C.A.; Deka, R.K.; Liu, W.Z.; Norgard, M.V. Insights into the potential function and membrane organization of the TP0435 (Tp17) lipoprotein from Treponema pallidum derived from structural and biophysical analyses. Protein Sci. 2015, 24, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janier, M. Ceftriaxone is effective for treating patients with primary syphilis. Sex. Transm. Dis. 1988, 15, 70. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kojima, N.; Park, H.; Konda, K.A.; Joseph Davey, D.L.; Bristow, C.C.; Brown, B.; Leon, S.R.; Vargas, S.K.; Calvo, G.M.; Caceres, C.F.; et al. The PICASSO Cohort: Baseline characteristics of a cohort of men who have sex with men and male-to-female transgender women at high risk for syphilis infection in Lima, Peru. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukehart, S.A.; Marra, C.M. Isolation and laboratory maintenance of Treponema pallidum. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2007, 7, 12A.1.1–12A.1.18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runina, A.V.; Katunin, G.L.; Filippova, M.A.; Zatevalov, A.M.; Kubanov, A.A.; Deryabin, D.G. Immunochip for Syphilis Serodiagnostics with the Use of Extended Array of Treponema pallidum Recombinant Antigens. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018, 165, 767–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studier, F.W. Protein production by auto-induction in high density shaking cultures. Protein Expr. Purif. 2005, 41, 207–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molini, B.; Fernandez, M.C.; Godornes, C.; Vorobieva, A.; Lukehart, S.A.; Giacani, L. B-Cell Epitope Mapping of TprC and TprD Variants of Treponema pallidum Subspecies Informs Vaccine Development for Human Treponematoses. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 862491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brautigam, C.A.; Deka, R.K.; Norgard, M.V. Purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of TP0435 (Tp17) from the syphilis spirochete Treponema pallidum. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2013, 69, 453–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, C.A.; Molini, B.J.; Lukehart, S.A.; Van Voorhis, W.C. Segregation of B and T cell epitopes of Treponema pallidum repeat protein K to variable and conserved regions during experimental syphilis infection. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 952–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lay, B.D.; Cameron, T.A.; De Lay, N.R.; Norris, S.J.; Edmondson, D.G. Comparison of transcriptional profiles of Treponema pallidum during experimental infection of rabbits and in vitro culture: Highly similar, yet different. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smajs, D.; McKevitt, M.; Howell, J.K.; Norris, S.J.; Cai, W.W.; Palzkill, T.; Weinstock, G.M. Transcriptome of Treponema pallidum: Gene expression profile during experimental rabbit infection. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 1866–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radolf, J.D.; Chamberlain, N.R.; Clausell, A.; Norgard, M.V. Identification and localization of integral membrane proteins of virulent Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum by phase partitioning with the nonionic detergent triton X-114. Infect. Immun. 1988, 56, 490–498. [Google Scholar]
- Hanff, P.A.; Bishop, N.H.; Miller, J.N.; Lovett, M.A. Humoral immune response in experimental syphilis to polypeptides of Treponema pallidum. J. Immunol. 1983, 131, 1973–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker-Zander, S.A.; Fohn, M.J.; Lukehart, S.A. Development of cellular immunity to individual soluble antigens of Treponema pallidum during experimental syphilis. J. Immunol. 1988, 141, 4363–4369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanff, P.A.; Fehniger, T.E.; Miller, J.N.; Lovett, M.A. Humoral immune response in human syphilis to polypeptides of Treponema pallidum. J. Immunol. 1982, 129, 1287–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, J.C.; Pope, C.D.; Moore, M.W.; Pope, J.; Kiely, T.G.; Radolf, J.D. Lipoprotein-dependent and -independent immune responses to spirochetal infection. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2005, 12, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexopoulou, L.; Thomas, V.; Schnare, M.; Lobet, Y.; Anguita, J.; Schoen, R.T.; Medzhitov, R.; Fikrig, E.; Flavell, R.A. Hyporesponsiveness to vaccination with Borrelia burgdorferi OspA in humans and in TLR1- and TLR2-deficient mice. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliprantis, A.O.; Yang, R.B.; Mark, M.R.; Suggett, S.; Devaux, B.; Radolf, J.D.; Klimpel, G.R.; Godowski, P.; Zychlinsky, A. Cell activation and apoptosis by bacterial lipoproteins through toll-like receptor-2. Science 1999, 285, 736–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brightbill, H.D.; Libraty, D.H.; Krutzik, S.R.; Yang, R.B.; Belisle, J.T.; Bleharski, J.R.; Maitland, M.; Norgard, M.V.; Plevy, S.E.; Smale, S.T.; et al. Host defense mechanisms triggered by microbial lipoproteins through toll-like receptors. Science 1999, 285, 732–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellati, T.J.; Bouis, D.A.; Caimano, M.J.; Feulner, J.A.; Ayers, C.; Lien, E.; Radolf, J.D. Activation of human monocytic cells by Borrelia burgdorferi and Treponema pallidum is facilitated by CD14 and correlates with surface exposure of spirochetal lipoproteins. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 2049–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.U.; Fakile, Y.F.; Chow, J.M.; Gustafson, K.J.; Jost, H.; Schapiro, J.M.; Novak-Weekley, S.; Tran, A.; Nomura, J.H.; Chen, V.; et al. Performance of Treponemal Tests for the Diagnosis of Syphilis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 68, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynes, A.M.; Godornes, C.; Ke, W.; Giacani, L. Evaluation of the Protective Ability of the Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum Tp0126 OmpW Homolog in the Rabbit Model of Syphilis. Infect. Immun. 2019, 87, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.; Nasereddin, T.; Alter, L.; Centurion-Lara, A.; Giacani, L.; Parveen, N. Treponema pallidum Lipoprotein TP0435 Expressed in Borrelia burgdorferi Produces Multiple Surface/Periplasmic Isoforms and mediates Adherence. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parveen, N.; Fernandez, M.C.; Haynes, A.M.; Zhang, R.L.; Godornes, B.C.; Centurion-Lara, A.; Giacani, L. Non-pathogenic Borrelia burgdorferi expressing Treponema pallidum TprK and Tp0435 antigens as a novel approach to evaluate syphilis vaccine candidates. Vaccine 2019, 37, 1807–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
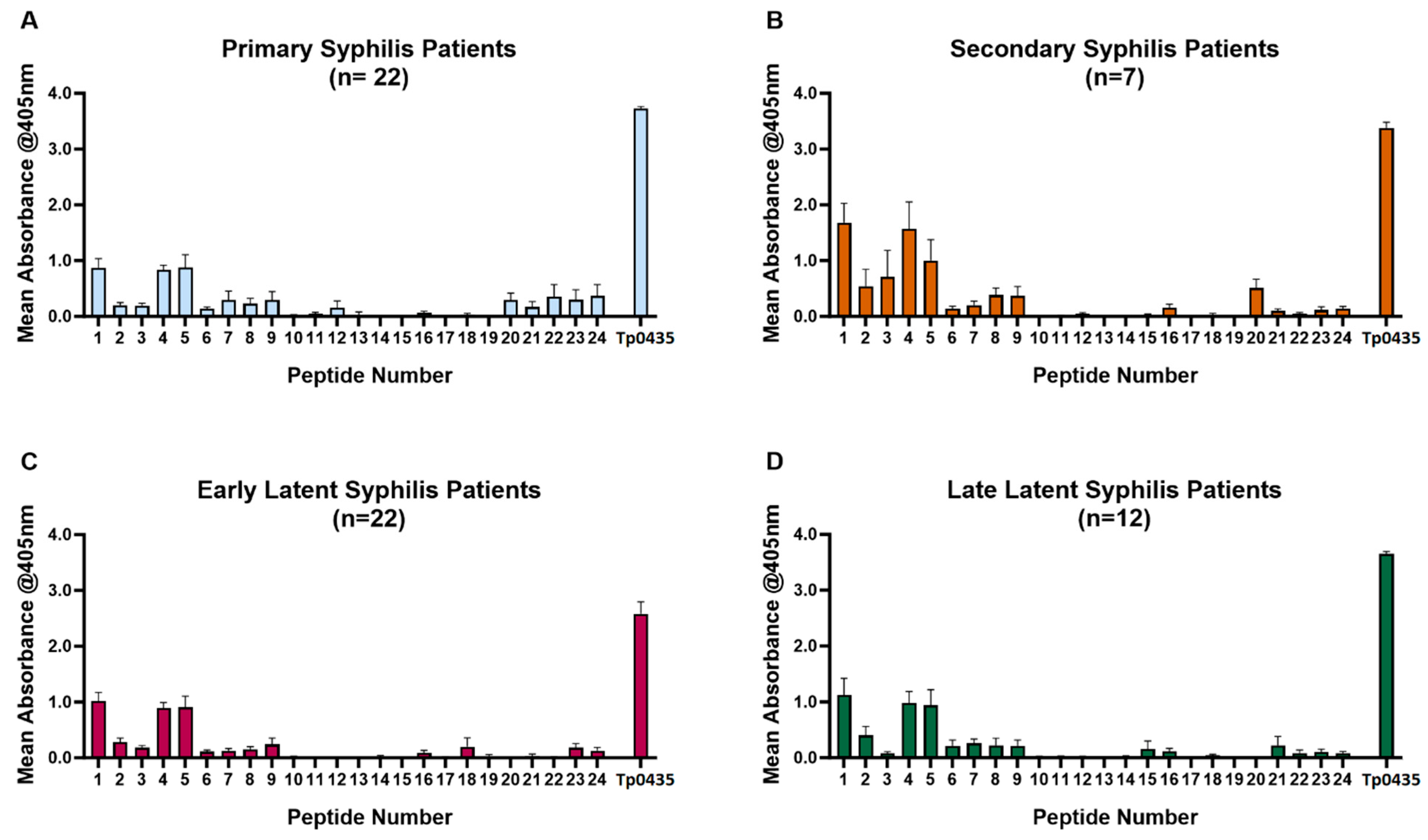


| Stage (Number of Patients) | Provided Gender (Number) | Age Range (Median Age) | HIV Status (Number) | History of Syphilis Infection (Number) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary (22) | Man (20) Trans-woman (1) Woman (1) | 20–46 (27.5) | Positive (11) Negative (11) | Positive (4) Negative (4) Unknown (14) |
| Secondary (7) | Man (7) | 19–46 (38) | Positive (4) Negative (3) | Positive (3) Negative (1) Unknown (3) |
| Early Latent (22) | Man (19) Trans-woman (2) Woman (1) | 18–37 (28.5) | Positive (5) Negative (17) | Positive (11) Negative (11) |
| Late Latent (12) | Man (10) Trans-woman (2) | 25–54 (34.5) | Positive (6) Negative (6) | Positive (12) |
| Peptide # (aa Position) 1 | Peptide Sequence 2 |
|---|---|
| 1 (25–44) | CTTVCPHAGKAKAEKVECAL |
| 2 (30–49) | PHAGKAKAEKVECALKGGIF |
| 3 (35–54) | AKAEKVECALKGGIFRGTLP |
| 4 (40–59) | VECALKGGIFRGTLPAADCP |
| 5 (45–64) | KGGIFRGTLPAADCPGIDTT |
| 6 (50–69) | RGTLPAADCPGIDTTVTFNA |
| 7 (55–74) | AADCPGIDTTVTFNADGTAQ |
| 8 (60–79) | GIDTTVTFNADGTAQKVELA |
| 9 (65–84) | VTFNADGTAQKVELALEKKS |
| 10 (70–89) | DGTAQKVELALEKKSAPSPL |
| 11 (75–94) | KVELALEKKSAPSPLTYRGT |
| 12 (80–99) | LEKKSAPSPLTYRGTWMVRE |
| 13 (85–104) | APSPLTYRGTWMVREDGIVE |
| 14 (90–109) | TYRGTWMVREDGIVELSLVS |
| 15 (95–114) | WMVREDGIVELSLVSSEQSK |
| 16 (100–119) | DGIVELSLVSSEQSKAPHEK |
| 17 (105–124) | LSLVSSEQSKAPHEKELYEL |
| 18 (110–129) | SEQSKAPHEKELYELIDSNS |
| 19 (115–134) | APHEKELYELIDSNSVRYMG |
| 20 (120–139) | ELYELIDSNSVRYMGAPGAG |
| 21 (125–144) | IDSNSVRYMGAPGAGKPSKE |
| 22 (130–149) | VRYMGAPGAGKPSKEMAPFY |
| 23 (135–154) | APGAGKPSKEMAPFYVLKKT |
| 24 (140–159) | KPSKEMAPFYVLKKTKK |
| Antigen | All Sera (63) | Primary Syphilis Sera (22) | Secondary Syphilis Sera (7) | Early Latent Syphilis Sera (22) | Late Latent Syphilis Sera (12) | Syphilis History 1 | HIV Status 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peptide 1 | 86% (54/63) | 86% (19/22) | 100% (7/7) | 82% (18/22) | 83% (10/12) | Y: 44% N: 30% U: 26% | P: 44% N: 54% |
| Peptide 4 | 94% (59/63) | 95% (21/22) | 100% (7/7) | 95% (21/22) | 83% (10/12) | Y: 42% N: 29% U: 29% | P: 48% N: 52% |
| Peptide 5 | 76% (48/63) | 77% (17/22) | 100% (7/7) | 73% (16/22) | 67% (8/12) | Y: 44% N: 28% U: 28% | P: 49% N: 51% |
| Peptide 1, 4, and 5 | 68% (43/63) | 68% (15/22) | 100% (7/7) | 63% (14/22) | 58% (7/12) | Y: 42% N: 28% U: 30% | P: 44% N: 56% |
| Peptide 1, 4, or 5 | 100% (63/63) | 100% (22/22) | 100% (7/7) | 100% (22/22) | 100% (12/12) | Y: 45% N: 42% U: 13% | P: 42% N: 58% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Keane, J.L.; Bose, M.; Molini, B.J.; Konda, K.A.; Vargas, S.K.; Reyes Diaz, M.; Caceres, C.F.; Klausner, J.D.; Treger, R.S.; Giacani, L. B-Cell Epitope Mapping of the Treponema pallidum Tp0435 Immunodominant Lipoprotein for Peptide-Based Syphilis Diagnostics. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111443
Keane JL, Bose M, Molini BJ, Konda KA, Vargas SK, Reyes Diaz M, Caceres CF, Klausner JD, Treger RS, Giacani L. B-Cell Epitope Mapping of the Treponema pallidum Tp0435 Immunodominant Lipoprotein for Peptide-Based Syphilis Diagnostics. Diagnostics. 2025; 15(11):1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111443
Chicago/Turabian StyleKeane, Jessica L., Mahashweta Bose, Barbara J. Molini, Kelika A. Konda, Silver K. Vargas, Michael Reyes Diaz, Carlos F. Caceres, Jeffrey D. Klausner, Rebecca S. Treger, and Lorenzo Giacani. 2025. "B-Cell Epitope Mapping of the Treponema pallidum Tp0435 Immunodominant Lipoprotein for Peptide-Based Syphilis Diagnostics" Diagnostics 15, no. 11: 1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111443
APA StyleKeane, J. L., Bose, M., Molini, B. J., Konda, K. A., Vargas, S. K., Reyes Diaz, M., Caceres, C. F., Klausner, J. D., Treger, R. S., & Giacani, L. (2025). B-Cell Epitope Mapping of the Treponema pallidum Tp0435 Immunodominant Lipoprotein for Peptide-Based Syphilis Diagnostics. Diagnostics, 15(11), 1443. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics15111443






